Stochastic Single-Allocation Hub Location Routing Problem for the
Design of Intra-City Express Systems
Yuehui Wu
1a
, Hui Fang
1
, Ali Gul Qureshi
2b
and Tadashi Yamada
2c
1
College of Transportation Engineering, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian, 116026, Liaoning, China
2
Department of Urban Management, Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University, Kyoto, 615-8246, Japan
Keywords: Intra-City Express, Stochastic Single-Allocation Hub Location Routing Problem, Multi-Stage Recourse Model,
Sample Average Approximation.
Abstract: The paper concentrates on designing an intra-city express system in a practical environment. In the target
networks, flows of parcels are exchanged between branch offices via a less-than-truckload hub-and-spoke
network in a stochastic environment. Hub and vehicle capacities are considered, and the flows between all
pairs of branch offices are assumed to be stochastic variables. The problem is modelled as a multi-stage
recourse model, named capacitated single-allocation hub location routing problem with stochastic demands
(CSAHLRPSD). A sample average approximation (SAA) framework is proposed, in which two variants of
adaptive large neighbourhood search algorithms are used to solve the SAA problem and to calculate the
recourse cost. The SAA framework is tested on benchmark instances, proving that it can efficiently deal with
the CSAHLRPSD. Also, the results indicate that employing the CSAHLRPSD can cut the operation cost in
comparison with the deterministic model in the practical and stochastic environment.
1 INTRODUCTION
Express service network design is significant in urban
logistics management as it can help reduce operation
costs and improve service levels. With the
development of e-commerce, intra-city express has
become an increasingly essential segment in urban
logistics systems. As a result, various cargo
companies are offering “delivery within the same day
in the city service”, “next day delivery service”, or
“delivery within 24 hours service”, e.g., SF Express,
Yamato Transport, Japan Post, and so on. For these
companies, how to satisfy the intra-city express
requests in a practical environment via a cost-efficient
way arises as an important issue. Moreover, this issue
is also significant for the urban management
department, as the delivery of intra-city expresses has
caused various social problems, e.g., traffic jams, air
pollution, and so on (Zhao et al., 2019).
In this study, we focus on the design of an intra-
city express system in a practical environment.
Parcels are transported from the origin branch offices
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1755-3360
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2832-2015
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-9937-951X
to the destination branch offices, resulting a many-to-
many distribution system. As the parcel and mail
flows are usually less-than-truckload (LTL), it is very
costly to link them directly, both from the economic
and social points of view (Gelareh & Nickel, 2011;
Sun, 2013). Instead, one method is to use the network
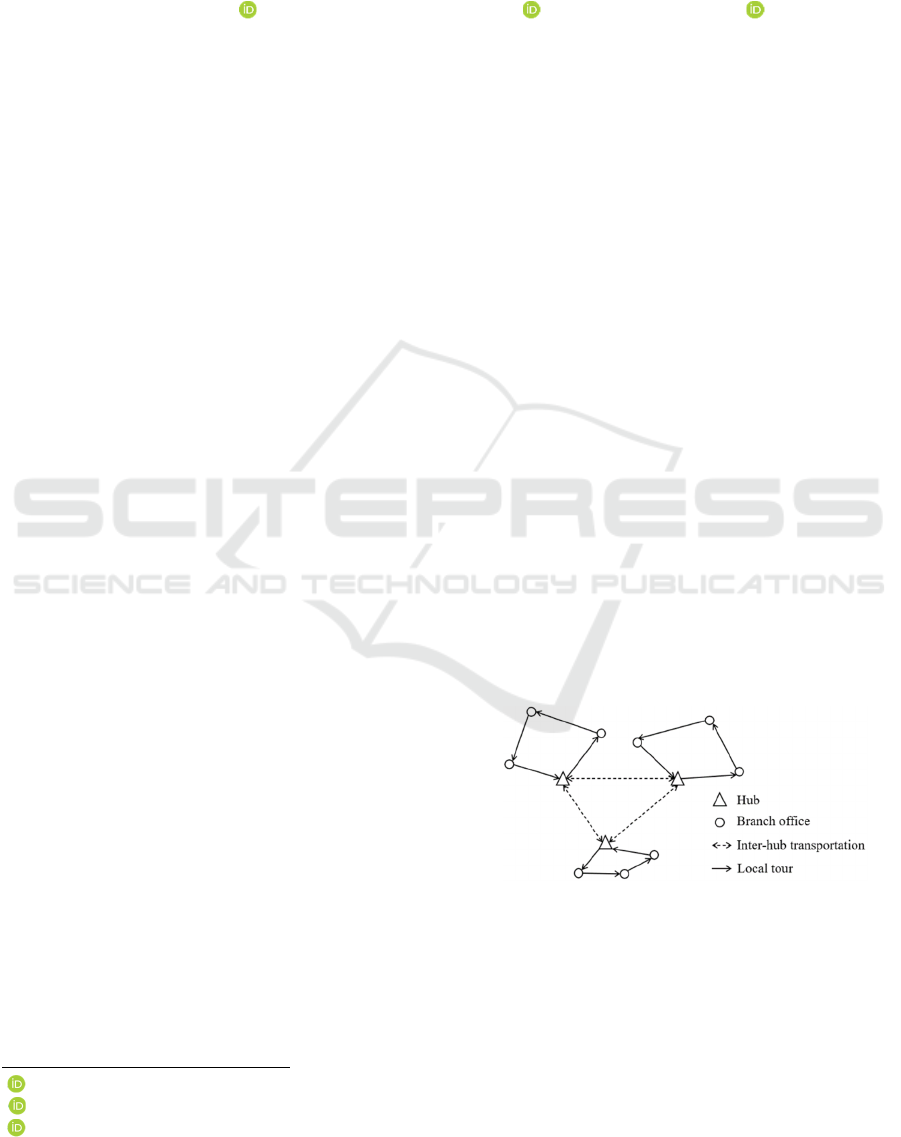
shown in Figure 1 to realize the flow exchange.
Figure 1: Hub-and-spoke network for intra-city express
systems.
This network is a variant of hub-and-spoke
networks specially designed for LTL transportation.
The hubs and branch offices are connected by local
tours instead of direct links, which is generally very
82
Wu, Y., Fang, H., Qureshi, A. and Yamada, T.
Stochastic Single-Allocation Hub Location Routing Problem for the Design of Intra-City Express Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0012311900003639
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES 2024), pages 82-91
ISBN: 978-989-758-681-1; ISSN: 2184-4372
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
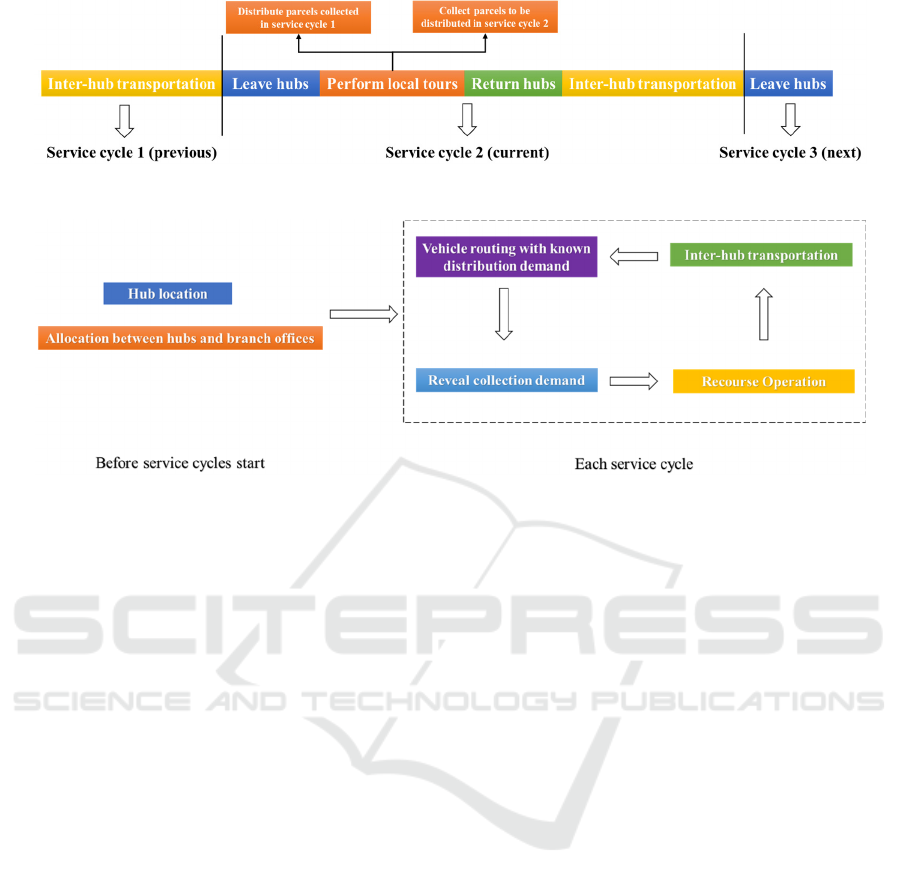
Figure 2: Hub-and-spoke network for intra-city express systems.
Figure 3: Stochastic decision process for intra-city express systems.
expensive (Kartal et al., 2017; Alumur et al., 2020).
The parcels are picked up at the origin branch
offices, sorted in the first hub, possibly transported to
the second hub, and delivered to the destination
branch offices. Moreover, the collection and
distribution processes are conducted at the same time
along local tours.
Branch offices usually do not own enough sorting
resources (e.g., labour, machines, spaces, and so on).
Therefore, parcels are collected in a mixed status and
have to be sorted based on their destinations in hubs
for further delivery. Consequently, the flow cannot be
exchanged directly, even along the same local tour.
More specifically, in the current service cycle (for
example, this morning), each vehicle leaves its
corresponding hub and traverses a subset of branch
offices, while distributing the parcels collected in the
previous service cycle (for example, yesterday
morning) and collecting the parcels to be distributed
in the next service cycle (for example, tomorrow
morning), i.e., the service system is a warmed-up
transportation system. Furthermore, inter-hub
transportation is conducted after the vehicles return to
the hubs (for example, at night). The whole procedure
is illustrated in Figure 2. Similar settings have been
applied in various studies related to the intra-city
express system design (such as in Sun, 2013; Karimi,
2018; Wu et al., 2023).
Based on the above descriptions, one can find that
the main decisions of the planning problem for the
referred system include hub location, allocation
between branch offices and hubs, and vehicle routing,
which should be resolved jointly. Moreover, the
following three practical conditions are considered:
(i) Capacity. Capacitated hubs and vehicles
should be employed due to the limitation of land
resources and the limitation of the use of large-
volume trucks in urban areas.
(ii) Single-allocation. In practical applications,
each branch office is usually served by precisely one
hub, as branch offices generally do not have enough
sort capacities.
(iii) Stochastic demand. The express company
might not know the parcel flows beforehand. For
instance, business activities might result in the
uncertainty of parcel flows, i.e., the intra-city express
demands are stochastic rather than deterministic. One
natural process to deal with the uncertainty is that the
hub location and allocation between hubs and branch
offices are decided before any random variable is
revealed (before service cycles start) since changing
these decisions for a warmed-up system is expensive.
In each service cycle, the vehicle routing is
determined with known distribution demand (since
these parcels have been collected in the previous
service cycle) and unknown collection demand.
Finally, recourse operations and inter-hub
transportation are conducted to finish the distribution
procedure. This process is shown in Figure 3.
With these considerations, we propose the
planning problem for the intra-city express system,
named capacitated single-allocation hub location
Stochastic Single-Allocation Hub Location Routing Problem for the Design of Intra-City Express Systems
83

routing problem with stochastic demand
(CSAHLRPSD), belonging to the field of the hub
location routing problem (HLRP). This problem has
been applied to the design of various many-to-many
systems, such as postal service systems (Bostel et al.,
2015), communication systems (Catanzaro et al.,
2015), ship cargo systems (Fontes & Goncalves,
2021), and so on. Please find more details of the
HLRP in Section 2.
The main contributions lay in three points: i) A
multi-stage recourse model is introduced to formulate
the CSAHLRPSD, which models the HLRP with
stochastic demand for the first time. ii) A sample
average approximation (SAA) framework, which is
embedded with two variants of the adaptive large
neighbourhood search (ALNS) algorithm, is
introduced as the solution approach. iii) Numerical
experiments are performed to prove the proposed
framework’s efficiency.
The remainder of the paper is structured as
follows: Section 2 reviews the HLRP and compares
our study with the existing ones. Section 3 defines the
CSAHLRPSD via a multi-stage recourse model.
Section 4 provides the solution methodology, whose
efficiency is tested in Section 5. Finally, Section 6
concludes the study.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
This section mainly reviews the works on the single-
allocation hub location routing problem (SAHLRP),
which is closely concerning to the CSAHLRPSD.
Nagy and Salhi (1998) first proposed the SAHLRP
with route length constraints to limit working hours.
They proposed an integer linear programming
formulation for this problem and utilised a locate
first–route second heuristic algorithm to solve it on a
single instance with 249 clients.
So far, most studies related to the SAHLRP have
concentrated on postal service networks, where the
collection and distribution processes usually
coincide. Bostel et al. (2015) focused on an SAHLRP
where the length of each vehicle route is constrained
by a maximum number of visited clients. A memetic
algorithm (MA) was introduced to solve instances
with up to 100 clients. Kartal et al. (2017)
investigated the operational characteristics of a
leading cargo company in Turkey. Three variants of
formulations were introduced, and a multi-start
simulated annealing algorithm and an ACO algorithm
were introduced to solve the problem. Numerical
results indicated that the proposed algorithms could
find high-quality solutions for instances with up to
200 nodes in reasonable computational time. Karimi
(2018) studied a capacitated SAHLRP with
simultaneous pickup and delivery for a warmed-up
postal system. The study introduced a polynomial-
sized mixed integer programming formulation and
several valid inequalities. Moreover, a tabu-search-
based heuristic was proposed to solve the problem.
The results from computational tests showed that the
proposed valid inequalities and algorithm worked
well for their model.
The pickup and delivery process can be distinct
for logistical or scheduling reasons, e.g., the case for
general freight forwarders. Sun (2015) investigated a
problem similar to the one in Sun (2013), in which
pickup and deliveries were assumed to be distinct. An
endosymbiotic evolutionary algorithm was
developed, simultaneously solving hub location and
vehicle routing problems. The algorithm’s
performance was tested on 20 instances with 100 and
200 customers. Experimental results showed that the
proposed algorithm could be used for supply-chain
network planning. More recently, Yang et al. (2019)
investigated the capacitated SAHLRP with distinct
collection and delivery processes. Moreover, they
proposed a new MILP model and developed a
memetic algorithm (MA) to solve larger-sized
problems. Numerical experiments showed that the
MA could find high-quality solutions in acceptable
computational time.
Most studies have employed heuristic algorithms
(Danach et al., 2019; Ratli et al., 2020; Pandiri &
Singh, 2021), and there are only a few attempts to
solve the problem exactly. de Camargo et al. (2013)
introduced a new SAHLRP model with simultaneous
collections and distributions. They assumed that a
fixed cost was imposed upon the hubs and vehicles.
Moreover, they decomposed the problem into two
subproblems: a transportation problem and a
feasibility problem. Then the problem was optimally
solved by a tailored Benders decomposition
algorithm. The results were compared to the CPLEX
solver, proving that this method was able to find
optimal solutions for instances with 100 clients.
Later, Rodriguez-Martin et al. (2014) investigated a
variant of SAHLRP in which a cyclical path
connected the uncapacitated hubs. In the problem,
each cluster of clients and assigned hub was
connected by precisely one local route cycle.
Furthermore, the number of visited clients of each
local route cycle is limited as a length constraint. The
problem was solved by a branch-and-cut algorithm.
Wu et al. (2023) provided a branch-and-price-and-cut
algorithm to solve the capacitated SAHLRP, which
were tested on benchmark instances. Numerical
ICORES 2024 - 13th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
84

results proved that the branch-and-price-and-cut
algorithm could efficiently deal with the capacitated
SAHLRP.
All the above works have focused on the
deterministic HLRPs, and there is only one work on
the stochastics HLRP. Mohammadi et al. (2013)
investigated a multi-objective chance-constrained
model of a stochastic green HLRP. In their problem,
stochastic travel time and service time were
considered. A multi-objective invasive weed
optimisation was introduced to solve the problem,
which was then compared with other multi-objective
algorithms on randomly generated instances.
As reviewed above, stochastic HLRP-related
literature is extremely limited. Our study is the first
one to investigate the HLRP with stochastic demands.
Moreover, our work is the first attempt to model the
stochastic HLRP via the recourse model.
3 MODEL FORMULATION
The CSAHLRPSD is defined on a complete
graph 𝐺 =
(
𝑉,𝐴
)
, in which 𝑉 and 𝐴 are vertex set
and edge set, respectively. Vertex set 𝑉 consists of
potential hub set 𝐻 and client (branch office) set 𝐶,
while edge set 𝐴 consists of edges between all
vertices. For each pair of clients 𝑖 ∈ 𝐶 and 𝑗 ∈
𝐶, 𝑑
represents the flow to be transported from 𝑖 to
𝑗 through local tours and hubs, which is assumed to
be a random variable with known and independent
distribution. Without loss of the generality, we
assume that all realizations of 𝑑
are greater than 0
and they do not exceed the vehicle capacity.
Moreover, the collection demand and distribution
demand of client 𝑖 ∈ 𝐶 is denoted as 𝑂
=
∑
𝑑
∈
and 𝐷
=
∑
𝑑
∈
, respectively.
Each potential hub has a capacity 𝑄
and a fixed
cost 𝐹
. As in Ernst and Krishnamoorthy (1999), Hu
et al. (2021) and Ghaffarinasab (2022), it is assumed
that only receiving flows from clients consumes hub
capacity since parcels are generally sorted in the
origin hubs and then transported to destination hubs
without further sorting operations. Local tours are
operated by an unlimited fleet of identical vehicles,
and each vehicle is associated with a capacity 𝑞 and a
fixed cost 𝑓. Furthermore, inter-hub transportation is
assumed to be realised by an unlimited fleet of
identical trucks, and there is no capacity limitation
and fixed cost of the trucks.
Each edge
(
𝑖,𝑗
)
∈𝐴 is addressed with a
nonnegative travel distance 𝑐
, satisfying the triangle
inequality. Local tour cost is dependent on the sum of
travel distances of the travelled edges, while inter-hub
transportation cost is calculated based on travel
distances and transferred flows (Karimi, 2018; Yang
et al., 2019). In addition, the unit inter-hub
transportation cost (¥/km.t) and unit local tour cost
(¥/km) are denoted as 𝛼 and 𝛽, respectively.
The CSAHLRPSD belongs to the field of
stochastic programming, which is generally
formulated by chance-constrained models and
recourse models. Based on the descriptions in Section
1, we model the CSAHLRPSD via a multi-stage
recourse model as follows:
i) In the first stage, the hub locations and the
allocation between clients and hubs (long-term
decisions) are determined before the random
variables (𝑑
|𝑖,𝑗 ∈ 𝐶) are realised.
ii) Then, in the second stage, the flows to be
delivered to each client 𝑖 ∈ 𝐶 (𝑑
|𝑗 ∈ 𝐶) are revealed
first (since these parcels have been collected in the
previous service cycle, as shown in Section 1),
forming the distribution demands (𝐷
|𝑖 ∈ 𝐶). After
the distribution demands are known, the vehicles are
routed to link the hubs and clients (short-term
decisions) before knowing the collection demands
(𝑂
|𝑖 ∈ 𝐶).
iii) In the third stage, the collection demands are
revealed, and a predetermined recourse policy is
applied when a failure occurs. The classical recourse
policy is employed, in which the vehicles return to the
hub, drop off the collected parcels, and continue their
planned route at the point of failure. Furthermore, if
the total collection demand assigned to a hub exceeds
its capacity due to uncertainty, a penalty cost must be
paid, representing the overwork cost. The unit
overwork cost is expressed as ω. Note that the inter-
hub transportation costs are also calculated in this
stage.
In other words, after the hub location and the
allocation between hubs and clients are determined, a
VRPSDSP is solved for each installed hub and the
clients assigned to it. Although these VRPSDSPs
need to be solved multiple times for all the service
cycles, we only model them once for simplicity, and
the fixed costs are distributed into each service cycle
to make long-term and short-term costs comparable.
For each edge (𝑖,𝑗) ∈ 𝐴, 𝑥
is a binary variable
equal to 1 if there is a vehicle travelling directly from
vertex 𝑖 to vertex 𝑗. 𝑧
(𝑖∈𝐶,𝑘∈𝐻) is a binary
variable equal to 1 if client 𝑖 is allocated to hub 𝑘. For
each vertex 𝑖 ∈ 𝑉, let 𝑣
be the delivery load on the
vehicle just after having served vertex 𝑖. 𝑏
is a binary
variable equal to 1 if potential hub 𝑘 ∈ 𝐻 is open.
Moreover, 𝑦
denotes the fraction flow from
client 𝑖 ∈ 𝐶 to client 𝑗 ∈ 𝐶 passing hub 𝑘 ∈ 𝐻 and
Stochastic Single-Allocation Hub Location Routing Problem for the Design of Intra-City Express Systems
85

hub 𝑙 ∈ 𝐻. Finally,
𝑒
denotes the overwork load of
hub 𝑘 ∈ 𝐻.
The CSAHLRPSD is modelled as (1)-(21), in
which 𝑄
(
𝒃,𝒛,𝝃
)
and 𝑄
(
𝒙,𝒃,𝒛,𝝃
)
are the optimal
value of the second stage problem and the third stage
problem. Random vector 𝝃 contains the flow 𝑑
to be
transported from client 𝑖 ∈ 𝐶 to 𝑗 ∈ 𝐶.
𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒 1 𝑚𝑖𝑛 𝐹
𝑏
∈
+𝐸[𝑄
(
𝒃,𝒛,𝝃
)
]
(1)
𝑠.𝑡.𝑧
∈
=1∀𝑖∈𝐶
(2)
𝑧
≤𝑏
∀𝑖 ∈ 𝐶,𝑘 ∈ 𝐻
(3)
𝑧
∈
0,1
∀𝑖 ∈ 𝐶, 𝑘 ∈ 𝐻
(4)
𝑏
∈
0,1
∀𝑘 ∈ 𝐻
(5)
Objective function (1) minimises the operation
cost, consisting of the hub fixed cost and expected
recourse cost. Constraint (2) guarantees the single-
allocation between clients and hubs. Only open hubs
can serve clients, which is ensured by Constraint (3).
Constraints (4) and (5) are variable domains.
𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒 2 𝑄
(
𝒃,𝒛,𝝃
)
=min𝑓𝑥
∈∈
+𝛽𝑐
𝑥
∈∈
+𝐸[𝑄
(
𝒃,𝒛,𝒙, 𝝃
)
]
(6)
𝑠.𝑡. 𝑥
=1∀𝑖∈𝐶
∈
(7)
𝑥
=𝑥
∈
∀𝑖 ∈ 𝑉
∈
(8)
𝑥
≤𝑧
∀𝑖 ∈ 𝐶, 𝑘 ∈ 𝐻
(9)
𝑥
≤𝑧
∀𝑖 ∈ 𝐶, 𝑘 ∈ 𝐻
(10)
𝑥
+𝑧
+𝑧
∈
≤2 ∀𝑖∈𝐶,
𝑗
≠𝑖∈𝐶,𝑘∈𝐻
(11)
𝑣
−𝐷
+𝑞(1−𝑥
)≥𝑣
∀𝑖 ∈ 𝑉,
𝑗
≠𝑖∈𝐶
(12)
𝑣
≤𝑞 ∀𝑖∈𝑉
(13)
𝑥
∈
0,1
∀𝑖 ∈ 𝑉,
𝑗
∈𝑉
(14)
𝑣
≥ 0 ∀𝑖 ∈ 𝑉
(15)
Objective function (6) minimises the vehicle fixed
cost, local tour cost, and expected recourse cost. Each
client should be visited by exactly one vehicle, which
is guaranteed by Constraint (7). Constraint (8)
balances the vehicle flow at each vertex. Constraints
(9)-(11) link the allocation variables with routing
variables. Constraint (12) describes the delivery load
on vehicles. Vehicle capacity constraints are imposed
via Constraint (13). Decision variables are defined by
Constraints (14)-(15).
𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒 3 𝑄
(
𝒃,𝒛,𝒙,𝝃
)
=𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑅
(
𝒙,𝝃
)
+𝜔𝑒
∈
+𝛼𝑑
𝑐
𝑦
∈∈∈∈
(16)
𝑠.𝑡.𝑦
=𝑧
∀𝑖 ∈ 𝐶,
𝑗
∈𝐶,𝑘∈𝐻
∈
(17)
𝑦
=𝑧
∀𝑖 ∈ 𝐶,
𝑗
∈𝐶,𝑙∈𝐻
∈
(18)
𝑒
≥ 𝑑
𝑦
−𝑄
∈∈∈
∀𝑘∈𝐻
(19)
0≤𝑦
≤1∀𝑖∈𝐶,
𝑗
∈𝐶,𝑘∈𝐻,𝑙∈𝐻
(20)
𝑒
≥0∀𝑘∈𝐻
(21)
Objective function (16) optimises the realised
recourse cost (𝑅
(
𝒙,𝝃
)
) and overwork cost. Also, the
inter-hub transportation cost is calculated via the third
term of it. Constraints (17)-(18) correlate the flow
variables and allocation variables. Note that
Constraints (17)-(18), along with Constraints (9)-
(11), connect the allocation variables 𝒛 , flow
variables 𝒚, and routing variables 𝒙, ensuring the
proper network flow assignment. Overwork cost for
each hub 𝑘 ∈ 𝐻 is calculated via Constraint (19).
Constraints (20)-(21) are variable domains. Since
there is no simple way to formulate the computation
of 𝑅
(
𝒙,𝝃
)
via decision variables and linear
relationships (Laporte et al., 2002), we do not provide
a specific formulation here. However, one can find a
way to calculate its expectation in Laporte et al.
(2002) and Hernandez et al. (2019).
4 SOLUTION METHODOLOGY
4.1 Sample Average Approximation
The key to solving model (1)-(21) is calculating
𝐸[𝑄
(
𝒃,𝒛,𝝃
)
], which is very difficult even under a
discrete distribution. Thus, we present an SAA-based
approach to approximate 𝐸
[
𝑄
(
𝒃,𝒛,𝝃
)
]
. The SAA
approach is presented by Kleywegt et al. (2002),
whose principle is that sampling problems can
approximate the numerical expectation. A random
sample with size 𝑁 is generated first. Then the
CSAHLRPSD can be approximated as below:
𝑆𝐴𝐴 𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑚:𝑚𝑖𝑛 𝐹
𝑏
∈
+
1
𝑁
𝑄
(
𝒃,𝒛,𝝃
𝒏
)
(22)
s.t. (2)-(5)
(23)
ICORES 2024 - 13th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
86
The obtained solution is evaluated on a larger
sample with size 𝑁
( 𝑁
≫𝑁) by obtaining the
approximate SAA gap and the variance of the gap
estimator. If they are small enough, the solution is
accepted as the CSAHLRPSD’s solution. Otherwise,
the sample sizes should be increased. This process is
shown in Algorithm 1. In the algorithm, 𝑧
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
and 𝑧
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
denote the objective function values of
the solution
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
on scenario 𝜉
and sample 𝑁′,
respectively. We define “sufficiently small” as:
𝜖
,
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
/𝑧
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
≤3% and 𝜎
,
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
/
𝑧
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
≤5%.
Input: the number of SAA replications 𝑀 and the sample
sizes, 𝑁 and 𝑁
(𝑁
≫𝑁)
Step 1:
For 𝑚 = 1,2,…,𝑀, do:
Generate a sample with size 𝑁 by realising 𝜉
, 𝜉
, …, 𝜉
;
Solve the SAA to get the solution
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
and the objective
value 𝑧
;
Obtain the statistical lower-bound 𝑧
=
∑
𝑧
;
Obtain the variance of the statistical lower-bound 𝜎
(
𝑧
)
=
()
∑
(𝑧
−𝑧
)
;
Generate a sample with size 𝑁
and get the upper-
bound 𝑧
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
and a estimate of variance of upper-bound
𝜎
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
=
(
)
∑
(𝑧
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
−𝑧
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
)
;
Select the solution
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
with best 𝑧
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
then ontain the
SAA gap 𝜖
,
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
=𝑧
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
−𝑧
;
Calculate the variance of the SAA gap 𝜎
,
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
=
𝜎
(
𝑧
)
+𝜎
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
;
If 𝜖
,
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
and 𝜎
,
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
sufficiently small:
Go to Step 3;
End
End
Step 2:
If 𝜖
,
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
and 𝜎
,
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
not sufficiently small:
Increase the sample size 𝑁 and/or 𝑁
and go to Step 1
End
Step 3: Output:
(
𝒃,𝒛
)
^
Stop
Algorithm 1: SAA algorithm.
The SAA problem is a special variant of the HLP.
More complex, calculating 𝑄
(
𝒃,𝒛,𝝃
)
is NP-hard
even when 𝑏
(𝑘 ∈ 𝐻) and 𝑧
(𝑖∈𝐶,𝑘∈𝐻) are
fixed. As a result, two ALNS algorithms are
introduced as the solution approach for solving the
SAA problem and getting 𝑄
(
𝒃,𝒛,𝝃
)
, respectively.
These two algorithms are designed according to the
one used by Wu et al. (2022), which has been proven
to solve the HLRP efficiently. For notation simplicity,
we name them ALNS-SAA and ALNS-RECOURSE,
respectively.
4.2 Adaptive Large Neighbourhood
Search
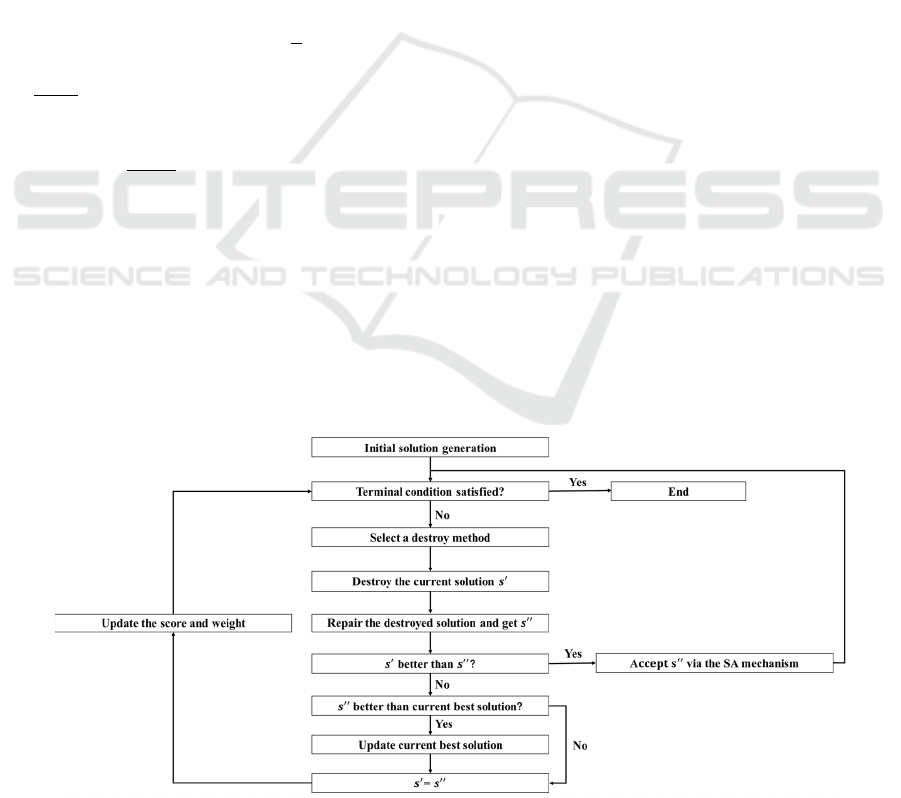
The ALNS algorithm has been successful in solving
various routing problems, e.g., vehicle routing
problem, pickup and delivery problem, location
routing problem, and so on. We follow the procedure
in Ropke and Pisinger (2006) to present the ALNS-
SAA and ALNS-RECOURSE: In each iteration, a
destroy method removes several clients from the
current solution, and then a repair method inserts
them into the destroyed solution to obtain a new
solution. Each method is associated with a weight and
is randomly selected based on their weights. The
weights are adjusted adaptively based on their
performance. The new solution is accepted is it is
Figure 4: ALNS algorithm
Stochastic Single-Allocation Hub Location Routing Problem for the Design of Intra-City Express Systems
87
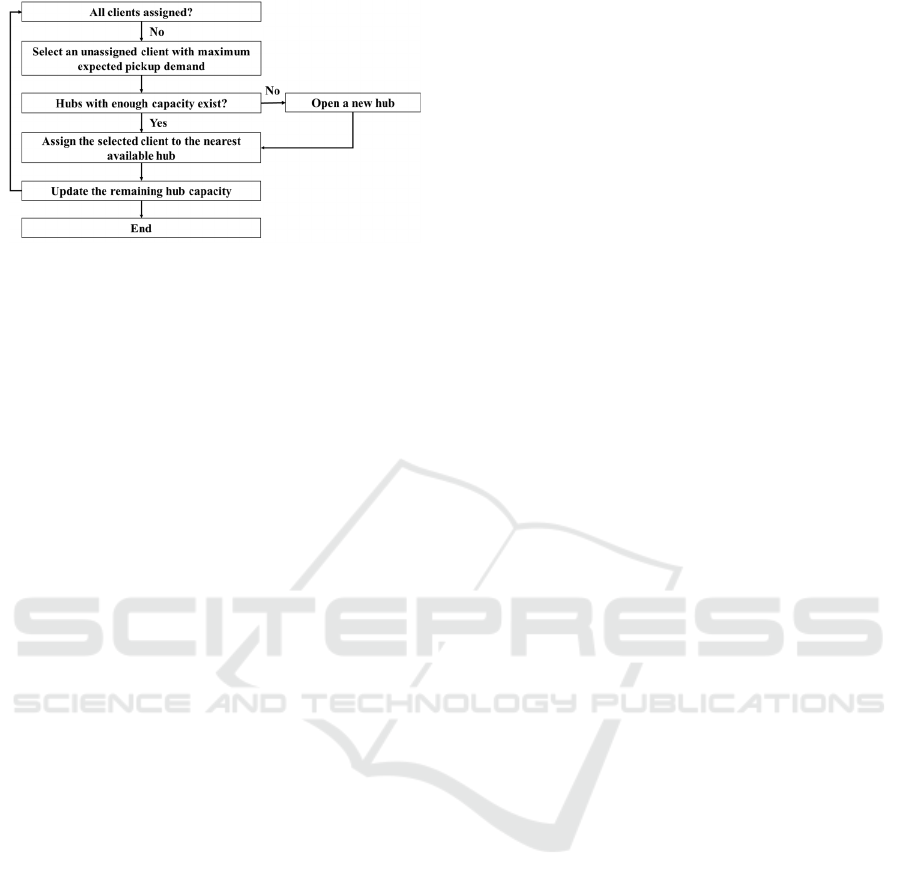
Figure 5: Greedy algorithm.
better than the current one. Otherwise, a simulated
annealing mechanism is applied to determine whether
the new solution is accepted. Although the ALNS-
SAA and ALNS-RECOURSE have the same
procedures, their destroy/repair methods and initial
solution generation methods are different, which will
be presented in Section 4.2.1 and Section 4.2.2.
Please refer to Wu et al. (2022) for the common parts
(e.g., weight adjustment, destroy/repair method
selection, and simulated annealing mechanism).
4.2.1 ALNS-SAA
a. Initial Solution Generation
We use the following greedy algorithm (Figure 5) for
the initial solution generation. The clients are
allocated to the nearest open hubs one-by-one. If such
hubs do not exist, a new hub is installed. The process
continues until all clients are assigned.
b. Destroy Method
Random Hub Removal: This method randomly
selects one open hub and closes it. All linked clients
are deleted from the current solution and added into
the client pool.
Worst Usage Hub Removal: This method closes
the open hub with the least utilisation ratio. All clients
allocated to it are deleted and added into the client
pool.
Random Hub Opening: This method randomly
selects one close hub and opens it. Then, several
clients are randomly selected, deleted from the
current solution, and then put in the client pool.
Random Allocation Change: This method aims
to optimise the allocation between clients and hubs.
The randomly-selected clients are deleted from the
current solution and inserted into the client pool.
Worst Allocation Removal: This method delates
some clients far from the hubs they are allocated to.
The distance is randomised and normalised to avoid
constantly selecting the same clients.
c. Repair Method
Greedy Insertion: The clients are inserted into
the solution randomly, one after the other, into the
position with minimum insertion cost.
4.2.2 ALNS-RECOURSE
a. Initial Solution Generation
The following nearest-neighbour algorithm
(Algorithm 2) is used to generate initial solutions for
calculating 𝑄
(
𝒃,𝒛,𝝃
)
.
For each open hub 𝑘:
While unlinked clients allocated to hub 𝑘 exist:
Initialise vertex 𝑣 = 𝑘
Initialize pickup capacity 𝑝=𝑞
Initialize delivery capacity 𝑑=𝑞
While available unrouted clients exist:
Select unrouted client 𝑖 nearest to 𝑣
𝑣=𝑖
𝑝=𝑝−𝐸[𝑂
],𝑑 = min
(
𝑝−𝑂
,𝑑−𝐷
)
End
End
End
Algorithm 2: Nearest-neighbour algorithm.
b. Destroy Method
Random Removal: This method chooses several
clients randomly and adds them into the client pool.
Worst Cost Removal: This method deletes some
clients far from the vertexs visited just before and
ahead of them.
Shaw Removal: This method aims to remove
clients similar to each other.
Random Route Removal: This method deletes a
randomly-selected route and adds its visited clients
into the client pool.
c. Repair Method
The same Greedy Insertion is used. However,
the clients can only be inserted into the routes
departing from their assigned hub.
5 NUMERICAL EXPERIMENTS
5.1 Instance Generation
The numerical experiments have been conducted on
the instances with up to 25 clients used in Wu et al.
(2023). These instances are generated from Australia
Post (AP) benchmark, and each instance is associated
with 5 potential hubs. In AP benchmark, two types of
capacities and fixed costs, tight (T) and loose (L), are
included. Hence, for each instance, four types of
ICORES 2024 - 13th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
88

Table 1: Experiment Results.
Instance
𝐹
𝐼𝑡𝑒 𝑇𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝐺𝑎𝑝
𝐶𝑜𝑣
Hub
𝐹
𝐺𝑎𝑝
10-L-L 222384.42 2 152.98 0.78 2.42 5 245590.46 9.45
10-L-T 241054.01 2 139.45 1.97 3.05 2,4 264116.68 8.73
10-T-L 248461.71 2 153.27 1.09 2.10 4,5 302806.87 17.95
10-T-T 281902.80 2 188.32 1.32 2.38 2,3,4 342478.48 17.69
15-L-L 287050.82 2 243.53 1.71 4.01 4,5 307109.76 6.53
15-L-T 332315.13 3 342.98 1.87 2.12 1,3 377309.28 11.93
15-T-L 348108.70 2 240.57 1.71 3.68 1,2,5 371482.83 6.29
15-T-T 382314.72 2 251.31 2.56 3.32 1,4 424999.28 10.04
20-L-L 333865.76 2 516.37 1.74 2.49 4,5 364298.63 8.35
20-L-T 351368.10 3 718.51 1.62 3.65 3,4 409825.32 14.26
20-T-L 392668.70 2 588.52 2.56 3.35 3,4,5 438775.19 10.51
20-T-T 428306.20 2 595.87 1.19 2.21 1,2,4 435075.15 1.56
25-L-L 346804.95 2 1011.23 2.05 1.70 2,5 372620.88 6.93
25-L-T 372854.75 2 1403.59 1.54 2.58 2,3 406846.89 8.36
25-T-L 415943.60 2 1236.84 1.63 4.43 2,3,4 427874.59 2.79
25-T-T 441345.67 2 1238.92 2.41 1.88 2,3,4 487703.49 9.51
problems (i.e., LL, LT, TL, and TT) can be created.
The used instances are named as N-Q-F, where 𝑁 ∈
10,15,20,25
denotes the number of clients,
and 𝑄 and 𝐹 indicate the type of hub capacity and
fixed cost (tight and loose), respectively. For
example, 15-L-L means an instance with 15 clients,
and its hub capacity and fixed cost are loose.
We have adjusted these instances and applied the
proposed SAA framework to them. The main
adjustments are:
(i) The flow 𝑑
of each pair of clients 𝑖 and
𝑗
(
𝑗≠𝑖
)
is assumed to be subject to a uniform
distribution [0.6𝑑
, 1.4𝑑
], in which 𝑑
is the value
provided by the generator.
(ii) Vehicle capacity and fixed cost were set as
850 and 3000 in all instances, respectively, ensuring
that each client could be served by a single vehicle.
The SAA framework is corded in Java, and a PC
with Intel i5-13600KF CPU and 32 GB RAM is used
to conduct the experiments.
5.2 Computation Results
In this section, the stochastic model and deterministic
model are compared. For the stochastic model, we
employ the SAA framework (𝑁=40,
𝑁′ = 2000,
𝑀=10) for each instance. For the deterministic
model, each instance is solved by the branch-and-
price-and-cut algorithm used in Wu et al. (2023), in
which the values of the random variables are set as
their mathematical expectations. After solving the
stochastic model and deterministic model, a new
sample with size 2000 (called evaluation sample) is
generated to compare their solutions’ qualities. The
comparison is concluded in Table 1. The definition of
the notations in it is presented below:
𝐹
: the operation cost of the evaluation
sample of the SAA framework.
𝐼𝑡𝑒: the number of SAA problems used to
achieve sufficiently small gap and variance.
𝑇𝑖𝑚𝑒: computational times (second) for the
SAA framework.
𝐺𝑎𝑝
: the SAA gaps.
𝐶𝑜𝑣
: the coefficient of variation (COV)
of the SAA approximator.
𝐹
: the operation cost of the evaluation
sample of the deterministic model.
𝐺𝑎𝑝
: the gap between 𝐹
and 𝐹
.
It can be concluded in Table 1 that the SAA
framework dealt with the CSAHLRPSD adequately:
𝐺𝑎𝑝
(1.74% on average and 2.56% in the worst
Stochastic Single-Allocation Hub Location Routing Problem for the Design of Intra-City Express Systems
89

case) and 𝐶𝑜𝑣
(2.84% on average and 4.43% in
the worst case) were small. Moreover, in 14 of 16
instances, two SAA replications are needed to reach
the small-enough 𝐺𝑎𝑝
and 𝐶𝑜𝑣
, indicating that
the sample size is chosen adequately. Furthermore,
the column “Time” demonstrated that the SAA
framework was able to solve the CSAHLRPSD in
acceptable calculational times, and all instances were
solved in less than 1500s. These computational times
are acceptable as long-term decisions need to be
determined only once for each network. Furthermore,
for each service cycle, the short-term decisions can be
determined in a very short time. Finally, one can find
that considering stochastic factors can effectively cut
down the cost: the average 𝐺𝑎𝑝
is 9.43%, while the
best 𝐺𝑎𝑝
is 17.95%.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we concentrated on the CSAHLRPSD
problem. The aim of the problem is to design an intra-
city express system in a practical environment.
Therefore, capacitated hubs and vehicles were
employed, and the flows were assumed to be
stochastic. The problem was formulated as a multi-
stage recourse model, and an SAA framework was
introduced to solve the problem. In the framework,
two variants of the ALNS algorithm were used to
solve the SAA problem and to calculate the recourse
cost. The proposed method was evaluated on the
benchmark instances, proving that the SAA
framework can solve the CSAHLRPSD in acceptable
computational times and that considering stochastic
factors can effectively decrease the operation cost (by
9.43% on average). Future studies include proposing
more efficient algorithms to calculate the recourse
cost and to apply the framework to more instances.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Japan Society for the
Promotion of Science (JSPS), Kakenhi (Grants-in-
Aid for ScientificResearch - C) [20K04739] and the
National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant
No. 72301052).
REFERENCES
Alumur, S. A., Campbell, J. F., Contreras, I., Kara, B. Y.,
Marianov, V., & O’Kelly, M. E. (2021). Perspectives
on modeling hub location problems. European Journal
of Operational Research, 291(1), 1-17.
Bostel, N., Dejax, P., & Zhang, M. (2015). A model and a
metaheuristic method for the hub location routing
problem and application to postal services. 2015
International Conference on Industrial Engineering and
Systems Management (pp. 1383-1389). IEEE.
Catanzaro, D., Gourdin, E., Labbé, M., & Özsoy, F. A.
(2011). A branch-and-cut algorithm for the
partitioning-hub location-routing problem. Computers
& operations research, 38(2), 539-549.
Çetiner, S., Sepil, C., & Süral, H. (2010). Hubbing and
routing in postal delivery systems. Annals of
Operations research, 181(1), 109-124.
Danach, K., Gelareh, S., & Monemi, R. N. (2019). The
capacitated single-allocation p-hub location routing
problem: a Lagrangian relaxation and a hyper-heuristic
approach. EURO Journal on Transportation and
Logistics, 8(5), 597-631.
de Camargo, R. S., de Miranda, G., & Løkketangen, A.
(2013). A new formulation and an exact approach for
the many-to-many hub location-routing problem.
Applied Mathematical Modelling, 37(12-13), 7465-
7480.
Ebery, J., Krishnamoorthy, M., Ernst, A., & Boland, N.
(2000). The capacitated multiple allocation hub
location problem: Formulations and algorithms.
European journal of operational research, 120(3), 614-
631.
Ernst, A. T., & Krishnamoorthy, M. (1999). Solution
algorithms for the capacitated single allocation hub
location problem. Annals of operations Research, 86,
141-159.
Fontes, F. F. D. C., & Goncalves, G. (2021). A variable
neighbourhood decomposition search approach applied
to a global liner shipping network using a hub-and-
spoke with sub-hub structure. International Journal of
Production Research, 59(1), 30-46.
Gelareh, S., & Nickel, S. (2011). Hub location problems in
transportation networks. Transportation Research Part
E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 47(6), 1092-
1111.
Ghaffarinasab, N. (2022). Stochastic hub location problems
with Bernoulli demands. Computers & Operations
Research, 145, 105851.
Hernandez, F., Gendreau, M., Jabali, O., & Rei, W. (2019).
A local branching matheuristic for the multi-vehicle
routing problem with stochastic demands. Journal of
Heuristics, 25, 215-245.
Hu, Q. M., Hu, S., Wang, J., & Li, X. (2021). Stochastic
single allocation hub location problems with balanced
utilisation of hub capacities. Transportation Research
Part B: Methodological, 153, 204-227.
Karimi, H. (2018). The capacitated hub covering location-
routing problem for simultaneous pickup and delivery
systems. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 116, 47-
58.
Kartal, Z., Hasgul, S., & Ernst, A. T. (2017). Single
allocation p-hub median location and routing problem
with simultaneous pick-up and delivery. Transportation
ICORES 2024 - 13th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
90

Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review,
108, 141-159.
Kleywegt, A. J., Shapiro, A., & Homem-de-Mello, T.
(2002). The sample average approximation method for
stochastic discrete optimisation. SIAM Journal on
optimisation, 12(2), 479-502.
Laporte, G., Louveaux, F. V., & Van Hamme, L. (2002).
An integer L-shaped algorithm for the capacitated
vehicle routing problem with stochastic demands.
Operations Research, 50(3), 415-423.
Li, X., & Zhang, K. (2018). A sample average
approximation approach for supply chain network
design with facility disruptions. Computers & Industrial
Engineering, 126, 243-251.
Mohammadi, M., Razmi, J., & Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.
(2013). Multi-objective invasive weed optimisation for
stochastic green hub location routing problem with
simultaneous pick-ups and deliveries. Economic
Computation & Economic Cybernetics Studies &
Research, 47(3).
Nagy, G., & Salhi, S. (1998). The many-to-many location-
routing problem. Top, 6(2), 261-275.
Pandiri, V., & Singh, A. (2021). A simple hyper-heuristic
approach for a variant of many-to-many hub location-
routing problem. Journal of Heuristics, 27(5), 791-868.
Ratli, M., Urošević, D., El Cadi, A. A., Brimberg, J.,
Mladenović, N., & Todosijević, R. (2020). An efficient
heuristic for a hub location routing problem.
Optimisation Letters, 1-20.
Rodríguez-Martín, I., Salazar-González, J. J., & Yaman, H.
(2014). A branch-and-cut algorithm for the hub location
and routing problem. Computers & Operations
Research, 50, 161-174.
Ropke, S., & Pisinger, D. (2006). An adaptive large
neighborhood search heuristic for the pickup and
delivery problem with time windows. Transportation
science, 40(4), 455-472.
Sun, J. U. (2013). An integrated hub location and multi-
depot vehicle routing problem. Applied Mechanics and
Materials, 409, 1188-1192.
Sun, J. U. (2015). An endosymbiotic evolutionary
algorithm for the hub location-routing problem.
Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015.
Wu, Y., Qureshi, A. G., & Yamada, T. (2022). Adaptive
large neighborhood decomposition search algorithm for
multi-allocation hub location routing problem.
European Journal of Operational Research, 302(3),
1113-1127.
Wu, Y., Qureshi, A. G., Yamada, T., & Yu, S. (2023).
Branch-and-price-and-cut algorithm for the capacitated
single allocation hub location routeing problem. Journal
of the Operational Research Society, 1-13.
Yang, X., Bostel, N., & Dejax, P. (2019). A MILP model
and memetic algorithm for the hub location and routing
problem with distinct collection and delivery tours.
Computers & Industrial Engineering, 135, 105-119.
Zhao, L., Wang, X., Stoeter, J., Sun, Y., Li, H., Hu, Q., &
Li, M. (2019). Path optimization model for intra-city
express delivery in combination with subway system
and ground transportation. Sustainability, 11(3), 758.
Stochastic Single-Allocation Hub Location Routing Problem for the Design of Intra-City Express Systems
91
