
Solving Many-Objective Optimization Problems Using Selection
Hyper-Heuristics
Adeem Ali Anwar
a
, Guanfeng Liu
b
and Xuyun Zhang
c
School of Computing, Macquarie University, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Keywords:
Hyper-Heuristic, Many-Objective Optimization, Knapsack Problem, Job-Shop Scheduling Problem.
Abstract:
To effectively solve discrete optimization problems, meta-heuristics and heuristics have been used but their
performance suffers drastically in the cross-domain applications. Hence, hyper-heuristics (HHs) have been
used to cater to cross-domain problems. In literature, different HHs and meta-heuristics have been applied to
solve the Many-objective Job-Shop Scheduling problem (MaOJSSP) and Many-objective Knapsack problem
(MaOKSP) but the results are not convincing. Furthermore, no researchers have tried to solve these problems
as cross-domain together using HHs. Additionally, the considered HH known as the cricket-based selection
hyper-heuristic (CB-SHH) has not applied to any variation of the Job-shop scheduling problem (JSP) and the
knapsack problem (KSP). This paper compares the performance of recently proposed HHs named CB-SHH,
H-ACO, MARP-NSGAIII, and meta-heuristics named MPMOGA, MOEA/D on MaOKSP, MaOJSSP and
benchmark problems. The performance of state-of-the-art HHs and meta-heuristics have been compared using
hypervolume (HV) and µ norm. The main contribution of the paper is to effectively solve the MaOJSSP and
MaOKSP using HHs and to prove the effectiveness of the best HHs on benchmark problems. It is proven
through experiments that the CB-SHH is the best-performing algorithm on 44 out of 48 instances across all
datasets and is the best cross-domain algorithm across the datasets.
1 INTRODUCTION
On the basis of objective functions, optimization
problems develop to discover the best possible solu-
tion. The objective functions are either maximized
or minimized depending on the specific problem at
hand. Depending on how many objective functions
are involved, there are several kinds of optimization
challenges. The primary focus of single-objective op-
timization problems (SOOPs) is the single-objective
function. Multiple but less than four objective
functions are taken into account in multi-objective
optimization problems (MOOPs), and lastly many-
objective optimization problems (MaOOPs) are those
which have four or more objective functions (Anwar
and Younas, 2020).
With the help of area experts, meta-heuristics
have successfully been used to solve computation-
ally hard optimization issues. These meta-heuristics,
however, frequently run into trouble when the prob-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6474-3810
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8980-4950
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7353-4159
lem is slightly altered. This challenge is addressed
by hyper-heuristics (HHs), which give a cross-domain
method for solving various optimization difficulties
with little need for customization. The two primary
categories of HHs are generation HHs and selection
HHs. Based on the kind of search space, categories
are created. The process of choosing the best low-
level heuristics (LLHs) for a particular optimization
issue is automated by the selection HHs. Whereas,
generation HHs automate the processes for creating
LLHs (Drake et al., 2020). In the selection HHs,
LLHs are selected using high-level techniques. LLHs
can be recombination operators, meta-heuristics, etc
(Drake et al., 2020).
JSSP is common in a variety of industrial and
technical management sectors, such as the fabrica-
tion of printed circuit boards, the supply chains for
the clothing industry, and cloud computing. In JSSPs,
a group of tasks must go through a predetermined
number of processes, and an industrial factory must
decide the best sequence in which these procedures
are carried out on the available equipment to meet
predetermined goals (Liu et al., 2021). To optimize
certain objectives, JSSPs need the use of algorithms
194
Anwar, A., Liu, G. and Zhang, X.
Solving Many-Objective Optimization Problems Using Selection Hyper-Heuristics.
DOI: 10.5220/0012314400003636
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2024) - Volume 3, pages 194-201
ISBN: 978-989-758-680-4; ISSN: 2184-433X
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

to choose the order of operations on each machine
while taking into account a variety of limitations (Liu
et al., 2021). The many-objective Job-Shop Schedul-
ing Problem (MaOJSSP), which has five optimiza-
tion goals of completion time, total tardiness, ad-
vance time, production cost, and machine loss, is
the subject of our study. The problem of balancing
the optimization of both time and cost targets must
be taken into consideration while designing the al-
gorithm since time and cost in MaOJSSP sometimes
clash with one another (Liu et al., 2021).
KSP is a well-known combinatorial optimization
problem. It involves a collection of things, each of
which has a weight and a value. The goal is to choose
the best goods to add to a collection while keeping
in mind that the overall weight must not go over a
certain threshold. Maximizing the combined worth
of the chosen things is the objective (Ishibuchi et al.,
2013). In this paper, we have considered the KSP with
4, 6, 8, and 10 objectives with 500 items (Ishibuchi
et al., 2013). The variations are generated from the
original problem of 2 objectives.
In literature, most of the studies based on many-
objective HHs fall behind in evaluating their HHs on
real-life applications. Moreover, the researchers have
proposed various many-objective HHs and applied
them to different real-life problems. They have con-
sidered the MaOJSSP, and MaOKSP separately and
tried to solve them through different meta-heuristics
and HHs, but their results have not been very effi-
cient. Furthermore, no researchers have tried to solve
these problems as cross-domain together using HHs.
Additionally, the considered HH (CB-SHH) has not
applied to any variation of JSP and KSP.
In this paper, we have considered three different
well-known HHs, A Cricket-Based Selection Hyper-
Heuristic (CB-SHH) (Anwar et al., 2022), ACO-
based HH known as H-ACO (Rivera et al., 2023), Ge-
netic programming HH with gaussian process-based
reference adaption known as MARP-NSGAIII (Ma-
sood et al., 2022) and two meta-heuristics named as
multiple population-based genetic algorithm known
as MPMOGA (Liu et al., 2021), multi-objective evo-
lutionary algorithm based on decomposition known
as MOEA/D (Ishibuchi et al., 2013). We have applied
these HHs and meta-heuristics on two well-known
and important MaOOPs known as MaOJSSP and
MaOKSP, along with benchmark datasets of DLTZ
and WFG. To the best of our knowledge, the CB-SHH
has not been applied to MaOJSSP and MaOKSP be-
fore and no researchers have tried to solve these prob-
lems as cross-domain together.
The main contribution of the paper is to effec-
tively solve the MaOJSSP and MaOKSP problem, to
choose the best HHs for MaOJSSP, and MaOKSP and
to prove the effectiveness of the best HHs on different
benchmark problems.
In conclusion, MaOJSSP, MaOKSP, DTLZ, and
WFG are solved using HHs and meta-heuristics
known as CB-SHH, H-ACO, MARP-NSGAIII, MP-
MOGA, and MOEA/D. To choose the best cross-
domain algorithm, different evaluation measures in-
cluding Hypervolume (HV), and µ norm have been
used. Experiments show the CB-SHH is the best-
performing algorithm on 44 out of 48 instances across
all datasets and is the best cross-domain algorithm on
all the datasets.
The remaining paper structure is as follows. The
related work is discussed in Section 2. The MaOJSSP
and MaOKSP are discussed in Section 3. The HHs
and meta-heuristics are explained in Section 4. Sec-
tion 5 discusses the empirical studies, whereas the last
section presents the conclusion and future work.
2 RELATED WORK
The following section discusses the recent related
work done for many-objective HHs, MaOJSSP and
MaOKSP.
Venske et al. (Venske et al., 2022) examined the
usefulness of HH in combinatorial optimization, par-
ticularly in the context of MOEA/DD and Differen-
tial Evolution. Four selection HHs: Self-Adaptive
Differential Evolution, Probability Matching, Adap-
tive Pursuit, and Thompson Sampling were stud-
ied thoroughly. A warm-up phase and a discard
mechanism were included in the suggested method
for choosing LLHs. To solve MaOOPs, Rivera et
al. (Rivera et al., 2023) proposed HyperACO, an
HH method that combines interval outranking mod-
els with MOEAs. Greater flexibility and adaptabil-
ity were possible due to HyperACO’s autonomous
search for the optimal set of outranking models to
take decision-maker preferences into account. An-
war et al. (Anwar et al., 2022) presented a sports-
based HH to solve the MaOOPs and were the first
ones to effectively propose any sports-based HHs
and solve the MaOOPs. (Anwar et al., 2023) in-
troduced a preference-based HH to effectively solve
the MaOOPs and tested its effectiveness on various
many-objective benchmark problems.
Masood et al. (Masood et al., 2022) improved
MaOJSSP by MARP-NSGA-III, a method that in-
tegrated a Gaussian Process-based reference point
adaption mechanism. Liu et al. (Liu et al., 2021)
proposed MaOJSSP that takes five goals for man-
ufacturers’ time and cost efficiency into account.
Solving Many-Objective Optimization Problems Using Selection Hyper-Heuristics
195
Unique multiple populations for multiple objectives
(MPMO) framework-based genetic algorithm named
MPMOGA was suggested to simultaneously optimize
these goals. Sang et al. (Sang and Tan, 2022b) tackled
the high-dimensional green MaOJSSP. The proposed
SV-MA incorporated a fitness calculation approach
based on shift-based density estimation and com-
bined the enhanced strength Pareto evolution method
(SPEA2) with variable neighborhood search. Ou et al.
(Qu et al., 2022) discussed the necessity for shop floor
schedules that concurrently take conventional goals,
energy use, and environmental considerations into ac-
count. The practical case study for MaOJSSP illus-
trated the many-objective model’s efficacy in lower-
ing energy usage and enhancing sustainability on the
shop floor. Sang et al. (Sang and Tan, 2022a) stud-
ied the MaOJSSP collaborative scheduling issue (Ma-
ODFJCSP), which was essential for developing adap-
tive, flexible, and green manufacturing processes. A
high-dimensional many-objective memetic algorithm
(HMOMA), combining an enhanced NSGA-III and
a local search technique, was suggested to success-
fully solve the problem. In order to solve the di-
versity problem in MOEA/D, Huang et al. (Huang
et al., 2020) suggested MOEA/D-DDC, a cooperative
evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition and
dominance. A decomposition-based population and
a dominance-based archive were used by MOEA/D-
DDC, with the decomposition-based population pro-
viding elite individuals to the archive and the archive
helping to restore the population and increase variety.
Ishibuchi et al. (Ishibuchi et al., 2013) studied the ef-
fectiveness of MOEA/D for multi-objective optimiza-
tion along with the effects of various scalarizing func-
tions. The weighted Tchebycheff and PBI functions
with the right parameter values beat the weighted sum
and PBI functions without penalty factors for two-
objective issues.
In conclusion, the researchers have proposed var-
ious many-objective HHs and applied them to differ-
ent real-life problems. Moreover, they have consid-
ered the MaOJSSP and MaOKSP separately, and tried
to solve them through different meta-heuristics and
HHs, but the results have not been very efficient. Most
of the researchers focused on solving one problem,
rather than using HHs to solve multi-domain prob-
lems, which is one of the issues which is being ad-
dressed in this paper. Furthermore, no researchers
have tried to use HHs to solve the MaOJSSP and
MaOKSP through the same HHs.
In this paper, we have considered three differ-
ent well-known HHs (CB-SHH, H-ACO, MARP-
NSGAIII) and two meta-heuristics (MPMOGA,
MOEA/D) and applied them to MaOJSSP and
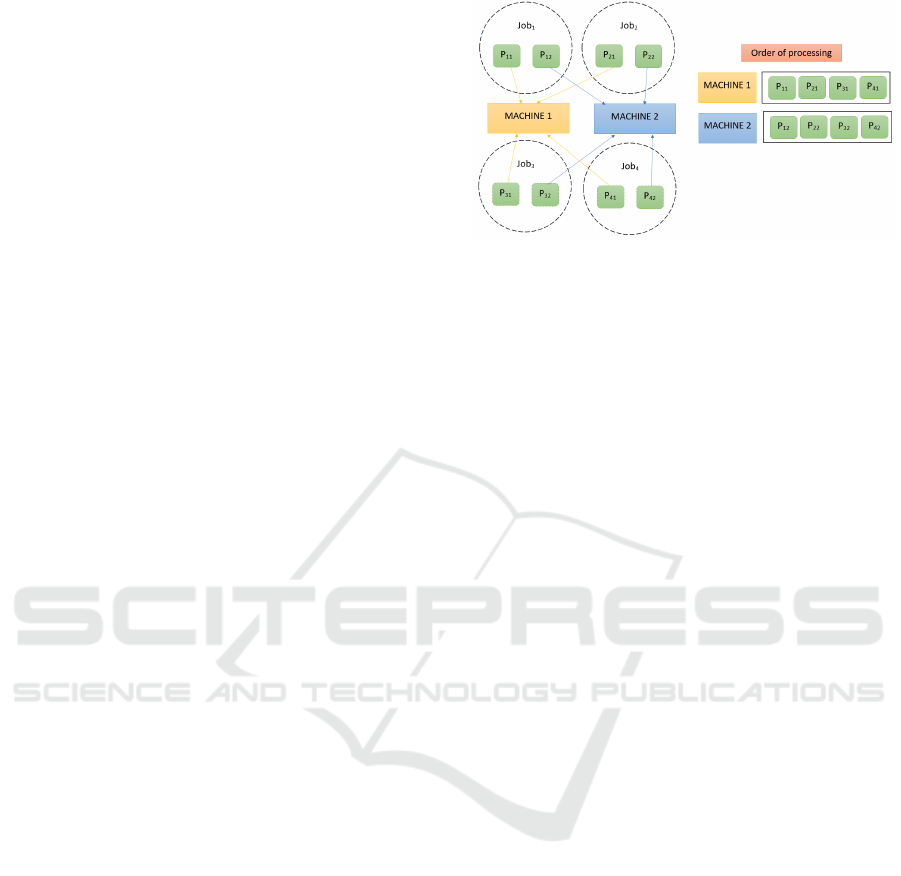
Figure 1: MaOJSSP.
MaOKSP, along with benchmark datasets of DLTZ
and WFG. To the best of our knowledge, the CB-SHH
has not been applied to MaOJSSP and MaOKSP be-
fore and no researchers have tried to solve these prob-
lems as cross-domain together. CB-SHH is the best-
performing algorithm on 44 out of 48 instances across
all datasets and is the best cross-domain algorithm on
all the datasets.
3 MANY-OBJECTIVE
OPTIMIZATION PROBLEMS
(MaOOPs)
In this section, the MaOOPs that are considered in
this paper are discussed. (Liu et al., 2021), (Ishibuchi
et al., 2013), (Deb et al., 2005), (Huband et al., 2005)
3.1 Many-Objective Job-Shop
Scheduling Problem (MaOJSSP)
In JSSPs, a group of tasks must go through a predeter-
mined number of processes, and an industrial factory
must decide the best sequence in which these proce-
dures are carried out on the available equipment to
meet predetermined goals (Liu et al., 2021). In Fig-
ure 1, there are four jobs and two machines. Every
job has two procedures. P
i
j, where i represents the
job and j represents the ranking. Jobs are allocated
to the machines based on their ranking and order. An
example of the order of processing is also shown on
the right side. In order to optimize certain objectives,
JSSPs need the use of algorithms to choose the order
of operations on each machine while taking into ac-
count a variety of limitations (Liu et al., 2021). Five
constraints are also considered. First of all, at time
0, every job is released. Second, because only one
procedure can be handled by each machine at once,
simultaneous processing is not possible. Thirdly, a
machine cannot move to another operation before the
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
196

present one is finished processing since disruptions
are not permitted during that time. Additionally, each
job’s processes need to be carried out in a specific or-
der based on a rating. Last but not least, each method
can only be executed once to prevent double process-
ing. The objectives are taken from (Liu et al., 2021)
and are represented as follows:
f unc
1
=
I
max
i=0
T
i
(1)
f unc
2
=
I
∑
i=0
max(T
i
−Y
i
, 0) (2)
f unc
3
=
I
∑
i=0
min(T
i
−Y
i
, 0) (3)
f unc
4
=
T
∑
t=1
(wt
t
∗ c w + st
t
∗ c s) (4)
f unc
5
=
T
∑
t=1
count
t
(5)
The goal is to minimize the five objectives (com-
pletion time, total tardiness, advance time, production
cost, and machine loss). Completion time is repre-
sented by T
i
, the Due date of a job is represented by Y
i
,
work time and sleep time are represented by wt
t
and
st
t
respectively. Production cost during working and
sleeping time is represented by c w and c s respec-
tively. MaOJSSP is considered with five objectives
represented by f unc. In f unc
1
, the maximum time
for completion of all jobs is calculated. Total tardi-
ness is denoted by f unc
2
. f unc
3
represents the total
time of the jobs that will be completed before the due
date. The cost of production during sleep and work-
ing time is represented by f unc
4
. f unc
5
calculates the
count of how many times, the machine changed from
sleeping to working mode.
3.2 Many-Objective Knapsack Problem
(MaOKSP)
The knapsack problem involves a collection of things,
each of which has a weight and a value. The goal is
to choose the best goods to add to a collection while
keeping in mind that the overall weight must not go
over a certain threshold. Maximizing the combined
worth of the chosen things is the objective (Ishibuchi
et al., 2013). KSP is stated as follows (Ishibuchi et al.,
2013):
f unc
j
(y) =
T
∑
k=1
p
jk
y
k
, j = 1, 2, ..., 10
sub ject to
T
∑
i=1
w
ji
y
i
≤ c
j
, i = 1, 2, ..., T
(6)
T is the number of items. p
jk
is the profit of k
item according to j knapsack. y is the binary string
of 500 bits. w
ji
is the weight of i item according to j
knapsack. c
j
is the constant value that represents the
capacity. Profit and weight values are generated ran-
domly between 10 and 100 and c
j
is the half of total
weights. The considered objectives are 4, 6, 8, and
10 with 500 items (T) and stated as follows (Ishibuchi
et al., 2013):
h
j
(y) = α f unc
2
(y) + (1 − α) f unc
j
(y)
f or j = 4, 6, 8, 10
(7)
where α is a co-relation strengths between the ob-
jectives. and its between 0 to 1.
4 ALGORITHMS FOR
COMPARATIVE STUDIES
4.1 A Cricket-Based Selection
Hyper-Heuristic (CB-SHH)
A selection HH approach called cricket-based selec-
tion hyper-heuristic (CB-SHH) is proposed by Anwar
et al. (Anwar et al., 2022) (shown in Figure 2. It
draws its inspiration from the game of cricket. The
striker and the non-striker are the only two batsmen
on the field at once in cricket. The side with the
most runs scored wins at the end (Anwar et al., 2022).
Their objective is to score as many runs as they can
(Anwar et al., 2022). While the non-striker waits un-
til the striker has scored a particular amount of runs
before taking the strike, the striker is the player that
actively plays the ball (Anwar et al., 2022). The most
effective batters are typically given opportunities first,
and depending on their historical scoring trends, their
future batting positions may alter. Similarly most ef-
fective LLHs are given chances at first and the best
LLHs are decided on how they performed before (An-
war et al., 2022). For MaOOPs, CB-SHH strives to
produce well-diverse and convergent optimum solu-
tions. The method’s use of delta evaluation, which
addresses a significant weakness of previous HHs, is
one of its important contributions. CB-SHH uses ran-
domization for exploration and a greedy technique for
exploitation. In addition, LLHs (many-objective algo-
rithms) are used to direct the CB-SHH search process
(Anwar et al., 2022).
4.2 H-ACO
This section introduces H-ACO, a cutting-edge HH
created to tackle MaOOPs by sequentially imple-
Solving Many-Objective Optimization Problems Using Selection Hyper-Heuristics
197
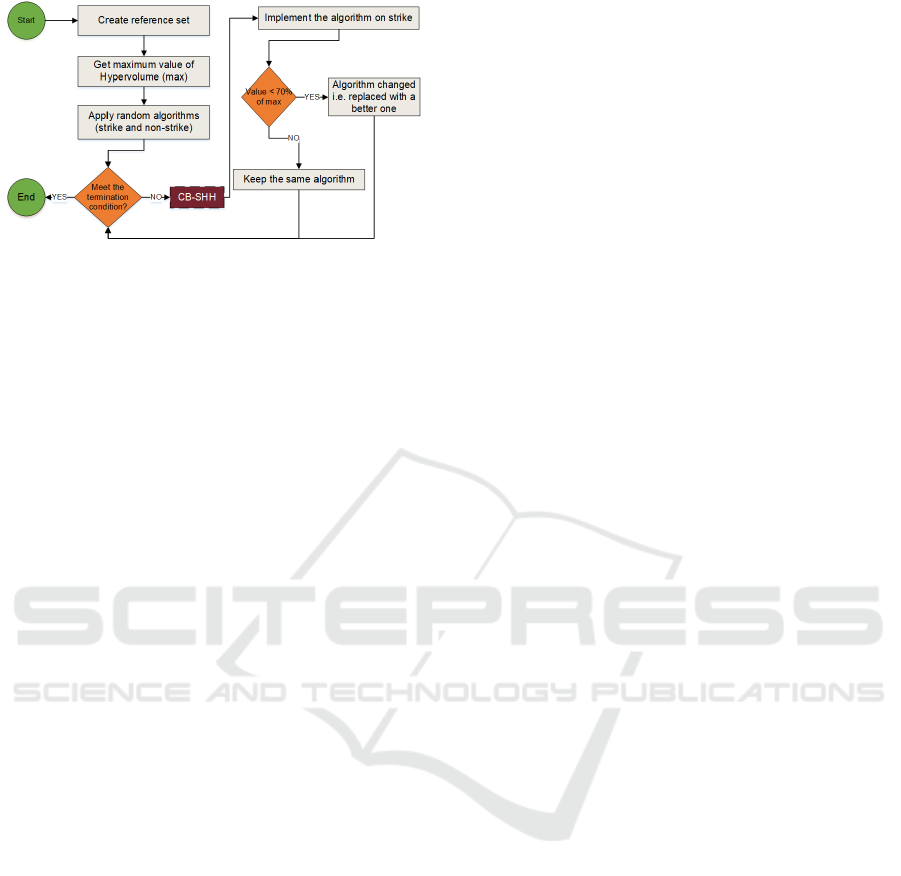
Figure 2: Flowchart of CB-SHH.
menting numerous MOEA/D/O variations (Rivera
et al., 2023). Decision makers (DMs) use out-
ranking models, which are frequently used in non-
compensatory H-ACO. The approach uses an Ant
Colony Optimisation (ACO) algorithm to determine
the best answer to a sequencing optimization problem
with discrete choice variables (Rivera et al., 2023). It
is made up of a high-level heuristic (HLH) (Rivera
et al., 2023). The goal functions to determine the
sequence that most closely matches the DM’s pref-
erences by evaluating the distance from the Region
of Interest (RoI) (Rivera et al., 2023). In addition,
LLHs try to find the best compromise solution in
MaOOPs with continuous decision variables by in-
cluding outranking relations into MOEA/D/O (Rivera
et al., 2023). In this instance, the objective functions
assess the effectiveness of the proposed solutions us-
ing the outranking model, taking into account both
their strengths and weaknesses (Rivera et al., 2023).
4.3 Genetic Programming HH with
Gaussian Process-Based Reference
Adaption (MARP-NSGAIII)
MARP-NSGAIII (Masood et al., 2022) is a ge-
netic programming-based HH that uses the Gaussian
method for reference points and is designed to solve
MaOJSSP. It is an advanced version of one of the most
famous algorithms NSGA-III (Deb and Jain, 2013).
The solutions that are lost from the final front and the
acceptable front members that couldn’t be completely
accommodated by NSGA-III are saved by MARP-
NSGA-III in a set, after finishing the non-dominated
sorting process. This method also makes use of the
simplexs’ preset positions as well as the set acquired
by NSGA-III.
Overall, Masood et al. (Masood et al., 2022)
improved MaOJSSP by MARP-NSGA-III, a method
that integrated a Gaussian Process-based reference
point adaption mechanism. Experimental compar-
isons showed that MARP-NSGA-III greatly improved
performance on a variety of benchmark datasets when
compared to well-known many-objective algorithms.
4.4 Multiple Population-Based Genetic
Algorithm (MPMOGA)
MPMOGA (Liu et al., 2021) is a genetic algorithm
based on multiple populations. MPMOGA is used
to address the MaOJSSP, which combines the advan-
tages of the MPMO (Multi-Objective Parallel Meta-
heuristic Optimisation) framework with Genetic Al-
gorithms (GA). The reason for using the MPMO
framework is based on its previous applications in
maximizing individual goals. An archive is created
within MPMOGA to keep the top-performing solu-
tions found throughout the evolutionary process. In
the crossover operation, Adaptive Selection Tech-
nique (AST) is used, which promotes co-evolution
across all populations. To further improve the cal-
iber of top solutions kept in the archive, an Adaptive
Update Strategy (AUS) is used as well.
4.5 Multi-Objective Evolutionary
Algorithm Based on Decomposition
(MOEA/D)
MOEA/D (Ishibuchi et al., 2013) is an evolution-
ary Algorithm based on Decomposition for multi-
objective optimization. This method divides a multi-
objective optimization issue into several smaller
scalar optimization problems and solves them all at
once. The computational cost in each generation is
greatly lowered since each sub-problem’s optimiza-
tion process only uses data from its nearby sub-
problems (Ishibuchi et al., 2013).
5 EMPIRICAL STUDIES
In this section, the empirical studies are discussed.
CB-SHH, H-ACO, MARP-NSGAIII, MPMOGA,
and MOEA/D have been applied on MaOJSSP,
MaOKSP, DTLZ, and WFG, and HV and µ norm
values have been calculated to provide the best algo-
rithm.
5.1 Experimental Settings
5.1.1 Datasets
For MaOJSSP, 12 datasets named as FT06, FT10,
FT20, LA01, LA05, LA10, LA15, LA20, LA25,
LA30, LA35, and LA40 have been used (JSSP
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
198

Figure 3: Mean HV values on MaOJSSP, MaOKSP, DTLZ and WFG.
Dataset, 2023). All of these datasets have different
dimensionality varying from 6 jobs and 6 machines
to 30 jobs and 10 machines (Liu et al., 2021). For
MaOKSP, 4 datasets have been considered with 500
items named 4-500, 6-500, 8-500, and 10-500. 4, 6, 8,
and 10 objectives have been considered respectively.
In benchmark datasets, DTLZ 1, 3, and 6 along with
WFG 1, 3, 6, 8, and 9 have been used (Deb et al.,
2005), (Huband et al., 2005). DTLZ 1 covers how
well the algorithm converges to the hyper-plane (Deb
et al., 2005). DTLZ 3 and 6 test the algorithms’ abil-
ity to converge towards optimal solutions (Deb et al.,
2005). WFG 1 is separable and has uni modality with
convex as well as mixed geometry, whereas WFG 3,
6, and 8 are non-separable with uni modality (Huband
et al., 2005). WFG 3 has linear as well as degenerate
geometry (Huband et al., 2005). WFG 6, 8, and 9
have concave geometry (Huband et al., 2005). WFG
9 is non-separable and has multi and deceptive modal-
ity (Huband et al., 2005).
5.1.2 Parameters Selections
The values for HHs and meta-heuristics are deter-
mined with 25 generations and 1 iteration. For MaO-
JSSP the objectives are 5, whereas for MaOKSP,
DTLZ, and WFG the objectives are 4, 6, 8, and 10.
To ensure fair outcomes, 5 seeds are used in every
experiment. In WFG, the distance and position vari-
ables are both set to 5. To demonstrate the relevance
of one method over other algorithms, a T-test is uti-
lized (al pha value is 0.05).
5.1.3 Evaluation Measures
Hypervolume (HV) (Liefooghe and Derbel, 2016) is
taken into consideration while comparing the values.
HV values range from [0,1], with 1 being the best.
To check the cross-domain ability of the algorithms
µ norm (Anwar et al., 2023) are calculated. It nor-
malizes the values from [0,1] and helps in comparing
different algorithms across different problems.
5.2 Experimental Results and
Sensitivity Analyses
5.2.1 Experimental Results
The following section describes the experiments.
HV mean values and µ norm have been computed
for 48 instances across multiple datasets of MaO-
JSSP, MaOKSP, DTLZ, and WFG on MOEA/D, MP-
MOGA, MARP-NSGAIII, H-ACO, CB-SHH.
Figure 3 shows the mean HV values of MaO-
JSSP datasets (FT06, FT10, FT20, LA01, LA05,
LA10, LA15, LA20, LA25, LA30, LA35, LA40)
on MOEA/D, MPMOGA, MARP-NSGAIII, H-ACO
and CB-SHH. The CB-SHH has performed better on
all datasets except FT06, LA10, and LA25. On these
three datasets, MPMOGA has performed the best.
Moreover, it shows the mean HV values of MaOKSP
datasets (4-500, 6-500, 8-500, 10-500), CB-SHH has
outperformed the other algorithms on these datasets.
Furthermore, the benchmark datasets have been con-
sidered (DTLZ 1, 3, 6, WFG 1, 3, 6, 8, 9). CB-
SHH has outperformed all other algorithms on these
datasets except for WFG3, on this MOEA/D has out-
performed the other algorithms.
Table 1 shows the cross-domain ability of algo-
rithms and the values are calculated using a well-
known cross-domain evaluation measure named µ
norm. CB-SHH has outperformed all the remain-
ing state-of-the-art algorithms. Whereas the MP-
MOGA is the second-best-performing algorithm. Ta-
ble 2 shows the significance of algorithms using a t-
test. CB-SHH is the best-performing algorithm out-
performing other algorithms on 83 instances out of
96 instances.
5.3 Analysis of the Best Performing
Algorithm (CB-SHH)
As meta-heuristics, CB-SHH as shown in Figure 2
employs MaOEAs because MaOOPs struggle with
Solving Many-Objective Optimization Problems Using Selection Hyper-Heuristics
199

Table 1: Values of µ norm of MaOJSSP, MaOKSP, DTLZ and WFG.
µ norm mean values
Datasets MOEA/D MPMOGA MARP-NSGAIII H-ACO CB-SHH
MaOJSSP 0.379356 0.724128 0.203776 0.311296 0.903517
MaOKSP 0.140000 0.676943 0.426615 0.271110 1
DTLZ 0.323390 0.324173 0.267647 0.441242 0.990754
WFG 0.544403 0.135912 0.122133 0.637191 0.847717
All Combined 0.346787 0.465289 0.255043 0.415210 0.935497
Algorithms Rank 4th 2nd 5th 3rd 1st
Table 2: Algorithm significance of algorithms using t-test at alpha 0.05.
Algorithms MOEA/D MPMOGA MARP-NSGAIII H-ACO CB-SHH
MOEA/D - +5/3/-16 +13/5/-6 +5/8/-11 +1/3/-20
MPMOGA +16/3/-5 - +12/11/-1 +15/3/-6 +2/3/-19
MARP-NSGAIII +6/5/-13 +1/11/-12 - +6/3/-15 +0/0/-24
H-ACO +11/8/-5 +6/3/-15 +15/3/-6 - +1/3/-20
CB-SHH +20/3/-1 +19/3/-2 +24/0/-0 +20/3/-1 -
Table 3: Analysis over different parameters considering selected datasets.
MaOJSSP (LA05) MaOKSP DTLZ3 WFG6
Objectives p1 p2 p1 p2 p1 p2 p1 p2
4 - - RA1 RA2 RA1 RA1 RA4 RA4
5 RA1 RA1 - - - - - -
6 - - RA1 RA1 RA1 RA1 RA1 RA1
8 - - RA1 RA1 RA1 RA1 RA1 RA1
10 - - RA1 RA1 RA1 RA1 RA1 RA1
MOEAs because of the larger number of objectives.
This has an impact on how optimal solutions work.
By taking into account the non-dominated solutions
from the previous generation and an original selection
mechanism, respectively, CB-SHH manages the off-
spring development and environmental selection suc-
cessfully. Additionally, the proper balance between
an algorithm’s exploration and exploitation is crucial
to obtaining a global optimal solution and is one of
the primary factors influencing the effectiveness of
the suggested technique (Anwar and Younas, 2020).
Because they aid in expanding the search area and ad-
vancing toward the best solutions, which are deter-
mined via greedy and random mechanisms, respec-
tively. The best meta-heuristics are chosen both ran-
domly and depending on their performance. Further-
more, handling the consequences and incentive values
in the scores represents the implementation of a rein-
forcement learning approach. As a result, both ran-
domization and the greedy strategy are used. resulting
in effective exploration and exploitation of solutions.
5.3.1 Parametrical Analysis
Two different sets of parameters have been taken
as described in Table 3. CB-SHH, MPMOGA, and
MOEA/D are represented by RA1, RA2, and RA4 re-
spectively. The original and new parameters are rep-
resented by p1, and p2 respectively. In p2, the gen-
erations are changed to 30, iterations to 10, and seeds
to 10. For analysis, 13 different datasets have been
taken across multiple problems. The different param-
eters still yielded similar results with one exception
on the 4-500 dataset of MaOKSP. Where MPMOGA
performed better than the CB-SHH by a small margin.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
CB-SHH, H-ACO, MARP-NSGAIII, MPMOGA,
and MOEA/D are applied to MaOKSP, MaOJSSP and
benchmark problems (DTLZ, WFG). The JSP is con-
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
200

sidered with 5 objectives whereas the KSP, DLTZ, and
WFG are considered with 4, 6, 8, and 10 objectives
each. To the best of our knowledge, no researchers
have solved these problems as cross-domain together
and the CB-SHH has not applied to any variations of
JSP and KSP. CB-SHH is the best-performing algo-
rithm on 44 out of 48 instances across all datasets and
is the best cross-domain algorithm on all the datasets.
The CB-SHH has performed better on all datasets
except FT06, LA10 and LA25, WFG3. Whereas
on FT06, LA10, and LA25, MPMOGA has outper-
formed other algorithms and MOEA/D has the best
results on WFG3. CB-SHH handles the balance be-
tween exploration and exploitation very intelligently
which is one of the main reasons for the algorithm
outperforming others.
In the future, more real-life many-objective
benchmark problems can be added to extend the stud-
ies.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Adeem Ali Anwar is the recipient of an iMQRES
funded by Macquarie University, Australia (allocation
No. 20213183).
REFERENCES
Anwar, A. A. and Younas, I. (2020). Optimization of many
objective pickup and delivery problem with delay time
of vehicle using memetic decomposition based evolu-
tionary algorithm. International Journal on Artificial
Intelligence Tools, 29(01):2050003.
Anwar, A. A., Younas, I., Liu, G., Beheshti, A., and Zhang,
X. (2022). A cricket-based selection hyper-heuristic
for many-objective optimization problems. In Inter-
national Conference on Advanced Data Mining and
Applications, pages 310–324. Springer.
Anwar, A. A., Younas, I., Liu, G., and Zhang, X. (2023).
A preference-based indicator selection hyper-heuristic
for optimization problems. In International Confer-
ence on Advanced Data Mining and Applications,
pages 447–462. Springer.
Deb, K. and Jain, H. (2013). An evolutionary many-
objective optimization algorithm using reference-
point-based nondominated sorting approach, part i:
solving problems with box constraints. IEEE trans-
actions on evolutionary computation, 18(4):577–601.
Deb, K., Thiele, L., Laumanns, M., and Zitzler, E. (2005).
Scalable test problems for evolutionary multiobjec-
tive optimization. In Evolutionary multiobjective op-
timization, pages 105–145. Springer.
Drake, J. H., Kheiri, A.,
¨
Ozcan, E., and Burke, E. K. (2020).
Recent advances in selection hyper-heuristics. Euro-
pean Journal of Operational Research, 285(2):405–
428.
Huang, H., Ying, W., Wu, Y., Zheng, K., and Peng, S.
(2020). A collaborative evolutionary algorithm based
on decomposition and dominance for many-objective
knapsack problems. In Artificial Intelligence Algo-
rithms and Applications: 11th International Sympo-
sium, ISICA 2019, Guangzhou, China, November 16–
17, 2019, Revised Selected Papers 11, pages 155–166.
Springer.
Huband, S., Barone, L., While, L., and Hingston, P.
(2005). A scalable multi-objective test problem
toolkit. In International Conference on Evolution-
ary Multi-Criterion Optimization, pages 280–295.
Springer.
Ishibuchi, H., Akedo, N., and Nojima, Y. (2013). A study
on the specification of a scalarizing function in moea/d
for many-objective knapsack problems. In Learning
and Intelligent Optimization: 7th International Con-
ference, LION 7, Catania, Italy, January 7-11, 2013,
Revised Selected Papers 7, pages 231–246. Springer.
JSSP Dataset (2023). https://ptal.github.io/scheduling-data.
html. Accessed: 2023-28-07.
Liefooghe, A. and Derbel, B. (2016). A correlation anal-
ysis of set quality indicator values in multiobjective
optimization. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evo-
lutionary Computation Conference 2016, pages 581–
588.
Liu, S.-C., Chen, Z.-G., Zhan, Z.-H., Jeon, S.-W., Kwong,
S., and Zhang, J. (2021). Many-objective job-
shop scheduling: A multiple populations for multiple
objectives-based genetic algorithm approach. IEEE
Transactions on Cybernetics.
Masood, A., Chen, G., Mei, Y., Al-Sahaf, H., and Zhang,
M. (2022). Genetic programming hyper-heuristic with
gaussian process-based reference point adaption for
many-objective job shop scheduling. In 2022 IEEE
Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), pages
1–8. IEEE.
Qu, M., Zuo, Y., Xiang, F., and Tao, F. (2022). An im-
proved electromagnetism-like mechanism algorithm
for energy-aware many-objective flexible job shop
scheduling. The International Journal of Advanced
Manufacturing Technology, 119(7-8):4265–4275.
Rivera, G., Cruz-Reyes, L., Fernandez, E., Gomez-
Santillan, C., Rangel-Valdez, N., and Coello, C. A. C.
(2023). An aco-based hyper-heuristic for sequencing
many-objective evolutionary algorithms that consider
different ways to incorporate the dm’s preferences.
Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 76:101211.
Sang, Y. and Tan, J. (2022a). Intelligent factory many-
objective distributed flexible job shop collaborative
scheduling method. Computers & Industrial Engi-
neering, 164:107884.
Sang, Y. and Tan, J. (2022b). Many-objective flexible job
shop scheduling problem with green consideration.
Energies, 15(5):1884.
Venske, S. M., Almeida, C. P., L
¨
uders, R., and Delgado,
M. R. (2022). Selection hyper-heuristics for the multi
and many-objective quadratic assignment problem.
Computers & Operations Research, 148:105961.
Solving Many-Objective Optimization Problems Using Selection Hyper-Heuristics
201
