
Exploring Unsupervised Anomaly Detection with Quantum Boltzmann
Machines in Fraud Detection
Jonas Stein
1
, Dani
¨
elle Schuman
1
, Magdalena Benkard
1
, Thomas Holger
1
, Wanja Sajko
1
,
Michael K
¨
olle
1
, Jonas N
¨
ußlein
1
, Leo S
¨
unkel
1
, Olivier Salomon
2
and Claudia Linnhoff-Popien
1
1
LMU Munich, Germany
2
Allianz, France
fi
Keywords:
Quantum Boltzmann Machine, Quantum Annealing, Anomaly Detection.
Abstract:
Anomaly detection in Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is a critical task in cybersecurity programs
of large companies. With rapidly growing amounts of data and the omnipresence of zero-day attacks, man-
ual and rule-based detection techniques are no longer eligible in practice. While classical machine learning
approaches to this problem exist, they frequently show unsatisfactory performance in differentiating mali-
cious from benign anomalies. A promising approach to attain superior generalization compard to currently
employed machine learning techniques is using quantum generative models. Allowing for the largest represen-
tation of data on available quantum hardware, we investigate Quantum-Annealing-based Quantum Boltzmann
Machines (QBMs) for the given problem. We contribute the first fully unsupervised approach for the prob-
lem of anomaly detection using QBMs and evaluate its performance on an EDR-inspired synthetic dataset.
Our results indicate that QBMs can outperform their classical analog (i.e., Restricted Boltzmann Machines) in
terms of result quality and training steps in special cases. When employing Quantum Annealers from D-Wave
Systems, we conclude that either more accurate classical simulators or substantially more QPU time is needed
to conduct the necessary hyperparameter optimization allowing to replicate our simulation results on quantum
hardware.
1 INTRODUCTION
Anomaly detection is the identification of abnormal
behavior in data, which manifests in individual data
points that differ significantly from the majority of
the data (Chandola et al., 2009). This task fre-
quently appears in many domains including finance,
medicine and telecommunications (Aleskerov et al.,
1997; Spence et al., 2001; Kumar, 2005). A particu-
larly challenging application of Anomaly Detection
can be found in Endpoint Detection and Response
(EDR), which aims at detecting and investigating sus-
picious activities on endpoints such as mobile phones
or workstations in cybersecurity (Chuvakin, 2023). In
practice, the respective networks can be comprised of
billions of nodes, generating an immense amount of
data, in which the search for extremely scarce, mali-
cious anomalies can be very tedious.
This vast number of typically high-dimensional
data points and additional impediments such as zero-
day attacks raise a demand for suitable anomaly de-
tection techniques deviating from the still widely-
used manual and rule-based approaches. While many
classical machine learning approaches to this mostly
unsupervised learning problem exist, (e.g., cluster-
ing (Muniyandi et al., 2012), autoencoders (Finke
et al., 2021) or Bayesian networks (Mascaro et al.,
2014)), the distinction between malicious and benign
anomalies frequently remains intractable due to insuf-
ficient generalization (Karami, 2018). This problem
substantiates in a trade-off between detecting an un-
acceptably high number of false positives (i.e., benign
data) and failing to reliably detect all true positives
(i.e., the malicious anomalies).
In search for alternative approaches that can cope
with the encountered real world data better, we inves-
tigate the application of Quantum Computing (QC)
to this problem, as QC has shown promising perfor-
mance in generative data modelling, which is a pop-
ular technique used in unsupervised anomaly detec-
tion (Zhu et al., 2022). The three most prominent
prospects of using QC-based approaches in this con-
text are likely (1) that they need less data points dur-
ing training (Caro et al., 2022), (2) that they can per-
Stein, J., Schuman, D., Benkard, M., Holger, T., Sajko, W., Kölle, M., Nüßlein, J., Sünkel, L., Salomon, O. and Linnhoff-Popien, C.
Exploring Unsupervised Anomaly Detection with Quantum Boltzmann Machines in Fraud Detection.
DOI: 10.5220/0012326100003636
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2024) - Volume 2, pages 177-185
ISBN: 978-989-758-680-4; ISSN: 2184-433X
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
177

form the central step of sampling from the model
distribution significantly more efficiently than their
classical analogs (Amin et al., 2018) and (3), that
they have shown the ability to efficiently sample
from some specific classically intractable data distri-
butions (Hangleiter and Eisert, 2023). The general
motivation behind using generative models specifi-
cally for unsupervised anomaly detection is that their
core functionality of replicating a given data distri-
bution yields a data model that closely represents the
input dataset with the exclusion of all anomalies, as
they are too scarce to be learned reliably. Therefore,
anomalies can be detected by verifying their absence
in the generated data distribution.
A particularly powerful type of quantum gen-
erative models are Quantum Boltzmann Machines
(QBMs) (Amin et al., 2018), which have been shown
to be universal approximators for probability distri-
butions (Sussmann, 1988; Younes, 1996; Amin et al.,
2018; Wiebe and Wossnig, 2019). QBMs can be un-
derstood as a quantum analog to classical Boltzmann
Machines. The core difference is displayed in the
sampling procedure, in which the QBM represents
an approximate Boltzmann distribution in a quantum
state, which generally allows for efficient sampling
via measurements. Curious to investigate the scal-
ing performance of such quantum approaches in terms
of, i.a., the dimensionality of the dataset, we select
a Quantum-Annealing-based implementation of this
sampling step, as its physical implementations have a
key advantage over the usage of gate based quantum
computers: They currently offer the highest number
of qubits, which is the central factor for the repre-
sentable dimensionality of the dataset.
Framed by related concepts in literature, we con-
tribute the first fully unsupervised anomaly detection
based on QBMs and evaluate its performance on suit-
ably generated synthetic datasets. Our core contribu-
tions to the investigation of the applicability of Quan-
tum Boltzmann Machines for unsupervised anomaly
detection amount to the following:
• We introduce the first fully unsupervised anomaly
detection approach using QBMs.
• We conduct a case study evaluating the presented
approach on two D-Wave Quantum Annealers
while using a similarly sized classical Restriced
Boltzmann Machine (RBM) as baseline.
The subsequent contents of this paper are struc-
tured as follows. In section 2, we explain the func-
tionality of Boltzmann Machines and their variants.
In section 3, we give an overview of related work.
In section 4, we present our methodology on how
Quantum Boltzmann Machines can be used to detect
anomalies in a fully unsupervised manner. In sec-
tion 5, we show how suitable hyperparameters can be
chosen and evaluate the results achieved, comparing
classical and quantum hardware. Finally, section 6
concludes our findings and demonstrates possible fu-
ture work.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Boltzmann Machines
A classical Boltzmann Machine (BM) is an undi-
rected, stochastic neuronal network, which typically
consists of two or more separate layers and is not
restricted in its nodes’ connections. For the sake of
simplicity, we assume a very basic BM consisting of
two layers in the following explanation. BMs contain
exactly one input layer which simultaneously acts as
the output layer and is also referred to as visible layer
v = (v
1
,...,v
N
) ∈ {0, 1}
N
, consisting of visible units
v
i
. The other layers are referred to as hidden lay-
ers h = (h
1
,...,h
M
) ∈ {0,1}
M
and likewise consist of
hidden units h
i
. Both hidden and visible units are re-
stricted to assume the values zero or one. The proba-
bility of a specific configuration of (v,h) occurring in
practice is determined by a stochastic distribution –
the Boltzmann distribution p (Fischer and Igel, 2012)
in which T > 0 denotes a specific parameter called
temperature, which we can assume as a given con-
stant for now:
p(v,h,θ) =
exp
−
E(v,h,θ)
T
Z
with Z =
∑
(v,h)∈{0,1}
N×M
exp
−
E(v,h,θ)
T
where θ ≡ {W
i j
,b
(0)
i
,b
(1)
j
} denotes the weights W
i j
be-
tween units as well as the biases and acting on all vis-
ible and hidden units b
(0)
i
and b
(1)
j
. The Boltzmann
distribution is determined by the energy function E,
which is generally expressed as an Ising Hamiltonian:
E(v,h,θ) = −
N
∑
i=1
M
∑
j=1
W
i j
v
i
h
j
−
N
∑
i=1
∑
k<i
W
ik
v
i
v
k
−
M
∑
j=1
∑
l< j
W
jl
h
j
h
l
−
N
∑
i=1
b
(0)
i
v
i
−
M
∑
j=1
b
(1)
j
h
j
(1)
Choosing the Kullback-Leibler divergence (KL diver-
gence) as the corresponding loss function and com-
bining it with training methods such as stochastic gra-
dient descent, BMs can be trained so that their Boltz-
mann distributions match the distribution of a given
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
178

dataset in a straightforward manner. The KL diver-
gence is a measure of similarity between two prob-
ability distributions, which becomes zero when the
two distributions are identical and yields higher val-
ues the more dissimilar the distributions are. Its gra-
dient, which is calculated repeatedly throughout the
BM’s training process, conveniently takes the follow-
ing simple form (Ackley et al., 1985):
∂D
KL
(P
data
|| P
model
)
∂W
i j
=⟨s
i
s
j
⟩
data
− ⟨s
i
s
j
⟩
model
(2)
∂D
KL
(P
data
|| P
model
)
∂b
(·)
i
=⟨s
i
⟩
data
− ⟨s
i
⟩
model
(3)
Here W
i j
is the weight associated with the connection
between the neurons s
i
,s
j
∈ {v
1
,...,v
N
,h
1
,...,h
M
}.
⟨s
i
s
j
⟩ denotes the expectation value of the product of
the neuron values s
i
and s
j
, i.e., the probability that
both neurons assume the value one. Analogously, ⟨s
i
⟩
denotes the probability of s
i
assuming the value one.
Computing the exact values for all partial deriva-
tives generally demands calculating the energy of ev-
ery possible combination of states v ∈ {0,1}
N
, h ∈
{0,1}
M
, making this approach intractable in prac-
tice as there are exponentially many in terms of the
input domain {0, 1}
N
. Fortunately, sufficiently well
approximating heuristic methods often exist that al-
low for a shorter runtime. The core idea for these
approaches is repeated sampling from the respective
distributions, represented by the BM, and averaging
the results. Sampling is generally performed in two
phases: First, in the clamped phase, the values of
the visible neurons are fixed to the bits of a ran-
domly selected data point. In this phase, only the
values s
i
of the hidden units, which now depend on
the data point’s value, are subsequently sampled from
the BM’s Boltzmann distribution. Together with the
input data point, these values can be viewed as a sam-
ple from the data’s probability distribution P
data
and
used to calculate ⟨s
i
⟩
data
and ⟨s
i
s
j
⟩
data
. The expec-
tation values ⟨s
i
⟩
model
and ⟨s
i
s
j
⟩
model
for the model
are then determined in the unclamped phase, by sam-
pling from the Boltzmann distribution associated with
the BM using techniques like Markov chain Monte
Carlo. These samples are subsequently used to cal-
culate ⟨s
i
⟩
model
and ⟨s
i
s
j
⟩
model
. In practice, sampling
from BMs is hence typically performed by iteratively
computing the values of each neuron, depending on
the values of its neighboring neurons, until an equi-
librium is reached. As this has to be done for each
sample, while multiple samples have to be calculated
for each data point in each training epoch, the train-
ing time quickly takes intractably long. (Amin et al.,
2018; Ackley et al., 1985; Adachi and Henderson,
2015)
2.2 Restricted Boltzmann Machines
When using Restricted Boltzmann Machines
(RBMs), considerably shorter training compared to
the standard BMs can be achieved. Analog to our
course of action for the standard BM, we also restrict
the content of this section to networks of a single
hidden and visible layer. RBMs restrict all possible
neuron connections so that only interlayer weights
can be non-zero, making it possible to sample from
the entire visible respectively hidden layer at once.
As hidden and visible units only depend on the
neuron values in the opposing layer, which are
known in the clamped phases, this allows for faster
sampling. For RBMs, the energy function is thus
reduced to (Fischer and Igel, 2012):
E(v,h,θ) =
N
∑
i=1
M
∑
j=1
W
i j
v
i
h
j
−
N
∑
i=1
v
i
b
(0)
i
−
M
∑
j=1
h
j
b
(1)
j
(4)
As it remains intractable to calculate the gradient of
the weights and biases directly, sampling from the
given Boltzmann distribution is mandatory. How-
ever, even for the RBM, drawing independent sam-
ples from the model in order to approximate the gra-
dient is computationally expensive. Even though ap-
proximate sampling techniques like Contrastive Di-
vergence can often be used effectively, their trade-
off in runtime against accuracy is frequently worse
than state-of-the-art classical generative models be-
sides BMs for big datasets. (Gabri
´
e et al., 2015)
2.3 Quantum Boltzmann Machines
A very promising approach towards speeding up the
time consuming sampling process in classical (re-
stricted) BMs are Quantum Boltzmann Machines
(QBMs), which use quantum algorithms to prepare a
quantum state that resembles the desired probability
distribution and allows for sampling from it via mea-
surements. One such quantum algorithm is Quantum
Annealing, which has been shown to be capable of ap-
proximating Boltzmann distributions when executed
on analog quantum hardware natively implementing
this algorithm, i.e., Quantum Annealers (Amin et al.,
2018). Quantum Annealing conducts a time evolu-
tion starting in the ground state of a known Hamilto-
nian that gradually evolves into an Ising Hamiltonian
ˆ
H
P
that is often used to model the cost landscape of
an optimization problem. When this time evolution
is done adiabatically (i.e., not too fast) and without
any hardware errors, the final state is guaranteed to
be the ground state of the Hamiltonian
ˆ
H
P
, i.e., the
global minimum of the cost function (Kadowaki and
Nishimori, 1998). When conducting this process on a
Exploring Unsupervised Anomaly Detection with Quantum Boltzmann Machines in Fraud Detection
179

physical Quantum Annealer however, the system nat-
urally interacts with the environment, which interest-
ingly perturbs the final state to approximate a classi-
cal Boltzmann distribution over the energy function
described by the Hamiltonian
ˆ
H
P
. The temperature
of the resulting approximate Boltzmann distribution
is determined by device specific properties in corre-
lation with the specific Ising Hamiltonian and can be
tuned by rescaling the weights and biases by the in-
verse of the so-called effective temperature, which
can be calculated efficiently as shown in (Benedetti
et al., 2016). (Adachi and Henderson, 2015; Yarkoni
et al., 2021; Benedetti et al., 2016)
As Quantum Annealing drastically reduces the
amount of steps needed to create a sample, a quantum
advantage in the form of a speedup can be expected
here. Experiments of (Amin et al., 2018) show that
QBMs can achieve better KL divergences than the
BMs employed in their study when given the same
runtime capabilities, suggesting that QBMs can also
outperform their classical analogs in terms of result
quality. Another advantage of QBMs is that they do
not require restricting the connectivity of the BMs ar-
chitecture, allowing for more complex models with a
higher number of connections (Hinton, 2012; Adachi
and Henderson, 2015).
3 RELATED WORK
Our contribution to existing literature is constituted
by the first successful application of QBMs for fully
unsupervised anomaly detection. This represents a
novel use case for QBMs trained using unsuper-
vised techniques, extending the portfolio of known
productive QBM applications like image reconstruc-
tion (Benedetti et al., 2017) or image generation (Sato
et al., 2021).
In regards to supervised learning, QBMs have
shown promising performance for anomaly detec-
tion in applications like the classification of cyber-
security data, for which (Dixit et al., 2021) showed
that their Quantum-Annealing-based RBM can pro-
vide similar results to comparable classical RBMs.
(Vyas et al., 2022) proposed a semi-supervised ap-
proach to anomaly detection for credit card trans-
action data that employs an ensemble of quantum-
inspired RBMs. For sampling, they use a set of
solvers from the “Azure Quantum-Inspired Optimiza-
tion (QIO)” suite instead of real quantum algorithms,
while excluding the anomalies from the training data.
They subsequently calculate the energy values of all
data points (i.e., including anomalies) for all RBMs of
the ensemble analytically and then identify an energy
threshold separating normal data from the anomalies.
Beyond QBMs, other quantum generative models
have been shown to perform well on similar tasks:
(Bermot et al., 2023) haven shown the effective ap-
plicability of Quantum Generative Adversarial Net-
works for anomaly detection in high energy physics,
(Ngairangbam et al., 2022) used a Quantum Autoen-
coder for a very similar use case, and (Schuhmacher
et al., 2023) applied a Quantum Support Vector Clas-
sifier to find beyond standard model physics in data
recorded at the LHC.
4 METHODOLOGY
In line with known techniques to use generative mod-
els for anomaly detection, we utilize a QBM as a gen-
erative model and subsequently identify anomalies by
their infrequence in the generated model (Hoh et al.,
2022; Luo et al., 2022; Dietrichstein et al., 2022;
Amin et al., 2018). More specifically, we classify a
given data point as anomalous if its energy value in
the QBM exceeds a specific limit. To implement the
presented approach, we now first specify the QBM
model architecture and then choose an energy thresh-
old separating normal from anomalous data.
4.1 QBM Model Architecture
To perform anomaly detection in a fully unsupervised
manner using a QBM, a suitable model architecture
must be selected. Inspired by the work of (Amin et al.,
2018), we also choose to employ a semi-restricted
QBM for unsupervised learning (i.e., a QBM with one
hidden layer, having lateral connection only between
the visible neurons). A general overview of this archi-
tecture can be found in figure 1b. More specifically,
we allow all neuron connections possible in this ar-
chitecture and treat the number of hidden neurons as
a hyperparameter, while the number of visible neu-
rons is completely dependent on the dimensionality
of the dataset.
4.2 Choosing an Energy Threshold
As stated previously, the identification of anomalies is
done by verifying their absence (or at least significant
infrequence) in the model distribution. For Energy
Based Models (EBMs) like the QBM, the probability
of a point in our model is fully dependent on its en-
ergy value by definition (Lecun et al., 2006). Thus,
the classification of data points as anomalous or nor-
mal can be achieved by drawing an energy thresh-
old between the two categories (Zhai et al., 2016;
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
180

Hidden
layer
Visible
layer
(a) RBM
Hidden
layer
Visible
layer
(b) QBM
Figure 1: Schematic visualization of the architecture of the
BMs used in this paper.
Do et al., 2018). This causes our model to classify
all points with energy values higher than the thresh-
old as anomalous and all points with lower energies
as normal. While related work in the quantum do-
main specified this threshold for anomaly detection
using (semi-) supervised learning (Vyas et al., 2022),
we draw the threshold in an unsupervised manner, by
having the Quantum Annealer return the energy val-
ues of all data points in the training dataset and sub-
sequently calculating the threshold as the p-th per-
centile, analog to (Zhai et al., 2016) and (Do et al.,
2018). For our evaluation in section 5, we chose
p = 95, analog to (Do et al., 2018), assuming that
no more than 5% of the training data is anomalous.
While this amount is unrealistically high for the data
employed in our use case, we choose it to increase the
likelihood of finding all anomalies in the test dataset.
If any kind of ad-hoc testing for the validity of an
anomaly is available, e.g., through human inspection
as is typically the case for EDR, this percentile can
be tuned accordingly (see, e.g., (Do et al., 2018; Zhai
et al., 2016)).
5 EVALUATION
To give an indication whether our proposed method
might provide a quantum advantage over purely clas-
sical EBM-based approaches, we compare our ap-
proach to a RBM with a similarly simple architec-
ture to our semi-restricted QBM: The chosen RBM
is described in section 2.2 and displayed in figure 1a.
As we treat the size of the hidden layer as a hyperpa-
rameter and as one hidden layer already suffices for
the RBM to be an arbitrary distribution approximator,
this choice yields a potent, practical, classical base-
line. Preparing for our experiments, we now select a
suitable dataset and conduct an in-depth hyperparam-
eter optimization. Note that we use a 50/50 train/test
split in this evaluation and only show the results from
test data.
5.1 Dataset
In lack of suitably small real world EDR datasets that
fit on current quantum hardware, we generate a syn-
thetic data set, aimed at matching the following prop-
erties found in real world data: (1) a high dimension-
ality to assess scaling performance, (2) scarce anoma-
lies and (3) a substantial number of data points. While
satisfying (2) and (3) is straightforward, (1) is directly
proportional to the number of visible units and thus
the space complexity. Compromising on (1) to fa-
cilitate a visual evaluation and retain enough space
for exploring a large space of hidden units for this
first case study on fully unsupervised anomaly detec-
tion using a QBM, we restrict the data set to three
dimensions. To satisfy (2) and (3) within the limita-
tions of current hardware capabilities, we thus gen-
erate 1007 3D data points x ∈ [0,...,127]
3
clustered
in five clusters and containing seven anomalies using
the method make blobs from scikit-learn (Pedregosa
et al., 2011). Therefore, seven bits are required per
dimension, which means that 21 visible neurons are
needed to represent the QBM’s input, i.e., a single
data point. Due to the 50/50 train/test split, the ra-
tio of anomalies is ≤ 7/500 ≈ 1%, satisfying (2). A
pairplot of the generated data set is displayed in fig-
ure 2.
5.2 Hyperparameter Optimization
Being generative models, the BMs have several hy-
perparameters which need to be optimized to achieve
decent results. Choosing a greedy optimization strat-
egy due to heavy computation time demands, we
tuned the following hyperparameters descending in
their typical relevance: (1) The number of hidden
neurons, (2) the number of epochs and finally (3)
the batchsize, while choosing standard values for the
latter ones inspired by (Hinton, 2012). Notably, the
learning rate was determined independent of all other
hyperparameters in an empirical pre-study to the eval-
uation. For details on our implementation, see https:
//github.com/jonas-stein/QBM-Anomaly-Detection.
As we estimate that the here conducted hyper-
parameter search would take roughly two days of
QPU time, our limited access to D-Wave’s Anneal-
Exploring Unsupervised Anomaly Detection with Quantum Boltzmann Machines in Fraud Detection
181
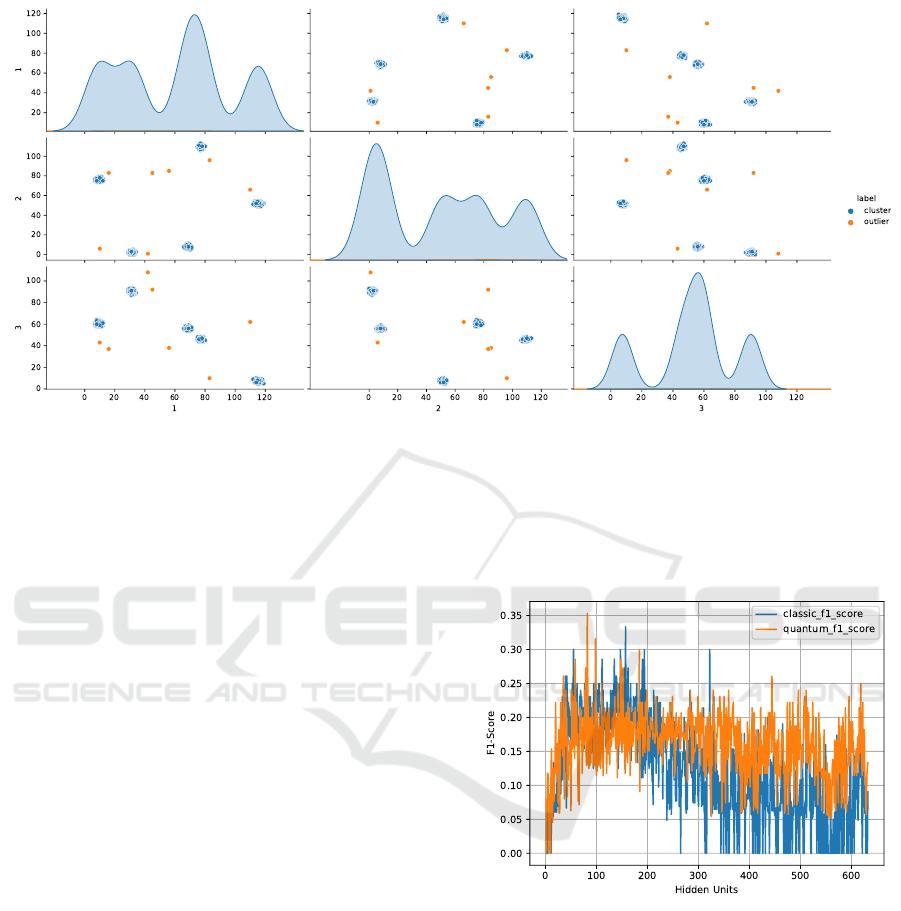
Figure 2: Visualization of the constructed 3D dataset comprised of 5 clusters and 7 anomalies. The diagonal shows the
distribution of the data in each dimension. The off-diagonal plots, show a 2D flattened version of the dataset for all dimension-
combinations.
ers (∼3 hours) necessitates a hyperparameter search
using classical simulators for sampling. As also prac-
tically employed in (Schuman et al., 2023), Simulated
Annealing (SA) can be a suitable choice for this, as it
(like a quantum annealer (Nishimori et al., 2015)) in-
trinsically approximates a Boltzmann distribution for
a given temperature when using a suitable annealing
schedule and neighbor generation (for details, see the
articles of (Crosson and Harrow, 2016; Denchev et al.,
2016)). Note that for other QUBO solvers such as
the D-Wave hybrid, it is a priori not clear if they also
possess this property. We strongly encourage future
work on this topic, as long as QPU availability does
not meet the needed requirements.
Starting our hyperparameter optimization with the
number of hidden neurons, we respect the physically
possible qubit embeddings on the employed D-Wave
QPUs, which empirically restricts us to a maximum
of 94 and respectively 632 hidden neurons for the D-
Wave 2000Q and the Advantage 4.1. Figure 3 illus-
trates that the QBM requires significantly fewer hid-
den neurons to reach its optimal F1 score compared to
the RBM: While the QBMs optimum is at 82 hidden
neurons with an F1 score of 0.35, the RBM reaches
its optimal F1 score of 0.33 at 157 hidden neurons.
Thus, the QBM achieves a better result with fewer re-
sources. This is most likely the case, as the QBM can
generally model complex dependencies better com-
pared to a similarly sized RBM, since it allows for
lateral connections. However, as the F1 scores show
a large variance for small changes in the number of
hidden units, caution has to be taken when conclud-
ing from these results, as it appears that the number
of employed seeds might be too low for undeniable
statistical relevance.
Figure 3: F1 score for increasing number of hidden neurons.
The blue line shows the classical RBM and the orange line
shows the QBM using the Simulated-Annealing-based sam-
pler.
Subsequently, the number of epochs was opti-
mized, while each approach was fitted with the pre-
viously determined optimal number of hidden neu-
rons. Figure 4 displays the results which clearly show
that the QBM again outperforms the RBM. While the
RBM reaches its optimum at 13 epochs, with an F1
score of 0.33, the optimum of the QBM is at 14 and 16
epochs, respectively, with an F1 score of 0.375. In ad-
dition, the QBM consistently yields better results than
the RBM approach at fewer epochs. At seven epochs,
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
182
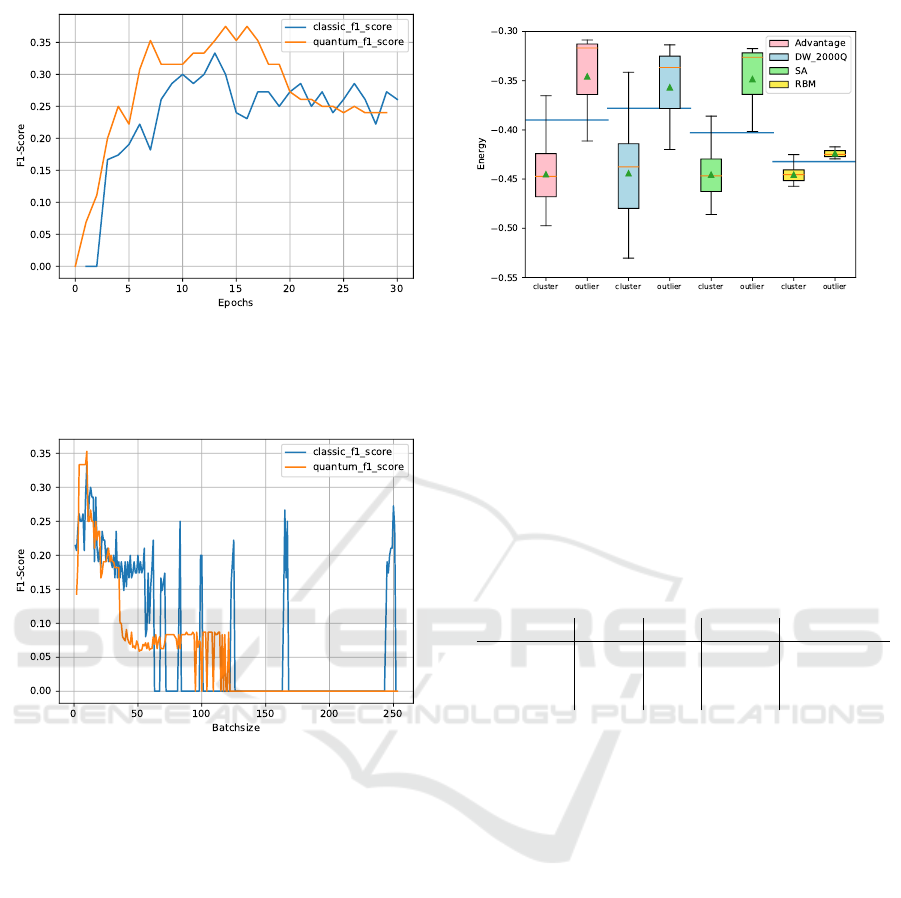
Figure 4: F1 score for increasing number of epochs. The
blue line shows the classical RBM and the orange line
shows the QBM using the Simulated-Annealing-based sam-
pler.
Figure 5: F1 score for increasing batch sizes. The blue
line shows the classical RBM and the orange line shows
the QBM using the Simulated Annealing based sampler.
the F1 score of the QBM already reaches 0.35, which
exceeds the global optimum of the RBM which is ob-
tained at 13 epochs. Thus, the QBM only needs about
half the number of epochs to reach an even better per-
formance than the RBM. Due to the limited available
computing time on quantum hardware, seven epochs
are chosen for further optimization steps, and 13 for
the RBM.
Concluding the hyperparameter optimization, Fig-
ure 5 shows that both the RBM and the QBM reach
their optimum at a batch size of ten. The RBM re-
mains at an F1 score of 0.33, while the QBM achieves
0.35.
5.3 QPU Results
Using the optimized hyperparameters, we now ex-
plore the result quality of the D-Wave 2000Q and the
Advantage 4.1 in comparison with the SA sampler
Figure 6: Normalized energies of anomalies and cluster
points for different approaches. The blue line represents the
chosen energy threshold separating normal from anomalous
data.
and the RBM baseline. Table 1 depicts the obtained
results, which show that the Quantum Annealers are
(still) outperformed by the classical approaches. Both
quantum annealers missed one anomaly and thus
achieved an identical recall. The Advantage 4.1 how-
ever identified less false positives according to its
62% higher precision.
Table 1: Result quality of all examined approaches.
RBM SA 2000Q Advantage
F1-Score 0.33 0.35 0.14 0.21
Recall 1 1 0.67 0.67
Precision 0.20 0.21 0.08 0.13
Fig. 6 shows a compact overview for comparing
the energy levels in form of a box plot. Interestingly,
the variance in the purely classical RBM approach is
significantly lower than for all QBM variants, which
might be caused by the less complex model, as it does
not have any lateral neuron connections. Compar-
ing the three QBM results, we clearly see that SA
achieved the best performance, which makes sense,
as the hyperparameters were trained for it. For the
D-Wave QPUs a clear improvement can be observed
for the newer Advantage 4.1 system compared to the
older 2000Q model, which gives the promising out-
look of outperforming purely classical approaches
with future hardware generations if this trend contin-
ues. We expect the main reasons for this to be the
higher error rate of the 2000Q and the larger num-
ber of employed qubits, as its weaker connectivity de-
mands for more ancillary qubits for the same number
of hidden units.
Exploring Unsupervised Anomaly Detection with Quantum Boltzmann Machines in Fraud Detection
183

6 CONCLUSION
Our results indicate that QBMs can outperform their
classically employed analog (RBMs) for unsuper-
vised anomaly detection in terms of (1) training steps
and (2) result quality. With limited access to quan-
tum hardware however, we were unable to yield evi-
dence for this claim when using Quantum Annealers
as samplers, most probably because the hyperparame-
ter tuning was conducted using a simulated annealing
sampler that merely approximates the QPU results.
Furthermore, the results show that the more recent D-
Wave Advantage 4.1 QPU achieves significantly bet-
ter performance than its predecessor D-Wave 2000Q,
even suggesting a possible quantum advantage in case
that the hardware performance continues to improve
similarly in the future.
To improve the results of the quantum approach
for future work, we suggest to implement a clas-
sical sampler that more closely matches the results
of the utilized quantum hardware in a high perfor-
mance computing oriented programming language to
improve the accuracy and statistical relevance of the
hyperparameter search. If successful, this should al-
low an upscaling to a more realistic dataset dimen-
sionality to gradually approach the limitations of clas-
sical approaches for this task. This should also facili-
tate the usage of a dataset containing benign and ma-
licious anomalies, to allow for comparing the results
of the QBM with classical baselines in this regard.
Furthermore, a closer evaluation in terms of training
steps for a higher number of data points would be very
interesting, as we expect our approach to be more effi-
cient than the classical baselines in this regard, based
on our experimental results.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper was partially funded by the German Fed-
eral Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Ac-
tion through the funding program ”Quantum Comput-
ing – Applications for the industry” based on the al-
lowance ”Development of digital technologies” (con-
tract number: 01MQ22008A).
REFERENCES
Ackley, D. H., Hinton, G. E., and Sejnowski, T. J. (1985). A
learning algorithm for boltzmann machines. Cognitive
science, 9(1):147–169.
Adachi, S. and Henderson, M. (2015). Application of quan-
tum annealing to training of deep neural networks.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1510.06356, page 3.
Aleskerov, E., Freisleben, B., and Rao, B. (1997). Card-
watch: a neural network based database mining sys-
tem for credit card fraud detection. In Proceedings of
the IEEE/IAFE 1997 Computational Intelligence for
Financial Engineering (CIFEr), pages 220–226.
Amin, M. H., Andriyash, E., Rolfe, J., Kulchytskyy, B.,
and Melko, R. (2018). Quantum boltzmann machine.
Physical Review X, 8(2):021050.
Benedetti, M., Realpe-G
´
omez, J., Biswas, R., and Perdomo-
Ortiz, A. (2016). Estimation of effective temperatures
in quantum annealers for sampling applications: A
case study with possible applications in deep learning.
Physical Review A, 94(2):022308.
Benedetti, M., Realpe-G
´
omez, J., Biswas, R., and Perdomo-
Ortiz, A. (2017). Quantum-assisted learning of
hardware-embedded probabilistic graphical models.
Physical Review X, 7(4):041052.
Bermot, E., Zoufal, C., Grossi, M., Schuhmacher, J.,
Tacchino, F., Vallecorsa, S., and Tavernelli, I. (2023).
Quantum generative adversarial networks for anomaly
detection in high energy physics. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2304.14439.
Caro, M. C., Huang, H.-Y., Cerezo, M., Sharma, K., Sorn-
borger, A., Cincio, L., and Coles, P. J. (2022). Gener-
alization in quantum machine learning from few train-
ing data. Nat. Commun., 13(1):4919.
Chandola, V., Banerjee, A., and Kumar, V. (2009).
Anomaly detection: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv.,
41(3).
Chuvakin, A. (2023). Named: Endpoint threat detection &
response.
Crosson, E. and Harrow, A. W. (2016). Simulated quantum
annealing can be exponentially faster than classical
simulated annealing. In 2016 IEEE 57th Annual Sym-
posium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS),
pages 714–723.
Denchev, V. S., Boixo, S., Isakov, S. V., Ding, N., Bab-
bush, R., Smelyanskiy, V., Martinis, J., and Neven,
H. (2016). What is the computational value of finite-
range tunneling? Phys. Rev. X, 6:031015.
Dietrichstein, M., Major, D., Trapp, M., Wimmer, M.,
Lenis, D., Winter, P., Berg, A., Neubauer, T., and
B
¨
uhler, K. (2022). Anomaly detection using gener-
ative models and sum-product networks in mammog-
raphy scans. In Mukhopadhyay, A., Oksuz, I., Engel-
hardt, S., Zhu, D., and Yuan, Y., editors, Deep Gen-
erative Models, pages 77–86, Cham. Springer Nature
Switzerland.
Dixit, V., Selvarajan, R., Aldwairi, T., Koshka, Y., Novotny,
M. A., Humble, T. S., Alam, M. A., and Kais, S.
(2021). Training a quantum annealing based restricted
boltzmann machine on cybersecurity data. IEEE
Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational
Intelligence, 6(3):417–428.
Do, K., Tran, T., and Venkatesh, S. (2018). Energy-based
anomaly detection for mixed data. Knowledge and
Information Systems, 57(2):413–435.
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
184

Finke, T., Kr
¨
amer, M., Morandini, A., M
¨
uck, A., and
Oleksiyuk, I. (2021). Autoencoders for unsupervised
anomaly detection in high energy physics. J. High En-
ergy Phys., 2021(6):161.
Fischer, A. and Igel, C. (2012). An introduction to restricted
boltzmann machines. In Iberoamerican congress on
pattern recognition, pages 14–36. Springer.
Gabri
´
e, M., Tramel, E. W., and Krzakala, F. (2015). Train-
ing restricted boltzmann machine via the thouless-
anderson-palmer free energy. Advances in neural in-
formation processing systems, 28.
Hangleiter, D. and Eisert, J. (2023). Computational advan-
tage of quantum random sampling.
Hinton, G. E. (2012). A practical guide to training restricted
boltzmann machines. In Neural networks: Tricks of
the trade, pages 599–619. Springer.
Hoh, M., Sch
¨
ottl, A., Schaub, H., and Wenninger, F. (2022).
A generative model for anomaly detection in time
series data. Procedia Computer Science, 200:629–
637. 3rd International Conference on Industry 4.0 and
Smart Manufacturing.
Kadowaki, T. and Nishimori, H. (1998). Quantum an-
nealing in the transverse ising model. Phys. Rev. E,
58:5355–5363.
Karami, A. (2018). An anomaly-based intrusion detection
system in presence of benign outliers with visualiza-
tion capabilities. Expert Systems with Applications,
108:36–60.
Kumar, V. (2005). Parallel and distributed computing
for cybersecurity. IEEE Distributed Systems Online,
6(10).
Lecun, Y., Chopra, S., Hadsell, R., Ranzato, M., and Huang,
F. (2006). A tutorial on energy-based learning. MIT
Press.
Luo, X., Jiang, Y., Wang, E., and Men, X. (2022). Anomaly
detection by using a combination of generative ad-
versarial networks and convolutional autoencoders.
EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process., 2022(1):112.
Mascaro, S., Nicholso, A. E., and Korb, K. B. (2014).
Anomaly detection in vessel tracks using bayesian
networks. International Journal of Approximate Rea-
soning, 55(1, Part 1):84–98. Applications of Bayesian
Networks.
Muniyandi, A. P., Rajeswari, R., and Rajaram, R. (2012).
Network anomaly detection by cascading k-means
clustering and c4.5 decision tree algorithm. Proce-
dia Engineering, 30:174–182. International Confer-
ence on Communication Technology and System De-
sign 2011.
Ngairangbam, V. S., Spannowsky, M., and Takeuchi,
M. (2022). Anomaly detection in high-energy
physics using a quantum autoencoder. Phys. Rev. D,
105:095004.
Nishimori, H., Tsuda, J., and Knysh, S. (2015). Compar-
ative study of the performance of quantum annealing
and simulated annealing. Phys. Rev. E, 91:012104.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V.,
Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer,
P., Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., Vanderplas, J., Passos,
A., Cournapeau, D., Brucher, M., Perrot, M., and
Duchesnay, E. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine learning
in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research,
12:2825–2830.
Sato, T., Ohzeki, M., and Tanaka, K. (2021). Assessment
of image generation by quantum annealer. Scientific
reports, 11(1):1–10.
Schuhmacher, J., Boggia, L., Belis, V., Puljak, E., Grossi,
M., Pierini, M., Vallecorsa, S., Tacchino, F., Barkout-
sos, P., and Tavernelli, I. (2023). Unravelling physics
beyond the standard model with classical and quantum
anomaly detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.10787.
Schuman, D., S
¨
unkel, L., Altmann, P., Stein, J., Roch, C.,
Gabor, T., and Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2023). Towards
transfer learning for large-scale image classification
using annealing-based quantum boltzmann machines.
In 2023 IEEE International Conference on Quantum
Computing and Engineering (QCE), volume 02, pages
42–47.
Spence, C., Parra, L., and Sajda, P. (2001). Detection, syn-
thesis and compression in mammographic image anal-
ysis with a hierarchical image probability model. In
Proceedings IEEE Workshop on Mathematical Meth-
ods in Biomedical Image Analysis (MMBIA 2001),
pages 3–10.
Sussmann, H. (1988). Learning algorithms for boltzmann
machines. In Proceedings of the 27th IEEE Confer-
ence on Decision and Control, pages 786–791 vol.1.
Vyas, A., Roberts, L., Gupta, S., and Patel, R. (2022).
Anomaly detection using azure quantum qio (quan-
tum inspired optimization) platform. Technical re-
port, Mphasis Corporation, New York, NY, USA. Ac-
cessed: 2022-08-21.
Wiebe, N. and Wossnig, L. (2019). Generative training
of quantum boltzmann machines with hidden units.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.09902.
Yarkoni, S., Raponi, E., Schmitt, S., and B
¨
ack, T. (2021).
Quantum annealing for industry applications: Intro-
duction and review. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.07491,
page 31.
Younes, L. (1996). Synchronous boltzmann machines can
be universal approximators. Applied Mathematics Let-
ters, 9(3):109–113.
Zhai, S., Cheng, Y., Lu, W., and Zhang, Z. (2016). Deep
structured energy based models for anomaly detec-
tion. In International conference on machine learning,
pages 1100–1109. PMLR.
Zhu, E. Y., Johri, S., Bacon, D., Esencan, M., Kim, J., Muir,
M., Murgai, N., Nguyen, J., Pisenti, N., Schouela,
A., Sosnova, K., and Wright, K. (2022). Genera-
tive quantum learning of joint probability distribution
functions. Phys. Rev. Res., 4:043092.
Exploring Unsupervised Anomaly Detection with Quantum Boltzmann Machines in Fraud Detection
185
