
Application of Formal Concept Analysis to Characterize Driving
Behaviors and Socio-Cultural Factors Related to Driving
Diogo Miranda, Luis Z
´
arate and Mark Song
Instituto de Ciencias Exatas e Inform
´
atica, Pontif
´
ıcia Universidade Catolica de Minas Gerais, Brazil
Keywords:
Formal Concept Analysis, Aggressive Driving Behaviors, Safe Driving Behaviors, Mindsponge Theory.
Abstract:
This article addresses the global concern for road safety, where frequent accidents on roads and streets result in
loss of human lives, severe injuries, and significant material damage, impacting not only the direct victims but
also their families and society at large. To tackle this challenge, it is crucial to analyze the factors contributing
to these accidents, particularly driver behaviors. This study investigates reckless behaviors such as speeding,
less obvious influences such as personality traits and sociocultural factors. Using Formal Concept Analysis
(FCA), the research examines a database containing information about Chinese drivers, aiming to provide
valuable insights for accident prevention and the promotion of safer road behaviors. In summary, the article
aims to deepen the understanding of factors related to traffic accidents with the goal of enhancing road and
street safety.
1 INTRODUCTION
Traffic accidents are a worldwide concern, claiming
lives, causing severe injuries, and resulting in signif-
icant material losses. These incidents occur daily on
the roads and streets of all nations and are one of the
leading causes of death. Their consequences impact
not only the direct victims but also their families and
society as a whole. To comprehend and mitigate this
problem, it is crucial to analyze and understand the
factors that contribute to the occurrence of these acci-
dents.
Traffic accidents result in approximately 1.3 mil-
lion fatalities every year (approximately 3,000 per
day), leaving both men and women injured in non-
fatal accidents around the world. (World Health Or-
ganization, 2023)
The study of traffic behaviors can provide insights
into areas that need to be addressed from a perspective
aimed at identifying behaviors and factors that lead to
these accidents, with the goal of reducing the number
of fatalities. This is a crucial aspect of a country’s
development process. Furthermore, studies on traffic
behaviors can reveal non-trivial aspects that are chal-
lenging to identify, such as the effects of personality
combined with socio-cultural characteristics, result-
ing in risks and contributing to these accidents, as in-
dicated in (Yang et al., 2013).
There is a factor analyzed in traffic accidents that
contributes to the cause of accidents, and that is reck-
less driving. This includes speeding, dangerous over-
taking, disregarding traffic laws, and the use of elec-
tronic devices while driving. In addition to these fac-
tors, socio-cultural and educational aspects have a sig-
nificant impact on road safety, as was analyzed in
(Houston et al., 2003).
In this article, the aim is to analyze the socio-
cultural aspects of these drivers, along with external
influences from friends and/or family, applying For-
mal Concept Analysis (FCA) to the database contain-
ing information about Chinese drivers (published in
August 2023), following a data processing available
in (Jin et al., 2023).
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Formal Concept Analysis
Formal Concept Analysis (FCA) can be used to rec-
ognize patterns with the help of association rules and
their implications. Formal Concept Analysis consists
of a set of objects in a formal context, formal con-
cepts, and rules. A formal context can be represented
as a triple K = (G, M, I), consisting of a set of G ob-
jects, a set of M attributes, and an incidence relation
I ⊆ G × M with (g, m) ∈ I meaning that object g has
56
Miranda, D., Zárate, L. and Song, M.
Application of Formal Concept Analysis to Characterize Driving Behaviors and Socio-Cultural Factors Related to Driving.
DOI: 10.5220/0012335000003657
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2024) - Volume 2, pages 56-62
ISBN: 978-989-758-688-0; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

attribute m.”. For a set of objects A ⊆ G, the set of
common attributes for the objects. of A is denoted by.
A :=
{
m ∈ M|∀g ∈ A : (g, m) ∈ I
}
, similarly, the set of
ommon attributes for the objects of B is denoted by
B :=
{
g ∈ G|∀m ∈ B : (g, m) ∈ I
}
.
A formal concept of a formal context K =
(G, M, I) is defined by pair (A, B) where A is called
extension and B is called intention. For a pair (A, B)
to be considered a concept, one needs to follow the
condition where. (A = B
′
) and (B = A
′
). The set of
formal concepts of a context K is said to be β (K).
Association rules are dependencies between elements
of a formal context.
The rule A → B is valid only if for every object
containing attributes B, it also contains attributes from
C. Given a rule r and parameters s and c, one can
denote:
s = suppr (r) =
|
A
′
∩B
′
|
|
G
′
|
- called the support of rule
r, and
c = con f (r) =
|
A
′
∩B
′
|
|
A
′
|
- called confidence.
When con f (r) = 100% the rule is referred to as
an implication. (Felde and Stumme, 2023)
Studies that explore domains that can be repre-
sented as a binary tabular base of objects and at-
tributes can often apply FCA. Longitudinal study ap-
proaches aim to investigate a sample of individuals
with certain characteristics over consecutive time pe-
riods, referred to as waves. On the other hand, FCA
is an approach in formal set theory that focuses on the
representation and analysis of the semantic structure
of data at a single point in time, without considering
evolution or changes over time.
FCA is based on the idea that concepts can be de-
fined based on the relationships between objects and
attributes, enabling the creation of conceptual hierar-
chies and the understanding of associations between
meaningful terms. It is a useful technique for orga-
nizing and extracting information from data sets.
The dimensionality of a database is a crucial point
when attempting to generalize and find relationships
within data. A low-dimensional database is one that
contains few samples from a specific domain. For
example, databases related to human behavior often
have low dimensionality when we want to analyze be-
havior within a certain population. One application
of FCA is to understand how the objects present in
these low-dimensional databases, along with their at-
tributes, can have implications.
2.2 Aggressive Behaviors in Traffic
Behaviors in traffic that can lead to accidents are char-
acterized into three main categories: 1) aggressive be-
haviors in traffic, 2) influence of friends and close ac-
quaintances, 3) family influence. These categories en-
compass a fourth one that is used as a threshold for
analysis, which is socio-cultural information about
the drivers. The information pertains to 1039 Chi-
nese drivers whose sociocultural factors were asso-
ciated with these behaviors. The database was col-
lected through an online survey, publicly available in
the Data in Brief journal. This study was published
in August 2023 and has the Bayesian Mindsponge
Framework (BMF) as a validation index, specifically
showing how safe driving behaviors are affected by
information that promotes safe driving, actively ab-
sorbed with the support of friends/colleagues and/or
the driver’s family.
A fundamental concept of the Mindsponge Theory
is that the human mind tends to be influenced by infor-
mation absorbed from external sources. As analyzed
in (Jin et al., 2023), the factors that contribute to safe
driving may be related to external factors from family,
friends, and/or colleagues. These factors, along with
socio-cultural factors, provide interesting information
to be analyzed in this issue.
The application of FCA to the dataset in question
can provide important insights into the behavior of
drivers in traffic leading to accidents. Rules of the
form A → B take into account that when drivers ex-
hibit a certain aggressive behavior A, it implies B.
2.3 Lattice Miner
The Lattice Miner 2.0 tool is a data mining prototype
developed under the supervision of Professor Rokia
Missaoui by the laboratory of the University of Que-
bec. This is a publicly available Java platform in
which the main functions include all low-level opera-
tions that allow the manipulation of input data, struc-
tures, and rule association. The platform enables the
generation of groups, called formal concepts, includ-
ing logical implications, thereby showing binary rela-
tionships between collections of objects and their sets
of attributes or properties.
3 RELATED WORKS
This work utilizes Formal Concept Analysis, and the
approach is justified through a relationship between
theoretical and practical knowledge of this subject.
Related works on this topic are presented below.
(Wei et al., 2018) analyzes the triadic approach of
formal concept analysis in four aspects: (i) the basic
approach of triadic concept analysis, (ii) triadic im-
plications and rules, (iii) the triadic factor of analysis,
Application of Formal Concept Analysis to Characterize Driving Behaviors and Socio-Cultural Factors Related to Driving
57

and (iv) the analysis of fuzzy triadic concepts.
(Biedermann, 1997) systematically demonstrates
the application of triadic formal concept analysis in
databases to represent complex concepts that are dif-
ficult to visualize. It also explains the generation of
rules and implications from an analyzed dataset.
The work (Ganter and Obiedkov, 2004) demon-
strates various biases that can be generated from tri-
adic formal concept analysis and their implications
in multiple scenarios. Given different interests that
can be addressed from the triadic context, the authors
provide extensive and concise descriptions through
implication-generating algorithms in the triadic con-
text. Examples of these interests from various do-
mains, but still addressable in a triadic context, are
found in (Kent and Neuss, 1997), where the focus is
on hypertext analysis, and in (Carullo et al., 2015),
which presents an approach of this method in online
recommendation systems.
In (Blevente Lorand Kis and Troanca, 2017), a
tool is presented that enables the visualization of these
concepts and rules, facilitating navigation and under-
standing of triadic concepts.
(Hu et al., 2004) presents modeling techniques
based on a logical description language in a can-
cer database. Results are presented that are gener-
ated from intentions and extensions of entities present
in these databases, obtained through formal concept
analysis.
In the work (Deivid Santos, 2022), an analysis of
infant mortality in two regions of Minas Gerais is con-
ducted. The process used the approach of triadic for-
mal concept analysis to extract rules and implications
from a database. The study generated a series of rules
with certain hierarchies characterizing this database.
In (Lucas Ferreira, 2021), an application of a
process to extract knowledge from a database gen-
erated by a study conducted on women undergo-
ing chemotherapy treatment for breast cancer is per-
formed. The application of the Formal Concept Anal-
ysis theory allowed for the extraction of a set of hi-
erarchically organized concepts, from which rules re-
lating them were extracted, thus describing the out-
comes of antiemetic treatments in this database.
In (Paulo Lana, 2022), a longitudinal analysis of
a Covid-19 database is conducted using the processes
of triadic formal concept analysis. The results of this
work provide implication rules that longitudinally de-
scribe the evolution of the Covid-19 pandemic at dif-
ferent time points.
4 METHODOLOGY
There are many articles that deal with formal concept
analysis applied to the field of health and human be-
havior. This specific article aims to investigate ag-
gressive behaviors of Chinese drivers in traffic, using
data collection, exploration, attribute selection, and
transformation, as well as the extraction of contexts
and rules (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Metodology.
4.1 Materials
The dyadic database used in this study is available
in (Jin et al., 2023). The database contains records
of 1039 Chinese drivers who responded to a ques-
tionnaire. The questionnaire consists of 37 variables,
including responses from different perspectives. Ta-
ble 1 shows an example of the attributes extracted
from these questionnaires, with only the first three
attributes from each category displayed for simplifi-
cation purposes. The study was divided into groups,
each about the analyzed subcategories. Each subcate-
gory has a specific number of attributes.
4.2 Methods
4.2.1 Preprocessing
The first step will be to collect the necessary data
and its description. Validated data is available in the
Data in Brief journal data repository (Jin et al., 2023).
The available data contains objects and attributes re-
lated to Chinese drivers, where attribute types can be
categorical and numerical. The database has been
pre-processed, with irrelevant attributes removed, and
outliers filtered. Data balancing was not performed,
HEALTHINF 2024 - 17th International Conference on Health Informatics
58

Table 1: Variables available in the database.
Category Variable Question
Driving and insurance purchasing information
A1 Commercial insurance for vehicle
A2 Frequency of driving for work
A3 Confidence in driving skills
Aggressive driving behaviors
B1 Speed limit: rarely exceed
B2 Normal speed, avoid weaving, reckless overtaking
B3 Safe distance, no tailgating
Friend/Peer Influence
C1 Supportive friends
C2 Advocating safe driving
C3 Caution against driving under the influence
Family Influence
D1 Planned driving
D2 Follow traffic rules
D3 Praise safe driving
Socio-demographic factors
E1 Gender
E2 Education level
E3 Monthly salary
as all data in the database corresponds to the class that
the study seeks to characterize.
It was necessary to create categories for the anal-
ysis of the objects at hand. To do this, sub-categories
were created, and the selection of which attributes
would be present in them was made. Initially, the
analysis to be conducted is about the influence of
external factors on the behavior of drivers in traffic.
For this purpose, a Cartesian product of general cat-
egories into sub-categories was performed. The at-
tributes in the categories related to driving and insur-
ance purchase information (A), socio-demographic
factors (E), and aggressive behaviors (B) were con-
sidered general attributes, meaning they are present in
all other sub-categories. The sub-categories analyzed
pertain to external factors that influence driver behav-
ior and/or attention.
4.2.2 Discretization
Next, to achieve the objectives of this article, it will
be necessary to transform the data into a formal con-
text, using the database as input for concept extraction
algorithms. For this purpose, the data should corre-
spond to binary attributes. Not all attributes have this
characteristic, as some are of a numeric and/or cate-
gorical type, within the range [1, 5], where the varia-
tion pertains to how much a driver agrees with a state-
ment (Table 2).
For the transformation of this data into a formal
context, an algorithm was used that considers value
ranges and separates them into two groups (binary),
indicating whether the data agrees or disagrees with
the question. A slight change in the algorithm is when
it is necessary to invert the values 0 and 1. In some
Table 2: Numeric Value and Meaning.
Valor Description
1 Strongly Disagree
2 Disagree
3 Neutral
4 Agree
5 Strongly Agree
cases, an attribute may yield an interesting rule if it is
marked as 1, not necessarily because it belongs to the
group containing values corresponding to 0.
After binarizing the values using the algorithm,
a formal context is obtained that will allow the ex-
traction of rules and implications from the database
(Table 3). This formal context was varied according
to the attributes of interest, separating them into dif-
ferent analyses. This was done due to the limitation
on the number of attributes that FCA algorithms can
handle. In each analysis, the maximum number of at-
tributes was 13, considering the Cartesian product of
attributes from different general categories with sub-
categories.
For the generation of rules, the Lattice Miner 2.0
tool will be used, a data mining prototype developed
under the supervision of Professor Rokia Missaoui
by the laboratory at the University of Quebec. This
is a publicly available Java-based platform where the
main functions include all low-level operations that
allow the manipulation of input data, structures, and
rule association. The platform enables the generation
of groups, called formal concepts, including logical
implications, thus showing binary relationships be-
Application of Formal Concept Analysis to Characterize Driving Behaviors and Socio-Cultural Factors Related to Driving
59
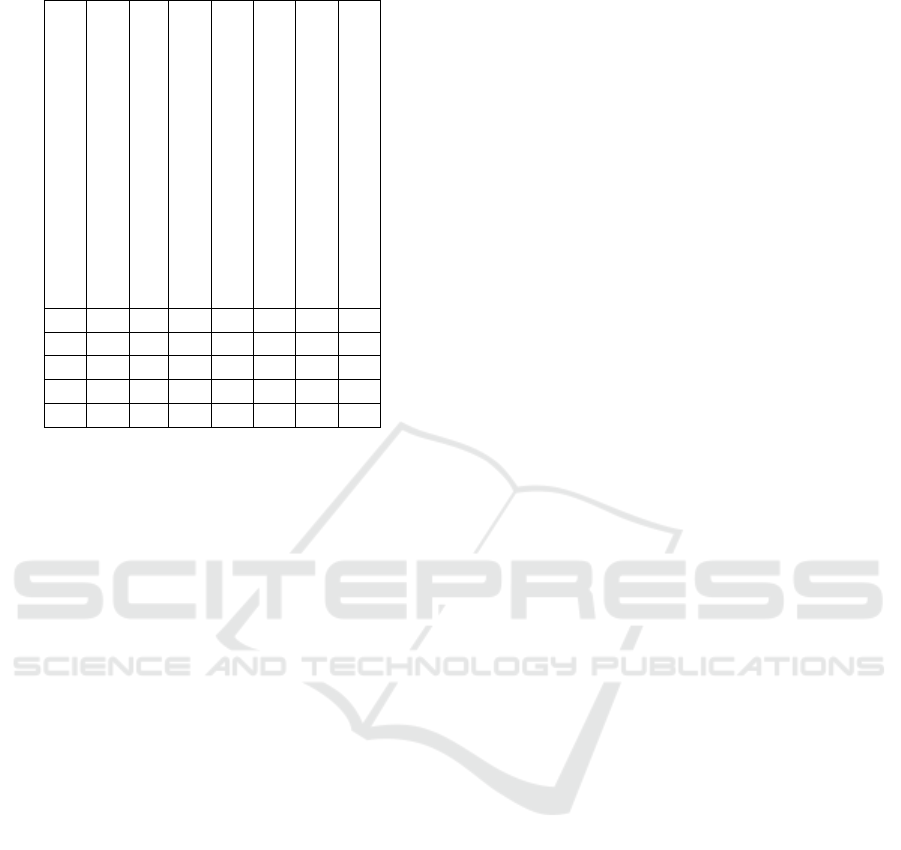
Table 3: Part of formal context.
less than 5 years of driver’s license
exceeds speed limit
drives under the influence of friends
drinks while driving
less than 40 years of age
has a college degree
drives carefully when with family
trusts driving skills
X X X X X
X X X X X
X X X
X X X
X X
tween collections of objects and their sets of attributes
or properties.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
When AFC was used, support values were set above
40% and confidence values above 60% in the Chi-
nese drivers’ scenario. The first analysis was per-
formed using sociocultural factors (age, educational
factor, and income) along with driving factors (time
spent driving, confidence in driving skills, driving fre-
quency, etc.), and aggressive driving behavior factors
(exceeding speed limits, maintaining safe distances,
etc.), generating two hundred and forty (240) rules.
It is possible to collect these results in XML for-
mat and analyze the rules in the form of A → B. As-
suming that B is a consequence, generating support
(sup) and confidence (conf) (Table 4) generates im-
plication rules pointing to attributes.
When we bring the ”Mindsponge Theory” into
analysis, which explores how external factors influ-
ence driver attitudes, we aim to examine these factors
through two analyses: the influence of friends and/or
close individuals on driving behavior and the influ-
ence of family on driving conduct. When considering
the former, attributes like ”the influence of alcohol
and drugs on driving” and ”whether or not there are
people in the car” are taken into account. Therefore,
the database was analyzed for external factors using
AFC, with a minimum support of 55% and a mini-
mum confidence of 88%, resulting in the extraction
of four hundred and sixty rules. The key rules can be
observed in Table 5.
These rules show an interesting characteristic of
the database, leading to the understanding that around
60% of the drivers present drive better and more cau-
tiously when accompanied by of friends and/or close
individuals, with a confidence level of approximately
88%.
Considering the Chinese socio-cultural context,
the three rules found primarily emphasize the impor-
tance of external factors in decision-making and in-
dicate that a significant portion of drivers who claim
to have aggressive behavior do not have this kind of
influence while driving.
On the other hand, an analysis was conducted
considering the category that references family influ-
ence during driving. This analysis considered socio-
cultural aspects along with factors related to family
members in the car, along with the driver. One hun-
dred and five (105) rules were extracted, with the
main ones documented in Table 6.
In this way, the main extracted rules show that
around 59% of drivers tend not to have aggressive be-
haviors influenced by the family, with a confidence
level of approximately 87%. With these rules, it can
be affirmed that drivers who have family influence are
generally less prone to exhibiting aggressive behavior
on the road.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper employs FCA, a novel method for exam-
ining driving behaviors from a large database, with
features that allow the application of this method
grounded in the theoretical framework of the ”Mind-
sponge Theory”. This approach is not commonly uti-
lized in the field of intelligent transportation and road
safety research.
The association of rules demonstrates characteris-
tics of aggressive behaviors associated with external
factors such as family and friends. It can be inferred
that this is an important factor in a driver’s decision-
making and may be a crucial factor in whether or
not accidents occur. These rules can be generalized
to the Chinese socio-cultural context, and efforts can
be made to understand the primary reasons why this
problem occurs.
On the other hand, it becomes difficult to accu-
rately characterize more specific individual aspects
due to subjectivity and bias involved in self-reported
survey data.
We had a geographical scope limitation as the
dataset only includes data from Chinese drivers which
may limit the generalizability of our research find-
HEALTHINF 2024 - 17th International Conference on Health Informatics
60

Table 4: Rules extracted considering only aggressive behaviors would be like.
N. Rules Sup Conf
1
IF A driver has less than 5 years of driving experience
and tends to drive cautiously
THEN they will not exceed the speed limit of the road.
49% 88%
2
IF A driver has less than 5 years of driving experience
and is under 40 years old
THEN they will yield the right of way to other drivers
40% 90%
3
IF The driver trusts their skills behind the wheel
and has more than 5 years of driving experience
THEN they will use their turn signal when changing lanes.
44% 80%
Table 5: Rules extracted considering the influence of friends and/or close individuals.
N. Rules Sup Conf
1
IF the driver has friends who
influence not drinking
THEN they will not exhibit aggressive behavior
60% 90%
2
IF the driver, even in a hurry, has friends
who encourage safe driving
THEN they will yield in traffic
61% 87%
3
IF the driver has friends who recommend
slowing down at the yellow signal
THEN they will slow down at the yellow signal
60% 87%
Table 6: Rules extracted considering family influence.
N. Rules Sup Conf
1
IF mhe driver has their family in the car
THEN they will not exhibit aggressive behavior
60% 86%
2
IF the driver is criticized by the family for irresponsible driving
THEN they will not exceed the speed limit of the road
58% 88%
3
IF the driver’s traffic behavior is monitored by the family
THEN they will not run yellow signals
59% 88%
ings. So, for future work, it will be necessary to
explore different scenarios and use different tools to
expand this analysis from the Chinese socio-cultural
context to a more general context, seeking impli-
cations that can lead to better understanding of the
causes of traffic accidents.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The present work was carried out with the sup-
port of Fundac¸
˜
ao de Amparo
`
a Pesquisa do Es-
tado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) under grant num-
ber APQ-01929-22. The authors thank CNPq, the
Pontif
´
ıcia Universidade Cat
´
olica de Minas Gerais –
PUC-Minas and Coordenac¸
˜
ao de Aperfeic¸oamento
de Pessoal de N
´
ıvel Superior – CAPES – (Grant
PROAP 88887.842889/2023-00 – PUC/MG, Grant
PDPG 88887.708960/2022-00 – PUC/MG - IN-
FORM
´
ATICA and Finance Code 001).
REFERENCES
Biedermann, K. (1997). How triadic diagrams represent
conceptual structures. In Lukose, D., Delugach, H.,
Keeler, M., Searle, L., and Sowa, J., editors, Concep-
tual Structures: Fulfilling Peirce’s Dream, pages 304–
Application of Formal Concept Analysis to Characterize Driving Behaviors and Socio-Cultural Factors Related to Driving
61

317, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Blevente Lorand Kis, C. S. and Troanca, D. (2017). Fca
tools bundle – a tool that enables dyadic and tri-
adic conceptual navigation. In Proceedings of the In-
ternational Conference on Formal Concept Analysis,
ICFCA ’17, pages 214–219.
Carullo, G., Castiglione, A., De Santis, A., and et al. (2015).
A triadic closure and homophily-based recommenda-
tion system for online social networks. World Wide
Web, 18(6):1579–1601.
Deivid Santos, Cristiane Nobre, L. Z. M. S. (2022). Ap-
plication of formal concept analysis and data mining
to characterize infant mortality in two regions of the
state of minas gerais.
Felde, M. and Stumme, G. (2023). Triadic exploration and
exploration with multiple experts. Knowledge & Data
Engineering Group, University of Kassel, Germany.
Ganter, B. and Obiedkov, S. (2004). Implications in tri-
adic formal contexts. In Wolff, K. E., Pfeiffer, H. D.,
and Delugach, H. S., editors, Conceptual Structures
at Work, pages 186–195, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer
Berlin Heidelberg.
Houston, J. M., Harris, P. B., and Norman, M. (2003). The
aggressive driving behavior scale: Developing a self-
report measure of unsafe driving practices. North
American Journal of Psychology, 5:193–202.
Hu, B., Dasmahapatra, S., Dupplaw, D., Lewis, P., and
Shadbolt, N. (2004). Managing patient record in-
stances using dl-enabled formal concept analysis. In
Motta, E., Shadbolt, N. R., Stutt, A., and Gibbins,
N., editors, Engineering Knowledge in the Age of the
Semantic Web, pages 172–186, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Jin, R., Wang, X., Nguyen, M.-H., La, V.-P., Le, T.-T., and
Vuong, Q.-H. (2023). A dataset of chinese drivers’
driving behaviors and socio-cultural factors related to
driving. Data in Brief, 49:109337.
Kent, R. E. and Neuss, C. (1997). Conceptual analysis of
hypertext, pages 70–89. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,
Berlin, Heidelberg.
Lucas Ferreira, Cristiane Nobre1, L. Z. M. S. (2021). Study
of the evolution of antiemetic treatment through the
application of triadic formal concept analysis.
Paulo Lana, Cristiane Nobre, L. Z. M. S. (2022). For-
mal concept analysis applied to a longitudinal study
of covid-19.
Wei, L., Qian, T., Wan, Q., and et al. (2018). A research
summary about triadic concept analysis. Interna-
tional Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics,
9(4):699–712.
World Health Organization (2023). Road safety.
Yang, J., Du, F., Qu, W., Gong, Z., and Sun, X. (2013).
Effects of personality on risky driving behavior and
accident involvement for chinese drivers. Traffic Inj
Prev, 14(6):565–571.
HEALTHINF 2024 - 17th International Conference on Health Informatics
62
