
Incorporating an Intelligent System Based on a Quantum Algorithm into
Predictive Analysis for Screening COVID-19 Patients
Arat
˜
a Andrade Saraiva
1,2,4,5,9 a
, Jo
˜
ao Paulo Oliveira da Silva
1,3 b
, Jos
´
e Vigno Moura Sousa
4 c
,
N. M. Fonseca Ferreira
6,7,8 d
, Salviano Pinto Soares
2,5,9 e
and Ant
´
onio Valente
2,8 f
1
LSC-EGN, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
2
School of Sciences and Technology-Engineering Department (UTAD), Vila Real, Portugal
3
Faculty of Technology of Piaui, Teresina, Piaui, Brazil
4
State University of Piaui, Piripiri, Piaui, Brazil
5
Institute of Electronics and Informatics Engineering of Aveiro (IEETA), University of Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal
6
ISEC Institute of Engineering of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
7
Knowledge Engineering and Decision-Support Research Center (GECAD) of the Institute of Engineering,
Polytechnic Institute of Porto, Portugal
8
INESC-TEC Technology and Science, Porto, Portugal
9
Intelligent Systems Associate Laboratory (LASI), Portugal
Keywords:
COVID, Artificial Intelligence, Quantum Computing, Diagnostics.
Abstract:
The work seeks to develop an expert prediction system based on artificial intelligence that can serve as a
tool for healthcare professionals, as a diagnostic aid when estimating whether a patient with COVID will
show rapid clinical improvement or whether they will be intubated. Such a system is important for hospital
management in relation to the acquisition of materials, in addition to enabling early treatment of patients
with COVID. The predictive analysis algorithm for screening COVID patients addressed was the Variational
Quantum Classifier (VQC) and Deep Neural Networks (DNN). As a result, an accuracy of 90% was obtained
for DNN and 96% for VQC.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the context of the pandemic of the new coro-
navirus or SARS-CoV-2, which causes the disease
called COVID-19, the advance of technologies that
allow precise information to be obtained and predic-
tions to be made using computational methods, is al-
ready a practice adopted in some hospitals, particu-
larly in intensive care units (ICUs).
The challenge of high cost continues to represent
an obstacle to the implementation of dedicated data
processing systems. Artificial intelligence (AI) tech-
niques illustrate an example of what can be used to
improve the hospital environment, proving useful in
detecting alarms related to clinically significant vi-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3960-697X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1984-0264
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5164-360X
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2204-6339
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5862-5706
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5798-1298
tal signs and predicting clinical deterioration (Parreco
et al., 2018).
COVID mainly targets the respiratory system, due
to the affinity of the SARS-CoV-2 virus for mucosal
cells and alveolar epithelial cells. In most cases, this
syndrome is mild, but in some cases it develops into
a serious condition. It can manifest as rapid pneumo-
nia with acute respiratory failure, leading, in extreme
situations, to death (Pessanha et al., 2021).
In general, it is recommended to use low-flow
oxygen therapy devices, such as a nasal catheter and
a non-rebreathing mask with a reservoir bag, to treat
this hypoxemic condition, in order to minimize the
dispersion of aerosols, since the disease is highly con-
tagious through droplets containing the virus (Silva
et al., 2020).
The appropriate use of non-invasive ventilation
(NIV) in COVID-19 patients improves oxygenation,
reduces the need for intubation and reduces mortal-
ity. Careful application of NIV is vital and must be
aligned with the stages of the disease. In the ICU, var-
ious methods are used, including high-flow oxygen
Saraiva, A., Oliveira da Silva, J., Sousa, J., Ferreira, N., Soares, S. and Valente, A.
Incorporating an Intelligent System Based on a Quantum Algorithm into Predictive Analysis for Screening COVID-19 Patients.
DOI: 10.5220/0012351100003657
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2024) - Volume 1, pages 111-116
ISBN: 978-989-758-688-0; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
111

therapy, NIV and invasive mechanical ventilation, de-
pending on severity (Wang et al., 2020) (Spadari and
Gardenghi, 2020).
(Gu
´
erin et al., 2020) the prone positioning tech-
nique, known as the prone position, which has been
used for years, is now recommended for sedated,
mechanically ventilated patients taking neuromus-
cular blockers, especially those suffering from se-
vere to moderate acute respiratory distress syndrome
(ARDS).
In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, a study
carried out in China with a sample of 1,009 patients
revealed that 41% of all patients required hospitaliza-
tion, with more than 70% of cases considered serious
requiring the administration of supplementary oxygen
(Siemieniuk et al., 2018).
For Elharrar (Elharrar et al., 2020), only 63% of
the total of 24 patients with hypoxemic respiratory
failure with COVID19 were able to endure more than
three hours in the prone position and oxygenation im-
proved in only 25% of this sample.
Patients who remained in the prone position for
three hours experienced an improvement in oxygena-
tion, while those who did so for just one hour had
unfavorable outcomes, including intubation (Elharrar
et al., 2020).
Some studies explore the application of computa-
tional methods for monitoring and predictions based
on hospital data. As an example, Meneses’ study
(Meneses, 2021) explores the use of machine learn-
ing algorithms, such as Random Forest and Gradient
Boost, to predict ICU patient admission based on data
from the first 24, 48 and 72 hours of hospitalization.
Using data from a real hospital during the COVID-
19 pandemic, Gradient Boost models showed the best
performance metrics. For example, for data from
the first 24 hours, Gradient Boost achieved AUROC
of 92.7%, Accuracy of 61%, Sensitivity of 81.6%,
Specificity of 86.1%, Accuracy of 85.1% and F1-
Score of 69.9%. The study suggests that this approach
can be an effective tool in predicting ICU admissions,
helping with hospital management.
(Fabrizzio et al., 2023) proposes the development
of a Web App using a decision tree model to estimate
the risk of ICU admission for patients with COVID-
19. Streamlit, created in Python, stratifies patients
based on variables associated with Precision Nursing,
assisting healthcare professionals in making clinical
decisions. Despite the possible impact of vaccination
on data, the Web App proved to be viable for pre-
senting research results in an understandable way and
supporting clinical decision-making.
Given the difficulties of treating respiratory failure
in COVID-19 patients and their current high mortality
rate, it is essential to develop software based on arti-
ficial intelligence to optimize this type of treatment.
The system would be based on AI to apply scales and
care flows objectively, learning from previous data to
improve the effectiveness of procedures and thus im-
prove care while reducing hospital costs.
This study presents a quantum computing al-
gorithm for predictive analysis in the screening of
COVID patients. This algorithm is based on the Vari-
ational Quantum Classifier (VQC). For comparison
purposes, a widely recognized deep neural network
(DNN) model was used.
The use of quantum computing is driven by im-
proved artificial intelligence, faster processing of ma-
trices and vectors and the joint properties of qubits.
Achieving the research objectives will allow pa-
tients to receive more effective treatment in cases of
readmission for similar reasons, as well as benefiting
new patients with similar profiles.
The article is carried out without any commercial
or financial relationship that could be interpreted as
a potential conflict of interest. It is divided into four
sections: section 2 deals with the computational tech-
nique used in the work, while section 3 describes the
results obtained and, finally, the conclusion.
2 METHODOLOGY
The representation of the process adopted can be seen
in the flowchart 1. First there is the data input, then
there are two architectures that can be used, flow 1 or
flow 2. Flow 1 is characterised by the use of the DNN
algorithm and flow 2 by the use of PCA followed by
the VQC algorithm. Finally, the classification result
is obtained.
2.1 Dataset
This project is based on the (Barros et al., 2022)
dataset, which was developed from an observational,
longitudinal and retrospective study of patients who
were exposed to respiratory failure treatment at a
reference hospital for the treatment of COVID-19
in Teresina-PI. Biometric data and monitoring signs
were taken into account.
The dataset shows only patients with respiratory
failure diagnosed with COVID-19 by the new SARS-
CoV-2 coronavirus defined by molecular tests (PCR-
RT).
The input elements that were part of the pro-
gramme and data collection were: oxygenation con-
trol indices such as PaO2/FiO2, age, gender, address,
pathological history, symptoms, monitoring data such
BIODEVICES 2024 - 17th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
112
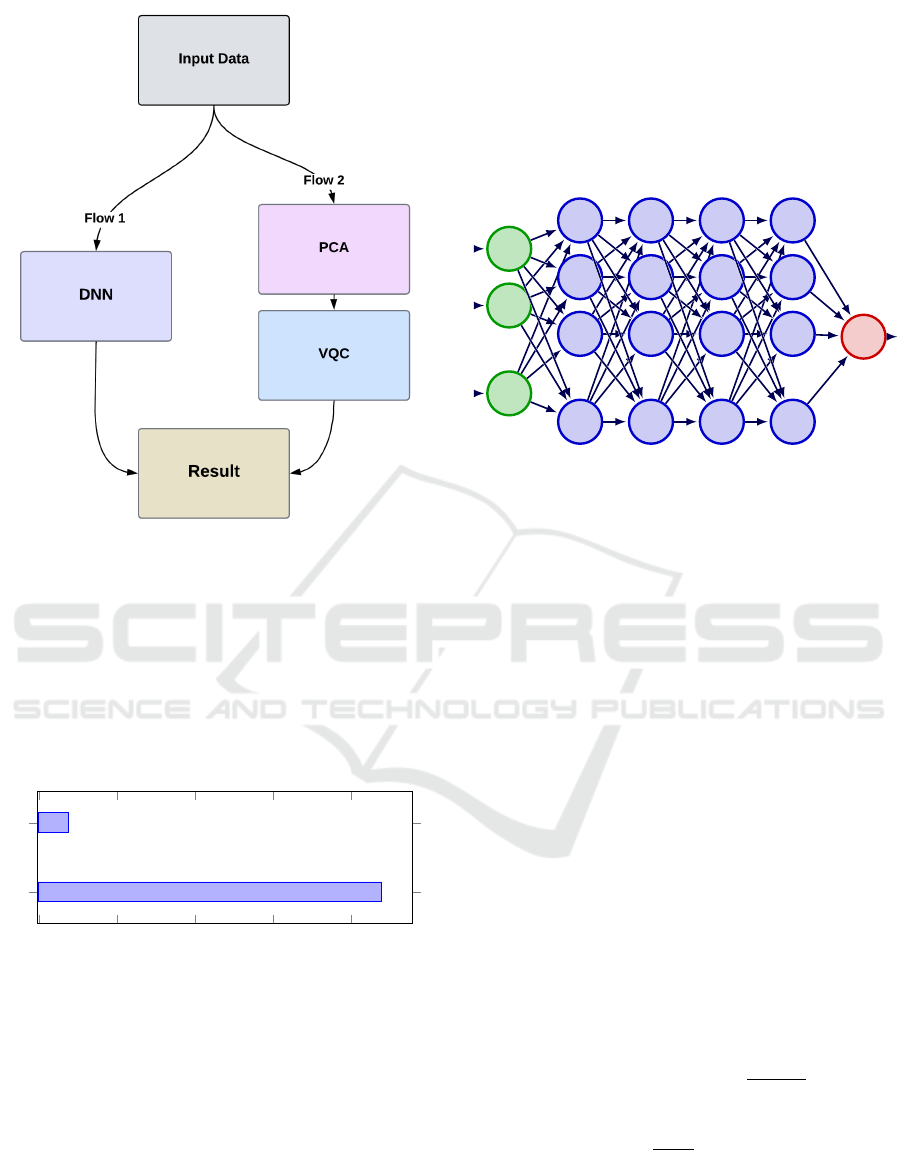
Figure 1: Flowchart of the process adopted in the study.
as: heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, imag-
ing reports, laboratory analysis data: lactate, platelets
and INR, blood gas data, defined care procedures, av-
erage execution times and respective results.
The amount of data used in the proposed archi-
tecture is 476 patients, 70% for training and 30% for
validation.
0
100
200
300
400
0
1
438
38
Count
Sample quantity for each case
Figure 2: Quantity of samples.
Figure 2 shows the distribution of the number of
samples in the dataset for different scenarios: 0 rep-
resents the cases in which there was clinical improve-
ment without the need for intubation, while 1 indi-
cates the patients who required intubation for treat-
ment.
2.2 Deep Neural Networks
The DNN belongs to the Artificial Neural Network
family (Passafaro et al., 2020). Figure 3 shows a rep-
resentation.
x
1
x
2
x
n
.
.
.
h
(1)
1
h
(1)
2
h
(1)
3
h
(1)
m
.
.
.
h
(2)
1
h
(2)
2
h
(2)
3
h
(2)
m
.
.
.
h
(3)
1
h
(3)
2
h
(3)
3
h
(3)
m
.
.
.
h
(4)
1
h
(4)
2
h
(4)
3
h
(4)
m
.
.
.
y
k
.
.
.
Input
layer
Hidden
layers h
1
Hidden
layers h
2
Hidden
layers h
3
Hidden
layers h
4
Output
layer
Figure 3: Schematic representation of DNN.
They are typically feed forward networks in which
the data flows from the input layer to the output layer
without backtracking and the connections between
the layers are unidirectional and never touch a node
again.
The outputs are obtained by supervised learning
with data sets of some information based on ”what
we want” by means of backpropagation.
The DNN architecture adopted in this work, as il-
lustrated in Figure 3, is composed of the input layer,
represented by the values x
1
, .. . , x
n
, responsible for
receiving the data without reducing resources. This
layer has 90 variables, with x
n
= 90.
Then, the information flow passes through four
hidden layers h
1
, . . . , h
4
. The first h
1
layer contains
16 units, while the second h
2
has 24 units, both us-
ing the ReLU activation function. To avoid overfit-
ting problems, a Dropout layer is incorporated with a
rate of rate = 0.5. Subsequently, two additional lay-
ers h
3
and h
4
are applied, each with 20 and 24 units,
respectively.
The output layer y
k
is composed of a sigmoid
function that maps any real value to the range between
0 and 1 (Zaheer and Shaziya, 2018).
f (x) = sigmoide(x) =
1
1 + e
−x
(1)
As x becomes large and positive, e
−x
approaches
zero, and the fraction
1
1+e
−x
approaches 1. Likewise,
when x becomes large and negative, e
−x
becomes
large and the fraction approaches 0. The output f (x)
is the classification probability, which can have two
values: The value ”0” corresponds to a patient who
Incorporating an Intelligent System Based on a Quantum Algorithm into Predictive Analysis for Screening COVID-19 Patients
113

will improve clinically without the need for intuba-
tion and the value ”1” corresponds to a patient who
will need to be intubated.
2.3 PCA
The visualisation of the PCA process adopted in the
methodology, as shown in the flowchart 4, is char-
acterised by data input, in which the dimension of
the existing columns in the data set is reduced from
90 variables to 2 characteristics, which is the number
of qubits used in this project. The technique used is
known as probabilistic principal component analysis
(PCA). More details on PCA can be found in the work
by Tipping (Tipping and Bishop, 1999).
Figure 4: Flowchart for using PCA on data.
This technique synthesizes information efficiently,
preparing the data for the proposed VQC quantum
model. The goal is to improve model efficiency, ex-
plore relationships and patterns, and make the data
structure easier to understand.
2.4 Variational Quantum Classifier
Variational circuits play a role in quantum machine
learning similar to that of neural networks in classi-
cal machine learning (Schuld et al., 2020). The vari-
ational circuit used consists of three main parts, as
shown in figure 5.
Figure 5: Schematic representation of the VQC.
The VQC consists of a |0 >
n
state preparation
phase, in which it encodes the x classical data into
qubits, using the AngleEmbedding encoder, which
encodes N features in the rotation angles of n qubits.
The N represents the number of input features to be
embedded, where N ≤ n.
Before the x input data reaches the U (x) coding
block, this data is pre-processed using PCA to reduce
the features, as illustrated in figure 4.
Given an encoded feature vector U(x), the layer
structure of the variational circuit represented by
block W (θ) maps the vector and applies different an-
gular rotations. Optionally, it includes some entangle-
ment gates between them.
The θ parameters of this circuit are then trained
in a classical optimisation cycle using the Adam opti-
miser. For more details on the optimiser, we suggest
reading (Kingma and Ba, 2017).
The output information is obtained by perform-
ing a measurement with an observable operator in the
base Z, which will be applied to a subset or all of the
qubits, thus obtaining a classical bit string z ∈ {0, 1}
n
.
The string is then mapped by a cost function C, given
by the equation 2. The real labels are compared
with the circuit labels {−1, 1}, where −1 corresponds
to the patient with clinical improvement without the
need for intubation and 1 to the patient who will need
to be intubated. The optimiser is then used to optimise
the circuit. And the results of the measurements tell
the classic optimiser how to adjust the θ parameters,
as shown in figure 5.
C(θ) =
∑
k
f
k
(Tr[O
k
U(θ)ρ
k
U
†
(θ)]) (2)
3 RESULTS
This section presents the results obtained in each de-
velopment flow of this article. A comparison is pre-
sented based on the accuracy of the implemented pre-
trained neural networks, as detailed in table 1. This
metric is critical, demonstrating the comprehensive
accuracy of the model.
Table 1: Accuracy comparison table between DNN and
VQC.
Models Accuracy
DNN 90%
VQC 96%
The red line in figure 6 shows the evolution of
accuracy over the seasons, with the value before the
second season reaching approximately 90% and re-
maining stable. The green line, meanwhile, shows the
losses, demonstrating the model’s consistency.
Figure 7 shows that accuracy reached a higher
value after the ninth season and was increasing. The
green line representing losses showed lower values
from the eighth season onwards than in figure 6.
Analysing figure 7, it can be seen that the quantum
algorithm adjusted to the data fed into it and was able
to maintain the training efficiently without any change
considered substantial in the results over the epochs.
BIODEVICES 2024 - 17th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
114
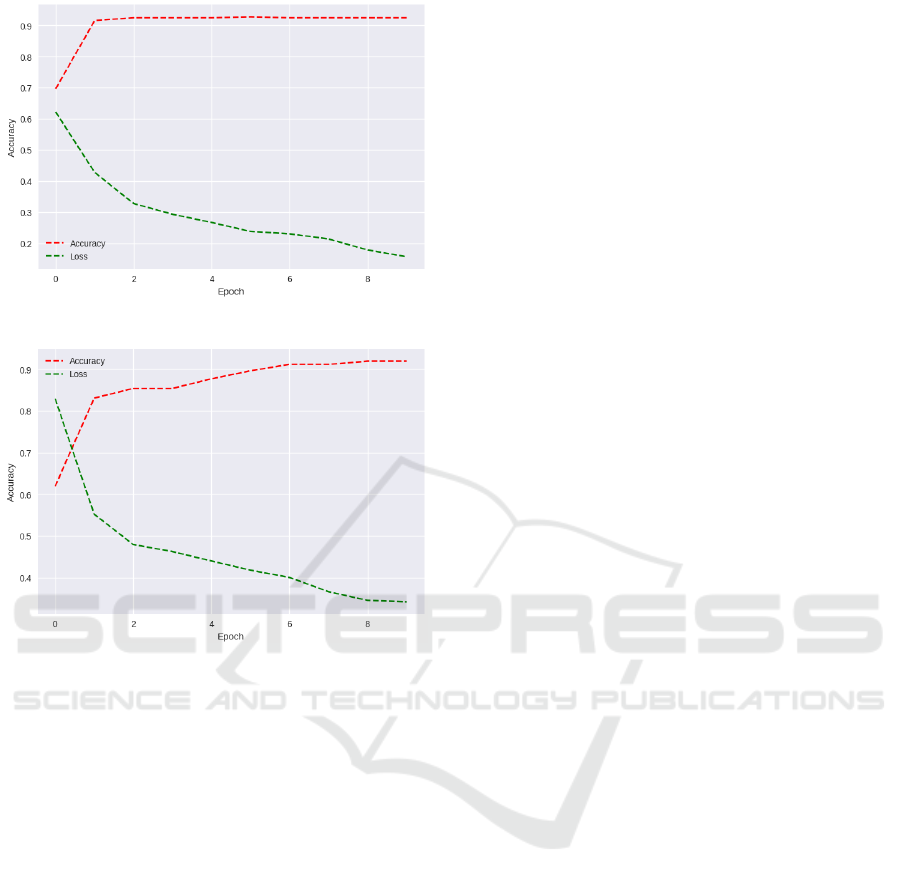
Figure 6: DNN accuracy and loss graph.
Figure 7: VQC accuracy and loss graph.
4 CONCLUSION
Thus, considering that the process of managing respi-
ratory failure is made up of a series of interconnected
diagnostic and therapeutic events with different speci-
ficities, it is suggested that a system be developed with
a view to progressively standardising care through AI,
in order to increase assertiveness and, consequently,
reduce hospital costs.
The study had two limiting factors, namely the
high number of variables analysed (90) and the small
number of patients.
Two artificial intelligence techniques were used,
DNN and VQC, with learning strategies. Based on the
results, the study showed that the quantum computing
algorithm (VQC) was able to predict different types of
data with a reduction in the errors to be processed and,
therefore, the possibility of carrying out the prediction
and classification process with greater precision.
Accuracy can be better observed in the table 1. It
can be seen that the VQC method is more accurate
than DNN, with accuracy results of 96% and 90% re-
spectively.
Future activities include testing other algorithms
and even developing an application for use by society.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was also partially funded by
FCT—Fundac¸
˜
ao para a Ci
ˆ
encia e a Tecnologia
(FCT) I.P., through national funds, within the scope
of the UIDB/00127/2020 project (IEETA/UA).
The elaboration of this work would not have been
possible without the collaboration of the Engineering
and DecisionSupport Research Center (GECAD) of
the Institute of Engineering, Polytechnic Institute of
Porto, Portugal and FAPEPI, Brazil . Also noteworthy
are LSC-EGN, UESPI, and UTAD.
REFERENCES
BARROS, R., Oliveira, J. P., Saraiva, A. A., Moura Sousa,
J. V., and De Oliveira Paula, N. R. (2022). Conjunto
de dados de prontu
´
arios m
´
edicos de paciente covid-
19. Mendeley Data, V5.
Elharrar, X., Trigui, Y., Dols, A.-M., Touchon, F., Martinez,
S., Prud’homme, E., and Papazian, L. (2020). Use
of Prone Positioning in Nonintubated Patients With
COVID-19 and Hypoxemic Acute Respiratory Fail-
ure. JAMA, 323(22):2336–2338.
Fabrizzio, G. C., Erdmann, A. L., and Oliveira, L. M. d.
(2023). Web app para a predic¸
˜
ao de internac¸
˜
ao em
unidade de terapia intensiva por covid-19. Revista
brasileira de enfermagem, 76(6).
Gu
´
erin, C., Albert, R. K., Beitler, J., Gattinoni, L., Jaber,
S., Marini, J. J., Munshi, L., Papazian, L., Pesenti, A.,
Vieillard-Baron, A., and Mancebo, J. (2020). Prone
position in ards patients: why, when, how and for
whom. Intensive care medicine, 46(12):2385–2396.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2017). Adam: A method for
stochastic optimization.
Meneses, A. C. F. (2021). Predic¸
˜
ao de necessidade de
uti hospitalar para pacientes internados utilizando
m
´
etodos de aprendizado de m
´
aquina.
Parreco, J., Hidalgo, A., Parks, J., Kozol, R., and Rat-
tan, R. (2018). Using artificial intelligence to
predict prolonged mechanical ventilation and tra-
cheostomy placement. The Journal of surgical re-
search, 228:179–187.
Passafaro, T. L., Lopes, F., Dorea, J., Craven, M., Breen,
V., Hawken, R., and Rosa, G. (2020). Would large
dataset sample size unveil the potential of deep neural
networks for improved genome-enabled prediction of
complex traits? the case for body weight in broilers.
BMC Genomics, 21.
Pessanha, K. F., Alexandre, L. F., De Souza, A. C. M.,
Esp
´
ındola, G. d. F. R., Nogueira, F. G. d. O., and Ro-
drigues, M. C. d. C. (2021). Covid-19:a infecC¸
˜
Ao
Incorporating an Intelligent System Based on a Quantum Algorithm into Predictive Analysis for Screening COVID-19 Patients
115

respirat
´
Oria aos dist
´
Urbios cardiovasculares. Revista
Cient
´
ıfica da Faculdade de Medicina de Campos,
16(1):79–89.
Schuld, M., Bocharov, A., Svore, K. M., and Wiebe, N.
(2020). Circuit-centric quantum classifiers. Physical
Review A, 101(3).
Siemieniuk, R., Chu, D., Kim, L., G
¨
uell-Rous, M.-R.,
Alhazzani, W., Soccal, P., Karanicolas, P., Darbel-
lay Farhoumand, P., Siemieniuk, J., Satia, I., Irusen,
E., Refaat, M., Mikita, J., Smith, M., Cohen, D.,
Vandvik, P., Agoritsas, T., Lytvyn, L., and Guyatt, G.
(2018). Oxygen therapy for acutely ill medical pa-
tients: A clinical practice guideline. BMJ, 363:k4169.
Silva, V. Z. M. d., Neves, L. M. T., and Forgiarini Junior,
L. A. (2020). Recomendac¸
˜
oes para a utilizac¸
˜
ao de
oxig
ˆ
enio suplementar (oxigenoterapia) em pacientes
com covid-19. ASSOBRAFIR Ci
ˆ
encia, 11(Supl1):87.
Spadari, J. A. A. and Gardenghi, G. (2020). Aspectos fi-
siopatol
´
ogicos do covid-19 e uso de ventilac¸
˜
ao n
˜
ao in-
vasiva.
´
E poss
´
ıvel? Revista Pesquisa em Fisioterapia,
10(3):372–375.
Tipping, M. E. and Bishop, C. M. (1999). Mixtures of
Probabilistic Principal Component Analyzers. Neural
Computation, 11(2):443–482.
Wang, D., Hu, B., Hu, C., Zhu, F., Liu, X., Zhang, J., Wang,
B., Xiang, H., Cheng, Z., Xiong, Y., Zhao, Y., Li, Y.,
Wang, X., and Peng, Z. (2020). Clinical Character-
istics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel
Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China.
JAMA, 323(11):1061–1069.
Zaheer, R. and Shaziya, H. (2018). Gpu-based empiri-
cal evaluation of activation functions in convolutional
neural networks. In 2018 2nd International Confer-
ence on Inventive Systems and Control (ICISC). IEEE.
BIODEVICES 2024 - 17th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
116
