
Comparing Variable Handling Strategies in BDI Agents: Experimental
Study
Frantisek Vidensky
∗ a
, Frantisek Zboril
∗ b
, Jan Beran
c
, Radek Koci
d
and Frantisek V. Zboril
e
Department of Intelligent Systems, Brno University of Technology, Bozetechova 2, Brno, Czech Republic
∗
These two authors contributed equally to this work
fi
Keywords:
BDI Agents, Agent Interpretation, AgentSpeak(L).
Abstract:
BDI (Belief-Desire-Intention) agents represent a paradigm in artificial intelligence, demonstrating proficiency
in reasoning, planning, and decision-making. They offer a versatile framework to construct intelligent agents
capable of reasoning about their beliefs, desires, and intentions. Our research focuses on AgentSpeak(L), a
popular BDI language, and its interpreter using late variable bindings. Unlike traditional interpreters, it defers
substitution selection until execution, enhancing rationality by preventing premature, erroneous selections. To
validate our approach, we conducted experiments in a virtual collectable card marketplace. We implemented
a system that can use both late and early variable binding strategies, comparing their performance. In shared
and independent experiments, the late bindings strategy outperformed the early bindings strategy, although
overhead costs were observed. We also conduct a brief discussion of the situations in which it is appropriate
to use late bindings given the structure of the declared plans.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Belief-Desire-Intention (BDI) (Rao and
Georgeff, 1997) agents represent a popular paradigm
in the field of artificial intelligence and autonomous
systems. These agents based on Bratman´s the-
ory (Bratman, 1987) of intentions are inspired by
human cognitive processes and exhibit remarkable
capabilities in reasoning, planning, and decision-
making. This process is called practical reasoning
and consists of two phases. The first phase called
deliberation, decides what goals we want to achieve.
The second phase known as means-ends reasoning
decides how we are going to achieve these goals
(Wooldridge, 1999). The BDI architecture offers
a versatile framework for constructing intelligent
agents capable of reasoning about their beliefs,
desires and intentions. Beliefs represent not only the
inherent state of the autonomous agent but also a
comprehensive portrayal of the state of the external
world in which the agent is situated. These beliefs
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1808-441X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7861-8220
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4737-191X
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1313-6946
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6965-4104
collectively constitute the foundational substrate
upon which the agent’s decision-making processes
are founded. Contrapuntally, desires represent
the state of the world that the agent would like to
achieve, delineating its pursuit of specific objectives.
Intentions are the persistent and goal-oriented aspects
of the agent’s architecture, representing objectives
toward which the agent has committed to directing
its resources and subsequent actions. These three
architectural components allow the autonomous
agents to make rational choices in dynamic and
uncertain environments.
Over the years, numerous implementations have
emerged (in (Silva et al., 2020) you can find a sys-
tematic review of the BDI agent architectures up to
the year 2020). Among the well-recognized ones
that have played a significant role in the development
of BDI systems, we can cite IRMA (Bratman et al.,
1988), PRS (Georgeff and Lansky, 1987), dMars
(d’Inverno et al., 1998) and 2APL (Dastani, 2008).
From the modern systems, we can mention JACK
(Winikoff, 2005) and JadeX (Pokahr et al., 2005).
Our work is based on the fundamental BDI lan-
guage AgentSpeak(L) (Rao, 1996). Several dialects
of this language have been developed, one of the most
used and still evolving is the ASL language for the
Jason system (Bordini et al., 2007). The principle of
Vidensky, F., Zboril, F., Beran, J., Koci, R. and Zboril, F.
Comparing Variable Handling Strategies in BDI Agents: Experimental Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0012358600003636
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2024) - Volume 1, pages 25-36
ISBN: 978-989-758-680-4; ISSN: 2184-433X
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
25

these systems is based on the choice of intention that
the agent has to achieve its goals. A goal is a state of
the system which the agent wants to achieve so goals
can be viewed as an adopted desire. An agent has
plans that are sets of instructions on how to achieve a
goal or react to an event. Each plan that has been se-
lected to achieve a goal can declare another (sub)goal,
so the goals are hierarchically ordered. If the top-level
plan that has been chosen to achieve a goal of an in-
tention is achieved, then intention is also achieved.
The authors of the AgentSpeak(L) language intro-
duced functions for event selection, a plan that will
be used to achieve the goal selection, and intention
selection, only in the abstract and introduced non-
determinism into its functionality. Over the years,
several approaches have been published to eliminate
this non-determinism and improve the rationality of
the autonomous agent. Several significant approaches
are listed in the following section.
We chose a different path to increase the rational-
ity of the agents. In our prior paper (Zboril et al.,
2022), we introduced a new AgentSpeak(L) language
interpreter, characterized by the utilization of late
bindings of variables. The agent maintains a set of
valid substitutions that remain continuously accessi-
ble in relation to the belief base. It defers the actual
selection of a substitution until such a time when it
becomes requisite, such as when the agent is about to
execute an action. This approach aims to avoid the
inadvertent selection of a substitution that could later
prove invalid, thereby mitigating the risk of plan fail-
ure during execution. Subsequently, our attention was
directed towards the design of the operational seman-
tics (Vidensky et al., 2023) of such an interpreter.
In this paper, we discuss a practical implementa-
tion of the interpreter using variable substitution. The
remainder is structured as follows. Section 2 contains
brief summary of works aimed at enhancing the ratio-
nality of autonomous agents. In Section 3, working
principles and key aspects of late variable bindings in
our interpreter are described. Section 4 describes two
experiments, together with a discussion of the results.
Section 5 deals with when it is possible to convert a
plan to another plan, and that the agent achieves the
same flexibility with early bindings as with late bind-
ings. The paper concludes with Section 6, where the
conclusion and possible future work are described.
2 RELATED WORKS
Over time, researchers have explored diverse method-
ologies aimed at enhancing the rationality of au-
tonomous agents. Significant attention has been di-
rected towards the refinement of intention selection
approaches. Typically, rational agents concurrently
embrace multiple intentions, and the strategic selec-
tion of these intentions can facilitate the fulfilment of
all intentions while mitigating potential conflicts.
For example, the authors of (Thangarajah et al.,
2003) presented a mechanism allowing agents to
identify and mitigate a specific type of adverse inter-
action, where the effects of one goal undo the con-
ditions crucial for the successful pursuit of another
goal. To detect these interactions, the paper proposes
the maintenance of summary information concerning
both definite and potential conditional requirements,
as well as the resultant effects of goals and their asso-
ciated plans. Work on this mechanism has continued
and has been practically verified to bring benefits even
though the cost of the additional reasoning is small
(Thangarajah and Padgham, 2011). The mechanism is
exemplified using goal-plan trees (GPTs), which can
be regarded as a representation of intention within the
context of BDI systems.
Researchers from the same university (Waters
et al., 2015) developed two new approaches. The first
approach, denoted as enablement checking takes into
account whether a suitable plan could be found in the
next step. The second one, referred to as low cover-
age prioritisation operates under the assumption that
a plan that can be safely executed only in a limited set
of possible knowledge base states should be preferred.
The team of authors also increased the flexibility and
robustness of an agent by relaxing a plan to a partial
plan that specifies which operators must be executed
but does not need to fully specify their order or vari-
able bindings (Waters et al., 2018). Subsequently, an
optimization method that involves adjusting both the
ordering and variable binding constraints was intro-
duced (Waters et al., 2021).
The CAN (Sardina and Padgham, 2011) language
has made notable contributions to increasing the flex-
ibility of the agent and robustness. One of its key in-
novations, among other things, is the introduction of
a failure-handling system. During the plan selection
process, other relevant plans are retained as alterna-
tive strategies. In the event of a (sub)goal failure, the
language tries to select another plan from these alter-
native strategies.
Other researchers took a different path and intro-
duced a meta-model which extends the BDI frame-
work to accommodate the representation of concepts
that the agent needs to select plans based on softgoals
(typically long-term goals that influence the choice of
plans) and preferences (Nunes and Luck, 2014).
State-of-the-art solutions for avoiding conflicts
between intentions are approaches based on the
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
26

Monte-Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) method (Yao et al.,
2014). The original approach has been improved
by allowing the interleaving of primitive actions in
different intentions and taking into account the dy-
namism of the environment and fairness when choos-
ing an intention (Yao and Logan, 2016). However,
the scheduler was only focusing on a single agent.
Recently, the approach has been extended to use for
multi-agent settings where the scheduler takes into
account other agents´ intentions (Dann et al., 2020;
Dann et al., 2021; Dann et al., 2022).
Despite the extensive historical background in the
realm of BDI system development and the consid-
erable volume of published literature that has con-
tributed to enhancing the rationality of autonomous
agents (the papers referred to in this section and others
are summarized in (Bordini et al., 2021)), it is impera-
tive to underscore that this domain of inquiry remains
ongoing and evolving.
3 LATE VARIABLE BINDINGS
As previously mentioned, the languages and systems,
based on AgentSpeak(L) (Rao, 1996), choose appro-
priate substitutions immediately during the plan se-
lection phase. However, these substitutions may be-
come invalid during the plan execution phase due to a
change in the environment or potential conflicts with
another intention in the use of limited resources. One
approach to handling the selection of substitutions
was introduced in the 2APL system (Dastani, 2008).
This system offers the possibility to create rules that
specify decision processes including the handling of
substitutions.
Our approach (Zboril et al., 2022) is based on
maintaining a set of all possible variable bindings and
working with this set during the execution phase of a
plan. When the step of the plan is executed, the set
may be limited and some substitutions are removed.
If at least one substitution remains in the set, the plan
can continue in execution. We call the set of substitu-
tions a context, and we have named this approach late
bindings.
All important operations and functions for late
bindings (Zboril et al., 2022) and the operational se-
mantics of our proposed interpreter (Vidensky et al.,
2023) have already been published. To recall and es-
pecially for the sake of completeness, we present the
most important definitions and a short description of
the deliberation and plan execution phases once more
in this paper.
The basic operation of our approach is broad uni-
fication.
Definition 1. Broad unification, denoted as ρU, is
formally defined as:
ρU(p, PS)
def
= {mgu(p, p
′
) : p
′
∈ PS}
The function maps the atom p and atom p
′
from the
set of atoms PS to a set of all possible most general
unifiers without variables renaming.
Since beliefs are in the form of atoms, the belief
base (BB) is also a set of atoms. We use the broad
unification function when we need a unification for a
single atom that is valid in BB in any interpretation.
The result of the function is a set of unifiers which
we call a possible unifier set (hereafter referred to as
PUS).
When a deliberation process selects a plan for an
event, it is associated with a PUS with which the agent
operates when it executes the plan. This PUS is called
the plan context and is changed as the agent performs
actions or achieves and tests goals. If an event is trig-
gered during the execution of a plan, the context of
that plan is associated with it, in which case we speak
of event context.
Instances of plans and events that have an asso-
ciated context are called weak instances. They are
formally defined as follows:
Definition 2. A weak plan instance (WPI) is a triple
⟨te,h,ctx⟩, where te is a plan’s triggering event, h =
h
1
;h
2
;...; h
m
is the plan’s body, and ctx is the plan’s
context.
Similarly, we can define a weak event instance.
Definition 3. A weak event instance (WEI) is a triple
⟨evt,ix,ctx⟩, where evt is an event, ix is an identifier
of the intention that raises the event (or null in case of
an external event) and ctx is a context.
The deliberation phase works with weak instances
in such a way that if there is a WEI, then a plan is rel-
evant if its triggering event and the event of this WEI
are unifiable concerning the WEI context. A plan is
applicable if each context condition is satisfied in the
current state of the agent’s belief base. This means it
is possible to find a PUS for each context condition
and then unify them.
A selected plan is adopted as an intention. In the
original system (Rao, 1996), an intention is defined
as a stack of partially instantiated plans. The delib-
eration process finishes with the insertion of the plan
with the corresponding intention structure.
In a system that uses late bindings, intentions must
work with WPI and WEI.
Definition 4. The intention is a structure containing
a WEI of a triggering event and a stack of WPIs. For-
mally, it is defined as follows:
Comparing Variable Handling Strategies in BDI Agents: Experimental Study
27

⟨evt,ix,ctx⟩[⟨te
1
,h
1
,ctx
1
⟩ ‡ ⟨te
2
,h
2
,ctx
2
⟩ ‡ ...
‡⟨te
n
,h
n
,ctx
n
⟩]
where the top of the stack is on the left and the ele-
ments of the stack are delimited by ‡.
If an external event occurs, in our case in the form
of WEI, a new intention is created for it. However, if
a new (sub)goal is created or an event is triggered dur-
ing the execution of an intention, again as some WEIs,
the selected WPI for that internal event is added to
the top of the stack of the currently executing inten-
tion. For more details, we refer to our previous works
(Zboril et al., 2022; Vidensky et al., 2023).
In order to correctly describe how a context mod-
ification is performed, we need to reintroduce two
more definitions.
Definition 5. The merging operation, denoted as ⋉,
maps two substitutions to one substitution so that the
substitution unifies two different atoms in two sets of
atoms and is defined as follows:
σ
1
⋉ σ
2
def
=
σ
1
∪ σ
2
iff ∀[t
1
/x
1
] ∈ σ
1
∀[t
2
/x
2
] ∈
σ
2
(x
1
= x
2
→ t
1
= t
2
)
/
0 else
This operation can be used to merge two unifiers.
If we want to modify a context with respect to another
context, we need to find all the pairs that produce a
non-empty set. The following definition is used for
this purpose:
Definition 6. The restriction operator, denoted as ⊓,
returns a set of unifiers that contain all the most gen-
eral unifiers that unify p
1
in PS
1
and p
2
in PS
2
is de-
fined as:
ρU
1
⊓ ρU
2
def
=
[
σ
1
∈ρU
1
,σ
2
∈ρU
2
σ
1
⋉ σ
2
where ρU
n
is a simplified form of notation for
ρU(p
n
,PS
n
).
For a more detailed description of this operation,
please refer to our previous papers.
During the execution phase, the context can be
modified at any step. When the goal test is executed,
the context is restricted to retain only those substitu-
tions for which the tested formula is a true belief. In
the case of the test goal ?g(t), we can define the con-
text modification as: ctx
1
= ctx ⊓ ρU(g(t), BB). The
belief base (BB) is a set of atoms, therefore it can be
used for broad unification.
After the successful execution of the achievement
goal, there was probably a change in the belief base.
The context of the plan that triggered the goal must
adequately react to these changes before continuing
the execution of the plan body. Also in this case the
context modification is done by a restriction opera-
tion. When an agent is about to execute an action, it
must create a ground atom for the action before exe-
cuting it. Thus, all free variables must be bound to a
specific atom. Consider an action of the format a(t),
where t is a term (atoms or variables). After the ac-
tion is executed, all variables from term t are uniquely
bound to the same variables in all substitutions in the
context.
3.1 Interpreter Overheads
Preserving context entails additional computational
costs for the agent’s interpretation. In our previous re-
search, we did not address these computational over-
heads, despite their significance in evaluating the ap-
propriateness of using an agent interpretation featur-
ing late bindings.
When we consider a WPI ⟨te,h,ctx⟩, created us-
ing plan P = te : b
1
∧... ∧b
n
← h, substitutions within
the context can bind variables from this plan. These
variables may be part of the triggering event, con-
text conditions, or the body of the plan. However,
it is crucial to note that the maximum number of vari-
ables that can be bound in this manner is limited to
|Var(P)|. These bound values can be viewed as re-
sources allocated by the agent (Waters et al., 2021).
Late bindings, as a strategy, allow for deferred re-
source allocation, maintaining a set of potential re-
sources that can be bound to a particular variable.
These potential resources remain in the set until the
agent requires the use of a particular resource. It is
important to highlight that this resource set is con-
structed within our system and, in accordance with
(Vidensky et al., 2023), it is created only when the
agent performs testing of its BB. In the case of other
internal actions, such as the addition or removal of
atoms from the BB, as well as external actions (hence-
forth referred to as ”acts”), the execution of these ac-
tions can yield only one answer. This answer takes
the form of free variable substitution within the atom
that defines such actions within the plan.
According to Definition 1, the result of a broad
unification is a set of substitutions denoted as
ρU(p,BB) = {σ
1
...σ
n
}. We assume that the agent’s
belief base BB contains only ground atoms and thus
every element of ρU(p,BB) is a ground substitution.
The cardinality of ρU (p,BB) is inherently con-
strained by the cardinality of BB, leading to the con-
clusion that |ρU(p,BB)| <= |BB|. The range of val-
ues to which variables from Var(p) can be bound is,
therefore, determined by the cardinality of BB.
Results arising from agent actions are added into
the context through restriction with the original WPI
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
28

context before act execution. Nevertheless, the defi-
nition of the restriction operation, as per Definition 6,
posits that no new element (resource) can be added to
this merged set. The set can either remain unchanged
or be reduced to one of its subsets. This deliberation
leads to the conclusion that the maximum cardinality
of the set for a variable is dictated by the cardinality
of the smallest set of answers to an act in which that
variable was used.
As previously indicated, the only type of act for
which such a cardinality can exceed one is the test
goal. Consequently, the maximum possible cardinal-
ity of the context within a WPI, created through the
execution of plan P, is M
|Var(P)|
. Here, M denotes the
largest cardinality observed within the set of answers
to all previously executed test goals, encompassing all
plans that are either currently in progress or have al-
ready been completed within the intention to which
this particular WPI belongs.
4 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
In this section, we compare the performance of the in-
terpreter that uses late bindings versus the interpreter
that uses an early bindings strategy. The system,
which we named the Flexibly Reasoning BDI Agent
(FRAg)
1
, that will perform the interpretation was de-
veloped in the SWI Prolog
2
environment. The Pro-
log language naturally supports working with predi-
cates, unifications, and substitutions, so it was a log-
ical choice for implementing a system that supports
the late bindings strategy. The system does not inter-
pret programs written directly in AgentSpeak(L), but
programs written in its dialect, which we designed
to be easily interpreted using the Prolog interpreter.
Agents can interact within an environment connected
via an interface of this system. During each cycle,
agents receive perceptions in the form of add and
delete lists, based on which they adjust their belief
base. Throughout the agent cycle, agents process in-
puts, perform practical reasoning and execute actions
if possible.
4.1 Experimental Environment
To compare early bindings and late bindings strate-
gies, we created a virtual marketplace environment.
The goods traded in this marketplace are collectable
cards. Each card has a trade price. However, as is
common in marketplaces, the final price is determined
1
https://github.com/VUT-FIT-INTSYS/FRAg
2
https://www.swi-prolog.org/
by how much sellers are willing to sell a card for and
whether any buyer is willing to accept that price. Buy-
ers and sellers come to the marketplace with the inten-
tion of buying or selling one particular card. If they do
not succeed within a certain period of time, they leave
in disappointment. Agents in this marketplace act as
resellers. Their job is to find a seller who sells a cer-
tain card and a buyer who wants to buy that card and is
willing to make a deal. More concretely, whether sell-
ers and buyers reach an agreement and make a trans-
action depends not only on the fact that they trade
with the same type of goods but also on whether the
seller’s requested price is below the buyer’s maximum
acceptable price.
Sellers and buyers enter and leave the market-
place while the system operates, so the environment
is naturally dynamic. We have modelled the above-
described scenario by assigning each card an initial
price, and both the seller and the buyer reduce this
price using a coefficient generated in the range
0,1
according to a normal distribution with certain param-
eters (mean and dispersion), µ
B
, σ
B
, and µ
S
, σ
S
. We
will use the indices S for sellers and B for buyers. The
arrival of customers to the marketplace (buyers and
sellers) is modelled according to a Poisson distribu-
tion with mean values λ
B
and λ
S
. Customers stay un-
til they are serviced but for a maximum of a predeter-
mined number of episodes, d
B
and d
S
. This duration
is measured in episodes.
4.1.1 Illustrative Example
In this subsection, we illustrate a scenario in which
the late bindings strategy has an advantage over early
bindings. A plan for an agent looking for a matching
offer to a demand can be written, in AgentSpeak(L)
language, as:
+! se ll : w a nt s ( Bu yer , CD , Ma x _P r i ce )
<- ? off e rs ( Sell er , CD , Pric e );
Price <= Ma x _Pr i c e ;
sel l ( S ell er , Buyer , CD , Pri ce )
! sell .
In this illustrative example, there will be only one
seller adam and two buyers betty and clara who want
to buy the card that adam is selling. Consider that the
set of base beliefs is given by
of fe r s ( adam , cd1 , 8 5) .
wa nt s ( be tty , cd1 , 6 0) .
wa nt s ( cl ara , cd1 , 9 0) .
In Figure 1, the left side shows the execution of
the plan by an interpreter using the early bindings
strategy. In this context, it is assumed that the inter-
preter selects beliefs in the order of their insertion into
Comparing Variable Handling Strategies in BDI Agents: Experimental Study
29
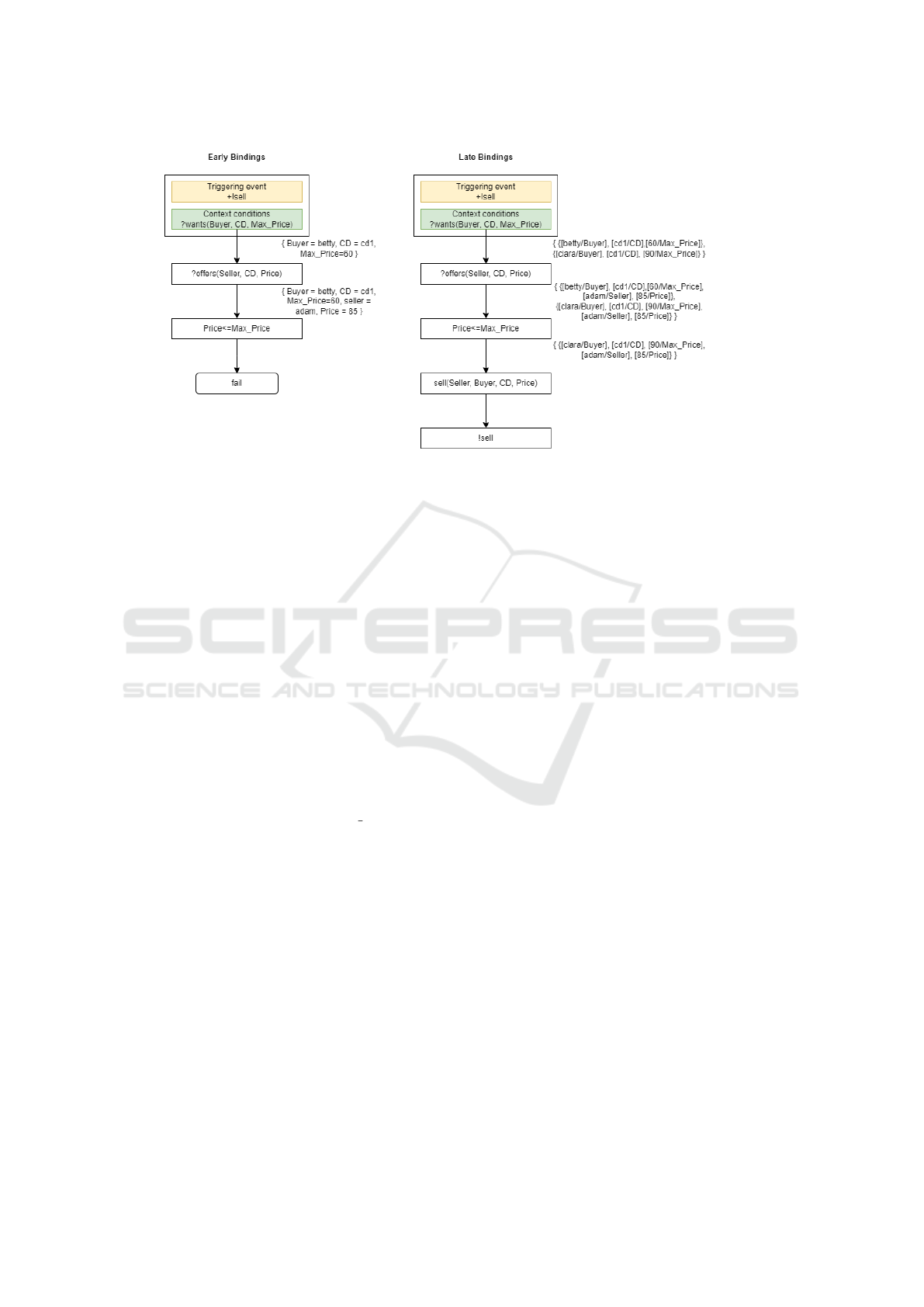
Figure 1: Illustrative example executed by interpreters using early and late bindings strategy.
the belief base. The interpreter successfully binds the
variables for the context conditions and for the test
goal. However, the price at which the card is sold is
higher than the maximum price the buyer is willing to
pay, so the result of the comparison is not true. At this
juncture, the execution of the plans becomes unfeasi-
ble, leading to failure. The interpreter must execute
the plan again from the beginning. On the second at-
tempt, it would select clara as the buyer and be suc-
cessful.
In the event of plan execution by an interpreter
using the late bindings strategy, the aforementioned
failure scenario can be preempted. As illustrated in
Figure 1 on the right side, this interpreter system-
atically maintains a set of all possible substitutions.
These substitutions are unified with new substitutions
for other variables that appear during the execution
of the body of the plan. If it is necessary to com-
pare the Price variable against the Max Price, the in-
terpreter strategically reduces the context and retains
only those substitutions for which this comparison is
true. Therefore, the substitution that substituted betty
for Buyer is removed. Before the action is performed,
substitutions are applied and execution of the plan
succeeds.
This example clearly illustrates that the use of late
bindings serves as an effective preventive measure
against both failure and the necessity for redundant
plan executions. But whether this strategy will actu-
ally perform better remains to be proven experimen-
tally.
4.2 Experiments
To compare both strategies, we conducted two experi-
ments. In the first experiment, two agents were placed
in the marketplace, each of them following a different
strategy. In this experiment, agents competed among
themselves to see who could make more deals. In the
second experiment, agents operated independently.
All experiments were run on the same personal
computer equipped with AMD Ryzen 5 6600U pro-
cessor (6 CPU cores and 12 threads) and 16 GB of
RAM.
4.2.1 Experiment 1 - Competition
In this experiment, two agents, using different bind-
ing strategies (Early and Late), compete to find more
pairs that want to trade the same card and make a deal.
A fixed value of 0.2 was experimentally chosen for
the parameters σ
B
and σ
S
. Parameters λ
B
and λ
S
were
always set to the same value, within the range of 0.02
to 0.22 with a step size of 0.02. The remaining two
parameters, µ
B
and µ
S
, were set to values in the range
of 0.4 to 0.6 with a step size of 0.1. In this experi-
ment, there are 8 different types of cards with which
customers can trade. Customers leave the market-
place if they have not been served after 100 episodes,
thus d
B
= d
S
= 100. We have also set the number of
episodes at which customers are added to the system
(and agents receive information about their presence
from the environment) to a constant value of 750. Ad-
ditionally, the number of episodes has been fixed at
5000 to ensure agents have the opportunity to serve
clients who arrive later. The length of one episode
was set to 0.5 milliseconds, and it was experimen-
tally determined that this was sufficient time for both
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
30
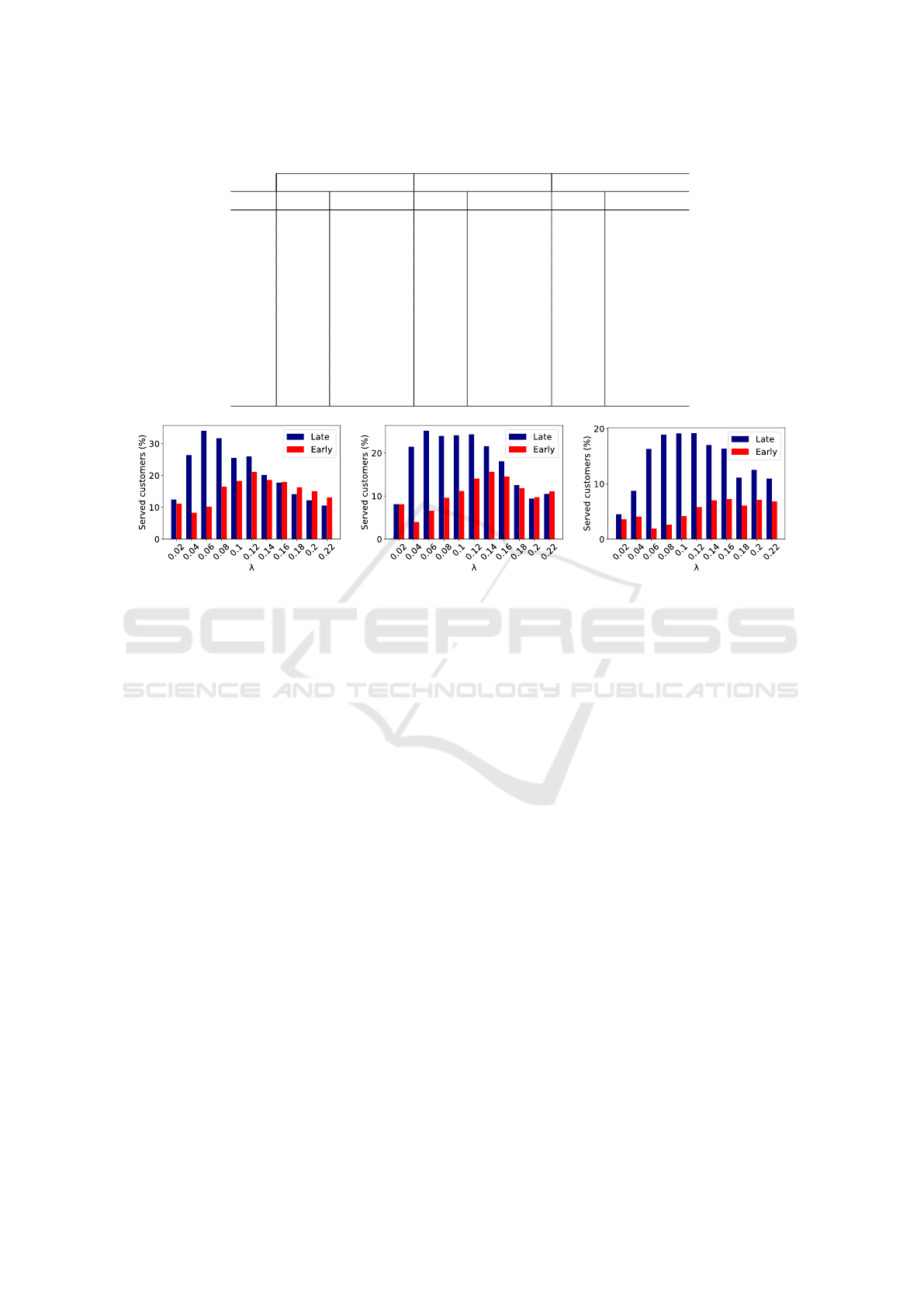
Table 1: Results of the comparison of both strategies working together in one environment.
µ
B
= 0.4 ; µ
S
= 0.6 µ
B
= 0.5 ; µ
S
= 0.5 µ
B
= 0.6 ; µ
S
= 0.4
λ Late Early Late Early Late Early
0.02 12.45 11.19 8.11 8.11 4.51 3.58
0.04 26.43 8.32 21.48 3.97 8.74 4.07
0.06 34.00 10.21 25.14 6.60 16.34 1.92
0.08 31.71 16.46 23.99 9.60 18.91 2.60
0.10 25.47 18.28 24.12 11.2 19.16 4.17
0.12 25.98 21.13 24.34 14.05 19.19 5.79
0.14 20.15 18.63 21.61 15.65 17.05 7.03
0.16 17.72 17.95 18.08 14.52 16.37 7.25
0.18 14.13 16.27 12.56 11.87 11.14 6.10
0.20 12.2 15.05 9.41 9.75 12.55 7.10
0.22 10.57 13.12 10.53 11.09 10.96 6.81
(a) µ
B
=0.4; µ
S
=0.6. (b) µ
B
=0.5; µ
S
=0.5. (c) µ
B
=0.6; µ
S
=0.4.
Figure 2: Competition experiment. Average percentage of served customers for the parameter variants used to generate the
price reduction coefficient.
agents to complete their tasks on the device where the
tests were run. During the interpretation of the early
bindings strategy, substitutions are selected randomly
instead of taking them from the first answer, which is
usual. This choice is made to avoid a high failure rate.
Table 1 shows the outcomes of the first experi-
ment. For each parameter combination, the exper-
iment was repeated 50 times, and the average per-
centage of customers served by each agent was com-
puted. The best results for each agent are highlighted
in bold. It is clearly visible that the late bindings
strategy exhibits superior performance compared to
the early bindings strategy across most parameter set-
tings. The early strategy outperforms the late strat-
egy only in scenarios where sellers reduce prices ei-
ther equally or more than buyers, while concurrently
witnessing a higher arrival of customers into the mar-
ketplace. This can potentially be attributed to the in-
terpreter using the early bindings strategy having an
increased likelihood of randomly selecting a seller
willing to offer an equivalent or higher price than
the buyer in such circumstances. Conversely, when
buyers lower prices more substantially, the late strat-
egy consistently attains superior results relative to the
early strategy. This discrepancy is attributed to a con-
siderably reduced probability of the agent randomly
selecting a suitable seller for the buyer in this context.
Consistently, in the experiment, both agents achieved
the best results when customer arrivals at the mar-
ketplace were frequent, and sellers reduced prices to
a greater extent than buyers. Consequently finding
a buyer who was willing to pay the price the seller
was asking has become more likely. These observed
trends are graphically illustrated in Figure 2. Note
that even in the optimal case, not all customers, both
buyers and sellers, can be served. A situation can and
has arisen where for some customers there was no
counterparty for them to trade with while they were
in the shop.
4.2.2 Experiment 2 - Independent Work
In this experimental setting, both agents operated in-
dependently, ensuring that the actions of one agent did
not influence the outcomes of the other agent.
The experimental configuration closely resem-
bled the preceding one, with the exception that the
episodes were not time-constrained. Instead, each
episode started at the moment when an agent per-
ceived the environment again. Furthermore, each ex-
periment was run 20 times and the number of episodes
during which the agents operated was reduced to
1000. In this experiment, alongside assessing the av-
erage percentage of served customers, we also paid
Comparing Variable Handling Strategies in BDI Agents: Experimental Study
31
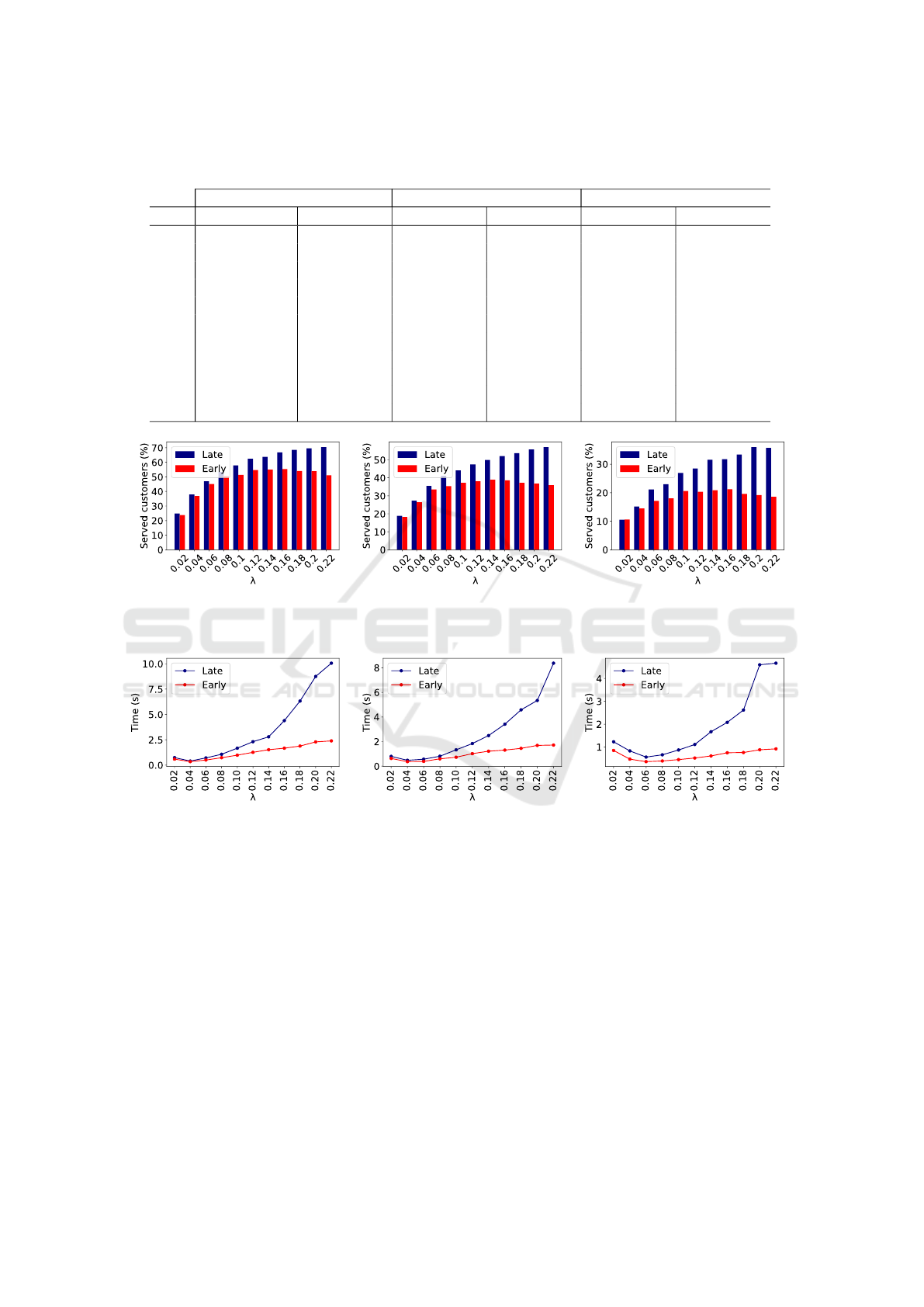
Table 2: Results of the comparison of both strategies working independently of each other. In parentheses are the average
times the agent spent computing.
µ
B
= 0.4 ; µ
S
= 0.6 µ
B
= 0.5 ; µ
S
= 0.5 µ
B
= 0.6 ; µ
S
= 0.4
λ Late Early Late Early Late Early
0.02 24.83 (0.74) 23.83 (0.59) 18.88 (0.80) 18.21 (0.63) 10.51 (1.23) 10.60 (0.85)
0.04 37.89 (0.40) 36.88 (0.34) 27.28 (0.48) 26.46 (0.37) 15.15 (0.83) 14.48 (0.47)
0.06 46.94 (0.71) 45.09 (0.50) 35.49 (0.57) 33.57 (0.39) 21.10 (0.56) 17.11 (0.36)
0.08 53.40 (1.07) 50.61 (0.73) 41.15 (0.81) 35.33 (0.60) 23.00 (0.66) 18.03 (0.39)
0.10 57.86 (1.67) 51.41 (0.98) 44.15 (1.33) 37.22 (0.73) 26.93 (0.87) 20.57 (0.45)
0.12 62.40 (2.31) 54.76 (1.26) 47.42 (1.84) 38.08 (1.02) 28.45 (1.11) 20.30 (0.52)
0.14 63.69 (2.79) 54.96 (1.52) 50.00 (2.49) 38.90 (1.22) 31.52 (1.67) 20.89 (0.61)
0.16 66.79 (4.39) 55.36 (1.67) 52.13 (3.41) 38.58 (1.31) 31.74 (2.08) 21.23 (0.75)
0.18 68.54 (6.32) 54.08 (1.88) 53.69 (4.58) 37.24 (1.45) 33.38 (2.62) 19.59 (0.76)
0.20 69.55 (8.75) 53.87 (2.29) 55.77 (5.34) 36.77 (1.69) 35.96 (4.60) 19.16 (0.88)
0.22 70.42 (10.06) 51.13 (2.39) 57.08 (8.37) 35.94 (1.72) 35.70 (4.67) 18.57 (0.92)
(a) µ
B
=0.4; µ
S
=0.6. (b) µ
B
=0.5; µ
S
=0.5. (c) µ
B
=0.6; µ
S
=0.4.
Figure 3: Independent work experiment. Average percentage of served customers for the parameter variants used to generate
the price reduction coefficient.
(a) µ
B
=0.4; µ
S
=0.6. (b) µ
B
=0.5; µ
S
=0.5. (c) µ
B
=0.6; µ
S
=0.4.
Figure 4: Independent work experiment. Average computation time for the parameter variants used to generate the price
reduction coefficient.
attention to the computational time spent by the agent.
To be specific, this measurement encompassed the en-
tire duration from the initiation to the completion of
the agent’s interpretive loop.
The outcomes of the experiment are presented in
Table 2, with the best results highlighted in bold. The
effectiveness of the agents in serving customers is vi-
sually represented in Figure 3. When comparing these
results with the results from the first experiment (Fig-
ure 2), noticeable differences are evident.
Notably, the differences between the agents are
less pronounced compared to the scenario in which
their actions could influence each other. Both agents
again achieved the best results under conditions where
customer arrivals were frequent, and sellers reduced
prices to a greater extent than buyers. This outcome
aligns with expectations, as it is inherently more fea-
sible to find a buyer in such circumstances.
Figure 4 presents a graphical representation of the
computational time consumed by the agents. The
charts show that for the agent using an early binding
strategy, the increase in computational time relative to
the number of customers is slow due to its reliance on
random selection, as previously explained.
Conversely, the results for the agent using the late
bindings strategy reveal a significant increase in com-
putational time. This is attributed to the agent’s ac-
tive management of the set of substitutions, with the
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
32

cardinality of this set expanding proportionally to the
growing number of customers present in the market-
place.
In the experiment, the agents exhibited the short-
est computational times when sellers reduced prices
more than buyers, and customer arrivals at the mar-
ketplace were very slow. We infer that this can be
attributed to the smaller customer pool, which facili-
tates the rapid finding of feasible pairs. However, this
circumstance may also result in the absence of such
pairs, consequently rendering the agents incapable of
proceeding with their tasks.
5 FLEXIBILITY OF EARLY
BINDINGS AT THE LEVEL OF
LATE BINDINGS THROUGH
PLANS MODIFICATIONS
In this section, we want to discuss several situations
where it is appropriate for an agent to use late bind-
ings and also when it is possible to modify the plan in
a way that gives the agent the same flexibility when
using both late and early bindings.
Our selected example showcased the application
of late and early variable binding in a program exe-
cuting two distinct queries within separate interpre-
tation cycles. The plan used in this program could
be phrased as: ”The agent, if there is a customer
or customers, will find out their requirements, check
whether they can be met and, if necessary, execute
the deal”. In essence, the agent periodically solicits
information about customer’s preferences and seller’s
offerings. This simple example could be rewritten,
however, since we assume that the agent has data for
both queries at the same time. Then it would still work
the same way for an agent executing a plan
+! se ll : w a nt s ( Bu yer , CD , Ma x _P r i ce )
& o f fe r s ( S eller , CD , Pri ce )
& P ric e <= Ma x _Pr i c e
<- Sel l ( Se ller , Buy er , CD , P ri ce );
! sell .
In this case, the problem of finding the buyer and
seller is solved implicitly by evaluating contextual
conditions. In general, we see an incentive to use late
bindings in agent execution when an action is or can
be performed between two test goals, i.e., the two test
goals are performed at different points in the agent’s
interpretation.
In the following paragraphs, we show cases where
an agent has reason to execute test goals in differ-
ent cycles, and what it would take to convert such a
plan to one that addresses the problem of possible bad
binding choices in an early bindings strategy.
I. By using goal testing we may want to guarantee
the agent’s safe execution of the plan. Usually, this in-
volves ensuring that resources are available before the
action is executed, but it can also be tested that some
resources will be available after the action or actions
are executed. In the latter case, the next action does
not determine a particular resource for the subsequent
execution of the action. For example, if we have a
plan that involves travel, the agent, given knowledge
of a car in the garage, may proceed to inspect whether
any of the cars are operational. If not, the agent has
the flexibility to choose an alternative activity. Such
a plan could include a body with a sequence of acts
as shown below. Here, the body of the plan is shown
as some part of it, and to illustrate this we show three
dots before and after such a part.
... ? is ( gar age , Ca r ); got o ( gar a ge );
? mo bi le ( Car );
! go ( Car , Des t i n ati o n ) .. .
In this particular example, we can assume that the
agent can re-execute the first test goal immediately
before executing the second test goal. For example,
such a transformation to a program that guarantees
flexible behaviour even when using an early binding
strategy would look like the following.
... ? is ( gar age , Ca r ); got o ( gar a ge );
! mo bi le ( C ar 2 );
! go ( Car2 , D es t i n a ti o n ) .. .
+! mob il e ( Car ):
? is ( g arag e , Car ) & ? m ob i le ( Car ).
II. In the usual way of processing environmen-
tal perceptions, which was used for example in the
MAPC2022 (Ahlbrecht et al., 2023) competition, the
agent’s belief base changes according to the provided
add and delete lists as a result of the perception of
the environment. Then, if the agent needs to store the
perceptions for future use, it can bind a variable to
the perception of interest and use this binding when
it has all the necessary information. To demonstrate
this, we will use a slightly different example than the
one used in the previous section. The agent observes
signs along the way that may help determine how to
proceed in the future. The following part of the body
of the plan demonstrates such an agent that, while ob-
serving the environment at one location, remembers
the sign seen by binding it to the variable Sign, which
Comparing Variable Handling Strategies in BDI Agents: Experimental Study
33

it then uses at a crossroad to decide which path to take
next.
... ? s ee s ( sign , Sig n );
got o ( cr o ssr o a d );
? sees ( De s ti na t io n , Sig n );
got o ( De s t i na t i o n ) . ..
However, if it saw more than one sign in the first
location, only one would be bound to the variable
when using the early bindings strategy. But then the
Destination would not necessarily be marked with
this Sign, but with another one that it also saw in the
first place, however, this Sign was not selected for
binding. In the case of late bindings, the agent in-
terpreter stores all these signs in context and, by re-
striction operation (Definition 6), selects a Destina-
tion based on the signs if it matches one of these signs.
In the case of early bindings, this situation could again
be handled by re-querying the agent using a sub-plan
in which an evaluation similar to the one in the pre-
vious section would be performed in the context con-
ditions. However, before doing so, it would be nec-
essary to store all previously seen tags in the agent’s
idea base.
III. The previous two problems can be solved by
correctly changing the plan’s design or plans, but the
programmer is responsible for the required function-
ality of the agent. The third argument for the use of
late bindings concerns the declaration of plans as such
if these plans can be chosen during consideration for
a WEI that has a non-empty context. That is, some
variables in the triggering event of such a WEI may
already have predetermined possible resources that
were created sometime earlier during the execution of
the intention under which this WEI was created. The
repetition of the query according to I and II is more
difficult. This is because the programmer would need
to know what queries over what beliefs were executed
during the execution of that intention.
These three examples show situations where the
programmer must be aware of the problems that can
arise when using an early bindings strategy. In the
third case, where a plan can be used as a sub-plan
within an intention, such a transformation would pre-
determine how the variables that are used as input
must be bound in the intention.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have extended our previous work by
introducing an implementation of a system capable of
using both late and early variable binding strategies.
These two approaches were experimentally compared
within the context of a virtual collectable card mar-
ketplace. The primary goal for agents in this dynamic
environment was to find buyers for sellers willing to
buy cards at specified prices.
Two experiments were conducted. In the first
experiment, two agents, each using distinct variable
binding strategies, operated on a shared marketplace.
The agent using the late binding strategy outper-
formed the second agent across most experiment pa-
rameters. In the second experiment, where agents op-
erated independently, the late binding strategy also
yielded better results, albeit with smaller differences
in performance.
It is worth noting that our approach has inherent
limitations. The maintenance and modification of a
set of potential substitutions (context) introduce over-
head costs for the interpreter. These costs were dis-
cussed and were evident in the results of the sec-
ond experiment, where we also focused on comput-
ing time. For the late binding strategy, computational
time increased significantly relative to the parameter
determining the rate of customer arrivals at the mar-
ketplace. With each additional customer, the size of
the context was increased. In contrast, the agent us-
ing the early binding strategy managed to work with
only a slight increase in computation time. While it is
theoretically possible to reduce this overhead by us-
ing other algorithms or modifying the current code, it
remains an intrinsic aspect of this approach.
Further enhancements to the system, beyond the
reduction of overhead costs, including the improve-
ment of the user experience. Currently, the system
interprets the dialect of the AgentSpeak(L) language
developed by us. We are actively working on a com-
piler for this language and its integration with a user
interface.
Future research directions involve the develop-
ment of intention-selection algorithms. In this do-
main, the state-of-the-art approach is based on the
Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) method. We in-
tend to incorporate this method into our system and
combine its advantages with those of the late variable
binding strategy. In addition, we intend to explore the
possibility of using this approach to detect similarities
between intentions that could lead to coordinated or
concurrent execution of such intentions or to decide
on the choice of specific variable bindings in order to
synthesize such intentions.
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
34

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by the internal BUT
project FIT-S-23-8151.
REFERENCES
Ahlbrecht, T., Dix, J., Fiekas, N., and Krausburg, T.
(2023). The multi-agent programming contest 2022.
In Ahlbrecht, T., Dix, J., Fiekas, N., and Krausburg,
T., editors, The Multi-Agent Programming Contest
2022, pages 1–18, Cham. Springer International Pub-
lishing.
Bordini, R. H., El Fallah Seghrouchni, A., Hindriks, K., Lo-
gan, B., and Ricci, A. (2021). Agent programming in
the cognitive era. In Proceedings of the 20th Interna-
tional Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-
Agent Systems, AAMAS ’21, page 1718–1720, Rich-
land, SC. International Foundation for Autonomous
Agents and Multiagent Systems.
Bordini, R. H., H
¨
ubner, J. F., and Wooldridge, M. (2007).
Programming multi-agent systems in AgentSpeak us-
ing Jason, volume 8. John Wiley & Sons.
Bratman, M. (1987). Intention, plans, and practical reason.
Harvard University Press.
Bratman, M. E., Israel, D. J., and Pollack, M. E.
(1988). Plans and resource-bounded practical reason-
ing. Computational intelligence, 4(3):349–355.
Dann, M., Thangarajah, J., Yao, Y., and Logan, B. (2020).
Intention-aware multiagent scheduling. In Proceed-
ings of the 19th International Conference on Au-
tonomous Agents and MultiAgent Systems, AAMAS
’20, page 285–293, Richland, SC. International Foun-
dation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Sys-
tems.
Dann, M., Yao, Y., Alechina, N., Logan, B., and Thangara-
jah, J. (2022). Multi-agent intention progression with
reward machines. In Raedt, L. D., editor, Proceed-
ings of the Thirty-First International Joint Conference
on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI-22, pages 215–222.
International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelli-
gence Organization. Main Track.
Dann, M., Yao, Y., Logan, B., and Thangarajah, J.
(2021). Multi-agent intention progression with black-
box agents. In Zhou, Z.-H., editor, Proceedings of the
Thirtieth International Joint Conference on Artificial
Intelligence, IJCAI-21, pages 132–138. International
Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organiza-
tion. Main Track.
Dastani, M. (2008). 2apl: a practical agent programming
language. Autonomous agents and multi-agent sys-
tems, 16:214–248.
d’Inverno, M., Kinny, D., Luck, M., and Wooldridge, M.
(1998). A formal specification of dmars. In Intelligent
Agents IV Agent Theories, Architectures, and Lan-
guages: 4th International Workshop, ATAL’97 Provi-
dence, Rhode Island, USA, July 24–26, 1997 Proceed-
ings 4, pages 155–176. Springer.
Georgeff, M. P. and Lansky, A. L. (1987). Reactive reason-
ing and planning. In AAAI, volume 87, pages 677–
682.
Nunes, I. and Luck, M. (2014). Softgoal-based plan se-
lection in model-driven bdi agents. In Proceedings
of the 2014 International Conference on Autonomous
Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, AAMAS ’14, page
749–756, Richland, SC. International Foundation for
Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems.
Pokahr, A., Braubach, L., and Lamersdorf, W. (2005).
Jadex: A BDI Reasoning Engine, pages 149–174.
Springer US, Boston, MA.
Rao, A. S. (1996). Agentspeak (l): Bdi agents speak
out in a logical computable language. In European
workshop on modelling autonomous agents in a multi-
agent world, pages 42–55. Springer.
Rao, A. S. and Georgeff, M. P. (1997). Modeling rational
agents within a bdi-architecture. Readings in agents,
pages 317–328.
Sardina, S. and Padgham, L. (2011). A bdi agent pro-
gramming language with failure handling, declarative
goals, and planning. Autonomous Agents and Multi-
Agent Systems, 23:18–70.
Silva, L. d., Meneguzzi, F., and Logan, B. (2020). Bdi
agent architectures: A survey. In Bessiere, C., editor,
Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Joint
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI-20, pages
4914–4921. International Joint Conferences on Artifi-
cial Intelligence Organization. Survey track.
Thangarajah, J. and Padgham, L. (2011). Computationally
effective reasoning about goal interactions. J. Autom.
Reasoning, 47:17–56.
Thangarajah, J., Padgham, L., and Winikoff, M. (2003).
Detecting & avoiding interference between goals in
intelligent agents. In Proceedings of the 18th Inter-
national Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
IJCAI’03, page 721–726, San Francisco, CA, USA.
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.
Vidensky, F., Zboril, F., Koci, R., and Zboril, F. V. (2023).
Operational semantic of an agentspeak(l) interpreter
using late bindings. In Proceedings of the 15th In-
ternational Conference on Agents and Artificial In-
telligence - Volume 1: ICAART, pages 173–180. IN-
STICC, SciTePress.
Waters, M., Nebel, B., Padgham, L., and Sardina, S. (2018).
Plan relaxation via action debinding and deordering.
In Twenty-Eighth International Conference on Auto-
mated Planning and Scheduling.
Waters, M., Padgham, L., and Sardina, S. (2015). Improv-
ing domain-independent intention selection in bdi sys-
tems. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems,
29(4):683–717.
Waters, M., Padgham, L., and Sardina, S. (2021). Optimis-
ing partial-order plans via action reinstantiation. In
Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Joint
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI’20.
Winikoff, M. (2005). Jack™ Intelligent Agents: An Indus-
trial Strength Platform, pages 175–193. Springer US,
Boston, MA.
Comparing Variable Handling Strategies in BDI Agents: Experimental Study
35

Wooldridge, M. (1999). Intelligent Agents, page 27–77.
MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA.
Yao, Y. and Logan, B. (2016). Action-level intention se-
lection for bdi agents. In Proceedings of the 2016
International Conference on Autonomous Agents &
Multiagent Systems, AAMAS ’16, page 1227–1236.
International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and
Multiagent Systems.
Yao, Y., Logan, B., and Thangarajah, J. (2014). Sp-mcts-
based intention scheduling for BDI agents. In Schaub,
T., Friedrich, G., and O’Sullivan, B., editors, ECAI
2014 - 21st European Conference on Artificial Intelli-
gence, 18-22 August 2014, Prague, Czech Republic -
Including Prestigious Applications of Intelligent Sys-
tems (PAIS 2014), volume 263 of Frontiers in Artifi-
cial Intelligence and Applications, pages 1133–1134.
IOS Press.
Zboril, F., Vidensky, F., Koci, R., and Zboril, V. F. (2022).
Late bindings in agentspeak(l). In Proceedings of the
14th International Conference on Agents and Artifi-
cial Intelligence - Volume 3: ICAART, pages 715–724.
INSTICC, SciTePress.
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
36
