
Towards Better Motif Detection: Comparative Analysis of Several
Symbolic Methods
Nour El Houda Fodil
1 a
, Damien Olivier
1 b
and Pierrick Tranouez
2 c
1
Litis, University of Le Havre Normandy, Le Havre, France
2
Litis, University of Rouen Normandy, Rouen, France
Keywords:
Motifs, Time Series, Pattern, Symbolic Representation, SAX, 1d-SAX, fABBA, Sequitur, UniformSAX.
Abstract:
Motif discovery in time series is a process aimed at finding significant original structures. Methods like SAX
rely on dimensionality reduction techniques to reduce computation time. Their inability to capture amplitude
variations is one of their limitations. By introducing a new representation named UniformSAX, we aim to
improve this aspect. We compare our approach to SAX, 1d-SAX, and fABBA, also introducing grammatical
inference. The results show that approaches relying exclusively on representations are more suitable for fixed-
length motifs but lose effectiveness for variable-length motifs.
1 INTRODUCTION
Motifs discovery in time series analysis refers to the
process of extracting hopefully meaningful informa-
tion from temporal continuous signals, through the
discovery of recurring sequences in data. It has
various applications in classification, prediction, and
anomaly detection tasks. The concept of a motif in the
context of time series analysis is nuanced, the defini-
tion of motif can differ across various research stud-
ies.
In the most general case: (1) There can be any
number of different motifs (for a given similarity mea-
sure). (2) There can be any number of instances of
each of these motifs. (3) The similarity between the
instances of a motif varies with the needs of the ap-
plication. (3) The motifs (i.e. the average length of its
instances) can be of any length.
In practice modelling and simplification decisions
must be made. Two main strategies are used: identify-
ing pairs of motifs and focusing on motif sets. Some
methods, like (Mueen et al., 2009) or (Yeh et al.,
2016), concentrate on finding the most similar pairs of
subsequences within a time series. Others, like Chiu’s
approach (Chiu et al., 2003), target the largest col-
lection of similar subsequences, often requiring prior
knowledge of motif size. To tackle the challenge of
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-4016-7524
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6552-8151
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1962-0782
varying motif sizes, some algorithms perform fixed-
size motif discovery for multiple sizes (Tanaka et al.,
2005), while others expand fixed-size motifs while
maintaining similarity (Ferreira et al., 2006). How-
ever, these methods often incur high computational
costs (Zhu et al., 2016), (Gao and Lin, 2018). An
alternative approach involves grammatical inference,
which generates hierarchical representations of re-
curring sequences, aiding in the automated detec-
tion of motifs of varying sizes (Li et al., 2012) and
(Senin et al., 2018). Techniques like Sequitur (Nevill-
Manning and Witten, 1997) and ”Re-Pair” compress
data by substituting repetitive subsequences with a
context-free grammar, resulting in a structured and
hierarchical representation. Dimensionality reduc-
tion, particularly the SAX method, is commonly used
in these approaches for its effectiveness in capturing
overall sequence information. While SAX is widely
used (Li et al., 2012) (Senin et al., 2018) (Tanaka
et al., 2005), its aggregated information may not al-
ways distinguish individual motifs. Therefore, al-
ternative representation methods have been proposed
to address SAX’s limitations. These methods have
shown effectiveness in classification tasks, but their
specific application and efficacy in motif discovery re-
quire further testing and evaluation.
In this study, we aim to complete these research
works by exploring various representation methods
and assessing their performance in the context of mo-
tifs discovery. Our objective is to examine the ef-
fectiveness of these alternative representations which
Fodil, N., Olivier, D. and Tranouez, P.
Towards Better Motif Detection: Comparative Analysis of Several Symbolic Methods.
DOI: 10.5220/0012368500003654
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2024), pages 311-319
ISBN: 978-989-758-684-2; ISSN: 2184-4313
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
311

was evaluated on tasks other than motif discovery, we
compare them to the widely used SAX representation
method. By conducting a comprehensive evaluation,
we gain insights into the suitability of different repre-
sentation approaches for motifs discovery tasks. Ad-
ditionally, we assess the value of incorporating gram-
matical inference. This is achieved by comparing mo-
tifs identification outcomes both in the absence and
presence of grammatical inference. We apply sequitur
on representations other than SAX. This results in
new methods for motifs discovery. Finally, we intro-
duce a search strategy for identifying motifs that are
of interest to the user through the learning of symbolic
representation of these interesting motifs.
2 BACKGROUND AND RELATED
WORKS
2.1 Overview of Representation
Methods
SAX. SAX (Symbolic Aggregate Approximation)
(Lonardi and Patel, 2002) is a method used to approx-
imately represent time series data by transforming it
into a sequence of symbols. It employs the Piecewise
Aggregate Approximation (PAA) technique to reduce
the dimensionality of the original time series and cre-
ate its symbolic representation. To create a SAX rep-
resentation, first, the time series data is z-normalised
and divided into equal-sized segments. Then, within
each segment, the average value of the data points is
computed, resulting in a reduced representation of the
original time series. Finally, symbols are assigned to
the Piecewise Aggregate Approximation values based
on predefined breakpoints. These breakpoints divide
the range of possible values into distinct regions based
on normal distribution. The use of PAA leads to cap-
ture general information about each segment. How-
ever, it may group segments with different behaviors
but similar average value into the same symbol.
1d-SAX. In 1d-SAX (Malinowski et al., 2013), the
linear regression of the series is calculated for each
segment rather than the mean. The regression is rep-
resented by the equation l(x) = sx + b. The segment
is then characterized by the slope s and the mean a of
its regression as follow:
s =
∑
L
i=1
(t
i
−
¯
T )V
i
∑
L
i=1
(t
i
−
¯
T )
2
, b =
¯
T − s ×
¯
V , a =
s(t
1
+t
L
) + b
2
(1)
Where, V
1
,...V
L
represent the values of the series V
over the time segment T = [t
1
,...,t
L
], and L denotes
the segment length.
¯
T and
¯
V represent the mean val-
ues of T and V . Once the pair (s,a) is calculated,
the algorithm transforms each value of the pair into
symbols based on normal distribution just like SAX.
These symbols are then combined to obtain the final
symbols on N levels.
ABBA. ABBA (Adaptive Brownian Bridge-based
symbolic Aggregation of time series) (Elsworth and
G
¨
uttel, 2020) is an adaptive symbolic representation
for time series data, where the representation length
and the number of symbols are determined adaptively.
The time series is approximated by a piecewise con-
tinuous linear function. Each linear piece is adap-
tively chosen based on a user-defined tolerance that
controls the approximation. This results is a sequence
of pairs, (len,inc), which represents the length of
each segment and its increment in value. Then, each
pair is assigned to a symbol corresponding to the
group to which it belongs. Groups are identified using
clustering techniques. fABBA (Fast Adaptive Brow-
nian Bridge-based symbolic Aggregation) (Chen and
G
¨
uttel, 2023) is an enhanced version of the ABBA
symbolic representation technique. fABBA addresses
the challenge of determining the optimal number of
clusters by improving the efficiency of the clustering
step.
2.2 Motif Discovery Using Grammar
Inference
Motif discovery methods employing grammar infer-
ence aim to apprehend motifs through the identifi-
cation of hierarchical representations within recur-
ring sequences. Two algorithms commonly used for
grammatical inference are Sequitur(Nevill-Manning
and Witten, 1997) and Re-Pair(Larsson and Moffat,
2000). According to (Senin et al., 2018), both algo-
rithms prove suitable for the discovery of recurrent
motifs. Senin’s findings indicate that the Re-Pair al-
gorithm tends to generate grammars characterized by
deeper hierarchies and more substantial variance in
between rule lengths compared to those produced by
Sequitur, which offers additional insights into the un-
derlying structure of the input data. Conversely, Se-
quitur’s grammar rules typically correspond to longer
subsequences, exhibiting higher within rule length
variance, which proves advantageous in the work-
flow of mining motifs of variable lengths. However,
it’s worth noting that Re-Pair is requiring significant
memory storage and operates in an offline manner
(Senin et al., 2018). In our study, we favor Sequitur,
taking into consideration its advantages for variable
length motif mining while acknowledging the trade-
offs associated with the specific characteristics of Re-
Pair.
ICPRAM 2024 - 13th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
312
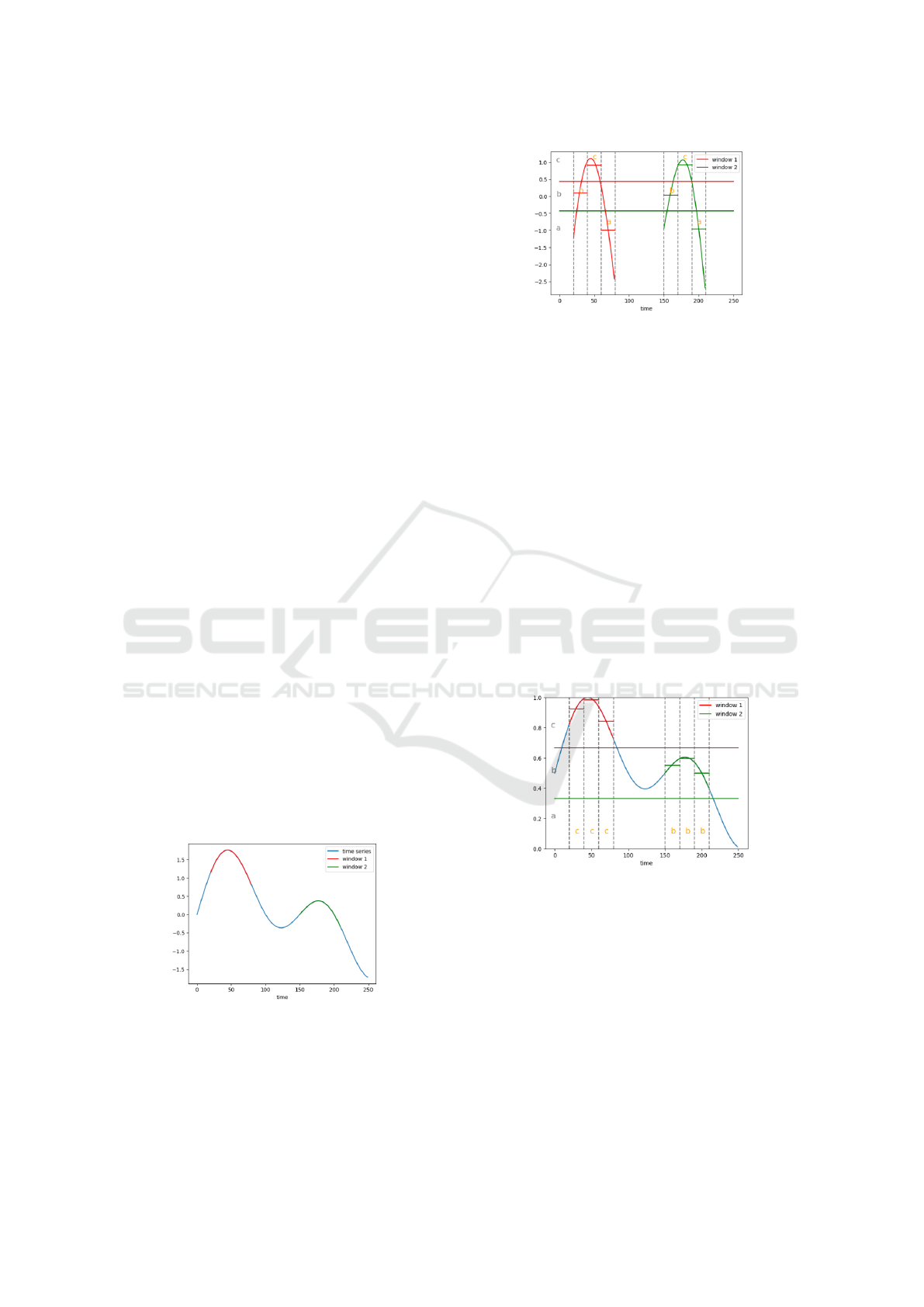
2.2.1 Motif Discovery Using Sequitur
Sequitur (Nevill-Manning and Witten, 1997) is a
text compression algorithm that infers a context-free
grammar from a sequence of discrete symbols by sub-
stituting repeated sequence of words in the given se-
quence with new rules and therefore producing a con-
cise representation of the sequence. In (Li et al.,
2012), an approach based on grammar induction us-
ing Sequitur has been proposed for the approximate
discovery of variable-length motifs. This approach
involves extracting subsequences of a specific length
from the time series using a sliding window. These
subsequences are then transformed into SAX words
which serve as atomic units representing the extracted
information (the SAX representation is discussed in
2.1). The Sequitur algorithm is employed to iden-
tify recurring subsequences of varying sizes within
the series. To complete the process, a post-processing
step is required, which involves mapping the fre-
quent rules back to the original subsequences of the
time series. (Balasubramanian et al., 2016) also used
SAX (Lonardi and Patel, 2002) and Sequitur (Nevill-
Manning and Witten, 1997) to find an hierarchy be-
tween one-dimensional sequences as a first step in the
multidimensional motif discovery process.
3 MOTIF DISCOVERY METHODS
In this section, we propose a modification of SAX
representation by window process (used in (Senin
et al., 2018)) that we call ”UniformSAX”. We also in-
troduce discovery methods with 1d-SAX and fABBA
in addition to UniformSAX.
3.1 UniformSAX
Figure 1: Non normalised time series. Green and red sub-
sequences have similar shapes but varying amplitudes.
In (Senin et al., 2018) the data are Z-normalized us-
ing a sliding window; i.e., each subsequence extracted
through the window is transformed to have a mean
equal to 0 and a standard deviation of 1. This transfor-
Figure 2: SAX representation of the two subsequences. De-
spite varied amplitudes, both represented as bca.
mation allows the focus to be on the shape of the motif
rather than their amplitude levels (figure 1, figure 2).
However, in real-life applications, motifs may have
similar shapes yet be semantically different. In such
cases, amplitude levels provide important informa-
tion for differentiating between motifs. This is why
we propose a modification of the SAX method called
UniformSAX that takes amplitude levels into account.
The data are normalized between 0 and 1 instead of z-
normalized. Note that we use min and max of all the
time series rather than min and max of the sequence
extracted by the window, then the window is divided
into segments, averaged and transformed into sym-
bols. Unlike the original SAX method, which uses
an equiprobable distribution for letter assignment, we
instead divide the interval [0, 1] into regions of equal
size. For example, for an alphabet of size 3, the re-
gions are [0,1/3],[1/3, 2/3], [2/3,1] (figure 3).
Figure 3: UniformSAX representation of the two sub-
sequences. Sub-sequences are mapped to the different
words.
3.2 Motif Discovery Using Sequitur
We picked three approaches for discovering motifs to
combine with Sequitur: UniformSAX, 1d-SAX and
fABBA. Each method begins by converting time se-
ries into symbols, proceeds to identify hierarchical
structures using Sequitur, and ultimately maps the
recognized structures to subsequences. The distinc-
tion among the methods lies in the techniques em-
ployed for representation.
Towards Better Motif Detection: Comparative Analysis of Several Symbolic Methods
313

3.2.1 Representation and Simplifying Symbols
UniformSAX Sequitur. In this representation, time
series are transformed to a sequence of symbols, as
described in section 3.1. This representation en-
ables the capture of general information about subse-
quences in addition to their amplitude levels. This al-
lows for distinguishing motifs of the same shape that
differ in amplitudes. Unlike SAX that ignores the am-
plitude aspect, enabling it to capture motifs of differ-
ent amplitudes but the same shape. UniformSAX Se-
quitur method requires three parameters: window size
(w), number of segment per sub-sequence extracted
through the sliding window (n) and the alphabet size
(a). The symbolic representation is performed using a
sliding window with a step size of 1. This means that
neighboring sequences are likely to exhibit similar-
ity, resulting in frequently recurring words formed by
symbolic representation. In order to address this issue
of trivial matches, we implement a preprocessing step
used in (Li et al., 2012) and (Senin et al., 2018). This
step involves eliminating consecutive occurrences of
identical words. In other words, we retain only the
first occurrence of each word while keeping track of
its offset. If a word reappears after the appearance of
one or more other words, we consider it once again.
1d-SAX Sequitur. We propose to enhance the
SAX Sequitur algorithm by replacing SAX with 1d-
SAX. The process involves extracting sub-sequences
through a sliding window. These sub-sequences are
then z-normalized and divided into equal-sized seg-
ments. For each segment, a linear regression is per-
formed, generating the mean and slope values. These
values are further transformed into symbols, which
are combined to create a single symbol representation
for each segment. After that, simplifying symbols is
performed as in 3.2.1. This approach requires four
parameters: Window size (w), number of segment per
sub-sequence extracted through the sliding window
(n), the alphabet size for quantifying the mean (a
m
)
and the alphabet size for quantifying the slope (a
s
).
fABBA Sequitur. By ignoring the contextual infor-
mation present in the neighboring data points, fixed-
size segmentation may miss important motifs that
span multiple segments. That why the sliding win-
dow is used in SAX Sequitur and 1d-SAX Sequitur.
fABBA uses data-adaptive segmentation through
polygonal approximation, which renders the sliding
window unnecessary. Additionally, as symbol as-
signment is performed through clustering, it becomes
more logical to apply this process to all segments of
the approximate representation rather than apply it on
the window. By considering all segments, we ensure
that the clustering process encompasses the entirety
of the data, providing a more comprehensive and rep-
resentative symbol assignment. In this method, the
time series is transformed into a symbolic representa-
tion based on the fABBA approach. This method re-
quires mainly two parameters: the tolerance (tol) that
determines how closely the polygonal chain approxi-
mation follows the original time series, and the alpha
(α) that controls how similar time series pieces need
to be in order to be represented by the same symbol.
Since segments do not overlap, there is no need for
simplifying symbols.
3.2.2 Grammar Inference
As in (Li et al., 2012) and (Senin et al., 2018), we
use Sequitur to identify recurring word sequences by
replacing them with context-free grammar rules. this
rules are considered as motifs representation. An ex-
ample of grammar generation by sequitur is presented
in table 1.
Table 1: Grammar generation with Sequitur for the se-
quence: aaa abc cbc aaa abc cbc ccc aaa abc.
Rule Word
S0 → R2 R2 ccc R1 aaa abc cbc aaa abc cbc ccc aaa abc
R1 → aaa abc aaa abc
R2 → R1 cbc aaa abc cbc
3.2.3 Indexing
Motifs or rules identified by Sequitur algorithm are
mapped to their original sub-sequences then indexed
in a dictionary with all their instances The rule num-
ber is the key, and the value is the list of its in-
stances. Each instance i is represented by a tuple
(a
i
,b
i
), where a
i
is the beginning instant of its orig-
inal sub-sequence and b
i
its end instant.
3.3 Motif Discovery Using Only
Representation Methods
To evaluate the effectiveness of alternative representa-
tions in identifying time series motifs and the impact
of using grammatical inference, we analyzed the per-
formance of representation methods independently of
Sequitur. This approach helped us understand their
ability to capture recurrent behavior in time series.
Additionally, comparing these findings with results
using Sequitur will provide insights into Sequitur’s
pros and cons. In this process, each unique word in
the three representations is considered an individual
motif, and we will index each word with all its occur-
rences, without any grouping or further processing.
ICPRAM 2024 - 13th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
314

4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Metrics and Measurements
Let E be the set of real instances of a motif, and D be
the set of detected instances. An instance r = (a,b)
represents the occurrence of the motif starting at point
a and ending at point b.
Intersection over Union (IOU). The overlapping
percentage of two instances r = (a,b) and ˆr = ( ˆa,
ˆ
b) is
defined as the ratio of the intersection to the union of
the instances. In this case, both r and ˆr are treated as
intervals, and the overlapping percentage is calculated
as follows:
p
r,ˆr
=
r ∩ ˆr
r ∪ ˆr
=
min(b,
ˆ
b) − max(a, ˆa) + 1
max(b,
ˆ
b) − min(a, ˆa) + 1
(2)
We consider that an instance ˆr, which corresponds
to the instance r in the real set, is properly detected if
p
r,ˆr
≥ γ.
Precision, Recall and f-Measure. Precision as-
sesses the relevance of the selected candidates, while
recall evaluates the algorithm success in selecting rel-
evant elements. The F-measure combines the two
measures.
Precision =
|E ∩ D|
|D|
=
|{p
r,ˆr
, r ∈ E, ˆr ∈ D, p
r,ˆr
≥ γ}|
|D|
Recall =
|E ∩ D|
|E|
=
|{p
r,ˆr
, r ∈ E, ˆr ∈ D, p
r,ˆr
≥ γ}|
|E|
F
measure
= 2 ×
Precision × Recall
Precision + Recall
Our methods generate more candidates than the
actual number of motifs implanted for a given exper-
iment. For example, as we do not impose any size
for the motif, we find subsequences of the implanted
motif, or (un)lucky appearances of repetitions in the
random noise. We therefore pick amongst the candi-
date the one that maximizes our measurement on the
implanted motifs.
4.2 Experimental Setup
In the first step of our study, we focus on fixed-length
motifs derived from devices taken from 18 different
datasets available in the UCR time series classifica-
tion archive (Anh et al., 2018). We generate our ex-
perimental datasets by planting motifs instances taken
from these UCR datasets into random signals.
Each instance of a motif corresponds to a row as-
sociated with a specific class within the UCR dataset.
We consider two types of dataset: (1) Single motif
datasets which consist of a single class of motifs. We
use 10 instances of the first motif each time. (2) Mul-
tiple motif datasets which contain several motifs. We
consider 2 motifs and use 5 instances for each motif.
We compare the proposed methods with Sax Se-
quitur (Li et al., 2012) and with a discovery method
using only Sax without Sequitur (following the same
process as in 3.3). Our goal is to assess the advan-
tages of alternative representations in the discovery of
time series motifs and the value of Sequitur in the pro-
cess. Hyperparameters of each method are optimised
on each dataset using a genetic algorithm. We aim to
maximise the ability of a method to extract motifs to
ensure a fair comparison. The objective functions are
defined as f
singleMoti f
= 1 − F
measure
(method(args))
for single motif datasets and f
multipleMoti f s
=
1
k
∑
(1 −
F
measure
(method(args),moti f )) for motif in real mo-
tifs set. For SAX Sequitur, UniformSAX Sequitur and
1d-SAX Sequitur, we vary the window size between
5 and 200. The maximum length of motif in selected
datasets is 144. The number of segments varies be-
tween 2 and 10. The alphabet size varies between 1
and 10. For fABBA Sequitur, tolerance and alpha val-
ues range from 0 to 10.
For all methods, we use an overlapping percent-
age of 75% and the F-measure for evaluating. SAX
is implemented in saxpy python package
1
. fABBA
is taken from the authors’ GitHub repository
2
. Se-
quitur uses scikit-sequitur python package
3
. 1d-sax,
UniformSAX, indexing and mapping sequences are
implemented from scratch
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
5.1 Single-Class Motif Discovery
There isn’t a best method applicable to all datasets.
Nevertheless, the SAX, UniformSAX, and 1D SAX
methods demonstrate comparable performance across
all single motif datasets. In contrast, fABBA consis-
tently lags behind the results of the other methods,
except for few datasets, particularly those where pat-
terns exhibit different shapes but share the same se-
mantics. In these specific case, shape-based meth-
ods like SAX, UniformSAX, and 1D SAX struggle to
capture the distinctive features needed to group cor-
responding subsequences into the same class. In this
situation, segmentation and clustering into a reduced
set of groups may be more effective.
1
https://github.com/seninp/saxpy
2
https://github.com/nla-group/fABBA
3
https://pypi.org/project/scikit-sequitur/
Towards Better Motif Detection: Comparative Analysis of Several Symbolic Methods
315

Table 2: Single motifs datasets evaluation using F
measure
and IoU = 0.75. In all 3 tables, bold indicates optimal performance
without Sequitur; underlined shows improvements with Sequitur (bold if surpassing all methods); dashed underlined values
indicate Sequitur-related decreases.
Dataset SAX
uniform
SAX
1d-
SAX
fABBA
SAX
Sequitur
uniform
SAX
Sequitur
1d-
SAX
Sequitur
fABBA
Sequitur
CBF 0,95 0,95 0,95 0,53 0,95 0,89 0,95 0,63
ECG200 1,00 1,00 1,00 0,67 1,00 1,00 1,00 0,75
ECG5000 0,95 0,95 0,90 1,00 0,95 0,95 0,90 0,95
ECGFiveDays 1,00 1,00 1,00 0,18 1,00 1,00 1,00 0,67
ElectricDevices 0,82 0,75 0,82 0,82 0,89 0,84 0,89 0,78
ItalyPowerDemand 0,95 1,00 1,00 0,57 1,00 0,95 0,90 0,63
MoteStrain 0,89 0,95 0,95 0,37 0,89 0,95 0,89 0,67
Plane 1,00 1,00 1,00 0,75 1,00 1,00 1,00 0,95
SonyAIBORobotS1 0,84 0,90 0,90 0,18 0,90 0,90 0,90 0,57
SonyAIBORobotS2 0,80 0,74 0,76 0,18 0,60 0,57 0,63 0,53
SyntheticControl 0,53 0,57 0,56 0,18 0,50 0,58 0,63 0,46
TwoLeadECG 1,00 1,00 1,00 0,46 1,00 1,00 1,00 0,95
TwoPatterns 0,71 0,67 0,74 0,57 0,62 0,67 0,71 0,53
BME 0,75 0,75 0,75 0,95 0,75 0,75 0,75 0,89
Chinatown 1,00 0,89 1,00 0,00 0,95 0,90 0,90 0,67
MelbournePedestrian 1,00 1,00 1,00 0,00 1,00 0,75 1,00 0,59
PowerCons 0,82 0,82 0,82 0,75 0,70 0,82 0,82 0,67
SmoothSubspace 0,71 0,64 0,67 0,71 0,47 0,67 0,50 0,71
Sequitur does not enhance the results in the dis-
covery of a single motif for SAX, 1d-SAX, and Uni-
fomSAX based discovery methods. When dealing
with a single motif where all instances have the same
size, representation-only methods are sufficient to
capture them. Sequitur introduces complexity by at-
tempting to extract hierarchical structures. In the ma-
jority of cases, Sequitur enhances the results com-
pared to fABBA alone. fABBA is used for classifi-
cation, so it is used for segmenting smaller signals
without noise. However, the optimization of fABBA
with Sequitur allows for the exploration of parameters
enabling the clustering of subsequences that Sequitur
can assemble to form motifs.
5.2 Multi-Class Motif Discovery
This section presents experiments on more complex
datasets, the datasets contain motifs in two classes.
We evaluate the ability of the algorithms to identify
and differentiate between the two motifs using the
mean F-measure. Results are shown in table 3.
As fABBA’s results were consistently inferior to
the other methods for the simple datasets, and were
worse in our preliminary tests on the multi motif
datasets, we focused our experiments on the SAX and
its derived methods.
The findings from the single motif discovery pro-
cess are generalized to multiple motifs discovery.
In other words, no single method is optimal for all
datasets; rather, the choice of a representation method
Table 3: Multiple motifs UCR datasets evaluation using F-
measure and IoU = 0.75.
Dataset SAX
Uniform
SAX
1d-
SAX
SAX
Sequitur
Uniform
SAX
Sequitur
1d-
SAX
Sequitur
CBF2 0,88 0, 90 0,88 0,88 0,88 0,88
ECG5000-2 0,94 0, 94 0,94 0,89 0,95 0,90
ECGFiveDays2 1,00 1, 00 1,00 1,00 1,00 1,00
ElectricDevices2 0,75 0,71 0,82 0,82 0,66 0,78
ItalyPowerDem2 0,57 0, 88 0,88 0,82 0,79 0,75
MoteStrain2 0,82 0, 82 0,82 0,82 0,82 0, 84
Plane2 1,00 1, 00 1,00 1,00 1,00 1,00
SonyAIBORS12 0,82 0,89 0,84 0,82 0,79 0,84
SonyAIBORS22 0,82 0,83 0,82 0,75 0,75 0,82
SyntheticControl2 0,63 0,65 0, 73 0,63 0,57 0,57
TwoLeadECG2 0,89 0,94 0, 94 0,95 1,00 0,94
TwoPatterns2 0, 78 0,71 0,78 0,66 0,68 0,67
BME2 0,79 0,83 0,88 0,82 0,79 0,88
Chinatown2 0,94 0,78 0,94 0,89 0,69 0,88
MelbourneP2 0,94 0,88 0,94 0, 95 0,82 0,88
PowerCons2 0,63 0,66 0,75 0,66 0,60 0,67
SmoothSubspace2 0,57 0,62 0, 63 0, 70 0,62 0,55
depends on the characteristics of motifs and datasets.
If motifs are of fixed length, relatively simple or
do not have hierarchical structures, representation-
only based methods, which focus on capturing mo-
tifs through symbolization, are sufficient and might
be more efficient. Sequitur’s strength lies in capturing
hierarchical structures, which may be more advanta-
geous for complex motifs.
To confirm this, we created synthetic datasets
with controlled motif characteristics and evaluate the
ICPRAM 2024 - 13th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
316

methods on these datasets. The outcomes are detailed
in Table 4. In datasets A1 to A5, motifs share a simi-
lar shape, and their distinguishing feature is their am-
plitudes. Conversely, motifs in datasets L1 to L3 ex-
hibit varying sizes and may possess either distinct or
similar shapes. We use for the evaluation the mean f-
measure with two overlap percentages: 0.75 and 0.90.
Table 4: Multiple motifs synthetic datasets evaluation using
F-measure.
Dataset SAX
Uniform
SAX
1d-
SAX
SAX
Sequitur
Uniform
SAX
Sequitur
1d-
SAX
Sequitur
A1
IOU = 0.75
0,90 1, 00 0,94 1,00 1,00 1,00
A2 1,00 1, 00 0,95 1,00 1,00 1,00
A3 0,95 1, 00 1,00 1,00 1,00 1,00
A4 1,00 1, 00 0,95 1,00 1,00 1,00
A5 0,94 1, 00 0,95 1,00 1,00 1,00
L1 0,50 0, 50 0,50 1,00 1,00 1,00
L2 1,00 1, 00 1,00 1,00 1,00 1,00
L3
0,95 0, 95 0,88 1, 00 1, 00 1, 00
A1
IOU = 0.90
0,90 1, 00 0,90 1,00 1,00 1,00
A2 0,94 1, 00 0,95 0,94 1,00 0,94
A3 0,95 1, 00 0,94 0,95 1,00 1,00
A4 0,90 1, 00 0,95 0,89 1,00 1,00
A5 0,90 1, 00 0,94 0,94 1,00 1,00
L1 0,50 0, 50 0,50 0,79 0,94 0,94
L2 0,50 0, 50 0,50 1,00 1,00 0,89
L3 0,50 0, 50 0,50 1,00 1,00 0,95
Results for datasets from A1 to A5 in table 4,
where the criterion for differentiating between motifs
is amplitude, shows that UniformSAX outperforms
the other representation methods. Sequitur improves
the results for SAX and 1dSAX, making it possible
to achieve UniformSAX results with an IOU of 0.75.
However, with an IOU=0.9, UniformSAX maintains
its performance compared with methods based on
SAX and 1d-sax. It means that the motifs detected
with UniformSAX are more precise on these datasets
where amplitudes are a key characteristic to differen-
tiate between motifs.
The results show that for variable-sized motif
datasets (L1, L2 and L3), optimizing representations-
only based methods fail to find a single window size
that captures all motifs effectively. Generally, opti-
mizing these methods results in a window size be-
tween the two sizes of motifs in the favorable case
(L2, L3 with an IoU=0.75). However, since motifs
can vary greatly in size, it may results in discover-
ing a smaller set of motifs since it fails to get a sin-
gle window size that capture all motifs. This is the
case of L1 with an IoU=0.75 and L1, L2, L3 with
an IoU=0.9 where only one motif was successfully
detected. Using Sequitur with these methods im-
proves significantly results, confirming our hypothe-
sis regarding the effectiveness of Sequitur in detecting
more complex motifs. Our variant UniformSAX com-
bined with Sequitur, obtains the best results on those
most difficult datasets (L1 to L3) in the stringent eval-
uation (IoU 0,9).
5.3 Training Architecture for
Learning-Based Motif Selection
In the same dataset, motifs may vary depending on
the application. For example, in the case of electro-
cardiograms (ECG), a motif could be interpreted in
several ways. One might consider the RR interval
4
as
the only motif, another might be the QT interval
5
, de-
pending on the specific goals of the application. Thus,
motifs vary depending on the context.
In our study, the methods we introduced gener-
ate multiple motifs candidates that may not carry sig-
nificance in the application context but align with
the concept of motifs as repeated sub-sequences.
Faced with this complexity, it becomes challenging to
choose among the detected candidate motifs the most
suitable to user expectations without prior knowledge
of what is specifically searched. For addressing this
issue, we introduced a motif detection approach that
relies on the learning of representations for desired
motifs using few examples. Suppose the goal is to
find all the occurrences of motifs M
1
,...,M
k
in an un-
known time series. A training dataset of time series
with occurrences of the motifs is built. The selected
method is optimized on the training dataset. It can be
hypothesized that this optimisation can be generalized
to other datasets containing occurrences of the same
motifs. To evaluate this hypothesis, a Test dataset
is built, with time series different from the Training
dataset, although containing occurrences of the mo-
tifs to be detected. The symbols of the motifs learned
on the Training set are searched in the Test set. Al-
though the training phase may use Sequitur, we do
not require this method during the search phase; we
simply represent the time series using the same rep-
resentation approach and optimized parameters, then
search for occurrences of these motif representations.
To assess this approach, we used the datastes L1,
L2, and L3 from Table 4 as training datasets and
created additional evaluation datasets with the same
motif class. We optimize the uniformSAX Sequitur
method to derive representations aligned with the two
desired patterns. Next, we applied the representation
method with optimal parameters to convert evalua-
tion time series into a symbolic representation. Then,
we search within this representation to identify occur-
4
The RR interval represents the duration of one com-
plete cardiac cycle
5
The QT interval represents the time it takes for ventric-
ular depolarization and repolarization
Towards Better Motif Detection: Comparative Analysis of Several Symbolic Methods
317

rences of the learned motif representations. We com-
pare identified motifs with expected motifs to evaluate
the method’s effectiveness. The evaluation results of
table 5 shows that UniformSAX Sequitur provides an
effective representation for motifs. These represen-
tations enable efficient localization of learned motifs
in another time series. This method enables real-time
learning of efficient representations for target motifs
and their search in real-time discretized series during
inference.
Table 5: Evaluation of training based approach using Uni-
formSAX Sequitur and IOU=0.75.
Training Evaluation
Dataset Motif F
measure
F
measure
L1
Motif 1 1 1
Motif 2 1 1
L2
Motif 1 1 0.75
Motif 2 1 0.89
L3
Motif 1 1 1
Motif 2 1 1
6 CONCLUSION
In our study, we assessed the 1d-SAX and fABBA
representation methods for motif discovery, compar-
ing them to SAX. We found that 1d-SAX performs
similarly to SAX, while fABBA is less effective and
harder to parameterize across multiple datasets. We
introduced UniformSAX, a method that excels in de-
tecting motifs with amplitude variations, outperform-
ing SAX and 1d-SAX in relevant datasets. We also
explored combining UniformSAX and 1d-SAX with
the Sequitur grammar inference method, finding them
viable alternatives to SAX Sequitur. Our results in-
dicate that Sequitur doesn’t add value in fixed-size
motif datasets but improves outcomes with variable-
size motifs. Lastly, we showed that motifs of inter-
est can be identified by learning representations with
UniformSAX Sequitur on limited labeled data, and
then applying these representations to detect motifs
in other time series.
REFERENCES
Anh, D. H., Eamonn, K., Kaveh, K., Michael, Y. C.-C., Yan,
Z., Shaghayegh, G., Ann, R. C., Yanping, Bing, H.,
Begum, N., Anthony, B., Abdullah, M., Gustavo, B.,
and Hexagon-ML (2018). The ucr time series classifi-
cation archive. https://www.cs.ucr.edu/
∼
eamonn/time
series data 2018/.
Balasubramanian, A., Wang, J., and Prabhakaran, B.
(2016). Discovering multidimensional motifs in
physiological signals for personalized healthcare.
IEEE journal of selected topics in signal processing,
10(5):832–841.
Chen, X. and G
¨
uttel, S. (2023). An efficient aggregation
method for the symbolic representation of temporal
data. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data, 17(1).
Chiu, B., Keogh, E., and Lonardi, S. (2003). Probabilis-
tic discovery of time series motifs. In Proceedings
of the ninth ACM SIGKDD international conference
on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pages 493–
498.
Elsworth, S. and G
¨
uttel, S. (2020). Abba: Adaptive brown-
ian bridge-based symbolic aggregation of time series.
Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 34(4):1175–
1200.
Ferreira, P. G., Azevedo, P. J., Silva, C. G., and Brito, R. M.
(2006). Mining approximate motifs in time series. In
International Conference on Discovery Science, pages
89–101. Springer.
Gao, Y. and Lin, J. (2018). Exploring variable-length time
series motifs in one hundred million length scale.
Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 32:1200–
1228.
Larsson, N. J. and Moffat, A. (2000). Off-line dictionary-
based compression. Proceedings of the IEEE,
88(11):1722–1732.
Li, Y., Lin, J., and Oates, T. (2012). Visualizing variable-
length time series motifs. In Proceedings of the 2012
SIAM international conference on data mining, pages
895–906. SIAM.
Lonardi, J. and Patel, P. (2002). Finding motifs in time se-
ries. In Proc. of the 2nd Workshop on Temporal Data
Mining, pages 53–68.
Malinowski, S., Guyet, T., Quiniou, R., and Tavenard, R.
(2013). 1d-sax: A novel symbolic representation for
time series. In Advances in Intelligent Data Analysis
XII: 12th International Symposium, IDA 2013, Lon-
don, UK, October 17-19, 2013. Proceedings 12, pages
273–284. Springer.
Mueen, A., Keogh, E., Zhu, Q., Cash, S., and Westover, B.
(2009). Exact discovery of time series motifs. In Pro-
ceedings of the 2009 SIAM international conference
on data mining, pages 473–484. SIAM.
Nevill-Manning, C. G. and Witten, I. H. (1997). Identify-
ing hierarchical structure in sequences: A linear-time
algorithm. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research,
7:67–82.
Senin, P., Lin, J., Wang, X., Oates, T., Gandhi, S., Boedi-
hardjo, A. P., Chen, C., and Frankenstein, S. (2018).
Grammarviz 3.0: Interactive discovery of variable-
length time series patterns. ACM Transactions on
Knowledge Discovery from Data (TKDD), 12(1):1–
28.
Tanaka, Y., Iwamoto, K., and Uehara, K. (2005). Dis-
covery of time-series motif from multi-dimensional
data based on mdl principle. Machine Learning,
58(2):269–300.
Yeh, C.-C. M., Zhu, Y., Ulanova, L., Begum, N., Ding,
Y., Dau, H. A., Silva, D. F., Mueen, A., and Keogh,
E. (2016). Matrix profile i: all pairs similarity joins
ICPRAM 2024 - 13th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
318

for time series: a unifying view that includes mo-
tifs, discords and shapelets. In 2016 IEEE 16th in-
ternational conference on data mining (ICDM), pages
1317–1322. Ieee.
Zhu, Y., Zimmerman, Z., Senobari, N. S., Yeh, C.-C. M.,
Funning, G., Mueen, A., Brisk, P., and Keogh, E.
(2016). Matrix profile ii: Exploiting a novel algorithm
and gpus to break the one hundred million barrier for
time series motifs and joins. In 2016 IEEE 16th in-
ternational conference on data mining (ICDM), pages
739–748. IEEE.
Towards Better Motif Detection: Comparative Analysis of Several Symbolic Methods
319
