
Gradient-Based Clean Label Backdoor Attack to Graph Neural
Networks
Ryo Meguro
1
, Hiroya Kato
2
, Shintaro Narisada
2
, Seira Hidano
2
, Kazuhide Fukushima
2
,
Takuo Suganuma
1
and Masahiro Hiji
1
1
Tohoku University, Miyagi, Japan
2
KDDI Research, Inc., Saitama, Japan
Keywords:
Graph Neural Networks, AI Security, Backdoor Attacks.
Abstract:
Graph neural networks (GNNs) can obtain useful information from graph structured data. Although its great
capability is promising, GNNs are vulnerable to backdoor attacks, which plant a marker called trigger in
victims’ models to cause them to misclassify poisoned data with triggers into a target class. In particular, a
clean label backdoor attack (CLBA) on the GNNs remains largely unexplored. Revealing characteristics of
the CLBA is vital from the perspective of defense. In this paper, we propose the first gradient based CLBA on
GNNs for graph classification tasks. Our attack consists of two important phases, the graph embedding based
pairing and the gradient based trigger injection. Our pairing makes pairs from graphs of the target class and
the others to successfully plant the backdoor in the target class area in the graph embedding space. Our trigger
injection embeds triggers in graphs with gradient-based scores, yielding effective poisoned graphs. We conduct
experiments on multiple datasets and GNN models. Our results demonstrate that our attack outperforms the
existing CLBA using fixed triggers. Our attack surpasses attack success rates of the existing CLBA by up to
50%. Furthermore, we show that our attack is difficult to detect with an existing defense.
1 INTRODUCTION
Graph structured data appear in various fields, such as
molecular structures, social networks, and web anal-
ysis. In recent years, GNNs have been researched
and utilized in fields such as security and commerce,
indicating their broad potential applications to graph
structured data. For example, research has been con-
ducted on the detection of fake news (Zhang et al.,
2020) and malware detection based on call graphs
(Feng et al., 2020). There are also many studies on
the application of GNNs in recommendation systems
(RSs), demonstrating the advantages of GNN-based
RSs over traditional methods (Qiu et al., 2020; Yang
et al., 2021; Guo et al., 2021).
However, as with other machine learning systems,
GNNs have been recognized to be vulnerable to ad-
versarial examples and poisoning attacks (Chen et al.,
2020; Z
¨
ugner et al., 2018; Kwon et al., 2019; Jiang
et al., 2022). Furthermore, studies on backdoor at-
tacks on GNNs (Zhang et al., 2021; Xi et al., 2021;
Yang et al., 2022; Xu and Picek, 2022) have been pre-
sented recently. The backdoor attacks plant a marker
called trigger in victims’ models to cause them to mis-
classify poisoned data with triggers into a target class.
In the context of graph domains, the trigger denotes
modified information such as edges or node features
in the graph. Backdoored models behaves normally
when clean data is given. This is why the backdoor
attack is highly favorable for attackers in terms of
stealthiness. Consequently, attackers may conduct the
backdoor attack on GNNs with the motive for disrupt-
ing security or gaining financial benefits. However,
effective defensive methods against backdoor attacks
have not been established in the GNN domain. From
the perspective of defense, revealing characteristics of
backdoor attacks is vital. Therefore, it is essential to
work on a study on backdoor attacks so as to ensure
robustness and security of GNNs.
There are two types of backdoor attacks, namely a
label flipping attack and a clean label backdoor attack
(CLBA). In the label flipping attack, labels of poi-
soned data injected into victim’s dataset are changed
to a target label. The CLBA does not alter labels of
poisoned data. In the GNN domain, the majority of
studies on backdoor attacks are based on label flip-
ping attacks (Zhang et al., 2021; Xi et al., 2021; Yang
et al., 2022). The potential risks of CLBAs remain
510
Meguro, R., Kato, H., Narisada, S., Hidano, S., Fukushima, K., Suganuma, T. and Hiji, M.
Gradient-Based Clean Label Backdoor Attack to Graph Neural Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0012369500003648
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2024), pages 510-521
ISBN: 978-989-758-683-5; ISSN: 2184-4356
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

largely unexplored. To our knowledge, there is only
one study (Xu and Picek, 2022) regarding CLBAs on
GNNs for graph classification tasks that utilizes fixed
subgraphs as triggers. There are two problems with
that existing CLBA (Xu and Picek, 2022). The first
problem is that the CLBA ignores the topological at-
tributes in each graph. Since ER model (Erdos, 1959)
is used to generate a trigger with a random structure,
the performance of the attack is solely dependent on
the trigger density. Thus, there are cases where the
attack does not succeed for certain datasets. The sec-
ond problem is that a fixed subgraph is utilized as the
trigger. The fixed trigger may be easily detected be-
cause the same structure always appears in all poi-
soned graphs. Therefore, assigning more adaptive
triggers to each graph is favorable for the effective
backdoor attack.
In this paper, we propose the first gradient based
CLBA on GNNs for graph classification tasks. Our
attack consists of two important phases, namely (1)
graph embedding based pairing, and (2) gradient
based trigger injection. In the graph embedding based
pairing, the attacker makes pairs from graphs of the
target class and the others on the basis of their dis-
tance in the graph embedding space. This pairing
is helpful in clarifying the direction of movement in
the graph embedding space during the trigger injec-
tion phase, enabling a more successful attack. In the
gradient based trigger injection, the attacker injects
tailored trigger edges on paired graphs chosen in the
pairing phase to create effective poisoned graphs. In
this part, gradient based edge scoring is introduced in
order to create triggers that enables the pairs to ap-
propriately approach each other in the graph embed-
ding space. This trigger injection is performed on a
graph-by-graph basis to enhance the attack effective-
ness. These phases realize topology-aware and graph-
adaptive triggers, which can address problems posed
by the existing CLBA.
Our Contributions. The main contributions of this
work are summarized as follows:
• We propose the first gradient-based CLBA on
GNNs for graph classification tasks. We intro-
duce the graph embedding based pairing and the
gradient based trigger injection to our CLBA for
creating effective poisoned graphs.
• We uniquely redefine the threat model of the
CLBA to correct the overestimation of the exist-
ing attack on GNNs.
• We conduct experiments on multiple datasets and
multiple experimental conditions, demonstrating
the effectiveness of our attack. Our attack im-
proves the attack success rate by up to over 50%
compared with the existing CLBA.
• We show that our attack is difficult to detect by an
existing defense method.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Backdoor Attacks
Backdoor attacks aim to change the model prediction
only for poisoned data that include triggers from a
true label to a desired label. These true and desired
labels are referred to as source and target labels, re-
spectively. In a backdoor attack, an attacker is in-
volved in both the training and inference phases of
a victim model. In the training phase, poisoned data
are generated by applying triggers to clean data. After
that, in order to poison victim’s model, the poisoned
data are injected into training datasets of victims in
some way. In the inference phase, the attacker injects
similar triggers to clean data with source labels which
leads to misclassification of those data.
BadNets (Gu et al., 2019) is a backdoor attack on
the image domain. In this attack, road signs are mis-
classified into the labels intended by the attacker us-
ing small image instances as triggers. Another back-
door attack on CNNs for image classification tasks
exists (Liao et al., 2018). In that backdoor attack, the
attacker generates adaptive trigger pixels, making it
more difficult for humans to visually identify the poi-
soned data. A more advanced backdoor attack that
utilizes encoders is proposed in (Li et al., 2021). That
attack is inspired by DNN-based image steganogra-
phy and designed to avoid trigger detection. As men-
tioned above, in the field of image processing, various
techniques for backdoor attacks have been studied, re-
vealing the presence of certain threats.
2.2 Backdoor Attacks on GNNs
Recently, backdoor attacks intended for GNNs have
been studied. In the graph domain, a subgraph is uti-
lized as a trigger for backdoor attacks. The poisoned
graphs are injected into the training dataset to make
a victim model associate the trigger edges or nodes
with the target labels during the model training. In
the inference phase, poisoned graphs for which at-
tackers desire to change the prediction are created by
assigning trigger edges or nodes to clean graphs with
source labels. As a result, trained models yield incor-
rect prediction for input data with triggers while mak-
ing correct predictions for clean data. For the sake
of simplicity, we refer to clean graphs with source
labels as “sources” and clean graphs with target la-
bels as “targets”. In addition, we call sources with
Gradient-Based Clean Label Backdoor Attack to Graph Neural Networks
511

triggers “poisoned sources” and targets with triggers
“poisoned targets”.
There are multiple scenarios of backdoor at-
tacks. In particular, existing backdoor attacks in the
graph domain are mainly divided into two directions,
namely a label flipping backdoor attack, and a CLBA
depending on whether attackers change labels of poi-
soned graphs. This label manipulation has a signifi-
cant impact on the difficulty of the attacks.
2.2.1 Label Flipping Backdoor Attacks
In label flipping backdoor attacks, an attacker changes
the labels of the poisoned graphs. In particular, the
attacker first generates poisoned data by embedding
trigger edges into sources. Then, their labels are
changed to target labels, and the poisoned data be-
come poisoned targets. As with general backdoor at-
tacks, such poisoned targets are injected into training
datasets to plant a hidden backdoor in victim mod-
els. In the inference phase, poisoned sources that
have similar triggers are input into victim models with
backdoors. A subgraph based backdoor attack (Zhang
et al., 2021) uses a fixed subgraph that is pregenerated
by connecting existing nodes randomly as the trig-
ger. In the above paper, experiments are conducted
on various trigger sizes, trigger densities, and other
parameters to show the effectiveness of the backdoor
attack using fixed triggers. GTA (Xi et al., 2021) is a
backdoor attack against pretrained GNN models that
optimizes both attack effectiveness and evasivenss by
bi-level optimization. That attack shows the high at-
tack performance in multiple datasets. Furthermore,
their results reveal that existing defense mechanisms
in other domains are ineffective in preventing that at-
tack. In a TRAP attack (Yang et al., 2022), graph
edges are perturbed on the basis of specific scores.
These scores are calculated using gradients of an at-
tacker’s model. The utilization of gradient informa-
tion to select modified edges is effective.
Since the original labels of poisoned targets are
the source labels in label flipping backdoor attacks,
it is relatively easy for the attacker to change decision
boundary of the victim model and to induce the model
to misclassify the poisoned sources. However, since
the labels and characteristics of data themselves are
inconsistent compared to those from legitimate tar-
gets, it is possible that poisoned targets are detected
as outliers, which is a limitation of label flipping at-
tacks.
2.2.2 Clean Label Backdoor Attack (CLBA)
To realize a more sophisticated attack, a CLBA is pro-
posed in the graph domain. In CLBAs, attackers cre-
ate poisoned targets by injecting triggers into targets.
In other words, their labels are consistent throughout
the entire attack process from beginning to end. This
is why their features tend to be almost consistent with
those of clean targets, meaning that poisoned targets
are more difficult to detect as outliers. These poisoned
targets are injected into training dataset. Then, as with
label flipping backdoor attacks, triggers are attached
to sources so as to create poisoned sources which are
input during the inference phase. Although there are
some CLBAs targeting node classification tasks (Dai
et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2023), there is currently only
one CLBA (Xu and Picek, 2022) targeting graph clas-
sification tasks. In that CLBA, a small, fixed random
graph is generated by utilizing the Erd
˝
os-R
´
enyi (ER)
model in advance (Erdos, 1959). This subgraph is
used as a common trigger among all poisoned graphs
for CLBAs.
2.3 Defense Against Backdoor Attacks
A defense method has been proposed in (Liu et al.,
2018). In this approach, a defender checks the distri-
bution of erroneously predicted results. However, this
approach has been shown to be ineffective in subse-
quent research. Neural Cleanse (Wang et al., 2019)
is a defense mechanism that has been shown to be ef-
fective in preventing backdoor attacks against DNNs.
In that method, a defender mitigates backdoor attacks
by utilizing reverse-engineered triggers.
Currently, there are a few defense mechanisms
against backdoor attacks in GNNs. For example,
there is randomized subsampling (Zhang et al., 2021)
that changes edge information of a graph to mitigate
the impact of trigger edges. However, such a de-
fense is not effective because the accuracy of the clean
model often decreases greatly or it cannot prevent at-
tacks in almost all cases (Yang et al., 2022). There
is another existing defense mechanism (Jiang and Li,
2022) against label flipping backdoor attacks. That
defense utilizes the explanation score and achieves
high detection rates of poisoned data in their experi-
ment. However, we find that that defense cannot work
well for our attack as shown in Section 5. Thus, more
effective defense methods against backdoor attacks
are still needed. To devise such effective methods,
we argue that the study of the backdoor attack is quite
important because it can reveal characteristics of poi-
soned data. Such revealed characteristics regarding
the topological structures allow us to utilize them for
defensive strategies.
ICISSP 2024 - 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
512

3 PRELIMINARIES
3.1 Graph Neural Networks (GNNs)
In this work, we consider graph classification as
the task. This type of task can be widely
utilized for various purposes such as the pre-
diction of the existence of enzymes in a pro-
tein molecule and cell lung cancer in chemicals.
Let D
train
= {(G
1
,y
1
),(G
2
,y
2
),...,(G
n
,y
n
)} denote a
training dataset. D
train
contains graphs G
i
= (A
i
,X
i
)
and their labels y
i
. A
i
∈ {0,1}
N×N
is the adjacency
matrix of the graph data that has N nodes, where
the existence of each edge is represented as 1. X
i
is
the feature matrix of nodes in G
i
. The goal of the
graph classification is to learn a model F that out-
puts a predicted label y
c
i
for a class out of classes in
C = {c
1
,c
2
,..., c
K
}. K is the number of classes. In
fact, F consists of two components, namely the graph
representation module f
GNN
and the classifier module
f
fc
, which means F = ( f
fc
◦ f
GNN
). f
GNN
is utilized so
as to learn useful information from graph structured
data. In general, f
GNN
generates node embeddings,
which are numerical vectors regarding node features.
On the other hand, f
fc
is equivalent to a fully con-
nected neural network or a traditional classifier such
as support vector machine.
As representative graph representation modules,
there are two GNN models for graph classification
tasks. The first one is Graph Convolutional Network
(GCN) (Kipf and Welling, 2016). In GCN architec-
ture, the one step of node embeddings generation is
formulated as follows:
h
(l+1)
= σ(
ˆ
D
−1/2
ˆ
A
ˆ
D
−1/2
h
(l)
W
(l)
). (1)
Here, σ is a nonlinear activation function like ReLU,
ˆ
A is the addition of an adjacency matrix A and the
identity matrix I. D is the the diagonal node degree
matrix of
ˆ
A, and W
(l)
is a weight matrix for the l-th
GNN layer. The other one is Graph Isomorphism Net-
work (GIN) (Xu et al., 2018). In GIN architecture, the
one step of node embeddings generation is formulated
as follows:
h
i
(l+1)
= MLP
(1 + ε
(l)
) · h
i
(l)
+
∑
j∈N(i)
h
j
(l)
!
. (2)
Here, MLP is multi-layer perceptrons, h
i
l
is the l-th
node embedding of node i and N(i) is the set of nodes
adjacent to node i.
In the graph classification, f
GNN
outputs a entire
graph representation h
G
i
obtained by aggregating fea-
tures of nodes in each graph. To this end, a readout
function is applied to h
l
i
. A simple summation or a
more sophisticated graph-level pooling function can
be utilized as a readout function. The resulting h
G
i
is
input to f
fc
for predicting a label of G
i
.
3.2 Threat Model
Attacker’s Goal. The attacker has two goals. The
first goal is to improve the attack effectiveness. This
goal is intended to ensure that the poisoned sources
input by the attacker during the inference phase are
misclassified to the target label y
t
. The second goal is
to improve the attack evasiveness. With this goal, the
attack is accomplished without the victim being aware
of it. To achieve these goals, the attacker plants trig-
gers in the victim’s model by poisoning their training
dataset with poisoned targets disseminated to public.
Attacker’s Capability. The attacker has his own
GNN model. We assume two attack scenarios for this
model, namely white- and gray-box scenarios. The
white- and gray-box scenarios are defined as follows:
White-Box. Attackers can access the whole informa-
tion about parameters of victim models and what
graph data are used for training dataset in this sce-
nario. This scenario is the worst-case scenario for
victims in the real world.
Gray-Box. Attackers cannot access any information
about victim models, as they know only about
what graph data are used for training. In other
words, attackers need to prepare surrogate mod-
els with different architectures and parameters to
conduct attacks. For example, if the victim model
is a GCN model, then the attacker’s model is a
GIN model, and vice versa.
Unlike existing work (Xu and Picek, 2022), we
uniquely assume that the attacker has the following
constraint on both the existing and proposed CLBAs.
Maintenance of the Clean Label Scenario. In the
CLBA, poisoned targets are injected into the train-
ing dataset of the victim model. Thus, an attacker
should select only from the targets that are correctly
classified as the target labels by the attacker’s model.
Choosing targets classified as source labels leads to
the association of source-like graphs with triggers, de-
spite the target labels being assigned to them. If such
targets mutate into poisoned targets to plant triggers
in the victim models, then the genuine CLBA is not
realized. In such a case, the success of the attack is
purely dependent on misclassification and label flip-
ping ability. In other words, the attack performance
of the existing attack is overestimated. This is why
we set up the above two scenarios both in the existing
attack and our attack to properly evaluate the CLBA
in our experiments while the attacker does not neces-
sarily need to utilize the information of models in the
existing attack.
Gradient-Based Clean Label Backdoor Attack to Graph Neural Networks
513

3.3 Problem Formulation
We formulate CLBAs that achieves the goal described
in Section 3.2 as follows:
F
θ
′
(G
g
y
s
) = y
t
s.t. θ
′
= argmin
θ
L
train
(F
θ
,D
train
∪ D
poison
),
(3)
F
θ
′
(G
y
s
) = F
θ
c
(G
y
s
), (4)
where F
θ
′
and F
θ
c
denote a backdoored model with
model parameters θ
′
and a clean one with model
parameters θ
c
, respectively. Furthermore, y
s
is the
source label. Let D
poison
denote the poisoned dataset
containing poisoned targets with y
t
. A poisoned tar-
get G
g
y
t
is created by injecting a trigger g into a clean
target G
y
t
. Similarly, a poisoned source G
g
y
s
is created
by injecting g into a clean source G
y
s
. L
train
is the loss
for training F
θ
on D
train
∪ D
poison
. Eq.(3) represents
the situation where the poisoned sources are misclas-
sified as the target labels by the backdoored model.
This equation is related to the attack effectiveness of
backdoor attacks. Moreover, Eq.(4) represents the sit-
uation where the backdoored model correctly outputs
the prediction for clean sources. This equation guar-
antees attack evasiveness.
4 PROPOSED ATTACK
4.1 Attack Overview
We propose the first gradient based CLBA on GNNs
for graph classification tasks. Our attack consists of
two important phases, namely, (1) graph embedding
based pairing and (2) gradient based trigger injec-
tion. In the first phase, the attacker forms pairs of
sources and targets on the basis of their distance in the
graph embedding space. This phase is divided into
two parts. First, the attacker selects the same num-
ber of sources as the number of targets that have been
correctly predicted by the attacker’s model. Second,
a source is paired with a target in a one-to-one cor-
respondence considering their positions in graph em-
bedding space. This pairing is helpful in clarifying
the direction of movement in the graph embedding
space during the trigger injection phase, enabling a
more successful attack. In the second phase, the at-
tacker attaches trigger edges on the graphs chosen in
the pairing phase to create poisoned sources and poi-
soned targets. In this part, gradient-based triggers are
assigned to the selected graphs, and the pairs are ap-
propriately guided to approach each other in the graph
embedding space. This optimization is performed on
a graph-by-graph basis to enhance attack effective-
ness. We provide an overview diagram of our attack
in Fig.1.
4.2 Graph Embedding Based Pairing
As shown in Subsection 4.1, this phase has two parts.
First, attackers select p sources which have smallest
prediction probability with respect to the source label
by the attacker’s model. The process of choosing a
source is described as follows:
argmin
G
y
s
∈S
F
′
(G
y
s
)
y
s
, (5)
where F
′
(G)
l
represents the prediction probability of
the attacker’s model F
′
for graph G regarding a label
l, and S is the set of sources. This data selection ap-
proach is repeated p times. We refer to these selected
p sources as S (different from S).
Attackers also choose the same number of p tar-
gets which are farthest from decision boundary. The
process of choosing such a target is described as fol-
lows:
argmax
G
y
t
∈T
F
′
(G
y
t
)
y
t
, (6)
where T is the set of targets. We refer to these p tar-
gets as T (different from T ). The reason for select-
ing data on the basis of distance from the decision
boundary is that moving sources in the direction of
paired targets is expected to cause the sources to in-
vade the target region when trigger edges are injected
into them.
Second, attackers pair sources and targets in a
one-to-one correspondence based on a greedy algo-
rithm. The greedy algorithm assigns G
y
t
∈ T that is
the closest to G
y
s
∈ S in the graph embedding space
one by one. Let h
G
y
t
and h
G
y
s
denote the graph em-
beddings of targets and sources, respectively. h
G
y
t
and
h
G
y
s
are obtained through F
′
θ
that is attacker’s model
trained on D
train
. In other words, h
G
y
t
= f
′
GNN
(G
y
t
)
and h
G
y
s
= f
′
GNN
(G
y
s
) where f
′
GNN
is a graph repre-
sentation module of the attacker’s model.
In this approach, G
y
t
is paired with G
y
s
as follows:
argmin
G
y
t
ℓ(h
G
y
s
,h
G
y
t
), (7)
where ℓ(·,·) is the loss function based on the cosine
similarity and is defined as
ℓ(h
G
y
s
,h
G
y
t
) = 1 − γ(h
G
y
s
,h
G
y
t
). (8)
Note that γ(·,·) is the cosine similarity.
ICISSP 2024 - 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
514
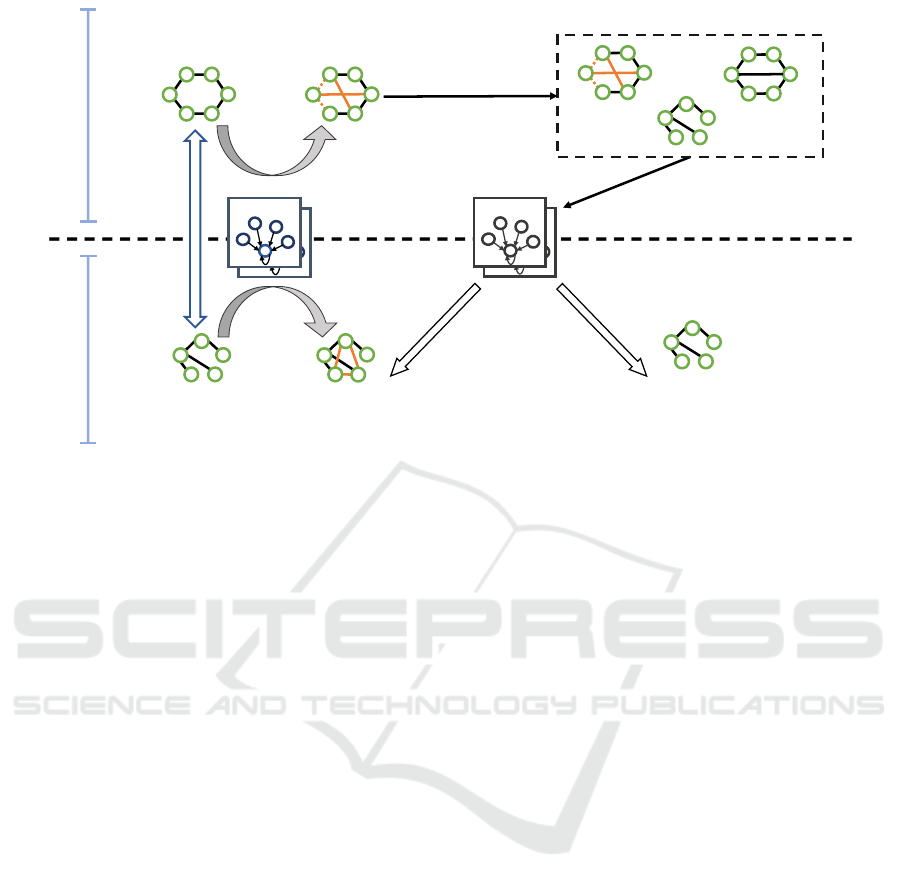
GNNLayer1
Target label:
protein
Target label:
protein
Victim GNN model
(3) Inject poisoned targets
True label:non-protein
Predicted:protein
(2) Inject
triggers
(1) Pairing
Source label:
non-protein
True label:non-protein
Predicted:non-protein
(5) Predict labels
Training dataset
(4) Train with contaminated
dataset
GNNLayer1
GNNLayer1
GNNLayer1
Attacker’s GNN model
Training phase
Inference phase
Figure 1: The proposed gradient-based CLBA.
4.3 Gradient Based Trigger Injection
Our trigger injection has two important points,
namely a gradient based edge scoring and the order
of trigger injection. In what follows, we elaborate on
them.
The gradient based edge scoring is useful in se-
lecting appropriate edges that constitute a trigger. Let
Score
i
denote the scores for edges in a graph G
i
.
Score
i
is calculated as follows:
Score
i
= (2 · A
i
− 1) · ∇
A
i
, (9)
where ∇
A
i
means the gradient of Eq.(8) with respect
to A
i
corresponding to edges in G
i
. The meaning
of this score is explained from here. First, consider
the existent edges. If the edge connecting nodes a
and b has a positive gradient value, deleting this edge
reduces the loss in Eq.(8), which brings the graph
data closer to the paired data in the graph embed-
ding space. If the gradient is negative, then we do
not delete the edge because doing so only increases
the loss. Next, we consider nonexistent edges. If the
gradient of the nonexistent edge between nodes a and
b is positive, then we do not connect them because
doing so only increases the loss. On the other hand,
if the gradient value is negative, then adding the edge
brings the graph data closer to the paired data in the
graph embedding space. In short, by inverting the in-
formation of “existent edges with positive gradients”
and “nonexistent edges with negative gradients”, the
pairs can be approached efficiently in the graph em-
bedding space. The larger the absolute values of the
gradients are, the closer to the paired data are when
these edges are changed. Therefore, to assign higher
scores to these edges, the sign is adjusted in the first
term in Eq.(9). The above score is calculated for each
value in A
i
to generate the score list. On the basis of
that score list, edge information with top m scores is
changed to attach triggers to graphs.
As for the order of trigger injection, the trig-
ger edges are first assigned to S to create poisoned
sources
ˆ
S. This is because the above order allows
the sources to move to the paired targets significantly,
which results in invading the target area in graph em-
bedding space. After that, poisoned targets
ˆ
T are cre-
ated by making T close to paired poisoned sources
in
ˆ
S. This process allows for the creation of effec-
tive poisoned targets. As a result, when the poisoned
targets are used for training the victim model, target
label area can be further expanded, causing misclas-
sification of the poisoned sources.
4.4 Algorithm
The complete attack process is presented in Algo-
rithm 1. After the initialization procedure (Line 1)
and obtaining F
′
θ
trained on D
train
(Line 2), poisoned
graphs are generated. In our attack,
ˆ
S is generated
prior to
ˆ
T . Let G
mod
and G
anch
denote the set of p
modified graphs and that of p anchor graphs, respec-
tively. Triggers are embedded in G
mod
i
∈ G
mod
so that
G
mod
i
are close to G
anch
i
∈ G
anch
. G
mod
and G
anch
are
changed depending on the type of graph that triggers
are embedded in. When
ˆ
S is generated, G
mod
and
G
anch
are S and T , respectively (Line 5). On the other
Gradient-Based Clean Label Backdoor Attack to Graph Neural Networks
515

Algorithm 1: Proposed gradient-based CLBA.
Input : S, T , F
′
θ
, and D
train
Output: Poisoned sources and targets (
ˆ
S,
ˆ
T )
1 (
ˆ
S,
ˆ
T ) ← (
/
0,
/
0)
2 Obtain F
′
θ
trained on D
train
3 while
ˆ
S =
/
0 or
ˆ
T =
/
0 do
4 if
ˆ
S =
/
0 then
5 G
mod
← S and G
anch
← T
6 else
7 G
mod
← T and G
anch
←
ˆ
S
8 P ,G
tmp
←
/
0,
/
0
9 for i = 1 to p do
10 Select G
mod
i
∈ G
mod
paired with
G
anch
i
∈ G
anch
based on Eq.(7)
11 P ← P ∪ (G
mod
i
,G
anch
i
)
12 for each pair (G
mod
i
,G
anch
i
) ∈ P do
13 ∇
A
mod
i
← ∇
A
mod
i
ℓ(h
G
mod
i
,h
G
anch
i
)
14 Score
i
← (2 · A
mod
i
− 1) · ∇
A
mod
i
15 Create
ˆ
G
mod
i
by reversing elements
with top m values of Score
i
in A
mod
i
16 G
tmp
← G
tmp
∪ {
ˆ
G
mod
i
}
17 if
ˆ
S =
/
0 then
18
ˆ
S ← G
tmp
19 else
20
ˆ
T ← G
tmp
21 return (
ˆ
S,
ˆ
T )
hand, when
ˆ
T is generated, G
mod
is T , and G
anch
is
ˆ
S
(Line 7). A set of paired graphs P is created by pair-
ing G
mod
i
with G
anch
i
on the basis of the greedy algo-
rithm (Lines 9-11). For each pair (G
mod
i
,G
anch
i
) ∈ P,
the gradient ∇
A
mod
i
of the loss function ℓ with respect
to the adjacency matrix A
mod
i
of G
mod
i
is calculated
(Lines 13). Then, Score
i
is calculated on the basis of
∇
A
mod
i
to determine the edges to reverse (Line 14). Af-
ter that, a poison graph
ˆ
G
mod
i
is created on the basis of
Score
i
(Line 15).
ˆ
G
mod
i
is stored in a temporary set
G
tmp
(Line 16). The above procedures are repeatedly
conducted for creating each of
ˆ
S and
ˆ
T . Finally,
ˆ
S
and
ˆ
T are returned.
5 ATTACK EVALUATION
In this section, we evaluate our attack effectiveness
and evasiveness. Specifically, in this experiment, we
aim to address the following questions.
1. How much does our attack effectiveness and eva-
siveness improve compared to those in the exist-
ing method?
2. To what extent does the threat model impact at-
tack performance?
3. Do existing defense methods effectively work
against our attack?
5.1 Experimental Settings
5.1.1 Datasets
We utilized four real-world datasets to evaluate our
attack effectiveness and evasiveness. The datasets
are MUTAG (Debnath et al., 1991), DHFR (Wale
et al., 2008), NCI1 (Dobson and Doig, 2003) and
PROTEINS-full (Morris et al., 2020). We now refer
to PROTEINS-full as PROTEINS. Table 1 presents
the summary of the datasets. The label of graph with
fewer instances is selected as the target label.
We use 80% of graphs for the training dataset and
the remaining 20% for the test dataset. When we di-
vide the dataset, we ensure that the ratio of labels is
maintained during the split. Both the attacker and
the victim train their models according to the above
data split scenario. The datasets are binary classifica-
tion datasets with labels 0 and 1. The labels refer to
the classification results of the molecular data in each
graph dataset.
5.1.2 Metrics
We use two metrics to evaluate our attack effective-
ness and evasiveness.
The first metric is the Attack Success Rate (ASR),
which is the proportion of misclassified samples in
the poisoned sources by the victim model and is de-
scribed as follows:
ASR =
∑
|
ˆ
S|
i=1
[F
θ
′
(
ˆ
S
i
) = y
t
]
|
ˆ
S|
.
ˆ
S is the set of poisoned sources, and F
θ
′
is the contam-
inated victim model. [A] represents 1 if proposition A
is true and 0 otherwise. Note here that the attacks are
considered successful only when a clean model cor-
rectly classifies clean data before the trigger edges are
inserted as the source label; however, the backdoored
model misclassifies poisoned data as the target label.
Although this scenario is challenging for attackers, it
is appropriate because it helps avoid overestimation
of the ASR due to coincidental misclassifications.
The second metric is the Clean Accuracy Drop
(CAD), which is the drop from clean accuracy to
ICISSP 2024 - 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
516
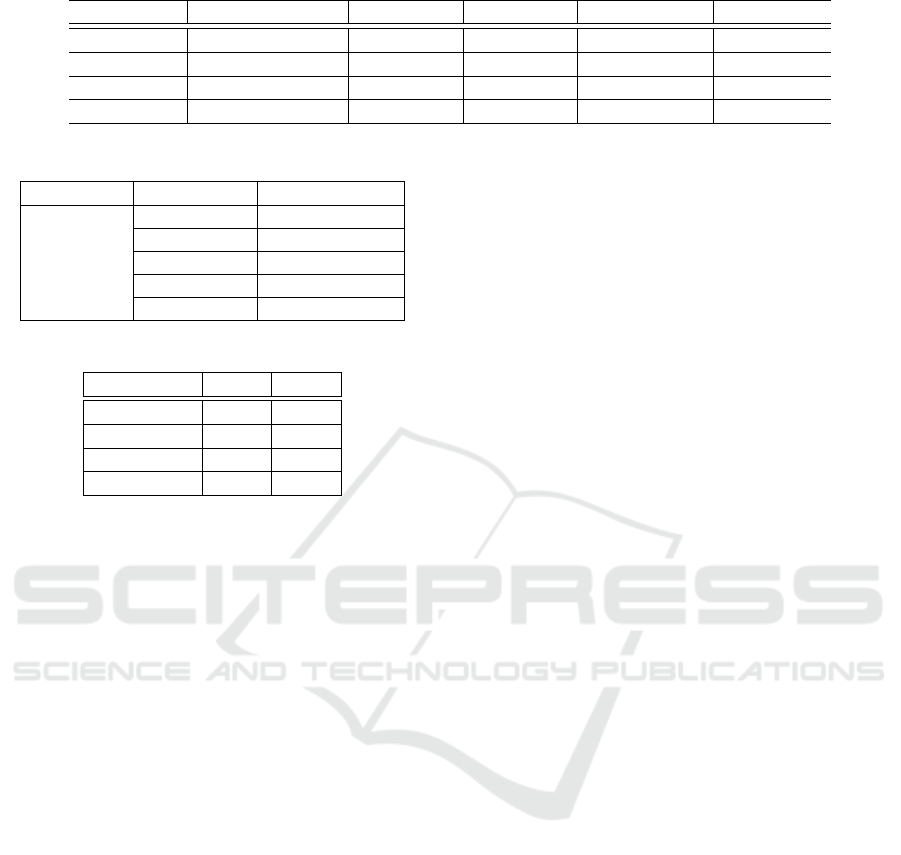
Table 1: Datasets summary.
Dataset Graphs in class Avg. nodes Avg. edges Node features Target label
NCI1 2053(0), 2057(1) 29.86 64.60 37 0
PROTEINS 663(0), 450(1) 39.05 145.63 32 1
DHFR 295(0), 461(1) 42.42 89.08 3 0
MUTAG 63(0), 125(1) 17.93 39.58 7 0
Table 2: GNN model.
GNN Parameter Settings
Architecture 2 Layers(16, 8)
Classifier Linear
GCN, GIN Aggregator Max Pooling
Optimizer Adam
Scheduler StepLR
Table 3: Clean Accuracy (%).
Dataset GCN GIN
NCI1 65.43 70.91
PROTEINS 74.43 74.61
DHFR 70.72 72.43
MUTAG 74.73 79.47
backdoored accuracy. Here, clean accuracy is the
accuracy of the model trained without poisoned tar-
gets, while backdoored accuracy is that of the model
trained with poisoned targets.
We evaluate the experimental values of the ASR
and CAD by taking the average of 10 repetitions for
each experimental condition. The existing attack is
executed in the condition that edge density for fixed
triggers is 0.8.
5.1.3 Model Settings
The composition of the GNN model is shown in the
Table 2. We use the Adam Optimizer and StepLR
scheduler in the training process. The model parame-
ters are selected on the basis of the results of the grid
search, with those that yield the maximum accuracies
being chosen. Table 3 shows the clean accuracy by
the models with the selected parameters.
5.2 Experimental Results
How Much Does our Attack Effectiveness and
Evasiveness Improve Compared to Those in the
Existing Method? Table 4 and Table 5 summarize
the experimental values for the 10% poisoning rate (or
the maximum poisoning rate) as numerical data. Our
attack outperforms the existing attack under almost
all conditions in terms of the ASR. We achieve an in-
crease of over 50% compared to the existing attack in
the gray-box scenario where the dataset is MUTAG.
This improvement is achieved due to the following
reason. In our attack, it is possible to induce mis-
classification effectively because our attack assigns
appropriate trigger edges tailored to each graph. In
contrast, the existing attack ignores the characteris-
tics of each graph and assigns a fixed trigger, which is
why its attack performance is considered unstable.
Fig.2–5 show the comparison of the ASR and the
CAD in our gray-box and white-box attacks when the
poisoning rate is varied at 1%, 3%, 5%, 7%, 9%, and
10%. Due to the limited number of graphs for creating
poisoned data, there are cases where the maximum
poisoning rate is less than 10%, and in such cases, we
stop the evaluation of metrics at the maximum data
size. Regarding the increase in the ASR with respect
to poisoning rate, our attack method shows a strong
upward trend as shown in Fig.2 and Fig.4. On the
other hand, the existing attack appears to remain rela-
tively stable. This suggests that our attack is capable
of generating effective poisoned data, which the ex-
isting attack is unable to produce. For example, when
the poisoning rate increased from 1% to 10%, the in-
crease of the ASR in the existing attack reaches at
most about 20%. In contrast, with our attack, the in-
crease can be over 40% at its maximum. Regarding
CAD as shown in Fig.3 and Fig.5, for the MUTAG
dataset, our attack shows an upward trend, indicating
suboptimal evasion performance. However, for other
datasets, even when compared to the existing attack,
CAD remains at similarly low levels of less than 5%
in most datasets. Therefore, it becomes possible to
execute our attack without being detected by the vic-
tim.
To What Extent Does the Threat Model Impact At-
tack Performance? As shown in Fig.2, there is a
case where the ASR of our gray-box attack dropped
by more than 20% compared to that of our white-
box attack when the dataset is MUTAG. However, in
other datasets, our attack maintains a high attack suc-
cess rate even in the gray-box scenario, demonstrat-
ing that our attack is feasible for attackers who do not
possess detailed information about the model. Fur-
thermore, there are cases where the gray-box scenario
shows better attack performance, but this finding can
be attributed to S whose labels are originally misclas-
Gradient-Based Clean Label Backdoor Attack to Graph Neural Networks
517
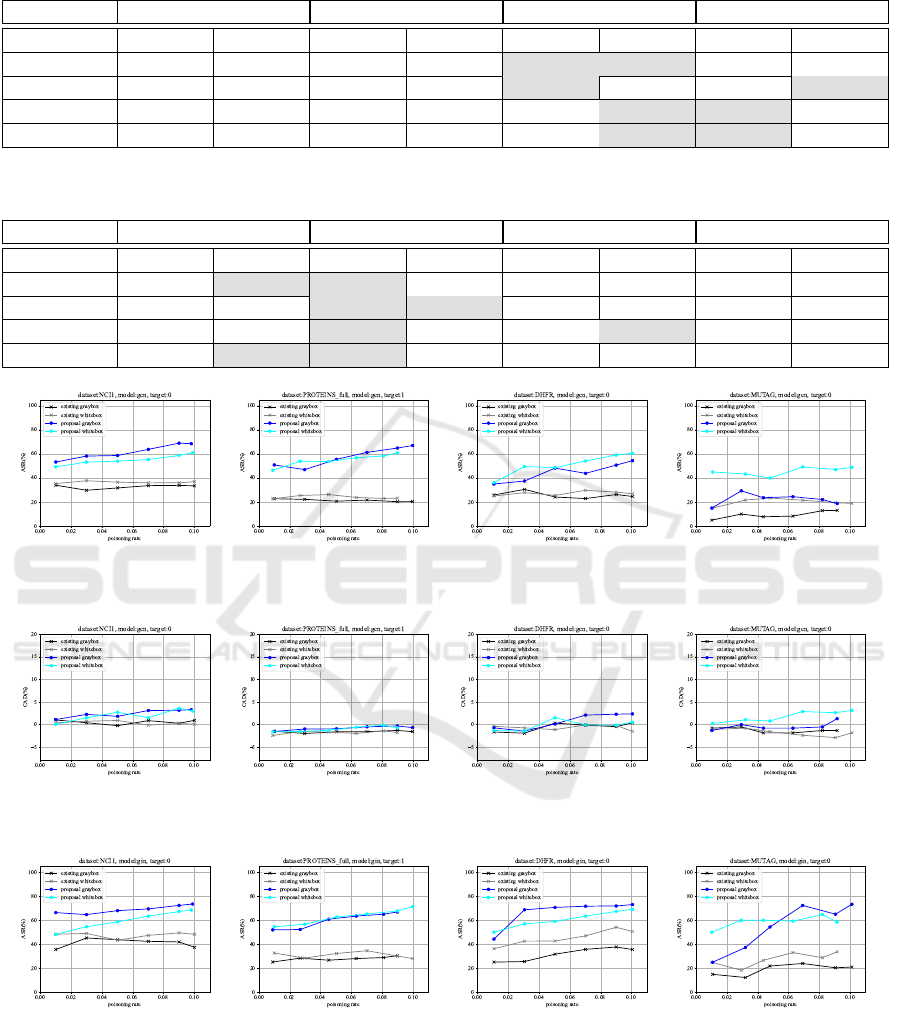
Table 4: ASR comparison of the existing attack, our whitebox and graybox attacks (poisoning rate=10%). Highest ASR cells
are grayed out.
Dataset Existing (graybox) Existing (whitebox) Proposal (graybox) Proposal (whitebox)
GCN GIN GCN GIN GCN GIN GCN GIN
NCI1 33.48 37.45 36.97 48.29 68.56 73.44 61.01 68.51
PROTEINS 20.39 30.49 23.24 28.10 67.03 66.82 60.80 71.25
DHFR 24.63 35.62 26.84 50.65 54.43 72.99 60.65 68.94
MUTAG 13.11 21.05 18.94 33.68 18.77 73.24 48.94 58.42
Table 5: CAD comparison of the existing attack, our whitebox and graybox attacks(poisoning rate=10%). Lowest CAD are
grayed out.
Dataset Existing (graybox) Existing (whitebox) Proposal (graybox) Proposal (whitebox)
GCN GIN GCN GIN GCN GIN GCN GIN
NCI1 0.93 0.75 0.09 2.00 3.31 2.83 3.00 2.91
PROTEINS -1.56 1.79 -1.74 0.98 -0.67 2.55 -0.71 3.45
DHFR 0.39 1.38 -1.51 1.57 2.36 -0.59 0.52 2.30
MUTAG -1.31 0.00 -1.84 1.57 1.31 7.89 3.15 2.89
(a) NCI1 (b) PROTEINS (c) DHFR (d) MUTAG
Figure 2: Comparison of the ASR in our attack and the existing attack (GCN).
(a) NCI1 (b) PEOTEINS (c) DHFR (d) MUTAG
Figure 3: Comparison of the CAD in our attack and the existing attack (GCN).
(a) NCI1 (b) PROTEINS (c) DHFR (d) MUTAG
Figure 4: Comparison of the ASR in our attack and the existing attack (GIN).
sified by the victim model, leading to the inability to
maintain the clean-label scenario. Therefore, it is not
always straightforward that the gray-box scenario is
superior to the white-box scenario.
Next, we explain the difference between the re-
sults reported in the existing attack’s paper (Xu and
Picek, 2022) and the results of our verification exper-
iments. In that paper (Xu and Picek, 2022), the ASR
is over 80% when datasets are NCI1 and MUTAG in
the condition that poisoning rate is 10%. However,
ICISSP 2024 - 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
518
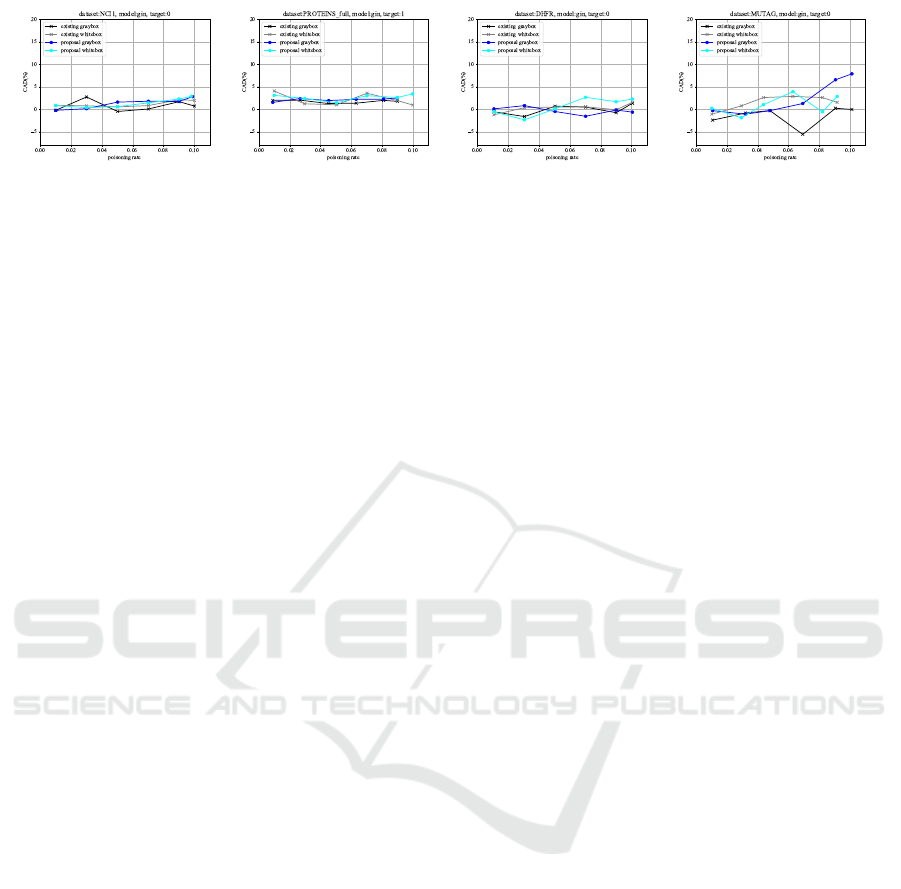
(a) NCI1 (b) PEOTEINS (c) DHFR (d) MUTAG
Figure 5: Comparison of the CAD in our attack and the existing attack (GIN).
according to our experimental results, the ASR is less
than 50% in all cases. This is because change of the
threat model enables proper evaluation of the ASR,
which corrects the overestimation. As a result, it is
revealed that the existing attack is not so successful in
practice.
Do Existing Defense Methods Effectively Work
Against our Attack? To evaluate our attack eva-
siveness, we apply an existing defense mechanism
(Jiang and Li, 2022) against label flipping backdoor
attacks. That defense utilizes explanation scores and
shows a high detection rate of poisoned data. In
this defense approach, the defender first adopts edges
that serve as explanations for the model’s predictions.
The explanations mean important edges that dictate
the prediction. Subsequently, based on explanation-
based scores, the defender detects the presence of
trigger edges in poisoned sources and removes those
edges. To be more specific, the defender calculates
an explanability score (ES) for each graph, identify-
ing graphs with high ESs as poisoned sources. The
threshold is set as the maximum value of benign data
in the test dataset, and any data with ESs exceeding
this threshold are considered malicious. The detec-
tion rate is the number of detected poisoned sources
divided by the number of all poisoned sources. Then,
the defender proceeds to guide predictions in the cor-
rect direction by removing the edges on the basis of
explanations. In this experiment, the number of re-
moved edges is equal to the trigger size of our attack.
We utilize the same dataset to evaluate our attack and
take this defensive approach under the condition that
the poisoning rate is the maximum value.
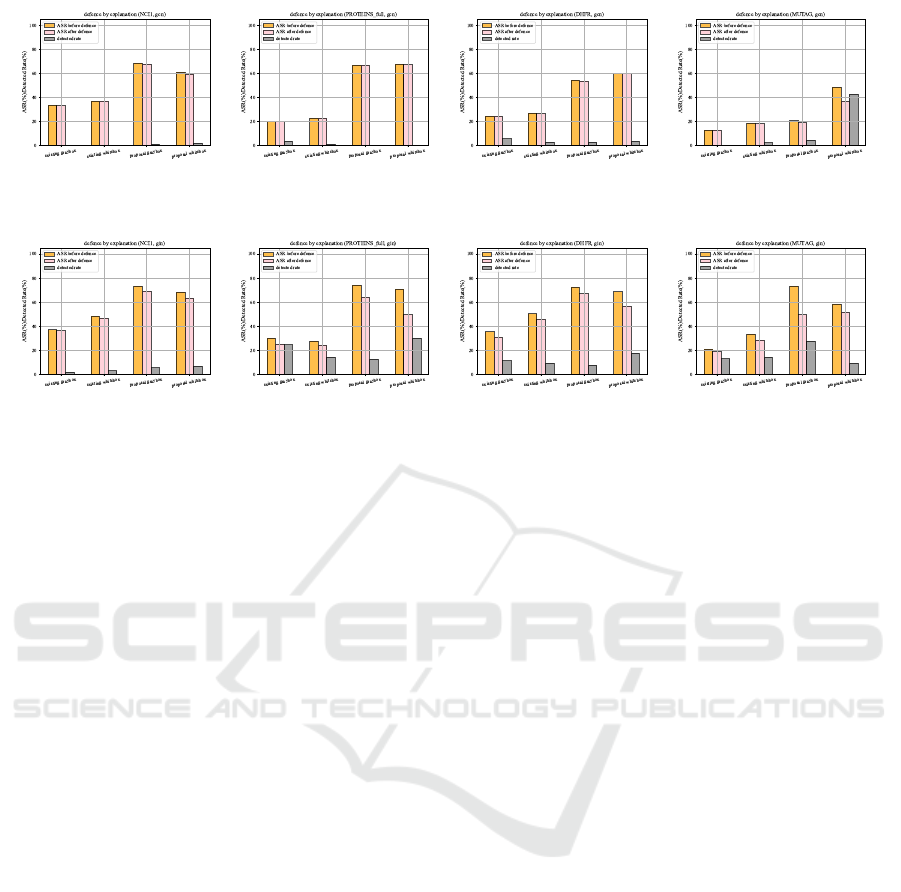
The results of defense by explanation are shown
in Fig.6 and Fig.7. The detection rate of the attack
is below 20% in most cases, indicating a high level
of attack evasiveness. There are conditions where
the partial detection rate is higher (Dataset: MUTAG,
Model: GCN, our whitebox attack). There are two
possible reasons for this. First, the average graph
size of MUTAG dataset is smaller than that of other
datasets. As a result, the trigger size decreases, and
the detection rate increases because the importance
of edges concentrated on specific edges. However,
it is important to note that in this case, the number of
edges adopted for explanation is equal to the trigger
size, and this defense is carried out under conditions
favorable to the defender. Therefore, in practice, de-
tection may be more challenging.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we propose the first gradient based
CLBA on GNNs for graph classification tasks. Our
attack introduces the graph embedding based pairing
and the gradient based trigger injection. We also re-
consider the threat model of backdoor attacks, define
a more practical threat model, and eliminate the over-
estimation of attack performance in the existing at-
tack. Under this threat model, our results demon-
strate that our attack outperforms the existing CLBA
in terms of the ASR metric and the existing CLBA is
not so successful in practice. We validate our attack
performance on multiple datasets and experimental
conditions, demonstrating the generalizability of our
attack approach. Furthermore, we confirm that the
existing defense cannot sufficiently detect our attack.
Therefore, the results clarify that devising more effec-
tive defense mechanisms against CLBAs are needed,
which stimulates further research in this area.
REFERENCES
Chen, L., Li, J., Peng, J., Xie, T., Cao, Z., Xu, K., He, X.,
Zheng, Z., and Wu, B. (2020). A survey of adversarial
learning on graphs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.05730.
Dai, E., Lin, M., Zhang, X., and Wang, S. (2023). Unnotice-
able backdoor attacks on graph neural networks. In
Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023, pages
2263–2273.
Debnath, A. K., Lopez de Compadre, R. L., Debnath, G.,
Shusterman, A. J., and Hansch, C. (1991). Structure-
activity relationship of mutagenic aromatic and het-
eroaromatic nitro compounds. correlation with molec-
ular orbital energies and hydrophobicity. Journal of
medicinal chemistry, 34(2):786–797.
Gradient-Based Clean Label Backdoor Attack to Graph Neural Networks
519
(a) NCI1 (b) PROTEINS (c) DHFR (d) MUTAG
Figure 6: Comparison of Defense results (GCN).
(a) NCI1 (b) PROTEINS (c) DHFR (d) MUTAG
Figure 7: Comparison of Defense results (GIN).
Dobson, P. D. and Doig, A. J. (2003). Distinguishing
enzyme structures from non-enzymes without align-
ments. Journal of molecular biology, 330(4):771–
783.
Erdos, P. (1959). On random graphs. Mathematicae, 6:290–
297.
Feng, P., Ma, J., Li, T., Ma, X., Xi, N., and Lu, D.
(2020). Android malware detection based on call
graph via graph neural network. In 2020 International
Conference on Networking and Network Applications
(NaNA), pages 368–374. IEEE.
Gu, T., Dolan-Gavitt, B., and Garg, S. (2019). Bad-
nets: Identifying vulnerabilities in the machine learn-
ing model supply chain.
Guo, L., Yin, H., Chen, T., Zhang, X., and Zheng, K.
(2021). Hierarchical hyperedge embedding-based
representation learning for group recommendation.
ACM Transactions on Information Systems (TOIS),
40(1):1–27.
Jiang, B. and Li, Z. (2022). Defending against backdoor at-
tack on graph nerual network by explainability. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2209.02902.
Jiang, C., He, Y., Chapman, R., and Wu, H. (2022). Cam-
ouflaged poisoning attack on graph neural networks.
In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference
on Multimedia Retrieval, pages 451–461.
Kipf, T. N. and Welling, M. (2016). Semi-supervised clas-
sification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1609.02907.
Kwon, H., Yoon, H., and Park, K.-W. (2019). Selec-
tive poisoning attack on deep neural network to in-
duce fine-grained recognition error. In 2019 IEEE
Second International Conference on Artificial Intel-
ligence and Knowledge Engineering (AIKE), pages
136–139. IEEE.
Li, Y., Li, Y., Wu, B., Li, L., He, R., and Lyu, S. (2021). In-
visible backdoor attack with sample-specific triggers.
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Con-
ference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pages 16463–
16472.
Liao, C., Zhong, H., Squicciarini, A., Zhu, S., and Miller, D.
(2018). Backdoor embedding in convolutional neural
network models via invisible perturbation.
Liu, Y., Ma, S., Aafer, Y., Lee, W.-C., Zhai, J., Wang, W.,
and Zhang, X. (2018). Trojaning attack on neural net-
works. In 25th Annual Network And Distributed Sys-
tem Security Symposium (NDSS 2018). Internet Soc.
Morris, C., Kriege, N. M., Bause, F., Kersting, K., Mutzel,
P., and Neumann, M. (2020). Tudataset: A collec-
tion of benchmark datasets for learning with graphs.
In ICML 2020 Workshop on Graph Representation
Learning and Beyond (GRL+ 2020).
Qiu, R., Huang, Z., Li, J., and Yin, H. (2020). Exploiting
cross-session information for session-based recom-
mendation with graph neural networks. ACM Trans-
actions on Information Systems (TOIS), 38(3):1–23.
Wale, N., Watson, I. A., and Karypis, G. (2008). Compar-
ison of descriptor spaces for chemical compound re-
trieval and classification. Knowledge and Information
Systems, 14:347–375.
Wang, B., Yao, Y., Shan, S., Li, H., Viswanath, B., Zheng,
H., and Zhao, B. Y. (2019). Neural cleanse: Identi-
fying and mitigating backdoor attacks in neural net-
works. In 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Pri-
vacy (SP), pages 707–723.
Xi, Z., Pang, R., Ji, S., and Wang, T. (2021). Graph back-
door. In 30th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX
Security 21), pages 1523–1540.
Xu, J. and Picek, S. (2022). Poster: Clean-label backdoor
attack on graph neural networks. In Proceedings of
the 2022 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and
Communications Security, pages 3491–3493.
Xu, K., Hu, W., Leskovec, J., and Jegelka, S. (2018). How
powerful are graph neural networks? arXiv preprint
arXiv:1810.00826.
ICISSP 2024 - 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
520

Yang, J., Ma, W., Zhang, M., Zhou, X., Liu, Y., and Ma, S.
(2021). Legalgnn: Legal information enhanced graph
neural network for recommendation. ACM Transac-
tions on Information Systems (TOIS), 40(2):1–29.
Yang, S., Doan, B. G., Montague, P., De Vel, O., Abra-
ham, T., Camtepe, S., Ranasinghe, D. C., and Kan-
here, S. S. (2022). Transferable graph backdoor at-
tack. In Proceedings of the 25th International Sympo-
sium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions and Defenses,
pages 321–332.
Yang, X., Li, G., Zhang, C., Han, M., and Yang, W. (2023).
Percba: Persistent clean-label backdoor attacks on
semi-supervised graph node classification.
Zhang, J., Dong, B., and Philip, S. Y. (2020). Fakedetector:
Effective fake news detection with deep diffusive neu-
ral network. In 2020 IEEE 36th international confer-
ence on data engineering (ICDE), pages 1826–1829.
IEEE.
Zhang, Z., Jia, J., Wang, B., and Gong, N. Z. (2021). Back-
door attacks to graph neural networks. In Proceedings
of the 26th ACM Symposium on Access Control Mod-
els and Technologies, pages 15–26.
Z
¨
ugner, D., Akbarnejad, A., and G
¨
unnemann, S. (2018).
Adversarial attacks on neural networks for graph data.
In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD interna-
tional conference on knowledge discovery & data
mining, pages 2847–2856.
Gradient-Based Clean Label Backdoor Attack to Graph Neural Networks
521
