
Physical Ergonomics Anticipation with Human Motion Prediction
Mattias Billast
1 a
, Jonas De Bruyne
2 b
, Klaas Bombeke
2 c
, Tom De Schepper
3,1 d
and Kevin Mets
4 e
1
University of Antwerp - imec, IDLab, Department of Computer Science, Sint-Pietersvliet 7, 2000 Antwerp, Belgium
2
Imec-mict-UGent, Department of Communication Sciences, Ghent, Belgium
3
AI & Data Department, Imec, Leuven, Belgium
4
University of Antwerp - imec, IDLab, Faculty of Applied Engineering, Sint-Pietersvliet 7, 2000 Antwerp, Belgium
Keywords:
Motion Prediction, Ergonomics, VR, AI.
Abstract:
Good physical ergonomics is a crucial aspect of performing repetitive tasks sustainably for a long period. We
developed a VR training environment that improves the ergonomics and experience of the user during a task.
Through human motion prediction, we can predict the posture of the user accurately up to three seconds ahead
of time. Based on this posture, a physical ergonomics score, called REBA (Hignett and McAtamney, 2000),
is computed and can warn the user ahead of time to adapt their posture. We used the lightweight STS-GCN
model (Sofianos et al., 2021) as it can infer predictions in real-time to give feedback to the users. We show in
our experiments that using multi-task learning improves human motion prediction significantly. Our method
is generally applicable for various manual tasks as almost all tasks can be simulated in a VR environment.
1 INTRODUCTION
Physical ergonomics need to be monitored for repet-
itive and/or heavy tasks to improve musculoskeletal
health (Jaffar et al., 2011) (Vandergrift et al., 2012).
To this end, long-term human motion prediction can
provide insights into ergonomics. Human motion
prediction anticipates the motions and behavior of
the subject. For many other real-time applications,
such as human-robot interactions, assemblies, opera-
tor safety, and visual surveillance, motion prediction
is a crucial improvement.
We created a solution to train users during manual
tasks to adopt an ergonomic posture by giving real-
time feedback. With human pose information, we can
predict the movement of the user before it happens.
A Virtual Reality (VR) environment can capture all
interactions from various sensors, such as the posi-
tions of the controllers and headset, eye-tracking in-
formation, and interactions with the virtual environ-
ment. And, we can provide feedback to the the user in
real-time. Currently, users develop, and test applica-
tions or products in real physical spaces, with real ob-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1080-6847
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6077-6084
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2056-1246
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2969-3133
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4812-4841
jects. We tackle motion prediction with human pose
data, captured with a depth camera, and combined
with metadata from the VR environment, i.e. indices
of begin- and endframe of user actions. The combina-
tion of the VR environment, physical ergonomics, and
safety is reported in this paper. Physical ergonomics
are analyzed based on the human pose and the goal
is to notify the user when they have or will have a
bad posture. Safety can be improved by tracking the
user and estimating intent so they can get an indica-
tion when they enter or will enter an unsafe situation.
The performance of human motion prediction is re-
ported when we use multiple modalities and different
prediction horizons.
2 RELATED WORK
Current human motion prediction models (Lyu et al.,
2022) reason over time and space. From natural lan-
guage processing, LSTM models perform well on
time-series (Hu et al., 2019; Chiu et al., 2019; Reza-
zadegan et al., 2018), but are less suited for the com-
plex spatial data of each body pose. They are a part of
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) (Martinez et al.,
2017). These RNN models work well with abun-
dant annotated data and without time constraints on
inference time, as they require updating millions of
Billast, M., De Bruyne, J., Bombeke, K., De Schepper, T. and Mets, K.
Physical Ergonomics Anticipation with Human Motion Prediction.
DOI: 10.5220/0012392500003660
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 19th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2024) - Volume 4: VISAPP, pages
539-548
ISBN: 978-989-758-679-8; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
539

parameters. Similar to RNN models, Transformer
models (Mart
´
ınez-Gonz
´
alez et al., 2021; Guan et al.,
2023) work well on time series but are also difficult
to train with limited data due to the size of the mod-
els. More recently latent diffusion models (Barquero
et al., 2023) have shown potential in generative tasks
such as image and text generation. Because of the
stochastic nature of long-term human motion predic-
tion, it also works well on motion prediction. It can
be used as a motion prediction model where priors are
defined to start the generation process, but also opens
possibilities for motion generation of a specific task.
We opted for a Graph Convolutional Network (GCN)
(Sofianos et al., 2021; Cui et al., 2020) as it can reason
over time and space efficiently, as input. GCN models
report low inference time with close to state-of-the-art
performance. The nature of Graph reasoning fits with
the data structure of human poses. The adjacency ma-
trices can be fixed to match the joint-bone connections
but can also be trainable parameters which in turn can
give feedback about the most important connections
for certain tasks. All previous works use a motion
prediction horizon between 80-1000ms. All datasets
are benchmarked on this interval of horizons as longer
horizons become difficult to predict because of unpre-
dictable and stochastic human behavior. Prediction
horizons above 1000ms are considered long-term and
are notoriously difficult to tackle. In our work, we
will push the boundaries of the prediction horizon to
anticipate motion in an assembly setting to improve
safety and ergonomics.
In (Billast et al., 2023), they show that using mul-
tiple modalities, such as actions or objects, improves
the results of motion prediction. To this end, we
highlight a few action recognition/prediction models
(Song et al., 2021) which can be helpful for our work.
Similar to motion prediction, for action prediction
there are GCN (Kilis et al., 2022), Transformer (Guan
et al., 2023), and LSTM (Rao et al., 2021) models
available.
To give feedback to the user about their physi-
cal ergonomics, the REBA (Rapid Entire Body As-
sessment) score is often used to assess postural
risk (Micheletti Cremasco et al., 2019; Hignett and
McAtamney, 2000). It is a metric between one and
twelve based on the human pose. First, it calculates
the ergonomics score for each body part, e.g. wrists,
trunk, neck, arms, and legs, by analyzing the angles
between joints. Secondly, it combines these separate
scores in a table to give a final REBA score. A score
up to three has low risks and requires no action, a
REBA score between four and seven is a medium risk,
a score between 8 and 9 is a high risk, and from 10
onward it is a very high risk.
The advantage of working in a VR/AR environ-
ment is that we can give feedback to the user in the
environment in the form of a sound or visual. This can
be advantageous for multiple applications, i.e. robot
interaction with path prediction (Lee et al., 2022),
medical training in VR (Xie et al., 2021), and assem-
bly tasks.
3 SETUP AND DATA
COLLECTION
The main focus of our applications is that users can
safely perform various tasks with a good posture. To
achieve this goal, we need models trained on qualita-
tive data, specific to the task. We captured data in a
VR setup (Joundi et al., 2022) to test our methods.
The advantage is that we can collect annotated data
directly and we have control of the environment to
create any task.
The setup consists of a VR room where the user
with a VR headset and hand controllers tries to solve
a plumbing task/puzzle on the virtual wall. Figure 1
shows the virtual room. Each user needs to solve 4
puzzles, 2 easy puzzles where the user matches the
numbers on the tiles, and two difficult puzzles that
are nearly impossible to solve. They get 15 minutes
to solve each puzzle, which creates time pressure for
the task at hand. They can ask for a hint at each
given moment but this will reduce their time by 30
seconds. The benefit of a hint button is that it gen-
erates extra metadata when the user is struggling to
solve the problem. While the user performs the task,
they are recorded from a physical RGBD camera, i.e.
the Kinect 2.0. This camera can provide 3D pose esti-
mations in real-time. The VR headset records an ego-
centric view in the virtual room together with eye mo-
tion recordings of the user. The positions/rotations of
the headset and controllers are also logged, together
with metadata of the experiment, i.e. time, time to
solve, age, gender, height, puzzle solution, positions
of sensors, gaze information, and actions with start
and end frame. We defined six different actions that
the subjects need to perform during the experiment.
• NA
• Grab Piece
• Move Piece
• Place Piece
• Searching
• Interacting with Tablet
These actions are automatically annotated based on
the timestamps of the controllers’ inputs.
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
540

(a) (b)
Figure 1: Example images showing what the virtual environment looks like and more specifically the plumbing task.
Figure 2: MPJPE on H36M dataset.
4 DATASET
The human pose data consists of 25 joints with XYZ
coordinates in each timeframe. Before running the
absolute positions through a model, the data is nor-
malized between -1 and 1 in the three dimensions.
Additionally, each frame has an action ID indicating
which one of the six actions the user is performing
based on the interactions of the controller with the en-
vironment.
Before we started data collection, we tested the
STS-GCN model on different dataset sizes to have
an initial idea of what the minimum data requirement
is. Table 2 shows the results of this test. We noticed
that the performance measured in Mean Per Joint Po-
sitional Error (MPJPE) does not increase much with
at least three hours of training data. In the first stage,
we collected all the data, which are the 3D human
poses and the generated metadata of the VR environ-
ment, from 12 subjects. The data was split into train-
ing, validation, and test data based on the subjects. 10
recordings of different subjects for training, one for
validation, and one for testing. This resulted in a little
over 8 hours of data at 25 frames per second. Each
subject solved 2 easy and 2 difficult puzzles they had
not seen before. There were never two easy or two
hard puzzles in a row. In the second stage, we pro-
vided real-time feedback to the user about their phys-
ical ergonomics. The goal is to prevent/correct bad
posture as training in a VR environment. We exper-
imented with different horizons of motion prediction
to give an anticipation signal to the user when needed.
The data captured in the first stage can be used to
test the accuracy of the predicted human poses and
their respective REBA scores. The data captured in
the second stage is different as the subjects get feed-
back in the form of a sound on their physical er-
gonomics based on the motion prediction. This means
that subjects corrected their posture and stopped their
natural motion, which means it is difficult to test the
accuracy of motion prediction on data of the second
stage as the nature of the data is inherently different.
All quantitative results are from the first stage.
We did test our models only on VR tasks as the
goal of this application is to guide and train users in
this VR setup with the idea that these users then can
perform these real-life comparable tasks with good
posture. The VR environment can emulate almost any
real-life tasks which makes our method generally ap-
plicable. In a later stage, the users can be monitored
and given feedback based on their REBA scores for
each action.
4.1 Equipment
To capture all the data, the following sensors are used,
i.e., HTC VIVE PRO EYE with controllers and base
stations, and Kinect 2.0 for Windows which captures
RGB and Depth information (RGBD).
5 METHOD
The main goal of this application is ergonomics. On
the one hand, there are ergonomic metrics based
on poses (REBA scores). On the other hand,
there are cognitive ergonomics based on cognitive
Physical Ergonomics Anticipation with Human Motion Prediction
541

loads/hesitations which are measured with gaze en-
tropy (De Bruyne et al., 2023). We focus on pose-
based ergonomics. If we can accurately predict the
user’s joint trajectories ahead of time, based on our
action- and motion prediction models, we can prevent
non-ergonomic actions.
5.1 Problem Formulation
Motion prediction estimates the 3D coordinates of V
joints for K frames given the previous T frames with
V joints’ coordinates as input. The goal is to min-
imize the MPJPE of the estimated joint coordinates
and their ground truths. The following equation gives
the MPJPE:
MPJPE =
1
V K
K
∑
k=1
V
∑
v=1
∥ ˆx
vk
− x
vk
∥
2
(1)
where ˆx
vk
and x
vk
are respectively the predicted coor-
dinates and the ground truth coordinates of joint v at
time k.
5.2 STS-GCN
For all the experiments, the STS-GCN model (Sofi-
anos et al., 2021) is used. It consists of Spatio-
Temporal Graph Convolutional layers (STGCN) fol-
lowed by Temporal convolutional layers (TCN), see
Figure 3. The STGCN layers allow full space-space
and time-time connectivity but limit space-time con-
nectivity by replacing a full adjacency matrix with the
multiplication of space and time adjacency matrices.
The obtained feature embedding of the graph layers is
decoded by four TCN layers which produce the fore-
casted human pose trajectories.
The motion trajectories in a typical GCN model
are encoded into a graph structure with VT nodes for
all body joints at each observed frame in time. The
edges of the graph are defined by the adjacency matrix
A
st
∈ R
V T ×V T
in the spatial and temporal dimensions.
The information is propagated through the network
with the following equation:
H
(l+1)
= σ(A
st−(l)
H
(l)
W
(l)
) (2)
where H
(l)
∈ R
C
(l)
×V T
is the input to GCN layer l with
C
(l)
the size of the hidden dimension which is 3 for the
first layer, W
(l)
∈ R
C
(l)
×C
(l+1)
are the trainable graph
convolutional weights of layer l, σ the activation func-
tion and A
st−(l)
is the adjacency matrix at layer l.
The STS-GCN model alters the GCN model by
replacing the adjacency matrix with the multiplication
of T distinct spatial and V distinct temporal adjacency
matrices.
H
(l+1)
= σ(A
s−(l)
A
t−(l)
H
(l)
W
(l)
) (3)
where T different A
s−(l)
∈ R
V ×V
describe the joint-
joint relations for each of T timesteps and V differ-
ent A
t−(l)
∈ R
T ×T
describe the time-time relations for
each of V joints. This version limits the space-time
connections and reports good performance (Sofianos
et al., 2021). This matrix multiplication is practically
defined as two einstein summations.
A
t−(l)
vtq
X
nctv
= X
t
ncqv
(4)
A
s−(l)
tvw
X
t
nctv
= X
st
nctw
(5)
It lowers the number of parameters needed which
is an advantage for real-time applications as it de-
creases inference speed. The trainable adjacency ma-
trices with full joint-joint and time-time connections
have attention properties as some nodes/timeframes
will be more important for the predicted motion.
Signed and directed graphs contain richer information
to represent a larger variation of embeddings. In other
words, the adjacency matrix can be asymmetrical with
positive and negative weights. These negative weights
have opposite semantic meaning, so a node can be af-
fected by another node in two opposite ways which
create greater variation.
5.3 STS-GCN-A
The STS-GCN model is adapted for motion predic-
tion, in (Billast et al., 2023), they argue that using
action labels as extra information improves motion
prediction. To this end, we embed the actions in the
features by changing the problem to a multi-task set-
ting, i.e. human motion prediction and action predic-
tion. More specifically, an action prediction is made
for each K frames based on the T input frames. Thus,
in addition to the STS-GCN model, there is also an
added block of Attention Feature Fusion (AFF) (Qin
et al., 2020). AFF combines features of multiple
modalities by fusing them together while focusing on
the most relevant parts. In this case, spatial and tem-
poral features from the STGCN layers are combined
with temporal features from the TCN layers. The
fused features, which are designed for motion predic-
tion, give a basis for well-reasoned action prediction.
Through backpropagation, information about the ac-
tions implicitly shapes the features of the STGCN and
TCN layers to improve motion prediction. After the
AFF module, a Fully Connected Layer (FCN) creates
a prediction vector. The loss function for the frame-
wise action prediction is a cross-entropy loss with 6
classes, as mentioned in Sectioned 3. The total loss
function is:
Loss
stsgcna
= MPJPE(Prediction, GT ) − θ
∑
K
c=1
∑
6
c=1
ylog(p)
(6)
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
542

Figure 3: Motion prediction and action prediction model
with attention feature fusion (AFF) where the backbone is a
series of STGCN layers, the motion branch consists of TCN
layers, and the action branch combines spatial and temporal
features with an AFF block.
with y the action of the ground truth frames, p the
predicted action, and θ a hyperparameter to optimize.
The full STS-GCN-Action (STS-GCN-A) model is
shown in Figure 3.
6 IMPLEMENTATION DETAILS
All models use 4 TCN layers, and 4 STGCN layers.
During training, a range of learning rates was tested
and the range of 2 × 10
−3
− 8 × 10
−3
gave the best
results. The batch size is 256 for all experiments.
To update the weights, an Adam optimizer is used
with β
1
= 0.9, β
2
= −.999, and weight decay pa-
rameter λ = 1 × 10
−2
. The numbers of channels for
the STGCN layers are respectively 3, 64, 32, and 64,
and the number of channels for all four TCN layers is
equal to the output time frame. All models are trained
for 50 epochs with a learning rate scheduler which
lowers the learning rate by a factor γ = 0.1 at epochs
10, 20, 30, and 40. The sampling of action classes is
balanced based on the number of occurrences in the
dataset.
6.1 Hyperparameter Tuning
The hyperparameters for this model are the learning
rate of the model, β
1
and β
2
of the Adam optimizer,
the number of epochs, and the θ parameter which is
the weight given to the action loss in comparison to
the motion loss. We tested the learning rate for a range
of 2 × 10
−2
− 2 × 10
−5
with each model trained with
a learning rate factor ten smaller than the previously
trained model. Afterward, an interval around the best
learning rate is chosen to further improve. We chose
β
1
and β
2
as the default values as it did not change
the results after minimal tweaking, and these values
are proven to work well in various tasks (Guo et al.,
2023). We varied the number of epochs from 25 to
200, after 50 epochs the model achieved their best
performance, as it starts to overfit from that point. The
Figure 4: Problem formulation of human motion prediction.
θ parameter is finetuned within a range of 0.5 to 1000.
The best motion results were acquired with θ = 10.
By increasing θ, the action prediction improves but
this was not the main focus of our research.
7 EXPERIMENTS
Motion and Action Prediction. We first tested var-
ious scenarios and models, and measured their per-
formance in terms of MPJPE and action accuracy. In
Table 1, the results are shown for the long-term mo-
tion prediction with a horizon varying from 1 to 4
seconds. The results show that the MPJPE increases
with the increasing horizon. This was expected, as hu-
man behavior gets more unpredictable and stochastic
for longer horizons, which makes it more difficult for
longer horizons to be accurate. Similar to the sec-
ondary task, the longer horizons make it more dif-
ficult to accurately predict the sequence of actions.
The models trained on longer horizons also compro-
mise their first-second performance to spread the error
more equally throughout the prediction span.
Table 2 shows the results of the STS-GCN model
without the action prediction. We tested this model
also with similar input lengths T as the STS-GCN-A
model but it performed best with T=10. We conclude
that it was not able to leverage the input information
as effectively as the STS-GCN-A model with the ac-
tion label information. If we compare the MPJPE
with Table 1, we conclude that the results improve
when action prediction is added to the task as it im-
plicitly incorporates information about the actions in
the features through backpropagation. As mentioned
in Section 5.2, this aligns with our hypothesis.
Table 3 shows the results of the STS-GCN-A
model trained on different training sample lengths and
tested on the same horizon of 4 seconds. We accom-
plish equal horizons with the different models by test-
ing the models with shorter clip lengths autoregres-
sively. This means using the predicted output as input
until the required horizon is reached. Testing autore-
gressively has the disadvantage that it increases infer-
ence times with decreasing clip length. From Table
3, we conclude that shorter clip lengths have a pos-
itive effect on the overall performance at the cost of
increased inference time.
Figures 5, 6, and 7 show qualitative examples of
motion prediction with the STS-GCN-A model com-
pared with the ground truth of the actual future mo-
Physical Ergonomics Anticipation with Human Motion Prediction
543
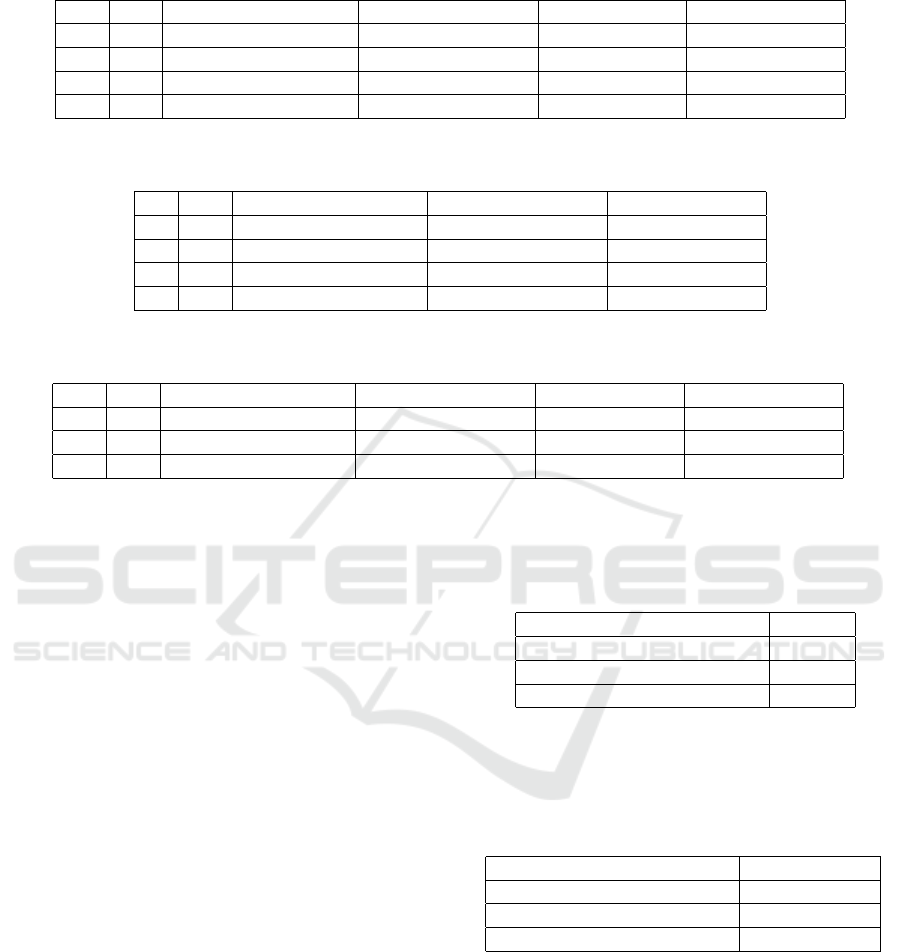
Table 1: MPJPE in mm, action prediction accuracies, and mRE for different output horizons from 1 (K=25 frames) to 4
(K=100 frames) seconds and corresponding input length T with the STS-GCN-A model.
T K MPJPE (full horizon) MPJPE first second action accuracy mRE
25 25 53.0920 53.0920 0.5735 0.3038 ± 0.2929
50 50 101.4193 65.6391 0.4926 0.4518 ± 0.3670
75 75 134.1750 70.5099 0.4912 0.4551 ± 0.3743
100 100 161.4547 81.6772 0.4166 0.4500 ± 0.3784
Table 2: MPJPE in mm for different output horizons from 1 (K=25 frames) to 4 (K=100 frames) seconds and corresponding
input length T with the STS-GCN model.
T K MPJPE (full horizon) MPJPE first second mRE
10 25 58.2540 58.2540 0.3330 ± 0.4125
10 50 112.3907 68.9235 0.4649 ± 0.5571
10 75 158.1349 77.3520 0.3330 ± 0.4125
10 100 184.4680 81.3914 0.3330 ± 0.4125
Table 3: MPJPE in mm, action prediction accuracies, and mRE for a 4 second (K=100 frames) horizon with (autoregressive)
STS-GCN-A models trained on different lengths T of training samples.
T K MPJPE (full horizon) MPJPE first second action accuracy mRE
25 100 144.5740 53.0920 0.5120 0.4185 ± 0.3761
50 100 153.3172 65.6391 0.4535 0.4922 ± 0.3910
100 100 161.4547 81.6772 0.4166 0.4500 ± 0.3784
tion. These figures also show the REBA score for
each frame. The STS-GCN-A model can closely
follow the actual motion with the correct predicted
REBA score.
REBA Analysis. Table 1 shows that the mean REBA
Error (mRE) is significantly better for short prediction
horizons but does not drop off further.
To gain more insight into the REBA scores, Fig-
ure 8 shows the distribution of REBA scores on the
ground truth poses directly from the Kinect sensor.
It can be seen that over 90% of the poses are er-
gonomically safe with REBA scores between 4 and
7. Only a few percentages of poses where our appli-
cation should give feedback to the user because of a
high-risk posture (REBA ≥ 8).
If we look at the REBA scores for higher values
which is also the main goal of the application to an-
ticipate high-risk postures, then we get the following
results, shown in Tables 4 and 5. This tells us that
the model is better at correctly predicting high REBA
scores when the Ground Truth (GT) poses also have
high (⩾ 7) REBA scores. The other way around the
performance drops as high predicted REBA scores
less often correspond to high GT REBA scores. This
means that the input poses cause a predicted pose one
second later to deviate towards high REBA scores
more often than necessary. This could mean that the
user corrected their posture within the second without
feedback or the model is biased towards higher REBA
scores.
Table 4: Percentages of the dataset where the absolute dif-
ference between the REBA scores of the Ground Truth (GT)
and the corresponding Prediction is smaller or equal to the
indicated number. The dataset consists of all samples where
the REBA score, calculated on the GT frames, is ⩾ 7.
|REBA(GT) − REBA(Pred)| GT ⩾ 7
0 56%
⩽1 84%
⩽2 99%
Table 5: Percentages of the dataset where the absolute dif-
ference between the REBA scores of the Ground Truth (GT)
and the corresponding Prediction is smaller or equal to the
indicated number. The dataset consists of all samples where
the REBA score, calculated on the Prediction frames, is ⩾
7.
|REBA(GT) − REBA(Pred)| Prediction ⩾ 7
0 53%
⩽1 54%
⩽2 99%
Ergonomic Feedback. In the second stage, we gave
feedback to the users by playing a sound when a
certain REBA threshold was reached. We chose a
threshold by making sure all users get feedback at
least once and minimizing the amount of feedback to
not overload the users with continuous sound nudges.
We chose a threshold REBA score of 8, which cor-
responds to a high-risk score. Only using sound is
potentially too vague to be helpful. We observed
users using the application and questioned them af-
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
544
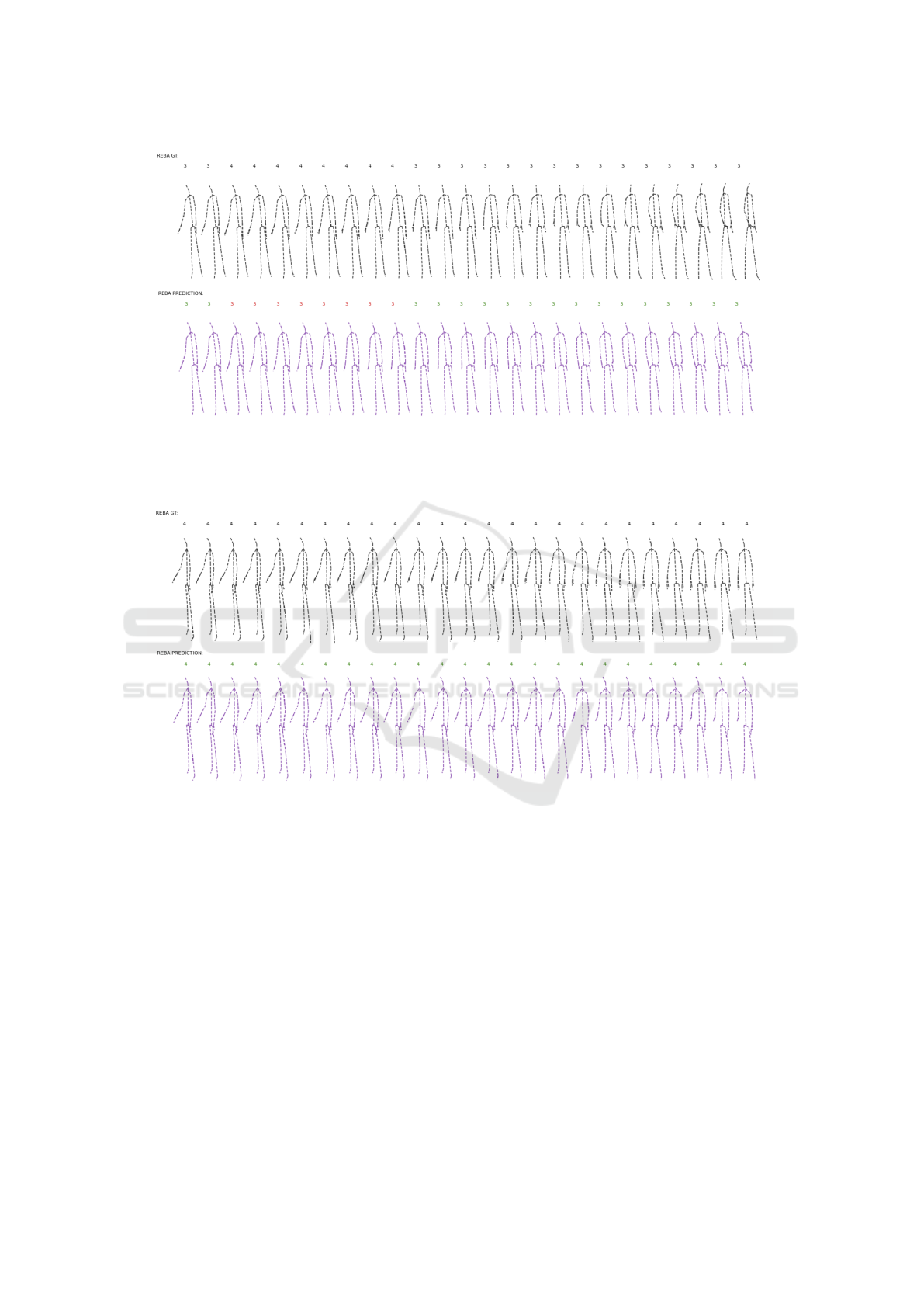

Figure 5: Qualitative example of human pose prediction of the next 25 frames with the STS-GCN-A model. The action
is ”Move Piece”, the top row shows the ground truth with the respective REBA score above the pose, and the bottom row
shows the predicted motion with their respective REBA scores. The predicted REBA scores are highlighted in green or red
depending on whether they correspond with the ground truth values or not.
Figure 6: Qualitative example of human pose prediction of the next 25 frames with the STS-GCN-A model. The action is
”Searching”, the top row shows the ground truth with the respective REBA score above the pose, and the bottom row shows
the predicted motion with their respective REBA scores. The predicted REBA scores are highlighted in green or red depending
on whether they correspond with the ground truth values or not.
terwards. Users continued the assembly without any
adaptations to their posture as they had no idea how
to correct it. To this end, we should look at ways to
give meaningful feedback to the user, i.e. a virtual an-
imation of their posture indicating which part of their
body posture they should adapt to be more ergonomic
and how they can be more ergonomic. The advan-
tage of VR is that the possibilities to give feedback
are endless, and should not be a limiting factor in the
training process.
Real-Time Performance. We ran the application in
real-time. This requires fast computations on the in-
coming data streams. We report an inference time of
0.004 seconds for the STS-GCN-A model with a clip
length of 25 frames on a Tesla V100-SXM3-32GB
GPU.
8 DISCUSSION AND FUTURE
WORK
Human motion prediction is a part of the analytics
of the application, which trains users in specific sce-
narios in VR. The motion prediction gives useful in-
sights about the user’s physical ergonomics ahead of
time, but we need to be careful with the conclusions.
We noticed that a one-second horizon is too short for
Physical Ergonomics Anticipation with Human Motion Prediction
545
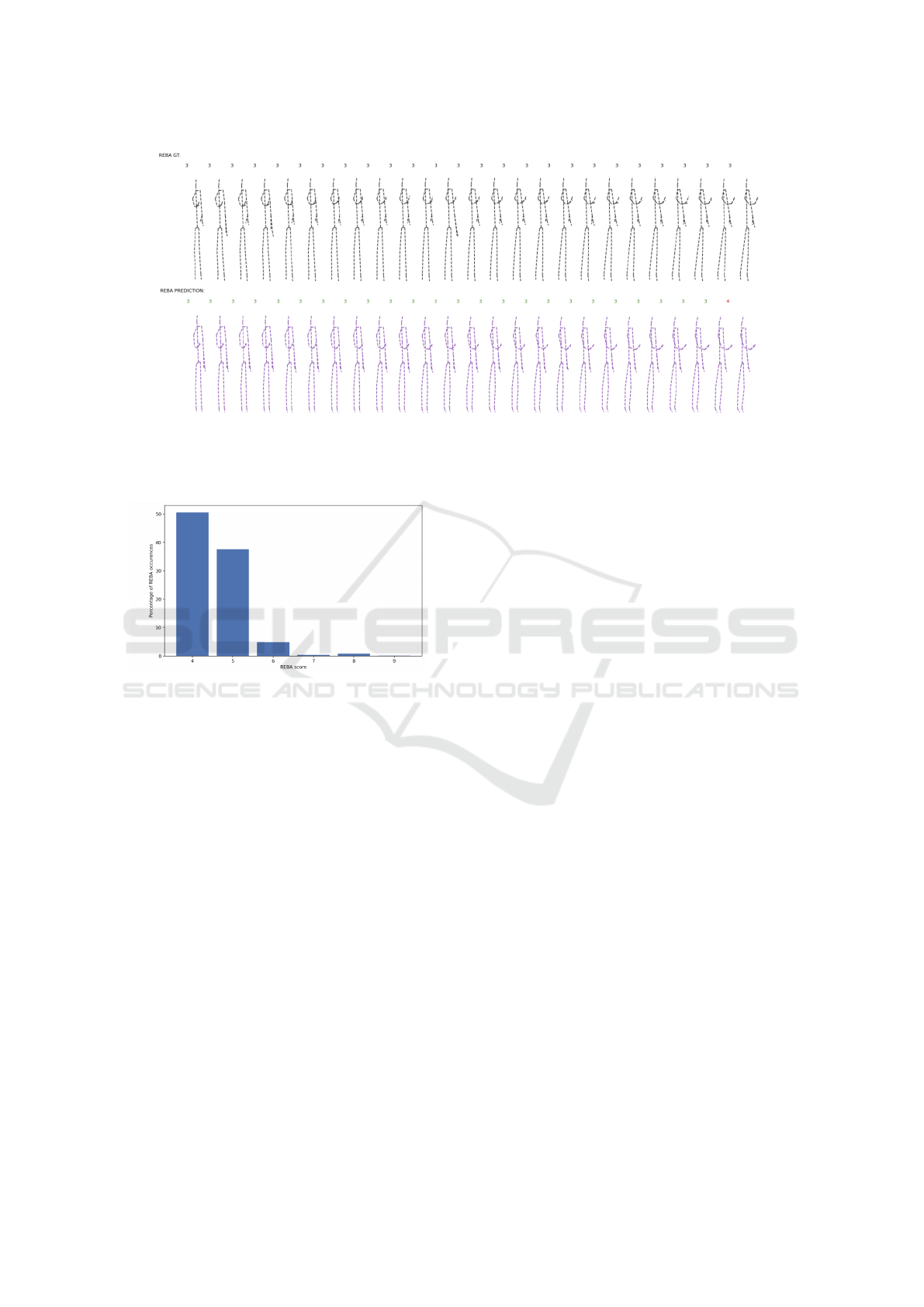
Figure 7: Qualitative example of human pose prediction of the next 25 frames with the STS-GCN-A model. The action
is ”Place Piece”, the top row shows the ground truth with the respective REBA score above the pose, and the bottom row
shows the predicted motion with their respective REBA scores. The predicted REBA scores are highlighted in green or red
depending on whether they correspond with the ground truth values or not.
Figure 8: Distribution of REBA scores for a single user.
users to adapt to a more ergonomic posture. That is
why we tried to push the boundaries of the prediction
horizon further, but horizons longer than 2-3 seconds
have mixed results due to the stochastic patterns of
human motion. And, in this setup, we gathered the
data for a certain environment with certain actions.
The models trained on this data will not generalize to
other VR environments with different tasks, but the
method is generally applicable.
Now we opted for an assembly setup that is phys-
ically and mentally demanding, but the analytics ex-
plained above is feasible with any application. We
want to focus on the analytics on top of the VR train-
ing, to give users more feedback and insights into
their behavior.
We conclude that with real-time human motion
prediction physical ergonomics can be calculated
ahead of time to prevent bad posture or unsafe situa-
tions. Adding extra information in the form of frame-
wise action classification has a positive effect on the
MPJPE. Lastly, This experiment shows the advan-
tages of VR as a training tool. It can gather annotated
data very quickly. It can simulate any environment
and any task. It can give feedback to the user during
or after the training based on several analytics.
For future work, we consider including motion
trajectory overlays in the virtual room which help the
operator to solve the problem when they are stuck. In
other scenarios, like human-robot interactions, these
overlays are a first step toward marking safety bound-
aries where the operator can safely move.
In this work, we do not focus on studying how
VR can efficiently collect annotated data in various
settings. This can be a future added value as col-
lecting data in real physical spaces is expensive with
limited data as a result. This data has to be manu-
ally annotated afterward, which is time-consuming.
A faster, more cost-effective way is to use a VR envi-
ronment. In VR, there can be automatic annotations
of actions, objects, people, and more. Viewpoints are
easy to adapt and the data from different sensors is
fully synced. In section 7, we show that additional in-
formation sources can improve the motion prediction
performance. Possible modalities that can be added
are heart rate, eye gaze information, and controller
inputs.
To improve generalization, a model can be trained
on large datasets, i.e. H36M (Ionescu et al., 2014) and
AMASS (Mahmood et al., 2019), with many different
actions, and finetuned with a target dataset specific to
the problem. To avoid catastrophic forgetting, this can
be done with continual learning methods (Yasar and
Iqbal, 2021).
The predicted REBA scores are close to the
ground truths, but we do notice that the REBA score
is sensitive to the error of the joint position. This can
also be a topic of future work, to analyze if another
representation helps, or if smoothing methods on the
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
546

pose’ joints have an effect.
We opted for a 3D joint representation of the data
which gives freedom to the model to minimize the dis-
tance between ground truth and prediction, but a case
can be made to use bone representation in the form of
rotation vectors. This way, the distance between spe-
cific joints is always the same to achieve more consis-
tent motion.
In (Billast et al., 2023), they show that it is pos-
sible to do motion prediction on just two joints, i.e.
the hands. This fits closely with the VR application
as we have the coordinates of the controllers at all
times which would mean that the extra depth sensor
becomes obsolete. Analysing physical ergonomics on
two joints is not feasible but recent VR setups try to
estimate the full body poses based on the headset and
controllers (Jiang et al., 2022).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research received funding from the Flemish Gov-
ernment under the “Onderzoeksprogramma Artificile
Intelligentie (AI) Vlaanderen” programme.
REFERENCES
Barquero, G., Escalera, S., and Palmero, C. (2023). Belfu-
sion: Latent diffusion for behavior-driven human mo-
tion prediction.
Billast, M., Mets, K., De Schepper, T., Oramas M, J., and
Latr
´
e, S. (2023). Human motion prediction on the
ikea-asm dataset. pages 906–914.
Chiu, H.-k., Adeli, E., Wang, B., Huang, D.-A., and
Niebles, J. C. (2019). Action-agnostic human pose
forecasting. In 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Ap-
plications of Computer Vision (WACV), pages 1423–
1432. IEEE.
Cui, Q., Sun, H., and Yang, F. (2020). Learning dynamic
relationships for 3d human motion prediction. In Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
De Bruyne, J., Joundi, J., Morton, J., Zheleva, A., Van Kets,
N., Van Wallendael, G., Talsma, D., Saldien, J.,
De Marez, L., Durnez, W., et al. (2023). I spy with
my ai: The effects of ai-based visual cueing on hu-
man operators’ performance and cognitive load in cctv
control rooms. International Journal of Industrial Er-
gonomics, 95:103444.
Guan, W., Song, X., Wang, K., Wen, H., Ni, H., Wang, Y.,
and Chang, X. (2023). Egocentric early action pre-
diction via multimodal transformer-based dual action
prediction. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Sys-
tems for Video Technology, pages 1–1.
Guo, W., Du, Y., Shen, X., Lepetit, V., Alameda-Pineda, X.,
and Moreno-Noguer, F. (2023). Back to mlp: A sim-
ple baseline for human motion prediction. In Proceed-
ings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applica-
tions of Computer Vision (WACV), pages 4809–4819.
Hignett, S. and McAtamney, L. (2000). Rapid entire body
assessment (reba). Applied ergonomics, 31(2):201–
205.
Hu, J., Fan, Z., Liao, J., and Liu, L. (2019). Predict-
ing long-term skeletal motions by a spatio-temporal
hierarchical recurrent network. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1911.02404.
Ionescu, C., Papava, D., Olaru, V., and Sminchisescu, C.
(2014). Human3.6m: Large scale datasets and pre-
dictive methods for 3d human sensing in natural envi-
ronments. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 36(7):1325–1339.
Jaffar, N., Abdul-Tharim, A., Mohd-Kamar, I., and Lop, N.
(2011). A literature review of ergonomics risk fac-
tors in construction industry. Procedia engineering,
20:89–97.
Jiang, J., Streli, P., Qiu, H., Fender, A., Laich, L., Snape,
P., and Holz, C. (2022). Avatarposer: Articulated
full-body pose tracking from sparse motion sensing.
In Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Ciss
´
e, M., Farinella,
G. M., and Hassner, T., editors, Computer Vision –
ECCV 2022, pages 443–460, Cham. Springer Nature
Switzerland.
Joundi, J., Bombeke, K., Saldien, J., Durnez, W.,
De Bruyne, J., Vanroelen, C., and Zheleva, A. (2022).
ExperienceDNA : a framework to conduct and analyse
user tests in VR. In Faculty of Engineering and Ar-
chitecture Research Symposium 2022 (FEARS 2022),
Abstracts, page 1.
Kilis, N., Papaioannidis, C., Mademlis, I., and Pitas, I.
(2022). An efficient framework for human action
recognition based on graph convolutional networks.
In 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Pro-
cessing (ICIP), pages 1441–1445. IEEE.
Lee, M.-L., Liu, W., Behdad, S., Liang, X., and Zheng, M.
(2022). Robot-assisted disassembly sequence plan-
ning with real-time human motion prediction. IEEE
Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Sys-
tems, 53(1):438–450.
Lyu, K., Chen, H., Liu, Z., Zhang, B., and Wang, R. (2022).
3d human motion prediction: A survey. Neurocom-
puting, 489:345–365.
Mahmood, N., Ghorbani, N., Troje, N. F., Pons-Moll, G.,
and Black, M. J. (2019). AMASS: Archive of motion
capture as surface shapes. In International Conference
on Computer Vision, pages 5442–5451.
Martinez, J., Black, M. J., and Romero, J. (2017). On
human motion prediction using recurrent neural net-
works. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
Mart
´
ınez-Gonz
´
alez, A., Villamizar, M., and Odobez, J.-M.
(2021). Pose transformers (potr): Human motion pre-
diction with non-autoregressive transformers. In Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference
on Computer Vision, pages 2276–2284.
Micheletti Cremasco, M., Giustetto, A., Caffaro, F., Colan-
toni, A., Cavallo, E., and Grigolato, S. (2019). Risk
Physical Ergonomics Anticipation with Human Motion Prediction
547

assessment for musculoskeletal disorders in forestry:
A comparison between RULA and REBA in the man-
ual feeding of a Wood-Chipper. Int J Environ Res
Public Health, 16(5).
Qin, X., Wang, Z., Bai, Y., Xie, X., and Jia, H. (2020).
Ffa-net: Feature fusion attention network for single
image dehazing. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference
on Artificial Intelligence, 34(07):11908–11915.
Rao, H., Xu, S., Hu, X., Cheng, J., and Hu, B. (2021).
Augmented skeleton based contrastive action learning
with momentum lstm for unsupervised action recog-
nition. Information Sciences, 569:90–109.
Rezazadegan, F., Shirazi, S., Baktashmotlagh, M., and
Davis, L. S. (2018). On encoding temporal evolution
for real-time action prediction.
Sofianos, T., Sampieri, A., Franco, L., and Galasso, F.
(2021). Space-time-separable graph convolutional
network for pose forecasting. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vi-
sion (ICCV), pages 11209–11218.
Song, L., Yu, G., Yuan, J., and Liu, Z. (2021). Human pose
estimation and its application to action recognition: A
survey. Journal of Visual Communication and Image
Representation, 76:103055.
Vandergrift, J. L., Gold, J. E., Hanlon, A., and Punnett, L.
(2012). Physical and psychosocial ergonomic risk fac-
tors for low back pain in automobile manufacturing
workers. Occupational and environmental medicine,
69(1):29–34.
Xie, B., Liu, H., Alghofaili, R., Zhang, Y., Jiang, Y., Lobo,
F. D., Li, C., Li, W., Huang, H., Akdere, M., et al.
(2021). A review on virtual reality skill training appli-
cations. Frontiers in Virtual Reality, 2:645153.
Yasar, M. S. and Iqbal, T. (2021). Improving human mo-
tion prediction through continual learning. CoRR,
abs/2107.00544.
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
548
