
ADMIn: Attacks on Dataset, Model and Input: A Threat Model for AI
Based Software
Vimal Kumar
a
, Juliette Mayo and Khadija Bahiss
School of Computing and Mathematical Sciences, University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand
Keywords:
Threat Modelling, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Taxonomy.
Abstract:
Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques have now become commonplace in software
products and services. When threat modelling a system, it is therefore important that we consider threats
unique to ML and AI techniques, in addition to threats to our software. In this paper, we present a threat
model that can be used to systematically uncover threats to AI based software. The threat model consists of
two main parts, a model of the software development process for AI based software and an attack taxonomy
that has been developed using attacks found in adversarial AI research. We apply the threat model to two real
life AI based software and discuss the process and the threats found.
1 INTRODUCTION
While research in Machine Learning (ML) has been
actively pursued for several decades, over the last
decade or so software products and services that use
Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence
(AI) have gained tremendous visibility. ML and AI
based software products and services have become
ubiquitous and seen in fields as diverse as healthcare,
finance, automotive, manufacturing, etc. ML and AI
are also extensively being used in cybersecurity for
various tasks such as endpoint protection, malware
detection, spam filtering, intrusion detection, authen-
tication and fingerprinting etc. In the rest of this pa-
per, we call software products and services that use
ML and AI algorithms, AI based software. The use
of AI provides advantages of efficiency, functionality
and innovation, but it also has the potential to intro-
duce vulnerabilities that are unique to AI based soft-
ware. The awareness of the risks posed by such vul-
nerabilities has been steadily growing exemplified by
the recently held AI safety summit and the Bletch-
ley declaration
1
at its conclusion as well as president
Biden’s executive order on AI
2
.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4955-3058
1
https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/ai-
safety-summit-2023-the-bletchley-declaration/the-
bletchley-declaration-by-countries-attending-the-ai-safety-
summit-1-2-november-2023
2
Executive order 14110: Safe, secure, and trustworthy
development and use of artificial intelligence.
Practitioners such as security managers, risk man-
agement professionals and CISOs also need to be
aware of AI risks when they are assessing Informa-
tion Security risks to their organisations. A cru-
cial aspect of risk management is threat enumera-
tion/identification. To assess AI risks, it is imperative
to identify the threats to the AI based software prod-
ucts and services being used in an organisation.
In spite of a large body of literature on adversarial
AI and ML, there is a lack of methods or methodolo-
gies that practitioners can use to systematically iden-
tify threats to AI based software being used in their
organisation. Consequently they rely on inconsistent
threat identification methods, based either on vendor
supplied information or on random threat enumera-
tion. In this paper we present a methodology to map
the existing adversarial AI threats to an AI software
development process, thereby creating a threat model
that can be used by anyone to detect threats in their
AI software.
The rest of this paper is organised as following.
We first discuss work related to threat modelling AI
based software in section 2. In section 3 we present
our software development process diagram for AI
based software, while section 4 presents our attack
taxonomy. In section 6 we show how the taxonomy is
mapped to the software development process. In sec-
tion 7 we discuss the case studies of employing our
method on real world software before concluding in
section 8.
170
Kumar, V., Mayo, J. and Bahiss, K.
ADMIn: Attacks on Dataset, Model and Input: A Threat Model for AI Based Software.
DOI: 10.5220/0012394100003648
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2024), pages 170-178
ISBN: 978-989-758-683-5; ISSN: 2184-4356
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

2 RELATED WORK
The purpose of threat modelling is to identify, cat-
egorise, and analyse potential vulnerabilities in ap-
plications (product, software, data, system, service,
etc. ). Threat modelling is done by analysing one or
more of the attacker’s motivation, goals, techniques,
and procedures in the context of the application that
is being threat modelled. It usually consists of two
main parts; modelling and enumeration. In mod-
elling, the entity conducting the exercise creates a
model of the system at hand. Common approaches
to do this include asset- and impact-centric, attack(er)
– and threat-centric, and software- and system-centric
approaches. (Martins et al., 2015; Selin, 2019). In
enumeration, this model is used to identify threats to
the system being studied usually aided by a taxonomy.
There has been substantial amount of work in ad-
versarial machine learning recently, spurred on by
the fundamental question on the security of machine
learning first asked in (Barreno et al., 2006) and (Bar-
reno et al., 2010). The works described in (Worzyk
et al., 2019) (Wang et al., 2020) (Hu et al., 2022)
(Moon et al., 2022) explore techniques that attack
specific AI models and their defences, while works
such as (Wang et al., 2022) (Greshake et al., 2023)
survey and summarise these techniques. (Mirsky
et al., 2023) on the other hand conducted a large-
scale survey and ranking of threats to AI. Not enough
attention, however, has been paid to the develop-
ment of techniques that can be used to systemati-
cally identify threats in AI based software. One of
the first attempts to do so was from MITRE who de-
veloped MITRE ATLAS (Adversarial Threat Land-
scape for Artificial-Intelligence Systems) (MITRE, ).
ATLAS is a knowledge-base that classifies adversary
tactics and techniques according to the well-known
ATT&CK framework. The European cybersecurity
agency ENISA also has overarching guidelines on the
risks to AI without specifying the methodology to
identify those risks (Caroline et al., 2021). The work
most closely related to ours is STRIDE-AI (Mauri
and Damiani, 2022), which is an asset-centric ap-
proach for threat modelling AI based software. It
relies on conducting an FMEA (Failure Modes and
Effects Analysis) on each individual information as-
set used in the AI based software development pro-
cess. The information gained from the FMEA analy-
sis is then mapped to STRIDE to enumerate possible
threats. It can be argued that an asset-centric approach
while useful for the developors and vendors may not
be the best approach for the organisations that are
the consumers of AI based software. Microsoft has
also utilised the FMEA approach along with bug bar
to create guidance on security development cycle for
AI based software (Marshall et al., ). This approach
is similar to the STRIDE-AI approach and uses the
STRIDE categorisation of threats. Finally, OWASP
has released the Machine Learning Security Top 10
for 2023 (Singh et al., 2023), which lists the top at-
tacks on AI based software. There is some overlap
in the threats covered in OWASP’s list and our taxon-
omy which suggests that the list could be integrated
with our threat model in future, however that integra-
tion is outside the scope of this paper. In addition to
the list, OWASP documentation provides guidelines
on mitigation as well as metrics on risk factors.
We proffer that an attack-centric approach (as op-
posed to an asset-centric approach) to threat mod-
elling provides a more straightforward way to relate
the current adversarial AI research to software devel-
opment, as a taxonomy can be developed from the ex-
isting literature. In the rest of this paper we present
this attack-centric approach.
3 MODELLING
The first step in threat modelling is to create an ab-
stract model of the system under investigation. Exist-
ing threat models have used a number of approaches
for this. STRIDE for example uses data flow dia-
grams (DFDs) to create a model and augments those
diagrams with trust boundaries.
We chose to use the software development
process of AI based software for modelling. The
software development process for AI based software
consists of three distinct phases, data processing,
model development and deployment, as shown in
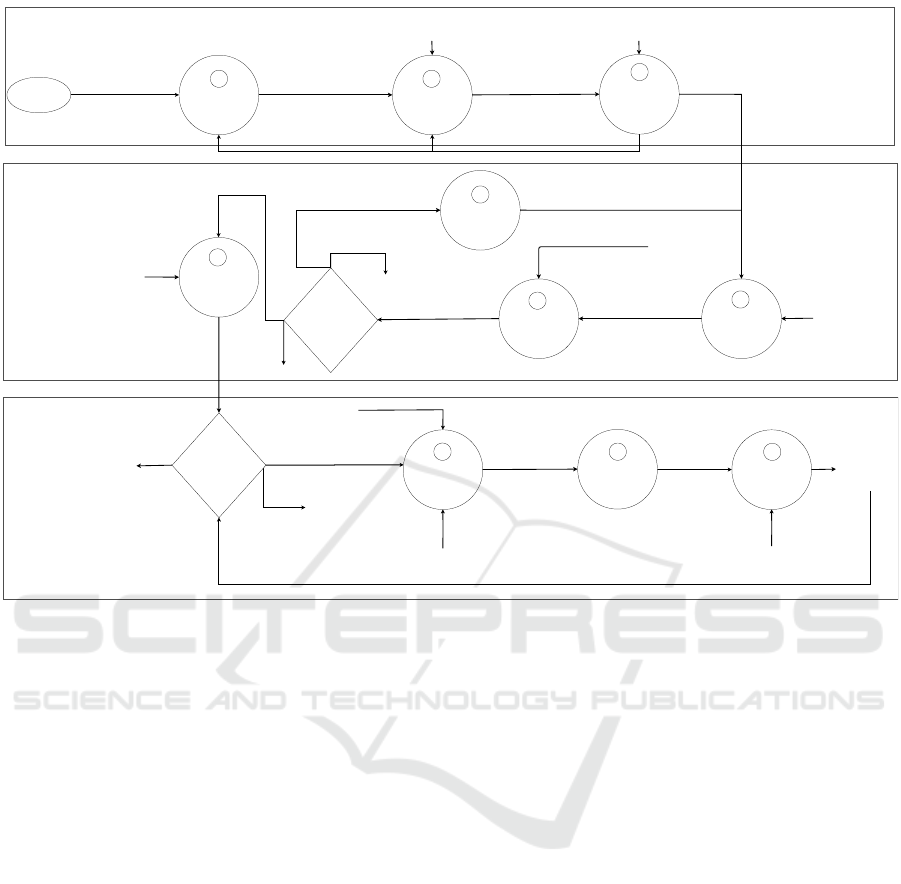
Figure 1. In the diagram presented in this paper we
have tried to strike a balance between readability for
cybersecurity practitioners, and the detail presented
in the diagram. In the rest of this section we go over
each of the phases one by one.
3.1 Data Processing
The main objective of this phase is to transform or
process datasets into a format that can be used to train
a model. We divide the work undertaken in this phase
into three processes, Requirement Engineering, Data
Cleaning and Feature Engineering & Labelling.
Requirement Engineering. The process of require-
ment engineering involves developers determining the
specifications of the client’s AI based software and
the requirements of needed datasets. According to
(ur Rehman et al., 2013) there are three inputs into the
ADMIn: Attacks on Dataset, Model and Input: A Threat Model for AI Based Software
171
System and Domain
Information,
Regulations,
Stakeholder and
Organisational
Requirements, etc.
1
Requirement
Engineering
Specifications
of Systems
and Models
&
Agreed
Requirements
2
Data
Preparation
Raw Dataset
Cleaned
Training
Dataset
3
Feature
Engineering
and Labelling
Manually created,
automated or
crowdsourced features
Refined
Training
Dataset
Is the Model
Adequate?
Machine
LearningAlgorithm
with
Hyperparameters
4
Model
Training
Process
Trained Model
5
Model
Evaluation
During
Development
Validation
Dataset
Model
Evaluation
Outcome
During
Development
7
Model
Evaluation
After
Development
Testing Dataset
Optimized
Trained Model
Tuning Method
Hyperparameter
Tuning and
Algorithm
Selection
6
New
Hyperparameters
Yes
No
Model
Evaluation
Outcome After
Development
Text
Is the Model
Adequate?
*
Data Input
Software
Deployment
8
Classification
or Prediction
Model
Evaluation
During
Deployment
10
Model
Evaluation
Outcome
During
Deployment
Yes
No
Start
DATA PROCESSING PHASE
MODEL DEVELOPMENT PHASE
DEPLOYMENT PHASE
*
*
*
Deployment
Environment
Deployment
Environment
Decision-
Making
Procedure
9
Yes
Yes
No
Classification ,
Prediction or
Decision
Figure 1: Software development process for AI based software. Circles represent processes, arrows represent inputs and
outputs, diamonds represent decisions and ‘*’ means that the arrow can point to any previous process.
requirement engineering process: system/domain in-
formation, stakeholder/organisational requirements,
and regulations. Such requirements are often gath-
ered via several different methods, such as traditional
(e.g., interviews), modern (e.g., prototyping), cogni-
tive (e.g., card sorting), group (e.g., brainstorming) or
contextual (e.g., ethnography) categories. In general,
the outputs of the requirement engineering process are
the agreed requirements and the specifications of the
systems and model being developed. Other, more spe-
cific details may be included as well, such as the plans
for acquiring the data, the amount of data needed and
how accurate the model needs to be.
Data Preparation. Once the specification of the soft-
ware and the requirements of the needed datasets have
been identified, work on collecting and cleaning data
is usually started. (Roh et al., 2019) have divided the
various methods of raw data collection into three cat-
egories, discovery, augmentation and generation. The
raw dataset thus collected can be in various forms,
such as, audio, video, text, time-series or a combina-
tion of such formats. It may also have errors, incon-
sistencies, omissions and duplications. Data clean-
ing involves finding and resolving these errors, incon-
sistencies, omissions and duplications. Data clean-
ing is a fundamental part of this process, and is often
used in combination with data collection and curation
(Symeonidis et al., 2022). Data preparation some-
times involves other techniques such as data transfor-
mation and is a vital step in the data processing phase
(Kreuzberger et al., 2023).
Feature Engineering & Labelling. Features are el-
ements used to describe specific objects in data. The
process of feature engineering involves creating fea-
tures for a dataset so it can be understood and used by
an algorithm (Dong and Liu, 2018). The Feature En-
gineering & Labelling process in our diagram may ad-
ditionally encompass related techniques of feature ex-
traction, feature construction, feature storage and fea-
ture encoding. There may be algorithms that do not
have a feature engineering part to them. Our model,
however, is created to be exhaustive so that it covers
most possibilities. As will be shown later, when this
diagram is used, processes that aren’t applicable to a
given scenario, can be removed.
Labelling is a related idea, often used in super-
vised or semi-supervised learning and involves as-
signing a category or tag to a given piece of data
(Grimmeisen et al., 2022), to help the model learn or
distinguish between objects.
ICISSP 2024 - 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
172

3.2 Model Development
The main objective of this phase is to train a model
and evaluate its performance. We divide the work
undertaken in this phase into four processes, Model
Training, Model Evaluation during Development, Hy-
perparameter Tuning and Model Evaluation after De-
velopment.
Model Training. The refined training dataset, and
features or labels produced from the preceding pro-
cess are used as inputs to the Model Training pro-
cess where an algorithm is trained on the data pro-
vided. Another input to this process is an algorithm
or model that is to be trained. Depending on the spe-
cific details of the AI model, the used algorithms will
differ. Examples of some algorithms that can be used
include neural networks, ensemble learning and other
supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised learning
methods. Model training is the most critical process
in the development of AI based software and outputs
a trained model to make classifications or predictions.
Model Evaluation During Development. In this
process, the trained model from the preceding process
is used as an input along with a validation dataset.
The validation dataset is used on the trained model
to measure model performance. This dataset can be
generated via several different methods. One method
is to split the training dataset into three subsets: the
training dataset, validation dataset and testing dataset.
Other methods include k-fold cross validation, which
involves splitting the dataset into ‘k’ subsets. In some
cases, multiple methods may be used.
Hyperparameter Tuning. If the outcome of model
evaluation during development is not adequate or the
developers want to improve model performance, the
process of hyperparameter tuning may occur. Some
examples of hyperparameters that are tuned are, the
learning rate, neural network architecture or the size
of the neural network used (Feurer and Hutter, 2019).
Alternatively, developers may also go back to the data
cleaning or the feature engineering & labelling pro-
cess or change the algorithm used to create the model.
In Figure 1 this is shown by a ‘*’. This process oc-
curs iteratively until the model is deemed satisfactory
by the developers.
Various different types of tuning methods ex-
ist, each with their own advantages and disadvan-
tages. Examples include random search, grid search,
or Bayesian optimisation. Meta-heuristic algorithms
such as particle swarm optimisation and genetic algo-
rithms are other popular tuning methods used as well
(Yang and Shami, 2020).
Model Evaluation after Development. At this stage
the model is evaluated once again. This process takes
two inputs, the optimised trained model produced af-
ter tuning and a testing dataset. The testing dataset is
used to assess the performance of the final optimised
trained model. If the outcome of the evaluation is ad-
equate, the deployment phase is executed. Otherwise,
depending on the situation, the model may need to
be retrained from the very beginning, or use different
training data, features, or labels.
3.3 Deployment
In this phase the model is deployed as part of a
software product or service in environments such as
cloud, server, desktop or mobile device. The work un-
dertaken in this phase is divided into three processes,
Software Deployment, Decision Making and Model
Evaluation during Deployment.
Software Deployment. This process involves the
fully developed AI based software being deployed in
different environments. The input into this phase is
the data the software uses. This data is used by the
software to output a classification or prediction, de-
pending on the problem that is being solved.
Decision Making. While in some cases the classifi-
cation or prediction may be the desired end-goal, in
other cases the classification or prediction output may
be fed into a process, which produces a decision based
on the input.
Model Evaluation During Deployment. To ensure
that the model does not drift overtime and is fit for
purpose, constant, iterative evaluation or monitoring
of a model during deployment is sometimes neces-
sary. The Model Evaluation during Deployment pro-
cess encapsulates this thinking. If the evaluation out-
come is adequate, the deployment phase is continued.
If the evaluation outcome is not adequate, the model
may be retrained from the start, or use different train-
ing data, features, or labels. This evaluation is usually
done periodically and not necessarily after each run
during deployment.
4 AI THREAT ENUMERATION
The second part of threat modelling is threat enumer-
ation. To understand the threats to AI, we explored
extensive research literature in adversarial AI. Our lit-
erature review has led to the creation of a taxonomy
of threats to AI shown in Figure 2. In our taxonomy,
all possible threats to AI based software are divided
into three main categories, attacks on data, attacks on
model and attacks on inputs, from which we derive
our acronym ADMIn.
ADMIn: Attacks on Dataset, Model and Input: A Threat Model for AI Based Software
173

Figure 2: Taxonomy of threats to AI.
4.1 Attacks on Data
In these type of attacks, the adversary’s focus is on
data. The adversary either attempts to steal propri-
etary data through the algorithm or tries to poison or
maliciously modify internal data and/or systems. This
category is further split into two types of attacks, data
exfiltration attacks and data poisoning attacks.
Data Exfiltration Attacks. In these attacks, the ad-
versary attempts to steal private information from the
target model’s dataset. This can take place in three
different ways. First, through property exfiltration at-
tacks, where the attack consists of an adversary steal-
ing data properties from the training dataset. Sec-
ond, through dataset theft attacks, where the attacks
involve the theft of the entire dataset. Finally, exfil-
tration can be achieved through datapoint verification
attacks. In these attacks, an adversary attempts to de-
termine if a specific datapoint is in the model’s train-
ing dataset via interactions with the model.
Data Poisoning Attacks. In these attacks, the adver-
sary deliberately attempts to corrupt the datasets used
by the AI based software. The adversary may poi-
son the dataset via adding new data, modifying exist-
ing data (e.g., content, labels, or features), or deleting
data in the model’s training or validation dataset, with
the aim of diminishing the model’s performance. An
attack consisting of addition of new datapoints into
the training data is performed with the intention of
adding biases to the model, so it mis-classifies inputs.
(Oseni et al., 2021)(Liu et al., 2022). Poisoning of
datasets may take place through the environment or
through the inputs to the model. Such attacks may
either be targeted or untargeted. In a targeted attack
an adversary may attempt to, for example have a mal-
ware classification model mis-classify the malware as
benign. In an untargeted attack, the adversary on the
other hand is looking to make the model mis-classify
the malware as anything but the actual classification.
Attacks where the adversary is looking to modify or
delete existing data, can be comparatively harder to
mount as such attacks require the knowledge of and
access to the training data. Such access and knowl-
edge however can be gained by exploiting software
vulnerabilities in the systems surrounding the dataset.
4.2 Attacks on Model
In these type of attacks, the adversary’s focus is on the
model being used. The adversary either attempts to
steal the proprietary model or tries to modify it. This
category is further split into three types of attacks,
model poisoning or logic corruption attacks, policy
exfiltration attacks and model extraction attacks.
Model Poisoning or Logic Corruption Attacks. In
these attacks the adversary attempts to maliciously
modify or alter the logic, algorithm, code, gradients,
rules or procedures of the software. This can result
in reduction of performance and accuracy, as well as
causing the model to carry out malicious actions (Os-
eni et al., 2021)(Benmalek et al., 2022)(Wang et al.,
2022). Such attacks can be hard to defend against but
usually require that the adversary has full access to
the algorithms used in the model. This makes these
attacks less likely to occur.
Policy Exfiltration Attacks. In policy exfiltration at-
tacks the adversary attempts to learn the policy that
the model is enforcing by repeatedly querying it. The
repeated querying may make evident the input/output
relationship and may result into the adversary learn-
ing the policy or rules being implemented.
Model Extraction Attacks. Also known as model
ICISSP 2024 - 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
174

stealing, the adversary in these types of attacks steals
the model to reconstruct or reverse engineer it (Hu
et al., 2022).This is usually done by deciphering infor-
mation such as parameters or hyperparameters. These
attacks require the inputs to the model be known to the
adversary whereby unknown parameters can be com-
puted using information from a model’s inputs and its
outputs (Chakraborty et al., 2021).
4.3 Attacks on Inputs
In these type of attacks, the adversary uses malicious
content as the input into a ML model during deploy-
ment. This category is further split into four types of
attacks, prompt injection attacks, denial of service at-
tacks, evasion attacks and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Prompt Injection Attacks. Prompt injection attacks
are a relatively new but well-known type of attack. It
consists of an adversary trying to manipulate a (nat-
ural language processing) system via prompts to gain
unauthorized privileges, such as bypassing content fil-
ters (Greshake et al., 2023). The ChatGPT service
for example responds to text prompts and may con-
tain text filters for commercial sensitivity, privacy and
other reasons. However, crafting prompts in certain
ways may allow users to bypass these filters in what
is known as a prompt injection attack. Prompt injec-
tion attacks can be harder to defend against compared
to other well known injection attacks such as SQL or
command injection because the data input as well as
the control input, both consist of natural language in
textual prompts.
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks. A DoS attack
consists of an adversary disrupting the availability of
a model by flooding its inputs with illegitimate re-
quests. DoS attacks are widely understood and in gen-
eral in such attacks the adversary can flood the model
with as many inputs as possible to make the soft-
ware unavailable to others, however an AI based soft-
ware can be susceptible to another kind of DoS attack
where the model is flooded with deliberately manipu-
lated inputs to cause purposeful mis-classifications or
errors (Oseni et al., 2021).
Evasion Attacks. In these attacks the adversary aims
to avoid accurate classification by a model. For ex-
ample, an adversary may craft spam emails in a cer-
tain way to avoid being detected by AI spam filters.
Evasion attacks can be undertaken via methods such
as changing the model’s policy. The techniques used
in evasion attacks are usually specific to the types of
inputs the model accepts. We have therefore sub-
classified these attacks based on the inputs; Natural
Language based attacks, image and video based at-
tacks and attacks that modify data in the real world.
Man-in-the-
middle Attacks
Model
Extraction
Attacks
Policy
Exfiltration
Attacks
Model Poisoning or
Logic Corruption
Attacks and Their
Subcategories
SPOOFING
TAMPERING
REPUDIATION
INFORMATION
DISCLOSURE
DENIAL OF
SERVICE
ELEVATION OF
PRIVILEGE
Prompt
Injection
Attacks
Denial of
Service
Attacks
Evasion
Attacks and
Their
Subcategories
Data Exfiltration
Attacks and
Their Subcategories
Data Poisoning
Attacks and
Their Subcategories
Attacks on the Dataset
Attacks on the Model
Attacks on the Inputs
STRIDE Classification
Figure 3: Threats to AI classified according to STRIDE.
A threat modeller can check if any category applies
to their specific AI based software by looking at the
specific type of input the model expects.
Man in the Middle Attacks. In these attacks, the
input or output of a deployed model is intercepted
and/or altered maliciously by an adversary (Moon
et al., 2022)(Wang et al., 2020). This is usually more
likely where an AI based software is being used as a
service but is also possible when the software is inter-
nally deployed as a product. As an example, an adver-
sary can intercept and alter system and network data
being input to a model to produce mis-classification
that ultimately results in defence evasion.
5 THREATS TO AI CLASSIFIED
ACCORDING TO STRIDE
In some cases, one may want to relate each attack
or threat to STRIDE if additional information is
required. STRIDE is a common threat model used
for software threats and as mentioned in section 2,
threat models from Microsoft and STRIDE-AI use
STRIDE. In this section we explain how the threats
in our taxonomy are related to STRIDE. This is
pictorially shown in Figure 3.
Spoofing
• In evasion attacks, the adversary modifies data in
the real world or uses other tactics such as modify-
ADMIn: Attacks on Dataset, Model and Input: A Threat Model for AI Based Software
175

ing images to avoid detection from a model. This
is a classic spoofing threat.
• In model poisoning, or data poisoning attacks, an
adversary may alter code or inputs to a model
to avoid detection by creating purposeful mis-
classifications.
Tampering
• In model poisoning, or data poisoning attacks, the
main goal of an adversary is to maliciously mod-
ify a model’s code or data. This is clearly a tam-
pering threat.
• In man-in-the-middle attacks, an adversary may
tamper with data that is being sent to and from the
model.
Repudiation
• As evasion attacks are considered spoofing at-
tacks, repudiation exists. This is because an ad-
versary can deny carrying out any malicious ac-
tions if robust audit logs are missing.
Information Disclosure
• In data, model or policy exfiltration attacks, the
main goal of the adversary is to steal the model,
it’s properties or dataset, which discloses confi-
dential information.
Denial of Service
• In DoS attacks, the adversary’s main goal is to
deny the software’s service to users.
Elevation of Privilege
• In prompt injection attacks, the adversary’s main
goal is to gain unauthorized privileges or access
via certain input prompts.
6 THREAT MODELLING
PROCESS
AI based software can be threat modelled by map-
ping the threats in the previously explained taxonomy
to the processes in the software development process
discussed in section 3, as described below.
• Obtain the software development process diagram
for AI based software as shown in Figure 1
• Remove any inputs, outputs, or processes that
are/were not used in the software.
• Add any additional inputs, outputs, or processes
that are/were used, but are not displayed in the
original diagram
• Sequentially for each process and its inputs and
outputs, add the attacks that apply to your soft-
ware by referring to the threats in the attack tax-
onomy shown in 2
• If additional information is required, relate the ad-
versarial attacks for each input, process, and out-
put on the ML diagram to STRIDE
7 CASE STUDIES
We used our threat modelling approach on two real
world AI based software and went through the process
with their developers to evaluate the effectiveness of
our approach. In this section, we go over the results
of the threat modelling exercises.
7.1 Case Study 1
A threat modelling case study was undertaken with
the app and website, ‘Aotearoa Species Classifier’
4
.
This software identifies animal and plant species from
all around New Zealand from a single photo. We
went through the 5 step threat modelling process as
described in section 6 with the developers.
Step 1. We used the software development process
diagram from Figure 1.
Step 2. The application used a convolutional neu-
ral network so the ‘Feature Engineering & Labelling’
process was removed from the diagram. The ‘Model
Evaluation During Deployment’ process was also re-
moved as it was not used.
Step 3. No additional inputs, outputs, processes, or
arrows were added to the diagram.
Step 4. The attack taxonomy was applied to the soft-
ware development process one by one. While the ex-
ercise took place by mapping the taxonomy to each
process, for brevity we describe the results in Table 1
in terms of attacks on dataset, model, and inputs.
Step 5. This step was not undertaken as additional
STRIDE information was not required.
7.2 Case Study 2
A threat modelling case study was undertaken with
an image-based AI software. This software is used
to improve roads and automatically detect roading
problems such as potholes. We went through the 5
step threat modelling process as described in section
6 with the developers.
4
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.wa
ikatolink.wit app
ICISSP 2024 - 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
176

Table 1: Comparing the possible threats to the AI based software in the case studies.
Attack on Case study 1 Case Study 2
Dataset The application was not susceptible to any of
the exfiltration attacks. The software and all its
data was open source, aspects such as the algo-
rithm, training data or hyperparameters cannot
be stolen as these were already publicly avail-
able.
It was however possible for the dataset to be
poisoned. Alhough the dataset is derived from
iNaturalist
3
, which is generally considered a
trusted source, it is possible that an adversary
can compromise the data repositories to poison
the data.
The training data for the application was pri-
vate and stored on cloud. It was discovered
that the data was susceptible to exfiltration via
dataset theft. The data was collected from cus-
tomers but it couldn’t be said if the data was
completely trustworthy. Therefore data poi-
soning was a valid threat.
Model It was possible for an adversary to poison the
model if the adversary had access to some
parts of the AI based software development
process. Policy Exfiltration and Model Extrac-
tion attacks were however not relevant due to
the software being open source.
It was possible for an adversary to poison the
model if the adversary has access to the some
parts of the AI based software development
process. Policy Exfiltration and Model Extrac-
tion attacks were however not relevant due to
the software being open source.
Input As the inputs into this model were images, at-
tacks that involve modifying the model’s en-
vironment and image-based evasion attacks
could occur. The web-based version of the ap-
plication was found to be vulnerable to DoS
attacks and man-in-the-middle attacks on both
the inputs and outputs. The application did not
take a prompt as input, therefore, it was not
susceptible to prompt injection attacks
As the software is only available to known
clients, DoS attacks were not considered to be
a threat. Although man-in-the-middle attacks
were a possibility, the developers trusted the
cloud provider’s security enough to not con-
sider it a relevant threat. Prompt injection at-
tacks were not relevant as the model only used
images. However, image-based evasion at-
tacks were considered relevant.
Step 1. We used the software development process
diagram from Figure 1.
Step 2. Since the application development process in-
cluded data labelling but not feature engineering, in-
puts related to feature engineering were omitted from
the diagram. The process of ‘Model Evaluation dur-
ing Deployment’ was removed as it was not used. The
yes arrow pointing to ‘*’ at the ‘Is the Model Ade-
quate?’ decision was removed, as it was never imple-
mented during the software deployment process.
Step 3. No additional inputs, outputs, processes, or
arrows were added to the diagram.
Step 4. The attack taxonomy was applied to the soft-
ware development process one by one. While the ex-
ercise took place by mapping the taxonomy to each
process, for brevity we describe the results in Table 1
in terms of attacks on dataset, model, and inputs.
Step 5. This step was not undertaken as additional
STRIDE information was not required.
8 CONCLUSION
A large number of software products and services
these days claim to utilize AI, and cybersecurity prac-
titioners are expected to manage cybersecurity risks
posed by such software. In this paper we have pre-
sented a systematic approach to identify the threats to
AI based software. Our threat model entitled ‘AD-
MIn’ is an attack-centric model, that categorises ad-
versarial AI attacks into three categories. These at-
tacks are mapped to the software development process
for AI based software, to ascertain the threats that are
applicable to the software under investigation.
Both AI and Cybersecurity are fields that are see-
ing rapid development and there is increasing aware-
ness of a need for threat modelling AI based software.
In future, we would investigate the integration of the
ADMIn threat model with OWASP ML Top 10 and
MITRE ATLAS. We would also like to build upon
ADMIn to create a Risk Assessment and Management
methodology for AI based software.
ADMIn: Attacks on Dataset, Model and Input: A Threat Model for AI Based Software
177

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge funding from
the New Zealand Ministry of Business, Innovation
and Employment (MBIE) for project UOWX1911,
Artificial Intelligence for Human-Centric Security.
REFERENCES
Barreno, M., Nelson, B., Joseph, A. D., and Tygar, J. D.
(2010). The security of machine learning. Machine
Learning, 81:121–148.
Barreno, M., Nelson, B., Sears, R., Joseph, A. D., and Ty-
gar, J. D. (2006). Can machine learning be secure? In
Proceedings of the 2006 ACM Symposium on Informa-
tion, computer and communications security, pages
16–25.
Benmalek, M., Benrekia, M. A., and Challal, Y. (2022).
Security of federated learning: Attacks, defensive
mechanisms, and challenges. Revue des Sciences
et Technologies de l’Information-S
´
erie RIA: Revue
d’Intelligence Artificielle, 36(1):49–59.
Caroline, B., Christian, B., Stephan, B., Luis, B., Giuseppe,
D., Damiani, E., Sven, H., Caroline, L., Jochen, M.,
Nguyen, D. C., et al. (2021). Securing machine learn-
ing algorithms.
Chakraborty, A., Alam, M., Dey, V., Chattopadhyay, A.,
and Mukhopadhyay, D. (2021). A survey on adversar-
ial attacks and defences. CAAI Transactions on Intel-
ligence Technology, 6(1):25–45.
Dong, G. and Liu, H. (2018). Feature engineering for ma-
chine learning and data analytics. CRC press.
Feurer, M. and Hutter, F. (2019). Hyperparameter optimiza-
tion. Automated machine learning: Methods, systems,
challenges, pages 3–33.
Greshake, K., Abdelnabi, S., Mishra, S., Endres, C., Holz,
T., and Fritz, M. (2023). More than you’ve asked for:
A comprehensive analysis of novel prompt injection
threats to application-integrated large language mod-
els. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.12173.
Grimmeisen, B., Chegini, M., and Theissler, A. (2022). Vis-
gil: machine learning-based visual guidance for inter-
active labeling. The Visual Computer, pages 1–23.
Hu, H., Salcic, Z., Sun, L., Dobbie, G., Yu, P. S., and Zhang,
X. (2022). Membership inference attacks on machine
learning: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR),
54(11s):1–37.
Kreuzberger, D., K
¨
uhl, N., and Hirschl, S. (2023). Ma-
chine learning operations (mlops): Overview, defini-
tion, and architecture. IEEE Access.
Liu, P., Xu, X., and Wang, W. (2022). Threats, attacks and
defenses to federated learning: issues, taxonomy and
perspectives. Cybersecurity, 5(1):1–19.
Marshall, A., Parikh, J., Kiciman, E., and Kumar, R. S. S.
Ai/ml pivots to the security development lifecycle bug
bar. https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/security/engin
eering/bug-bar-aiml. Accessed: 2023-10-26.
Martins, G., Bhatia, S., Koutsoukos, X., Stouffer, K., Tang,
C., and Candell, R. (2015). Towards a systematic
threat modeling approach for cyber-physical systems.
In 2015 Resilience Week (RWS), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Mauri, L. and Damiani, E. (2022). Modeling threats to ai-
ml systems using stride. Sensors, 22(17).
Mirsky, Y., Demontis, A., Kotak, J., Shankar, R., Gelei, D.,
Yang, L., Zhang, X., Pintor, M., Lee, W., Elovici, Y.,
and Biggio, B. (2023). The threat of offensive ai to
organizations. Computers & Security, 124:103006.
MITRE. Mitre atlas, adversarial threat landscape for
artificial-intelligence systems. https://atlas.mitre.org.
Accessed: 2023-10-26.
Moon, S., An, G., and Song, H. O. (2022). Preemptive im-
age robustification for protecting users against man-
in-the-middle adversarial attacks. In Proceedings of
the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol-
ume 36, pages 7823–7830.
Oseni, A., Moustafa, N., Janicke, H., Liu, P., Tari, Z., and
Vasilakos, A. (2021). Security and privacy for artifi-
cial intelligence: Opportunities and challenges. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2102.04661.
Roh, Y., Heo, G., and Whang, S. E. (2019). A survey on
data collection for machine learning: a big data-ai in-
tegration perspective. IEEE Transactions on Knowl-
edge and Data Engineering, 33(4):1328–1347.
Selin, J. (2019). Evaluation of threat modeling methodolo-
gies.
Singh, S., Bhure, S., and van der Veer, R. (2023). Owasp
machine learning security top 10 - draft release v0.3.
Symeonidis, G., Nerantzis, E., Kazakis, A., and Papakostas,
G. A. (2022). Mlops-definitions, tools and challenges.
In 2022 IEEE 12th Annual Computing and Commu-
nication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), pages
0453–0460. IEEE.
ur Rehman, T., Khan, M. N. A., and Riaz, N.
(2013). Analysis of requirement engineering pro-
cesses, tools/techniques and methodologies. Interna-
tional Journal of Information Technology and Com-
puter Science (IJITCS), 5(3):40.
Wang, D., Li, C., Wen, S., Nepal, S., and Xiang, Y. (2020).
Man-in-the-middle attacks against machine learning
classifiers via malicious generative models. IEEE
Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing,
18(5):2074–2087.
Wang, Z., Ma, J., Wang, X., Hu, J., Qin, Z., and Ren, K.
(2022). Threats to training: A survey of poisoning at-
tacks and defenses on machine learning systems. ACM
Computing Surveys, 55(7):1–36.
Worzyk, N., Kahlen, H., and Kramer, O. (2019). Phys-
ical adversarial attacks by projecting perturbations.
In 28th International Conference on Artificial Neu-
ral Networks, Munich, Germany, pages 649–659.
Springer.
Yang, L. and Shami, A. (2020). On hyperparameter opti-
mization of machine learning algorithms: Theory and
practice. Neurocomputing, 415:295–316.
ICISSP 2024 - 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
178
