Aligning Strategies: How Digital Health Technologies Are Used by a
Swiss Insurance Company to Foster a Sustainable Healthcare
Landscape
Alina Liebich
1a
, Livia Jacob
2
and Tobias Kowatsch
1,3,4 b
1
School of Medicine, University of St. Gallen, Switzerland
2
SWICA Krankenversicherung AG, Switzerland
3
CDHI Department of Management, Technology, and Economics, ETH Zurich, Switzerland
4
Institute for Implementation Science in Health Care, University of Zurich, Switzerland
Keywords: Digital Health Technology, Disease Prevention, Integrated Care, Health Insurance.
Abstract: Escalating healthcare costs, as well as an outdated traditional healthcare landscape, are placing considerable
strain on European healthcare systems, pushing society to re-evaluate current business models. Sustainable
solutions require stakeholders to collaborate and innovate. For this Position Paper, we interviewed a
representative of SWICA, one of Switzerland’s largest health insurance companies, to gain insight into their
perspective and expectations regarding the upcoming challenges. The results show that SWICA has developed
a portfolio of multiple digital health technologies to promote an integrated and preventive care approach in
collaboration with new partners in the healthcare system.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recent trends demonstrate an increasing burden of
morbidity (Collaborator, 2020), primarily driven by
an aging population and the rising prevalence of non-
communicable diseases (NCDs), such as
cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer
(Garmany, Yamada, & Terzic, 2021). The associated
escalating healthcare costs, with NCDs accounting
for 80% of these expenses (Wieser et al., 2014), are
placing considerable strain on European healthcare
systems, pushing society to re-evaluate the traditional
healthcare landscape. Several factors, as summarized
in Table 1, have been identified that require
innovative solutions that are sustainable for society
(BAG, 2023; Statistics, 2023).
1.1 A National Strategy Is Required
The Swiss Ministry of Health has developed a
"Health2030" strategy to address these challenges to
alleviate the rising cost and disease burden for the
Swiss population (BAG, 2023). The specific goals
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-2475-2060
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5939-4145
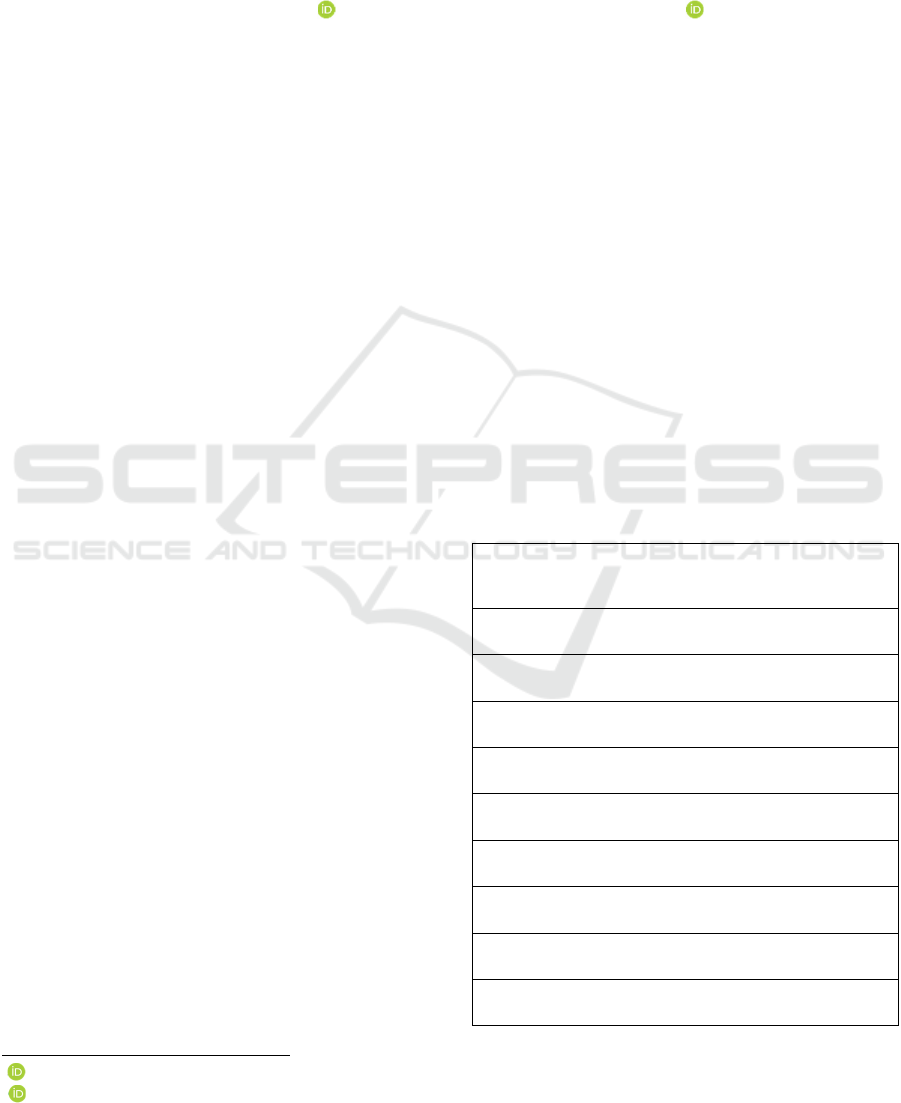
Table 1: Challenges the Swiss healthcare system is facing
(BAG, 2023; Statistics, 2023).
• Inefficient traditional care models, e.g.,
communication between specialists and
community care or data exchange
• "One-size-fits-all" medicine
• Increasing workloads
• Shortage of qualified healthcare professionals
• Untransparent cost structures
• Socioeconomic and geographical disparities
regarding healthcare access and outcomes
• Unmet patient expectations for affordability,
accessibility, and reduced waiting times
• Passive patient participation
• Slowed digitalization of the healthcare sector
compared to other industries
• Higher focus on acute care compared to chronic
care
894
Liebich, A., Jacob, L. and Kowatsch, T.
Aligning Strategies: How Digital Health Technologies Are Used by a Swiss Insurance Company to Foster a Sustainable Healthcare Landscape.
DOI: 10.5220/0012402400003657
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2024) - Volume 2, pages 894-899
ISBN: 978-989-758-688-0; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

include improved health literacy, promotion of
healthy aging initiatives, and increased treatment
quality while guaranteeing the affordability of
healthcare. Traditional models have yet to keep pace
with increased workload (Hickmann, Richter, &
Schlieter, 2022). Therefore, emerging scalable
business models are required to achieve these goals.
The proposed national strategy focuses on preventing
NCDs and implementing digital health technologies
(DHT) (Alliance, 2023), including telemedicine,
mobile health apps, wearable devices, electronic
health records, and artificial intelligence. These
technologies hold the potential to reshape the whole
patient journey from the prevention and diagnosis of
disease, assisted decision support, and personalized
therapy to more efficient disease monitoring and
management (Mumtaz et al., 2023). For the
sustainable implementation of the national strategy,
close collaboration and tight coordination of various
stakeholders, including healthcare insurance
providers, is essential to build the necessary
infrastructure and use resources efficiently (Essén et
al., 2022). For this Position Paper, we partnered with
a representative of SWICA, one of Switzerland’s
largest health insurance companies, to gain insight
into their perspective and expectations regarding the
upcoming challenges.
1.2 Accepting the Challenge
SWICA counts 1.6 million insured individuals and
serves 30,000 business clients, making it one of
Switzerland's leading health insurance companies
(SWICA, 2023b). Established in 1992, it follows the
paradigm of delivering medical care to help its
customers stay healthy, get healthy, and live well with
a disability (SWICA, 2023a). The Company's
primary objective lies in the satisfaction of its
customers, which the Company demonstrated again
in 2023 by ranking first regarding best customer
satisfaction compared to other Swiss health insurers
(SWICA, 2023d). SWICA's primary concern is the
expected demographic change of an aging population.
The Company aims to address the cost implications
of this change with various offerings for its insured
members, ranging from disease prevention and
healthy aging initiatives to extended integrated care
solutions. Most of these offerings are part of
SWICA's digital transformation, which began gaining
traction in 2008 with the launch of the sante24 health
advice telemedicine helpline.
2 METHODS
An initial search about SWICA's history, current
goals, and initiatives was performed using annual
company reports. Afterward, we conducted a semi-
structured online interview with a Senior Digital
Health Specialist at SWICA using Zoom. The
Interview took place on the 5th of October and was
guided by the topics suggested in the Scale-IT-up
2024 workshop (BIOSTEC, 2023). The workshop
explores emerging business models in preventive care
using DHTs. The following section summarizes the
qualitative results obtained in the interview. Further,
we analyzed the new business models around
SWICA’s preventive care efforts using Gassmann’s
Business Model Navigator framework (Gassmann,
2020). A conclusion, including an outlook, follows
the discussion.
3 SWICA’S APPROACH TO
BECOME A SUSTAINABLE
HEALTH INSURANCE
COMPANY
Sustainability can be defined as a governing principle
shaping the activity of a system to preserve resources
(Rashdan & Csepy, 2022). The sustainability of the
Swiss healthcare system is next to environmental and
financial ambitions, one of the four declared
sustainability focus areas of SWICA. Specific goals
include maintaining the health of its members and
improving the quality and efficiency of the healthcare
system (SWICA, 2023c). These goals triggered the
company to redefine its responsibilities as a
healthcare insurer. SWICA`s role has since shifted
from being a traditional health insurer to becoming a
holistic health care organization that plays an active
role in various parts of the lives of its members. The
focus is on offering products and services that have
an additive effect on existing models, as SWICA
wants to avoid direct interference with the work of
traditional healthcare providers. The company aims to
offer solutions characterized by easy accessibility,
scalability, and personal customization. SWICA thus
focused on creating new business models around
DHTs. DHTs allow the incorporation of those three
characteristics. SWICA’s DHT spectrum ranges from
disease prevention to diagnosis and management and
can be structured into two main categories (Figure 1):
(1) DHTs for integrated care and (2) DHTs for
preventive care.
Aligning Strategies: How Digital Health Technologies Are Used by a Swiss Insurance Company to Foster a Sustainable Healthcare
Landscape
895

Figure 1: SWICA’s approach towards becoming a
sustainable health insurance company.
3.1 Integrated Care at the Front
Establishing an integrated healthcare system aims to
promote connections and coordination across
different levels and sites of care within and beyond
the health sector according to the patient’s needs
(Goodwin, 2016). One objective is to support
individuals with chronic or multiple illnesses in
managing their health while identifying and
preventing overuse or gaps in the patient journey.
These advancements are essential to increase
efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the quality of
care. Part of integrated care are Disease-management
programs (DMPs) that primarily cater to chronically
ill patients and patients with multiple diseases. The
goal is to support and integrate them actively in their
patient journey. A recent intervention study of
SWICA demonstrated the positive effects on
treatment quality and hospitalization rates through
intensified DMPs (Carlander, 2021).
3.2 Scale-up Prevention
SWICA offers traditional in-person as well as new
digital prevention solutions. Some target the
prevention of specific diseases, while other, more
general solutions encourage a healthy lifestyle.
General prevention covers well-being, exercise, and
nutrition programs, while specific options include
disease counseling and education. Further, SWICA
subsidizes several external prevention programs
organized by third parties. Some of these prevention
initiatives align with their broader mission to promote
healthy aging. SWICA’s "Demographic
Development and Aging" strategy focuses on the
demographic changes associated with an aging
population. SWICA has actively created new
products and business models to alleviate age-related
health challenges as part of this strategy. The target
population for individual projects, such as "Health
Promotion Golden Age," comprises insured
individuals aged 60 and above. SWICAs own
offerings in that domain include mainly the use of
DHTs. However, they also cooperate with partners,
such as the University Hospital of Zurich or Spitex, a
local care provider, to offer in-person support.
SWICA also has a dedicated “Health in Aging”
section on its website and hosted the 2023 SWICA
Symposium on “Health in Aging,” uniting academics
and industry representatives to explore future
solutions. These efforts highlight the holistic
approach to promoting healthy aging, encouraging
customer self-empowerment and education while
actively supporting health engagement through
innovative product offerings.
3.3 Tightening the Knots with New
Partners
SWICA acknowledges that many aspects are beyond
the company's control or capacity. This includes
aspects such as medical care reimbursement or
technical innovation expertise. SWICA, therefore,
believes in interprofessional collaborations to
develop new business models with various partners in
preventive and integrated care initiatives. The
company depends on new partners to successfully
implement SWICA’s ambitions and positions itself as
a co-creator of new structures. On several projects,
SWICA cooperates with other stakeholders in the
Swiss healthcare industry to use resources efficiently
and ease the way for a common sustainable health
landscape. The development of new DHTs primarily
relies on external innovations and collaborations with
other stakeholders.
4 HALLMARKS OF EMERGING
BUSINESS MODELS- AN
ANALYSIS
A business model reflects the firm's strategy
(Casadesus-Masanell, 2009). SWICA’s ambition is to
make prevention successful and reduce the misuse of
healthcare resources. The company has, therefore,
developed multiple DHTs targeting disease
prevention and extending its integrated care
approach. In the following section, we used
Gassmann’s Business Model Navigator framework to
assess the individual DHTs SWICA chose to
implement its strategy (Gassmann, 2020). His model
consists of four dimensions:
Healthcare
Sustainability
Integrated
Care
Preventive
Care
Scale-IT-up 2024 - Workshop on Emerging Business Models in Digital Health
896

• WHO are the target customers?
• WHAT is offered to them?
• HOW is the value created?
• WHY does it generate value?
4.1 DHTs for Integrated Care
SWICA combines different technologies to promote
integrated care solutions for its customers. Its focus
lies on telecommunication and app-based product
offerings.
4.1.1 Telemedicine Advanced
One of SWICA's first and most used DHTs is the
Sante24 telemedicine service, which was launched in
2008 and works as an independent center, offering
various products concerning disease prevention,
diagnosis, and management. All insured individuals
may call Sante24 24/7 without any cost incurred and
are initially guided by a health coach. The patient will
be directed to a doctor for further consultation if
necessary. Members benefit from medical
consultation and coaching. Through telemedicine, the
barrier to receiving medical expertise is lowered
significantly (Haleem, Javaid, Singh, & Suman,
2021). SWICA expects that by offering the
telemedical service free of charge, healthcare costs in
the traditional system will be saved, and overall costs
for SWICA will be reduced. Sante24 is supported by
other DHTs developed by SWICA, strengthening the
digital integrated care approach.
Another telemedicine tool is the TytoHome
device. Initially an Israeli startup, it enables
customers to conduct home-based examinations and
share the results with santé24 autonomously. The
target audience includes families with young
children, but all insured members can order a
TytoHome device for a fee. Members no longer need
to go physically to a doctor, as this DHT integrates
them actively in the diagnosis process. The cost
depends on their insurance coverage, while subsequent
usage and telemedical consultations are free.
4.1.2 An App-Based Integrated Care Model
Through SWICA’s Benecura app, the patient may do
a digital symptom check-up, for example, on their
phone, and share the results with their Sante24 coach,
making the anamnesis process for the doctor and
patient more efficient. The app is a triage tool to
assess urgency, prepare the patient, and recommend
the next steps. Further, it allows the user to save and
share all his medical records in a digital format, with
the required data security structure integrated. The tool
increases efficiency and simultaneously enhances
patient autonomy. Benecura is free for insured
members, and approximately 50,000 of them have used
it so far. The project is funded through SWICA's IT
budget. The whole project aims to increase financial
efficiency in the long run and increase customer
satisfaction for the company. SWICA is also working
on versions specifically tailored to chronically ill
patients, such as COPD patients. In these cases, the
questionnaires are intended for ongoing disease
monitoring, allowing doctors to detect therapy-relevant
changes early to support their DMPs. In the future, the
Benecura app will integrate the five most critical
chronic diseases to improve disease monitoring.
4.2 DHTs for Disease Prevention
SWICA has developed its products as summarized in
Table 2, that encourage a generally healthy lifestyle.
Additionally, SWICA is benefitting from synergies
with the offerings of Sante24 to support its members
in staying healthy. All members have access to
SWICA’s prevention programs. SWICA hopes to
attract healthy future customers and maintain health
among its insured people, thus saving healthcare costs
in the long run. Benevita is an app that was released
in 2020. It acts as a digital health coach and engages
the participants through exercise, nutrition, and well-
being challenges. Customers may earn points in the
challenges that lead to premium discounts or can be
converted into digital vouchers or donated to
charitable causes.
Table 2: An overview of DHTs aiming to prevent disease
and their delivery mode.
Product Domain Delivery mode
Benevita
• Exercise
• Nutrition
• Well-
b
ein
g
• App
Fall
prevention
• Exercise
• Nutrition
• Medical therapy
• Telemedicine
• Video tutorial
• Online self-
assessment
Prevent
sleep
disorders
• Sleep hygiene • Telemedicine
• Online self-
assessment
• Online education
Sport
Classes
• Pilates
• Yoga
• Specific
Exercises
• Youtube Video
Coach
• Nutrition
• Medication
• Exercise etc.
• Telemedicine
Aligning Strategies: How Digital Health Technologies Are Used by a Swiss Insurance Company to Foster a Sustainable Healthcare
Landscape
897

More specific DHTs include a fall prevention
program conducted in collaboration with santé24 and
uses an online assessment on the website to identify
at-risk individuals and provide help through
telephone counseling.
5 THE POTENTIAL OF DHTS TO
ALIGN STRATEGIES WITHIN
THE HEALTHCARE
LANDSCAPE
In their Four Steps to Sustainable Business Model
Innovation Guide, Boston Consulting Group
Managing Director David Young highlights the
importance of listening to external stakeholders
(Young, 2021). SWICA has not only heard the Swiss
Ministry of Health’s call for action but has
internalized the stated goals of improved health
literacy, promotion of healthy aging initiatives, and
increased quality of affordable healthcare in its core
business model. To tackle the challenges stated in
Table 1 successfully, SWICA’s strategy has been to
build up a growing portfolio of DHTs that are, in their
nature, easily accessible and scalable while
simultaneously benefitting from synergies. DHTs
focusing on integrated and preventive care, such as
the Benecura App, Benevita App, and Sante24
Telemedicine service, aim to increase efficiency in
the Swiss healthcare system by reducing workloads
of traditional healthcare models while improving
healthcare accessibility and shifting the focus on
chronic care. Further, most tools require the user's
participation, empowering members to become active
in their health journey. Other health insurance
companies, such as the CSS, are joint in these efforts
and follow a similar approach to align with the
national strategy (CSS, 2023).
SWICA’s DHTs share a common approach to
business model innovation as they overlap in the
WHO and WHY dimensions of Gassmann’s business
model navigator framework (Gassmann, 2020). All
DHTs are directly targeted at members to establish a
personal interaction and are expected to raise a return
on investment through long-term cost savings. The
values created for the members range from increased
patient empowerment to better health and improved
access to medical care if needed.
6 CONCLUSION
Escalating healthcare costs and an outdated
traditional healthcare landscape are placing
considerable strain on European healthcare systems,
pushing society to re-evaluate current business
models. Sustainable solutions require stakeholders to
collaborate and innovate. SWICA has demonstrated
through various initiatives that it views itself as a key
stakeholder in the fight against NCDs and has taken
responsibility to actively co-create part of the solution
within its dimensions through DHTs. In the future,
SWICA aims to design more specific DHTs for
chronically ill patients. However, to achieve a
meaningful contribution towards a sustainable
healthcare system, SWICA should aim to increase the
adoption of these new DHTs by its insured
individuals in the future.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
AL and TK are affiliated with the Centre for Digital
Health Interventions (CDHI), a joint initiative of the
Institute for Implementation Science in Health Care,
University of Zurich; the Department of
Management, Technology, and Economics at Swiss
Federal Institute of Technology in Zürich; and the
Institute of Technology Management and School of
Medicine at the University of St Gallen. CDHI is
funded in part by CSS, a Swiss health insurer, MTIP,
a Swiss investor company, and MavieNext, an
Austrian healthcare provider. TK is also a co-founder
of Pathmate Technologies, a university spin-off
company that creates and delivers digital clinical
pathways. However, neither Pathmate Technologies,
CSS, MTIP nor MavieNext was involved in this
research.
REFERENCES
Alliance, D. T. (2023). Digital Health Technology
Ecosystem Categorization. Retrieved from https://dtxa
lliance.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/DTA_FS_DH
T-Ecosystem-Categorization.pdf
BAG, B. f. G. (2023). Gesundheitspolitische Strategie des
Bundesrats 2020–2030. Retrieved from https://www.
bag.admin.ch/bag/de/home/strategie-und-politik/gesun
dheit-2030/gesundheitspolitische-strategie-2030.html
BIOSTEC. (2023). Workshop on Emerging Business
Models in Digital Health—Scale-IT-up 2024. Scale-IT-
up 2024. Retrieved from https://biostec.scitevents.
org/Scale-IT-up!.aspx
Scale-IT-up 2024 - Workshop on Emerging Business Models in Digital Health
898

Carlander, M. (2021). SWICA Disease Management
Programm Diabetes Mellitus. Retrieved from
https://digitalcollection.zhaw.ch/bitstream/11475/2195
6/3/2021_Carlander-etal_Wissenschaftliche-
Begleitevaluation-2021.pdf
Casadesus-Masanell, R. (2009). From Strategy to Business
Models and to Tactics. Harvard Business School.
Collaborator, G. D. a. I. (2020). Global burden of 369
diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories,
1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden
of Disease Study 2019. Lancet (London, England),
396(10258), 1204-1222. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)
30925-9
CSS. (2023). Geschäftsbericht 2022.
Essén, A., Stern, A. D., Haase, C. B., Car, J., Greaves, F.,
Paparova, D., Bates, D. W. (2022). Health app policy:
international comparison of nine countries’ approaches.
npj Digital Medicine, 5(1), 31. doi:10.1038/s41746-
022-00573-1
Garmany, A., Yamada, S., & Terzic, A. (2021). Longevity
leap: mind the healthspan gap. npj Regenerative
Medicine, 6(1), 57. doi:10.1038/s41536-021-00169-5
Gassmann, O., Frankenberger, K., & Choudury, M. (2020).
The Business Model Navigator: The strategies behind
the most successful companies (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle
River, NJ: FT Press. (2020). The Business Model
Navigator: The strategies behind the most successful
companies (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River: NJ: FT Press.
Goodwin, N. (2016). Understanding Integrated Care. Int J
Integr Care, 16(4), 6. doi:10.5334/ijic.2530
Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Singh, R. P., & Suman, R. (2021).
Telemedicine for healthcare: Capabilities, features,
barriers, and applications. Sens Int, 2, 100117.
doi:10.1016/j.sintl.2021.100117
Hickmann, E., Richter, P., & Schlieter, H. (2022). All
together now - patient engagement, patient empower-
ment, and associated terms in personal healthcare. BMC
Health Serv Res, 22(1), 1116. doi:10.1186/s12913-022-
08501-5
Mumtaz, H., Riaz, M. H., Wajid, H., Saqib, M., Zeeshan,
M. H., Khan, S. E., Vohra, L. I. (2023). Current
challenges and potential solutions to the use of digital
health technologies in evidence generation: a narrative
review. Frontiers in Digital Health, 5.
doi:10.3389/fdgth.2023.1203945
Rashdan, O., & Csepy, G. (2022, 2022//). Sustainable
Business Models in Healthcare: A Scoping Review of
the Quality and Quantity of Literature. Paper presented
at the Sustainable Finance in the Green Economy,
Cham.
Statistics, E. (2023). Unmet health care needs statistics.
Retrieved from https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-
explained/index.php?title=Unmet_health_care_needs_
statistics#Unmet_needs_for_health_care
SWICA. (2023a). Die SWICA Gesundheits-organisation.
Retrieved from https://www.swica.ch/de/ueber-swica/
portrait/ueberblick
SWICA. (2023b). Geschäftsbericht 2022.
SWICA. (2023c). Geschäftsbericht Nachhaltigkeit.
Retrieved from https://report.swica.ch/de/bericht/nach
haltigkeit/
SWICA. (2023d). Nr. 1 Kundenzufriedenheit. Retrieved
from https://www.swica.ch/de/private/warum-swica/
kundenzufriedenheit
Wieser, S., Tomonaga, Y., Riguzzi, M., Fischer, B., Telser,
H., Pletscher, M., Schwenkglenks, M. (2014). Die
Kosten der nichtübertragbaren Krankheiten in der
Schweiz: Schlussbericht. Retrieved from Bern:
https://digitalcollection.zhaw.ch/handle/11475/14988
Young, D. (2021). Four Steps to Sustainable Business
Model Innovation. ustainable Business Model
Innovation. Retrieved from https://www.bcg.com/publi
cations/2021/four-strategies-for-sustainable-business-
model-innovation
Aligning Strategies: How Digital Health Technologies Are Used by a Swiss Insurance Company to Foster a Sustainable Healthcare
Landscape
899
