
GOLOG++ Hits the (Right) Spot: Interfacing Golog with a Quadruped
Rescue Robot for High-Level Missions
Maximillian Kirsch, Shubham Pawar, Alexander Ferrein
a
and Stefan Schiffer
b
Mobile Autonomous Systems and Cognitive Robotics Institute (MASCOR),
Keywords:
Robot High-Level Control, Mission Level Planning, GOLOG, ROS, Quadruped Robot.
Abstract:
The Robot Operating System has become the de facto standard middleware in the robotics field. ROS offers
a large variety of state-of-the-art algorithms and solutions for robotics problems ranging from localisation to
manipulator control. For most robot systems available on the market, a ROS or ROS2 driver exists. When it
comes to high-level control, relatively few packages and approaches exist inside the ROS ecosystem. In this
paper, we report on our efforts to integrate the well-known action language GOLOG with ROS2 in order to
enable rescue missions for our Boston Dynamic Spot robot in the RoboCup Rescue scenario.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Robot Operating System (ROS and ROS2 (see
e.g. (Maruyama et al., 2016))), has become
the de facto standard middleware in the robotics
field. With initiatives like ROS-Industrial
1
indus-
trial robot manufacturers acknowledge the potential
of ROS and ROS2, respectively, as a robot middle-
ware. The Github repository "vmayoral/ros-robotics-
companies"
2
mentions more than 900 companies that
make use of ROS. ROS offers a large variety of state-
of-the-art algorithms and solutions for robotics prob-
lems ranging from localisation to manipulator con-
trol. For most robot systems available on the market,
a ROS or ROS2 driver exists.
In contrast to this, the variety of ROS pack-
ages for high-level missions of mobile autonomous
robots is quite limited. There exists some ROS
packages for formulating finite state machines such
as RAFCON (Brunner et al., 2016), the package
behaviour_tree (Segura-Muros and Fernández-
Olivares, 2017) for behaviour trees, or the PDDL-
based rosplan package (Cashmore et al., 2015).
While it is not an official ROS package, an-
other PDDL-based planning package is available,
which interfaces the production system CLIPS with
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0643-5422
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1343-7140
1
https://rosindustrial.org/
2
https://github.com/vmayoral/ros-robotics-companies
ROS (Niemueller et al., 2019).
On the other hand, there are many control lan-
guages from the autonomous agent or cognitive
robotics community, but they have not yet found their
ways into the ROS ecosystem in numbers.
In this paper, we report on our efforts to integrate
the well-known action language GOLOG (Levesque
et al., 1997) with ROS2 in order to enable rescue
missions for our Boston Dynamic Spot robot in the
RoboCup Rescue scenario (Kitano and Tadokoro,
2001).
In order to solve the problems proposed in the
RoboCup rescue scenario, our Spot is equipped with
additional sensors and a manipulator. We developed
a ROS2 driver for the Spot in cooperation with the
Boston Dynamic AI Institute.
3
A paper describing
the features of the ROS2 Spot driver is in preparation.
Our GOLOG/ROS2 integration is based on our
previous work on golog++ (Mataré et al., 2021;
Kirsch et al., 2020). The contribution in this paper
is two-fold. We describe the golog++/ROS2 integra-
tion in detail showing how high-level actions can be
executed as ROS action servers. Also as a running ex-
ample, we show how the famous blocksworld task is
solved by Spot with our manipulator using GOLOG
and ROS2 deploying a decision-theoretic planning
approach.
In the next section, we discuss related work in
the area of action-based high-level and planning ap-
3
See https://github.com/bdaiinstitute/spot_ros2 for the
GitHub Repo.
1052
Kirsch, M., Pawar, S., Ferrein, A. and Schiffer, S.
GOLOG++ Hits the (Right) Spot: Interfacing Golog with a Quadruped Rescue Robot for High-Level Missions.
DOI: 10.5220/0012433400003636
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2024) - Volume 3, pages 1052-1059
ISBN: 978-989-758-680-4; ISSN: 2184-433X
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

proaches for mobile robot and in particular related
work about GOLOG. The golog++ system is outlined
in Section 3. In Section 4, we make a walk-through
the blocksworld program, before we give the details
of integrating golog++ with ROS2 in Section 5. We
conclude with Section 6.
2 RELATED WORK
Related to this work is also the rich body of papers
about different extensions of the original GOLOG
language (Levesque et al., 1997). With its origi-
nal semantics based on the Situation Calculus (Mc-
Carthy, 1963), GOLOG is well-suited for modelling
behaviours in dynamically changing worlds. It has
been deployed in a wide variety of tasks ranging from
semantic web applications (McIlraith and Son, 2001)
or domestic robot applications (Schiffer et al., 2012)
to robotic soccer (eg. (Ferrein et al., 2005)). Exten-
sions include to deal with exogenous events, concur-
rency, allow for decision-theoretic planning, or con-
tinuous changes in the world, to name but a few (see,
for instance, (De Giacomo et al., 2009; Boutilier et al.,
2000) for further details). While classical implemen-
tations of GOLOG are based on Prolog, there have
also been attempts to utilize alternative interpreters,
(eg. (Eckstein and Steinbauer, 2020)).
Outside of the GOLOG community, we see more
diverse approaches to high-level interfacing. The Se-
mantic Robot Description Language (SRDL) (Kunze
et al., 2011) implements a framework that describes a
robot platform with its components, and how they can
be used to realize certain actions. As such, it serves
a different purpose, namely mapping an abstract ac-
tion concept to a realization strategy on a particular
robot platform. To the framework we envision here,
actions are opaque units, so a system like SRDL could
be used as an action execution backend.
PRS/OpenPRS (Ingrand et al., 1996) and the
ecosystem around them are worth noting because they
also serve the purpose of a high-level control lan-
guage, but found much wider use than any GOLOG
dialect. However PRS does not set itself apart through
better theoretical foundations or through greater ex-
pressivity. The issue where PRS clearly has the lead
on any GOLOG dialect is usability, developer support,
integration, i.e. tool support in general.
The same applies to the C-Language Integrated
Programming System (CLIPS, cf. (Wygant, 1989)).
From a theoretical point of view, the language should
be less expressive and less practical for high-level
control application than GOLOG. But nonetheless, it
is used much more widely
4
. While some of CLIPS’
lead on GOLOG could be explained by the more gen-
eral, rule-based language paradigm, its clear advan-
tages are still a coherent language specification and
well-designed, stable C/C++ bindings.
3 GOLOG++
3.1 System Overview
golog++ is a framework designed for the execution
of the action-based logic language GOLOG on real
robots. It focuses on enhancing usability and plat-
form interfacing by addressing three key global sys-
tem concerns: the representation of a GOLOG pro-
gram, both static and runtime semantics, and act-
ing/sensing functionalities.
golog++ defines a specific syntax and comes with
a parser, which transforms the agent program code
into a metamodel implemented in C++ (Mataré et al.,
2021). This metamodel serves both, for keeping a
static representation of the program and for storing
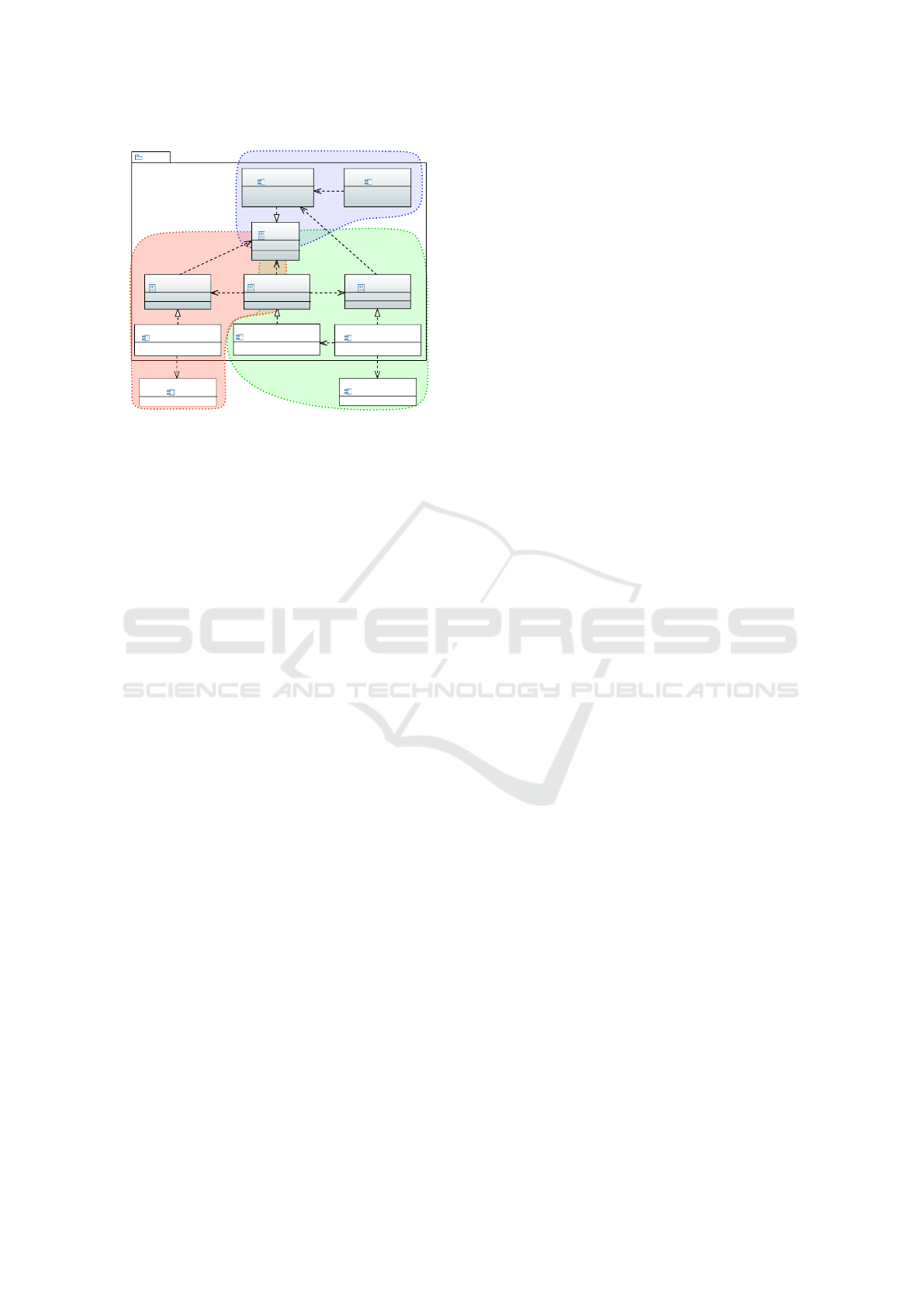
the program state while executing a program. Fig-
ure 1 gives an overview of the system architecture.
The static part (shown in blue in Figure 1) consists
of the parser and the static metamodel. As one can
see from the figure, the front-end in blue is com-
pletely separated from the semantic backend part in
the architecture. This was one of the design goals
of golog++, as previous implementations of GOLOG
in Prolog were mixing up implementation details
of the interpreter with the GOLOG language. This
also has the advantage that the execution model of
golog++ can be changed in the background without
the need to modify the GOLOG programs. Currently,
for the backend implementation, READYLOG (Ferrein
and Lakemeyer, 2008) is deployed. To facilitate its
functionality, golog++ embeds the eclipse-clp inter-
preter (Schimpf and Shen, 2012), loads READYLOG
and uses its Semantics for runtime implementation.
The ReadylogSemantics creates Transitions, and once
a legal transition is identified, it is then passed to the
PlatformBackend, which specifically handles acting
and sensing tasks.
golog++ provides both a ROS1 and a ROS2 plat-
form backend for executing actions on real robots.
During the execution of an agent the ExecutionCon-
text will inform the RosPlatformBackend, when an
action has to be executed. The RosPlatformBackend
4
See also 418 questions tagged “clips” on stackoverflow
(stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/clips) vs. 2 questions
tagged “golog”
(stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/golog).
GOLOG++ Hits the (Right) Spot: Interfacing Golog with a Quadruped Rescue Robot for High-Level Missions
1053
runtime
semantics
representation, static semantics
«component»
readylog interpreter
golog++
«component»
metamodel
«Interface»
Semantics
acting/sensing
«component»
EclipseExecutionContext
«component»
parser
«component»
RosPlatformBackend
«component»
ReadylogSemantics
«Interface»
Transition
«Interface»
PlatformBackend
«Interface»
ExecutionContext
«component»
ROS
«use»
«use»
construct
«use»
«use»
«use»
Figure 1: System architecture of the Framework golog++.
during(grab(banana)) {
say("Trying␣to␣grab␣banana.");
} on_fail {
say("Failed␣to␣grab␣banana.");
} on_cancel {
say("Grabbing␣attempt␣cancelled.");
}
Figure 2: Concurrent tasks.
accepts the call from the ExecutionContext, executes
the action and responds with the outcome and an op-
tional result.
3.2 Language Constructs
golog++ contains imperative instructions common to
classical programming languages and to GOLOG di-
alects. Actions in golog++ are imperative statements
that can be executed within a while-loop, a condi-
tional branch, and within a concurrent block to han-
dle multiple imperative branches in parallel. They can
also be executed within an ordinary code block, both
asynchronously and synchronously.
An action be can executed concurrent, and its out-
come and status can trigger reactions such as a suc-
ceed, failed and cancel case. This capability can be
used to create finite automata with golog++. See Fig-
ure 2 for an example.
Two instructions for nondeterminism are foreseen
that are intended to be used within a planning in-
struction block, where they will be resolved in such
a way that the entire block becomes executable. One
instruction involves non-deterministic choice over an
imperative statement, while the other involves select-
ing an argument for a given code block, for instance,
as an argument in an action call.
Using the test(b) instruction, the agent will halt
until the boolean expression b evaluates to true. When
combined with an exogenous event that can set a
exog_action
order_received(string what,number id){
mapping:
"OrderInterface" {
order_name = what,
order_id = id
}
effect:
pending_order(id) = what;
}
Figure 3: Exogeneous action exmaple.
symbol domain block = {a, b, c}
symbol domain location =
block | {t1, t2, t3}
location fluent loc(block x) {
initially:
(a) = t1;
(b) = t2;
(c) = t3;
}
Figure 4: Location fluent.
boolean within its effect, this test(...) instruction can
effectively control the execution of an action within a
concurrent branch by causing a block in the program
flow. See Figure 3 for an example from a logistic
scenario, where the robot waits for an external order,
which is beyond its own control, is being received.
4 THE BLOCKSWORLD
EXAMPLE
The Basic Action Theory (BAT) outlines the relevant
subjects in the world along with the actions available
to a robot, including their preconditions and effects.
It specifies the preconditions necessary for their ex-
ecution and describes how these actions affect the
world. In the following we outline the BAT for the
blocksworld scenario. The task for the robot is to
stack three blocks that are laid out in front of it in
any order to a tower, where the blue block is on top,
then comes the green block, and the red block is at the
bottom.
First, we define the relevant fluents. In our case
only the location of the blocks a, b, c (Figure 4). To
define the blocks, golog++ offers a domain which is
a typified set of values that can be used to restrict the
possible arguments of an action or a fluent. With a
compound list, elements can be iterated together using
the pick statement. The elements t1, t2, t3 are utilized
for locations on the table, facilitating easier control of
the manipulator. The fluent loc evaluates the current
location of a specified block and establishes the ini-
tial situation. The initial configuration of loc can be
altered prior to executing the planner.
This can be accomplished through active/passive
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1054

action update_block_pose(block x) {
senses:
loc_response() =
sense_result("/get_block_pose");
mapping:
"/get_block_pose" {
block = x
}
effect:
loc(x) = sym_to_loc(loc_response());
}
(a) Active sensing action.
action stack(block x, location y) {
precondition:
x != y
& loc(x) != y
& (!exists(block z) loc(z) == x)
& (!exists(block z) loc(z) == y)
mapping:
"/stack" {
block = x,
location = y
}
effect:
loc(x) = y;
}
(b) Stack Action.
Figure 5: Examples of actions in the blocksworld scenario.
sensing actions. In our blocksworld scenario, we opt
for an active sensing action to update the location of
the blocks on the table before creating an action se-
quence.
Thus, the initial location of the blocks is adapt-
able. The action update_block_pose() (Figure 5a) takes
a block as an argument and has no preconditions.
Within the senses field, one single sensing result can
be provided, allowing for a single assignment instruc-
tion.
Each active sensing result is generated by an exog.
function with an argument, mapping to the low-level
action that returns the result. On the right side of the
assignment, we utilize the exog_function sense_result()
with an argument leading to a ROS2 action. On the
left, side we store the outcome of the low-level action
in a temporary fluent. The effect updates the location
of the block to our fluent loc() after converting to the
symbol to location type (Figure 6).
The mapping specifies the actual action that should
be triggered in the platform backend to execute a
given action, along with how its arguments should
be passed on (Figure 5b). The action stack(x, y)
(Figure 5b) accepts arguments of the domain, namely
location and block. The precondition is defined by an
arbitrary Boolean formula that determines when the
action becomes executable, such as when a block can
be placed in a specific location.
In the mapping field, the name "/stack" directs the
platform backend to a ROS2 action, utilizing the ar-
symbol exog_function
sense_result(string ros_action_name);
symbol fluent loc_response() {
initially:
() = a;
}
location function
sym_to_loc(symbol sym) = sym
Figure 6: Function for handling sensing results.
guments of block x and location y as parameters to per-
form the low-level instructions for the manipulator.
The effect assigns the updated location of block x.
The main procedure is shown in Figure 7. Both
imperative and declarative instructions for planning
are employed within the program’s procedures. Every
golog++ agent starts in the procedure main(){...} and
can invoke or branch to other procedures using the
concurrent instruction.
An action can be executed with the start(...) state-
ment for asynchronous execution and with end(...)
defining when the action has to finish. With
during(...) construct concurrent tasks are also possi-
ble and enable error handling to react on a failed or
cancelled action.
Once an action is executed, it can fail. During on-
line execution the program will block if an impossi-
ble instruction is encountered whereas during offline
planning, the search will backtrack until all possibili-
ties have been exhausted.
The solve(h, f){...} statement finds executable
choices for all nondeterminism within the impera-
tive code that results in the highest cumulative re-
ward function f. Thereby the search depth is limited
to the horizon h. The nondeterminism is realised by
the statements choose{...} selecting one of the given
statements inside that block and pick(...) to choose
an argument for the given imperative statements like
actions.
5 INTERFACING GOLOG++
WITH SPOT
To solve the blocksworld with a real robot, low-level
actions have to be implemented. The robot should ini-
tially approach the table, utilise its sensors to identify
the locations of the blocks, and finally, employ the
manipulator to pick up and place the blocks. In or-
der to execute actions using golog++, it is necessary
to interface low-level implementations, such as ROS2
actions and services, with the RosPlatformBackend
(inside the red area of acting/sensing in the architec-
ture overview shown in Figure 1).
GOLOG++ Hits the (Right) Spot: Interfacing Golog with a Quadruped Rescue Robot for High-Level Missions
1055

bool function goal() =
loc(b) == a & loc(c) == b
number function reward() =
if (goal()) 100
else -1
procedure main() {
update_block_pose(a);
update_block_pose(b);
update_block_pose(c);
start(navigateToFrame("target"));
setManipulatorJoints(0, 36, -84, 0, -60, 90);
end(navigateToFrame("target"));
solve(8, reward())
while (!goal())
pick (block x in {a, b, c})
pick(location y in {t1, t2, t3, a, b, c})
stack(x, y);
setManipulatorJoints(0, 15, -130, 0, 55, 90);
setManipulatorJoints(0, -105, -148, 0, -60, 90);
}
Figure 7: The Main Procedure of our blocksworld agent.
The Spot ROS2 driver provides all functions
of Spot by topics, services, and actions and can
be directly connected with the RosPlatformBackend.
However, for the blocksworld, additional actions are
necessary such as detecting the location of the blocks
and controlling the manipulator.
To detect the blocks and approach the table, we
have implemented ROS2 services and actions to de-
tect AR tags positioned on both the blocks and the
table. The manipulator, a Kinova Gen3, is controlled
using the ROS MoveIt package and compound actions
and services to execute a stack(x,y) action, which pro-
vides the ability to place a block at a specific location.
The purpose of the Spot ROS2 driver is to map
the functionalities accessible via the Spot SDK/API to
ROS2 functionalities as actions, services and topics.
Thereby the driver is represented as a ROS2 node, an
executable process, that is able to communicate with
different nodes, like a golog++ agent. For instance,
the Spot ROS2 driver launches a service server for
stand and sit. Upon request, it creates a message filled
with instructions for commanding Spot to stand up or
sit down, sends the message, and waits for a reply.
The Spot SDK offers access to every function that
can be executed via the operator tablet that comes
with the robot over a Python or C++ API. Notably,
there is no complete control over all functions, in-
cluding access to motors. Instead, multiple services
are running internally, which can be accessed over a
LAN or WiFi connection. When establishing a con-
nection with Spot, protobuf messages has to be gener-
ated and sent to Spot via a client/server model, using
its SDK. Using the ROS2 driver eliminates the need
to learn the intricacies of the Spot SDK and reduces
the effort required to utilize other ROS2 packages.
The RosPlatformBackend
The RosPlatformBackend is a ROS2 package which
contains a node to load a golog++ program. To exe-
cute low-level actions triggered by the golog++ agent
program, this node has to be modified to establish a
connection between them. golog++ defines, with the
PlatformBackend as an abstract class, how an action
has to be executed and which functions require a real
implementation when executing on a real robot.
When the agent is executed and it decides that a
certain action has to be executed, a function exe-
cute_activity() is called. This function passes an
activity containing the mapping as unique name and
possible arguments used for parameterization of the
action. Once an action is executed, golog++ waits for
the outcome. When the action is completed, a func-
tion must be called to inform the agent if the action
either SUCCEEDED, FAILED or was CANCELLED.
When passing this outcome, it is possible to pass one
value from the low-level action as sensing result: a
string, int, bool or float.
Exogenous event are incidents that occur within
the robot’s environment, and the agent can to react on
those event. A ROS2 message on a topic that triggers
the exogenous event inside the agent can be filled with
parameters. Those parameters can be converted to
golog++ values and used to set fluents in the effects
of the exog_action.
To enhance the usability of the interface and re-
duce boilerplate code, the RosPlatformBackend de-
fines Action-/ Service- and ExogManager as template-
classes. In golog++ durative actions are re-
alised by using the keyword start(action(args)) and
end(action(args)). Between those commands differ-
ent actions can be executed. However, in ROS2, the
implementation of action execution is seperated with
ROS2 actions, and services. The ActionManager and
ServiceManager encapsulates the interface and exe-
cution with ROS2 action execution. A user only has
to create a single function for every action, which is
always about the conversion of a golog++ value to a
ROS2 message or vice versa.
These Manager template-classes generate clients
for ROS2 action or service server that must imple-
ment the low-level actions. Also, all necessary func-
tions to start and wait for the end of an action are gen-
erated.
For instance, every underlying ROS2 action has to
implement the build_goal() function, which maps,
in our example, the arguments of the stack action to a
goal message for a ROS2 action server. In the fu-
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1056

ture we plan to overcome this last repetitive boiler-
plate code with ROS2 introspection.
ActionManager: The mapping of the action stack()
is shown in Figure 8. Inside mapping field, the first
statement has to be the topic name of the correspond-
ing action or service server as string.
When execute_activity() is called inside the Ros-
PlatformBackend it passes an activity storing the
mapping of an action, such as the topic name. This
name is used to find the corresponding ActionMan-
ager object, which handles the execution. To cre-
ate an ActionManager object, the ROS2 action type
has to be passed as template argument, along with the
topic name of the corresponding action server(Figure
8a line 1).
Then a mapping for the arguments has to be cre-
ated. In the BAT, on the right side of the assignment,
the arguments of the action itself are listed (yellow).
On the left side, unique names must to be selected.
Through these unique name, the values of the argu-
ments can be accessed inside the RosPlatformBack-
end.
To interface with an existing ROS2 action server,
an explicit function called build_goal() has to be im-
plemented. This function maps those golog++ argu-
ments to variables of a ROS2 goal message. These
arguments have to be cast into a ROS2 message data
type. Therefore, depending on the datatype of the
golog++ value, different casts must be performed
(e.g. string, int, float, bool).
This goal message is send to the ROS2 action
server (Figure 8c), which utilizes the arguments to de-
cide where to place which block. The ROS2 action
server have to set a outcome either to SUCCEEDED,
FAILED or CANCELLED. When the server finishes, a
callback inside the RosPlatformBackend is triggered
which passes this outcome to golog++.
The ActionManager executes every action asyn-
chronously, and it is decided inside the golog++
agent whether to start an action synchronously or
asynchronously.
ServiceManager: In our blocksworld ex-
ample, we employ active sensing with the
action update_block_pose(block x) (Figure 5a) to update
the location of the blocks in our agent from the ROS2
ecosystem. This sensing action is implemented as
a ROS2 service, and it will only return a block or a
table position for a given block.
Despite the implementation of a ROS2 service that
provides a location, the RosPlatformBackend only re-
quires an explicit template function, build_request(),
to convert a ROS2 message value into a golog++
action stack(block x , location y ) {
precondition:
x != y
& loc(x) != y
& (!exists(block z) loc(z) == x)
& (!exists(block z) loc(z) == y)
mapping:
" /stack " {
block = x ,
location = y
}
effect:
loc(x) = y;
}
(a) Agent stack action mapping.
create_ActionManager<spot_msgs::action::Stack>(" /stack ");
template<>
ActionManager<spot_msgs::action::Stack>::GoalT
ActionManager<spot_msgs::action::Stack>::
build_goal(const gpp::Activity &a) {
auto goal = spot_msgs::action::Stack::Goal();
goal.block =
std::string(a.mapped_arg_value(" block "));
goal.location =
std::string(a.mapped_arg_value(" location "));
return goal;
}
(b) Stack action mapped to ROS2 action server in RosPlat-
formBackend.
def begin_stacking( stack_gh ):
block = stack_gh.request.block.lower()
location = stack_gh.request.location.lower()
# Calculate target angle
target_angles, sec, nanosec =
service_client.send_request(block, location,
is_block=True,
is_above=True)
# Set target angle
moveit_action_client.send_goal(target_angles, sec, nanosec)
action_server = ActionServer(
stacker_node,
Stack,
’ /stack ’,
begin_stacking)
(c) ROS2 action server executes goal to stack blocks.
Figure 8: Interfacing the ROS2 Action Manager.
value for interfacing with this sensing action. This
function is mandatory like the build_goal function of
the ActionManager.
A ROS2 service server can provide a result in
its response message. When setting the outcome for
golog++, the result inside the response of the service
can be passed along. Therefore the template function
to_golog_constant has to be overridden and the result
converted into a golog++ value.
Within the agent, this result will be available with
the type and value created from a ROS2 message con-
verted with this function. In this context, the location
GOLOG++ Hits the (Right) Spot: Interfacing Golog with a Quadruped Rescue Robot for High-Level Missions
1057

(a) Boston Dynamics’ Spot solving blocksworld. (b) Visualisation of the robot’s world state on a handheld
controller.
Figure 9: The blocksworld task in real world.
provided from a response of a service server is stored
in a SymbolType.
ExogManager: For our blocksworld example, no
exogenous event is necessary. However, to use a
exog_action an ExogManager has to be created in-
side the RosPlatformBackend. The ExogManager ob-
ject is bound to a ROS2 topic and it will invoke the
exog_action inside the agent every time a message is
published to that topic. Therefore, a node is required
that publishes a single message to the topic when the
exog_action should be executed.
When initializing an ExogManager object, a tem-
plate type as ROS2 message type has to be passed
along with the topic name to react to. The template
implementation generates all necessary instructions
to create a ROS2 subscriber to this topic and a call-
back to react on the event. To pass values to the
agent, an explicit function has to be written to convert
the values of the ROS2 message to golog++ values.
Those values can be used inside the effect field of the
exog_action inside the agent.
On the mascor github page is a detailed descrip-
tion of interfacing ROS2 with golog++ and a debian
package for installation.
Preparation
Figure 9b shows the user interface of the agent,
running on a handheld controller, for executing the
blocksworld agent. The interface includes the Robot-
Model on the left side, along with an octomap and
the trajectory of Spot’s path. Camera streams from
Spot’s grayscale and mounted RealSense cameras are
visible, alongside buttons for execution control.
Initially, we sense the table pose and the locations
of the cubes by clicking the Scan Blocks button (Fig-
ure 9b). This triggers a ROS2 node, calculating the
position for all blocks with respect to the fluent loc().
First it detects the aruco markers positioned on the
table and cubes. Then transforms are calculated, and
converted to an element from our domain, and made
available to a ROS2 topic for the sensing action to up-
date the current location before planning. For easier
placement of the cubes with the manipulator, the lo-
cation domain includes the symbol elements t1, t2, t3
for predefined positions of the blocks.
Following this preparation, the locations of the
cubes are displayed on the handheld controller. The
output here is b, t1 ,t2, which means a is on b, b on t1,
and c on t2. This output allows an operator to verify
the setup before executing the agent.
Execution
When initiating the agent, first the
action update_block_pose() gets executed for all
blocks, thereby updating the fluent loc(block x) for
every block (see Figure 4). An underlying ROS2
service is then invoked to subscribe to the last
message or the latest detected location, which is
provided through the RosPlatformBackend as a
domain symbol (see Figure 5a). The location was
made available during the preparation step through a
ROS2 topic.
The ROS2 Spot driver enables the robot to move
to a pose or frame along a 2D plane using a ROS2
action. The action navigateToFrame() is interfaced with
this action and passes a frame as a string type in its ar-
guments. A target pose is defined based on the range
of the manipulator, considering the distance between
the table and Spot.
The actions navigateToFrame("target") and
setManipulatorJoints(..), (Figure 7), run asyn-
chronously. start() triggers the asynchronous
process, and end() specifies its expected completion.
As navigateToFrame is already running in parallel, there
is no need for start() statement for the second action.
Subsequently, the solve(...) statement generates
an action sequence to stack the blocks from the initial
to the goal situation. For instance, when stack(a,t2)
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1058

is called, the custom action server, implemented with
MoveIt, approaches the block, picks it up, moves to
the target location, and places the block.
The last two setManipulatorJoints(..) commands re-
tract the manipulator and return it to a safe home po-
sition.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we showed our approach to interface
the high-level action language golog++ with our Spot
robot. As a real world example, we showed how
low-level actions implemented as ROS2 actions are
mapped to golog++ high-level actions in a unified
way in order to execute actions such as stacking
blocks with the Kinova Gen3 manipulator mounted
on the robot with a handheld controller. In fu-
ture work we plan to control multiple robots with
golog++ and a handheld controller.
REFERENCES
Boutilier, C., Reiter, R., Soutchanski, M., and Thrun, S.
(2000). Decision-theoretic, high-level agent program-
ming in the situation calculus. In AAAI/IAAI, pages
355–362.
Brunner, S. G., Steinmetz, F., Belder, R., and Dömel, A.
(2016). Rafcon: A graphical tool for engineering com-
plex, robotic tasks. In 2016 IEEE/RSJ International
Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS),
pages 3283–3290. IEEE.
Cashmore, M., Fox, M., Long, D., Magazzeni, D., Ridder,
B., Carrera, A., Palomeras, N., Hurtos, N., and Car-
reras, M. (2015). Rosplan: Planning in the robot oper-
ating system. In Proceedings of the international con-
ference on automated planning and scheduling, vol-
ume 25, pages 333–341.
De Giacomo, G., Lespérance, Y., Levesque, H. J., and Sar-
dina, S. (2009). Indigolog: A high-level programming
language for embedded reasoning agents. In Multi-
Agent Programming:, pages 31–72. Springer.
Eckstein, T. and Steinbauer, G. (2020). Action-based pro-
gramming with YAGI - an update on usability and per-
formance. In IEA/AIE, volume 12144 of Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 557–569. Springer.
Ferrein, A., Fritz, C., and Lakemeyer, G. (2005). Us-
ing golog for deliberation and team coordination in
robotic soccer. KI - Künstliche Intelligenz.
Ferrein, A. and Lakemeyer, G. (2008). Logic-based robot
control in highly dynamic domains. Robotics and Au-
tonomous Systems, 56(11):980–991.
Ingrand, F. F., Chatila, R., Alami, R., and Robert, F. (1996).
PRS: A high level supervision and control language
for autonomous mobile robots. In IEEE International
Conference on Robotics and Automation, volume 1,
pages 43–49.
Kirsch, M., Mataré, V., Ferrein, A., and Schiffer, S.
(2020). Integrating golog++ and ROS for practical
and portable high-level control. In ICAART (2), pages
692–699. SCITEPRESS.
Kitano, H. and Tadokoro, S. (2001). Robocup rescue: A
grand challenge for multiagent and intelligent sys-
tems. AI magazine, 22(1):39–39.
Kunze, L., Roehm, T., and Beetz, M. (2011). Towards se-
mantic robot description languages. In IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Robotics and Automation, pages
5589–5595.
Levesque, H. J., Reiter, R., Lespérance, Y., Lin, F., and
Scherl, R. B. (1997). Golog: A logic programming
language for dynamic domains. The Journal of Logic
Programming, 31(1-3):59–83.
Maruyama, Y., Kato, S., and Azumi, T. (2016). Ex-
ploring the performance of ros2. In Proceedings of
the 13th International Conference on Embedded Soft-
ware, pages 1–10.
Mataré, V., Viehmann, T., Hofmann, T., Lakemeyer, G.,
Ferrein, A., and Schiffer, S. (2021). Portable high-
level agent programming with golog++. In ICAART
(2), pages 218–227. SCITEPRESS.
McCarthy, J. (1963). Situations, Actions and Causal Laws.
Technical report memo 2, AI Lab, Stanford Univer-
sity, California, USA. Published in Semantic Informa-
tion Processing, ed. Marvin Minsky. Cambridge, MA:
The MIT Press, 1968.
McIlraith, S. and Son, T. C. (2001). Adapting golog for pro-
gramming the semantic web. In Fifth International
Symposium on Logical Formalizations of Common-
sense Reasoning, pages 195–202.
Niemueller, T., Hofmann, T., and Lakemeyer, G. (2019).
Goal reasoning in the clips executive for integrated
planning and execution. In Proceedings of the In-
ternational Conference on Automated Planning and
Scheduling, volume 29, pages 754–763.
Schiffer, S., Ferrein, A., and Lakemeyer, G. (2012). CAE-
SAR – An Intelligent Domestic Service Robot. Jour-
nal of Intelligent Service Robotics, 23(Special Issue
on Artificial Intelligence in Robotics: Sensing, Repre-
sentation and Action):259–273.
Schimpf, J. and Shen, K. (2012). Eclipse–from lp to clp.
Theory and Practice of Logic Programming, 12(1-
2):127–156.
Segura-Muros, J. Á. and Fernández-Olivares, J. (2017). In-
tegration of an automated hierarchical task planner in
ros using behaviour trees. In 2017 6th International
Conference on Space Mission Challenges for Infor-
mation Technology (SMC-IT), pages 20–25. IEEE.
Wygant, R. M. (1989). CLIPS – a powerful development
and delivery expert system tool. Computers & indus-
trial engineering, 17(1-4):546–549.
GOLOG++ Hits the (Right) Spot: Interfacing Golog with a Quadruped Rescue Robot for High-Level Missions
1059
