
Occlusion-Robust and Efficient 6D Pose Estimation with Scene-Level
Segmentation Refinement and 3D Partial-to-6D Full Point Cloud
Transformation
Sukhan Lee
1,* a
, Soojin Lee
1
and Yongjun Yang
2
1
Department of Artificial Intelligence, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Republic of Korea
2
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Republic of Korea
Keywords: Object 6D Pose, Panoptic Segmentation, Dual Associative Point Autoencoder, Point Cloud, Occluded Object.
Abstract: Accurate estimation of the 6D pose of objects is essential for 3D scene modeling, visual odometry, and map
building, as well as robotic manipulation of objects. Recently, various end-to-end deep networks have been
proposed for object 6D pose estimation with their accuracies reaching the level of conventional regimes but
with much higher efficiency. Despite progress, the accurate yet efficient 6D pose estimation of highly
occluded objects in a cluttered scene remains a challenge. In this study, we present an end-to-end deep network
framework for 6D pose estimation with particular emphasis on highly occluded objects in a cluttered scene.
The proposed framework integrates an occlusion-robust panoptic segmentation network performing scene-
level segmentation refinement and a dual associative point autoencoder (AE) directly reconstructing the 6D
full camera and object frame-based point clouds corresponding to a captured 3D partial point cloud through
latent space association. We evaluated the proposed deep 6D pose estimation framework based on the standard
benchmark dataset, LineMod-Occlusion (LMO), and obtained the top-tier performance in the current
leaderboard, validating the effectiveness of the proposed approach in terms of efficiency and accuracy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Fast and accurate 6D pose estimation of objects in a
scene is essential for various 3D applications in the
field of robotic manipulation and navigation as well
as augmented and mixed realities. Recent
advancements in the end-to-end deep learning
approaches to object 6D pose estimation have shown
their feasibility in real-time processing of 6D pose
estimation with the pose accuracy competitive to
conventional engineering state-of-the-arts accurate
but computationally burdensome. Despite advances
in deep network approaches, to widen their
applications into real-world problems, further
improvement in object 6D pose estimation is
necessary not only in terms of accuracy and speed but
also in terms of dealing with objects that are heavily
occluded in a dynamic and cluttered environment.
In this study, we present an end-to-end deep
learning approach to accurate yet efficient 6D pose
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1281-6889
*
Corresponding author: Sukhan Lee (lsh1@skku.edu)
estimation of objects, in particular, heavily occluded
in a cluttered scene. To this end, the proposed
approach integrates an occlusion-robust panoptic
segmentation network with a highly efficient 6D pose
estimation network. The occlusion-robust panoptic
segmentation network was built by cascading YOLO-
YOLACT networks, in which the object boxes
detected by YOLO (Redmon et al., 2016) are fed
individually into YOLACT (Bolya et al., 2019) for
multi-object segmentation. To achieve the occlusion-
robust panoptic segmentation, first, we applied depth-
based tone mapping (Lee et al., 2012) to individual
YOLO box images such that the overlapped object
images are better distinguished from each other based
on the difference in their surface depths. Then, we
performed novel scene-level segmentation
refinement by fusing multiple redundant YOLACT
segmentations obtained from the overlapped YOLO
boxes to achieve accurate segmentation boundaries.
On the other hand, the highly efficient 6D pose
estimation network was configured by the dual
Lee, S., Lee, S. and Yang, Y.
Occlusion-Robust and Efficient 6D Pose Estimation with Scene-Level Segmentation Refinement and 3D Partial-to-6D Full Point Cloud Transformation.
DOI: 10.5220/0012457700003660
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 19th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2024) - Volume 2: VISAPP, pages
763-771
ISBN: 978-989-758-679-8; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
763
associative point AE which estimates object 6D pose
in the process of transforming a 3D partial point cloud
directly into the corresponding 6D full point cloud,
representing the camera and object frame-based full
point clouds, through a latent space association
network. We achieved highly efficient yet occlusion-
robust 6D pose estimation of heavily occluded objects
by integrating the panoptic segmentation reinforced
by scene-level segmentation refinement and the 6D
pose estimation based on direct 3D partial-to-6D full
point cloud transformation.
2 RELATED WORKS
2.1 Panoptic Segmentation
Panoptic segmentation was first introduced by
Kirillov et al. (Kirillov et al., 2019) for segmenting
objects in terms of both instance and semantic
segmentation points of view. As for panoptic
segmentation, Cheng et al. (Cheng et al., 2021, 2022)
proposed MaskFormer in which the Resnet-based
pixel embedding and the transformer-based mask
embedding are combined to achieve effective
panoptic segmentation. Jain et. al (Jain et al., 2023)
proposed OneFormer, a transformer-based multi-task
universal image panoptic segmentation framework
that takes a task token as an input. OneFormer and
MaskFormer represent currently the state-of-the-arts
in panoptic segmentation in terms of the panoptic
quality (PQ) metric (Kirillov et al., 2019), although
their inference time needs improvement.
2.2 Deep 6D Pose Estimation
Deep learning approaches to object 6D pose
estimation are based either on RGB or RGB-D data.
As for the RGB-based approaches, GDR-Net (Wang
et al., 2021) directly regressed 6D object pose from
RGB images by an end-to-end patch PnP network
performing 2D-to-3D dense mapping and surface
region attention. PFA-Pose (Hu et al., 2022)
presented, in particular, a pose refinement process
based on the difference between the real and multiple
perspective-rendered images from the initially
estimated pose. As for the RGB-D-based approaches,
DenseFusion (Wang et al., 2019) predicted 6D pose
based on the pixel-wise color and geometry
embedding extracted from segmented objects, by
CNN and PointNet, respectively, finalizing with an
end-to-end iterative pose refinement of pose
residuals. PVN3D (He et al., 2020) presented an
RGB-D-based deep point-wise 3D key point voting
network for 6D pose estimation where the 3D key
points of objects were detected by a deep Hough
voting network. GDRNPP (Sundermeyer et al., 2022)
further improved GDR-Net based on domain
randomization and depth-based pose refinement.
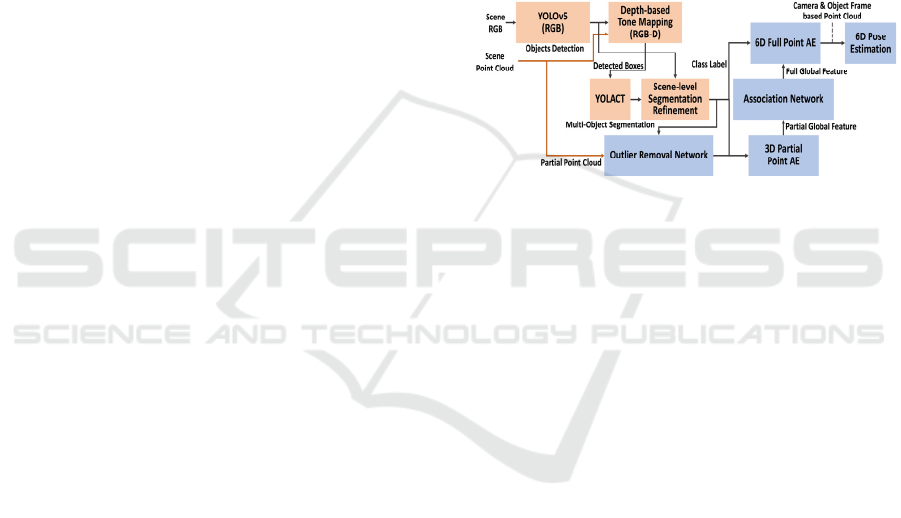
3 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
Figure 1 illustrates the overall architecture of the
proposed RGB-D-based object 6D pose estimation
framework composed of the cascaded YOLO-
YOLACT network for panoptic segmentation (red
box) and the dual associative point AE for 6D pose
estimation (blue box).
Figure 1: The architecture of the proposed RGB-D-based
object 6D pose estimation framework in the integration of
the occlusion-robust panoptic segmentation (orange) and
the efficient 6D pose estimation (blue).
The cascaded YOLO-YOLACT panoptic
segmentation network is supported by a novel pre-
processing of depth-based image tone mapping and
post-processing of scene-level segmentation
refinement for accurately identifying object
boundaries under heavy occlusion. On the other hand,
the dual associated point AE is composed of 3D
partial and 6D full point AEs the global features of
which are linked by an association network. The 6D
pose estimation network is supported by an outlier
removal network that removes outliers included in
partial point clouds. Notably, the output of the full
point AE is 6D vectors formed by concatenating the
camera frame-based and the object frame-based 3D
full point clouds. The dual associated point AE
transforms a 3D partial point cloud into the
corresponding 6D full point cloud in such a way that
object 6D poses are computed directly from the
reconstructed 6D point cloud.
4 OCCLUSION-ROBUST
PANOPTIC SEGMENTATION
As described in Section 3, the proposed panoptic
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
764
segmentation achieves occlusion-robustness based on
the depth-based tone mapping of the YOLOv5 box
images and the scene-level segmentation refinement
by fusing redundant segmentations generated by the
overlapped YOLO box images before and after
YOLACT multi-object panoptic segmentation,
respectively, to obtain accurate object boundaries.
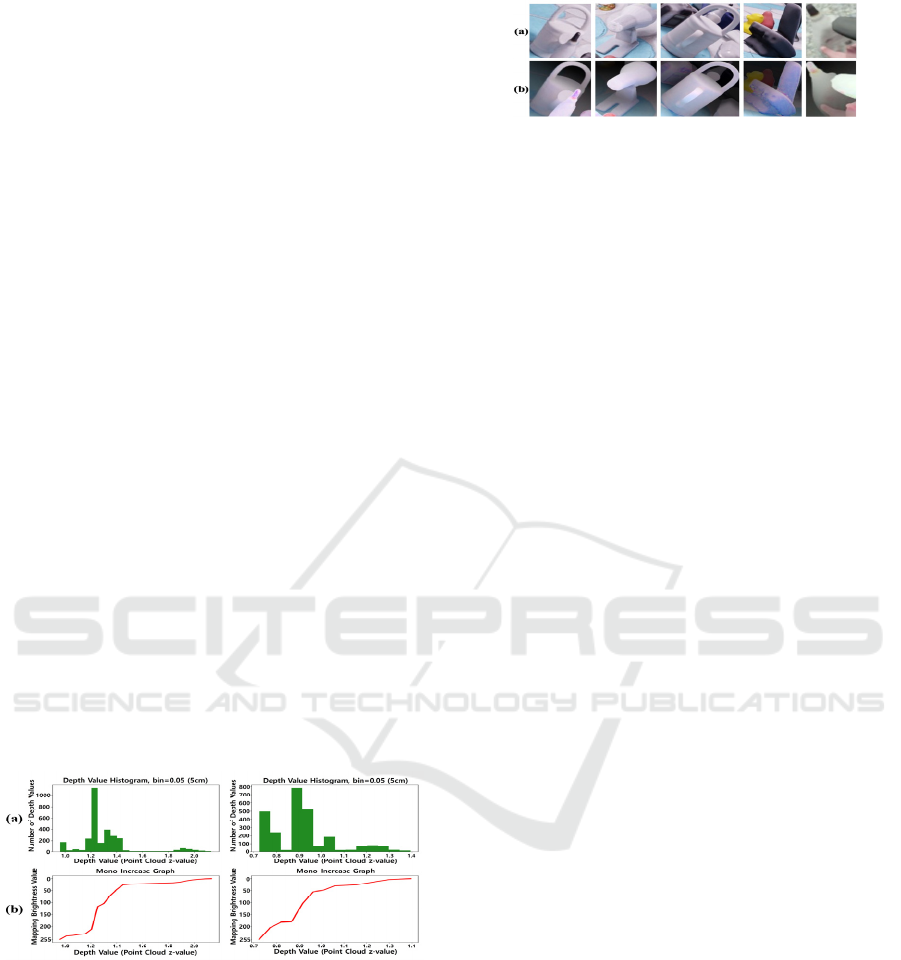
4.1 Depth-Based Tone Mapping
The proposed tone-mapping of YOLOv5-produced
object box images uses the depth value (z-axis) from
the point cloud captured by the RGB-D sensor to
adjust the brightness of the image in such a way as to
incorporate the depth information into the image
representation. To this end, we made the pixels closer
to the camera brighter than those farther away while
retaining their original R, G, and B intensity ratios.
Specifically, the point cloud cropped for a box image
is represented by a histogram depicting the number of
points distributed along the distance from the camera,
as exemplified in Figure 2 (a) with 5cm distance
intervals. Then, we assigned to each bin of the
histogram a brightness value by dividing the
predefined brightness range for the entire points
according to the ratio of the number of points in each
bin of the histogram, following the rule that the closer
to the camera the higher the assigned brightness, as
illustrated in Figure 2 (b) with the predefined
brightness range of [0-255]. Finally, the brightness of
individual image pixels is modified according to the
brightness assigned to the corresponding points while
maintaining their original R, G, and B intensity ratios.
Figure 2: (a) Depth-pixel count histograms for YOLO box
images (depth bin size =0.05), (b) the proposed depth-
brightness mapping in proportion to the accumulated
histogram.
Figure 3 illustrates the comparison of the box
images before (a) and after (b) the proposed depth-
based tone mapping is applied. Notice that the pixels
closer to the camera become brighter while the pixels
farther away become darker.
In the case where multiple objects of similar
colors are heavily occluded in a scene, it is difficult
Figure 3: Examples of depth-based tone-mapped RGB-D
images: (a) original RGB YOLO box images and (b) the
corresponding tone-mapped RGB-D images.
for panoptic segmentation to properly segment out
those objects from the scene image. However, the
depth-based tone mapping modifies the brightness of
objects in the scene image according to their depths,
making panoptic segmentation feasible. In addition, it
is often the case that the background of a scene is
farther away from the camera such that the proposed
depth-based tone mapping naturally tone-downs the
background of the scene image to better condition for
segmentation. Also, the proposed depth-based tone
mapping tends to emphasize the detected foreground
object while deemphasizing neighboring objects,
which helps for both panoptic segmentation and
scene-level segmentation refinement.
4.2 Scene-Level Segmentation
Refinement
The depth-based tone-mapped object box images
detected by YOLOv5 are fed into YOLACT for
multi-object panoptic segmentation. Then, YOLACT
performs multi-object panoptic segmentation by
assigning to individual pixels of a box image the
probabilities that they belong to particular object
classes. Since, for a highly cluttered scene, the object
box images are often highly overlapped such that an
object may be present in multiple box images either
as a main (detected by YOLO) or a surrounding
object. This results in redundancy in object
segmentation or object class probabilities assigned to
individual pixels. The cascaded YOLO-YOLACT
network is proposed to take advantage of such
redundancy in object segmentation to perform a
scene-level fusion of redundant pixel class
probabilities to accurately refine object boundaries
under heavy occlusions. The proposed scene-level
segmentation refinement fuses the information on the
bounding box and its class label and confidence score
from YOLO and YOLACT and the object classes and
class probabilities associated with individual pixels
from YOLACT. Specifically, the scene-level
segmentation refinement process consists of three
steps (refer to Figure 4): The first step defines a set of
overlapping YOLO boxes by calculating the
intersection of union (IoU) between YOLO boxes.
Occlusion-Robust and Efficient 6D Pose Estimation with Scene-Level Segmentation Refinement and 3D Partial-to-6D Full Point Cloud
Transformation
765

The second step corrects the inconsistent class labels
associated with YOLACT and YOLO boxes. This is
achieved by determining the main YOLACT boxes
associated with all the YOLO boxes overlapped with
the YOLO box currently in processing. For a given
YOLO box, the YOLACT boxes the class labels of
which are consistent with that of the YOLO are
recognized as the main objects with correct class
labels. If no YOLACT box with a consistent class
label is found, the YOLACT box of the highest IoU
with and the smallest distance from the YOLO box is
chosen as the main object the class label of which is
determined by whichever has a higher confidence
score between YOLO and the YOLACT boxes. Note
that the class label of the YOLACT box representing
a surrounding object follows the class label of the
overlapping YOLO box that takes the surrounding
object as its main object. The third step refines the
object boundaries in the scene-level by finalizing the
object class labels of individual pixels. Since
individual pixels of the YOLO box currently in
processing may be associated with multiple object
class labels and probabilities from multiple
overlapped YOLO boxes, the scene-level
segmentation refinement selects the maximum
probability of object classes for individual pixels.
Figure 4: A schematic diagram of the proposed scene-level
segmentation refinement based on fusing multiple
YOLACT segmentations from overlapped YOLO boxes.
5 EFFICIENT 6D POSE
ESTIMATION
The panoptic segmentation allows to capture of
partial point clouds from the visually accessible
surfaces of individual objects. The proposed dual
associative point AE obtains the object 6D pose by
directly transforming a 3D partial point cloud into the
corresponding 6D point cloud formed by the two 3D
full point clouds with reference to the respective
camera and the object frames. This makes the
proposed 6D pose estimation highly efficient. The
proposed 6D pose estimation process consists of three
steps. The first step removes any outliers that may be
included in the partial point clouds captured from
panoptic segmented object surfaces. The second step
transforms 3D partial point clouds into the
corresponding 6D full point clouds based on the dual
associative point AE. The third step computes object
6D poses based on the camera and object frame-based
6D full-point clouds.
5.1 Outlier Removal Network
A deep outlier removal network is constructed to
eliminate noisy points often generated around the
segmented boundaries as the outliers of partial point
clouds. To this end, we trained a point AE (refer to
Figure 5) in such a way that the network segments out
the outlier points from the inlier points while the
reconstruction process is carried out. The training
dataset is obtained by simulating the way outliers are
generated in realistic scenarios by randomly
disturbing the contours of the segmented object
boundaries. We used the point AE configured by the
KC-Net encoder and BID decoder (Lee et al., 2022).
Figure 5: The proposed outlier removal network
segmenting a partial point cloud into inlier and outlier
clusters.
5.2 Dual Associative Point AE
Figure 6 shows the architecture of the dual associative
point AE proposed for 3D partial-to-6D full-point
cloud transformation.
Figure 6: The proposed dual associative point AE which
transforms a 3D partial point cloud into the corresponding
6D full point clouds through the association of global
features.
The network is configured with 3D partial and 6D full
point AEs that are linked by a fully connected
association network. The 3D partial and 6D full point
AEs encode the global features in their respective
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
766

latent spaces while reconstructing 3D partial and 6D
point clouds, respectively. The association network
transforms the 3D partial global feature into the 6D
full global feature through the global feature
transformation such that 6D full point clouds can be
reconstructed based on 3D partial point clouds given
as the input. In implementing point AEs, we used KC-
net as encoders and BID net as decoders. The object
class label identified by the panoptic segmentation is
concatenated with the global feature as the input to
BID decoders for reconstruction.
The proposed dual associative point AE is trained
in an end-to-end manner based on the 3D partial and
6D full point cloud reconstruction losses as well as
the association loss. In testing, only 3D partial point
clouds are given as the input for the reconstruction of
the corresponding 6D full point cloud. We used
Chamfer Distance (CD) error and Euclidian distance
error, respectively, for computing the point cloud
reconstruction and association losses. Note that, for a
symmetric object, the same partial point cloud is
captured by an RGB-D sensor at the symmetric poses
of the object, such that multiple 6D full point clouds
can possibly correspond to a single partial point
cloud. This causes one-to-many relations in the
partial-to-full association such that the training
dataset collected without consideration of object
symmetries can become ineffective. To deal with this
problem, the training dataset for a symmetric object
is collected only in the pose range within which the
one-to-one relations in the partial-to-full association
are ensured.
5.3 6D Pose Estimation
Once 6D full point clouds are obtained, the
corresponding object 6D poses can be readily
computed based on the camera frame-based 3D full
point cloud and the object frame-based 3D full point
cloud as the individual points of the two 3D full point
clouds are concatenated under exact one-to-one point
correspondences. We used Rigid Transform 3D
(Nghia et al., 2020) to compute the coordinate
transformation.
6 EXPERIMENTS
6.1 Datasets
We used the Linemod (LM) PBR-synthetic dataset as
well as the custom-built real-synthetic data for
training and the LineMod-Occlusion (LMO)
(Brachmann et al., 2014) dataset for testing. The
datasets offer ground truth segmentations and 6D
poses of 15 different objects of various levels of
occlusions. Specifically, the LM dataset provides one
annotated object of mild occlusion per scene while
the LMO dataset provides annotations for all the
objects of interest for the chosen real-synthetic LM
test dataset with heavy occlusion. In addition, we
built a customized real-synthetic dataset for training
based on self-supervised augmentation of object
layouts and occlusions (Figure 7 (b)).
Figure 7: Illustration of (a) PBR-synthetic LM and (b)
custom-built real-synthetic datasets used for training and
testing.
6.2 Panoptic Segmentation Results
The performance of the proposed panoptic
segmentation tested based on the LMO testing dataset
is summarized in Table 1 in terms of the mIoU and
PQ scores.
Table 1: Performance of proposed panoptic segmentation
with and without the scene-level segmentation refinement.
mIoU
Panoptic
Q
ualit
y
Proposed approach with scene-
level se
g
mentation refinement
0.6792 0.6393
Proposed approach without scene-
level se
g
mentation refinement
0.4465 0.4214
Mask RCNN-CosyPose
p
anoptic
se
g
mentation
0.6129 0.5962
Table 1 indicates that the proposed panoptic
segmentation shows the PQ of about 0.64 with scene-
level segmentation refinement. Table 1 validates the
effectiveness of the proposed scene-level
segmentation refinement as it results in a large
performance improvement of PQ from 0.42 to 0.64.
In addition, we compared the proposed panoptic
segmentation with the Mask RCNN-based CosyPose
(Labbé et al., 2020) panoptic segmentation,
representing one of the state-of-the-arts. As shown in
the third row of Table 1, we found that the PQ of
about 0.64 by the proposed approach surpasses that of
the Mask RCNN-based CosyPose segmentation of
about 0.60 when tested with the LMO dataset. Note
Occlusion-Robust and Efficient 6D Pose Estimation with Scene-Level Segmentation Refinement and 3D Partial-to-6D Full Point Cloud
Transformation
767

that the current state-of-the-art PQ performance based
on the COCO dataset is about 0.58 by OneFormer,
which can serve as an indirect performance indicator.
Figure 8 illustrates typical panoptic segmentation
results of the proposed approach applied to PBR-
synthetic LM (a) and LMO (b) testing datasets.
Figure 8: Typical panoptic segmentation results of the
proposed approach applied to (a) PBR-synthetic and (b)
LMO datasets.
Figure 9 illustrates the boundaries of heavily
occluded objects that are refined accurately by the
proposed scene-level segmentation refinement. In
Figure 9, the boundaries (b) within yellow circles
show the corrected erroneous boundaries (a) after the
scene-level segmentation refinement is applied.
To further validate the particular strength of the
proposed approach in occlusion-robust panoptic
segmentation, we constructed a new test dataset by
selecting only those scenes of the LMO test dataset
that are heavily occluded. Then, we again compared
the performance of the proposed approach with that
of the Mask RCNN-based CosyPose to investigate if
any comparative advantage exists when heavy
occlusions are involved. The results are summarized
in Table 2.
Figure 9: Improvement of segmented boundaries in highly
occluded environments from (a) “before” to (b) “after” the
scene-level segmentation refinement.
Comparing Table 2 and Table 1, we can observe
that the proposed approach shows even a significantly
higher PQ for the heavily occluded test dataset while
the Mask RCNN-based CosyPose shows the
degraded PQ, which validates the effectiveness of the
proposed depth-based tone mapping and scene-level
segmentation refinement for the panoptic
segmentation of heavily occluded scenes.
Table 2: Performance comparison of the proposed panoptic
segmentation with the Mask RCNN-based CosyPose for
heavily occluded scenes.
mIoU
Panoptic
Qualit
y
Proposed approach with scene-
level segmentation refinement
0.7376 0.7329
CosyPose panoptic segmentation 0.6474 0.5270
Figure 10 illustrates three salient panoptic
segmentation results that reveal the strength of the
proposed approach (b) in identifying accurate
boundaries (within yellow circles), compared to the
Mask RCNN-based CosyPose segmentation (a).
Figure 10: Comparative illustration of boundary
segmentation accuracies in highly occluded scenes
between: (a) the proposed approach and (b) Mask RCNN-
based CosyPose segmentation.
In particular, we found that the proposed approach
is more effective for segmenting thin or small size of
objects, such as occluded kettle handles and spouts,
than the Mask RCNN-based CosyPose segmentation.
6.3 Efficient 6D Pose Estimation
6.3.1 Outlier Removal
A partial point cloud may include outliers generated
in the process of sampling points from panoptic-
segmented scene images. We trained and tested the
outlier removal network introduced in Section 5.1 by
generating simulated partial point cloud outlier
datasets based on the LM dataset. The trained outlier
removal network achieved an overall accuracy of
99.84%, as summarized by the confusion matrix of
Figure 11.
Figure 11: The confusion matrix depicting the test
performance of the proposed outlier removal network.
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
768
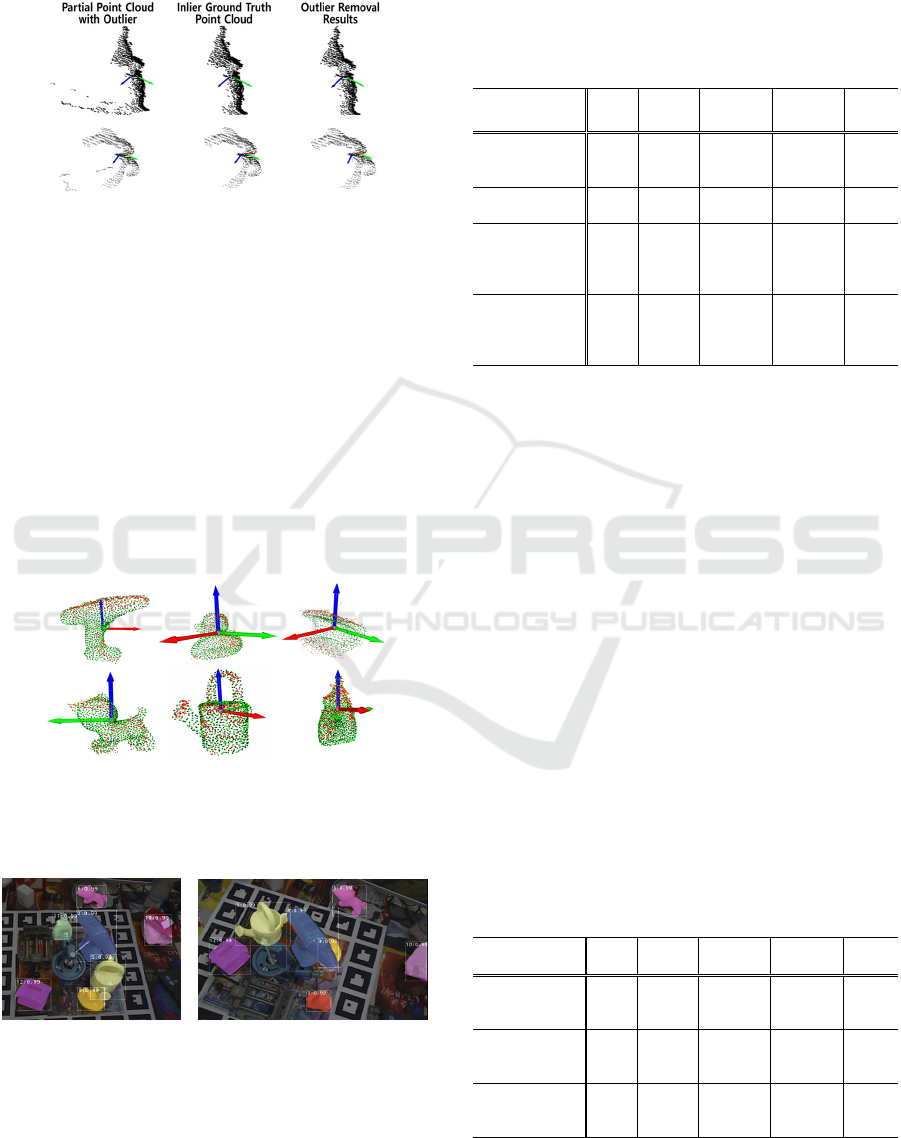
Figure 12 exemplifies the outliers included in
partial point clouds that are removed out by the outlier
removal network.
Figure 12: Examples of outliers included in partial point
clouds that are removed by the outlier removal network.
6.4 6D Pose Estimation
Figure 13 visualizes the result of 6D pose estimation
using LMO testing objects, where the camera frame-
based input partial (red) and reconstructed full (green)
point clouds as well as the object frame-based
reconstructed full (black) point clouds are overlapped
based on the estimated 6D object poses.
In Figure 14, typical 6D pose estimation results
obtained by the proposed approach are illustrated in
terms of captured partial point clouds (grey) and the
full object models (color) placed in the scene based
on their estimated 6D poses.
Figure 13: Visualization of the camera frame-based input
partial (red) and reconstructed full (green) point clouds as
well as the object frame-based reconstructed full (black)
point clouds that are overlapped.
Figure 14: Illustration of typical 6D pose estimation results
with the full object models (color) placed in the scene based
on their estimated 6D poses.
The overall performance of the proposed 6D pose
estimation approach is summarized in Tables 3 and 4.
In Table 3, the average recall (AR) performance of
the proposed approach is compared to the top-tier
performances in the LMO leader board based on
RGB-D.
Table 3: Performance comparison of the proposed approach
to top-tier approaches in the LMO leaderboard.
AR
AR
(
VSD
)
AR
(
MSSD
)
AR
(
MSPD
)
Time
(
sec
)
Propose
d
w/o Iterative
Refinement
0.775 0.738 0.792 0.796 0.145
GPose2023
1
,
R
ank 1
0.805 0.664 0.852 0.900 5.723
RADet+PFA-
MixPBR-
RGBD
2
,
R
ank 2
0.797 0.658 0.843 0.890 1.743
GDRNPP
3
w/ Iterative
Refinement,
R
ank
7
0.792 0.651 0.836 0.889 0.177
1
GPose2023: Not yet published.
2
PFA: Hu et al., 2022
3
GDRNPP: Sunderme
y
er et al., 2022
Table 3 indicates that the proposed 6D pose
estimation positions in the leader board as one of the
top-tier performances, in particular, listing the top
performance in AR(VSD) metric and the processing
time per scene. As for the computational efficiency, the
proposed approach requires about 145ms in total as an
integrated framework, in which only 30ms are taken
for the 6D pose estimation by the dual associative point
AE. Note that, unlike other top-tier performances, the
performance of the proposed approach listed in Table
3 is obtained without using an additional iterative pose
refinement process. Therefore, we were interested in
comparing the performance of the proposed approach
with the cases in the leader board that use no pose
refinement process. Table 4 presents the comparative
performance of the proposed approach to the top-tier
performances in the LMO leader board without
iterative pose refinement processes.
Table 4: Performance comparison of the proposed approach
to top-tier approaches in LMO leader board that do not use
iterative pose refinement processes.
AR
AR
(
VSD
)
AR
(
MSSD
)
AR
(
MSPD
)
Time
(
sec
)
Propose
d
w/o Iterative
Refinement
0.775 0.738 0.792 0.796 0.145
HCCePose
1
w/o Iterative
Refinement
0.768 0.615 0.787 0.902 N/A
SurfEmb
2
w/o Iterative
Refinement
0.760 0.615 0.809 0.856 11.943
1
HCCePose: Not yet published.
2
SurfEmb: Hau
g
aard et al., 2022
Occlusion-Robust and Efficient 6D Pose Estimation with Scene-Level Segmentation Refinement and 3D Partial-to-6D Full Point Cloud
Transformation
769

Table 4 indicates that, without taking account of
iterative pose refinement processes, the proposed
approach shows the top performance in AR, AR
(VSD), and the processing time. Note that the same
testing dataset provided by the benchmark was used
by the approaches under comparative evaluation. In
sum, through experiments, we validated the
effectiveness of the proposed framework in terms of
its top-tier performance in the accuracy of estimated
poses as well as in the computational efficiency.
7 CONCLUSION
In this study, we presented an end-to-end deep
network framework for the 6D pose estimation of
objects under heavy occlusions in cluttered scenes.
The proposed framework integrates the cascaded
YOLO-YOACT-based occlusion-robust panoptic
segmentation network with the dual associative point
AE-based efficient 6D pose estimation network. In
particular, we achieved the occlusion-robust panoptic
segmentation based on such novel regimes as 1) the
depth-based tone mapping of YOLO box images and
2) the scene-level segmentation refinement by fusing
multiple YOLACT segmentations generated from
overlapped YOLO boxes. We also achieved highly
efficient 6D pose estimation by directly transforming
a 3D partial point cloud into the corresponding 6D
full point cloud represented in the combined camera
and object frames. The robustness of the proposed
panoptic segmentation against heavily occluded
scenes is verified by ablation and comparative studies.
The effectiveness of the integrated 6D pose
estimation framework is validated by the experiments
using the standard benchmarking datasets, LM and
LMO. We showed a top-tier performance in the LMO
leader board in terms of both accuracy and efficiency,
in particular, in AR (VSD) and computation time,
despite that no additional 6D pose refinement process
is employed. We are currently developing a 6D pose
refinement process to be attached to the current
framework. We also plan to apply our framework to
various pick-and-place operations for the industry.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was supported, in part, by the ‘‘Intelligent
Manufacturing Solution under Edge-Brain
Framework’’ Project of the Institute for Information
and Communications Technology Promotion (IITP)
under Grant IITP-2022-0-00067 (EdgeBrain-2) and
IITP-2022-0-00187 (EdgeBrain-3) and, in part, by AI
Graduate School Program, Grant No. 2019-0-00421,
and by ICT Consilience Program, IITP-2020-0-
01821, of the Institute of Information and
Communication Technology Planning & Evaluation
(IITP), sponsored by the Korean Ministry of Science
and Information Technology (MSIT).
REFERENCES
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., & Farhadi, A. (2016).
You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection.
In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer
vision and pattern recognition (pp. 779-788).
Bolya, D., Zhou, C., Xiao, F., & Lee, Y. J. (2019). Yolact:
Real-time instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision
(pp. 9157-9166).
Lee, S., Mai, K. T., & Jeong, W. (2012, February). Virtual
high dynamic range imaging for robust recognition. In
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on
Ubiquitous Information Management and
Communication (pp. 1-6).
Kirillov, A., He, K., Girshick, R., Rother, C., & Dollár, P.
(2019). Panoptic segmentation. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition (pp. 9404-9413).
Cheng, B., Schwing, A., & Kirillov, A. (2021). Per-pixel
classification is not all you need for semantic
segmentation. Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems, 34, 17864-17875.
Cheng, B., Misra, I., Schwing, A. G., Kirillov, A., &
Girdhar, R. (2022). Masked-attention mask transformer
for universal image segmentation. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition (pp. 1290-1299).
Jain, J., Li, J., Chiu, M. T., Hassani, A., Orlov, N., & Shi,
H. (2023). Oneformer: One transformer to rule
universal image segmentation. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (pp. 2989-2998).
Wang, G., Manhardt, F., Tombari, F., & Ji, X. (2021).
GDR-net: Geometry-guided direct regression network
for monocular 6d object pose estimation. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 16611-
16621).
Hu, Y., Fua, P., & Salzmann, M. (2022, October).
Perspective flow aggregation for data-limited 6d object
pose estimation. In European Conference on Computer
Vision (pp. 89-106). Cham: Springer Nature
Switzerland.
Wang, C., Xu, D., Zhu, Y., Martín-Martín, R., Lu, C., Fei-
Fei, L., & Savarese, S. (2019). Densefusion: 6d object
pose estimation by iterative dense fusion. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer
vision and pattern recognition (pp. 3343-3352
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
770

He, Y., Sun, W., Huang, H., Liu, J., Fan, H., & Sun, J.
(2020). Pvn3d: A deep point-wise 3d keypoints voting
network for 6dof pose estimation. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition (pp. 11632-11641).
Sundermeyer, M., Hodaň, T., Labbe, Y., Wang, G.,
Brachmann, E., Drost, B., ... & Matas, J. (2023). Bop
challenge 2022 on detection, segmentation and pose
estimation of specific rigid objects. In Proceedings of
the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (pp. 2784-2793).
Lee, S., Cheng, W., & Yang, Y. (2022). Bias-Induced Point
Auto-Encoder and Comparative Analysis of Point
Encoder-Decoder Combinations. IEEE Access, 10,
61617-61630.
Nghia Ho. (2020). rigid_transform_3D. https://github.com/
nghiaho12/rigid_transform_3D
Brachmann, E., Krull, A., Michel, F., Gumhold, S.,
Shotton, J., & Rother, C. (2014). Learning 6d object
pose estimation using 3d object coordinates. In
Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European
Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6-12,
2014, Proceedings, Part II 13 (pp. 536-551). Springer
International Publishing.
Labbé, Y., Carpentier, J., Aubry, M., & Sivic, J. (2020).
Cosypose: Consistent multi-view multi-object 6d pose
estimation. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th
European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28,
2020, Proceedings, Part XVII 16 (pp. 574-591).
Springer International Publishing.
Haugaard, Rasmus Laurvig, and Anders Glent Buch.
"Surfemb: Dense and continuous correspondence
distributions for object pose estimation with learnt
surface embeddings." Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition. 2022.
Occlusion-Robust and Efficient 6D Pose Estimation with Scene-Level Segmentation Refinement and 3D Partial-to-6D Full Point Cloud
Transformation
771
