
MBSE to Support Engineering of Trustworthy AI-Based Critical
Systems
Afef Awadid
1a
, Boris Robert
2
and Benoît Langlois
3
1
Technological Research Institute SystemX, Palaiseau, France
2
Technological Research Institute Saint Exupéry, Toulouse, France
3
Thales, Vélizy-Villacoublay, France
Keywords: Engineering Processes, Methodological Guidelines, Trustworthiness Environment, MBSE, Arcadia Method,
AI-Based Critical Systems, Machine Learning.
Abstract: Because of the multidisciplinary nature of the engineering of a critical system and the inherent uncertainties
and risks involved by Artificial Intelligence (AI), the overall engineering lifecycle of an AI-based critical
system requires the support of sound processes, methods, and tools. To tackle this issue, the Confiance.ai
research program intends to provide a methodological end-to-end engineering approach and a set of relevant
tools. Against this background, an MBSE approach is proposed to establish the methodological guidelines
and to structure a tooled workbench consistently. In this approach, the system of interest is referred to as the
"Trustworthiness Environment" (i.e. the Confiance.ai workbench). The approach is an adaptation of the
Arcadia method and hence built around four perspectives: Operational Analysis (the engineering methods and
processes: the operational need around the Trustworthiness Environment), System Analysis (the functions of
the Trustworthiness Environment), Logical Architecture and Physical Architecture (abstract and concrete
resources of the Trustworthiness Environment). Given the current progress of the Confiance.ai program, this
paper focuses particularly on the Operational Analysis, leading to the modeling of engineering activities and
processes. The approach is illustrated with an example of a machine learning model robustness evaluation
process.
1 INTRODUCTION
The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques is
becoming increasingly popular in various
applications (Miglani and Kumar, 2019), as the
technologies mature and become more affordable
(Boardman and Butcher, 2019). These techniques
could be physically embodied as in the case of safety-
critical systems such as electricity grids or on-board
aircraft networks or exist only as software agents that
autonomously process data at speeds or for durations
that humans are not capable of.
Applying AI techniques can confer a competitive
advantage to industry by providing not only high
value-added products and services but also support to
decision-makers (Mattioli et al, 2023). In this sense,
production efficiency, product quality, and service
level will be improved by AI (Li et al, 2017).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7525-613X
However, while AI has much potential for innovative
applications, it raises several concerns such as
security and safety (El-Sherif et al, 2022). These
concerns are even more salient when it comes to
critical systems.
AI-based critical systems are defined as systems
containing at least one subsystem or component using
AI technology (the most representative today being
Machine Learning), alongside traditional software
components, and whose failure leads to unacceptable
circumstances such as loss of human lives (Mwadulo,
2016). The engineering of such systems is regarded
as a multi-engineering process that addresses
conventional engineering disciplines (i.e., data and
knowledge engineering, algorithm engineering,
system and software engineering, safety and cyber-
security engineering, and cognitive engineering) with
respect to the effects induced by the use of AI
(Adedjouma et al, 2022).
280
Awadid, A., Robert, B. and Langlois, B.
MBSE to Support Engineering of Trustworthy AI-Based Critical Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0012463600003645
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering (MODELSWARD 2024), pages 280-287
ISBN: 978-989-758-682-8; ISSN: 2184-4348
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

Given this multidisciplinary process for
engineering a critical system and the inherent
uncertainties and risks involved by AI, the overall
engineering lifecycle of a trustworthy AI-based
critical system requires the support of sound
processes, methods, and tools (Mattioli et al, 2023).
To address this issue, the Confiance.ai research
program
2
aims to provide a methodological end-to-
end engineering approach and a set of tools consistent
with this approach. Considering the complexity and
heterogeneity of the intended outcome, we have
applied a Model-Based Systems Engineering
(MBSE) approach allowing to establish and formalize
the methodological guidelines and to structure a
tooled workbench consistent with these guidelines.
This paper therefore attempts to answer the
research question of how to support the engineering
of trustworthy AI-based critical systems with the help
of the modeling of methodological guidelines.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 introduces the context and motivation of
this work. The proposed MBSE approach for
supporting the engineering of trustworthy AI-based
critical systems is presented in Section 3. In Section
4, the utility of the approach is illustrated with an
example of formalized engineering activities and
processes (methodological guidelines) for AI-based
systems. The paper is rounded off with some general
conclusions and plans for future works in Section 5.
2 CONTEXT AND MOTIVATION
This section presents the overall problem that the
Confiance.ai research program aims to tackle
(Section 2.1), the ambition of an integrated solution
developed by Confiance.ai (Section 2.2), and the
more specific problem that the work presented in this
paper aims to help solve (Section 2.3).
2.1 Trustworthiness in AI-Based
Systems
An AI-based system integrates at least one subsystem
or component using AI technology. In our work we
have reduced AI to Machine Learning, since it is the
AI technique mostly considered currently by
industries for integration in their systems. Such
integration has consequences on the development of
the system, for example:
The benefit of enhancing the system with more
autonomy;
2
https://www.confiance.ai/
The drawback of unpredictability, which deters
reliability;
The legal and moral obligation to respect duties
such as the AI Act, explainability, and the place
of humans at the center of decision-making;
The evolutivity of the system in an ever-
changing environment to be periodically
reconsidered, for instance through monitoring
that can provide feedback to the learning
process.
A key value that must be introduced before
deploying an AI-based system, especially for critical
systems, is trustworthiness. Trustworthiness is not
reduced to predictability. It includes all the AI-related
quality attributes of an AI-based system (Mattioli et
al, 2023). Moreover, trustworthiness must be
considered along all the steps the engineering cycle
of a critical system (as early as the business/mission
analyses, then during specification, architecture,
development, implementation, integration,
verification, validation, qualification, deployment),
and at each systemic level (system, component, ML
model, data…).
To make sure that trustworthiness is considered at
each of these steps and levels, it is necessary to have
a consistent end-to-end engineering approach that
considers the trustworthiness properties through
dedicated engineering activities and processes (to
identify them, specify them, allocate them, develop
them by construction, evaluate them, etc.), using
relevant methods and tools.
2.2 Confiance.ai’s Trustworthiness
Environment
To support the French industry on this matter of
trustworthiness in AI-based systems, the Confiance.ai
research program aims to develop a set of consistent
methods and tools addressing, for example, AI
robustness, AI monitoring, AI explainability, AI
embeddability, and so on. These methods and tools
shall not be disparate standalone objects. On the
contrary, they shall be consistently integrated in an
end-to-end approach that covers all the necessary
engineering steps.
To this end, the Confiance.ai research program
provides a tooled workbench called the
Trustworthiness Environment, that integrates the
software tools developed within Confiance.ai. The use
of this workbench will be consistent with an end-to-end
engineering method that integrates the local methods
elaborated for each Confiance.ai’s research topic.
MBSE to Support Engineering of Trustworthy AI-Based Critical Systems
281

The focus of this paper is not to present all the
local topic-specific answers provided by Confiance.ai
(how to develop an ML model robust by design, how
to make an ML model explainable, how to embed an
ML model, etc.), but to propose an MBSE-based
approach that allows the complex methodological
integration necessary to build an end-to-end
engineering method for critical AI-based systems.
2.3 Lack of Formalization of AI
Engineering
Classical systems engineering and software
engineering (i.e. for systems and software that do not
embed AI components) are already widely
normalized: at a generic high-level through standards
that are not new (for example ISO/IEC/IEEE 15288
and ISO/IEC/IEEE 12207), and at a more specific
low-level through domain-specific standards and
company internal methods & processes.
This is not yet the case for AI, more particularly
for Machine Learning (ML) technologies that are the
main focus of Confiance.ai. There is no detailed step-
by-step guide yet for the development of a critical
system that embeds ML technology. There are two
main reasons for this. Firstly, Systems Engineering
and ML engineering are two separate engineering
domains with different cultures and the connection
between them is currently relatively weak. Secondly,
ML engineering processes are not yet formally
described. This is, in part, due to the fact that this
technology is still evolving rapidly.
To facilitate the integration of ML into critical
systems, it is essential to provide a comprehensive
description of ML engineering processes and
establish connections with traditional
systems/software engineering processes. If required,
modifications or adaptations to the existing
engineering practices should be made to ensure a
seamless integration of ML technology.
There is such ongoing work at standardization
level: ISO/IEC DIS 5338 for example, which
completes ISO/IEC/IEEE 15288 and ISO/IEC/IEEE
12207 for AI-specific matters, or AS 6983 from SAE.
We take into account the available drafts of these
future standards to structure our approach, and thus
make sure that our end-to-end engineering method
will, by construction, be consistent with them.
However, these standards are, by nature, generic, and
our ambition is to go deeper at low-level engineering
activities to provide concrete solutions to engineers
involved in the development of ML-based critical
systems.
3 MBSE TO SUPPORT
ENGINEERING OF
TRUSTWORTHY AI-BASED
CRITICAL SYSTEMS
This section focuses on the chosen MBSE
method/tool used as bases for our approach (Section
3.1), the specialization of the MBSE approach to our
goal related to Confiance.ai’s Trustworthiness
Environment (Section 3.2), and the work strategy
used to gather the necessary inputs for elaborating our
end-to-end engineering method (Section 3.3).
3.1 Choice of ARCADIA/ Capella as
Bases for MBSE Method/ Tool
Several methods and tools are available for
formalization and modeling (e.g. BPMN methods and
tools for the modeling of processes). However, our
ambition is not only to model a set of engineering
activities and processes for critical AI-based systems,
but also to specify and structure a tooled workbench,
the Trustworthiness Environment, consistent with
these engineering activities and processes.
Therefore, we decided to base our modeling
approach on the MBSE method/tool couple
ARCADIA/Capella, by adapting the definition of the
four ARCADIA/Capella perspectives in the
following way, as shown in Figure 1:
Operational Analysis: the operational need
around the Trustworthiness Environment, that
is to say, the engineering methods and
processes that the Trustworthiness
Environment shall support.
System Analysis: the functions/services that
the Trustworthiness Environment shall provide
in order to support the engineering processes
defined in the Operational Analysis
perspective.
Logical Architecture: the abstract resources to
be used by the Trustworthiness Environment.
Physical Architecture: the concrete resources
to be used by the Trustworthiness Environment
(mainly, the software tools developed by
Confian.ce.ai to adress AI trustworthiness).
As an MBSE tool, Capella was chosen also
because we knew that the Viewpoints needed for our
modeling (cf. next Section 3.2) would not necessarily
be natively consistent with any method/tool, and
given the openness of Capella, we were confident that
we would be able to have Capella adapted to our need.
MODELSWARD 2024 - 12th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
282

Figure 1: The ARCADIA modeling pyramid applied to Confiance.ai’s Trustworthy Environment.
3.2 Specialization of the MBSE
Approach for the Trustworthy
Environment
In order to explain how an MBSE approach can be
applied to our need to model the Trustworthiness
Environment, it is useful to set the key concepts
contextualizing such application. To do so, we are
inspired by the standard-based conceptual model of
reference architecture (Awadid, 2022) defined in
accordance with the ISO/IEC/IEEE 42020 standard
(ISO/IEC/IEEE 42020, 2019). The resulting
conceptual model is presented in Figure 2.
In this conceptual model, the concepts of
"Stakeholder", "Concern", "Viewpoint" and "View"
are defined by the ISO/IEC/IEEE/DIS 42010
standard (ISO/IEC/IEEE/DIS 42010, 2020) as
follows.
Figure 2: Conceptual model for the description of the
Trustworthiness Environment.
Stakeholder: “role, position, individual,
organization, or classes thereof having an interest,
right, share, or claim in an entity or its architecture”.
In our context, it refers to the engineering roles that
will use the Trustworthiness Environment.
Concern: “a matter of relevance or importance to
one or more stakeholders regarding an entity of
interest”. For our approach, it refers to the
expectations of the engineers regarding the support to
their activities that the Trustworthy Environment
shall provide.
Viewpoint: “conventions for the creation,
interpretation, and use of an architecture view to
frame one or more concerns”. We had to build our
own meta-model to establish the concepts and
relationships between concepts necessary to produce
our Views.
View: “information item comprising part of an
architecture description that expresses the
architecture of an entity of interest, and that is
governed by an architecture viewpoint”. The Views
of our modeling approach need to have the
expressivity necessary to describe activities,
processes, tools supporting the engineering of critical
ML-based systems.
Perspective: this term is specific to
ARCADIA/Capella, it refers to each
analysis/architecture phase of the ARCADIA
method, as shown in Figure 1. Since we based our
MBSE approach on ARCADIA/Capella, our Views
are captured in an ARCADIA/Capella perspective.
MBSE to Support Engineering of Trustworthy AI-Based Critical Systems
283
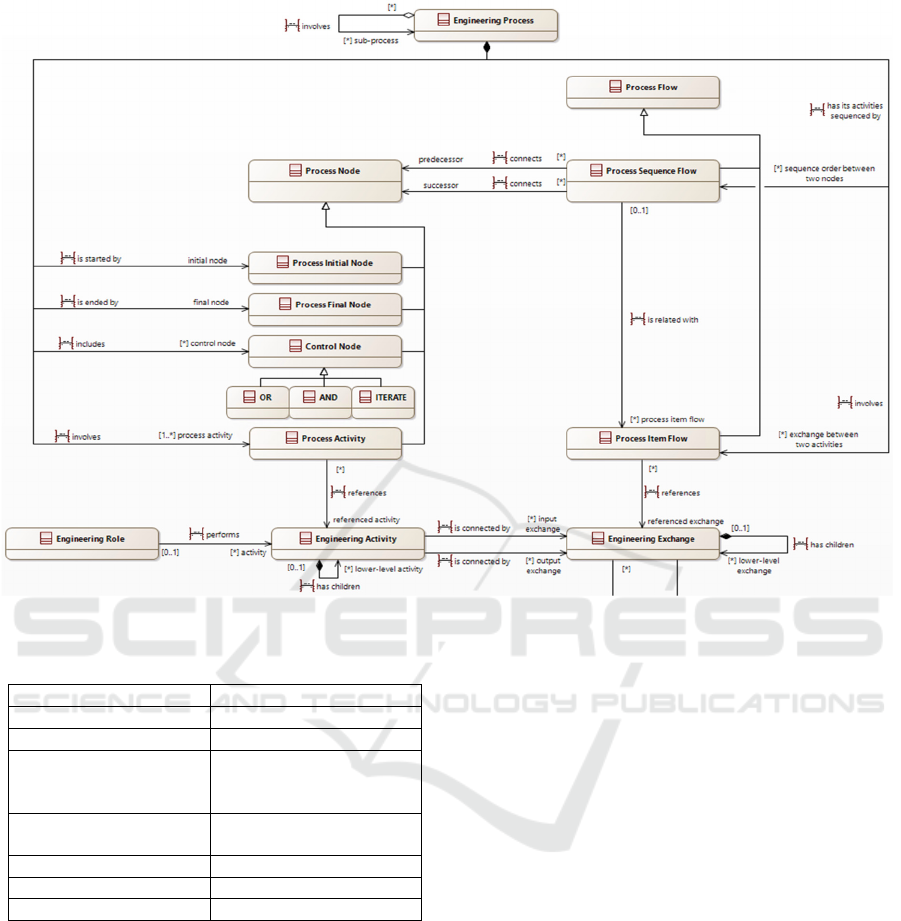
Figure 3: "Engineering Activities for trustable AI" Viewpoint.
Table 1: Correspondence with Capella objects.
Meta-model concept Capella object
Engineering Process Operational Process
Process Se
q
uence Flow Se
q
uence Lin
k
Process Activity Operational Process
Involvement Operational
Activit
y
Process Item Flow Operational Process
Involvement Lin
k
En
g
ineerin
g
Role Role
En
g
ineerin
g
Activit
y
O
p
erational Activit
y
Engineering Exchange Operational Interaction
Figure 3 above shows the meta-model of one of
the main Viewpoints of our approach, that governs
the Views describing the engineering activities and
processes. Concepts and their relationships were
defined in a tool-agnostic way. Then, the concepts of
this meta-model were mapped to objects of Capella’s
Operational Analysis perspective (see Table 1).
Since Capella had restrictions regarding the
implementation of these concepts and their relations
ships, the Confiance.ai program had a Capella plug-in
developed in order to have our Viewpoints matched.
Therefore, the modeling approach we used is not
exactly the ARCADIA method and the Capella tool,
it is an adaptation of ARCADIA/Capella fitting our
modeling need.
3.3 Work Method
In order to build the Operational Analysis perspective
of our model, that is to say, formalize the engineering
activities and processes for critical ML-based
systems, two strategies are combined:
Top-down, drafts of standards that address the
subject of ML-based systems (ISO/IEC DIS
5338, AS 6983…) are taken into account, in
order to provide the overall structure for our
end-to-end engineering approach. Figure 4
below shows the main engineering steps of our
end-to-end method, organized according to the
traditional “V” cycle (“W” cycle at ML model
level).
Bottom-up, the various research works of the
Confiance.ai program are analyzed (produced
documents, interviews of researchers) in order
to identify the methods and tools that zoom in
the ML-specific details of one of the main
engineering steps, with the condition of being
mature enough for integration in the end-to-end
engineering method.
MODELSWARD 2024 - 12th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
284
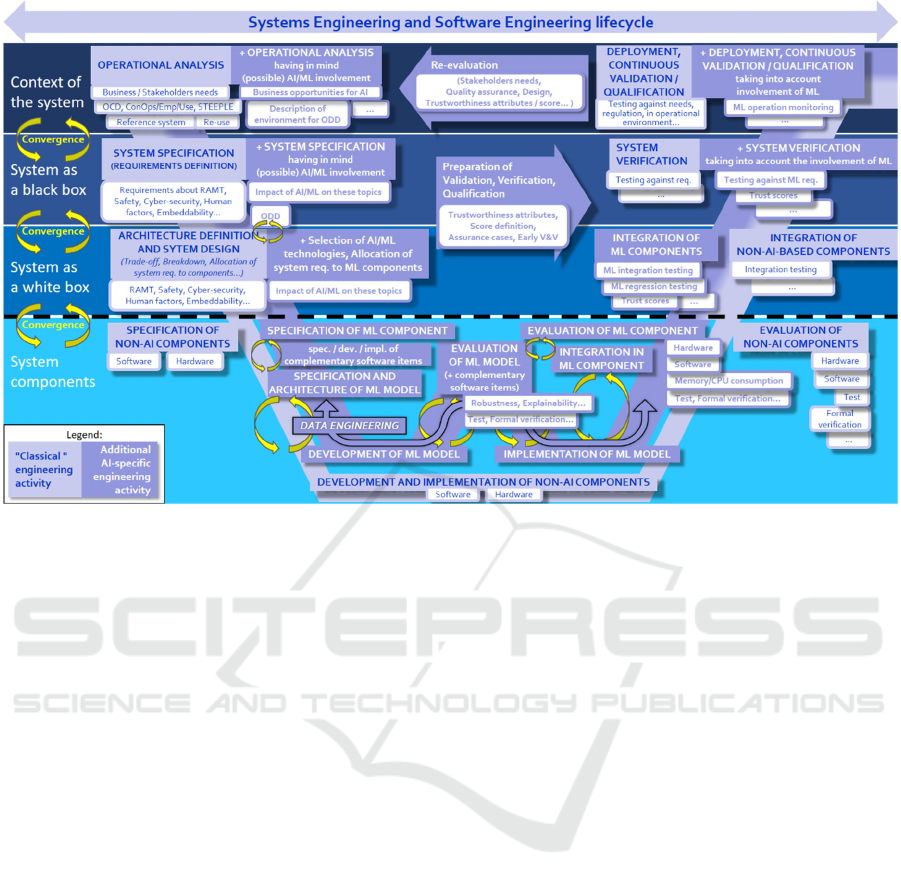
Figure 4: End-to-end engineering cycle for ML-based systems.
4 EXAMPLE OF A FORMALIZED
ENGINEERING PROCESS
Once an ML model has been developed (built,
configured, trained), it needs to be evaluated, to make
sure that all the required properties are reached. One
of the important trustworthiness attributes to be
considered is the robustness. To evaluate this aspect,
the Confiance.ai has explored two techniques. The
first one uses testing: the ML model is executed with
a perturbed dataset, and the deviation of the model
from its nominal behavior is measured. The second
ones uses formal verification: model robustness,
expressed by formal properties, is mathematically
verified by accessing the internal structure of the
model. Given the cost of formal verification,
Confiance.ai recommends to start by robustness
testing, and to perform robustness formal verification
only once testing has shown satisfactory results.
This is illustrated by the following Figure 5.
Given the size of the Capella diagrams, the detail of
each diagram may be difficult to read, but the detail
of each modelled process is not the point of this paper.
The point is rather to show that MBSE enabled the
formalized construction of a complex and
comprehensive multi-level workflow supporting the
engineering of critical AI-based systems.
The first diagram at the top of Figure 5 is the
modelling of the full engineering cycle (equivalent to
the Figure 4 previously shown).
The “pink zoom” of Figure 5 expands the content
of the “Evaluate the trained ML Model” first-level
engineering activity and focuses on a key
trustworthiness attribute: robustness, thus showing a
second diagram that describes the “Evaluate
robustness of the trained ML Model” second-level
engineering activity.
The “green zoom” of Figure 5 expands the content
of the first phase of this second-level engineering
activity, thus showing a third diagram that describes
the “Evaluate robustness of the trained ML Model with
sampling and perturbation” third-level activity.
This third diagram contains the lowest-level
engineering activities, directly corresponding to
methods and tools developed or recommended by the
Confiance.ai research team having the expertise in
model robustness test.
Such “zooms” are possible for any step of the
overall engineering cycle. The engineering of ML-
based critical systems is thus supported. Going through
the whole cycle, from system to component then to ML
model and data, from specification to development
then to IVV, engineers can zoom to the engineering
activities specific to ML-based systems, for the
required trustworthiness aspects (safety, robustness,
explainability, embeddability…), and be assisted by
the methods and tools associated to these activities.
MBSE to Support Engineering of Trustworthy AI-Based Critical Systems
285
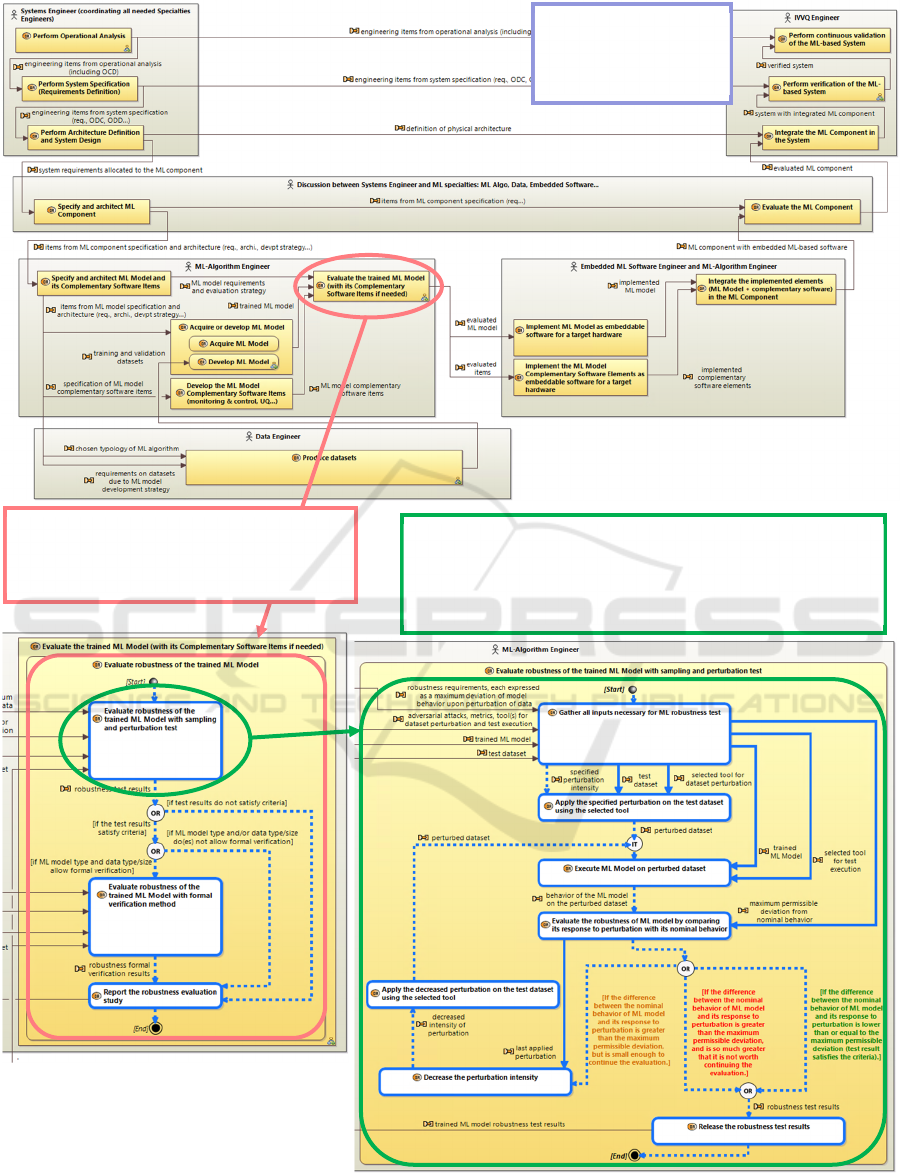
Figure 5: Zoom on the evaluation of ML model robustness by test of its response upon perturbation of input data.
Modeling of the full
engineering cycle,
as per Figure 4.
Zoom on the “ML model evaluation”
step, with focus on one trustworthiness
property: robustness.
Zoom on the first phase of the “ML model robustness
evaluation” process. This is the lowest-level diagram,
where activities can supported by tools developed or
recommended by the Confiance.ai research program.
MODELSWARD 2024 - 12th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
286

5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORKS
This paper proposed an MBSE approach (based on a
modification of ARCADIA/Capella) to support the
complex engineering of trustworthy AI-based critical
systems.
The system of interest of our modelling is the
Trustworthy Environment, the tooled workbench to be
delivered by the Confiance.ai research program. At our
current stage of progress, we are primarily focused on
the "Operational Analysis" perspective of the proposed
modeling approach. This involves identifying and
formalizing the activities and processes required for
engineering an AI-based critical system, with the
ambition to obtain in this way an applicable end-to-end
engineering method. To do so, we rely, on one hand,
for higher-level engineering activities and processes
(structure of our approach), on in-work standards such
as ISO 5338 and AS 6983, and on the other hand, for
lower-level engineering activities and processes
(details of our approach), on the expertise of the
various research teams of Confiance.ai.
Several future works are planned. First, we need
to consolidate and complete the approach along the
full engineering cycle. Currently, not all engineering
steps are covered yet.
Second, Confiance.ai intends to publish the
obtained end-to-end engineering method through a
website. This entails work to make our modeling as
graphic and easily navigable as possible.
Third, the obtained end-to-end engineering
approach needs to be evaluated against use cases.
Each specific method integrated in our approach has
already been locally, on its own, evaluated against a
use case. What remains to be done is evaluating
portions of our obtained end-to-end engineering
method, i.e. successions of engineering activities and
processes, involving different methods and tools on a
same use case.
Fourth, the modeling approach has to be
continued by the System Analysis (functional
specification of the Trustworthy Environment) and by
the Logical and Physical Architecture (architecture of
the Trustworthy Environment). Confiance.ai’s
Trustworthy Environment is already under
construction, by collecting and integrating all
software tools developed by the various teams of the
research program. However, having a full modeling
from Operational Analysis to Physical Architecture
will ensure full consistency and traceability between
the methodological guidelines described in our
Operational Analysis and the relevant tools to be
considered in the Physical Architecture.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work has been supported by the French
government under the “France 2030” program.
REFERENCES
Miglani, A., & Kumar, N. (2019). Deep learning models for
traffic flow prediction in autonomous vehicles: A review,
solutions, and challenges. Vehicular Communications,
20, 100184.
Boardman, M., & Butcher, F. (2019). An exploration of
maintaining human control in AI enabled systems and
the challenges of achieving it. In Workshop on Big Data
Challenge-Situation Awareness and Decision Support.
Brussels: North Atlantic Treaty Organization Science
and Technology Organization. Porton Down: Dstl
Porton Down.
Mattioli, J., Le Roux, X., Braunschweig, B., Cantat, L.,
Tschirhart, F., Robert, B., ... & Nicolas, Y. (2023,
September). AI engineering to deploy reliable AI in
industry. In AI4I.
Li, B. H., Hou, B. C., Yu, W. T., Lu, X. B., & Yang, C. W.
(2017). Applications of artificial intelligence in
intelligent manufacturing: a review. Frontiers of
Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 18,
86-96.
El-Sherif, D. M., Abouzid, M., Elzarif, M. T., Ahmed, A.
A., Albakri, A., & Alshehri, M. M. (2022, February).
Telehealth and Artificial Intelligence insights into
healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic. In
Healthcare (Vol. 10, No. 2, p. 385). MDPI.
Mwadulo, M. W. (2016). Suitability of agile methods for
safety-critical systems development: a survey of
literature. International Journal of Computer
Applications Technology and Research, 5(7), 465-471.
Adedjouma, M., Adam, J. L., Aknin, P., Alix, C., Baril, X.,
Bernard, G., ... & Morvan, M. (2022). Towards the
engineering of trustworthy AI applications for critical
systems-The Confiance. ai program.
Awadid, A. (2022, March). Reference Architectures for
Cyber-Physical Systems: Towards a Standard-Based
Comparative Framework. In Future of Information and
Communication Conference (FICC). San Francisco,
USA. (pp. 611-628) Springer International Publishing.
ISO/IEC/IEEE 42020:2019:2019-07.: Software, systems
and enterprise — Architecture processes. Int. Organ.
Stand. Geneva, Switzerland (2019).
ISO/IEC/IEEE/DIS 42010:2020.: Draft International
Standard for Systems and Software Engineering—
Architecture Description.
Mattioli, J., Sohier, H., Delaborde, A., Amokrane, K.,
Awadid, A., Chihani, Z., ... & Pedroza, G. (2023b,
March). An overview of key trustworthiness attributes
and kpis for trusted ml-based systems engineering. In
Workshop AITA AI Trustworthiness Assessment-
AAAI Spring Symposium.
MBSE to Support Engineering of Trustworthy AI-Based Critical Systems
287
