
Generation of H&E-Stained Histopathological Images Conditioned on
Ki67 Index Using StyleGAN Model
Lucia Piatrikov
´
a
a
, Ivan Cimr
´
ak
b
and Dominika Petr
´
ıkov
´
a
c
Faculty of Management Science and Informatics, University of
ˇ
Zilina,
ˇ
Zilina, Slovakia
Keywords:
Hematoxylin and Eosin, Ki67, Conditional GAN, StyleGAN, Digital Pathology.
Abstract:
The analysis of tissue staining is a crucial aspect of cancer diagnosis. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining
captures fundamental morphological structures, while analysing Ki67-stained images provides deeper infor-
mation about the tissue. However, this method is more expensive and time-consuming. Integrating machine
learning techniques into pathologists’ workflow can save time and resources and provide reproducible results
without intra- and inter-observer variability. However, the model must be explainable to be applicable in clin-
ical practice. A generative model can add supplementary information that serves as an explanation for model
predictions. This paper demonstrates the preliminary results of the conditional StyleGAN model trained on
H&E-stained images conditioned on the corresponding Ki67 indexes. In our future research, StyleGAN will
be part of a model for the estimation of Ki67 index from H&E staining and will generate explanations for the
model’s predictions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Pathologists diagnose cancer by scrutinising tissue
sections under a microscope or images acquired by
digital scanners. Tissue sections are stained to visu-
ally distinguish various tissue components. The anal-
ysis of stained tissue is a crucial factor in diagnosing
different cancer types, influencing tumour classifica-
tion and treatment recommendation.
Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining is the gold
standard commonly utilised in cancer diagnosis (Gur-
can et al., 2009). The H&E-stained sections depict
essential morphological structures (Wittekind, 2003).
To obtain more information from a tissue, patholo-
gists often use Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining.
IHC analysis evaluates the expression of a specific
protein in a tissue. Protein Ki67 indicates cell pro-
liferation, and the Ki67 index reckons its expression
as the percentage of Ki67-positive cells. While Ki67
staining provides more profound information about a
tissue than H&E staining, it comes with higher time
and cost requirements.
Deep learning models hold promise for improv-
ing medical diagnoses by delivering prompt, cost-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8763-4975
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0389-7891
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8309-1849
effective, and consistent decisions. However, a model
must be explainable before it can be used in clini-
cal practice. Particularly in medical contexts, mis-
takes can endanger human lives. Furthermore, the
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) (Regula-
tion, 2020) in the European Union requires algorithm
transparency as a prerequisite for its application in pa-
tient care.
Combining a deep learning model with a genera-
tive model can provide additional information serving
as explanations for model predictions, e.g., it can gen-
erate counterfactual examples. Counterfactual exam-
ples search for a minimal modification in the original
data, leading the model to reverse its prediction, e.g.,
shifting the label from healthy to unhealthy in medical
image analysis.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) intro-
duced by (Goodfellow et al., 2014) can generate new,
realistic samples from the high-dimensional train-
ing data distribution. GAN is composed of a gen-
erator that creates new images and a discriminator
that decides whether the generated image is similar
to the ones in the training set. Conditional GAN
(Mirza and Osindero, 2014) utilises an additional la-
bel of the training samples, making both the genera-
tor and discriminator conditioned on this information.
StyleGAN is an improved GAN model proposed by
NVIDIA researchers (Karras et al., 2019). It has en-
512
Piatriková, L., Cimrák, I. and Petríková, D.
Generation of H&E-Stained Histopathological Images Conditioned on Ki67 Index Using StyleGAN Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0012464200003657
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2024) - Volume 1, pages 512-518
ISBN: 978-989-758-688-0; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright © 2024 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

hanced generator and discriminator architecture based
on the principle of progressive growing, which leads
to high-resolution image generation. It automatically
separates high-level image features, thus building the
latent space with higher interpretability.
The goal of our research is to create an explain-
able model for the prediction of Ki67 index from an
H&E-stained image. In our research, we apply gen-
erative models to the histopathology domain in order
to add explainability to our predictions and study the
hidden relationship between H&E and Ki67 staining.
Currently, we explore conditional StyleGAN model to
generate synthetic H&E-stained images conditioned
on Ki67 indexes. We utilise a histopathological im-
age dataset consisting of pairs of adjacent H&E and
Ki67-stained tissue sections. Additionally, we have
the corresponding Ki67 indexes for the H&E-stained
images. The paper demonstrates our preliminary re-
sults.
The paper is organised as follows. Section 2 dis-
cusses related works which apply StyleGAN model
to histopathology image generation. In Section 3, we
introduce our dataset and explain the model. Section
4 reports our preliminary results, and section 5 con-
cludes with future work.
2 RELATED WORK
Some works have applied StyleGAN model to
histopathology. The study of (Quiros et al., 2019)
introduces PathologyGAN, designed for generat-
ing 224 × 224 H&E-stained histopathological image
patches from interpretable latent space. Pathology-
GAN utilises the BigGAN architecture (Brock et al.,
2018), combined with few StyleGAN features. Re-
searchers’ experiments with linear interpolation be-
tween two latent vectors illustrate a realistic transition
from benign to malignant tissue with a growing num-
ber of cancer cells.
The paper (Schutte et al., 2021) utilises StyleGAN
model with Convolutional Neural Network as encoder
and logistic regression for generating a series of syn-
thetic images depicting the evolution of pathology.
The proposed approach generates images from the
shortest path in latent space between two vectors with
opposite model predictions. One of the applications
analysed in the paper is changing the probability of
tumour in H&E-stained image patches. However, the
model cannot appropriately reconstruct histopatho-
logical images.
The work of (Daroach et al., 2021) employs Style-
GAN for the generation of H&E-stained prostatic his-
tology images. Specifically, the authors use Style-
GAN2 (Karras et al., 2020), which is the improved
version of the original StyleGAN (Karras et al.,
2019). Their model generates new realistic 1024 ×
1024 patches proved by expert pathologists. Further-
more, researchers do various experiments, e.g., with
latent space representations at different StyleGAN
generator levels, in order to explore their influence on
different histologic morphologies. In the next experi-
ment, scientists group generated samples into classes
and recognise that the class’s latent space mean rep-
resents particular morphological information. In an-
other experiment, researchers explore the interpola-
tion between two latent vectors of images with dif-
ferent histologic labels. Authors conclude that gen-
erated images look realistic but do not imitate legiti-
mate physical transitions. Nevertheless, the work of
(Daroach et al., 2021) proves that StyleGAN model
can learn and subsequently generate high-resolution
histopathological images.
Our research adopts a similar approach as
(Daroach et al., 2021). However, we employ condi-
tional StyleGAN3 with additional Ki67 index infor-
mation about H&E-stained image patches.
3 METHODS
This study demonstrates the use of conditional Style-
GAN model to generate H&E-stained tissue images
for given Ki67 indexes. Specifically, we aim the
model to generate H&E staining corresponding to a
specific Ki67 index.
3.1 Dataset
The dataset was constructed from H&E and Ki67-
stained whole slide images (WSI) of seminoma, tes-
ticular tumor. Images were provided by the De-
partment of Pathology, Jessenius Medical Faculty of
Comenius University and University Hospital. Alto-
gether, 84 pairs of H&E-stained tissue scans and cor-
responding Ki67-stained tissue scans were available.
H&E and Ki67 staining were applied to adjacent sec-
tions to ensure the tissues were as similar as possible,
although they did not match at the cellular level. Nev-
ertheless, we assume the tissues in both images from
the same region have similar characteristics.
Apart from the images, the dataset did not contain
any labels, so it was necessary to annotate the data
first. To do this, we used an improved semi-automated
approach based on (Petr
´
ıkov
´
a et al., 2023), which
contains three main steps: tissue registration, cluster-
ing into primary colours and quantification of Ki67
index. Due to the huge size of the scans and limited
Generation of H&E-Stained Histopathological Images Conditioned on Ki67 Index Using StyleGAN Model
513

Figure 1: Example of corresponding H&E and Ki67 patches
from the dataset.
computational capacity, we processed images from
the first level, i.e., with the second-highest resolution.
Ki67 indexes were estimated from Ki67 patches using
image analysis methods. Each calculated Ki67 index
was then assigned as the label to the corresponding
H&E patch cut in the same position. An example
of a H&E patch and the corresponding original Ki67
patch is shown in Figure 1. The third clustered Ki67
patch was generated as a result of clustering. Clus-
tered Ki67 patches were used to estimate the Ki67 in-
dexes as a ratio of the area with the brown and blue
pixels.
The training dataset for StyleGAN consists of
256×256 square patches of H&E images. Each H&E
patch is labelled with the Ki67 index calculated from
the corresponding clustered Ki67 patch. An example
of H&E patches with Ki67 labels from our dataset is
illustrated in Figure 3. The training dataset contains
49 tissue scans cut into 189602 patches.
3.2 Model
StyleGAN allows high-resolution image generation,
which is essential for microscopic histopathology im-
ages. We utilise StyleGAN3 (Karras et al., 2021),
which is equivariant to translation and rotation.
Specifically, we adopt conditional StyleGAN model
to H&E image patch generation conditioned on the
Ki67 index. StyleGAN generates synthetic H&E-
stained image patches from an input latent vector and
given Ki67 index. The model is illustrated in Figure
2. For the training, we use the pairs of H&E patches
with corresponding Ki67 indexes. Our goal is that
pathologists cannot distinguish between real and syn-
thetically generated H&E images.
Figure 2: StyleGAN model.
Figure 3: Example of H&E patches with Ki67 index labels
from the dataset.
4 RESULTS
We trained StyleGAN3, specifically the transla-
tion and rotation equivariant StyleGAN3-R model,
from the official GitHub NVlabs repository (NVlabs,
2023). The regularisation parameter gamma was set
to 2, and adaptive discriminator augmentation (ADA)
was enabled. The final model viewed 5 343 000 image
patches (5343 kimgs) during the training, meaning
it iterated through the whole dataset about 28 times.
The training ran for 3 days and 8 hours on two GPUs,
namely NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 and NVIDIA
GeForce RTX 3080 Ti.
The sample of images generated by our StyleGAN
model is presented in Figure 4. Images are arranged
according to the increasing value of the input Ki67
index. The Ki67 index value is written above each
generated image.
We evaluated the quality of generated images and
latent space using two metrics. Fr
´
echet Inception Dis-
tance (FID) (Heusel et al., 2017) assesses the qual-
ity and diversity of generated images by comparing
them to real data distribution. It was calculated for
the whole training dataset and 50 000 generated im-
ages. Perceptual Path Length (PPL) was introduced
together with StyleGAN model (Karras et al., 2019).
It quantifies the disentanglement of latent space by
analysing interpolation between latent vectors. It was
calculated as mean for 50 000 samples. FID and PPL
must be minimised for more realistic generated im-
ages and higher quality latent space.
The final model was evaluated by FID and PPL
metrics. The value of the FID is 16.62, while the PPL
metric is 118.74. Additionally, we compared the val-
ues of these two metrics with models from the work
of (Daroach et al., 2021). Firstly, their best FID model
achieved FID value of 2.86 and PPL of 139.34. Sec-
ondly, their best PPL model achieved FID of 3.69 and
PPL of 33.25. Researchers obtained mostly better re-
sults; however, these values are not fully compara-
ble because models were trained on different datasets,
and correspondingly the metrics were calculated on
the different data.
The progress of intermediate models is illustrated
in Figure 5a by FID metric and in Figure 5b by
PPL metric. Metrics were calculated after every 200
BIOINFORMATICS 2024 - 15th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
514

Figure 4: Sample of generated images.
Generation of H&E-Stained Histopathological Images Conditioned on Ki67 Index Using StyleGAN Model
515
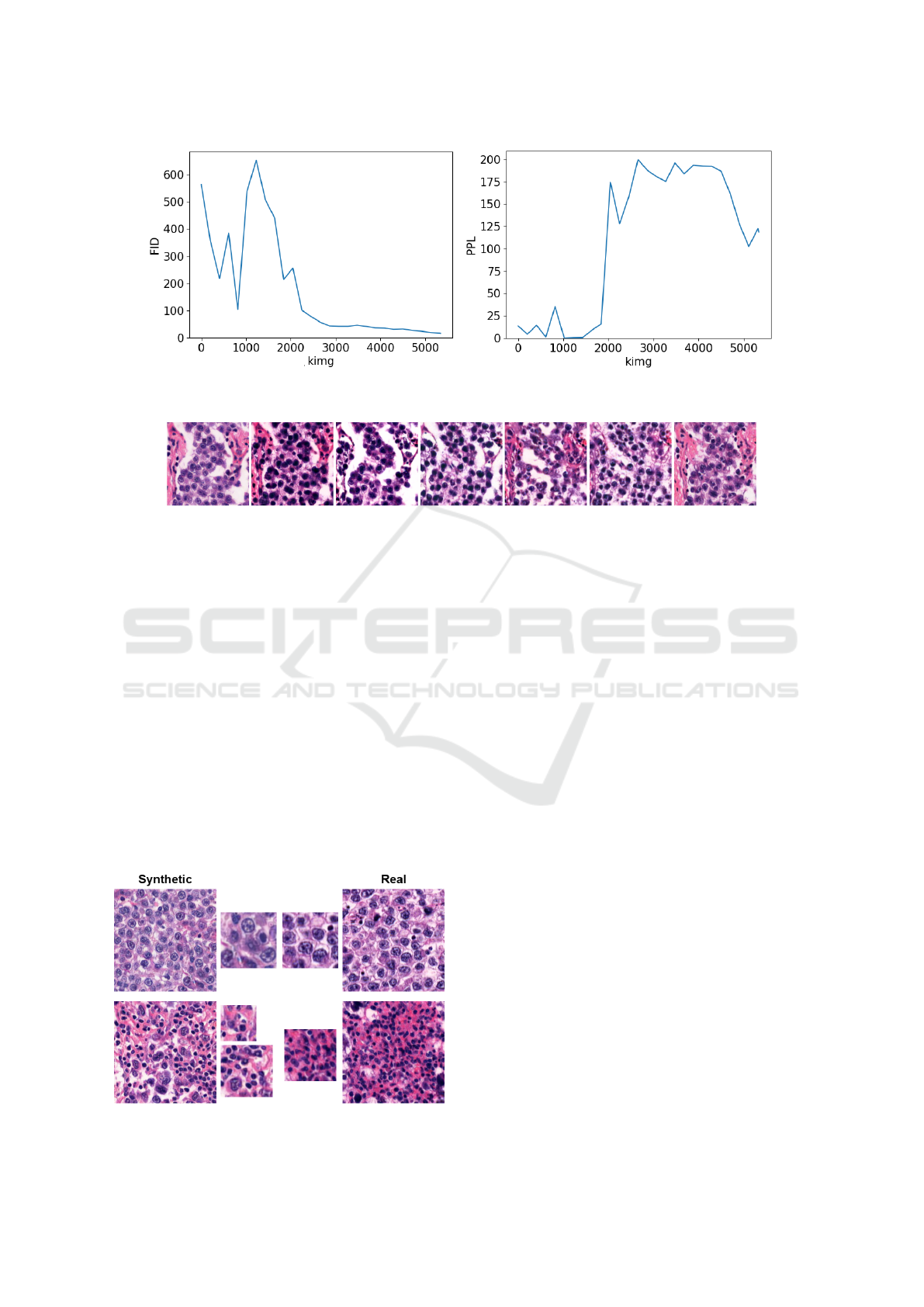
(a) The progress of FID metric. (b) The progress of PPL metric.
Figure 5: The progress of metrics.
Figure 6: Example of similar pattern occurring in generated images.
kimgs. As depicted in the figures, the FID metric de-
creased during the training. However, the PPL metric
started with low values because the model generated
low-quality blurred images which were not diverse at
the beginning of the training. Therefore, PPL values
increased after 2000 kimgs when the image genera-
tion quality and diversity raised. At the end of the
training, the PPL value started decreasing. It will
probably decrease more if the training is longer.
We can observe several structures and patterns in
generated images when we study them in more detail.
An example of such structures is illustrated in Fig-
ure 7, where synthetic images are placed in the first
column, and selected similar real images are in the
second column. Both synthetic and real images have
one or two zoomed parts next to the image for mutual
comparison. In the first row, we can observe that the
structure of synthetic cells contains similar patterns
Figure 7: Comparison of synthetic and real images.
and is considerably more regular compared to real
cells. The second row shows the case when cells are
arranged in regular structures, such as regular circles
or arcs, which do not appear in real H&E images. An-
other undesirable phenomenon appears in the layout
of images resembling each other. Consequently, sev-
eral generated images follow a similar pattern in their
layout. An example of generated images with compa-
rable layouts demonstrating this problem is shown in
Figure 6. Furthermore, we also notice typical Style-
GAN artifacts which resemble water droplets in gen-
erated images.
Additionaly, the quality of generated images was
evaluated by an expert pathologist from the Depart-
ment of Pathology, Jessenius Medical Faculty of
Comenius University and University Hospital. For
this purpose, we created a sample of 30 synthetic and
30 real images arranged in random order. The evalua-
tion was divided into two parts, namely fast and slow
estimation. In fast estimation, the pathologist quickly
looked at an image and estimated its realism at first
glance. In slow estimation, the pathologist was al-
lowed to analyse images for an unlimited time. For
each image, the pathologist marked one of five cate-
gories, which were certainly real, rather real, certainly
synthetic, rather synthetic, or they could not decide.
Table 1 shows fast and slow estimation results. In
fast estimation, the pathologist could not decide about
eight images, three of which were synthetic. Then
was convinced that six synthetic images were real and
another six synthetic images were rather real. These
12 best-ranking generated images are shown in Fig-
BIOINFORMATICS 2024 - 15th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
516

Figure 8: Best-ranking synthetic images.
Table 1: Pathologist estimation results.
Fast Pathologist Estimation
Certainly Real Rather Real Undecided Rather Synthetic Certainly Synthetic
Real 11 10 5 4 0
Synthetic 6 6 3 7 8
Slow Pathologist Estimation
Certainly Real Rather Real Undecided Rather Synthetic Certainly Synthetic
Real 16 9 5 0 0
Synthetic 0 2 0 2 26
Table 2: Pathologist estimation Confusion Matrix.
Fast Pathologist Estimation
Estimated Real Estimated Synthetic
Actual
Real
21 4
Actual
Synthetic
12 15
Slow Pathologist Estimation
Estimated Real Estimated Synthetic
Actual
Real
25 0
Actual
Synthetic
2 28
ure 8. In summary, 15 synthetic images deceived the
pathologist that they were real or the pathologist was
not sure about, and 15 images were correctly labelled
as synthetic. In slow estimation, the pathologist could
correctly determine almost all synthetic images, ex-
cept for two, which were labelled as rather real. The
pathologist was certain about 26 synthetic images.
Considering real images, the pathologist was correct
for almost all of the examples in both fast and slow
estimations. To conclude, generated images could
persuade pathologists when estimating at first glance;
however, the pathologist could detect synthetic exam-
ples after a more detailed analysis.
Comprehensive results from Table 1 are processed
into confusion matrices in Table 2, omitting the Un-
decided category and merging Certain and Rather cat-
egories. In fast estimation, the accuracy of the pathol-
ogist’s estimations was 69.23%, meaning the pathol-
ogist was unsure about choices. On the contrary, in
slow estimation, the pathologist was almost confident
with an accuracy of 96.36%.
5 CONCLUSION
Preliminary results demonstrate that conditional
StyleGAN model is capable of generating high-
quality H&E-stained histopathological images.
Pathologists could distinguish real and synthetic
images at first glance with an accuracy of 69.23%.
However, after a more detailed analysis of the images,
their accuracy increased to 96.36%. Therefore, the
generated image quality still needs to be enhanced.
To improve the quality of image generation, Style-
GAN hyperparameters can be tuned, e.g., gamma reg-
ularisation weight or augmentation settings. In the
next iteration, we will use a bigger dataset with more
slides cut into patches and run the training for more
Generation of H&E-Stained Histopathological Images Conditioned on Ki67 Index Using StyleGAN Model
517

kimgs. We also plan to experiment with different im-
age patch resolutions and WSI zoom levels.
The following research will analyse the Ki67 in-
dex captured in StyleGAN latent space and the rela-
tionship between H&E and Ki67 staining. We expect
that the Ki67 information improves the structure of
latent space.
In our future research, we will train a model for re-
verse mapping to StyleGAN latent space. The model
will estimate a latent vector and Ki67 index of real
H&E image. Mapping real H&E images to latent
space will enable different experiments with Style-
GAN model, e.g., to generate counterfactual exam-
ples as an explanation of Ki67 index prediction. We
can modify an input image’s Ki67 index or latent
vector and investigate StyleGAN’s outputs. Another
experiment can analyse linear interpolation in latent
space, similarly to (Daroach et al., 2021). These ex-
periments can potentially unveil concealed associa-
tions between H&E and Ki67 tissue staining, expand-
ing scientific knowledge.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by the Ministry of Ed-
ucation, Science, Research and Sport of the Slovak
Republic under the contract No. VEGA 1/0369/22.
Gratitude is extended to K. Tobi
´
a
ˇ
sov
´
a for her assess-
ment of generated images and to L. Plank and K.
Tobi
´
a
ˇ
sov
´
a for their collaboration in the preparation of
the dataset.
REFERENCES
Brock, A., Donahue, J., and Simonyan, K. (2018). Large
scale gan training for high fidelity natural image syn-
thesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.11096.
Daroach, G. B., Yoder, J. A., Iczkowski, K. A., and LaVi-
olette, P. S. (2021). High-resolution controllable pro-
static histology synthesis using stylegan. BIOIMAG-
ING, 11.
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B.,
Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., and Ben-
gio, Y. (2014). Generative adversarial nets. In Ghahra-
mani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., and
Weinberger, K., editors, Advances in Neural Infor-
mation Processing Systems, volume 27. Curran Asso-
ciates, Inc.
Gurcan, M. N., Boucheron, L. E., Can, A., Madabhushi, A.,
Rajpoot, N. M., and Yener, B. (2009). Histopatho-
logical image analysis: A review. IEEE reviews in
biomedical engineering, 2:147–171.
Heusel, M., Ramsauer, H., Unterthiner, T., Nessler, B., and
Hochreiter, S. (2017). Gans trained by a two time-
scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium.
Advances in neural information processing systems,
30.
Karras, T., Aittala, M., Laine, S., H
¨
ark
¨
onen, E., Hellsten, J.,
Lehtinen, J., and Aila, T. (2021). Alias-free generative
adversarial networks. In Proc. NeurIPS.
Karras, T., Laine, S., and Aila, T. (2019). A style-based
generator architecture for generative adversarial net-
works. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference
on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages
4401–4410.
Karras, T., Laine, S., Aittala, M., Hellsten, J., Lehtinen,
J., and Aila, T. (2020). Analyzing and improving
the image quality of stylegan. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition, pages 8110–8119.
Mirza, M. and Osindero, S. (2014). Conditional generative
adversarial nets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.1784.
NVlabs (april 2023). Alias-free generative adversarial net-
works (stylegan3) - official pytorch implementation of
the neurips 2021 paper.
Petr
´
ıkov
´
a, D., Cimr
´
ak, I., Tobi
´
a
ˇ
sov
´
a, K., and Plank, L.
(2023). Semi-automated workflow for computer-
generated scoring of Ki67 positive cells from he
stained slides. In BIOINFORMATICS, pages 292–
300.
Quiros, A. C., Murray-Smith, R., and Yuan, K. (2019).
Pathologygan: Learning deep representations of can-
cer tissue. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.02644.
Regulation, G. D. P. (2020). Art. 22 gdpr. automated indi-
vidual decision-making, including profiling. Intersoft
Consulting, https://gdpr-info. eu/art-22-gdpr.
Schutte, K., Moindrot, O., H
´
erent, P., Schiratti, J.-B., and
J
´
egou, S. (2021). Using stylegan for visual inter-
pretability of deep learning models on medical im-
ages. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.07563.
Wittekind, D. (2003). Traditional staining for routine diag-
nostic pathology including the role of tannic acid. 1.
value and limitations of the hematoxylin-eosin stain.
Biotechnic & histochemistry, 78(5):261–270.
BIOINFORMATICS 2024 - 15th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
518
