
Cross-Domain Classification of Domain Entities into Top-Level Ontology
Concepts Using BERT: A Study Case on the BFO Domain Ontologies
Alcides Lopes
a
, Joel Carbonera
b
, Nicolau Santos
c
, Fabricio Rodrigues
d
, Luan Garcia
e
and Mara Abel
f
Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Institute of Informatics, Porto Alegre, Brazil
Keywords:
Top-Level Ontology Classification, Cross-Domain Classification, Informal Definition, Language Model.
Abstract:
Classifying domain entities into top-level ontology concepts using informal definitions remains an active re-
search area with several open questions. One of these questions pertains to the quality of proposed pipelines
employing language models for classifying informal definitions when training and testing samples are from
different knowledge domains. This can introduce challenges due to varying vocabularies across domains or the
potential for an entity to belong to different top-level concepts based on its domain. In this study, we present
a study case where terms and informal definitions are extracted from 81 domain ontologies organized into 12
knowledge domains. We investigate the performance of a pipeline that utilizes the BERT language model for
classifying domain entities into top-level concepts within a cross-domain classification scenario. Additionally,
we explore various pipeline setups for input, preprocessing, and training steps. Our optimal classifier setup
employs an unbalanced training methodology, no text preprocessing, and the concatenation of terms and in-
formal definitions as input. Furthermore, we demonstrate that BERT yields promising results in classifying
domain entities into top-level concepts within a cross-domain classification scenario.
1 INTRODUCTION
The explosion of digital data and the proliferation of
information sources have created an urgent need for
effective methods to organize and classify domain en-
tities. Ontologies, serving as structured and formal
knowledge representations, are pivotal in integrating
information across domains. Top-level ontologies,
which define high-level and domain-independent con-
cepts and relationships, are key to achieving data
interoperability among various domain ontologies.
However, the classification of domain entities into
concepts defined in top-level ontologies is tradition-
ally manual and demands significant expertise in the
target domain and ontology engineering (Lopes et al.,
2022). The automation of this classification process is
essential for streamlining ontology development, po-
tentially saving time and effort for engineers. Despite
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0622-6847
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4499-3601
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0901-2465
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0615-8306
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9328-9007
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9589-2616
some progress, the field still faces unresolved chal-
lenges.
This study focuses on classifying domain enti-
ties into top-level ontology concepts across different
knowledge domains. We analyze 81 domain ontolo-
gies across 12 knowledge domains, using the Basic
Formal Ontology (BFO) (Arp et al., 2015) for our tar-
get top-level ontology concepts, diverging from previ-
ous works that employed Dolce-Lite-Plus (DLP) (Jul-
lien et al., 2022; Lopes et al., 2022; Lopes et al.,
2023). By leveraging the BERT language model (De-
vlin et al., 2018) in the classification model proposed
in (Lopes et al., 2023), we investigate various aspects
of classification, including input structure and prepro-
cessing and the balance of the classes in the training
data.
In the scope of this work, we are not interested
in evaluating the performance of state-of-the-art lan-
guage models, such as Llamma (Touvron et al., 2023),
and Mixtral (Jiang et al., 2024), or the current trends
in ChatGPT and prompt engineering (Sahoo et al.,
2024). Still, we step back to analyze the conse-
quences of the decision-making while developing a
classification pipeline using an already tested related
pipeline. From that, in our experiments, we showed
Lopes, A., Carbonera, J., Santos, N., Rodrigues, F., Garcia, L. and Abel, M.
Cross-Domain Classification of Domain Entities into Top-Level Ontology Concepts Using BERT: A Study Case on the BFO Domain Ontologies.
DOI: 10.5220/0012557600003690
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2024) - Volume 2, pages 141-148
ISBN: 978-989-758-692-7; ISSN: 2184-4992
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
141

that using unbalanced training and without text pre-
processing achieved the best overall results with an
average of 62% in the macro F-score across all the
12 domains evaluated. Although this average result
seems not so expressive, our experiments demonstrate
that we achieve more than 90% in F-core for many
target classes in many domains, contributing to the
ongoing discussion on cross-domain classification of
domain entities into top-level ontology concepts.
The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2,
we present the background notions supporting this
case study, revisiting ontologies, top-level ontologies,
and the Open Biological and Biomedical Ontologies
(OBO) Foundry. In Section 3, we describe the re-
search questions we aim to answer in this case study
and how we extracted the datasets from the OBO
Foundry. Section 4 showcases the experiments per-
formed using the extracted datasets from different
knowledge domains and presents the obtained results.
Finally, Section 5 offers concluding remarks on our
work.
2 RELATED WORK
This section covers three primary topics. First, we
delve into ontologies, exploring their significance in
knowledge modeling, knowledge-sharing, and inter-
operability, with a specific focus on the OBO Foundry
and the Basic Formal Ontology (BFO). Second, we
provide an overview of language models, with a par-
ticular emphasis on BERT, highlighting their capac-
ity to comprehend human language. Finally, we dis-
cuss various approaches to classify domain entities
into top-level ontology concepts.
2.1 Ontologies, OBO Foundry and the
Basic Formal Ontology
Ontologies serve as structured frameworks for rep-
resenting and organizing domain-specific knowledge.
They are formally and explicitly specified shared
conceptualizations that capture entities, relationships,
and constraints within domains (Studer et al., 1998).
Also, ontologies support knowledge sharing and com-
munication between humans and machines, offering
a common vocabulary and defined relationships for
data integration and interoperability across systems
and applications. The Open Biological and Biomedi-
cal Ontologies (OBO) Foundry is an initiative aimed
at developing interoperable ontologies to represent
and integrate data across various knowledge domains,
including biomedicine, agriculture, and information
technology, among others (Jackson et al., 2021; Smith
et al., 2007). It provides a framework for ontology
creation, maintenance, and sharing, following princi-
ples of open use, collaborative development, and con-
tent specificity with common syntax and relations.
The OBO Foundry includes ontologies from di-
verse domains, such as agriculture, anatomy, biolog-
ical systems, and health, totaling 185 domain ontolo-
gies available on its website. These ontologies cover
concepts, relationships, and instances, integrating in-
formation from dictionaries, glossaries, and other re-
sources. To ensure semantic interoperability among
these ontologies, the Basic Formal Ontology (BFO)
is employed as a top-level ontology within the OBO
Foundry. BFO facilitates the creation of domain-
specific ontologies by addressing the most general as-
pects of reality in a domain-independent way (Arp
et al., 2015). Approximately half of the domain on-
tologies in the OBO Foundry utilize BFO, enhanc-
ing their interoperability. For instance, the Environ-
ment Ontology (ENVO) (Buttigieg et al., 2013) in-
tegrates elements from other domain ontologies that
also use BFO as top-level ontology, such as the Plant
Ontology (PO) (Jaiswal et al., 2005), the Relation On-
tology (RO)
1
, the Food Ontology (FoodOn) citedoo-
ley2018foodon, and the Chemical Entities of Biolog-
ical Interest (ChEBI) (Degtyarenko et al., 2007).
2.2 Language Model
Language models are computational models that un-
derstand and generate human language by being
trained on large text datasets (Touvron et al., 2023;
Jiang et al., 2024). They use statistical learning to
encode semantic and syntactic information, facilitat-
ing a wide range of tasks such as machine translation,
sentiment analysis, and information retrieval. These
models employ word embeddings, dense vectors that
capture relationships between words and sentences, to
process and generate language meaningfully. In this
context, BERT (Devlin et al., 2018) plays a signif-
icant advancement by using a transformer-based ar-
chitecture to understand the bidirectional context in
text. From that, BERT improves word embeddings
by considering the full context of words in both di-
rections, employing two unsupervised tasks for pre-
training: Masked Language Model (MLM) and Next
Sentence Prediction (NSP). In MLM, it predicts ran-
domly masked tokens, while in NSP, it determines if
one sentence logically follows another.
In this work, BERT is preferred over state-of-the-
art language models like Llama (Touvron et al., 2023)
and Mixtral (Jiang et al., 2024), because its architec-
ture and pre-training approach offer specific advan-
1
https://github.com/oborel/obo-relations
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
142

tages for our experiments. In an analogy, employ-
ing newer language models is like shooting a duck
with a missile because we are trying to understand the
nuances of classifying domain entities into top-level
ontology concepts using informal definitions. How-
ever, these newer models are much bigger and require
too much computational power and time to fine-tune.
In this context, BERT has the advantage of using a
bidirectional training strategy that allows understand-
ing the context from both directions of the sentences,
providing a deeper understanding of language struc-
ture and meaning. Additionally, BERT has a smaller
model size compared to newer ones, without the need
to reduce the float point precision in our resource-
constrained environment with a single RTX 3060 with
12GB of VRAM, and then BERT can be used at its
full power.
2.3 Strategies for Classification of
Domain Entities into Top-Level
Ontology Concepts
Approaches to classify domain entities into top-level
ontology concepts typically use text representation
and machine learning. Typically, domain entities
are represented by their names, example sentences,
or informal definitions. This representation is cru-
cial for addressing challenges like polysemy, where
a term may have multiple meanings. (Lopes et al.,
2022) combine word embeddings of terms and infor-
mal definitions to reduce polysemy, using a model
that merges a feed-forward neural network with a bi-
LSTM. However, this requires the term’s presence in
a pre-trained model. (Jullien et al., 2022) suggest us-
ing a term concatenated with an example sentence
as input for the BERT model, although this method
faces challenges with polysemy and dependency on
the term’s inclusion in the Brown corpus (Francis,
1965). (Lopes et al., 2023) propose a more effec-
tive strategy by combining terms and informal defini-
tions into a single text input, thus avoiding reliance on
external corpora. They fine-tuned various language
models focusing on concepts from the Dolce-Lite and
Dolce-Lite-Plus top-level ontologies. While effective,
the adaptability of this method across different on-
tologies and domains and under varied preprocessing
and training conditions remains to be fully explored.
3 THE STUDY CASE
In this section, we delineate the scope of this work
and describe the research questions we aim to answer
in the proposed study case. Additionally, we present
how we extract the dataset from the OBO Foundry,
which we used for a cross-domain classification of
domain entities into top-level ontology concepts de-
fined in the Basic Formal Ontology (BFO).
3.1 Scope and Research Questions
This study explores the effectiveness of the pipeline
detailed in (Lopes et al., 2023) in classifying domain
entities into top-level concepts within a cross-domain
classification scenario, incorporating top-level con-
cepts from a different ontology. Additionally, we
investigate various modifications introduced during
the input, preprocessing, and training stages of the
original pipeline. Figure 1 illustrates four distinct
pipelines, with P1 serving as our baseline and P2
to P4 representing step-wise modifications at each
stage. Through our investigation and the examination
of these pipelines, we aim to address the following
research questions:
1. Research Question: How Do the Classifica-
tion Pipelines Perform Using Only the Infor-
mal Definitions as Input Rather than Combin-
ing Them with the Terms?
Explanation: In (Lopes et al., 2023), the au-
thors advocate combining the term representing
a domain entity with its informal definition in
a single text sentence to address the polysemy
problem and eliminate dependencies on external
knowledge sources, such as the Brown Corpus or
pre-trained word embeddings. However, utilizing
only the informal definition also mitigates these
challenges. This research question delves into
the performance implications of employing both
terms and informal definitions versus using only
Term+informal
definition
Only informal
definition
Input Preprocessing
Not performed
Not performed
Training
Balanced
Balanced
P1
P2
Term+informal
definition
Term+informal
definition
Without stop
words
Not performed
Balanced
Unbalanced
P3
P4
Pipelines
Stages
Figure 1: Pipelines for classifying domain entities into top-
level ontology concepts, where P1 is our baseline pipeline,
and for P2 to P4, we modify each stage at a time.
Cross-Domain Classification of Domain Entities into Top-Level Ontology Concepts Using BERT: A Study Case on the BFO Domain
Ontologies
143

informal definitions as the input for the pipelines
outlined in Figure 1.
2. AP Research Question: How Do the Classifica-
tion Pipelines Perform by Removing the Stop
Words from the Input Sentence?
Explanation: Stop words, including common
terms like ”a,” ”an,” ”the,” and ”of,” are frequently
occurring words in textual sentences. In our per-
spective, these stop words play a vital role in
shaping sentence structures from which language
models, such as BERT, can learn patterns to dis-
tinguish the top-level concept of a domain entity.
This research question delves into the impact of
stop words on classification results by conducting
experiments both with and without them in the in-
put sentence.
3. Research Question: How Do the Classification
Pipelines Perform Using Balanced and Unbal-
anced Training?
Explanation: In (Lopes et al., 2023), an un-
balanced training methodology was employed to
address the characteristic class imbalance in the
datasets, where few classes have the majority of
instances. However, this strategy is computation-
ally expensive due to the size of the training set.
On the other hand, (Lopes et al., 2022) explored a
balanced training methodology, i.e., all the classes
have the same number of training instances. How-
ever, in their work, they reduced the number of
target classification classes to the 30 most popu-
lated ones, resulting in faster training times but
poorer results due to the exclusion of significant
training data. This research question assesses the
performance of these diverse training methodolo-
gies to comprehend their impact, considering the
four target classes utilized in this study.
4. Research Question: How Do the Classification
Pipelines Perform with Other Top-Level On-
tology Concepts?
Explanation: Previous studies have primarily fo-
cused on evaluating classification pipelines using
the Dolce-Lite and Dolce-Lite-Plus top-level con-
cepts. While these ontologies offer diverse con-
cepts, the generalizability of the pipeline to other
top-level ontologies, such as the Basic Formal On-
tology (BFO), remains untested. To address this
gap, our experiments target four BFO top-level
concepts: independent continuant, generically de-
pendent continuant, specifically dependent con-
tinuant, and process. Although BFO encompasses
numerous top-level concepts, our selection con-
centrates on these four, which represent all the
concepts in level 3 of the BFO taxonomy and are
subsumed by all domain-specific entities in our
dataset.
5. Research Question: How Do the Classification
Pipelines Perform in a Cross-Domain Classifi-
cation Scenario?
Explanation: Current datasets for classifying do-
main entities into top-level concepts often rely on
aligning WordNet with the Dolce-Lite-Plus top-
level ontology (Gangemi et al., 2003). While
valuable insights can be drawn from experiments
on domain-independent datasets, the majority of
domain ontologies include entities specific to their
domains that are not present in WordNet or other
broader knowledge domains. Hence, this research
question investigates the performance of the clas-
sification pipeline in a cross-domain classification
scenario, where the training and testing datasets
originate from different knowledge domains.
3.2 Dataset Preparation
Our research questions prompted an exploration be-
yond the Dolce-Lite-Plus and Dolce-Lite top-level
ontologies. In this context, we also assess the effec-
tiveness of the pipelines outlined in Figure 1 within a
cross-domain classification scenario. A notable con-
tribution of this study is the introduction of a novel
dataset for classifying domain entities into top-level
ontology concepts. To achieve this, we extracted
the target classes from the Basic Formal Ontology
(BFO) top-level ontology, along with the correspond-
ing terms and informal definitions, utilizing the re-
sources available in the OBO Foundry.
To identify suitable domain ontologies within the
OBO Foundry aligning with the objectives of our
study, we employed three criteria: the presence of Ba-
sic Formal Ontology (BFO) as the top-level ontology,
the feasibility of performing reasoning, and the avail-
ability of terms and informal definitions for domain
entities. Table 1 illustrates the outcome of this selec-
tion process, wherein 81 domain ontologies were cho-
sen from the 154 listed in the OBO Foundry reposi-
tory. These selected ontologies are categorized into
12 distinct knowledge domains, contributing a total
of 218,630 domain entities for our analysis. Also, we
excluded the Phenotype knowledge domain from our
study due to the lack of consensus in the literature re-
garding the definition of a phenotype concerning the
target concepts of independent continuant or specifi-
cally dependent continuant.
In the OBO Foundry, many ontologies incorporate
common domain entities from diverse knowledge do-
mains, leading to instances shared among ontologies.
To address this, we adopted a specific approach for
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
144
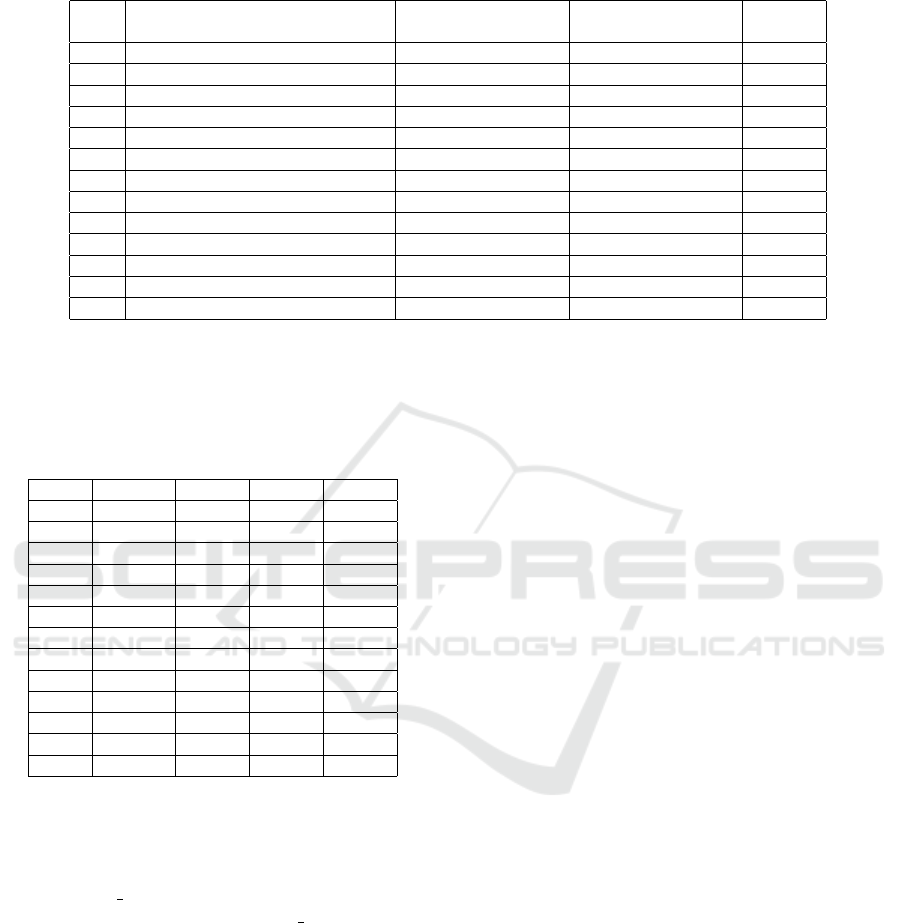
Table 1: The description of the knowledge domains explored in this work and the number of domain ontologies and entities
in each domain.
ID Domain
Nº of available
Domain Ontologies
Nº of selected
Domain Ontologies
Nº of
entities
D1 Agriculture 2 2 954
D2 Anatomy and development 35 12 37,641
D3 Biological systems 7 5 44,420
D4 Chemistry and biochemistry 16 7 59,157
D5 Diet, metabolomics, and nutrition 6 4 18,463
D6 Environment 7 6 8,257
D7 Health 37 17 22,481
D8 Information 11 6 1,415
D9 Information technology 4 3 1,324
D10 Investigations 13 11 8,059
D11 Microbiology 2 1 3,019
D12 Organisms 14 7 13,440
Total 154 81 218,630
Table 2: The number of domain entities of each top-level
ontology concept evaluated in this work, in which ID means
Independent Continuant, SDC means Specifically Depen-
dent Continuant, GDC means Generically Dependent Con-
tinuant and P means Process.
ID IC SDC GDC P
D1 219 327 112 296
D2 37,017 6 - 618
D3 4,196 105 99 40,020
D4 50,537 2,490 2,490 4,359
D5 16,230 1,643 350 240
D6 4,218 394 32 3,613
D7 1,603 9,411 661 10,806
D8 32 49 1,044 290
D9 8 8 1,047 261
D10 1,180 687 3,191 3,001
D11 2,996 23 - -
D12 5,819 1,559 1,555 4,507
Total 124,055 15,983 10,581 68,011
identifying domain entities within each ontology. For
instance, in the Agronomy Ontology, we considered
only those concepts and instances bearing ”AGRO”
in the IRI prefix as domain entities. Consequently,
while ”AGRO 00001” is recognized as a domain en-
tity in the Agronomy Ontology, ”GO 00001,” despite
its presence in the Agronomy Ontology, is not con-
sidered a domain entity of this ontology. A similar
processing approach was applied to each domain on-
tology utilized in this study.
Table 2 outlines the instance distribution across
domains and target classes. The Independent Con-
tinuant (IC) class emerges as the most populous,
boasting 124,055 instances, followed by the Process
(P), Specifically Dependent Continuant (SDC), and
Generically Dependent Continuant (GDC) classes
with 68,011, 15,983, and 10,581 instances, respec-
tively.
4 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
In this section, we explain how we create the cross-
domain evaluation scenario, detailing what we used
for training, evaluating, and testing the classifier.
Also, we show the results achieved by performing the
experiments with each pipeline described in Figure 1
and pointing out the result analysis according to each
research question detailed in Section 3.1.
4.1 Evaluation Procedure
To assess the effectiveness of our study case in a
cross-domain classification scenario, we systemati-
cally excluded each domain dataset from training
and merged all the remaining datasets to train the
pipelines described in Figure 1. From that, we
used the excluded dataset from training to test each
pipeline. Also, we employed a stratified k-fold cross-
validation approach with k = 10 for leveraging the
pipeline’s performances across different subsets of the
training data. In addition, we used the Early Stopping
technique to evaluate the pipeline’s performances in
each training epoch, with a patience parameter set to
3. As the loss function, we used the categorical cross-
entropy (Equation 1).
L(
b
y, y) = −
K
∑
k
y
(k)
log
b
y
(k)
(1)
where K is the set of classes, y
(k)
indicates
whether class label k is the correct classification, and
b
y
(k)
is the probability of being the class k.
To evaluate the results of each experiment, we em-
ployed the F1-score (Equation 2), with TP, FP, and
FN denoting true positives, false positives, and false
Cross-Domain Classification of Domain Entities into Top-Level Ontology Concepts Using BERT: A Study Case on the BFO Domain
Ontologies
145
negatives, respectively. The experiments were con-
ducted on a machine equipped with an Intel i7-10700
CPU (4.8GHz), 32 GB of RAM, and a GeForce RTX
3060 GPU with 12GB of VRAM
23
.
F
1
=
2 ∗ T P
2 ∗ T P + FP + FN
(2)
4.2 Experimental Results
As previously mentioned, our experiments involved
the evaluation of five pipelines, including the base-
line classifier (P1) and variations at each step. The
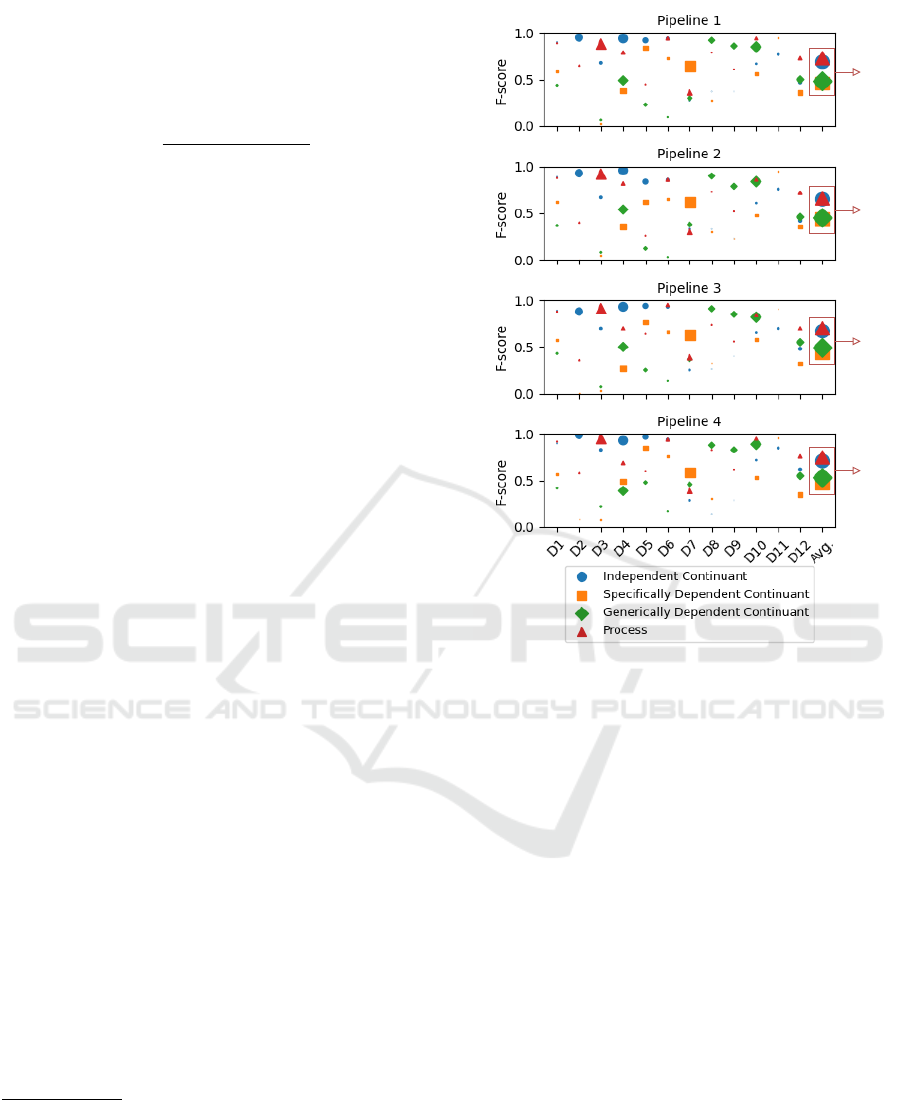
F-score results for the baseline pipeline (P1) on the
12 domain datasets are presented at the top of Fig-
ure 2. Notably, we achieved F-score results exceeding
90% for at least one class in numerous datasets, un-
derscoring the adaptability of the pipeline proposed
by (Lopes et al., 2023) in cross-domain classification
scenarios and with BFO top-level ontology. The Pro-
cess class demonstrated the highest average F-score at
73%, showcasing promising results across diverse do-
mains. However, the Specifically Dependent Contin-
uant and Generically Dependent Continuant classes
exhibited lower results, often attributed to the limited
number of instances, as observed in D2, D3, D6, D9,
and D11 datasets. Alternatively, these lower results
might be linked to the process of creating informal
definitions for other datasets. Based on this analysis
of the baseline results, we proceeded to evaluate each
research question outlined in Section 3.1, as detailed
below:
1. Research Question: How Do the Classifica-
tion Pipelines Perform Using Only the Infor-
mal Definitions as Input Rather than Combin-
ing Them with the Terms?
Result Analysis: The plot of Pipeline 2 (P2) in
Figure 2 demonstrates that despite achieving F-
scores above 90% for numerous domains, the re-
sults are comparatively poor when compared to
the baseline pipeline (P1). This suggests that re-
lying solely on informal definitions as input sen-
tences is less effective than combining them with
entity terms, emphasizing the crucial role of in-
cluding terms for training and classifying using
the pipeline proposed in (Lopes et al., 2023). In
2
The source code and data are available at https://
github.com/BDI-UFRGS/MultiDomainClassification
3
We try to use newer models like Mixtral and Llama 2 in
our experiments. However, each one would take around 125
days to just generate the embeddings for all the instances in
our dataset. Also, we would have to use a reduced floating
point precision to 4 bits to be able to fit the language models
to the GPU used.
avg.
59%
avg.
55%
avg.
57%
avg.
62%
Figure 2: Results achieved by performing each pipeline in a
cross-domain classification scenario. The size of the marks
is in relation to the number of instances of each class in each
domain to the total of all domains.
other words, terms carry characteristics necessary
for classifying domain entities into top-level on-
tology concepts. Essentially, as ontology entities’
terms are established before their informal defi-
nitions during ontology development, excluding
them in the training process appears counterpro-
ductive. Overall, pipeline P2 achieved an average
F-score 4% below the baseline.
2. AP Research Question: How Do the Classifica-
tion Pipelines Perform by Removing the Stop
Words from the Input Sentence?
Result Analysis: The plot of Pipeline 3 (P3)
in Figure 2 shows the results of removing stop
words from the input sentences. The hypothe-
sis was that removing stopwords might enhance
the focus on key terms and possibly improve the
classification F-score. The results, however, de-
pict a nuanced picture. While for some domains,
the removal of stopwords resulted in a marginal
increase in F-score, indicating a slight improve-
ment in focus on relevant terms, for other do-
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
146

mains, the impact was negligible or even nega-
tive, leading to a decrease in classification accu-
racy. This variation suggests that the role of stop-
words is context-dependent and can vary signifi-
cantly across different domains. In comparison to
the baseline pipeline (P1), where sentences were
used with their original structure (including stop-
words), the overall performance of pipeline P3 is
slightly poor, showing a 2% decrease in F-score
compared to P1. The analysis indicates that while
stopwords are often considered as ’noise’ or irrel-
evant in text processing, their role might be more
complex than traditionally assumed. They can
provide essential context or grammatical structure
that aids in the understanding of sentences, espe-
cially in specific domains.
3. Research Question: How Do the Classification
Pipelines Perform Using Balanced and Unbal-
anced Training?
Result Analysis: The plot of Pipeline 4 (P4) in
Figure 2 describes the results of using an unbal-
anced training scenario, i.e., where the classes
have different numbers of instances. In P4, the
hypothesis was that balanced training, with equal
representation of classes, would enhance the clas-
sification F-score across different domains. Con-
trary to this assumption, the results reveal that the
unbalanced training approach consistently outper-
formed the balanced one in all examined domains.
This led to a noticeable increase in F-score across
all classes. Compared to the baseline pipeline
(P1), which utilized balanced datasets, the over-
all performance of pipeline P4 demonstrated a
significant improvement, averaging around a 3%
higher F-score. These findings suggest a potential
paradigm shift in dataset preparation for the task
of classifying domain entities into top-level on-
tology concepts, underscoring the importance of
aligning training data with the natural class distri-
bution.
4. Research Question: How Do the Classification
Pipelines Perform with Other Top-Level On-
tology Concepts?
Result Analysis: Considering the performance
of various classification pipelines across top-level
ontology concepts, it is evident that Pipeline P4,
which utilizes unbalanced training datasets, con-
sistently outperforms the others. P4 demonstrates
the highest F-scores in all categories, including
Independent Continuant, Specifically Dependent
Continuant, Generically Dependent Continuant,
and Process. On the other hand, pipeline P2,
which relies solely on informal definitions, gener-
ally shows the weakest performance, highlighting
the importance of including specific entity terms
in training. The Pipeline P3, focusing on stop-
words removal, offers mixed results with some
improvements in certain areas but does not consis-
tently outperform the baseline pipeline P1. Over-
all, the effectiveness of each pipeline varies signif-
icantly with the ontology concept, suggesting that
unbalanced training datasets are more universally
effective in this context.
5. Research Question: How Do the Classification
Pipelines Perform in a Cross-Domain Classifi-
cation Scenario?
Result Analysis: In examining the cross-domain
classification performance of various pipelines, a
detailed analysis of the specific F-score values for
each class within domains reveals insightful con-
trasts. For Pipeline P4, high F-scores are ob-
served in D2 for Independent Continuant (99%)
and in D11 for Specifically Dependent Contin-
uant (96%), contrasting with significantly lower
scores in D8 for Independent Continuant (14%)
and Generically Dependent Continuant (88%).
Pipeline P3 shows effectiveness in D5 (Indepen-
dent Continuant at 94%, Specifically Dependent
Continuant at 77%), yet experiences a dip in D2
(Specifically Dependent Continuant at 0%) and
D7 (Independent Continuant at 25%). Conversely,
Pipeline P2 demonstrates strong results in D4 for
Independent Continuant (96%) and in D11 for
Specifically Dependent Continuant (95%), but un-
derperforms in domains such as D9 (Independent
Continuant at 23%) and D2 (Specifically Depen-
dent Continuant at 0%). These specific values
highlight the nuanced and variable performance of
each pipeline across different domains, emphasiz-
ing the complexity and necessitating tailored ap-
proaches in the cross-domain classification task.
5 CONCLUSION
The study focuses on classifying domain entities into
top-level ontology concepts of the Basic Formal On-
tology (BFO) using a proposed pipeline with the
BERT language model in a cross-domain scenario.
In this context, we examined the impact of several
modifications of this pipeline, considering the input,
the processing, and the training stages. The exper-
iments were conducted on a novel dataset derived
from OBO Foundry, involving 81 domain ontologies
across 12 knowledge domains, revealing that combin-
ing terms with informal definitions typically yields
better performance than using only informal defini-
tions. In addition, removing stop words does not
Cross-Domain Classification of Domain Entities into Top-Level Ontology Concepts Using BERT: A Study Case on the BFO Domain
Ontologies
147

significantly enhance performance, while unbalanced
training demonstrates superior results compared to
balanced training, underscoring the importance of
natural class distribution in training datasets. This
research contributes to understanding the automated
classification of domain entities and has implications
for developing more effective ontology-based classi-
fication systems. For future work, we aim to explore
using other advanced language models in the classifi-
cation pipeline, like Llama and Mixtral.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Research supported by Higher Education Person-
nel Improvement Coordination (CAPES), code 0001,
Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Techno-
logical Development (CNPq), and Petrobras.
REFERENCES
Arp, R., Smith, B., and Spear, A. D. (2015). Building on-
tologies with basic formal ontology. Mit Press.
Buttigieg, P. L., Morrison, N., Smith, B., Mungall, C. J.,
Lewis, S. E., and Consortium, E. (2013). The en-
vironment ontology: contextualising biological and
biomedical entities. Journal of biomedical semantics,
4:1–9.
Degtyarenko, K., De Matos, P., Ennis, M., Hastings, J.,
Zbinden, M., McNaught, A., Alc
´
antara, R., Dar-
sow, M., Guedj, M., and Ashburner, M. (2007).
Chebi: a database and ontology for chemical enti-
ties of biological interest. Nucleic acids research,
36(suppl
1):D344–D350.
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., and Toutanova, K.
(2018). Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional trans-
formers for language understanding. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1810.04805.
Francis, W. N. (1965). A standard corpus of edited present-
day american english. College English, 26(4):267–
273.
Gangemi, A., Navigli, R., and Velardi, P. (2003). The on-
towordnet project: Extension and axiomatization of
conceptual relations in wordnet. In Meersman, R.,
Tari, Z., and Schmidt, D. C., editors, On The Move
to Meaningful Internet Systems 2003: CoopIS, DOA,
and ODBASE, pages 820–838, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Jackson, R., Matentzoglu, N., Overton, J. A., Vita, R., Bal-
hoff, J. P., Buttigieg, P. L., Carbon, S., Courtot, M.,
Diehl, A. D., Dooley, D. M., et al. (2021). Obo
foundry in 2021: operationalizing open data princi-
ples to evaluate ontologies. Database, 2021.
Jaiswal, P., Avraham, S., Ilic, K., Kellogg, E. A., McCouch,
S., Pujar, A., Reiser, L., Rhee, S. Y., Sachs, M. M.,
Schaeffer, M., et al. (2005). Plant ontology (po): a
controlled vocabulary of plant structures and growth
stages. Comparative and functional genomics, 6(7-
8):388–397.
Jiang, A. Q., Sablayrolles, A., Roux, A., Mensch, A.,
Savary, B., Bamford, C., Chaplot, D. S., Casas, D.
d. l., Hanna, E. B., Bressand, F., et al. (2024). Mixtral
of experts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.04088.
Jullien, M., Valentino, M., and Freitas, A. (2022). Do
transformers encode a foundational ontology? prob-
ing abstract classes in natural language. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2201.10262.
Lopes, A., Carbonera, J., Schmidt, D., and Abel, M. (2022).
Predicting the top-level ontological concepts of do-
main entities using word embeddings, informal defi-
nitions, and deep learning. Expert Systems with Ap-
plications, 203:117291.
Lopes, A., Carbonera, J., Schmidt, D., Garcia, L., Ro-
drigues, F., and Abel, M. (2023). Using terms
and informal definitions to classify domain entities
into top-level ontology concepts: An approach based
on language models. Knowledge-Based Systems,
265:110385.
Sahoo, P., Singh, A. K., Saha, S., Jain, V., Mondal, S., and
Chadha, A. (2024). A systematic survey of prompt
engineering in large language models: Techniques and
applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.07927.
Smith, B., Ashburner, M., Rosse, C., Bard, J., Bug, W.,
Ceusters, W., Goldberg, L. J., Eilbeck, K., Ireland, A.,
Mungall, C. J., et al. (2007). The obo foundry: coor-
dinated evolution of ontologies to support biomedical
data integration. Nature biotechnology, 25(11):1251–
1255.
Studer, R., Benjamins, V. R., and Fensel, D. (1998). Knowl-
edge engineering: Principles and methods. Data &
knowledge engineering, 25(1-2):161–197.
Touvron, H., Martin, L., Stone, K., Albert, P., Almahairi,
A., Babaei, Y., Bashlykov, N., Batra, S., Bhargava,
P., Bhosale, S., Bikel, D., Blecher, L., Ferrer, C. C.,
Chen, M., Cucurull, G., Esiobu, D., Fernandes, J., Fu,
J., Fu, W., Fuller, B., Gao, C., Goswami, V., Goyal,
N., Hartshorn, A., Hosseini, S., Hou, R., Inan, H.,
Kardas, M., Kerkez, V., Khabsa, M., Kloumann, I.,
Korenev, A., Koura, P. S., Lachaux, M.-A., Lavril, T.,
Lee, J., Liskovich, D., Lu, Y., Mao, Y., Martinet, X.,
Mihaylov, T., Mishra, P., Molybog, I., Nie, Y., Poul-
ton, A., Reizenstein, J., Rungta, R., Saladi, K., Schel-
ten, A., Silva, R., Smith, E. M., Subramanian, R.,
Tan, X. E., Tang, B., Taylor, R., Williams, A., Kuan,
J. X., Xu, P., Yan, Z., Zarov, I., Zhang, Y., Fan, A.,
Kambadur, M., Narang, S., Rodriguez, A., Stojnic, R.,
Edunov, S., and Scialom, T. (2023). Llama 2: Open
foundation and fine-tuned chat models.
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
148
