
A Reflective Architecture for Agent-Based Models Applied to Social
Network Sites
Diego Nu
˜
nez, Tom
´
as V
´
elez, Paul Leger
a
and Daniel San Mart
´
ın
b
School of Engineering, Catholic University of the North, Larrondo 1281, Coquimbo, Chile
Keywords:
Word-of-Mouth, Agent-Based Model, Simulation, Social Media, Open Implementations, Tower Reflection.
Abstract:
Social network sites serve as effective platforms for word-of-mouth marketing (WOM), often analyzed through
Agent-Based Models (ABMs). However, implementing ABMs can be daunting, with programmers facing
the choice of building from scratch or using frameworks. To tackle this, we propose FASOW (Flexible
Agent Simulator for Open WOM) architecture, employing the Reflective Tower design. FASOW’s four
layers cater to varying complexities, simplifying implementation by breaking down models into manageable
sub-layers. We validate FASOW through a case study on Twitter, examining agent saturation effects in
WOM marketing. Results indicate FASOW’s efficacy, though further use cases are needed for comprehensive
evaluation. Additionally, we offer an online proof-of-concept for this architecture.
1 INTRODUCTION
People seek opinions from relatives, friends,
or experts about products before purchasing,
both offline and online (Kaplan and Haenlein,
2010). This form of communication, known as
Word-Of-Mouth (WOM), is highly valued for its
credibility and influence (Hennig-Thurau et al.,
2004). Consequently, companies aim to leverage
WOM to organically shape public perception of
their products or services (Kozinets et al., 2010).
WOM offers ease and convenience in information
sharing for both customers and businesses (Gupta
and Harris, 2010; Hennig-Thurau et al., 2015; Jansen
et al., 2009). Recognizing its significance, WOM has
emerged as a potent marketing tool, referred to as
word-of-mouth marketing (Gupta and Harris, 2010).
This strategy involves disseminating a message about
a product or service to a group of initial customers
(referred to as ”seeds”), with the aim of encouraging
them to further propagate the message (Shen and
Hahn, 2007).
An Agent-Based Model (ABM) (Goldenberg
et al., 2001; Rand and Rust, 2011; Grimm et al.,
2006) is a technique that allows researchers to model
real-world situations by abstracting and identifying
only the crucial elements to study a phenomenon. By
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0969-5139
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5274-0148
using this technique, we can simulate and analyze
the behavior and the interactions that take place
among agents in a determined environment. Agents
can be considered as individuals who follow a
behavior, have a defined and mutable state, and can
interact with other agents. By using ABMs, we
can model a real-world-like representation of social
network sites, where agents can share messages that
can be read by other agents and where agents can
influence decisions of other agents. Thanks to ABMs,
researchers in WOM marketing can test hypothetical
scenarios achieving more success when implementing
marketing strategies (L
´
opez et al., 2023; Araya et al.,
2019).
Two approaches exist for implementing
agent-based simulations: building from scratch
or using frameworks like NetLogo (Wilensky, 2023),
Repast (North et al., 2013), or MASON (Luke
et al., 2005). Building from scratch is complex
due to the need to handle numerous abstractions,
while frameworks offer pre-built solutions but may
require learning and customization, especially with
Repast. Regardless of the approach chosen, deep
knowledge of software development is necessary. To
address these challenges, the FASOW architecture
is proposed, leveraging the Reflective Tower design
strategy. This architecture organizes layers to
facilitate the gradual implementation of complex
ABM models, providing flexibility as complexity
increases.
Nuñez, D., Vélez, T., Leger, P. and San Martín, D.
A Reflective Architecture for Agent-Based Models Applied to Social Network Sites.
DOI: 10.5220/0012615100003690
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2024) - Volume 1, pages 981-988
ISBN: 978-989-758-692-7; ISSN: 2184-4992
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
981

We validated the FASOW architecture through
one case that applied to the Twitter site. This
case is presented in (L
´
opez et al., 2023) to analyze
the saturation effect on agents when repeatedly
interacting with a WOM advertising message. Our
paper aims to develop a software architecture
for Agent-Based Models (ABMs), making use of
abstractions present in programming languages to
facilitate the learning and use of the software during
the implementation of ABM models on WOM
marketing campaigns.
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2
presents the concepts that are required to understand
FASOW. Section 3 describes the FASOW architecture
for the simulation of WOM marketing campaigns.
Section 4 discusses two frameworks to simulate
ABM (Repast Simphony, Simudyne) with FASOW.
Section 5 introduces a preliminary validation aimed
at testing the capabilities of our architecture. This
validation is conducted on a pre-existing model
focused on WOM marketing campaigns for Twitter.
Section 6 presents the conclusions and its current
limitations.
2 BACKGROUND
This section establishes the fundamental concepts
necessary for a clear comprehension of our proposal.
It is divided into three subsections: An Introduction
explaining what WOM marketing campaigns are and
how they work, a Description of agent-based models
and their applications to WOM marketing campaigns
and the reflection tower concept.
2.1 WOM-Based Marketing Campaigns
When a consumer is going to decide to purchase a
new product, they must first be aware of its existence
and its characteristics (Iyengar et al., 2011). Several
marketing studies indicate that to create awareness
about the existence of a product, it is essential to
spread information about it (L
´
opez and Sicilia, 2013),
which is why word-of-mouth (WOM) has become a
very useful tool for companies (Gupta and Harris,
2010). We can find an electronic version of this
type of communication through the Internet, which is
called (eWOM) electronic word-of-mouth (L
´
opez and
Sicilia, 2014). This type of communication is defined
as any opinion spread over the Internet by consumers
about any product or company (Hennig-Thurau et al.,
2004).
The rise of electronic Word-of-Mouth (eWOM)
has been fueled by the vast amount of information
shared online, empowering consumers to exchange
insights via social networking platforms (Cheung
and Thadani, 2012). This digital discourse
allows individuals to form opinions and make
purchasing decisions without traditional face-to-face
interactions. Social environments, including friends
and acquaintances, directly influence consumer
choices, alongside opinions shared by fellow
consumers online. For instance, product reviews
from experienced users can significantly sway
decisions.
When companies encourage consumers to
spread information about their products, it’s
termed Word-of-Mouth (WOM) marketing (Araya
et al., 2019). This approach has become a vital
communication channel for companies, often
initiated through strategic campaigns involving
diverse “seed” consumers. These seeds, possessing
varied characteristics, are pivotal in effectively
disseminating targeted information. Research
has identified different user types, such as “hub”
users with extensive connections, who accelerate
information spread and impact market size (Libai
et al., 2013). Studies have explored various WOM
campaign strategies, including the influence of
distinct consumer types on content dissemination
through platforms like retweet (da Chen et al., 2002;
Hinz et al., 2011).
2.2 Agent-Based Model in WOM
Marketing Campaigns
An Agent Based-Model (ABM) (Leger et al.,
2016) simulates the behavior of the members of
a population, which change due to the interaction
that each of them has with its neighbors (Neumann
and Burks, 1966). It is a model in which, in an
environment, there are agents or individuals with a
finite number of possible states which are updated
based on discrete time intervals. A simulation has
advantages over similar methods that also study the
relationship between entities (Araya et al., 2019),
such as: (1) describing complex systems from simple
real-world rules; (2) the possibility of simulating
interactions between entities, regardless of the lack
or limitation of data; (3) the ease of testing different
hypothetical scenarios by modifying the variables
present in the computational environment of the
simulation; and (4) a low-cost methodology, since its
validity does not lie in the amount of data but in the
strength of the theory. The main components of an
agent-based simulation model are:
Environment. Corresponds to the space where agents
interact with others (Goldenberg et al., 2001). This
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
982
environment can simulate different scenarios, either
online, such as a social network, or offline (offline),
such as a network of neighbors.
Agent. Agents represent individuals or some entity
with a state and behavior capable of interacting with
its environment. They have different properties and
behaviors (Rand and Rust, 2011).
Action. Agents execute actions that will eventually
affect others, for each time interval based on the
previously defined set of rules (Libai et al., 2013). For
example, in a social network, an agent may take the
action of sharing certain information.
Rules. Given an agent in a specific environment
and time, the rules define the dynamics of how the
model (Araya et al., 2019) will evolve. These can be
probabilistic or deterministic and can vary between
agents.
Period. For each period, an agent can perform one
action, and each period represents a specific discrete
time (Libai et al., 2013).
Using ABMs to model WOM marketing
campaigns (Chica and Rand, 2017) is useful since
it does not require a large amount of data, but only
the necessary to calibrate and validate the model.
Therefore, it is not a requirement for researchers to
know the emergent behaviors of a population, but
only individual knowledge of each agent is necessary.
An ABM is appropriate when an environment is
complex and dynamic, just like a social network.
Mainly when the marketing interest is a result of
interactions between consumers (Chica and Rand,
2017).
2.3 Reflection Tower
A reflection tower is a reflective system that is formed
by N levels of segmentation. Each level contains its
degree of introspection on a specific program. This
concept can be decomposed into two processes, called
reification and reflection, both of which correspond to
the process of moving up or down the tower (Ibrahim,
1992).
Reification is the process where the current
working level is manipulated and transformed so that
a higher level can work with it. Reflection is the
process by which the data corresponding to the higher
level is reinstated at a lower level. Introspection is
the ability of a program to reason about its reification
or another aspect of itself. Therefore, the reflective
structure denotes a program’s capacity to access its
representation and structure, while reflective behavior
refers to a program’s dynamic ability to access
itself (Ibrahim, 1992). Keeping these concepts in
Instrospection Level N
Instrospection Level 3
Instrospection Level 2
Instrospection Level 1
(Base Interface)
Meta Interface
Developer
Reification
Reflection
Figure 1: Reflection Tower and Open Implementations.
mind, reflection can be viewed as the capability
to inspect and/or manipulate the implementation
structures of other systems utilized by a program.
Figure 1 schematically depicts the reflection tower
and illustrates the concept of an open implementation.
As defined in (Kiczales et al., 1997), an open
implementations is characterized by a system offering
a minimum of two interconnected interfaces to
its clients: 1) a base-level interface providing
access to the system’s core functionality and 2) a
meta-level interface that discloses certain aspects of
the implementation underlying the base interface.
In these principles, the reflection tower serves as
a mechanism to achieve an open implementation,
enabling the exposition of the implementation details
of specific components to users.
A reflective implementation of Agent-Based
Models (ABMs) can encompass a multitude of
interconnected concepts. For example, adopting the
reflection tower offers a systematic methodology
for understanding and incrementally implementing
Agent-Based Modeling (ABM) concepts. This
involves categorizing the concepts related to an
ABM model into distinct levels. The reflective
implementation becomes achievable through this
segmented, level-based approach, where each
introspection level supports a specific module linked
to the ABM.
3 FASOW: A REFLECTIVE
ARCHITECTURE FOR ABMs IN
SOCIAL NETWORKS
This section introduces our approach, named FASOW
(Flexible Agent Simulator for Open WOM), a
reflective architecture for the simulation of social
networking sites for WOM marketing based on
A Reflective Architecture for Agent-Based Models Applied to Social Network Sites
983
the reflection tower of the open implementation in
programming languages (Demers and Malenfant,
1995).
The development of the FASOW architecture
follows the guidelines for conceptually describing
Agent-Based Models (ABMs), as articulated
by (Grimm et al., 2006). In addition to adhering to
these recommendations, the architecture integrates
the concept of the ”reflection tower,” a pervasive
motif found in programming languages such as
3-Lisp, Java, or Smalltalk (Malenfant et al., 1996).
Furthermore, the implementation capitalizes on
well-established software design patterns, with the
Factory pattern (Gamma et al., 1993) serving as an
exemplar.
In FASOW, the reflection tower was designed to
implement an open architecture to support different
models of WOM marketing ABMs, which formalizes
the design of these ABMs and segments the models
into complexity levels. As the complexity of the
features to be added increases, the designer must
move through the different levels of the reflection
tower to add specific modules that represent the
changes he needs. By adopting a design approach
that segments complexity based on the features to
be added, the architecture encourages a structured
hierarchy.
Each level of this reflection tower serves as an
accessible entry point for developers. This tiered
design not only facilitates a systematic understanding
of the software but also offers scalability by enabling
the gradual addition of modules. As the need arises
to implement more specific features in a model, the
reflection tower becomes a powerful tool, allowing
developers to access varying levels of complexity to
obtain specific perspectives on the problem. This
streamlined approach simplifies both comprehension
and implementation of the model.
As follows, we present the FASOW architecture
and a description of FASOW using the ODD Protocol.
3.1 FASOW Architecture
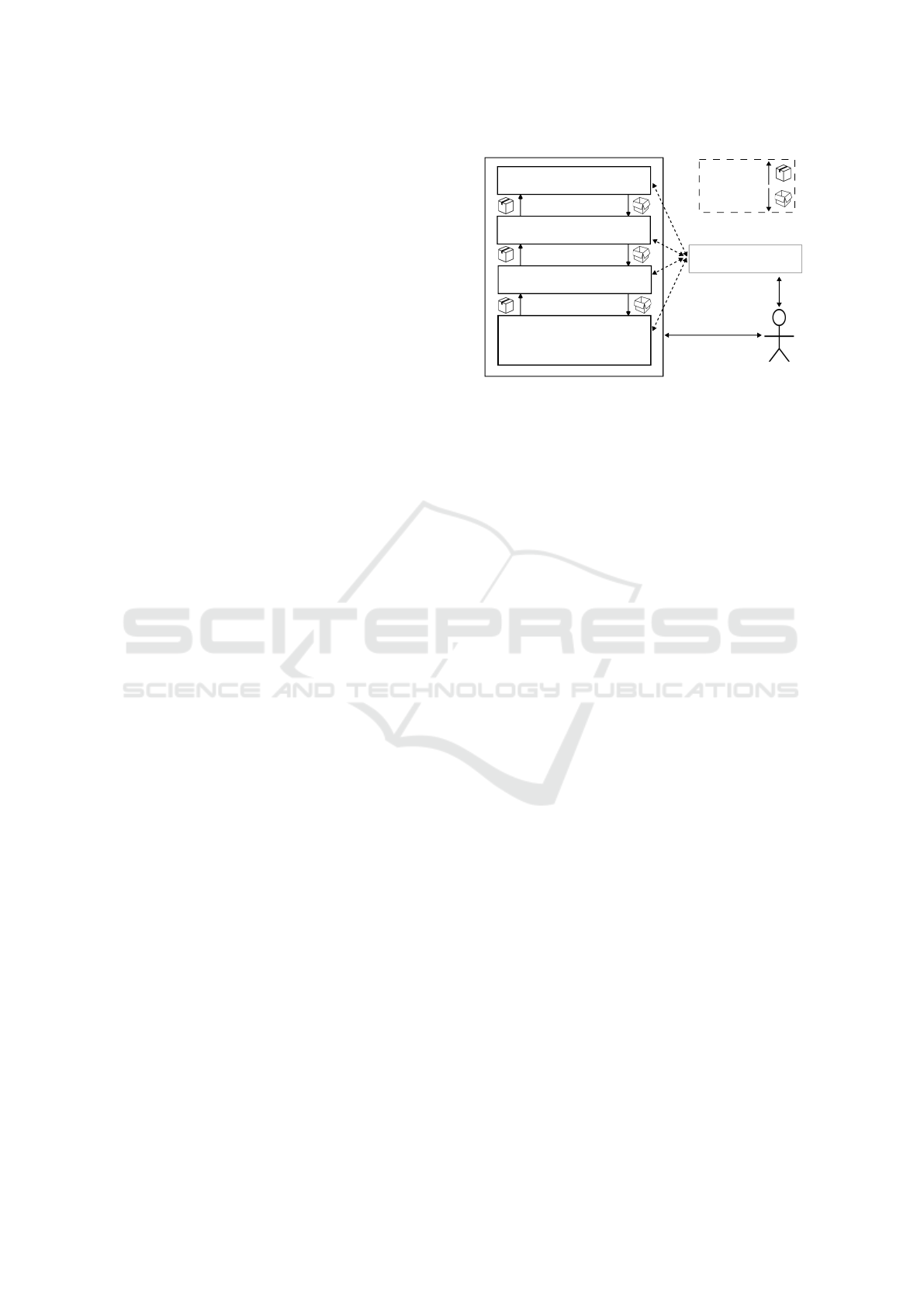
Figure 2 introduces the FASOW architecture.
The layered, tower-like structure of FASOW
facilitates diverse levels of abstraction, enabling
the simulation of WOM marketing models tailored
for social networks. The FASOW layers are (1)
Experiment, (2) Environment, (3) Agent, (4)
Action. Additionally, we can find three modules:
a meta-programming module that controls the
reflection tower called TowerHandler, a module to
generate and control the output of the simulation
called DataHandler, and a module that handles
the time and the repetitions of the simulation,
that is called TimeKeeper. In the following, the
functionality and objective of the tower layers are
explained.
Action
Agent
Environment
Experiment
TimeKeeper
FASOW
DataHandler TowerHandler
create()
create()
create()
select()
QueryData/SelectOutput
QueryData/SelectOutput
QueryData/
SelectOutput
Figure 2: FASOW Architecture.
Experiment. This layer enables the simulation of a
model using a familiar language to people immersed
in WOM marketing.
When introducing new features that need
modifications to the core FASOW structure,
adjustments should be initially made in the
Experiment layer. Subsequently, as required,
modifications should be extended to the upper layers
of the reflection tower using the TowerHandler.
Environment. This layer allows users to set up the
behavior of the simulation during the step-by-step
running.
Agent. This layer allows users to create, group,
and combine different types of agents. It also
allows users to relate the agents with their respective
configurations and their set of possible actions, as
well as to establish the order of execution of these.
Action. This layer allows the creation of new actions.
Actions are functions that are executed by agents, and
handle how they react when receiving a message.
Data Handler. The DataHandler module allows
developers to define the output to be expected at the
end of the simulation.
Tower Handler. TowerHandler module is an API for
interacting between tower layers. It uses the Facade
pattern to hide the complexity behind the levels of
abstraction, acquiring the ability to intervene in the
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
984
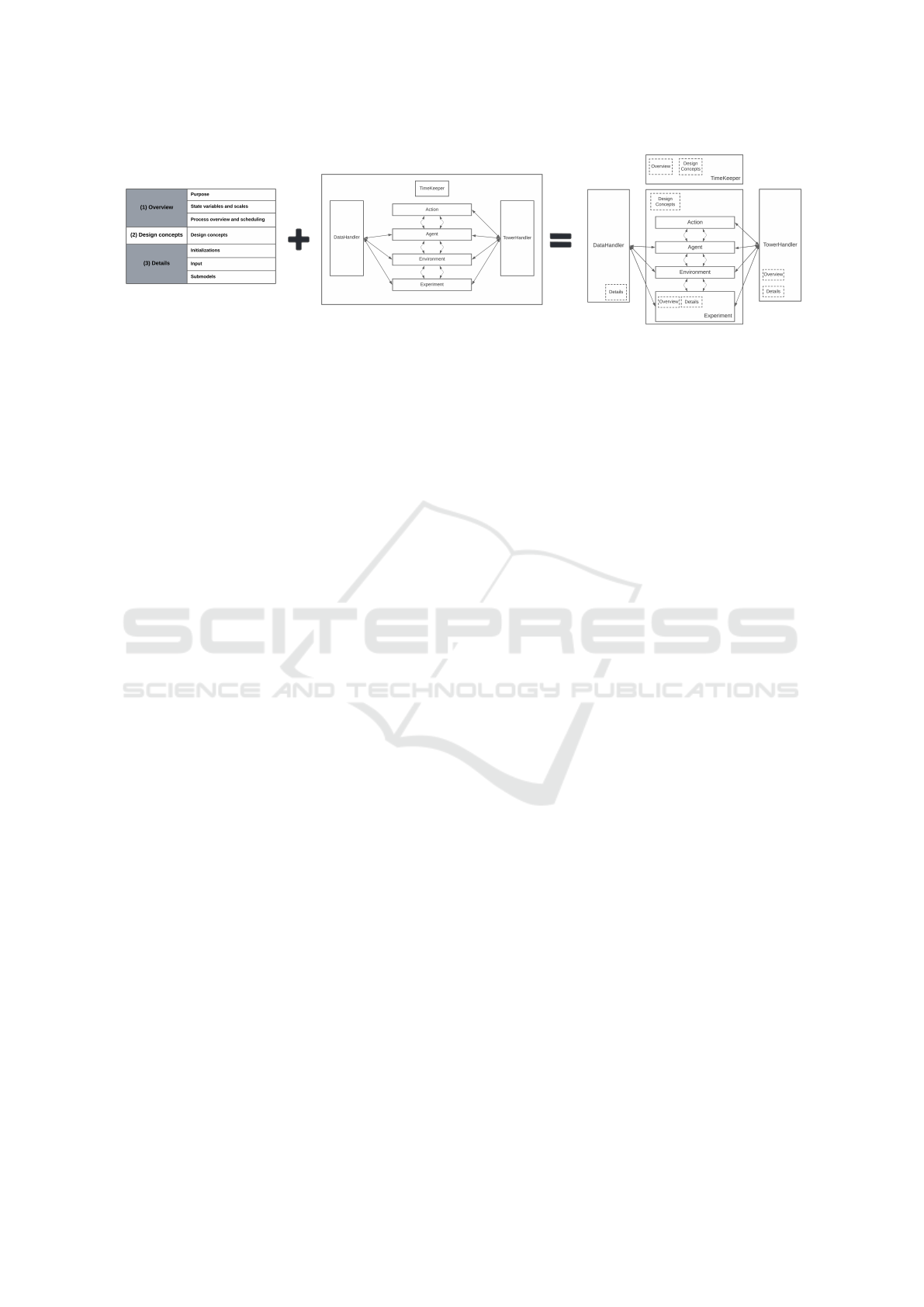
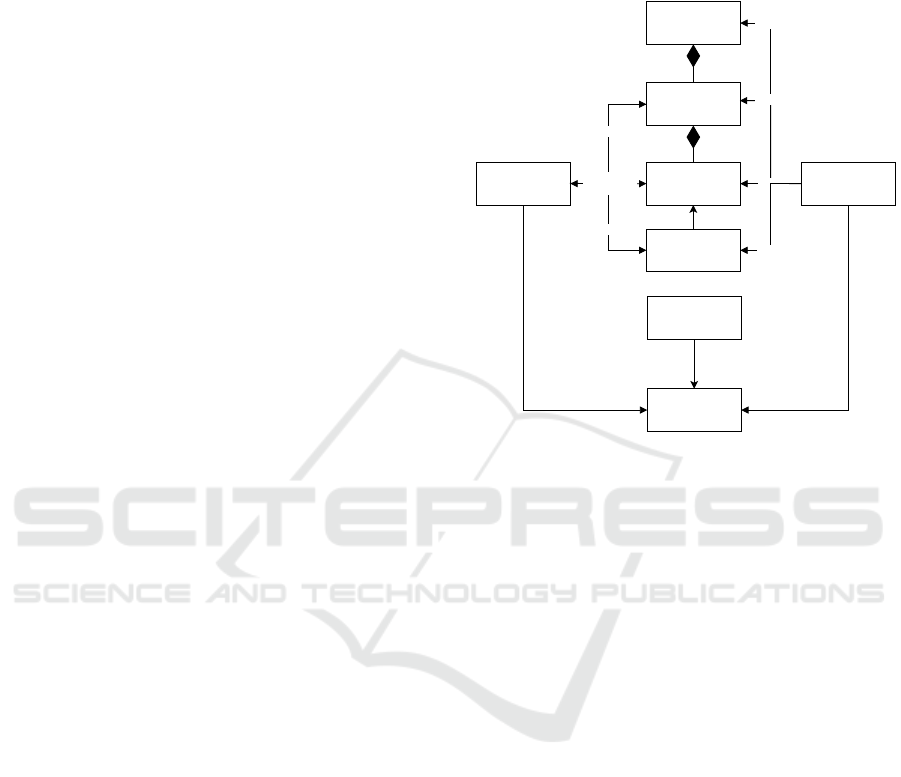
Figure 3: Our proposal, FASOW, merges the guidelines for describing ABMs proposed by Grimm et al. (Grimm et al., 2006)
and developing adaptive software introduced by Kiczales et al. (Kiczales et al., 1997).
deep levels of the tower and communicate them, this
without having to know everything behind each level.
TimeKeeper. This module handles time in the
simulation, allowing to set the maximum time to run
the simulation and the maximum number of times that
can be repeated.
In the FASOW architecture, the TimeKeeper
informs the DataHandler when a simulation step
concludes, facilitating the collection of data to
generate the final output.
3.2 FASOW Description
This subsection explains the description of FASOW
through the Overview Design concepts and Details
(ODD) protocol outlined in (Grimm et al., 2006).
The ODD protocol delineates three distinct groups
of elements for constructing an Agent-Based Model
(ABM): (1) Overview, (2) Design concepts, and
(3) Details, as illustrated in Figure 3. The
first element articulates the purpose and offers a
concise introduction to the model. The second
element defines the operational mechanics essential
for the ABM under construction. The final element
delves into the specifics of the ABM, encompassing
details such as initialization and input parameters.
Subsequent sections will delve into a comprehensive
exploration of these three integral elements.
Overview. As we see in the previous subsection 3.1,
the Experiments in FASOW correspond to an
implementation of a model of a WOM marketing
campaign model in a Social Network Site (SNS)
where the agents of the model are the users of the
site. These agents follow rules that are defined by the
marketing campaign of the model that is simulated.
For all cases, FASOW uses a discrete quantity of time,
which increases one by one, to handle the time in the
simulation. The description of the architecture of this
element can see graphically in Figure 3.
Design Concepts. We operate within the realm of
WOM marketing, with SNSs detailed in subsection
2.1. To encapsulate this context within our
architecture, we previously defined the Environment
as the representation of the SNS where the WOM
campaign unfolds. This Environment serves as a
foundation for managing Agents, which, in turn,
embody the users involved in the WOM campaign.
The interaction between the Environment
and the Agents delineates the dynamics of user
communication during information sharing. For
agents to participate in a WOM campaign, they
must adhere to specific rules, the occurrence of
which is contingent upon predefined conditions. This
introduces stochastic in the campaign results, as
the occurrence of these rules is probabilistic. The
impact on the model is managed by repeating the
Experiment, as detailed in Subsection 3.1. A visual
representation of the concept described above is
presented in Figure 3.
Details. The initialization of the Experiment is
performed by the loading of the configuration that
was defined in the strategy. After that loading, the
TowerHandler starts to create the Environment as a
Social Network Site (SNS), the Agents as the users of
the network, and their Actions as a part of the rules
of the campaign. Done that, the followers are added,
ending with the initialization of the TimeKeeper in
zero. The DataHandler can manage part of the
dynamic variables that can vary in the simulation, like
the state of some agent, by decorating that variable as
part of the output. Finally, it is essential to clarify
that FASOW does not support the seeds configuration
to define the randomness. These modules are part of
this element, as seen in Figure 3.
4 RELATED WORK
This section compares FASOW to other
ABM frameworks: Repast Symphony (North
A Reflective Architecture for Agent-Based Models Applied to Social Network Sites
985
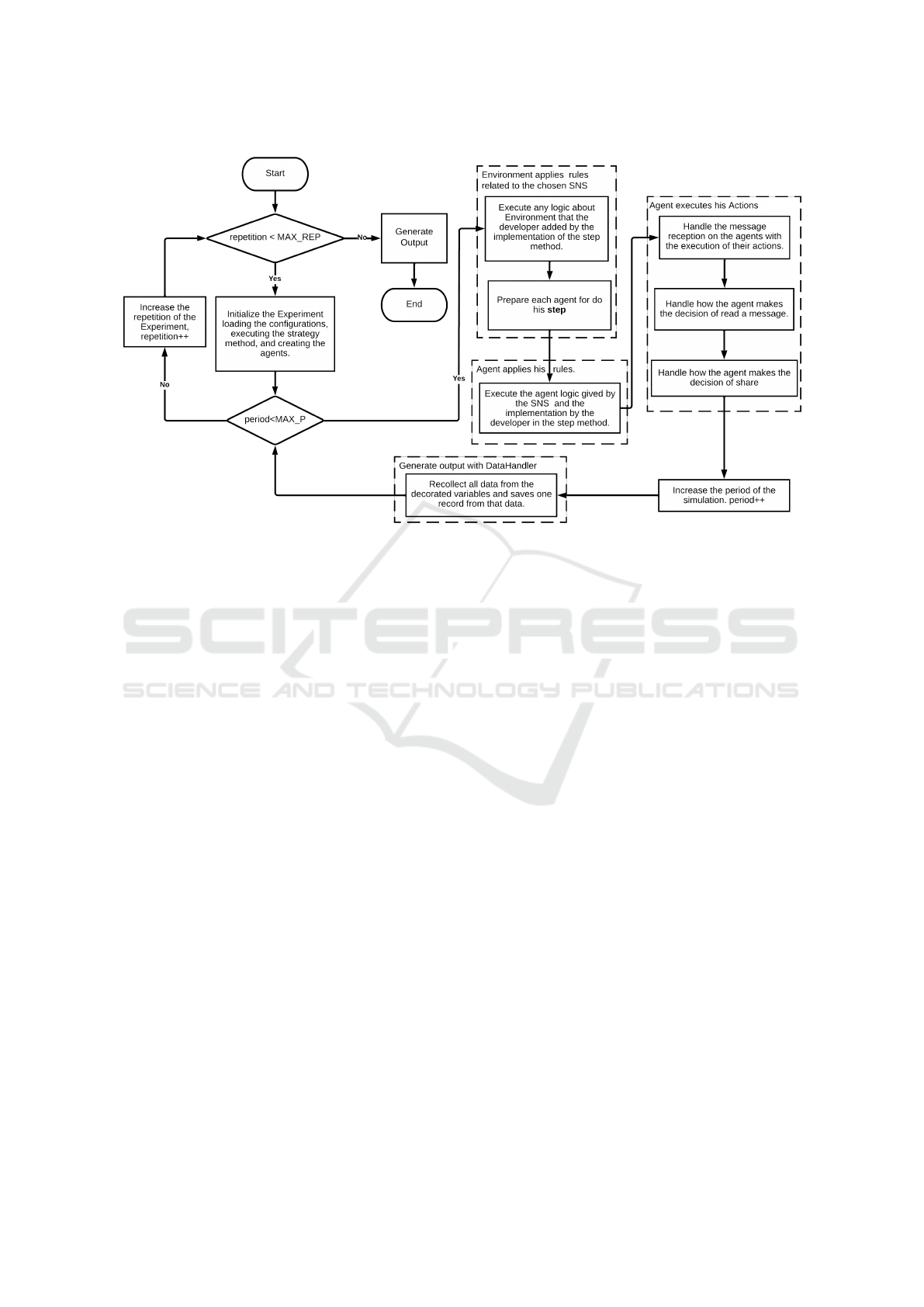
Figure 4: WOM Communication Process.
et al., 2013), Simudyne (Simudyne, 2023) and
SocLab (Rodr
´
ıguez Zoya et al., 2018). These
frameworks will be described and contrasted against
FASOW.
Repast Symphony. This software is an open software
that is used for implementing ABMs, and it is highly
configurable. In Repast, agents belong to a context,
and the context contains projections, where agents
live. Their projections can be graphs, matrices,
or even three-dimensional spaces. This allows for
managing an agent’s physical location at a certain
point in a simulation.
Simudyne. This software is also used for
implementing ABMs, especially ones based on
graphs, since it allows the creation of connections
and relationships between agents, which in this case
are nodes, creating a topology. The communication
between agents is based on “messages”; therefore,
it uses message-oriented programming. One of the
critical features of Simudyne is the use of decorators
for the output. This means that the information can
be processed or changed for each iteration, enabling
the possibility of more clean and comprehensive
production.
SocLab. is a software that allows modeling different
types of social organizations and studying the
interaction between agents. SocLab’s purpose is
to formalize social theories in a meta-model for
modeling and social simulation of organizations.
It is based on entities called Organizations,
containing Actors and Relationships, which interact
under Controls, Stakes, Effects, Solidarities, and
Constraints.
FASOW. Our software primarily focuses on
simulating WOM marketing campaigns through
ABMs, while the alternatives provide a more
extended range of purposes. While this might seem
a disadvantage, FASOW allows developers to run
experiments based on already-defined models for
simulating social sites, thus removing the necessity
of creating extra classes that implement social site
behaviors. Furthermore, since the software is very
flexible, developers can gradually implement changes
on each level of the Reflective Tower, simplifying the
implementation according to what is needed. Like
Simudyne, FASOW also uses decorators to produce
the experiment’s output.
A concrete implementation of FASOW
is available on https://github.com/sasow-org/
fasow-monorepo (rev. 4283028), and an
online proof-of-concept of our proposal is on
https://sasow-org.github.io/fasow-monorepo.
5 VALIDATION
Recalling our approach, Figure 4 illustrates the four
stages comprising the FASOW simulation process
as part of the validation proposal. The initial
stage is dedicated to overseeing repetitions and
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
986
initializing the Experiment. This involves loading
the configuration specified within it and creating
the necessary agents. Subsequently, the following
stage initiates the simulation, dispatching WOM
marketing campaign messages from the seed agents,
and executing the iterations.
The penultimate stage takes charge of
handling message reception and their subsequent
retransmission through the execution of agent
actions. Ultimately, in the concluding stage, the
iteration wraps up, and the system processes the
culmination of this cycle. It proceeds to generate
the row corresponding to the output for this
period, setting the stage for the repetition of the
entire process. In order to validate our proposal,
we implemented an ABM that was previously
published (L
´
opez et al., 2023). This implementation
shows how the use the capabilities of our architecture
with its reflective tower. The ABM is about how
the repetition of the messages in a WOM marketing
campaign can saturate agents. The impact of message
repetition (L
´
opez et al., 2023) examines saturation
effects on agents in WOM marketing campaigns
where messages are repeatedly circulated. Seed
agents initiate and potentially resend messages
multiple times, influencing other agents’ perceptions
of the advertised product or service.
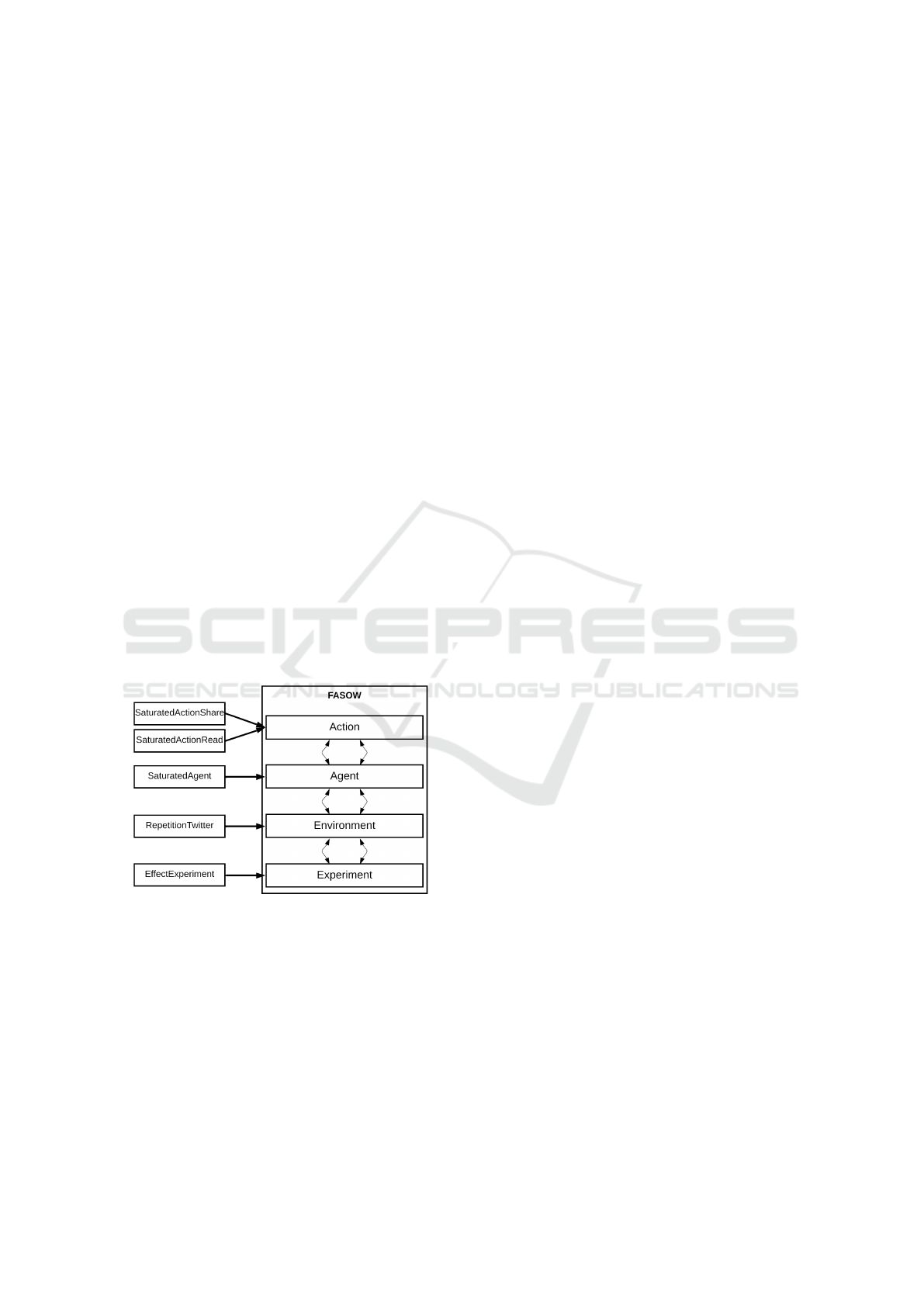
Figure 5 illustrates architecture modifications for
implementing this model, spanning all layers.
Figure 5: Case: Message Repetition Implementation.
This entails integrating specialized modules and
extending FASOW’s Twitter implementation. New
components include an Experiment for simulation, an
Environment supporting message repetition, updated
Agents managing saturation and repetition, and
Actions triggering agent saturation upon repeated
message exposure. Simulation setup involves
registering modules with the TowerHandler and
configuring Experiment parameters like action
probabilities, agent population percentage, message
repetitions, and maximum TimeKeeper ticks. This
exemplifies the modular thinking facilitated by the
reflective tower. It prompts developers to consider
Experiment creation first, followed by Environment
setup, Agent behavior, and Actions management,
aligning with the reflective tower’s structured
approach.
6 CONCLUSION
Word-of-mouth (WOM) marketing is a way to share
information between people through a conversation
about some product or service, where the consumer
opinion about the product can be influenced. An
electronic version of this marketing (eWOM) can
be found on social network sites (SNSs), where
people share their opinions on these sites. An
agent-based Model (ABM) is a technique that
allows the creation and study of models that
represent a real-world phenomenon. Therefore,
WOM marketing researchers can use ABM to test
hypothetical scenarios and could be more assertive
when implementing a marketing strategy in the real
world.
We propose a Flexible Agent Simulator for Open
WOM (FASOW), a software architecture that allows
the implementation of ABMs of WOM marketing in
SNSs. This architecture is based on the strategy of
the concept of reflective tower, which was presented
in programming languages. Our proposal allows
developers to open implementation details to adjust
the specific and potentially unforeseen needs of ABM
models for SNSs. Additionally, FASOW facilitates a
gradual implementation of complex features through
layers. These layers represent the concept of a
reflection tower, which helps to divide an ABM model
into modules that are being progressively added. This
gradualness in how the modules are added is directly
proportional to the complexity of the model.
REFERENCES
Araya, N., Leger, P., and Lopez, M. (2019). Whom
do i Choose to Diffuse Information onTwitter? An
Agent-Based Model Approach. IEEE Latin America
Transactions, 17(4):677–683.
Cheung, C. M. and Thadani, D. R. (2012). The
impact of electronic word-of-mouth communication:
A literature analysis and integrative model. Decision
Support Systems, 54(1):461–470.
Chica, M. and Rand, W. (2017). Building Agent-Based
Decision Support Systems for Word-of-Mouth
A Reflective Architecture for Agent-Based Models Applied to Social Network Sites
987

Programs: A Freemium Application. Journal of
Marketing Research, 54(5).
da Chen, L., Gillenson, M. L., and Sherrell, D. L.
(2002). Enticing online consumers: An extended
technology acceptance perspective. Information and
Management, 39(8):705–719.
Demers, F.-N. and Malenfant, J. (1995). Reflection in
logic, functional and object-oriented programming: a
short comparative study. In Proceedings of the IJCAI,
volume 95, pages 29–38.
Gamma, E., Helm, R., Johnson, R., and Vlissides, J.
(1993). Design patterns: Abstraction and reuse
of object-oriented design. In European Conference
on Object-Oriented Programming, pages 406–431.
Springer.
Goldenberg, J., Libai, B., and Muller, E. (2001). Talk
of the Network: A Complex Systems Look at the
Underlying Process of Word-of-Mouth. Marketing
Letters, 12(3):211–223.
Grimm, V., Berger, U., Bastiansen, F., Eliassen, S., Ginot,
V., Giske, J., Goss-Custard, J., Grand, T., Heinz,
S. K., Huse, G., Huth, A., Jepsen, J. U., Jørgensen,
C., Mooij, W. M., M
¨
uller, B., Pe’er, G., Piou, C.,
Railsback, S. F., Robbins, A. M., Robbins, M. M.,
Rossmanith, E., R
¨
uger, N., Strand, E., Souissi, S.,
Stillman, R. A., Vabø, R., Visser, U., and DeAngelis,
D. L. (2006). A standard protocol for describing
individual-based and agent-based models. Ecological
Modelling, 198(1):115–126.
Gupta, P. and Harris, J. (2010). How e-wom
recommendations influence product consideration
and quality of choice: A motivation to process
information perspective. Journal of Business
Research, 63(9):1041–1049.
Hennig-Thurau, T., Gwinner, K. P., Walsh, G., and
Gremler, D. D. (2004). Electronic word-of-mouth
via consumer-opinion platforms: What motivates
consumers to articulate themselves on the Internet?
Journal of Interactive Marketing, 18(1):38–52.
Hennig-Thurau, T., Wiertz, C., and Feldhaus, F. (2015).
Does twitter matter? the impact of microblogging
word of mouth on consumers’ adoption of new
movies. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science,
43:375–394.
Hinz, O., Skiera, B., Barrot, C., and Becker, J. U. (2011).
Seeding strategies for viral marketing: An empirical
comparison. Journal of Marketing, 75(6):55–71.
Ibrahim, M. H. (1992). Reflection in object-oriented
programming. International Journal on Artificial
Intelligence Tools, 1(01):117–136.
Iyengar, R., van den Bulte, C., and Valente, T. W. (2011).
Opinion leadership and social contagion in new
product diffusion. Marketing Science, 30(2):195–212.
Jansen, B. J., Zhang, M., Sobel, K., and Chowdury,
A. (2009). Twitter power: Tweets as electronic
word of mouth. Journal of the American
Society for Information Science and Technology,
60(11):2169–2188.
Kaplan, A. M. and Haenlein, M. (2010). Users of the world,
unite! The challenges and opportunities of Social
Media. Business Horizons, 53(1):59–68.
Kiczales, G., Lamping, J., Lopes, C. V., Maeda, C.,
Mendhekar, A., and Murphy, G. (1997). Open
implementation design guidelines. In Proceedings
of the 19th international conference on Software
engineering, pages 481–490, Boston, United States.
Kozinets, R. V., Valck, K. D., Wojnicki, A. C., and Wilner,
S. J. (2010). Networked narratives: Understanding
word-of-mouth marketing in online communities.
Journal of Marketing, 74(2):71–89.
Leger, P., L
´
opez, M., Hildago-Alc
´
azar, C., and Fukuda, H.
(2016). An open agent-based model to simulate the
effect of wom marketing campaigns. EAI Endorsed
Transactions on Smart Cities, 1(4).
Libai, B., Muller, E., and Peres, R. (2013). Decomposing
the value of word-of-mouth seeding programs:
Acceleration versus expansion. Journal of Marketing
Research, 50(2):161–176.
L
´
opez, M., Hidalgo-Alc
´
azar, C., and Leger, P. (2023).
The effect of message repetition on information
diffusion on twitter: An agent-based approach. IEEE
Transactions on Professional Communication, pages
150–169.
L
´
opez, M. and Sicilia, M. (2013). How WOM marketing
contributes to new product adoption: Testing
competitive communication strategies. European
Journal of Marketing, 47(7):1089–1114.
Luke, S., Cioffi-Revilla, C., Panait, L., Sullivan, K., and
Balan, G. (2005). Mason: A multiagent simulation
environment. SIMULATION, 81(7):517–527.
L
´
opez, M. and Sicilia, M. (2014). Determinants of
E-WOM influence: The role of consumers’ internet
experience. Journal of Theoretical and Applied
Electronic Commerce Research, 9(1):28–43.
Malenfant, J., Jacques, M., and Demers, F. N. (1996).
A tutorial on behavioral reflection and its
implementation. In Proceedings of the Reflection,
volume 96, pages 1–20.
Neumann, J. V. and Burks, A. W. (1966). Theory of
Self-Reproducing Automata. University of Illinois
Press, USA.
North, M. J., Collier, N. T., Ozik, J., Tatara, E. R., Macal,
C. M., Bragen, M., and Sydelko, P. (2013). Complex
adaptive systems modeling with repast simphony.
Complex Adaptive Systems Modeling, 1(1).
Rand, W. and Rust, R. T. (2011). Agent-based modeling in
marketing: Guidelines for rigor. International Journal
of Research in Marketing, 28(3):181–193.
Rodr
´
ıguez Zoya, L. G., Aguirre, J. L., and Roggero, P.
(2018). Using SocLab for modeling and simulating
political clientelism.
Shen, W. and Hahn, J. (2007). Impact of online
word-of-mouth on the market for consumer goods:
The interplay between adoption rate, product market
life and market size. In ACR Pre-Conference on
Consumer Behavior Online.
Simudyne (2023). Enterprise Simulation Software: AI
Technology (v.2.6). https://simudyne.com.
Wilensky, U. (2023). Netlogo: A multi-agent
programmable modeling environment (v.2.11).
https://ccl.northwestern.edu/netlogo.
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
988
