
Evaluating UX Factors on Mobile Devices: A Feasibility Study
Adriana Lopes Damian
a
, Cinthia Carrenho
b
, Graziela Martin
c
, Lucas Castro
d
, Bruna Brotto
e
,
Frederick Lucan
f
and Raquel Pignatelli da Silva
g
Eldorado Research Institute, Brazil
Keywords:
User Experience, UX Factors, UX Characteristics, Evaluation Methods.
Abstract:
The acceptance of consumers regarding software products determines their success of technologies, making
it a crucial topic in industrial research. In this context, the evaluation of User Experience (UX) can provide
benefits in understanding for practitioners and researchers before the launch of products in the market. The
literature encompasses works that focus on the assessment of UX for various software products, emphasizing
the importance of clearly evaluating UX characteristics for those involved in a project. This paper presents a
feasibility study with the participation of 25 practitioners engaged in the evaluation of UX for mobile devices,
analyzing UX problems concerning different UX factors presented in the literature. The application of these
factors was deemed easy and useful in understanding the quality of mobile devices before their market release.
The study aims to contribute to practitioners and researchers involved in the assessment of UX for mobile
devices, addressing different perspectives on product quality.
1 INTRODUCTION
The acceptance of consumers regarding software
products determines their success of technologies
(Wang et al., 2013). In this context, User Experience
(UX) can contribute to the acceptance of these prod-
ucts. Researchers and practitioners understand the
importance of providing a good user experience when
developing interactive software products (Kou and
Gray, 2019). For example, (Lallemand et al., 2014)
conducted a survey with 758 participants from differ-
ent fields and 35 nationalities, revealing that 83.9%
consider UX as central or very central to their practi-
tioner work. Thus, the prior evaluation of UX prod-
ucts can significantly contribute to product success.
Some works present studies from different per-
spectives of UX evaluation (Alves et al., 2021) (Je-
sus et al., 2022), focusing on experiments conducted
through sessions with users, providing insights for fu-
ture improvements. However, UX evaluations over
a longer period contribute to collecting more data
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0072-6958
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-3730-9308
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-8203-4049
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8640-0034
e
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-9599-8519
f
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-2540-1640
g
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-1203-877X
about the quality of a given product. One approach
that has been adopted by UX evaluation by compa-
nies is Dogfooding (Harrison, 2006). Through this
approach, company employees experience their prod-
ucts and services before they are launched in the mar-
ket. This can be a way for an organization to test
its products in the real world, obtaining feedback on
how end-users would use them. This approach has
been used by well-known technology market play-
ers such as Apple, Facebook, and Google (Soderquist
et al., 2016). For mobile devices, for example, we
can understand positive and negative aspects, such as
camera quality and adaptation of different used ap-
plications. In addition, equally important to conduct
UX evaluation is the understanding of different UX
characteristics discussed in the literature (Nakamura
et al., 2022) because it helps software development
team make decisions about product quality (Schrepp
et al., 2023), including the practitioners’ perceptions
concerning such characteristics.
Our paper presents a feasibility study that aims
to assess the practitioners’ perceptions, that working
in UX evaluation using Dogfooding approach about
factors that can characterize UX through evaluations
(Nakamura et al., 2022). To guide our research, we
explored the following research questions: RQ1 - Is
the use of UX factors understandable for practi-
tioners during problem analysis? and RQ2 - What
Damian, A., Carrenho, C., Martin, G., Castro, L., Brotto, B., Lucan, F. and Pignatelli da Silva, R.
Evaluating UX Factors on Mobile Devices: A Feasibility Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0012623600003690
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2024) - Volume 1, pages 265-272
ISBN: 978-989-758-692-7; ISSN: 2184-4992
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
265

is the level of participants’ acceptance for this type
of analysis in mobile device development projects?
Our investigation was based on an action research
methodology (Petersen et al., 2014), which combines
theory and practice for the development of solutions
to real problems through collaboration between re-
searchers and practitioners. The results indicated that
the analysis of UX factors is feasible, as the factors
were applied coherently with the expectations of the
researchers. Furthermore, this study showed a pos-
itive acceptance from practitioners involved in UX
evaluation for a better understanding of the accep-
tance of consumers regarding mobile devices. Thus,
our work can contribute to other practitioners and re-
searchers working on UX evaluation, providing valu-
able insights for the continuous improvement of this
user experience dimension.
2 BACKGROUND
ISO 9241-210 defines UX as “a person’s perceptions
and responses that result from the use and/or antici-
pated use of a product, system, or service” (de Nor-
malisation, 2010). UX encompasses both pragmatic
aspects, focusing on the traditional usability features
that aid in task accomplishment and hedonic aspects,
involving sentiments and emotional responses from
using a product (Hassenzahl, 2018). For instance, a
product may be perceived as pragmatic if it efficiently
facilitates task completion, while it may be seen as
hedonic if it provides stimulation, identification or
evokes memories.
In terms of UX evaluation, practitioners and re-
searchers recognize its importance as it enables an un-
derstanding of how users apply and perceive a prod-
uct or service, facilitating improvements aligned with
user expectations (Moreno et al., 2013). This ap-
proach allows the identification of potential problems
in the applications usage, their causes and provides
suggestions for improvement. While various methods
exist for evaluating the UX of system products (Mar-
ques et al., 2018), many works primarily offer indi-
cations about the overall experience, necessitating a
deeper understanding of issues that can lead to a neg-
ative user experience.
Schrepp et al. (2023) investigated the importance
of UX aspects for different product types through
five independent studies, involving 361 participants.
They found that the significance of UX quality aspects
varies depending on the product type, offering valu-
able guidelines for UX developers and researchers
during the design and evaluation phases of interac-
tive products. Their conclusion emphasized that the
relevance of UX factors is subjective, varying among
individuals and different product categories.
Nakamura et al. (2022) conducted a systematic
mapping of UX factors for mobile devices based on
user reviews in app stores. The study identified 31
distinct factors, such as Compatibility, measured by
issues on a specific device or operating system version
and Attractiveness, defined as the user’s experience
and feelings towards a product in a particular situation
during evaluative judgment.
Given the escalating interest in UX within the sci-
entific community and industry, it is crucial to com-
prehend UX characteristics specific to certain types
of products. In addition, it is important to investigate
UX factors presented in the literature concerning the
practitioners’ perceptions.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
It is crucial to analyze the UX characteristics for dif-
ferent types of products to make decisions about prod-
uct quality, as highlighted by (Schrepp et al., 2023).
In our work, we are examining the feasibility of us-
ing a set of UX factors identified from user reviews
for mobile devices in general. In other words, partic-
ipants in UX evaluations use mobile devices in their
daily lives and share their perceptions about aspects
such as camera quality, connectivity, and available
applications in the market. For this purpose, a fea-
sibility study involving practitioners from a Brazilian
company has been planned. This company is involved
in both local and international projects, including the
evaluation of UX for mobile devices before their mar-
ket release.
3.1 UX Factors in UX Evaluation
In our previous work (Damian et al., 2023), we in-
vestigated the possibility of applying the factors iden-
tified by Nakamura et al. (2022) in the context of
UX evaluation of mobile devices. Twelve researchers
in three weekly meetings internally discussed this
work. The factors related to UX were reviewed and
problems from four mobile devices were selected to
be evaluated. After applying the factors to different
products, the researchers noticed that some of them
were not applicable to the context of product evalua-
tion. As a result, the factors are presented in Table 1.
Nevertheless, since this was an internal effort by the
involved researchers to create a new approach for en-
hancing UX analysis, it was decided that it would be
valuable to evaluate the perception of other individu-
als involved in this type of evaluation.
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
266

Table 1: Adapted UX Factors for Mobile Devices UX Evaluation.
UX Factors Description
Accuracy
Characterizes discrepancies between the proximity of aspects experienced by
users and the value obtained in data measurement.
Attractiveness
Characterizes discrepancies representing positive and negative perceptions of a
product. What attracts the customer to that product.
Comparison
Characterizes discrepancies with comparisons to other products or comparisons
within the same product but in different software versions.
Ease of Use
Characterizes discrepancies about the effort required to use a specific functionality
or feature of the product. Ease of use can also be related to tutorials with missing
information. It does not characterize problems with the app/feature itself; the focus
here is on the user experience.
Satisfaction Characterizes praise and criticism regarding product features during its use.
Screen Interface
Discrepancies related to the appearance of the product (display), font and color
schemes, and icons.
Performance Discrepancies related to the product’s performance, given the configuration.
Customization
Characterizes discrepancies related to screen and feature/functionality
customization.
Bugs
Characterizes discrepancies about functionalities with issues during the use of
the product.
Crash
Characterizes discrepancies that present constant crashes in the use of a
functionality or feature.
Network Issues Discrepancies related to telephony network problems.
Exceeded Resources
Discrepancies related to excessive consumption of product resources, such as
memory and battery.
Software Update
Discrepancies related to updates, improvements, and changes to the operating
system.
Hardware Component
Hardware component that was implemented in different versions of the phone
hardware.
3.2 Feasibility Study Design
The feasibility study was meticulously planned to be
conducted in the industry within the scope of UX
evaluations for mobile devices before their market
launch. This scope encompasses both new devices
and operating system updates.
3.2.1 Context of UX Evaluation
Regarding UX evaluation participants, the company’s
own employees use these products and share their
perceptions of their quality via the Dogfooding ap-
proach. The product evaluation cycle begins with an
analysis of the minimum requirements to be met in
mobile devices, covering both hardware and opera-
tional system version. During the evaluation cycle,
which lasts an average of three to four months, vari-
ous methods are employed to characterize UX, such
as focus groups, weekly meetings, surveys, and the
use of an application that records suggestions for im-
provement/problem and automatically collects device
logs. Related to this last aspect, this contributes to
a more in-depth analysis of problems by developers.
Moreover, different roles play specific functions in
this type of analysis, such as UX analysts, analysts
responsible for problem screening, leaders for recruit-
ing and engaging participants, engineers responsible
for the tools used during evaluation and product man-
agers. These practices significantly contribute to the
improvement of product UX, as scenarios often not
identified by the testing team are revealed in such
evaluations (Silva et al., 2019). Additionally, we have
observed that it is possible to obtain a preview of end-
users’ perceptions.
3.2.2 Problem Selection
Sixteen problems reported by different users, from
eight different mobile devices and two Operating Sys-
tems, were randomly selected for analysis in the
study. This amount was chosen based on the aver-
age analysis workload of a practitioner responsible for
tracking issues reported by users during the review cy-
cle, forwarding them to different development teams,
such as camera experts, battery specialists, and others.
Evaluating UX Factors on Mobile Devices: A Feasibility Study
267

3.2.3 Participant Selection
Invitations were extended to practitioners with differ-
ent roles in mobile device UX evaluation to partic-
ipate in the study. Approximately 40 practitioners
were contacted and, of these, 25 voluntarily agreed
to participate. The study’s objective was explained to
the participants, emphasizing that they were to ana-
lyze problems reported in review cycles and classify
the most relevant UX factor. It was clarified also that
a single issue could be associated with more than one
factor. The study was planned to take place over a
7-day period, during which participants would con-
duct the analysis and remotely submit the results. Fol-
lowing this phase, a post-study questionnaire, consist-
ing of both open-ended and closed questions, was de-
signed to collect participants’ insights on the activity.
3.2.4 Questionnaire
Regarding participants’ acceptance, we applied
a questionnaire based on Technology Acceptance
Model (TAM) (Venkatesh and Davis, 2000) adding
also some open questions. This model has been ap-
plied to evaluate the acceptance of a large set of tech-
nologies about users’ perceived ease of use, the de-
gree to which a person believes that using a specific
technology will be free effortless and the perceived
usefulness that a person believes that using a spe-
cific technology will enhance his or her work per-
formance (Maranguni
´
c and Grani
´
c, 2015). In addi-
tion, according to TAM, the user’s behavioral inten-
tion to use a specific technology is determined by
perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use. The
TAM statements adapted for our study are presented
below. Regarding the adapted TAM statements, par-
ticipants provided their answers on a seven-point Lik-
ert scale, as follows: “Totally Agree, Strongly Agree,
Partially Agree, Neutral, Partially Disagree, Strongly
Disagree and Totally Disagree”.
PERCEIVED EASE OF USE: E1. My interaction
(comprehension of the information) with these UX
factors was clear and understandable; E2. Interact-
ing (comprehension of the information) with these UX
factors does not require a lot of mental effort; E3. I
find these factors easy to understand about user ex-
perience information products; and E4. I find it easy
to make these factors do what I want (user experience
information product overview).
PERCEIVED USEFULNESS: U1. Using these fac-
tors improves my performance to better understand
aspects of the product; U2. Using these factors in my
work has improved my productivity in understanding
aspects of the product; U3. Using these factors en-
hances my effectiveness in understanding aspects of
the product; U4. I consider these factors useful for
product analysis.
INTENTION TO USE: I1. Assuming I had enough
time to analyze the UX of a product, I do intend to
use these factors; I2. Whereas if I could choose any
method to analyze the UX of a product, I predict I
would use these factors.
3.2.5 Feasibility Study Execution
For the execution of the study, a questionnaire con-
taining the description of UX factors and the list of
issues was provided to the participants. This allowed
them to categorize the problems based on the most
relevant factors and they also had the opportunity to
review each factor. After completing this phase, a
post-study questionnaire was sent to each participant.
We conducted a pilot study with four participants,
according to the planned procedures. After analysing
the problems and completing the questionnaires, we
held a meeting with the participants to assess whether
they faced any challenges with the study materials and
to gather their insights on this type of research. After
this meeting, we determined that there were no im-
pediments to continuing the study with the remaining
participants.
4 RESULTS
Below are the results obtained in the evaluation of the
feasibility of applying UX factors. Table 2 shows the
number of problems analyzed in the study and the
factors applied by one of them. Regarding the de-
scription of the problems, we omitted it in Table 2
due to the confidential rules of our projects. Table 2
also highlights the factors expected to be applied by
researchers. Given the qualitative nature of this anal-
ysis, it is expected that a problem may be related to
more than one UX factor explored in this study. Re-
garding the analysis conducted, it’s possible to notice
that each one of the factors was utilized by the partic-
ipants, although, they utilized one or more of the fac-
tors. In the case of Problem 2, for example, it can be a
problem related to device functionality (Bugs) after a
software update (Software Update) that impacted the
Wi-Fi connection (Network Problem).
Regarding the TAM indicators, participants pro-
vided their answers regarding the level of acceptance
of the statements of each indicator using a seven-point
scale, with response options ranging from Strongly
Agree to Strongly Disagree. Figure 1 shows the par-
ticipants’ level of acceptance for the indicator Ease of
Use (P1 to P4), Usefulness (U1 to U4) and Intention
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
268
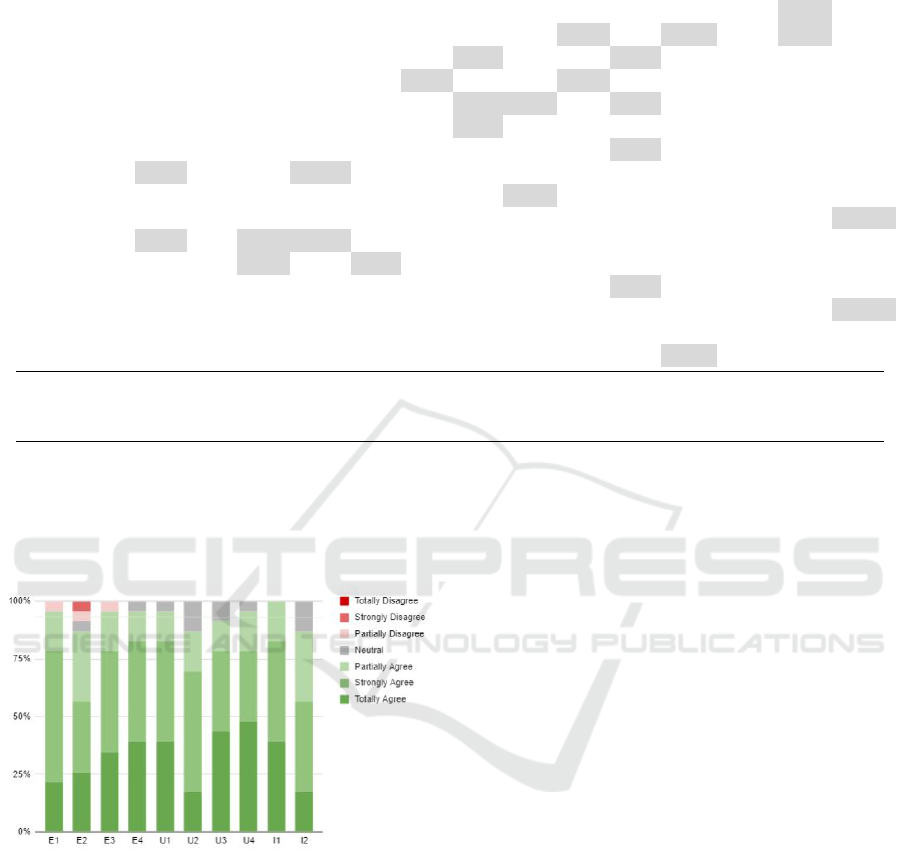
Table 2: UX problems concerning UX factors.
UX Problem Ac. At. Co. E.U. Sa. S.I. Pe. Cu. Bu. Cr. N.I. E.R. S.U H.C.
Problem 1 5 1 2 1 6 1 1 25
Problem 2 1 3 1 17 7 11 12
Problem 3 1 10 6 22 5
Problem 4 13 6 19 5 3
Problem 5 8 6 10 21 2
Problem 6 2 5 24 3 2 3
Problem 7 3 10 25
Problem 8 13 15 8 5 6
Problem 9 8 7 8 21
Problem 10 6 12 21
Problem 11 14 8 13 9 6
Problem 12 23 14 3
Problem 13 5 9 24
Problem 14 9 8 22
Problem 15 15 12 17
Problem 16 3 8
24
Ac. - Accuracy; At. - Attractiveness; Co. -Comparison; E.U. - Ease of Use; Sa. - Satisfaction;
S.I. - Screen Interface; Pe. - Performance; Cu. - Customization; Bu. - Bugs; Cr. - Crash, N.I. -
Network Issues, E.R. - Exceeded Resources, S.U. - Software Update, and H.C. - Hardware Component.
to Use (I1 and I2), where the vertical axis of the graph
refers to the statements of each of the indicators and
the horizontal axis refers to the participants’ level of
acceptance. The bars represent the participant codes
(P1, P2, and so on).
Figure 1: Participants’ acceptance of UX factors.
The majority of responses were positive, indicat-
ing a positive acceptance of the UX problem analysis
process. We organized the participant’s answers into
different categories, which represent the participants’
perceptions. In terms of the Ease of Use construct, P6
and P9 state that they did not encounter difficulties
applying this type of analysis: ’It was smooth; the de-
scription of the factors was very helpful’ and ’The de-
scription of the factors was clear and for most cases,
the application was intuitive.’ Although the major-
ity stated that this is an ease-to-implement analyti-
cal process, it was noticed in the feedback the diffi-
culty in understanding some factors: ’In my opinion,
some factors do not have a very clear description;
more examples could be given to facilitate its appli-
cation’ (P3) and ’I had doubts in some answers, espe-
cially between Bug, Crash and Accuracy; they seemed
like the same response’ (P15). To enhance the under-
standing of each factor, some participants suggested
the inclusion of more examples for a better com-
prehension of a UX factor based on the problems,
as mentioned by P8: ’User reports do not always di-
rectly indicate all the UX factors that could be linked
to that problem.’ We agreed that providing more ex-
amples could reduce uncertainty for some participants
during the analysis, as observed in the report from P2:
’In some cases where I couldn’t fit the problem into
the available options, I used the Bug option.’ An-
other aspect noticed by the participants was the lack
of clarity in the problem reports from UX evalua-
tion participants, which is a limitation in this type of
evaluation, as reported by P20: ’Most of the factors
seemed clear and sufficient to categorize user issues.
However, I think that a few pieces of feedback don’t fit
completely,’ and P10: ’The majority of feedback were
easy to understand, but there are always cases that
require a bit more attention to be comprehended.’
Regarding the usefulness of this type of anal-
ysis, different participants affirm that this analysis
supports the understanding of the device features
that are affected and the development of quality
metrics during the project and after the products
are launched in the market, as seen in the follow-
ing quotes: ’I think these factors are highly useful;
they serve as a comprehensive classifier and filter for
Evaluating UX Factors on Mobile Devices: A Feasibility Study
269

problems and device features...’ (P4); ’The utility of
the factors could collaborate with metrics during the
project development and after its launch’ (P5); ’...
serve as a well-elaborated foundation for analyzing
CRs and user feedback’ (P8); ’I believe it is useful
during the evaluation cycle to map the most affected
areas and, overall, what the user is reporting’ (P13);
’The factors are extremely useful, whether in the im-
plementation phase, pre-launch maintenance or post-
launch in the market’ (P16). Additionally, a better
understanding of the affected areas of the products
and the problems fix, which are included in weekly
releases, contributes to the engagement of users par-
ticipating in the UX evaluation, as perceived by P14:
’I agree because the improvement of the UX always
leads to their loyalty to the brand, caused by the feel-
ing of being heard and having their problems solved’.
The participants’ responses also indicate that
through the ’analysis of UX factors, a better un-
derstanding for those involved in product quality
can be achieved: ’I agree that the analysis of each
of the factors shown in the research can help im-
prove the quality of the product’ (P15); ’The user
responses, whether from end consumers or partici-
pants in the evaluation, actively shape the actions, im-
provements and corrections of the product. Therefore,
understanding this information is a crucial step in
decision-making in the process for product improve-
ment’ (P16); ’UX factors play a fundamental role in
product quality analysis, being extremely useful in all
stages of development’ (P17). Consequently, differ-
ent stakeholders in project management, such as man-
agers, developers, testers and UX specialists, can pri-
oritize issue resolutions and product improvements.
Regarding the intention to use, we’re aware that
a new activity in an ongoing process may not be ac-
cepted by all those involved. However, the responses
to most open-ended questions from participants sug-
gest a positive predisposition for the adoption of this
type of analysis. P5 and P17 state that such analy-
sis would support a better understanding of a prob-
lem before forwarding it to the development team:
’I would apply it in my daily activities; I believe it
would help in a better understanding of the problems’
(P5) and ’The application of these factors is crucial to
ensure that products meet user expectations, are intu-
itive to use, and offer a pleasant experience. There-
fore, the application of these factors through a system
would be a highly recommended choice to improve the
quality and success of new products’ (P17).
Still, when applying these factors in practice, it is
beneficial to adapt the process of evaluating prob-
lems reported during UX analyses. This allows for
a deeper understanding of the key roles involved in
this analysis, such as UX analysts and developers.
P11 and P22, for example, provided such insights: ’If
we raise awareness and discuss new good practices
for factors, it would be a viable option to adopt simi-
lar practices globally’ (P11) and ’As a developer, it is
unclear to me how and when these factors will be as-
signed to a CR (Change Request). During triage? In
this case, would the factors already be applied when
I receive the CR?’ (P22). Thus, the factors can be
widely adopted and viewed by all those involved in
the project. Consequently, it is possible to observe
that incorporating these factors into problem analy-
sis can positively contribute to product development
projects that will be launched in the market.
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Findings
In reference to our findings regarding to RQ1 (Is the
use of UX factors comprehensible by practitioners
during problem analysis?), the results presented in
Table 2 indicated that the majority of the employed
factors are related to the analysis expected by the
main researchers. Since this is a qualitative analy-
sis, we understand that the use of most factors for a
specific problem may indicate that the participants un-
derstood them. However, some aspects were observed
that could affect this analysis, such as the lack of in-
formation from users who submit their evaluations of
the products. As the problem sample was randomly
selected, there were some reports with limited infor-
mation. Additionally, some participants had difficul-
ties with the factors’ description, indicating the need
for more examples in this context to minimize un-
certainties in the use of factors during problem anal-
ysis. Therefore, we plan to include more examples
in the description of the factors and also incorporate
this activity into our analysis process, indicating the
key roles involved in this analysis and the stage at
which such problems can be evaluated regarding UX
aspects. Thus, the results of the feasibility study indi-
cate that the description of the factors is feasible and
it was possible to understand the main limitations for
the use of these factors during evaluation.
For RQ2 (What is the level of participants’ accep-
tance for this type of analysis in mobile device devel-
opment projects?), utilizing the TAM revealed partic-
ipants’ acceptance of this analysis type. The quan-
titative results demonstrated predominantly positive
responses, as depicted in Figure 1. Regarding user
perceptions, while some indicated difficulties in un-
derstanding factor descriptions and others felt a lack
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
270

of examples, the majority of participants highlighted
the importance of this type of analysis. They empha-
sized the ability to comprehend the affected character-
istics of the device and the potential to formulate met-
rics to evaluate product quality. Based on the partic-
ipants’ responses, it became apparent that the aspect
that most influences the intention to use the factors is
their utility in analyzing product quality.
5.2 Threats to Validity
The threats that may affect the validity of our study re-
sults (Falessi et al., 2018) are described below, along
with the treatment for each of them.
Internal Validity. An identified threat is the sharing
of information between participants during the study.
To address this threat, the study’s selection and ma-
terials were individually sent to participants, as par-
ticipants don’t need to be close. This minimizes the
identification of other participants, thus reducing the
possibility of communication between them. Limited
information regarding problems can also affect the in-
terpretation of UX factors.
External Validity. Validity of the assessed problems
as a representative sample. To mitigate this threat,
16 problems were randomly selected from different
projects. Additionally, this number is related to the
average number of problems analyzed by a triage an-
alyst, reflecting a real activity in this company.
Construct Validity. Regarding UX factors, as these
are qualitative data, they were discussed in vari-
ous meetings by the researchers beforehand to mit-
igate misunderstanding about the problems. About
the adoption of TAM, it has been employed and
adapted for the evaluation of different technologies
(Maranguni
´
c and Grani
´
c, 2015).
Conclusion Validity. The short period of use of UX
factors in problem analysis. However, this is an initial
result and the findings cannot be generalized.
6 RELATED WORKS
Soleimani and Law (2017) present an empirical study
and highlight the importance of using a methodolog-
ical approach to measure UX. The main objective of
this study was to recognize emotions via the Think-
Aloud technique. The empirical study was carried out
with 46 participants using an online shopping plat-
form to evaluate each person’s emotional experiences
in different sessions. As the study was exploratory
in nature, the main intention was to develop a practi-
cal approach to explore momentary perceptions and
user interactions regarding the qualities of a prod-
uct/service. The techniques applied do not require any
additional expense or equipment and they can be im-
plemented in any work environment.
Fernandez et al. (2013) present the results of a
family of empirical experiments executed to compare
the proposed inspection method WUEP (Web Usabil-
ity Evaluation Process) with a well-known inspection
method - HE (Heuristic Evaluation) regarding its Ef-
fectiveness, Efficiency, Perceived ease of use and Per-
ceived satisfaction of use. To evaluate the results, the
authors did a quantitative analysis of the results and
tested all the null hypotheses. The statistical analy-
sis and meta-analysis of the data obtained separately
from each experiment indicated that WUEP is more
effective and efficient than HE in the detection of us-
ability problems. The evaluators were also more satis-
fied when applying WUEP and found it easier to use
than HE. The experiment concluded that the WUEP
method performed better for all the 4 points analyzed.
Regarding the works above, we notice the impor-
tance of evaluating the UX of a system and show a
specific approach to supporting the collection of user
feedback through evaluation sessions (Soleimani and
Law, 2017). Our work, on the other hand, evaluates
UX during a period of 3 to 4 months, including the
methods to support it, which allows us to figure out
the users’ perceptions. While the paper from (Fer-
nandez et al., 2013) evaluated usability for web appli-
cations during the development process considering
Effectiveness, Efficiency, Perceived ease of use and
Perceived satisfaction, our work evaluated the appli-
cation of 14 factors in different types of real issues
reported by users of your daily life. Our work focuses
on UX factors, that can help to figure out pragmatic
or hedonic aspects of mobile devices, contributing to
the quality of these products.
7 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presented a feasibility study on the appli-
cation of UX factors in the analysis of real problems
in mobile devices’ UX evaluations. Considering the
action research methodology, we systematically eval-
uated UX factors for mobile devices, identifying key
elements for use in projects focusing on UX evalua-
tion. This kind of analysis can contribute to understat-
ing the main problems, both pragmatic and hedonic,
that may impact the end user’s perception of mobile
devices before their market launch. Based on the re-
sults obtained, the consensus among practitioners is
that this form of analysis is valuable for comprehend-
ing the fundamental factors of UX. While the majority
agreed that it is easy to implement this type of anal-
Evaluating UX Factors on Mobile Devices: A Feasibility Study
271

ysis, we observed the need for improvements in de-
scribing the factors to be implemented in the daily ac-
tivities of the practitioners dealing with the UX eval-
uation. Our perspective is that these factors can high-
light the hedonic aspects related to the UX in evalu-
ations, once the predominant focus of developers lies
in fixing and enhancing the pragmatic aspects.
For future work, we intend to incorporate exam-
ples of problems related to the factors to facilitate
the UX problem analysis. Additionally, we intend
to refine the problem analysis process to incorporate
UX factors, covering the necessary activities and met-
rics that can assist this type of evaluation in future
projects. Moreover, it will also be possible to ana-
lyze the contributions of UX factors toward a deeper
software quality comprehension in this aspect.
REFERENCES
Alves, F., Aguiar, B., Monteiro, V., Almeida, E., Marques,
L. C., Gadelha, B., and Conte, T. (2021). Immersive
ux: A ux evaluation framework for digital immersive
experiences in the context of entertainment. In ICEIS
(2), pages 541–548.
Damian, A. L., Teixeira, L., Carrenho, B. C., Ferreira, B. B.,
Bentes, B. A., Tordin, M. G., Martin, M. G., Castro,
M. L., Brotto, M. B., Pereira, B. V., et al. (2023). Ex-
ploring ux factors through the dogfooding approach:
An experience report. In Proceedings of the XXII
Brazilian Symposium on Software Quality, pages 236–
243.
de Normalisation, O. I. (2010). Iso 9241-210: Ergonomics
of human-system interaction-part 210: Human-
centered for interactive systems. International Orga-
nization for Standardization.
Falessi, D., Juristo, N., Wohlin, C., Turhan, B., M
¨
unch, J.,
Jedlitschka, A., and Oivo, M. (2018). Empirical soft-
ware engineering experts on the use of students and
professionals in experiments. Empirical Software En-
gineering, 23:452–489.
Fernandez, A., Abrah
˜
ao, S., and Insfran, E. (2013). Em-
pirical validation of a usability inspection method for
model-driven web development. Journal of Systems
and Software, 86(1):161–186.
Harrison, W. (2006). Eating your own dog food. IEEE
Software, 23(3):5–7.
Hassenzahl, M. (2018). The thing and i: understanding the
relationship between user and product. Funology 2:
from usability to enjoyment, pages 301–313.
Jesus, E. A., Guerino, G. C., Valle, P., Nakamura, W. T.,
Oran, A. C., Balancieri, R., Coleti, T. A., Morandini,
M., Ferreira, B., and Silva, W. (2022). An experimen-
tal study on usability and user experience evaluation
techniques in mobile applications. In ICEIS (2), pages
340–347.
Kou, Y. and Gray, C. M. (2019). A practice-led account
of the conceptual evolution of ux knowledge. In Pro-
ceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Fac-
tors in Computing Systems, pages 1–13.
Lallemand, C., Koenig, V., and Gronier, G. (2014). How
relevant is an expert evaluation of user experience
based on a psychological needs-driven approach? In
Proceedings of the 8th Nordic conference on human-
computer interaction: Fun, fast, foundational, pages
11–20.
Maranguni
´
c, N. and Grani
´
c, A. (2015). Technology accep-
tance model: a literature review from 1986 to 2013.
Universal access in the information society, 14:81–
95.
Marques, L. C., Nakamura, W. T., Valentim, N. M. C.,
Rivero, L., and Conte, T. (2018). Do scale type tech-
niques identify problems that affect user experience?
user experience evaluation of a mobile application (s).
In SEKE, pages 451–450.
Moreno, A. M., Seffah, A., Capilla, R., and Sanchez-
Segura, M.-I. (2013). Hci practices for building usable
software. Computer, 46(04):100–102.
Nakamura, W. T., de Oliveira, E. C., de Oliveira, E. H., Red-
miles, D., and Conte, T. (2022). What factors affect
the ux in mobile apps? a systematic mapping study on
the analysis of app store reviews. Journal of Systems
and Software, 193:111462.
Petersen, K., Gencel, C., Asghari, N., Baca, D., and Betz,
S. (2014). Action research as a model for industry-
academia collaboration in the software engineering
context. In Proceedings of the 2014 international
workshop on Long-term industrial collaboration on
software engineering, pages 55–62.
Schrepp, M., Kollmorgen, J., Meiners, A.-L., Hinderks, A.,
Winter, D., Santoso, H. B., and Thomaschewski, J.
(2023). On the importance of ux quality aspects for
different product categories.
Silva, E., Tanaka, E., and Tordin, G. (2019). Dogfooding:
” eating our own dog food” in a large global mobile
industry player. In Proceedings of the 14th Interna-
tional Conference on Global Software Engineering,
pages 52–57.
Soderquist, K., Tirabeni, L., and Pisano, P. (2016). Em-
ployee engagement practices in support of open inno-
vation. In 3rd Annual World Open Innovation Confer-
ence, pages 15–16.
Soleimani, S. and Law, E. L.-C. (2017). What can self-
reports and acoustic data analyses on emotions tell us?
In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Designing
Interactive Systems, pages 489–501.
Venkatesh, V. and Davis, F. D. (2000). A theoretical exten-
sion of the technology acceptance model: Four longi-
tudinal field studies. Management science, 46(2):186–
204.
Wang, T., Oh, L.-B., Wang, K., and Yuan, Y. (2013). User
adoption and purchasing intention after free trial: an
empirical study of mobile newspapers. Information
Systems and e-Business Management, 11:189–210.
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
272
