
Pareto-Optimal Execution of Parallel Applications with Respect to Time
and Energy
Thomas Rauber
1 a
and Gudula R
¨
unger
2 b
1
Department of Computer Science, University of Bayreuth, Germany
2
Department of Computer Science, Chemnitz University of Technology, Germany
Keywords:
Numerical Solution Methods, Parameter Selection, Runtime Performance, Energy Consumption.
Abstract:
Compute-Bound numerical solution methods have a high demand for computational power and, thus, for
energy. Both depend strongly on the numerical accuracy required for the approximation solution. A higher
numerical accuracy often requires more execution time and energy. However, this dependence is more subtle
and diverse. That means for a given numerical problem, different settings of the solution process, such as the
use of different solvers, different implementation variants, different numbers of cores, or different operational
frequencies result in a large number of different possibilities for the solution process, each of which may
lead to a potentially different execution time and energy consumption. The best combination also depends
on the specific execution platform used. Using different tolerance values for the time steps in the solution
process adds another degree of complexity with a potentially different accuracy of the resulting approximation
solution. The goal of this article is to investigate the selection process of performance-optimal variants of all
these computation possibilities when solving a given numerical problem. In particular, a selection process
is proposed determining Pareto-optimal computation variants of the numerical method. As representative
numerical solution method, explicit solution methods for ordinary differential equations are considered.
1 INTRODUCTION
The execution of software on computing devices con-
sumes more and more energy and it is an important
concern to reduce this energy consumption for envi-
ronmental reasons (OECD, 2023). The energy con-
sumption can be reduced by employing hardware sys-
tems that are more energy-efficient or by developing
methods to execute the software in a more energy-
efficient way (Brown and Reams, 2010). In this arti-
cle, the second aspect is considered in more detail.
Energy efficiency is especially important for
compute-intensive applications that are executed on
large parallel systems, since these applications often
use large amounts of energy (Orgerie et al., 2014).
Many compute-intensive applications come from the
area of scientific computing, especially from the nu-
merical solution of differential equations modeling
phenomena in science and engineering, including
classical physics, economy, chemistry, and engineer-
ing. In most cases, it is not possible to represent the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3102-6858
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5364-2088
exact solution in closed form and, therefore, the so-
lution has to be approximated by a numerical tech-
nique. The solution of differential equations requires
the use of suitable numerical methods, which are of-
ten compute-bound and require a large amount of exe-
cution time and energy. Approximations usually pro-
duce an error due to the numerical calculations per-
formed, and it is an important concern to determine
how good the approximation fits to the real solution at
the approximation points (Deuflhard and Hohmann,
2003). This is denoted as the accuracy of the solu-
tion. For many numerical methods, the accuracy can
be influenced by algorithmic parameters, such as tol-
erance values and error bounds that are used to decide
whether a computation step is accepted or needs be
repeated.
The execution time and energy consumption of the
execution of a numerical method strongly depends on
the execution platform and the execution parameters
that are used for the execution. Usually, the numeri-
cal method is implemented as parallel software sys-
tem and the number of execution units (processors
or cores) used for the execution has a large influence
on the execution time and energy consumption. Us-
Rauber, T. and Rünger, G.
Pareto-Optimal Execution of Parallel Applications with Respect to Time and Energy.
DOI: 10.5220/0012627100003714
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems (SMARTGREENS 2024), pages 65-72
ISBN: 978-989-758-702-3; ISSN: 2184-4968
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
65

ing a larger number of execution units often reduces
the execution time until a certain saturation point is
reached, which depends on the algorithmic structure
and parallel implementation of the numerical method.
However, the energy consumption may exhibit a dif-
ferent characteristic of the growth behavior depending
on the amount of parallelism. Different selections of
execution parameters may lead to the smallest execu-
tion time or the smallest energy consumption, respec-
tively.
On recent multicore architectures, the computa-
tion time and the energy consumption of program ex-
ecutions can further be influenced by the setting the
operational frequency of the execution units (Sch
¨
one
et al., 2019). Smaller operational frequencies usu-
ally increase the execution time, but may lead to a
smaller energy consumption due to a reduced power
consumption. The interactions may be complex and
they depend on the computational and memory access
behavior of the software code executed.
In addition to the algorithmic and execution pa-
rameters mentioned above, there might exist differ-
ent implementation variants of the same numerical
method, which again may also lead to different per-
formance results. When combining all these differ-
ent possibilities, a large variety of different solution
variants results and it is usually not a priory obvious
which variant provides the solution run with the best
or optimal performance or energy consumption for a
given accuracy requirement. It may even be possible
that a best or optimal parameter setting for both exe-
cution time and energy consumption does not exist an
a certain compromise has to be chosen. This article
provides a study of these multi-dimensional require-
ments for compute-bound numerical computations.
As running example, an Runge-Kutta (RK) solution
method for ordinary differential equations (ODEs) is
considered (Hairer et al., 1993).
In particular, the problem of finding an optimal
implementation variant for an RK method is consid-
ered by considering the problem as a multi-criteria
decision problem considering execution time, energy
consumption and numerical accuracy together. The
set of different ODE solver variants form a decision
space for which a Pareto-optimal solution is deter-
mined according to the position of the performance
values in the criterion space. Thus, the problem of
finding a performance-optimal solution is considered
as a data-science problem by first generating a com-
plete set of performance data for the criterion space
to be analyzed. The data analysis of the performance
data exploits the elimination of certain variants, if
these implementation variants are dominated by other
variants. The article proposes a selection process and
demonstrates its usage for the solution of an ODE
problem.
The rest of the article is structured as follows. Sec-
tion 2 discusses related work. Section 3 describes
the variant selection process. Section 4 considers the
analysis of the performance data with an emphasis on
the relation between accuracy and energy and/or exe-
cution time. Section 5 describes the experiments and
measurements. Section 6 concludes the paper.
2 RELATED WORK
Many different aspects of energy-aware and green
computing are addressed in (Ahmad and Ranka,
2012). The handbook considers hardware aspects
such as energy-efficient CPU architectures, energy-
efficient storage systems, intelligent energy-aware
networks, algorithmic aspects of energy-aware algo-
rithms with an emphasis of energy-efficient schedul-
ing methods. Other aspects include real-time systems,
monitoring and evaluation methods, data centers and
large-scale systems, as well as social and environmen-
tal issues. Similar topics with a focus on distributed
systems, high-performance systems, and cloud sys-
tems are covered in (Zomaya and Lee, 2012). The
scheduling of parallel tasks with energy and time
constraints on multiple manycore processors are ad-
dressed in (Li, 2016) and (Li, 2018). Scheduling al-
gorithms are proposed and worst-case asymptotic per-
formance bounds and average-case asymptotic per-
formance bounds are derived for the algorithms pro-
posed. The analytical results are verified by extensive
simulations.
The bi-objective optimization of data-parallel ap-
plications on homogeneous multicore clusters for
performance and energy consumption has been ad-
dressed in (Manumachu and Lastovetsky, 2018;
Manumachu et al., 2023). In particular, it is shown
by experiments on modern multicore CPUs that the
relationship between execution time and energy con-
sumption is complex. The paper formulates the bi-
objective optimization problem for performance and
energy is formulated as mathematical problem and a
global optimization algorithm is proposed to deter-
mine globally Pareto-optimal solutions. As examples,
matrix multiplication and fast Fourier transform are
considered. For these applications, the only algorith-
mic parameter is the input size. In contrast, the RK
methods considered in this article are more complex
and the tolerance value for the error control is an addi-
tional algorithmic parameter that has a large influence
on the numerical accuracy of the resulting approxi-
mative solution. Moreover, matrix multiplication and
SMARTGREENS 2024 - 13th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
66
fast Fourier transform can be more easily captured by
an analytical modeling than the RK methods because
the time-stepping nature of the RK methods.
The work in (Manumachu and Lastovetsky, 2018)
has been extended in (Lastovetsky and Manumachu,
2023) to include heterogeneous platforms. There are
other approaches in this direction, including (Fard
et al., 2012) addressing heterogeneous environments,
(Mezmaz et al., 2011) considering cloud computing
systems, and (Freeh et al., 2007) investigating the oc-
currence of memory and communication bottlenecks
in cluster systems.
3 VARIANT GENERATION
This section describes the process of generating dif-
ferent execution variants of numerical methods using
different algorithmic parameters and execution pa-
rameters.
3.1 Execution Preliminaries
For the execution, we assume that the numerical
method is provided as a parallel program. In the fol-
lowing, we assume that a multi-threaded implemen-
tation of the numerical method is available for shared
address spaces and that a multi-core platform is used
for the execution.
We assume that the hardware platform used sup-
ports DVFS (Dynamic Voltage Frequency Scaling).
Frequency scaling for DVFS processors includes the
implicit or explicit selection of the operational fre-
quency from a discrete set of frequency values in the
range [ f
min
, f
max
]. Which frequencies are available
depends on the specific hardware system used.
3.2 Variant Generation Process
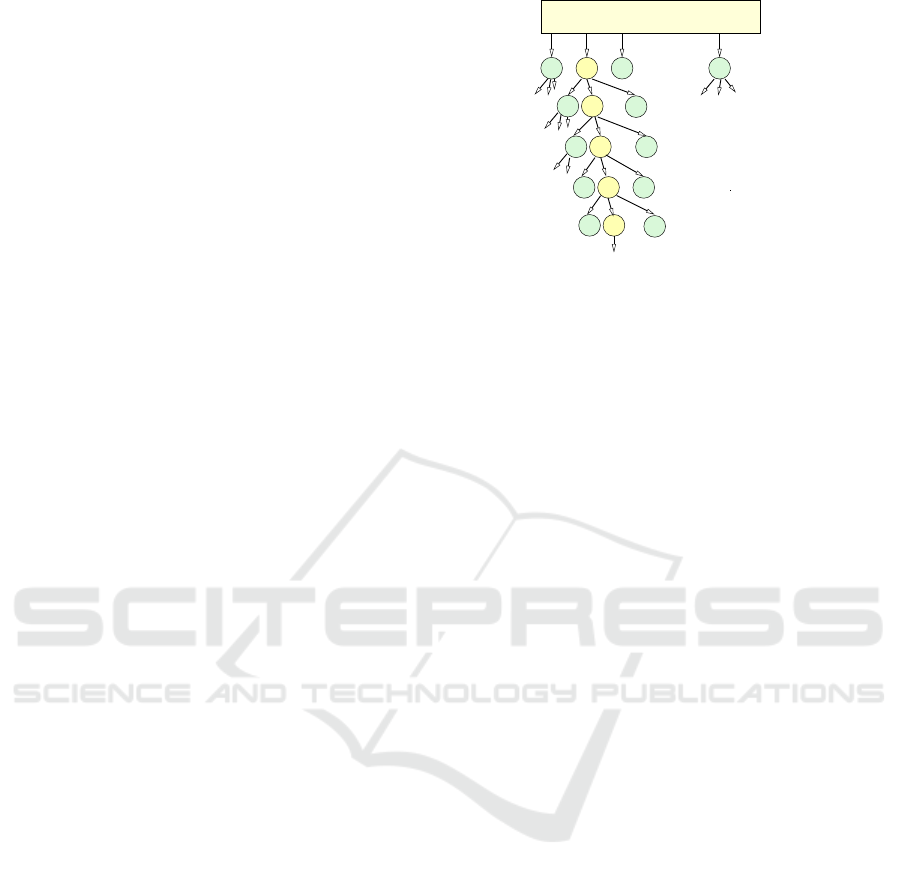
Figure 1 illustrates the generation of different vari-
ants of numerical solution methods at different lev-
els of the execution pipeline. Starting from a spe-
cific numerical solution method, different implemen-
tation variants can be generated by different coding of
the main computation loops, e.g., by using different
computation schemes and applying different algorith-
mic optimizations and different program transforma-
tions, including standard transformations such as loop
tiling, loop interchange, loop fusion or loop unrolling.
Each of the different program versions can be
compiled with different compiler options such as op-
tions to enable vectorization, loop optimizations or
alignment. Standard compiler offer a huge number of
different compiler options: the gcc compiler supports
...
...
implementation
variants
...
...
...
number of threads
DVFS settings
compiler options
tolerance values
performance
energy
...
...
...
coding timecompile timeruntime
numerical solution method
Figure 1: Illustration of the variant generation process at
different stages of software development and execution, i.e.,
coding time, compile time and runtime. In each level of the
decision tree, a specific choice of a value for a parameter
can be taken, such that a selection path (depicted as yellow
circles) in the decision tree results. The leaf of a selected
path corresponds to a specific variant with individual per-
formance and energy data.
more than 200 options and the LLVM compiler has
more than 150 compiler passes (Ashouri et al., 2018).
This large number of options potentially leads to the
possibility to generate a huge number of different exe-
cutables, each with potentially different performance
characteristics. Each of these executables can be ex-
ecuted with different DVFS settings for the cores and
uncores of the execution platform. Moreover, differ-
ent numbers of threads can be employed for the exe-
cution. To control the global error of the approxima-
tion solution, different tolerance values can be used to
control the execution of the numerical method. Over-
all, a potentially huge number of execution variants
results, each with a different performance and energy
behavior.
3.3 Performance of Variants
The execution of an implementation variant V can be
assessed with several performance metrics, such as
the execution time or the energy consumption.
The energy E consumed for the execution of an
implementation variant V during the execution inter-
val [0,t
end
] depends on the given hardware platform
and the power drawing P during the execution time
T = t
end
. The power drawing P may vary during
the execution of the code. Thus, E is expressed as
E =
R
t
end
t=0
P(t)dt, assuming that the program is exe-
cuted from time t = 0 to time t = t
end
and that P(t) is
the power drawing at time t.
Several implementation variants can be generated
for a single version of the numerical method. For a
multicore system with p
max
cores, variants for any
Pareto-Optimal Execution of Parallel Applications with Respect to Time and Energy
67
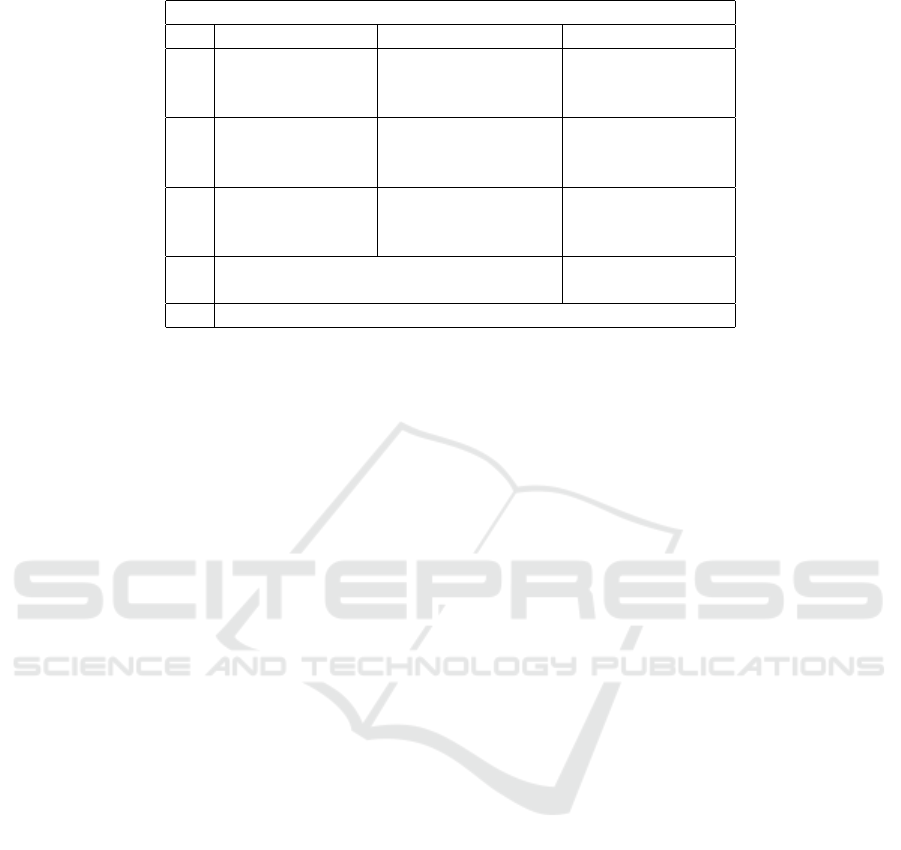
Table 1: Optimization goals for execution time, energy consumption, and numerical accuracy.
Optimization goals with constraints
execution time energy consumption accuracy
1. minimize no constraint no requirement
2. minimize constraint < E
max
no requirement
3. minimize no constraint requirement < eps
4. no constraint minimize no requirement
5. constraint < T
max
minimize no requirement
6. no constraint minimize requirement < eps
7. no constraint no constraint requirement < eps
8. no constraint constraint < E
max
requirement < eps
9. constraint < T
max
no constraint requirement < eps
10. Pareto-optimization of time and energy no requirement
11. Pareto-optimization of time and energy requirement < eps
12. Pareto optimization of time and energy and accuracy
number of cores between 1 and p
max
can be used. For
DVFS systems with operational frequencies f ranging
between a minimum frequency f
min
and a maximum
frequency f
max
, variants for all available frequencies
can be generated. Starting from f
max
, the maximal
possible scaling factor is s
max
= f
max
/ f
min
. The power
drawing P varies with the number of threads p used
for the execution and the operational frequency f cho-
sen, so that the power P can be expressed as a function
of p and f , i.e., P = P(p, f ), see (Rauber and R
¨
unger,
2012) for more details.
4 ANALYSIS OF PERFORMANCE
DATA
This section is concerned with the performance and
energy data of the calculation of an approximation
solution by a numerical method and the quality of the
approximation solution itself in terms of accuracy. An
analysis of the data provides insight into several ques-
tion with respect to the quality of the solution.
4.1 Performance Optimization Problem
The data concerning the execution time T, the energy
consumption E, the power P as well as the accuracy
Acc in dependence of the operational frequency f ,
the number of threads p and the chosen TOL values
provides a large set of performance data available for
analysis. This data set raises several interesting ques-
tions concerning the behavior that can be investigated
with a suitable data analysis. Especially, the perfor-
mance behavior for computing an approximation be-
havior is an optimization problem to which optimal
or Pareto-optimal solutions are to be found. The opti-
mization problem concerns performance, energy and
accuracy data. The analysis of these performance data
includes the following issues:
• Which relation can be observed between the ex-
ecution time and the energy consumption when
all independent variables f , p,TOL are set to the
same values? Is the relation a linear one or are
there exceptions, e.g., caused by a varying power
consumption?
• How can a best solution be identified in the two-
dimensional solution space of execution time and
energy consumption? Is there a unique best so-
lution for optimizing both, execution time and
energy consumption, in dependence of p, f and
TOL? Or can a set of of Pareto optimal solutions
be identified?
• Given an upper bound of the energy consumption
to be invested and an upper bound of the accuracy
(a) Is it possible to find suitable values for p, f ,
and T OL so that the related approximation solu-
tion fulfills the constraint? (b) In case that several
feasible solutions are available, which one is the
best or which ones are in the set of Pareto-optimal
solutions?
These questions describe specific optimization
problems which are of interest. Table 1 summarizes
twelve optimization problems which are possibly in-
teresting to consider. Optimization problems (1) - (3)
minimize the execution time with different constraints
for the energy consumption and the numerical accu-
racy. Problems (4) - (6) minimize the energy con-
sumption with different constraints. Problems (7) -
(9) address minimum requirements for the numeri-
cal accuracy. The three last optimization problems
(10) - (12) describe Pareto-optimal solutions for two
or three objectives, which is formalized in the next
subsection.
SMARTGREENS 2024 - 13th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
68
4.2 Defining Pareto-Optimal
Performance of Variants
The problem of finding an optimal implementation
variant for a numerical solution method can be con-
sidered as a multi-criteria decision problem consider-
ing execution time, energy consumption and numer-
ical accuracy together. For this problem, a decision
space and a criterion space are defined as follows.
Definition 1. The decision space represents all possi-
ble implementation variants, potentially executed on
a certain number of cores with individual frequency
scaling. The feasible set A is a subset of the decision
space that contains the variants that are available for
the optimization problem.
Definition 2. The criterion (or objective) space is
the image of the decision space under the objec-
tive function mapping, which are the execution time,
the energy consumption, and the numerical accuracy.
The criterion space for execution time and energy
consumption can be represented by a diagram in
which the x-axis denotes the execution time and the
y-axis denotes the energy consumption.
Each feasible implementation variant V is repre-
sented by a criterion value according to its execution
time and its energy consumption. The image of the
set A under the mappings execution time T : A → R
and energy consumption E : A → R form the feasi-
ble set in the criterion space. The set of feasible
solutions A is built up according to variant generation
process given in Figure 1. The image in the criterion
space is determined by measuring the execution time
and the energy consumption of the different variants
available. The definition of an efficient implementa-
tion variant in the decision space and the related def-
inition of non-dominated points in the criterion space
are given as follows (Rauber and R
¨
unger, 2019a):
Definition 3. An implementation variant V is called
efficient (also called Pareto optimal), if there is no
other implementation variant
˜
V such that T (
˜
V ) <
T (V ) and E(
˜
V ) < E(V ). If V is efficient, its entry
(T (V ), E(V )) ∈ R × R in the criterion space is called
non-dominated point. The set of efficient implemen-
tation variants is denoted by A
e f f
. The set of all non-
dominated points is called the non-dominated set.
An implementation variant V
1
dominates an imple-
mentation variant V
2
, if T (V
1
) ≤ T (V
2
) and E(V
1
) ≤
E(V
2
).
Thus, for the elements in A
e f f
, there exists no al-
ternative that has both a smaller execution time and a
smaller energy consumption. The set of efficient so-
lutions is sometimes also called a Pareto set (Ehrgott,
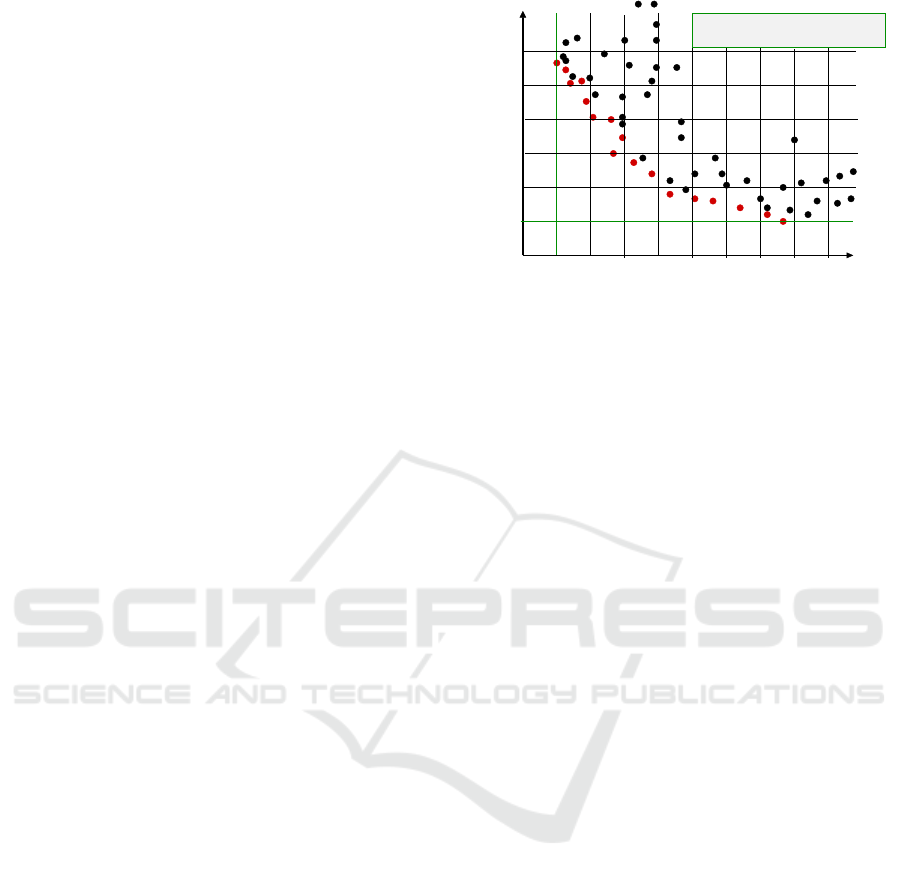
execution time [sec]
energy consumption [J]
Emin
Tmin
Emin: minimum energy consumption
Tmin: minimum execution time
Figure 2: Illustration of the two-dimensional criterion
space with execution time and energy consumption. Each
point represents a different implementation variant. The red
points are the Pareto-optimal points (Rauber and R
¨
unger,
2019a).
2005). In Figure 2, the non-dominated points are de-
picted in red, whereas the black points are points that
are dominated by other points and, therefore, do not
need to be considered further (Rauber and R
¨
unger,
2019a). All red points together represent the Pareto
set. All implementation variants that are not efficient
can be excluded from the search for an optimal so-
lution. For the computation of non-dominated points
and, thus, implementation variants, we use the algo-
rithm in Figure 3.
4.3 Summary of Variant Selection
Figure 3 illustrates the variant selection process for a
parallel application algorithm based on performance
data. In the first step (variant generation), a suitable
application algorithm is selected according to the re-
quired accuracy of the solution. The specific appli-
cation problem to be solved and its characteristics
are taken into consideration for this selection. Usu-
ally, several application algorithms are suitable for the
combination of application problem and the required
accuracy. These different choices lead to different ba-
sic variants to be considered further in the selection
process. Each of these variants potentially leads to
different performance and energy requirements. Each
of the basic variants can be executed with different
parameters of the execution platform, such as differ-
ent numbers of threads and different operational fre-
quencies. Moreover, different implementation vari-
ants can be generated by modifying the loop structure
of the underlying implementation using loop transfor-
mations or by using different compiler options, see
Fig. 3. This potentially leads to a large number of im-
plementation variants that can be executed on the ex-
ecution platform. During the execution, performance
Pareto-Optimal Execution of Parallel Applications with Respect to Time and Energy
69
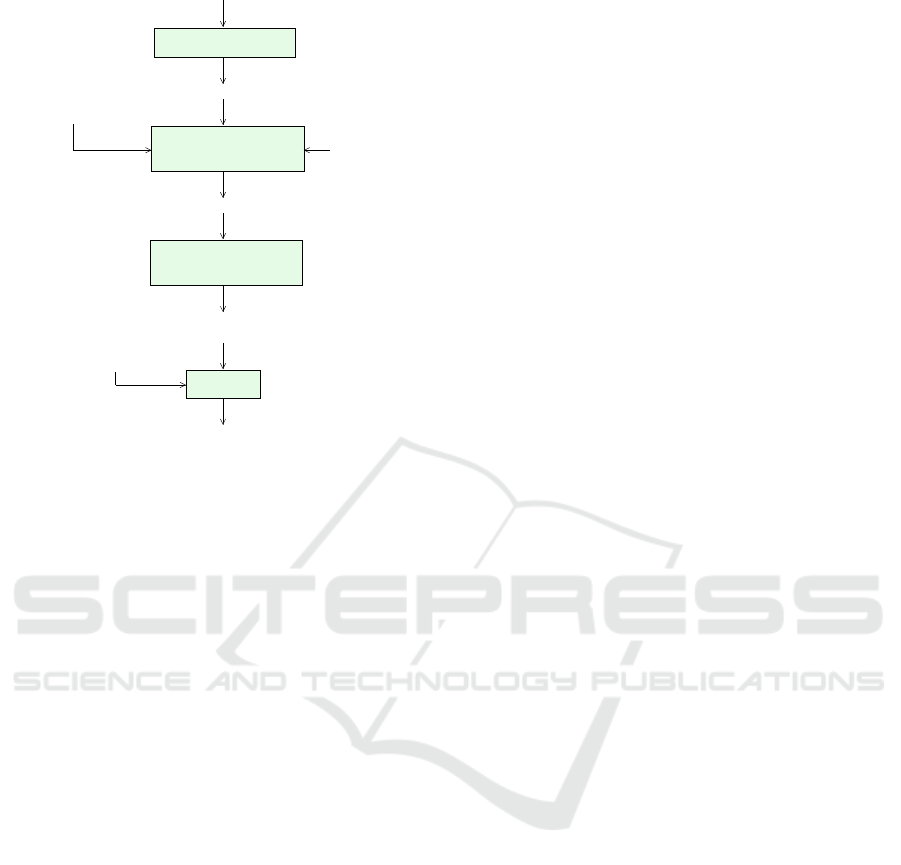
selection
solver variants
execution modes
performance data
specialized
goal
parameters
(DVFS)
optimization
application algorithm
application problem
application variant
application variants
variant generation
cost determination
accuracy measurement
nondominated elements
generation of
Figure 3: Illustration of the variant selection process for a
parallel application algorithm.
data can be collected, including execution times, en-
ergy consumption and numerical accuracy. These
data can then be used construct the time-energy cri-
terion space according to Fig. 2 and to determine the
Pareto set of the variants selected.
The variant selection can be supported by suitable
optimization techniques, see (Gill et al., 1981) for a
detailed treatment. The optimization goal would be
to determine the parameters such that the resulting
energy consumption is minimized. The energy con-
sumption could be captured by a modeling equation
with the expression for T (p, f ) and P(p, f ) written in
such a way that the parameters selected (in this case
the number of threads p and the operational frequency
f ) occur in the expression. Suitable techniques in-
clude constrained methods, where the constraints de-
fine a maximum number of resources that are avail-
able for the execution or a frequency range in which
the frequency value f determined by the optimization
method has to fit.
5 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
The variant selection process is applied to perfor-
mance data of measurements for solving an ODE
test problem with an RK method, see (Rauber and
R
¨
unger, 2019b) for a detailed description of the RK
solution method. The test ODE results from a spatial
discretization of a two-dimensional time-dependent
partial differential equation describing a reaction-
diffusion (RD) problem of two chemical substances
(Hairer et al., 1993). Discretizations with different
grid sizes N lead to different sizes of the resulting
ODE system.
5.1 Hardware Platforms
For the experimental evaluation, an Intel Broad-
well processor (i7-6950X) has been used. The In-
tel Broadwell i7-6950X CPU has 10 cores on one
socket, running at 3.0 GHz. The TDP is 140 Watt.
Hyper-threading is supported. The memory hierar-
chy includes a 25 MB shared L3 cache, a 256 KB L2
cache and a 32 KB L1 cache per core. The main mem-
ory size is 32 GB. The frequency range supported lies
between 1.2 GHz and 2.9 GHz. Only a discrete set
of frequencies is available: {1.2 GHz, 1.3 GHz, 1.4
GHz, 1.6 GHz, 1.7 GHz, 1.8 GHz, 1.9 GHz, 2.0 GHz,
2.2 GHz, 2.3 GHz, 2.4 GHz, 2.5 GHz, 2.6 GHz, 2.8
GHz, 2.9 GHz }.
The compilation has been performed with the
gcc compiler (Version 7.3.1) using the highest opti-
mization level -O3. The time and energy measure-
ments have been performed using the Running Aver-
age Power Limit (RAPL) interface and sensors of the
Intel architecture (Rotem et al., 2012; Intel, 2011).
RAPL sensors can be accessed by control registers,
known as Model Specific Registers (MSRs) (Intel,
2011). In particular, the likwid tool-set, especially
the likwid-perfctr tool in Version 4.3.2 (Treibig et al.,
2010) has been used for the experimental evaluation.
The likwid tool-set provides an easy access to the
MSRs. For the experiments with frequency scaling,
likwid-setFrequencies has been used to set the opera-
tional frequency to a fixed value. For the experiments,
only the core frequency has been changed, the uncore
frequency with the memory controller remained un-
changed. The runtime and energy measurements have
been performed with no other user on the system and
no other process except the operating system running
to keep disturbance effects as small as possible.
5.2 Selection of Pareto-Optimal
Variants
In the following, the variant selection process is illus-
trated for the operational frequency used. The vari-
ant selection process is applied to a parallel multi-
threaded implementation version of the DOPRI5 RK
method (Rauber and R
¨
unger, 2019b). As application
problem, the RD ODE using N = 4096 on the Broad-
well processor is considered.
Figure 4 shows the execution time (x-axis) and en-
SMARTGREENS 2024 - 13th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
70
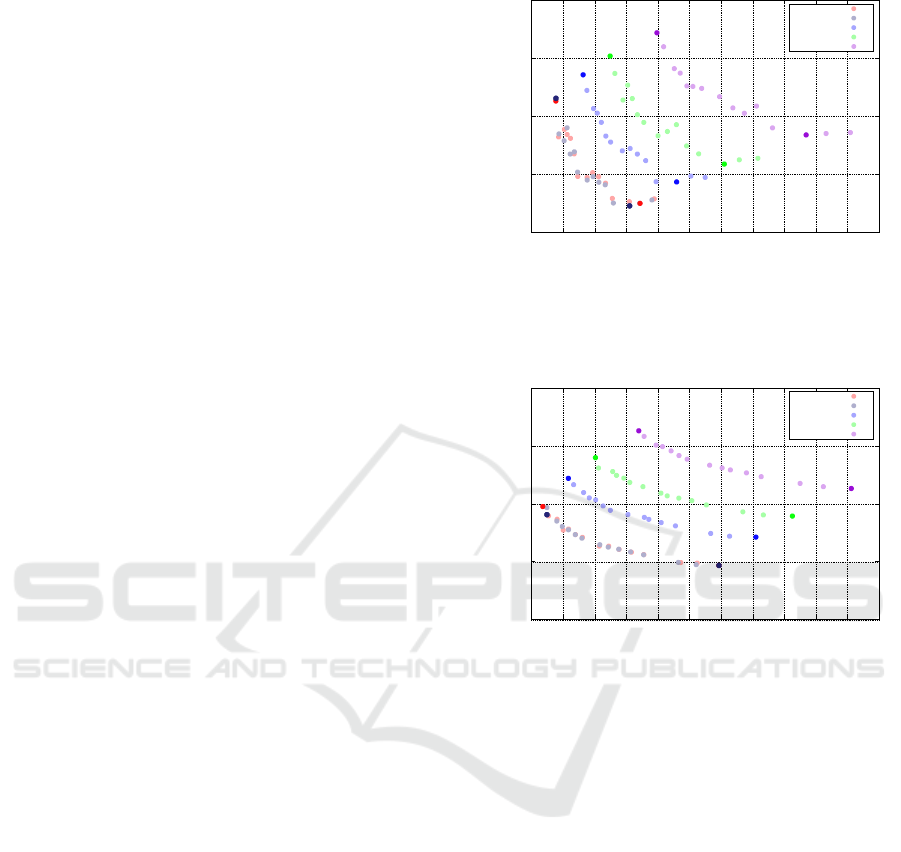
ergy consumption (y-axis) of different implementa-
tion variants executed sequentially on one core of the
Broadwell processor, using different operational fre-
quencies and different tolerance values TOL between
10
−2
and 10
−6
for the error control and the stepsize
selection. Each dot in the decision space denotes
the value (T (V ),E(V )) for a specific variant V gen-
erated with a fixed frequency and a predefined toler-
ance value. The diagram shows five convex curves for
the family of variants that are executed with the same
tolerance value TOL ∈ {10
−3
,10
−4
,10
−5
,10
−6
}. For
each curve, the frequencies decrease from left to right.
The figure shows that smaller tolerance values
such as 10
−6
lead to larger execution times and larger
energy consumptions that the usage of larger toler-
ance values. This is caused by a higher computational
effort due to the execution of a larger number of time
steps of the ODE method when using a smaller step-
size. The execution times and energy consumptions
for the tolerance values 10
−2
and 10
−3
are quite close
together due to a similar number of time steps.
Figure 4 also shows that the use of the highest op-
eration frequencies leads to the largest energy con-
sumption and the smallest execution time for each of
the different tolerance values. Decreasing the oper-
ational frequency increases the execution time, and
the largest execution time results when using the the
smallest operational frequency. However, the use of
the smallest operational frequency (1.2 GHz) does
not lead to the smallest energy consumption. Instead,
the smallest energy consumption results by using a
slightly higher operational frequency. This frequency
is 1.4 GHz for all tolerance values except 10
−3
, for
which the smallest energy consumption results for 1.3
GHz. Since each of the five curves represents differ-
ent tolerance values that lead to different numerical
accuracies, the curves have to be considered in isola-
tion. For each of the five curves, most of the points de-
picted are Pareto points. However, for each of the five
curves, two important Pareto points can be identified
that correspond to the smallest energy consumption
and the smallest execution time compared to the other
variants with the same tolerance value. These impor-
tant Pareto points are shown as solid dots in the dia-
gram to distinguish them from the other points, which
are depicted in a lighter color.
Figure 5 shows the same information as Figure
4 using a multithreaded execution with 10 threads.
Again, for each curve the frequencies decrease from
left to right. The important Pareto points are again
shown as solid dots in the diagram. Similar to the
sequential case, the use of smaller tolerance values
leads to larger execution times and larger energy con-
sumptions that the usage of larger tolerance values.
64
128
256
512
1024
40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 260
energy [Joule]
execution time [sec]
time/energy for RD ODE p=1 on Broadwell
TOL=10-2
TOL=10-3
TOL=10-4
TOL=10-5
TOL=10-6
Figure 4: Execution time and energy for different frequen-
cies and different tolerance values on Broadwell using a se-
quential execution.
128
256
512
1024
2048
25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80
energy [Joule]
execution time [sec]
time/energy for RD ODE p=10 on Broadwell
TOL=10-2
TOL=10-3
TOL=10-4
TOL=10-5
TOL=10-6
Figure 5: Execution time and energy for different frequen-
cies and different tolerance values on Broadwell using a par-
allel execution with 10 threads.
Moreover, the use of the highest operation frequen-
cies leads to the largest energy consumption and the
smallest execution time for each of the different toler-
ance values.
However, there are also several differences be-
tween the diagrams in Figures 4 and 5: For the par-
allel case, the use of the smallest operational fre-
quency always leads to the smallest energy consump-
tion. Moreover, the energy consumption for the paral-
lel execution with 10 threads is much larger than the
energy consumption for a sequential execution. This
is caused by the significantly larger power consump-
tion for 10 threads, which cannot be compensated by
a corresponding reduction in execution time.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The execution time and energy consumption for long-
running applications often exhibit a complex interac-
Pareto-Optimal Execution of Parallel Applications with Respect to Time and Energy
71

tion. There are many influencing parameter both from
the underlying algorithm and the execution environ-
ment and it is not a priori clear which combination of
parameter values may lead to the best runtime perfor-
mance and the smallest energy consumption.
This article explores the interactions between the
influencing parameters for a complex example from
numerical analysis and provides a detailed experi-
mental evaluation. The experimental evaluation is
performed for three parameters, one algorithmic pa-
rameter (the tolerance value for the error control) and
one execution parameter (the operational frequency).
The evaluation shows that the interaction between
the runtime performance and the energy consump-
tion is complex and that there is no best combination
that optimizes both the execution time and the energy
consumption. Instead, there are two different Pareto
points, one that minimizes the execution time and one
that minimizes the energy consumption.
REFERENCES
Ahmad, I. and Ranka, S. (2012). Handbook of Energy-
Aware and Green Computing. Chapman & Hall/CRC.
Ashouri, A. H., Killian, W., Cavazos, J., Palermo, G., and
Silvano, C. (2018). A survey on compiler autotun-
ing using machine learning. ACM Comput. Surv.,
51(5):96:1–96:42.
Brown, D. J. and Reams, C. (2010). Toward energy-efficient
computing. Commun. ACM, 53(3):50–58.
Deuflhard, P. and Hohmann, A. (2003). Numerical Analysis
in Modern Scientific Computing, volume 43. Springer.
Ehrgott, M. (2005). Multicriteria Optimization. Springer-
Verlag.
Fard, H. M., Prodan, R., Barrionuevo, J. J. D., and
Fahringer, T. (2012). A multi-objective approach for
workflow scheduling in heterogeneous environments.
In 2012 12th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on
Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing (ccgrid 2012),
pages 300–309.
Freeh, V. W., Lowenthal, D. K., Pan, F., Kappiah, N.,
Springer, R., Rountree, B. L., and Femal, M. E.
(2007). Analyzing the energy-time trade-off in high-
performance computing applications. IEEE Transac-
tions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 18(6):835–
848.
Gill, P. E., Murray, W., and Wright, M. H. (1981). Practical
optimization. Academic Press Inc. [Harcourt Brace
Jovanovich Publishers], London.
Hairer, E., Nørsett, S., and Wanner, G. (1993). Solving
Ordinary Differential Equations I: Nonstiff Problems.
Springer–Verlag, Berlin.
Intel (2011). Intel 64 and IA-32 Architecture Software De-
veloper’s Manual, System Programming Guide.
Lastovetsky, A. and Manumachu, R. R. (2023). Energy-
efficient parallel computing: Challenges to scaling.
Information, 14(4).
Li, K. (2016). Energy and time constrained task scheduling
on multiprocessor computers with discrete speed lev-
els. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing,
95:15–28. Special Issue on Energy Efficient Multi-
Core and Many-Core Systems, Part I.
Li, K. (2018). Scheduling parallel tasks with energy and
time constraints on multiple manycore processors in
a cloud computing environment. Future Generation
Computer Systems, 82:591–605.
Manumachu, R. R., Khaleghzadeh, H., and Lastovetsky,
A. (2023). Acceleration of bi-objective optimization
of data-parallel applications for performance and en-
ergy on heterogeneous hybrid platforms. IEEE Ac-
cess, 11:27226–27245.
Manumachu, R. R. and Lastovetsky, A. (2018). Bi-objective
optimization of data-parallel applications on homoge-
neous multicore clusters for performance and energy.
IEEE Transactions on Computers, 67(2):160–177.
Mezmaz, M., Melab, N., Kessaci, Y., Lee, Y., Talbi, E.-
G., Zomaya, A., and Tuyttens, D. (2011). A paral-
lel bi-objective hybrid metaheuristic for energy-aware
scheduling for cloud computing systems. Journal
of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 71(11):1497–
1508.
OECD (2023). World Energy Outlook 2023. OECD.
Orgerie, A.-C., Assuncao, M. D. d., and Lefevre, L. (2014).
A survey on techniques for improving the energy effi-
ciency of large-scale distributed systems. ACM Com-
put. Surv., 46(4):47:1–47:31.
Rauber, T. and R
¨
unger, G. (2012). Energy-aware Execution
of Fork-Join-based Task Parallelism. In 20th IEEE
International Symposium on Modeling, Analysis, and
Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication Sys-
tems (MASCOTS’12), pages 231–240. IEEE.
Rauber, T. and R
¨
unger, G. (2019a). A Scheduling Selection
Process for Energy-efficient Task Execution on DVFS
Processors. Concurrency and Computation: Practice
and Experience, 31.
Rauber, T. and R
¨
unger, G. (2019b). On the Energy Con-
sumption and Accuracy of Multithreaded Embedded
Runge-Kutta Methods. In Proceedings of the The In-
ternational Conference on High Performance Com-
puting & Simulation (HPCS 2019), volume 15, pages
382–389. IEEE.
Rotem, E., Naveh, A., Ananthakrishnan, A., Rajwan, D.,
and Weissmann, E. (2012). Power-Management Ar-
chitecture of the Intel Microarchitecture Code-Named
Sandy Bridge. IEEE Micro, 32(2):20–27.
Sch
¨
one, R., Ilsche, T., Bielert, M., Gocht, A., and Hack-
enberg, D. (2019). Energy efficiency features of the
intel skylake-sp processor and their impact on perfor-
mance. In 2019 International Conference on High
Performance Computing and Simulation (HPCS),
pages 399–406.
Treibig, J., Hager, G., and Wellein, G. (2010). LIKWID:
A Lightweight Performance-Oriented Tool Suite for
x86 Multicore Environments. In 39th International
Conference on Parallel Processing Workshops, ICPP
’10, pages 207–216. IEEE Computer Society.
Zomaya, A. Y. and Lee, Y. C. (2012). Energy Efficient Dis-
tributed Computing Systems. Wiley-IEEE Computer
Society Pr, 1st edition.
SMARTGREENS 2024 - 13th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
72
