
Enhancement of the Online Presence of Small and Medium Sized
Enterprises with Minimum Impact on Traditional Business Activities in
Towns and Cities
Mar
´
ıa Garrido, Jos
´
e Jes
´
us Castro-Schez, Rub
´
en Grande, Santiago Schez-Sobrino and David Vallejo
School of Computer Science, Department of Technologies and Information Systems, University of Castilla-La Mancha,
Paseo de la Universidad 4, 13071 Ciudad Real, Spain
Keywords:
Electronic Commerce, Recommendation System, Digital Transformation.
Abstract:
This paper introduces an innovative strategy for an e-commerce portal designed to support small and medium-
sized enterprises (SMEs), integrating local businesses not directly related to product sales, referred to as “satel-
lite businesses”, such as bars, restaurants, cinemas or sports facilities. This proposal modifies the existing
VR-ZOCO e-commerce portal structure to strengthen local economies, facilitating a symbiosis between on-
line shopping and physical leisure activities. Following a purchase on the portal, users are offered the option
to collect their products at specific local points. Linked to this collection act, personalized “leisure plans” are
generated, based on “leisure activities” from satellite businesses. This initiative not only promotes the digital
growth of SMEs but also encourages the revitalization and sustainable development of local communities.
This paper details the fundamental concepts emphasizing how the interaction between online shopping and
physical leisure activities can enrich the consumer experience and simultaneously support local businesses.
The research proposes a balanced solution that aligns with modern consumer expectations and contributes
to local economic and social growth, representing a significant advancement in the digital transformation of
SMEs.
1 INTRODUCTION
In today’s business landscape, the role of e-commerce
is crucial. It acts as a key driver for organizations
aiming to expand their market presence and improve
operational efficiency (Jain et al., 2021).
E-commerce provides SMEs a chance to boost
efficiency and narrow the productivity divide with
larger companies (Ministerio de Asuntos Econ
´
omicos
y Transformaci
´
on Digital, Gobierno de Espa
˜
na,
2021). Although the advantages of e-commerce are
evident, particularly in the post-COVID era (Pavlova
et al., 2021), it brings about notable challenges, par-
ticularly for SMEs, such as digital skills deficiency,
financial constraints for digital transformation, and
difficulty in keeping up with technological advances
(Eller et al., 2020).
The digital skills gap is a major hurdle for SMEs
and start-ups, impeding their growth and competitive-
ness. Limited proficiency in digital processes among
employees hampers efficiency, innovation, and adap-
tation to market trends. Addressing this skill defi-
ciency is vital for sustained success in a digitalized
business landscape.
On the other hand, the challenge of insufficient
funding for digital transformation is a critical issue
for SMEs. These businesses often lack the financial
resources necessary to undergo digital transformation
and to initiate the development of their online pres-
ence. This funding gap hinders their ability to adapt
to the digital age, where an online presence is increas-
ingly crucial for reaching customers and competing in
the market. Without adequate funding, SMEs struggle
to invest in necessary technologies, digital marketing,
e-commerce platforms, and the training required to
effectively utilize these tools. This not only affects
their current operations but also impacts their long-
term sustainability and growth prospects.
With regard to the last point, the expeditious adop-
tion and integration of technologies such as Artifi-
cial Intelligence (AI) and Virtual Reality (VR), are
imperative for SMEs within the context of their e-
commerce solutions. This proactive approach is nec-
essary to prevent SMEs from consistently falling
behind the innovative advancements introduced by
larger corporate entities. AI allows for the person-
Garrido, M., Castro-Schez, J., Grande, R., Schez-Sobrino, S. and Vallejo, D.
Enhancement of the Online Presence of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises with Minimum Impact on Traditional Business Activities in Towns and Cities.
DOI: 10.5220/0012630600003690
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2024) - Volume 1, pages 989-996
ISBN: 978-989-758-692-7; ISSN: 2184-4992
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
989

alization (Isinkaye et al., 2015), optimization (Goli
et al., 2021), and automation of various facets of com-
merce (Lundstr
¨
om, 2021).
However, it is crucial to emphasize that efforts
aimed at the digitization of SMEs, through the es-
tablishment of their online presence, should not lead
to neglecting their physical operations. The duality
between the digital (shopping online) and the phys-
ical (in-store shopping) is essential for preserving
the local business and the vitality of urban centers.
Solely focusing on online commerce could have ad-
verse consequences, contributing to the desertion of
urban cores (Zhang et al., 2016) and impacting other
associated businesses, such as dining establishments,
businesses in the entertainment, culture, and arts sec-
tor, sports facilities, and more. In this regard, a bal-
anced strategy that values both digital presence and
the maintenance of physical establishments is cru-
cial for the sustainable and harmonious development
of SMEs in the contemporary business environment
(Helmy Mohamad et al., 2022).
This work introduces an innovative strategy to
aid SMEs in embarking on their digital transfor-
mation journey. It specifically tackles initial chal-
lenges, aiming for seamless integration and balance
between physical and online realms. The central goal
is to unify traditional urban business activities with
electronic commerce, fostering a comprehensive ap-
proach to digital integration.
In this context, it is essential to introduce VR-
ZOCO, a platform aimed at aiding small businesses
in their innovations. VR-ZOCO provides SMEs with
the visibility they need through various modules, one
of which is the recommendation of leisure plans in-
tertwined with the purchase experience. This paper
focuses on elucidating one such module, aimed at en-
hancing the e-commerce experience for SMEs while
ensuring the vitality of their physical presence. The
aim is to enhance the user’s shopping experience and
make the portal a destination for premium and cul-
turally enriched experiences. These efforts are in line
with modern consumer expectations and support busi-
ness growth without compromising local social and
economic life.
Following this introduction, the remainder of the
paper is organized as follows. Some important con-
cepts, such as “satellite businesses”, “leisure activ-
ity”, “leisure plan” or “user profile” are defined in
Section 2. The algorithm suggested to obtain the
leisure plans is presented in Section 3. In Section 4,
an example of application of the suggested algorithm
to generate leisure plan is shown. Finally, our conclu-
sions and the future work are presented.
2 FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS
This section is dedicated to explain key concepts that
will serve as the foundation for a full exploration of
the portal. We will look at key terms such as “satellite
business”, “leisure activity”, “user profile”, “pickup
point” and “leisure plan”, providing a concise and es-
sential insight into these fundamental elements within
the context of the portal.
2.1 Satellite Business
The satellite businesses within the portal’s framework
offer users a range of experiences, including cafes,
theaters, and sports clubs. These establishments en-
rich the user experience and contribute significantly to
the local economy, infusing vitality into the commu-
nity. Their range of services aims to meet the needs
of users while also encouraging a deeper exploration
of the city’s cultural and recreational landscape.
In the database, key information about these satel-
lite businesses is meticulously stored to facilitate
seamless user interactions and support local eco-
nomic growth. Crucial data fields include an iden-
tifier (id) that distinguishes each business uniquely,
the business name (name) for identification purposes,
the physical address for precise location (address),
and geographical information such as latitude and
longitude to facilitate accurate spatial representation
(latitude and longitude). Furthermore, the business
credentials, encompassing email (email) and pass-
word (pwd), are stored to ensure security and authen-
tication in interactions with the portal. Formally, a
satellite business (noted as SB) can be defined as:
SB = (id,name, address, latitude, longitude, email, pwd)
(1)
All satellite businesses in the city that want to of-
fer leisure activities can register on the VR-ZOCO
portal. In this way, a number of satellite businesses
will exist on the portal, which we will refer to as LSB
(i.e. LSB = {SB
1
, SB
2
, . . . , SB
n
}).
2.2 Leisure Activity
Leisure activities, orchestrated by the diverse satel-
lite businesses within the portal, constitute a tapestry
of engaging events. These carefully curated events
go beyond typical product-focused transactions, pro-
viding users with a dynamic array of engaging expe-
riences. Whether it is the excitement of a football
match, the cultural immersion of a live performance,
or the conviviality of a restaurant gathering, leisure
activities are intended to captivate and enhance the
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
990

user experience. The portal will have a list of leisure
activities (LLA) where the necessary information for
each leisure activity (LA) can be stored and provided.
Within the database architecture, the organiza-
tion of data ensures each leisure activity LA is seam-
lessly identified and comprehensively represented.
A unique identifier is assigned to each leisure ac-
tivity (id), also an activity description is stored
(description). It consists of a brief phrase or label
that assists in the differentiation of that particular ac-
tivity from all others. In addition, a business-specific
identifier (id sb) is stored to link the leisure activity to
the satellite business offering it. Each leisure activity
is classified within one or more of the existing prod-
uct categories on the portal (category). The catego-
rization allows users to easily explore a wide range of
activities. This flexibility allows the portal to develop
leisure plans for users based on a variety of interests.
The inclusion of the event date (date), along with pre-
cise start and end times (start and end), ensures users
are well-informed about the temporal aspects of their
chosen plans. Moreover, the “type” designation dis-
tinguishes between plans hosted at dedicated facili-
ties and those intrinsic to businesses like restaurants,
where the experience is an inherent part of the es-
tablishment rather than a scheduled occurrence. For-
mally LA can be defined respectively as follows:
LA = (id , description, id sb, category, date, start, end, type)
(2)
In this way, a number of leisure activities will ex-
ist on the portal, which we will refer to as LLA (i.e.
LLA = {LA
1
, LA
2
, . . . , LA
m
}).
2.3 User Profile
The user profile will be obtained by a fuzzy clustering
algorithm, and it allows us to identify user preferences
across different product categories.
First, we compute the different similarity matrices
for the relevant characteristic of the user (i.e. his/her
preferences, his/her age and his/her previous spending
on the portal). In this case, we calculate the following
similarity matrices:
• User Category Preferences (MP). This refers
to the matrix that captures the similarity between
users based on their preferences across different
product categories from C. User preferences are
derived from both explicit information provided
by user and implicit interactions with products.
Explicit preferences are obtained directly from
user input or feedback. In this context, users fill
out a form indicating the categories they are in-
terested in, generating a vector EP of dimensions
|C|. The user’s u
x
preferences for each category
c
i
of C are stored in EP
u
x
[i]. A value of 0 will be
used in categories where the user has no interest
and a value greater than 0 in those where the user
does have some interest (i.e. EP
u
x
[i] ∈ [0, 1]).
Implicit preferences, on the other hand, are in-
ferred from the user’s behaviour on the portal,
taking into account aspects such as purchase his-
tory (P) or browsing patterns, such as 3D manip-
ulation (M), viewing (V ) and teleportation (T ) in
each category c
i
∈ C. These user’s behaviour fea-
tures are weighted using various coefficients to in-
dicate their importance (i.e. α
V
, α
M
, α
T
and α
P
).
These weights are adjustable factors that allow for
greater or lesser importance to be placed on each
component when calculating the degree of inter-
est based on the system’s requirements and user
preferences.
The implicit preference of the user u
x
in the each
category c
i
∈ C (i.e. IP
u
x
[i]) is calculated accord-
ing to the Equation 3.
IP
u
x
[i] =
P
u
x
(c
i
)×α
P
+M
u
x
(c
i
)×α
M
+V
u
x
(c
i
)×α
V
+T
u
x
(c
i
)×α
T
P
u
x
(C)×α
P
+M
u
x
(C)×α
M
+V
u
x
(C)×α
V
+T (C)×α
T
(3)
where P
u
x
(c
i
), M
u
x
(c
i
), V
u
x
(c
i
) and T
u
x
(c
i
) reflect
the user’s u
x
purchases, 3D manipulations, views
and teleportations within the product category c
i
.
And P
u
x
(C), M
u
x
(C), V
u
x
(C) and T
u
x
(C) reflect the
user’s total purchases, 3D manipulations, views
and teleportations of products in the portal within
any of the portal categories.
To obtain the user category preferences matrix
of a user u
x
, noted as MP
u
x
, user’s explicit pref-
erences EP
u
x
and implicit preferences IP
u
x
are
weighted following the Equation 4.
MP
u
x
[i] = α
IP
× IP
u
x
[i] + α
EP
× EP
u
x
[i] (4)
where α
IP
and α
EP
are two parameters that al-
low us to determine the importance of each of the
two preferences (i.e. implicit and explicit prefer-
ences).
The matrix capturing the similarity between users
according to their preferences matrices MP
u
x
in
the different product categories of C, denoted as
MP, is calculated according to the equation 5.
MP[u
x
, u
y
] =
|C|
∑
i=1
|MP
u
x
[i] − MP
u
y
[i]| (5)
• User Age (MA). This refers to the similarity ma-
trix that assesses how similar users are based on
Enhancement of the Online Presence of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises with Minimum Impact on Traditional Business Activities in
Towns and Cities
991
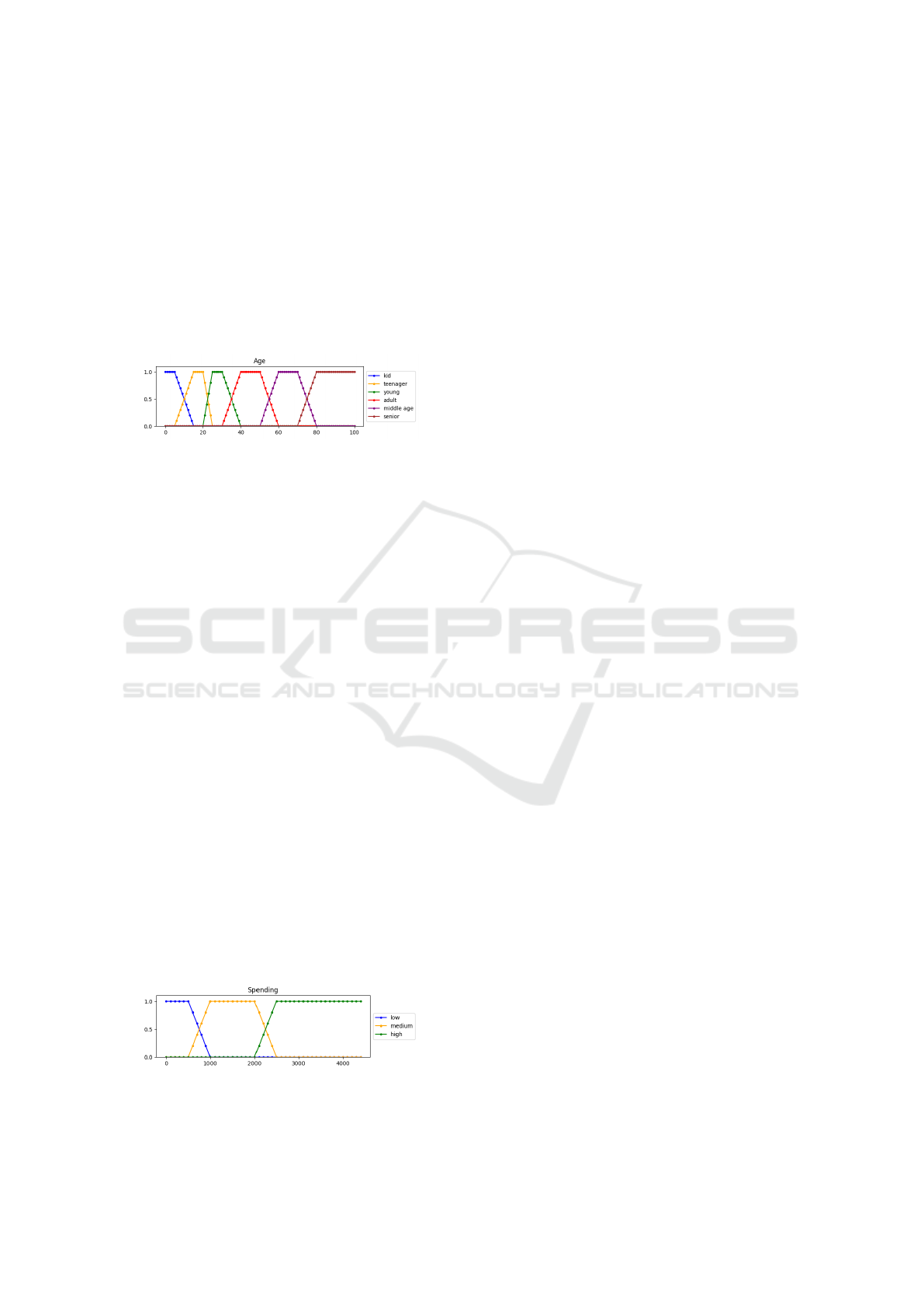
their age groups. Fuzzy logic is employed to cat-
egorize users into age groups following the mem-
bership function seen in Figure 1. In this way we
transform raw age data into a set of fuzzy values,
such as ‘kid’, ‘teenager’, ‘young’, ‘adult’, ‘middle
age’, or ‘senior’, taking into account the gradual
transitions between categories. The resulting ma-
trix helps to understand how users in similar age
groups may share common characteristics, pro-
viding valuable insights for user similarity anal-
ysis and recommendation systems.
Figure 1: Membership function of variable age.
The matrix that captures the similarity between
users u
x
and u
y
according to their fuzzy ages, de-
noted MA, is calculated according to the equation
6.
MA[u
x
, u
y
] = Sep(age
u
x
, age
u
y
) (6)
where Sep is the measure of comparison S pro-
posal in (Castro-Schez et al., 2004) and age
u
x
and
age
u
y
will be values present in the domain of defi-
nition of the variable age, see Figure 1, represent-
ing the fuzzy ages of the user u
x
and u
y
.
• User Monetary Spending (MS). This refers
to the similarity matrix used to evaluate user
spending patterns across different product cat-
egories. Using fuzzy logic, users are catego-
rized into spending levels (low, medium and high)
within each product category following the mem-
bership function seen in Figure 2. The resulting
matrix offers a measure of affinity among users
based on their purchasing behaviors, enabling a
nuanced understanding of shared financial pref-
erences. Fuzzy logic plays a pivotal role in cat-
egorizing users into spending levels, taking into
account gradual transitions between these cate-
gories. This not only reflects the inherent variabil-
ity in users’ spending habits but also allows for
capturing subtle nuances in financial preferences.
Figure 2: Membership function of variable spending.
The matrix capturing the similarity between users
according to their monetary spending in each cat-
egory, denoted as MS , is calculated according to
the equation 7.
MS[u
x
, u
y
] =
|C|
∑
i=1
Sep(Spend
u
x
[i], Spend
u
y
[i]) (7)
where Spend
u
z
[i] is the fuzzy value taken from the
definition domain of the variable spending shown
in Figure 2, which represents what the user u
z
has
spent in the category c
i
.
These matrices constitute a crucial element of our
recommendation system. Following the derivation of
these matrices, a composite matrix (M) is computed
using equation 8.
M[u
x
, u
y
] =α
MP
× MP[u
x
, u
y
] + α
MA
× MA[u
x
, u
y
]
+ α
MS
× MS[u
x
, u
y
]
(8)
Once the weighted matrix M of distances between
users is obtained, the fuzzy c-means clustering algo-
rithm is applied. We choose |C| as the number of clus-
ters we want to obtain (i.e. the number of categories
that are available on the portal).
The algorithm produces a vector (MC) with di-
mension |C| that shows the membership degrees of
each user for each cluster (i.e. each category). The
user’s u
x
membership degrees for each cluster i is
stored in MC(u
x
)[i] and represents the categorization
of the user as a user who is interested in the category
i. The possibility of belonging partially to several
clusters captures the ambiguity inherent in users’ pur-
chase decisions, as well as their implicit and explicit
preferences.
Each cluster (i.e. each category) will be repre-
sented by its cluster centers.
2.4 Pickup Point
Pickup points are designated physical locations where
users can collect their purchased products. Users en-
joy the flexibility to choose their preferred pickup
point from a selection of pre-designated stores, with
the added convenience of selecting an approximate
pickup time.
The system stores essential information for each
pickup point, including a unique identifier (id), the
point’s name (name), its geographical coordinates
(latitude and longitude) and its credential informa-
tion, email and password (email and pwd). Formally
pickup points (PP) can be formally defined as:
PP = (id, name, latitude,longitude, email, pwd,time) (9)
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
992

2.5 Leisure Plan
Leisure plans in the portal are crafted to create a
unique connection between leisure activities and the
individual profiles of users. These plans are dynami-
cally generated based on the preferences and behavior
of each user, offering a personalized leisure experi-
ence that complements their online purchase. When
a user makes a purchase, they receive a leisure plan
(LP) comprising customized suggestions for leisure
activities (LAs). The LP is defined as a collection of
these activities (i.e. LP = {LA
x
, LA
y
, . . . , LA
k
}, each
chosen to align with the user’s unique interests and
the timing of the activities (i.e. LAs ∈ LP are ordered
in based on their times (start and end)).
The concept of leisure plans extends beyond just
providing entertainment suggestions. It strategically
enhances local cultural and entertainment offerings,
with the dual aim of enriching the user’s experience
and stimulating the local economy. These plans are
tied to the user’s chosen product pickup point, ensur-
ing convenience and encouraging engagement with
nearby leisure activities.
Leisure plans are integral to the user’s post-
purchase journey on the portal, offering a blend
of product collection convenience and personalized
leisure recommendations. This approach not only
makes the user experience more engaging but also
supports local economic development. By connecting
users to diverse cultural and leisure activities, the por-
tal facilitates the discovery of new experiences within
the city, thus contributing to the diversification and
strength of the local economy. This synergy between
users and local businesses fosters a mutually bene-
ficial environment, enriching user experiences while
sustaining the vitality of local businesses.
3 LEISURE PLAN GENERATOR
ALGORITHM
This section introduces a specialized framework tai-
lored explicitly for plan recommendation. The aim
is to understand user preferences and provide finely-
tuned recommendations, carefully curated around ac-
tivities, events or experiences.
The leisure plan generator algorithm provides per-
sonalized recommendations to users based on the
cluster they belong to.
To initiate the process, the first step involves de-
termining the cluster or clusters to which the user be-
longs. This is achieved by employing Algorithm 1,
which evaluates the membership degree (MC) to each
cluster. It checks whether the maximum MC exceeds
the threshold α. If not, it verifies whether the dif-
ference between these MC values is less than another
threshold β. If so, the user is associated with multiple
clusters; otherwise, the user is assigned to the cluster
with the highest membership degree.
Data: membership degrees vector MC, α, β
Result: Relevant category/categories for the
user (C AT ).
max val = max{MC[i]}
CAT =
/
0;
if max val > α then
CAT = CAT ∪ {i | max
i
{MC[i]}}
else
for i = 1 to |C| do
if |MC[i] − max value| < β then
CAT = CAT ∪ {i}
end
end
end
return CAT
Algorithm 1: Dominant cluster algorithm.
Once the dominant categories of the user who has
made the purchase have been obtained (i.e. CAT ), the
algorithm that generates the leisure plan will be exe-
cuted, taking into account the pick-up point, the date
and time at which the user will go to pick it up (Algo-
rithm 2).
The Algorithm 2 employs a multi-faceted filtering
process. Firstly, it ensures that the leisure activities
align with the user’s specified pickup date. Then, it
selectively includes activities that fall under the cate-
gories represented by the user’s dominant preferences
(CAT ). Next, the algorithm calculates distances be-
tween each leisure activity and the designated pickup
point. The approach selectively includes only leisure
activities that are within a reasonable proximity, en-
suring that the calculated distances do not exceed
the specified threshold α. This mitigates potential
user discomfort associated with distant locations. Fi-
nally, any leisure activities that occur before the user-
specified pickup time are excluded.
Within the Algorithm 2, distance is a function that
calculates the distance between the place where the
leisure activity takes place and the pickup point. And
arrange is a function that randomly selects a number
of different leisure activities from the list and arranges
them according to their start and end times, ensuring
that they do not overlap and that there is a margin of
time between them to allow for displacement (β).
The implementation of these steps leads to the cre-
ation of a customized leisure plan based on the user’s
preferences, ensuring an engaging and tailored expe-
rience.
Enhancement of the Online Presence of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises with Minimum Impact on Traditional Business Activities in
Towns and Cities
993
Data: CAT , α, β and pickup point PP, date and
time of pick-up, LLA
Result: Leisure Plan LP.
LP = LLA;
for each LA
i
in LP do
if LA
i
.date ̸= date then
LP = LP − {LA
i
}
end
end
for each LA
i
in LP do
if LA
i
.category ∩CAT =
/
0 then
LP = LP − {LA
i
}
end
end
for each LA
i
in LP do
if distance(LA
i
, PP) > α then
LP = LP − {LA
i
}
end
end
for each LA
i
in LP do
if LA
i
.start < time then
LP = LP − {LA
i
}
end
end
LP = arrange(LP, β)
return LP;
Algorithm 2: Leisure Plan Generator Algorithm.
4 ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE OF
THE PROPOSED ALGORITHM
In creating the virtual landscape for the VR-ZOCO
platform, we strategically chose Ciudad Real as our
focus city for a number of compelling reasons. Ciu-
dad Real not only embodies a rich cultural heritage,
but also boasts a diverse range of businesses, making
it an ideal setting for our empirical study. The city’s
unique blend of cultural richness and urban vibrancy
serves as a canvas for our exploration of the dynamics
of leisure links within a virtual realm.
For this specific use case within the VR-ZOCO
platform, our focus is narrowed down to 14 key busi-
ness satellites selected throughout Ciudad Real de-
scribed in Table 4 and located in Fig. 3. Each location
acts as a representative hub, offering unique leisure
activity in six different categories C - beauty, culture,
home, fashion, sport and technology. We have also in-
cluded two establishments that are considered restau-
rants or cafes that belong to multiple categories simul-
taneously.
We introduce the user X as a representative user,
offering an insight into his purchases and interactions
within the portal. User X serves as an illustrative case
study for our investigation into personalized user ex-
periences. The user X named Ana, a 25-year-old in-
terested in sports and technology, provides a nuanced
lens through which to evaluate the efficacy of our sys-
tem.
After collecting Ana’s data, we proceed to con-
struct her user profile using a clustering approach.
The obtained results for each cluster are as follows
in Table 1.
Table 1: Initial membership degree (MC) results.
Beauty Culture Fashion Home Sport Technology
0.112596 0.076077 0.081246 0.075429 0.340955 0.313697
As expected, higher values are observed in clus-
ters associated with sports and technology, accurately
reflecting Ana’s initial preferences. Following var-
ious interactions with products of interest, such as
views on sports and technology-related items, as well
as 3D manipulations for each, Ana ultimately decides
to purchase a technology product. Using the Algo-
rithm 1, Ana has 2 dominant clusters: sports and
technology (see Table 1). The product purchase trig-
gers different leisure activities, taking temporal con-
straints, distance from the pickup point to the satellite
business, and user profile into account, the results are
then arranged in Table 2. The outcome for the first
leisure plan is “Espacio Serendipia” from the technol-
ogy category.
Table 2: Proposals for the first Leisure Link.
Satellite Business Leisure Plan Category
Espacio Serendipia Machines learning, humans on alert Technology
Living Room Math Street Fighter: Maths vs Humans Technology
Polideportivo Rey Juan Carlos Provincial Swimming Championship Sport
Bar Entretapas - *
Quijote Arena Handball Match Caser
´
ıo CR vs Sinfin Sport
A Pares - *
Subsequently, the generation of the second leisure
plan takes place. Here, it’s essential to acknowledge
that the first plan concludes at 20:00. The results are
represented in Table 3. In this case, the distance from
the first leisure plan generated, the user profile and
temporal constraints are taken into account. As a re-
sult, “Bar Entretapas” emerges as the recommended
option, providing a holistic and tailored sequence of
activities that not only adheres to Ana’s preferences
but also factors in practical considerations for a seam-
less and enjoyable experience.
Table 3: Proposals for the second Leisure Link.
Satellite Business Leisure Plan Category
Bar Entretapas - *
Quijote Arena Handball Match Caser
´
ıo CR vs Sinfin Sport
A Pares - *
Ultimately, the leisure plan generated for Ana con-
sists of picking up the purchased product from the
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
994
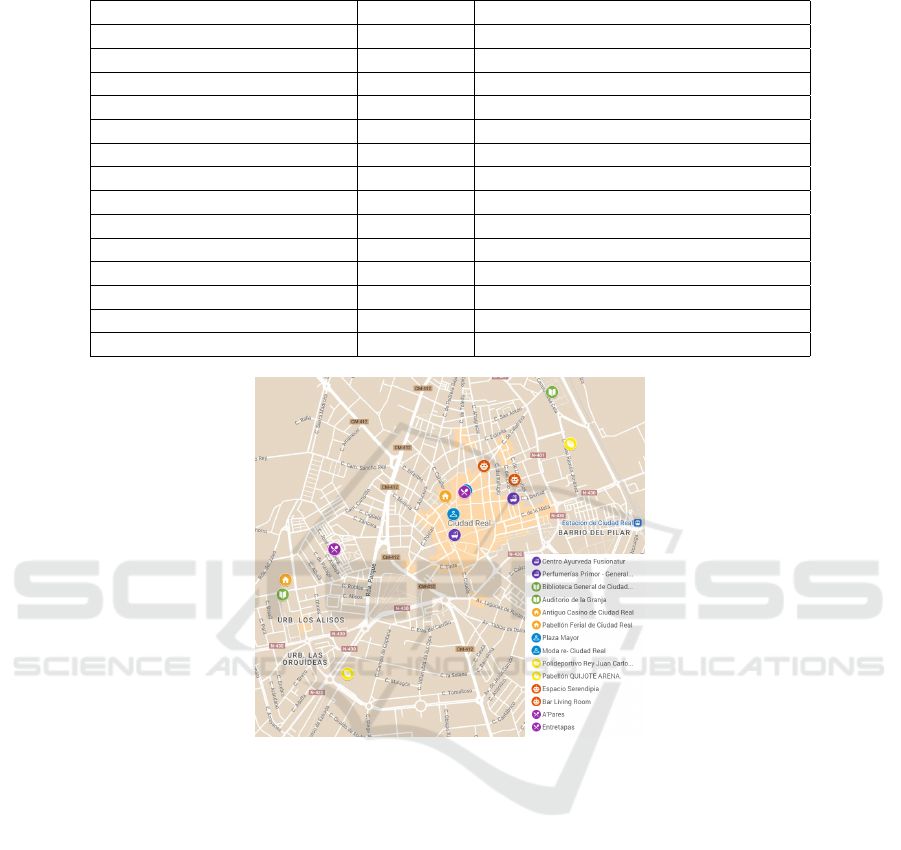
Table 4: Locations and Leisure Proposals.
Place name Category Leisure Proposal
Centro Ayurveda Fusionatur Beauty Massage Session
Primor Beauty Make-up Course
Biblioteca de Ciudad Real Culture Videogame Saturday
Auditorio de la Granja Culture Concert: Pablo L
´
opez
Antiguo Casino Home Casa y Jard
´
ın Expo 2023
Pabell
´
on Ferial Home ExpoHogar
Plaza Mayor Fashion Fashion Trend Showcase 2023
Moda re- Ciudad Real Fashion Charity Clothes Collection
Polideportivo Rey Juan Carlos Sport Provincial Swimming Championship
Quijote Arena Sport Handball Match Caser
´
ıo CR vs Sinfin
Espacio Serendipia Technology Machines learning, humans on alert
Living Room Technology Math Street Fighter: Maths vs Humans
A’Pares * -
Entretapas * -
Figure 3: Locations of Leisure Proposals.
pickup point “PCBox”, followed by a visit to “Espa-
cio Serendipia” for a technology talk. Subsequently,
there is the opportunity to unwind and enjoy refresh-
ments at “Bar Entretapas”. This carefully curated
itinerary is visualized in Figure 4, presenting a seam-
less sequence of activities tailored to Ana’s prefer-
ences. Figure 4 serves as a comprehensive representa-
tion of the suggested journey, providing a visual guide
for Ana to make the most of her personalized and en-
joyable experience.
This sequence of activities not only maximizes
Ana’s satisfaction by aligning with her interests but
also promotes the local economy by encouraging par-
ticipation in nearby events. This personalized rec-
ommendation approach, tailored to Ana’s preferences
and behaviors, underscores our model’s capacity to
provide unique and relevant experiences for each user.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In conclusion, this paper extends an innovative ar-
chitecture that represents a significant advancement
in the evolution of e-commerce portals, especially
in supporting small and medium-sized enterprises
(SMEs). The integration of “satellite businesses” di-
versifies the traditional product-centric focus of e-
commerce, fostering a synergistic relationship be-
tween online shopping and physical leisure activities.
Users can collect purchases at specific local points,
streamlining logistics and helping the environment.
This also promotes the generation of personalized
“leisure plans” based on the offerings of these satellite
businesses.
Enhancement of the Online Presence of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises with Minimum Impact on Traditional Business Activities in
Towns and Cities
995

Figure 4: Representation of Leisure Links.
As a future research effort, enhancing the arrange-
ment function (arrange) within Algorithm 2 is pro-
posed. Instead of a random approach, the aim is to de-
velop a more sophisticated method that optimizes the
arrangement of leisure activities, accounting for indi-
vidual preferences, distances between locations, and
temporal constraints. This refinement seeks to further
enrich the users’ experience by providing more per-
sonalized leisure recommendations aligned with their
specific preferences.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been founded by the Span-
ish Ministry of Science and Innovation
MICIN/AEI/10.13039/501100000033, and the
European Union (NextGenerationEU/PRTR), u nder
the Research Project: Design and development of
a platform based on VR-Shopping and AI for the
digitalization and strengthening of local businesses
and economies, TED2021-131082B-I00.
REFERENCES
Castro-Schez, J., Castro, J., and Zurita, J. (2004). Fuzzy
repertory table: a method for acquiring knowledge
about input variables to machine learning algorithm.
IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 12(1):123–139.
Eller, R., Alford, P., Kallm
¨
unzer, A., and Peters, M. (2020).
Antecedents, consequences, and challenges of small
and medium-sized enterprise digitalization. Journal
of Business Research, 112:119–127.
Goli, A., Khademi-Zare, H., Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.,
Sadeghieh, A., Sasanian, M., and Kordestanizadeh,
R. M. (2021). An integrated approach based on arti-
ficial intelligence and novel meta-heuristic algorithms
to predict demand for dairy products: a case study.
Network: Computation in Neural Systems, 32(1):1–
35.
Helmy Mohamad, A., Farouk Hassan, G., and S. Abd El-
rahman, A. (2022). Impacts of e-commerce on plan-
ning and designing commercial activities centers: A
developed approach. Ain Shams Engineering Journal,
13(4):101634.
Isinkaye, F., Folajimi, Y., and Ojokoh, B. (2015). Recom-
mendation systems: Principles, methods and evalua-
tion. Egyptian Informatics Journal, 16(3):261–273.
Jain, V., Malviya, B., and Arya, S. (2021). An overview
of electronic commerce (e-commerce). Journal of
Contemporary Issues in Business and Government,
27(3):665–670.
Lundstr
¨
om, L. (2021). Dynamic pricing services in e-
commerce ecosystems: An exploratory study of con-
text, technologies, and practices.
Ministerio de Asuntos Econ
´
omicos y Transformaci
´
on
Digital, Gobierno de Espa
˜
na (2021). Sme digital-
isation plan 2021-2025. https://portal.mineco.gob.
es/RecursosArticulo/mineco/\ministerio/ficheros/
210902-digitalisation-smes-plan.pdf. Accessed:
15/12/2023.
Pavlova, V., Murovana, T., Sarai, N., Velychko, V.,
Illyashenko, K., and Hrysshyna, H. (2021). Crisis
phenomena as an incentive to intensify e-commerce
of the enterprise. Journal of Theoretical and Applied
Information Technology, 99(19):4646–4657.
Zhang, D., Zhu, P., and Ye, Y. (2016). The effects of e-
commerce on the demand for commercial real estate.
Cities, 51:106–120. Current Research on Cities.
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
996
