
Modeling Organizational Culture, Transformational Leadership,
Motivation, Job Satisfaction: Muhammadiyah Aisyiyah College’s
Nursing Lecturer
Miciko
1a
and Dewi Nusraningrum
2b
1
Education Management, Jakarta State University, Jl. R.Mangun Muka Raya No.11, Jakarta, Indonesia
2
Department of Management, Universitas Mercu Buana, Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Organizational Culture, Transformational Leadership, Motivation, Job Satisfaction, Nursing Lecturer,
Muhammadiyah Aisyiyah College.
Abstract: Research on the effect of organizational culture and transformational leadership on the job satisfaction of
nursing lecturers mediated by motivation has never been conducted at Muhammadiyah Aisyiyah College
(PTMA). The study's objective is to analyze the influence of organizational culture and transformational
leadership on job satisfaction through motivation as mediation. 230 nursing faculty lecturers in Central Java,
Indonesia became respondents to this study. SEM analysis is used to test hypotheses with the help of the
SmartPLS analysis tool. The findings in this research specify that organizational culture and motivation have
no direct consequence on job satisfaction. Organizational culture, besides transformational leadership, directly
impacts motivation, and transformational leadership to job satisfaction. However, motivation does not have
an intermediating role in the connection between organizational culture and transformational leadership to
job satisfaction. The results of this study revealed that PTMA's organizational culture has become part of the
work culture for lecturers at the nurse faculty.
1 INTRODUCTION
The character of higher education is significant,
especially in implementing culture and leadership to
motivate the academician and pursue job satisfaction.
Therefore, research-based higher education must
encourage more open knowledge that can improve
human welfare (Asfahani, 2023). Healthy higher
education will be a spring of life for the progress of
the nation. Developed countries are always supported
by a pool of talents and highly educated human
capital who are creative, innovative, and productive.
The human capital that has a noble character, with the
soul of Pancasila, has competencies that are in line
with the needs and changing times. Citizens of the
world who are global-minded and have global
competitiveness but are not uprooted from their
nation's cultural roots (Idris et al., 2021). Sadya
(2023) explains that based on its status, there were
184 units of state universities in Indonesia.
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-9737-4150
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4386-2877
Meanwhile, 3,820 campuses are private universities.
This shows the enormous level of competition to
make tertiary institutions superior (Nusraningrum et
al., 2023)
Teachers of Higher Education who have a
strategic part in all academic actions must have a field
of study of knowledge, skills in statement (written
and verbal); control and application of information
and communication technology (ICT); building
extensive networks with the world of work and
industry; sensitive to the changes and developments
that occur around, as well as forward-looking
(Nusraningrum et al., 2023). Based on data from the
Global Competitiveness Report for Indonesia, the
aspects that are considered weak and need to be
improved are training higher education, and
innovation (Japir Bataineh et al., 2023). Work
involves collaboration with colleagues and leaders,
subsequent organizational guidelines and policies,
assembly performance standards, existing working
situations that are fewer than perfect, and the like
112
Miciko, . and Nusraningrum, D.
Modeling Organizational Culture, Transformational Leadership, Motivation, Job Satisfaction: Muhammadiyah Aisyiyah College’s Nursing Lecturer.
DOI: 10.5220/0012650000003717
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business (FEMIB 2024), pages 112-119
ISBN: 978-989-758-695-8; ISSN: 2184-5891
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

(Colquitt, 2023). Muhammadiyah is an Islamic
movement that carries the mission of da'wah and
tajdid, based on Islam, based on the Qur’an and As-
Sunnah, aiming to create a truly Islamic society
founded by Ahmad Dahlan. Muhammadiyah
Aisyiyah Universities that hold nursing education,
there are 44 universities. (PP Muhammadiyah,
2010).
Many factors can affect lecturer job satisfaction in
tertiary institutions together with transformational
leadership, organizational culture, and work
motivation which can affect lecturer job satisfaction.
Organizational culture affecting job satisfaction is
rarely discussed in universities, especially the
organizational culture of Muhammadiyah, which has
become a color in the implementation of Catur
Dharma of Muhammadiyah Higher Education, i.e.:
Education and teaching, Research, Community
Service, and strengthening of al-Islam
Kemuhammadiyahan.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Job Satisfaction (JS)
Job satisfaction is an established of assessments,
attitudes, moods, expectations, also desires of an
individual/lecturer for his exertion, whether satisfied
or dissatisfied as a result of someone's interaction
related to aspects such as his work, work
environment, awards, relationships with colleagues,
culture and values and norms in the work
environment, career development and organizational
structure in the workplace, leadership attention, a
sense of security at work (Kelly et al., 2020; Rafique
et al., 2022). Human resource management strategies
in an organization can be in the form of work climate,
employee benefits, interpersonal relationships,
employee welfare, and the nature of supervision
contribute to job satisfaction (Aung et al., 2023;
Cabaron & Oco, 2023; Dorta-Afonso et al., 2023;
Huang et al., 2023; Mustafa et al., 2023). Based on
the consequences of the study described there is a
stimulus between organizational culture, leadership,
and motivation on employee job satisfaction in
various types of jobs.
2.2 Organizational Culture (OC)
OC is a set of intellectual frameworks comprising of
beliefs, morals, customs, and hopes that are owned by
affiliates of the association that form harmony with
indicators of adaptability, integrity, collaboration,
result-oriented, customer-oriented, and detail-
oriented memberships of the organization, and are
adhered to by members that distinguish the society
from other groups (Arabeche et al., 2022; Doghan et
al., 2022; Ginting, 2023; Hung et al., 2022; Kaur
Bagga et al., 2023). Organizational culture at
Muhammadiyah Aisyiyah Higher Education (PTMA)
is values such as professionalism, fingerprint,
Amanah, fatonah, and sincerity in working as worship
within an organizational culture originating on the
Qur'an and the Sunnah of the Prophet will lead to a
strong attitude of self-confidence because there is a
sense of pride in having a high status as a member. A
conducive organizational culture will foster work
harmony within the organization in addition to
encouraging work which will ultimately provide job
satisfaction. Lecturers who have high work
enthusiasm will always work firmly to overcome all
kinds of complications in anticipation of completing
satisfactory outcomes. Therefore, organizational
culture is thought to directly influence lecturer work
motivation (Cabaron & Oco, 2023; Qomariah et al.,
2022).
2.3 Transformational Leadership (TL)
TL is a groundbreaker who encourages the cohorts to
put aside the particular benefits for the respectability
of the association and can focus on achieving the
vision and mission, coping with change and
innovation, building trust, and having the power to
influence, move, guide, motivate and direct group
members for the overall accomplishment of the areas
and purposes set for better changes in the future
(Awan et al., 2023; Ayik & Alpullu, 2022; Nastavia
& Lista, 2022; Rahmawati et al., 2022). The
indicators of TL include charisma, communication,
controlling subordinates, responsibility, and
emotional control. A good leader will always treat his
subordinates well, fairly, and without favoritism
(Nusraningrum, 2018). If the lecturer has a good
impression of his boss, then the lecturer will be
motivated to complete the assigned responsibilities
with full seriousness and responsibility. If TL is not
good, the lecturer will be less motivated to carry out
the task which will eventually lead to dissatisfaction
at work. A good leader will be able to foster the trust
of the lecturers so that they will be able to carry out
their duties properly (Hoai et al., 2022). Based on this
framework, it can be presumed that there is an impact
of Transformational Leadership on lecturer
motivation (Ángeles López-Cabarcos et al., 2022).
Modeling Organizational Culture, Transformational Leadership, Motivation, Job Satisfaction: Muhammadiyah Aisyiyah College’s Nursing
Lecturer
113
2.4 Motivation (M)
Work motivation is a set of external and internal
forces that arouse, direct, and maintain human
behavior related to work, and determine the direction,
intensity, and persistence to achieve a goal (Royani et
al., 2022; Yusuf et al., 2022). Work enthusiasm can
be perceived in how to exertion such as the will to
work, irritation to practice the time to effort as
proficiently as possible, and great responsibility for
work with indicators; trying to excel at work,
complete tasks well, and be rational in achieving
success, like challenges, accept responsibility and
like work circumstances with private responsibility,
advice and a standard level of hazard (Smith et al.,
2008). Work motivation can be seen from the way of
work such as the readiness to work, irritation to use
the time to effort as professionally as possible, and
great responsibility towards work (Nusraningrum &
Dores, 2018)Lecturers who have high motivation will
get a high awareness of their duties and will try hard
to reach outcomes and feel happy about their work
(Shahzad et al., 2023), and get satisfaction. So, it can
be said that motivation affects job satisfaction.
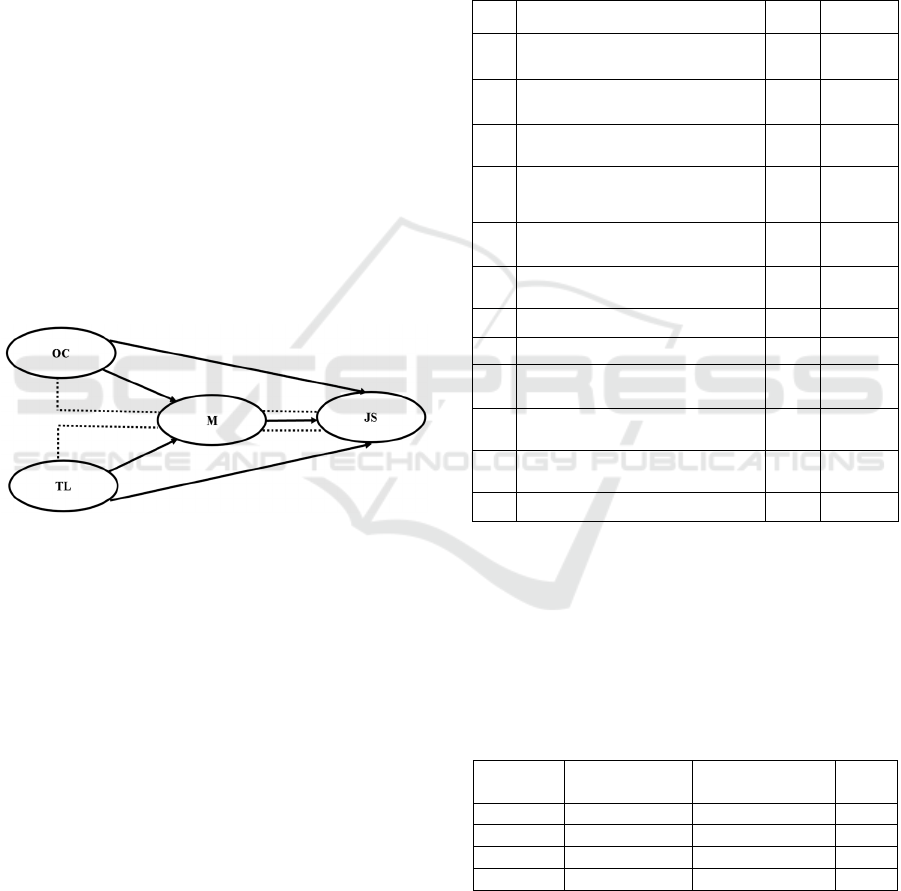
Figure 1: Conceptual Framework.
From the literature review and research conceptual
framework, research hypotheses are compiled: ⎯ H1:
OC affects JS ⎯ H2: TL affects JS ⎯ H3: OC affects
M ⎯ H4: TL affects M ⎯ H5: M affects JS ⎯ H6 &
H7:M can mediate OC against JS, and TL against JS.
3 METHOD
This research was conducted at the Muhammadiyah
Aisyiyah College (PTMA) which is spread across the
province of Central Java. The time of research was
carried out from May to July 2023. This research
method is quantitative research which is defined as a
technique constructed on the positivist philosophy.
Data assembly uses research tools through survey
types. Testing a hypothesis by using statistical
calculations using path analysis or variance-based
path analysis known as Partial Least Square (PLS)
analysis. Muhammadiyah Aisyiyah College (PTMA),
which organizes nursing education, has been
accredited in the Central Java region with a total
population of 230 lecturers, it consists of 11 colleges.
The research sample used in this research has criteria,
namely holding Nursing Education at both diploma,
undergraduate, and nursing profession levels, being
accredited, and having the status of a lecturer.
Table 1: Number of Samples.
No PTMA name Sample %
1 Muhammadiyah Surakarta
University
18 8,12
2 Semarang Muhammadiyah
University
28 12.55
3 PKU Solo Health and Science
Technology Institute
19 7,38
4 Muhammadiyah University
Purwokerto
30 12.92
5 Gombong Muhammadiyah
University
23 11.44
6 Muhammadiyah University of
Ma
g
elan
g
17 7.75
7 Muhammadiyah University of
Kl t
26 8.86
8 Aisyiyah University Surakarta 21 6,64
9 Pekajangan Muhammadiyah
University
23 11.44
10 Muhammadiyah University of
Kudus
16 7,38
11 Muhammadiyah Kendal
Universit
y
9 5.54
Total 230 100%
The study respondents were dominated by women,
married, aged between 31 to 40 years, who had
experience as lecturers for more than five years,
undergraduate, with positions as assistant professors.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Table 2: Measurement Model Evaluation.
Variables Cronbach's
Al
p
ha
Composite
Reliabilit
y
AVE
JS 0.904 0.922 0.598
OC 0.868 0.901 0.602
TL 0.953 0.960 0.684
M 0.920 0.933 0.609
The construction factor loading is obtained which
ranges from 0.7 and 0.90, offering a satisfactory
good-of-suitable for the approach. Cronbach's α is
bigger than 0.8, which means the variables can
explain the latent variable to a quite high level.
FEMIB 2024 - 6th International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
114
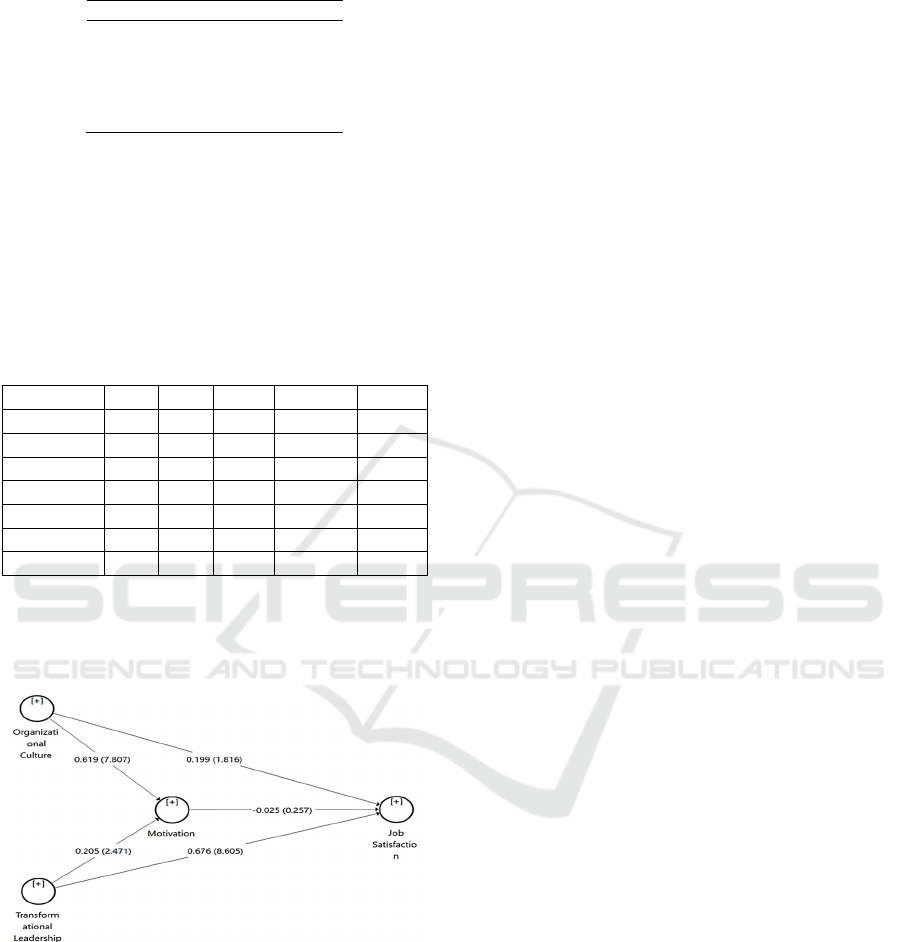
Table 3: Fornell-Larcker Criterion.
OC TL JS M
OC 0.776
TL 0.639 0.827
JS 0.612 0.788 0.774
M 0.750 0.600 0.530 0.781
The chi-square of the goodness-of-fit of the
hypothetical design has 4 degrees of freedom, i.e.: χ
2 = 7.196 and p = 0.126 (good fit between the
theoretical model and the sample data). The other
indices, χ 2/df = 1.799, AGFI = 0.939, GFI = 0.993,
RMR = 0.010, CFI = 0.997, RMSEA = 0.055, IFI =
0.997, and NFI = 0.994, all show a satisfactory
goodness-of-fit in the overall model.
Table 4: Structural equation modeling analysis.
O M STDEV O/STDEV| P values
OC -> JS 0.199 0.210 0.109 1,825 0.069
OC -> M 0.619 0.623 0.079 7,815 0.000
TL -> JS 0.676 0.670 0.080 8,436 0.000
TL -> M 0.205 0.207 0.082 2,507 0.013
M -> JS -0.025 -0.027 0.105 0.239 0.811
OC-> M -> JS -0.016 -0.020 0.067 0.231 0.818
TL -> M -> JS -0.005 -0.002 0.022 0.229 0.819
We found that OC has a direct effect on JS, TL has a
direct effect on JS, and M. Table 6 also presents that
motivation does not have a mediating part in the
connection between OC and TL to JS.
Figure 2: PLS Bootstrapping.
H1 shows that there is no organizational influence
on job satisfaction. Muhammadiyah organizational
culture can vary from one educational institution to
another, although there are general principles held.
This culture usually includes Islamic values, ethics,
morality, and approaches to education.
Muhammadiyah's organizational culture may not
directly influence lecturer satisfaction in the nursing
faculty, including; lecturers at the nursing faculty
may have values or expectations that are different
from the values espoused in the Muhammadiyah
organizational culture, policies or rules implemented
by Muhammadiyah institutions may not always
support the needs or desires of lecturers in nursing
faculties. Lecturers in nursing faculties may feel that
opportunities for career development or skill
improvement are inadequate or do not meet their
expectations, even though there is a strong
organizational culture. A strong organizational
culture may place additional pressure on faculty to
adhere to organizational values or demands, which
may impact work-life balance and personal
satisfaction. The most important thing is to create an
organizational culture that includes Islamic values
that exist within the Muhammadiyah organization so
that these values can provide competitive value for
organizational culture in running the organization
(Arifin et al., 2023; Rachma et al., 2023). H2 result is
matched with (Ginting, 2023) when employees are
capable of comprehending organizational culture
well, they will be capable of increasing their
motivation. Organizational culture as social
knowledge that is carried out together fosters shared
motivation in an association concerning norms, rules,
and values that form the behavior and attitudes of the
employees, in this case, lecturers. The emergence of
organizational culture as a conventional of traditions,
norms, values, and beliefs that are owned by the
lecturer of Higher Education. Every organization has
its specific cultural values, and it plays an imperative
role in the organization (Cherian et al., 2021). H3
result corresponds to the findings of (Fütterer et al.,
2023; Ginting, 2023) which show that
transformational leadership and organizational
culture are proven to be able to raise job satisfaction,
but are not able to encourage civil servant
performance. The important point that leaders need to
consider when they carry out their functions. Then a
leader with a transformational style is needed who
works through other staff to optimally transform
administrative resources to complete meaningful
goals by the accomplishment aims, which has been
set up. This can be seen from the organizational
culture under the auspices of Muhammadiyah. The
applied transformational leadership style used by a
manager in the Muhammadiyah organization by
widening the boundaries and performance beyond the
status quo of the organization so that the organization
can achieve a whole new set of organizational goals,
and also try to make cultural changes (Kaur Bagga et
al., 2023). H4 result is consistent with previous
research (Nurjanah et al., 2020) which shows
transformational leadership can encourage an
Modeling Organizational Culture, Transformational Leadership, Motivation, Job Satisfaction: Muhammadiyah Aisyiyah College’s Nursing
Lecturer
115

intensification in worker motivation directly and has
a significant positive relationship with the intrinsic
motivation of the mediator (Khan et al., 2020). H5 is
rejected. Some studies have also found that
motivation does not affect job satisfaction because
one of them is age. H5 found that there is no influence
between motivation to job satisfaction, the results of
this study are in line with the results of (Riyanto et al.,
2023; Widyanty et al., 2020) which show that
motivation has no significant effect on employee job
satisfaction. In general, for employees who have
worked for a long time and do not get a promotion, it
can affect their motivation for job satisfaction.
The results of testing the beta coefficient -0.016,
the t-statistic 0.231 is less than the T table 1.96, the p-
value is 0.818 greater than 0.05 with these results
there is no indirect impact of organizational culture
over motivation on job satisfaction. (Nie et al., 2015)
research illustrates which organizational culture can
encourage job satisfaction that has competitiveness,
although other aspects of work culture such as
employee treatment can have an impact on job
satisfaction that is different. Therefore,
organizational culture and satisfaction have a
relationship to create organizational competitiveness.
Finally, there is no direct relationship between
organizational culture and transformational
leadership through motivation to job satisfaction (H6
& H7). Intrinsic motivation is a key factor in
encouraging employee satisfaction (Adeel et al.,
2023; Saleh & Atan, 2021). The motivation for
Muhammadiyah's charitable efforts is influenced by
several factors, originating from a). biographical
characteristics of the individual; gender, age, marital
status, years of service, number of dependents, and
level of education are factors in individual
biographies that influence work motivation (Akunne
et al., 2023; Alamri, 2023; Arifin et al., 2023; Rachma
et al., 2023; Taryana et al., 2023). Age has a close
relationship with maturity in organizational life and
task skills. Gender has implications for the treatment
that will be received by individuals according to
organizational members which affects motivation at
work.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Faculty satisfaction can be influenced by many
factors, including work environment, compensation,
development opportunities, leadership qualities,
institutional policies, and organizational culture.
Muhammadiyah organizational culture can vary from
one educational institution to another, although there
are general principles held. This culture usually
includes Islamic values, ethics, morality, and
approaches to education. Identifying factors such as
management quality and others and improving them
can help increase the motivation and satisfaction of
lecturers in nursing faculties. It is important to
conduct further research to understand in depth why
Muhammadiyah's organizational culture does not
have a significant effect on lecturer satisfaction in
nursing faculties. This may involve interviews with
faculty, analysis of institutional policies, and an in-
depth assessment of the organization's culture and
values.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to thank you for the doctoral program
research grant to the Ministry of Education, Culture,
Research, and Technology.
REFERENCES
Adeel, A., Batool, S., & Madni, Z.-A. (2023). Intrinsic
Motivation and Creativity: the Role of Digital
Technology and Knowledge Integration Ability in
Facilitating Creativity. International Journal of
Management Studies, 30(1), 1–36. https://doi.org/10.32
890/ijms2023.30.1.1
Akunne, L. I., Nwadinobi, V. N., Mokwelu, O. B., &
Ezeokafor, S. C. (2023). The Relationship between
Teacher’s Motivation and their Job Satisfaction in
Secondary Schools in Onitsh Education Zone, Anambra
State, Nigeria. Asian Journal of Education and Social
Studies, 42(1). https://doi.org/10.9734/ajess/2023/v42i
1907
Alamri, M. M. (2023). A Model of E-Learning through
Achievement Motivation and Academic Achievement
among University Students in Saudi Arabia.
Sustainability (Switzerland), 15(3). https://doi.org/
10.3390/su15032264
Ángeles López-Cabarcos, M., Vázquez-Rodríguez, P., &
Quiñoá-Piñeiro, L. M. (2022). An approach to
employees’ job performance through work
environmental variables and leadership behaviours.
Journal of Business Research, 140, 361–369.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.11.006
Arabeche, Z., Soudani, A., Brahmi, M., Aldieri, L., Vinci,
C. P., & Abdelli, M. E. A. (2022). Entrepreneurial
Orientation, Organizational Culture and Business
Performance in SMEs: Evidence from Emerging
Economy. Sustainability (Switzerland), 14(9).
https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095160
Arifin, A., Harahap, M. A. K., Aziz, N., Nur, M., & Pranata,
S. (2023). The Analysis of Role of Job Satisfaction and
Motivation on Teachers Performance in Integrated
FEMIB 2024 - 6th International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
116

Islamic High School. Journal on Education, 5(4).
https://doi.org/10.31004/joe.v5i4.2475
Asfahani, A. M. (2023). Green HRM and Servant
Leadership: Driving Competitive Advantage and
Environmental Performance in Higher Education.
Sustainability (Switzerland), 15(10). https://doi.org/
10.3390/su15107921
Aung, Z. M., Santoso, D. S., & Dodanwala, T. C. (2023).
Effects of demotivational managerial practices on job
satisfaction and job performance: Empirical evidence
from Myanmar’s construction industry. Journal of
Engineering and Technology Management - JET-M,
67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jengtecman.2022.101730
Awan, F. H., Dunnan, L., Jamil, K., & Gul, R. F. (2023).
Stimulating environmental performance via green
human resource management, green transformational
leadership, and green innovation: a mediation-
moderation model. Environmental Science and
Pollution Research, 30(2), 2958–2976. https://doi.org/
10.1007/s11356-022-22424-y
Ayik, Ö., & Alpullu, A. (2022). Investigating the
Relationship between Transformational Leadership and
Job Satisfaction: An Application on Trainers.
International Journal of Sport, Exercise & Training
Sciences, 8(4), 119–131. https://doi.org/10.18826/use
eabd.1163328
Cabaron, G. J., & Oco, R. M. (2023). Teachers’ Level of
Motivation and Job Satisfaction. Asian Journal of
Education and Social Studies, 45(1). https://doi.org/
10.9734/ajess/2023/v45i1971
Cherian, J., Gaikar, V., Paul, R., & Pech, R. (2021).
Corporate culture and its impact on employees’
attitude, performance, productivity, and behavior: An
investigative analysis from selected organizations of
the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Journal of Open
Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 7(1),
1–28. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc7010045
Colquitt, J. ; L. J. ; W. M. (2023). Organizational Behavior:
Improving Performance and Commitment in the
workplace (8th ed.). McGraw Hill.
Davidescu, A. A. M., Apostu, S. A., Paul, A., & Casuneanu,
I. (2020). Work flexibility, job satisfaction, and job
performance among romanian employees-Implications
for sustainable human resource management.
Sustainability (Switzerland), 12(15). https://doi.org/
10.3390/su12156086
Doghan, M. A. A., Abdelwahed, N. A. A., Soomro, B. A.,
& Alayis, M. M. H. A. (2022). Organizational
Environmental Culture, Environmental Sustainability
and Performance: The Mediating Role of Green HRM
and Green Innovation. Sustainability (Switzerland),
14(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127510
Dorta-Afonso, D., Romero-Domínguez, L., & Benítez-
Núñez, C. (2023). It’s worth it! High performance work
systems for employee job satisfaction: The mediational
role of burnout.
International Journal of Hospitality
Management, 108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.20
22.103364
Eliyana, A., Ma’arif, S., & Muzakki. (2019). Job
satisfaction and organizational commitment effect in
the transformational leadership towards employee
performance. European Research on Management and
Business Economics, 25(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.iedeen.2019.05.001
Fütterer, T., van Waveren, L., Hübner, N., Fischer, C., &
Sälzer, C. (2023). I can’t get no (job) satisfaction?
Differences in teachers’ job satisfaction from a career
pathways perspective. Teaching and Teacher
Education, 121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2022.10
3942
Ginting, J. G. (2023). Organizational culture: An overview
and bibliometric analysis. Asian Journal of Economics
and Business Management, 2(2), 534–542.
https://doi.org/10.53402/ajebm.v2i2.318
Groysberg, B., Lee, J., Price, J., & Cheng, J. Y. (2018). The
Leader’s Guide to Corporate Culture: Changing your
organization’s culture can improve its performance.
Here’s how to do that. In Harvard Business Review
(Issue January-February).
Hoai, T. T., Hung, B. Q., & Nguyen, N. P. (2022). The
impact of internal control systems on the intensity of
innovation and organizational performance of public
sector organizations in Vietnam: the moderating role of
transformational leadership. Heliyon, 8(2).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e08954
Huang, S. S., Chen, C. Y., Kau, K., Tsai, J. M., & Tsay, S.
L. (2023). Key determinates of job satisfaction for acute
care nurse practitioners in Taiwan. BMC Nursing,
22(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-022-01156-x
Hung, Y. C., Su, T. C., & Lou, K. R. (2022). Impact of
Organizational Culture on Individual Work
Performance with National Culture of Cross-Strait
Enterprises as a Moderator. Sustainability
(Switzerland), 14(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/su1411
6897
Idris, AS, N., Soetjipto, B. E., & Supriyanto, A. S. (2021).
Predicting factors of organizational citizenship
behavior in Indonesian nurses. Heliyon, 7(12).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08652
Japir Bataineh, M. A., Ghasemi, M., & Ghadiri Nejad, M.
(2023). The Role of Green Training in the Ministry of
Education’s Corporate Environmental Performance: A
Mediation Analysis of Organizational Citizenship
Behavior towards the Environment and Moderation
Role of Perceived Organizational Support.
Sustainability (Switzerland), 15(10). https://doi.org/
10.3390/su15108398
Kaur Bagga, S., Gera, S., & Haque, S. N. (2023). The
mediating role of organizational culture:
Transformational leadership and change management
in virtual teams. Asia Pacific Management Review,
28(2), 120–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmrv.2022.
07.003
Kelly, C. M., Rofcanin, Y., Las Heras, M., Ogbonnaya, C.,
Marescaux, E., & Bosch, M. J. (2020). Seeking an “i-
deal” balance: Schedule-flexibility i-deals as mediating
mechanisms between supervisor emotional support and
employee work and home performance. Journal of
Vocational Behavior, 118. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.jvb.2019.103369
Modeling Organizational Culture, Transformational Leadership, Motivation, Job Satisfaction: Muhammadiyah Aisyiyah College’s Nursing
Lecturer
117

Khan, H., Rehmat, M., Butt, T. H., Farooqi, S., & Asim, J.
(2020). Impact of transformational leadership on work
performance, burnout and social loafing: a mediation
model. Future Business Journal, 6(1).
https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-020-00043-8
Lohela-Karlsson, M., Jensen, I., & Björklund, C. (2022).
Do Attitudes towards Work or Work Motivation Affect
Productivity Loss among Academic Employees?
International Journal of Environmental Research and
Public Health, 19(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph190
20934
Mittal, S., & Dhar, R. L. (2016). Effect of green
transformational leadership on green creativity: A study
of tourist hotels. Tourism Management, 57, 118–127.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.05.007
Mustafa, M., Ramos, H. M., & Zainal Badri, S. K. (2023).
Determining nonfamily employees’ job satisfaction and
turnover intentions: the roles of job autonomy and work
passion. Journal of Family Business Management,
13(2). https://doi.org/10.1108/JFBM-08-2020-0079
Mysirlaki, S., & Paraskeva, F. (2020). Emotional
intelligence and transformational leadership in virtual
teams: lessons from MMOGs. Leadership and
Organization Development Journal, 41(4).
https://doi.org/10.1108/LODJ-01-2019-0035
Nastavia, P., & Lista, M. (2022). The Effect of
Transformational Leadership on Employee
Performance Through Job Satisfaction and
Organizational Commitment. IAIC Transactions on
Sustainable Digital Innovation (ITSDI), 4(1), 8–21.
https://doi.org/10.34306/itsdi.v4i1.565
Nie, Y., Chua, B. L., Yeung, A. S., Ryan, R. M., & Chan,
W. Y. (2015). The importance of autonomy support and
the mediating role of work motivation for well-being:
Testing self-determination theory in a Chinese work
organisation. International Journal of Psychology,
50(4). https://doi.org/10.1002/ijop.12110
Nurjanah, S., Pebianti, V., & Handaru, A. W. (2020). The
influence of transformational leadership, job
satisfaction, and organizational commitments on
Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) in the
inspectorate general of the Ministry of Education and
Culture. Cogent Business and Management, 7(1).
https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2020.1793521
Nuryanto, & Pambuko, Z. B. (2019). A study on the effect
of human resource empowerment on productivity:
Evidence from Indonesian higher education.
Management Science Letters, 9(12).
https://doi.org/10.5267/j.msl.2019.7.008
Nusraningrum, D. (2018). Top management vision through
role models, determination and dicsiplines. In
International Journal of Economics and Business
Administration (Vol. 6, Issue 4, pp. 48–61).
Nusraningrum, D., & Dores, A. (2018). the Workforce
Quality of Asean Economic Community: Case in
Indonesia. Pdfs.Semanticscholar.Org, 1(1).
Nusraningrum, D., Mekar, T. M., Ahmad, F. S., Wibowo,
M. W., & Hanafiah, A. (2023). Improving the Green
Behavior of Millennials at HEIs: Green
Transformational Leadership and Digital Green
Campaign on Green Thinking in Indonesia. Migration
Letters, 20(7), 1203–1220. www.migrationletters.com
PP Muhammadiyah. (2010). Tanfidz Keputusan Muktamar
Satu Abad Muhammadiyah.
Putra, G. N. S., & Dewi, I. G. A. M. (2019). Effect of
transformational leadership and organizational culture
on employee performance mediated by job motivation.
International Research Journal of Management, IT and
Social Sciences, 6(6), 118–127. https://doi.org/
10.21744/irjmis.v6n6.778
Qomariah, N., Lusiyati, Nursaid, & Martini, N. N. P.
(2022). Motivation in Improving Employee
Performance : With Job Satisfaction. Jurnal Aplikasi
Manajemen, 20(3).
Rachma, Y. E., Mokan, A., Badriyyah, E. S. R., Gusliana,
E., & Tawil, M. R. (2023). The Effect of Principal
Transformational Leadership and Motivation on
Performance of Teacher in Islamic Elementary School.
Journal on Education, 5(3). https://doi.org/10.31004/
joe.v5i3.1493
Rafique, M. A., Hou, Y., Chudhery, M. A. Z., Waheed, M.,
Zia, T., & Chan, F. (2022). Investigating the impact of
pandemic job stress and transformational leadership on
innovative work behavior: The mediating and
moderating role of knowledge sharing. Journal of
Innovation and Knowledge, 7(3). https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.jik.2022.100214
Rahmawati, Y., Hariri, H., riswanti, R., & Sowiyah. (2022).
Transformational and Instructional Leadership Styles to
Improve Teacher Performance: Literature Review.
International Journal of Current Science Research and
Review, 05(07), 2757–2764. https://doi.org/10.47191/
ijcsrr/V5-i7-61
Riyanto, S., Handiman, U. T., Gultom, M., Gunawan, A.,
Putra, J. M., & Budiyanto, H. (2023). Increasing Job
Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and the
Requirement for Competence and Training. Emerging
Science Journal, 7(2). https://doi.org/10.28991/ESJ-
2023-07-02-016
Roscoe, S., Subramanian, N., Jabbour, C. J. C., & Chong,
T. (2019). Green human resource management and the
enablers of green organisational culture: Enhancing a
firm’s environmental performance for sustainable
development. Business Strategy and the Environment,
28(5). https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2277
Royani, I., Mudhofir, M., Muharom, F., & Rabbani, I.
(2022). The Effect of Training and Work Motivation on
Lecturer Performance Study at Zainul Hasan Genggong
University. Tadbir : Jurnal Studi Manajemen
Pendidikan, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.29240/jsmp.v6i1.4
665
Sadya, S. (2023, April 10). Ada 4.004 Perguruan Tinggi di
Indonesia pada tahun 2022. dataindonesia.id/ragam/
detail/ada-4004-perguruan-tinggi-di-indonesia-pada-
2022
Saeedi, M., & Parvizy, S. (2019). Strategies to promote
academic motivation in nursing students: A qualitative
study. Journal of Education and Health Promotion,
8(1). https://doi.org/10.4103/jehp.jehp_436_18
FEMIB 2024 - 6th International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
118

Saleh, R., & Atan, T. (2021). The involvement of
sustainable talent management practices on employee’s
job satisfaction: Mediating effect of organizational
culture. Sustainability (Switzerland), 13(23).
https://doi.org/10.3390/su132313320
Santoso, H., Elidjen, Abdinagoro, S. B., & Arief, M.
(2019). The role of creative self-efficacy,
transformational leadership, and digital literacy in
supporting performance through innovative work
behavior: Evidence from telecommunications industry.
Management Science Letters, 9(Spceial Issue 13),
2305–2314. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.msl.2019.7.024
Setyaningsih, D., Tinggi, S., Islam, A., Sultan, N., & Riau,
A. K. (2021). Implementasi Manajemen Strategi Dalam
Meningkatkan Mutu Pendidikan.
Shahzad, M., Qu, Y., Ur Rehman, S., Ding, X., & Razzaq,
A. (2023). Impact of stakeholders’ pressure on green
management practices of manufacturing organizations
under the mediation of organizational motives. Journal
of Environmental Planning and Management, 66(10).
https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2022.2062567
Smith, J. R., Farias, M. C. Q., Carvalho, M. M., & Alencar,
M. S. (2008). Digital television broadcasting in Brazil.
IEEE Multimedia, 15(2). https://doi.org/10.1109/
MMUL.2008.25
Taryana, T., Riniati, W. O., Haddar, G. Al, Sembiring, D.,
& Mutmainnah, M. (2023). The Influence of Teacher
Certification and Teaching Motivation on Teacher
Performance. Journal on Education, 5(3).
https://doi.org/10.31004/joe.v5i3.1455
Wang, X., Zhou, K., & Liu, W. (2018). Value congruence:
A study of green transformational leadership and
employee green behavior. Frontiers in Psychology,
9(OCT). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01946
Widyanty, W., Daito, A., Riyanto, S., & Nusraningrum, D.
(2020). Gaining a competitive advantage through
strategic human resource management in Indonesian
construction industry. Management Science Letters,
10(9), 2021–2028. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.msl.20
20.2.010
Yusuf, M., Haryoto, C., & Husainah, N. (2022). The Effect
of Self-Efficiency and Organizational Justice On
Lecturers’ Career Development With Work Motivation
as A Variable Mediation At Muhammadiyah Higher
Education In DKI Jakarta. Devotion Journal of
Community Service, 3(14). https://doi.org/10.36418/
dev.v3i14.322
Modeling Organizational Culture, Transformational Leadership, Motivation, Job Satisfaction: Muhammadiyah Aisyiyah College’s Nursing
Lecturer
119
