
Enhancing Constructivist Learning: The Role of Generative AI in
Personalised Learning Experiences
Hua Guo
1
, Weiqian Yi
2
and Kecheng Liu
3
1
School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science, Queen Mary University of London, London, U.K.
2
Harrow School, Druries House, London, U.K.
3
Informatics Research Centre, University of Reading, Reading, U.K.
Keywords: Generative AI & AI-Generated Content in Higher Education, Constructivist Learning, Authentic Learning.
Abstract: This paper explores the transformative role of generative AI in enhancing constructivist learning, where
students actively construct knowledge through meaningful experiences. By investigating the synergies
between generative AI and constructivist learning, the study uncovers how AI fosters personalized educational
experiences. The research underscores the profound influence of generative AI on constructivist learning,
empowering students to become active, motivated, and lifelong learners by tailoring their education, fostering
creativity and collaboration, and upholding ethical principles. The study advocates for the responsible and
purposeful integration of generative AI, which would revolutionize education and prepare students for future
challenges.
1 INTRODUCTION
Generative AI represents a tipping point in the
development of AI with huge adoptions from various
industrial users. It has the potential to change the way
we interact with and leverage artificial intelligence in
our daily life, revolutionising how we access
information, use information, reshape the learning
curve and solve problems.
In higher education, generative AI tools are
widely adopted by students. Cassidy (2023) statistics
shows that one-fifth of students using AI programs in
assessment tasks just two months after Chat-GPT
release. Another survey conducted in January 2023
(Intelligent, 2023) reported that over one-third were
using Chat-GPT for assessment writing. Of these
students, 75% thought it counted as cheating but did
so anyway. Furthermore, over 40 per cent of
universities are investigating students for using
ChatGPT to cheat (Snepvangers, 2023). Based on the
above research, it is apparent that ChatGPT has
garnered significant adoption among college students
and lecturers urged to review assessments in the UK
amid concerns over the new AI tool (Weale, 2023).
The question for universities is how to use generated
AI tools safely, effectively, and appropriately, rather
than ban them from students. Consequently, it
becomes imperative to engage in a thoughtful
discussion regarding the pedagogical applications of
AI.
This paper will focus on the applications of
generative AI in higher education, along with
pedagogical methods, to explore how generative AI
enhance teaching and learning.
2 CONSTRUCTIVIST LEARNING
THEORY AND ITS
SIGNIFICANCE IN HIGH
EDUCATION
Constructivism is a learning theory that has
significant implications for higher education. It
emphasizes the learner's active role in constructing
understanding and knowledge through meaningful
experiences and interactions. In the context of higher
education, constructivism shifts the focus from
passive knowledge transmission to active
engagement and critical thinking.
Key principles of constructivism in higher
education:
Active Learning: A subject process.
Constructivism promotes active learning
Guo, H., Yi, W. and Liu, K.
Enhancing Constructivist Learning: The Role of Generative AI in Personalised Learning Experiences.
DOI: 10.5220/0012688700003690
In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2024) - Volume 1, pages 767-770
ISBN: 978-989-758-692-7; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright © 2024 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
767
strategies such as discussions, problem-
solving, projects, and hands-on experiences.
Students are encouraged to explore and
discover knowledge rather than passively
receiving information.
Prior Knowledge: Prior knowledge and
experiences play a crucial role in the learning
process. Educators recognize and build upon
students' existing knowledge, integrating new
information with their mental frameworks.
Social Interaction: Social interactions and
collaborative learning are essential in
constructivist classrooms. Students engage in
discussions, debates, and group work to co-
construct knowledge through dialogue and
shared experiences.
Student-Centred Approach: Constructivism
places students at the centre of the learning
process. It tailors instruction to individual
needs, interests, and learning styles, fostering a
more personalized and meaningful learning
experience.
Reflection and Metacognition: Students are
encouraged to reflect on their learning process
and think metacognitively about their own
thinking. Self-assessment and self-regulation
of learning are integral to the constructivist
approach.
Real-World Relevance: Constructivist
educators aim to connect classroom learning to
real-world contexts and applications, making
the learning experience more authentic and
meaningful.
In line with the principles of constructivism, the
learning process is viewed as a journey of knowledge
construction. Through comprehending both the sign
and its meaning, individuals can effectively apply the
acquired knowledge (as shown in Figure 1).
Figure 1: Learning as knowledge construction from
semiotics (modified (Liu and Li, 2015)).
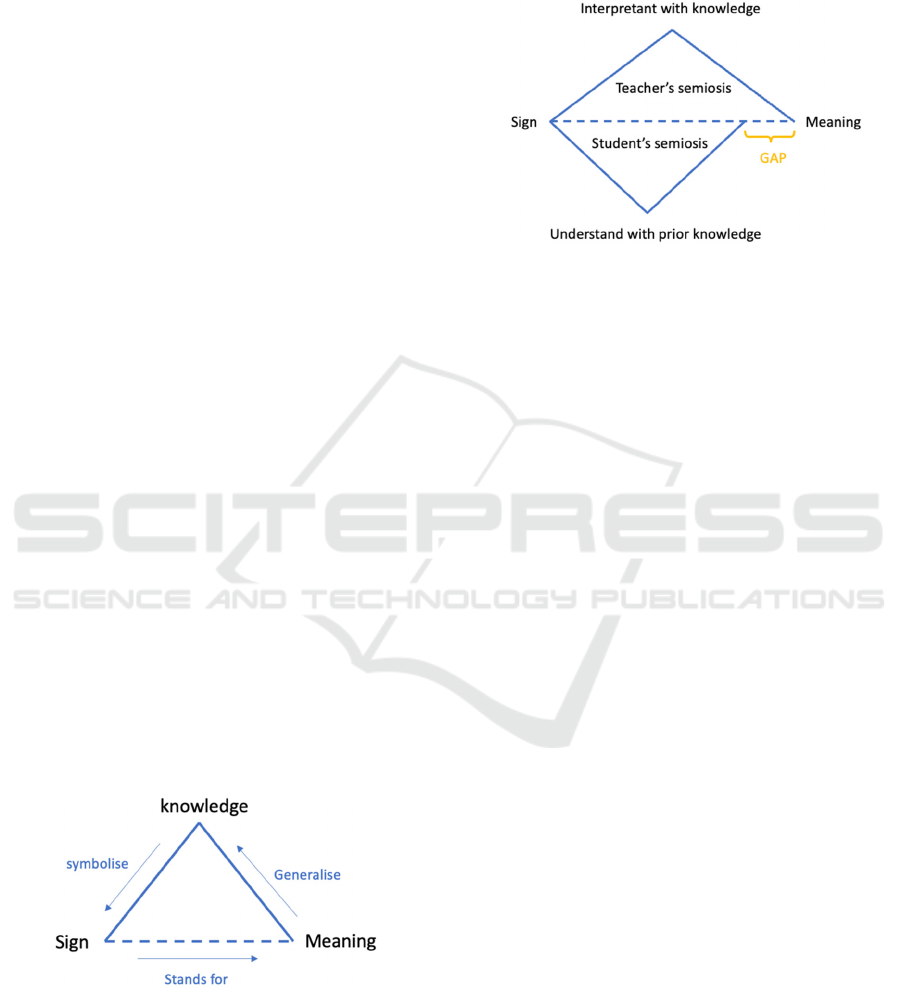
As knowledge construction is a subjective
process, there must be a gap between the teacher and
the learner. As shown in Figure 2, the learning
process is a sense-making process navigated by prior
knowledge. As the students have different knowledge
contexts from their lecturers, the gap generates and
hinders quality learning.
Figure 2: The gap between teacher and student knowledge
understanding generated by different prior knowledge
(modified (Liu and Li, 2015)).
Concerning the subjective nature of the learning
process, generative AI tools serve as ideal adaptive
assistants for students acquiring new knowledge,
responding to their personalized questions with
precision.
The next section explores the various approaches
of integrating generative AI applications in
educational settings.
3 INTEGRATING GENERATIVE
AI IN HIGHER EDUCATION
Generative AI tools play a pivotal role in facilitating
adaptive learning through personalised feedback,
supporting research and data analysis, automating
administrative service, and contributing to the
development of innovative assessments (Rasul et al.,
2023). This paper focuses on the following four
specific tools: Chat-GPT(Rudolph et al., 2023), Bing
Chat, Bard, Ernie (Teubner et al., 2023), with the
objective of exploring the synergies between
constructivist learning and generative AI.
3.1 Personalised Learning with
Generative AI
Personalised learning has the potential to address the
longstanding challenges in education, such as
addressing learning gaps, accommodating diverse
learning styles, and promoting students’ engagement.
Through the utilization of generative AI embedding
alongside adaptive learning algorithms, instructors
have the ability to customize education, feedback, and
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
768

assistance to match the individual learning profile of
each student. This component of the investigation
will specifically examine three perspectives:
Adaptive content generation and customised
learning pathways
AI-driven individualised feedback and support
The role of generative AI in catering to diverse
learning styles
3.2 Fostering Engagement and
Creativity with AI-Generated
Content
AI-driven creative content includes a diverse array of
educational resources, such as interactive
simulations, virtual reality experiences, adaptive
learning modules, personalised quizzes and
assessments, and AI-generated educational games
and activities. These customised instructional
resources can boost student motivation by offering
individualised and engaging learning opportunities
that captivate individuals' interests and cultivate their
inherent drive to learn. In this section, the following
three perspectives will be investigated.
AI-Powered Creative Content and Its Impact
on Student Motivation
Using AI for Dynamic Simulations and Real-
World Problem-Solving
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality
(VR) Applications in Constructivist Learning
3.3 Collaborative Learning
Empowered by Generative AI
Collaborative learning environments can enhance the
effectiveness and efficiency of group-based/cohort-
based learning activities. When generative AI can be
applied into collaborative learning settings, the
learning processes can be optimised for individual
needs, and knowledge synthesis facilitated by AI can
enhance the personalised learning experiences. This
section will dive into the following three perspectives
to explore the role of generative AI in project support,
interaction and feedback, as well as problem solving
activities.
AI-Driven Group Formation and Collaborative
Project Support
Facilitating Peer Interaction and Constructivist
Feedback
Leveraging AI for Collaborative Problem-
Solving Activities
3.4 Ethical Considerations and
Challenges in AI Integration
As generative AI tools have been widely adopted by
students in higher education, there is an urgent need
to provide guidelines on how to use AI in their
learning processes and to ensure equitable use of
these technologies in educational environments. This
section will explore the potential challenges of
integrating AI into educational systems from the
following three points.
Ensuring Ethical Use of AI in Education
Addressing Bias and Fairness in AI Algorithms
Privacy and Security Concerns in AI-Driven
Educational Environments
Challenges in Implementing Generative
AI for Constructivist Learning
By examining the challenges, educators and
researchers can identify potential barriers and
obstacles that may hinder the effective
implementation of Generative AI in constructivist
learning environments. The challenges mainly come
from the privacy and data security concerns and the
ethical issues.
Ethical Considerations and Bias in AI
Algorithms
Addressing Privacy and Data Security
Concerns
Empowering Educators to Leverage AI
Effectively
4 A PILOT RESEARCH ON
STUDENT USE OF
GENERATIVE AI
Understanding the gaps in teaching and learning, as
well as the difficulties students encounter in their
learning process, is essential for formulating effective
questions that promote personalised learning. Figure
3 depicts the implementation of the constructivist
learning concept in practical teaching.
We are currently developing a tool designed to
identify AI-generated content within students' essays.
Due to privacy and ethical considerations, it is not
feasible for educators to upload students' essays to
third-party tools. This tool will serve to pinpoint
sentences or paragraphs that have been generated by
AI algorithms. By analysing this content, educators
can gain insights into the challenges students face
Enhancing Constructivist Learning: The Role of Generative AI in Personalised Learning Experiences
769
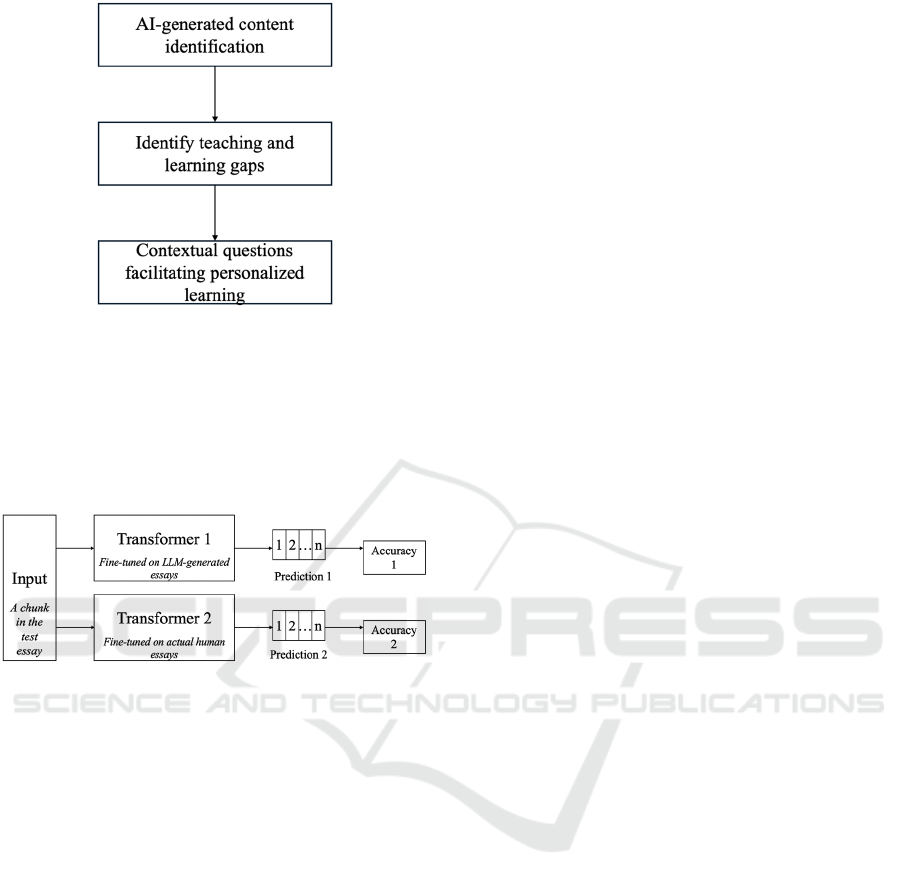
Figure 3: The process of applying constructivist learning.
when writing essays. For instance, students may
struggle with defining concepts clearly or providing
precise application scenarios. Additionally, the tool
will aid in identifying areas where students may
require further guidance or support in their writing
process.
Figure 4: Content identification process.
As shown in Figure 4, a pre-trained text-
generation transformer model, such as GPT-2
(Lysandre, 2023) can be fine-tuned separately with
human essays and machine-generated essays. For a
test human essay, the transformer trained on human
essays should be able to predict words in the essay
more accurately. Transformers can be further fine-
tuned on a specific topic or author, giving more
accurate results.
An example dataset is available on Kaggle
(https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/llm-detect-
ai-generated-text/data), containing human and LLM
generated essays. Academic papers are widely
available on the internet, while LLM essays can be
generated with the ChatGPT API.
5 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
Examining the adoption of generative AI tools in
curriculum design reveals key findings that enhance
understanding of the role of AI tools in teaching and
learning activities. This contributes to achieving
constructivist alignment by clarifying the needs of
students with diversified backgrounds. Furthermore,
exploring the implications and future applications of
AI in higher education elucidates its potential to
foster comprehensive and constructivist learning
experiences.
REFERENCES
Cassidy, C. 2023. Lecturer detects bot-use in one fifth of
assessments as concerns mount over AI in exams
[Online]. Available: https://www.theguardian.com/
australia-news/2023/jan/17/lecturer-detects-bot-use-in-
one-fifth-of-assessments-as-concerns-mount-over-ai-
in-exams [Accessed].
Intelligent 2023. Nearly 1 In 3 College Students Have Used
Chatgpt On Written Assignments.
Liu, K. & LI, W. 2015. Organisational semiotics for
business informatics, Routledge.
Lysandre. 2023. gpt2 [Online]. Available: https://
huggingface.co/openai-community/gpt2/tree/main
[Accessed].
Rasul, T., Nair, S., Kalendra, D., Robin, M., De Oliveira
Santini, F., Ladeira, W. J., Sun, M., Day, I., Rather, R.
A. & Heathcote, L. 2023. The role of ChatGPT in
higher education: Benefits, challenges, and future
research directions. Journal of Applied Learning and
Teaching, 6.
Rudolph, J., Tan, S. & Tan, S. 2023. ChatGPT: Bullshit
spewer or the end of traditional assessments in higher
education? Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching,
6.
Snepvangers, P. 2023. Over 40 per cent of universities are
investigating students for using ChatGPT to cheat.
Teubner, T., Flath, C. M., Weinhardt, C., Van Der Aalst,
W. & Hinz, O. 2023. Welcome to the era of chatgpt et
al. the prospects of large language models. Business &
Information Systems Engineering, 65, 95-101.
Weale, S. 2023. Lecturers urged to review assessments in
UK amid concerns over new AI tool.
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
770
