
Unveiling the Potential: Assessing the Role of SSI Wallets in Promoting
Sustainability in Federated Learning Environments
Damanpreet Singh Walia
1 a
, Ksenia Neumann
1 b
, Visman Jeet Singh Walia
1
, Malte Rathjens
1
,
Stefan Weidner
2
and Klaus Turowski
1,2
1
BIRD Lab, Faculty of Computer Science, Otto-von-Guericke University, Universit
¨
atsplatz 12, Magdeburg, Germany
2
SAP University Competence Center, Otto-von-Guericke University, Magdeburg, Germany
Keywords:
SSI, Self-Sovereign Identity, Wallet, BIRD, Sustainability, Federated Learning Environment, Education, UN,
Sustainable Development Goals, SDG, Education for Sustainable Development, ESD.
Abstract:
Quality Education is listed as goal number four among the seventeen Sustainable Development Goals mani-
fested by the United Nations. There exist an endless number of ways to positively influence the quality of ed-
ucation in a given country. This paper proposes how it can be accomplished by unveiling the potential of Self-
Sovereign Identity Wallets in federated learning environments such as National Educational Platform. The
specific scenario described in this work is based on the research conducted within the project Bildungsraum
Digital, funded by the NextGenerationEU and German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
1 INTRODUCTION
”Digital technologies can accelerate achievement of
the SDGs but only if governments act now” (Vora and
Ingram, 2023). Not only German Government has
been proactively advocating for and supporting the
United Nations (UN) Sustainable Development Goals
(SDG) in general since the beginning (BMZ, 2023), it
has also undertaken numerous actions such as a) en-
forcing digitization within educational institutions by
passing new laws (BMI, 2024) and b) funding digi-
tization projects such as Nationale Bildungsplattform
(NBP; eng.: “National Education Platform”) (BMBF,
2024), Bildungsraum Digital (BIRD; eng.: “Digi-
tal Educational Space”) (DAAD, 2024), eService-
Agentur Hochschulen Sachsen-Anhalt (eng.: ”eS-
ervice office for higher education Saxony-Anhalt”)
(eSALSA, 2024) and others. This and more has
been done in order to provide German citizens with
a higher level of education, which directly and posi-
tively influences the overall future welfare of a coun-
try (Neumann et al., 2023) and, thus, automatically
committing to the UN SDG Number 4 for Quality
Education. Fulfilling this goal can be accomplished
through various means such as decreasing the bureau-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-4044-5613
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3713-8893
cracy level at educational institutions, abolishing un-
necessary print-outs, reducing the number of accounts
across various systems i.e. making the data storage
more efficient and sustainable. COVID-19 (Coron-
avirus SARS-CoV-2) pandemics, analogue to a lit-
mus test, allowed to clearly identify major sustain-
ability problems in the federated learning environ-
ments. Combating these problems means increasing
the level of digitization among Higher Education In-
stitutions (HEI) (Staegemann. et al., 2022) processes.
This work is undertaking another step towards
tackling the problem of enhancing the level of sustain-
ability within the federated learning environments.
The approach proposed in this paper is to apply Self-
Sovereign Identity (SSI) Wallet technology within
German universities, in order to simplify the technol-
ogy usage (lower the entry barrier) in general, im-
prove university processes, decrease the level of bu-
reaucracy as well as to save human and system re-
sources by decreasing the number of accounts com-
pared to a common current set up at HEI.
The underlying paper is structured as follows.
Subsequently to the introduction, the second part
briefly provides the current state of related research
and past findings in the area of using wallets in the
federated learning environments. Section 3 in de-
tail introduces the concept and architecture of the
BIRD Wallet. It also presents possible use cases
502
Walia, D., Neumann, K., Walia, V., Rathjens, M., Weidner, S. and Turowski, K.
Unveiling the Potential: Assessing the Role of SSI Wallets in Promoting Sustainability in Federated Learning Environments.
DOI: 10.5220/0012693400003693
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2024) - Volume 1, pages 502-509
ISBN: 978-989-758-697-2; ISSN: 2184-5026
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

for sustainable future and how the BIRD Wallet can
be integrated within federated learning environments.
Thereafter, a possible estimation of the current re-
search’s impact is provided in Section 4 along with
a discussion and outlook on possible application sce-
narios for future research. Finally, the paper is sum-
marized in the Conclusion as well as implications
on the operating federated learning environments are
provided.
2 RELATED WORK
This section provides current state-of-the-art in the re-
search related to the usage of mobile wallets in the
federated learning environments such as universities
as well as on whether and how it affects the sustain-
ability aspect.
The federated learning environment can also be
viewed as a federation in which all educational actors
come together to form a group (Guo and Zeng, 2020)
and provide seamless accessibility to a group of edu-
cational services for educational users. For example
Project BIRD (DAAD, 2024).
As stated in the Brundtland’s World Commission
on Environment and Development book by (Brundt-
land, 1987) social, economic, and environmental di-
mensions of sustainability are interdependent. It im-
plies that if one strives to improve sustainability by
affecting the environmental dimension, the other two
dimensions would be affected as well. Substan-
tial research has been done for examining this inter-
dependency.
An empirical study by (Katini et al., 2023) has
examined the factors influencing the relationship be-
tween the mobile wallet use and the environmental
sustainability. The outcome of the study identified
that such factors as perceived security, performance
expectancy and several others positively impact mo-
bile wallet usage and, thus, contribute towards envi-
ronmental sustainability. The authors also state that
mobile wallet usage would reduce all forms of pollu-
tion. However, this paper focuses solely on the mobile
wallets used for payments. There have been several
attempts towards applying SSI technology in educa-
tional domain such as (Kortemeyer, 2022), (Kavas-
salis, 2020) and (Strack et al., 2022). Addition-
ally, a technical exploration provided by Samenwerk-
ende Universitaire Rekenfaciliteiten (eng.: Collabo-
rating University Computing Facilities) (van Dijk and
Rikken, 2023) states that SSI wallet usage offers vari-
ous advantages for education and research, providing
a proof of concept.
2.1 Sustainable University
Sustainable universities play a pivotal role in advanc-
ing Sustainable Development, with HEI assuming a
distinct social responsibility for shaping future lead-
ers’ education and fostering widespread public aware-
ness of sustainability (Amaral et al., 2015). Serv-
ing as catalysts for collaboration between government
and industry (SDSN, 2020), sustainable universities
are characterized by four dimensions: Education, Re-
search, Community Outreach, and Campus Opera-
tions (Alshuwaikhat and Abubakar, 2008).
The evolution from Information and Communica-
tion Technologies to Clean Technologies, which em-
phasize environmentally friendly practices, is notable.
HEI are increasingly embracing digital services, elim-
inating the necessity for physical presence and align-
ing with the principles of clean technologies to pro-
mote sustainability . (Abad-Segura et al., 2020)
In the realm of education, the integration of Digi-
tal Transformation represents a dynamic process that
necessitates an evolution in teaching methodologies.
This transformation aims to enhance the overall edu-
cational experience, fostering efficiency and facilitat-
ing collaboration (Verhoef and Du Toit, 2018). HEI
are adopting hybrid approaches, blending traditional
and virtual spaces, thereby bridging online and of-
fline learning modalities. This shift is indicative of
a broader trend, including contemporary educational
methods such as Do It Yourself education (Abad-
Segura et al., 2020).
Beyond the considerations of physical sustainabil-
ity, another facet of Sustainable Education can be de-
lineated with respect to enduring equitable education
and the promotion of Lifelong Learning.
This second aspect is also included within SDG
Number 4, as the Key elements of the SDG Number 4
are Lifelong Learning Journey and ”by 2030 Ensure
equal access for all men and women to quality techni-
cal, professional and superior training, including uni-
versity education” (United Nations, 2015). Integrat-
ing Digital learning within the institute facilitates the
above goals as well as it also contributes to improved
student academic performance and disabling the need
of the physical classes (Benta et al., 2015).
2.2 Self-Sovereign Identity
SSI epitomizes a paradigm shift in digital identity
management, endowing individuals with the auton-
omy to selectively share information. This not only
imparts a heightened level of security but also stands
in stark contrast to traditional, centralized identity
providers. The decentralized nature of SSI ensures
Unveiling the Potential: Assessing the Role of SSI Wallets in Promoting Sustainability in Federated Learning Environments
503
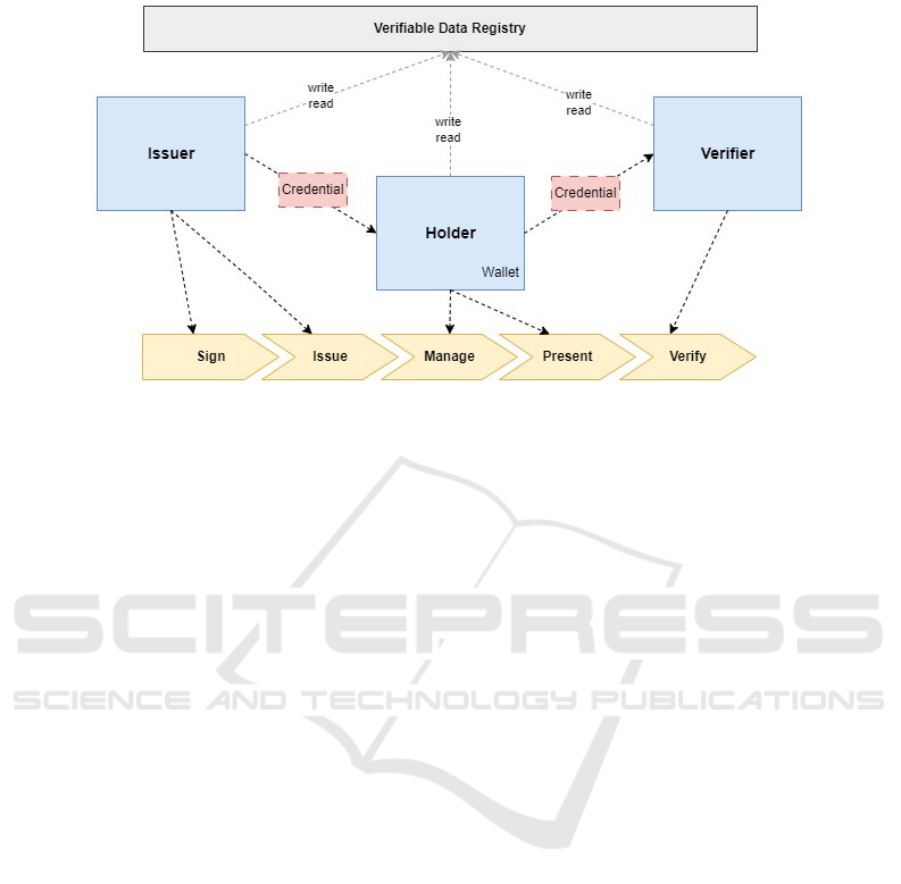
Figure 1: Entities of SSI and trust triangle, taken from (Walt.id, 2024).
individuals maintain control over their personal data,
thereby mitigating the risks inherent in centralized
databases. This enhanced security, coupled with the
individual’s authority to determine the extent of in-
formation disclosure, positions SSI as a robust solu-
tion for digital identity management. Its implications
for privacy and security resonate significantly in our
increasingly interconnected world. (Tobin and Reed,
2016)
SSI comprises of three integral components as
shown in Figure 1:
• Holder. Someone who can receive, manage and
share their digital Verifiable
• Issuer. Party with the authority to issue the digital
Verifiable Credentials (VC)
• Verifier. Party verifying the digital VC
This tripartite structure not only streamlines identity
processes but also reinforces the security and privacy
foundations upon which SSI is built.
2.3 Self-Sovereign Identity in Higher
Education Institutions
A variety of stakeholders are actively working to-
wards integrating SSI wallets within the educational
sector, notably in HEI. These efforts largely empha-
size the efficiency gains brought forth by the digiti-
zation of processes. To realize this goal, the encryp-
tion of data and the establishment of trust are essential
components inherent to the SSI framework (van Dijk
and Rikken, 2023).
However, it remains unclear what potential ex-
ists, or could be achieved, for equitable and Lifelong
Learning through the use of SSI Wallets in the educa-
tional context. These aspects are incorporated into the
use case of the NBP presented in subsequent section.
3 BIRD WALLET
The BIRD project (DAAD, 2024), a prototype initia-
tive under the NBP, has embraced the evolving con-
cept of SSI wallet to facilitate digitalization. The
rationale behind incorporating the SSI wallet in this
project is to establish a robust and sustainable dig-
ital infrastructure specifically tailored for federated
learning environments. To comprehensively explore
the implications of this integration, it is imperative to
delve into the design of the wallet, its seamless inte-
gration with the learning environment, and the various
use cases that contribute to fostering a sustainable fu-
ture.
3.1 Wallet Design
The interoperable BIRD Wallet as depicted in Figure
2, a customized Enmeshed app, maintains a consis-
tent operational principle, as depicted in the layered
architecture of the Enmeshed app illustrated in Figure
3. This wallet incorporates SSI principles, empower-
ing users with control over their data while improv-
ing security through a zero-knowledge backbone ar-
chitecture — without the use of decentralized ledger
technologies such as blockchains. Notably, the back-
bone employs state-of-the-art encryption to store data,
ensuring that even the backbone administrator cannot
access users’ personal data.
The Enmeshed architecture comprises of follow-
CSEDU 2024 - 16th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
504
Figure 2: BIRD Wallet.
ing three main components (Enmeshed, 2024):
• App
The end-user software client provides an applica-
tion for utilizing wallet functionalities. Users can
securely store and share messages and documents
through the free to download wallet app. This
component serves as the interface for interacting
with the wallet, facilitating user engagement and
data management.
• Backbone
Functioning as a centralized encrypted storage
and communication component, the backbone
plays a pivotal role in facilitating message routing
with zero-knowledge. This component serves as
the cornerstone for communication between var-
ious elements of the system and functions as a
data-access, backup, and synchronization helper
for user identities. Notably, the backbone en-
sures robust security measures, preventing even
the backbone administrator from accessing sensi-
tive personal data.
• Connector
Designed as a software client for organizations,
the connector is intended to be hosted on-site for
seamless integration of business logics. It features
a REST API that integrates all wallet function-
alities, and it is responsible for encryption and
decryption on the fly. The connector acts as a
bridge between the wallet and organizational sys-
tems, facilitating secure communication and data
exchange.
The layered diagram and components of the En-
meshed app provide a comprehensive and high-level
overview of the design of the BIRD Wallet. This de-
sign not only emphasizes user-centric features, such
as secure messaging and document sharing but also
underscores the importance of robust security mea-
sures, particularly in the context of zero-knowledge
architecture. The BIRD Wallet, with its tailored im-
plementation within the Enmeshed framework, aims
to strike a balance between user empowerment and
data security, offering a promising solution in the
landscape of digital wallets and identity management
systems.
3.2 Use Cases for Sustainable Future
The preceding research outlines four conceivable sce-
narios for a German National Education Platform cur-
rently undergoing prototyping in the BIRD Lab: clas-
sical learning environments, simulation games, ex-
tracurricular certifications, and the digitization of ad-
ministrative processes (Staegemann. et al., 2022).
These scenarios are centered around HEI, where the
BIRD Wallet reveals several potential use cases:
• Administrator
Receive digital documents or identity data, Re-
ceive course fees, Send notifications, Send digital
VC, Sendreceive queries
• Applicant
Submit digital documents or identity data for
course applications, Pay course fees, Receive no-
tifications or digital VC from the institute, Store
and manage digital VC, Sendreceive queries
• Student
Submit digital assignments, tests, or exams, Re-
ceive notifications from teachers, departments, or
the institute, Receive digital VC from the institute,
Store and manage digital VC, Secure access to
digital educational services, Send/receive queries
• Lecturer
Send lecture material or announcements to stu-
dents, Secure access to digital educational ser-
vices, Send/receive queries
Furthermore, the BIRD platform fosters a fed-
erated learning environment where users can search
Unveiling the Potential: Assessing the Role of SSI Wallets in Promoting Sustainability in Federated Learning Environments
505
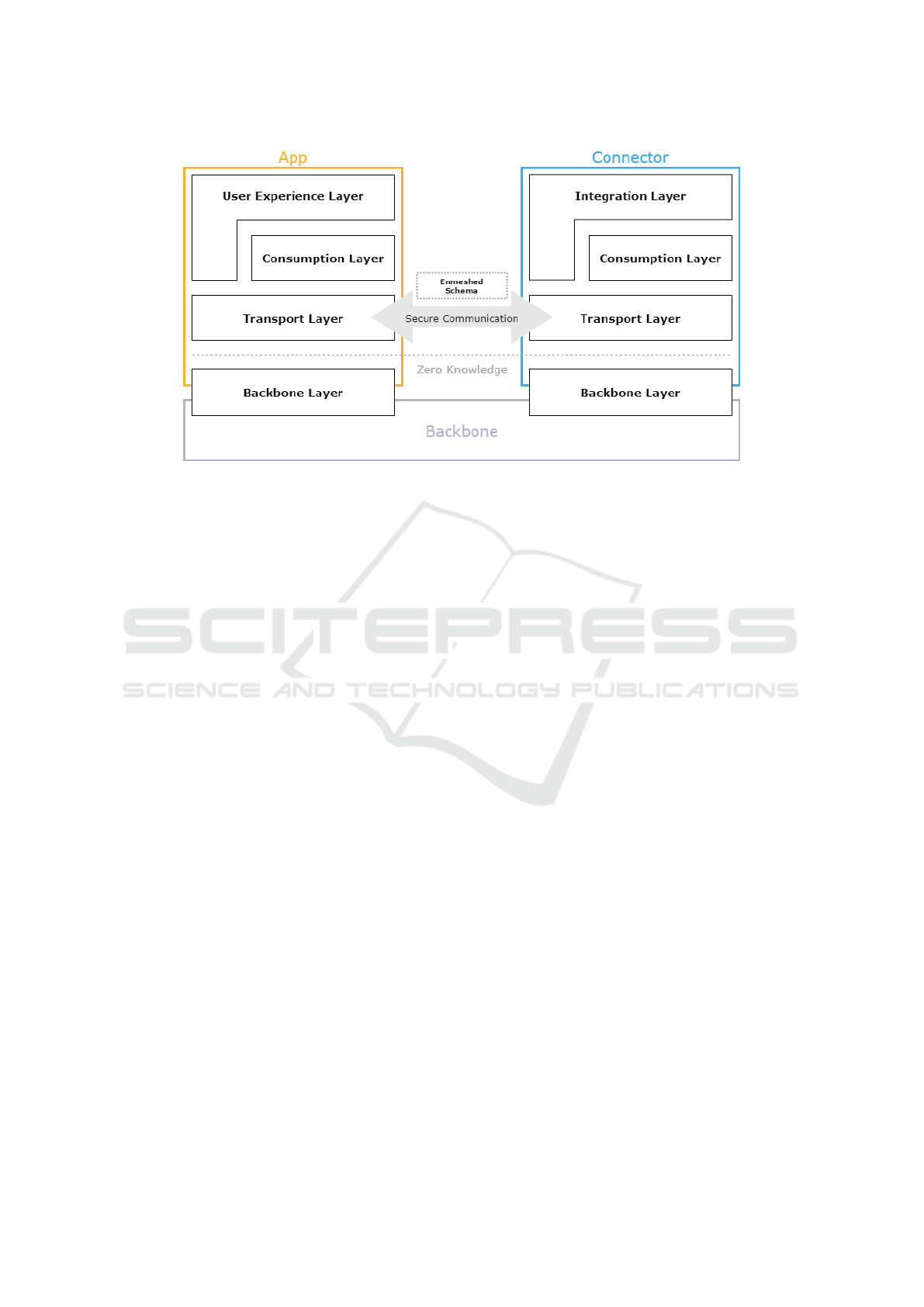
Figure 3: Wallet’s layer architecture, taken from (Enmeshed, 2024).
self-assessment tests, preparatory courses, language
courses, vocational courses, and degree programs us-
ing the ”Learning Path Finder” tool borrowed from
Digitaler Campus (Bock and Jelinski, 2023). Adher-
ing to Privacy by Design principles, the platform en-
sures that user search data is neither stored nor re-
trieved from cookies. Users can also schedule tasks
through the ”Task Scheduler” tool on the BIRD plat-
form, leading to additional use cases for BIRD plat-
form users leveraging the BIRD Wallet:
• Sharing digital VC to facilitate trusted user
searches
• Sharing attributes to filter search results
• Receiving notifications of scheduled tasks
• Secure access to the platform
This delineation underscores the several ways in
which the BIRD Wallet can be integrated into digi-
tal learning infrastructures, envisioning a sustainable
future for education. The seamless alignment of the
BIRD Wallet with diverse user roles and functional-
ities within the educational ecosystem contributes to
its potential as a robust and versatile tool for enhanc-
ing the overall learning experience.
3.3 Integration to Federated Learning
Environment
To actualize the aforementioned use cases, the inte-
gration of the BIRD Wallet with both the BIRD plat-
form and university systems is imperative. The use
cases on the BIRD platform, with the exception of se-
cure access, have already been implemented by seam-
lessly integrating the BIRD Wallet into the platform,
as illustrated in the system architecture depicted in
Figure 4. Adhering to the principles outlined by En-
meshed, the BIRD platform extends features to wallet
users by hosting the wallet connector. The communi-
cation between the hosted connector and wallet takes
place through the secure backbone, which also facili-
tates storage and management functionalities.
The integration with university systems is a criti-
cal step towards the realization of all presented poten-
tial use cases. The blueprint for this implementation is
elucidated in the system architecture diagram in Fig-
ure 5. Existing university systems include the Identity
and Access Manager, Campus Management System,
and Learning systems. Parallel to the integration with
the BIRD platform, a prototypical integration of the
wallet with a Campus Management System has al-
ready been accomplished to enable the sharing of doc-
uments bidirectionally. As part of the BIRD project, a
signature service named Signier Service has been pro-
totyped. Given the criticality of ensuring trust in dig-
ital credentials, the integration of Signier Service is
currently in progress. Simultaneously, efforts are un-
derway to integrate the wallet with learning systems.
In addition to these integrations, an ongoing pre-
liminary study is examining the feasibility of lever-
aging SSI principles for identity management. This
study aims to explore the potential utilization of the
BIRD Wallet in providing secure access in a more
user-centric manner. The exploration of SSI as an
Identity Manager aligns with the broader goals of the
BIRD project, emphasizing a user-centric approach to
secure access and identity management.
In summary, the integration efforts encompass
both the BIRD platform and university systems,
paving the way for a comprehensive implementation
CSEDU 2024 - 16th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
506
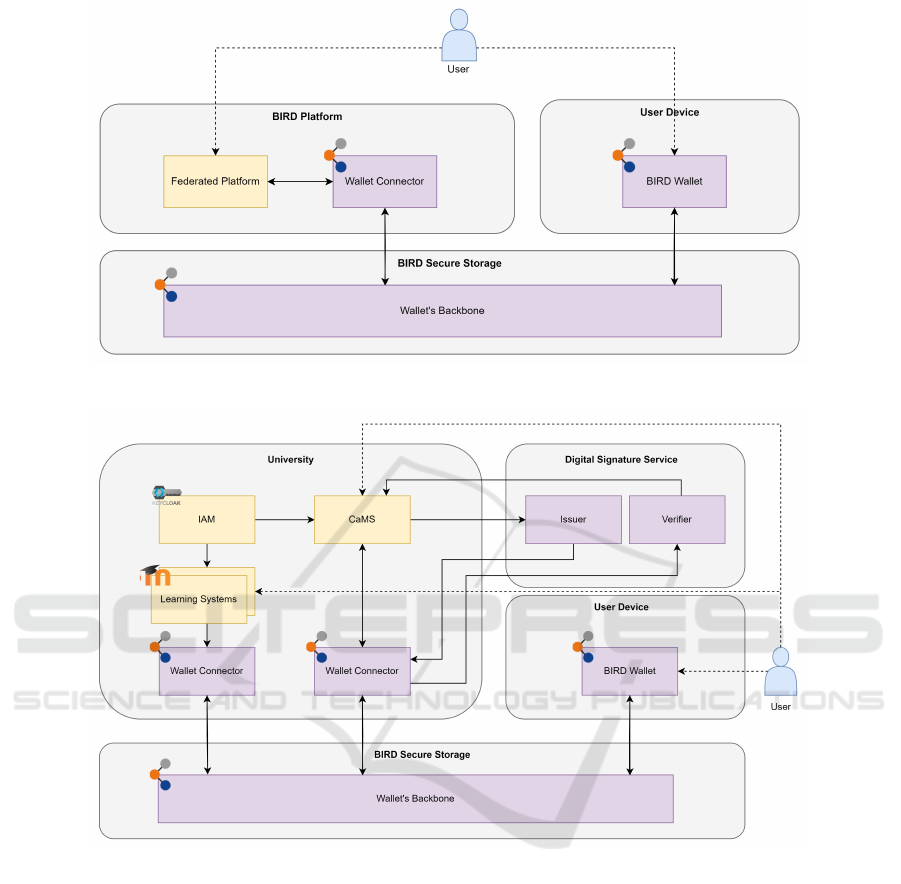
Figure 4: System architecture: BIRD Wallet integration with BIRD platform.
Figure 5: System architecture: BIRD Wallet integration with University systems.
of the BIRD Wallet across diverse use cases. This in-
tegration not only enhances the functionalities avail-
able to users but also contributes to the realization of
a secure, user-centric, and versatile digital learning
ecosystem.
4 DISCUSSION & OUTLOOK
Various parties such as government, academic actors
and businesses are paying close attention to the de-
velopment of the SSI wallets in context of HEI. As
SSI technology offers numerous benefits and advan-
tages, it becomes lucrative also for the educational in-
stitutions to integrate the SSI wallets in their system
landscapes. The related work demonstrates the po-
tential use cases of SSI wallets getting unveiled in ed-
ucational settings to increase security and streamline
processes. Using the potential of this secure and user-
centric technology could lead to not only simplifying
the user experience but also positively impacting the
sustainability aspect within the federated learning en-
vironment.
This paper contributes to the discourse by propos-
ing several application scenarios and use cases, as
well as suggests system architectures for integrating
the SSI wallet. In addition to streamlining process and
increasing security, this approach also exhibits how
SSI wallets can enable digital educational infrastruc-
tures to support Lifelong Learning. It is also conceiv-
Unveiling the Potential: Assessing the Role of SSI Wallets in Promoting Sustainability in Federated Learning Environments
507

able that the integration of SSI wallets into the sys-
tem architectures of HEI could lead to an increased
number of digital teaching offerings. Concomitantly,
the simplification of administrative processes at HEI
may allow access to courses and content for indi-
viduals who, due to their socio-economic situation,
would otherwise be excluded in a present environ-
ment. Thus, the deployment of this technology can
also support equal education and thereby contribute to
the achievement of other sub-goal(s) of SDG Number
4. However, as it is a proposition paper and imple-
mentation is currently in the prototypical state. The
authors have not yet provided any empirical evidence
actually improving the sustainability or measuring by
how much it was improved compared to the existing
system architectures. Further investigations are in-
tended to assess how the integration of SSI wallets
into the federated learning system affects the behav-
ior of stakeholders in education, particularly students.
Consequently, assessing the impact on the sustain-
able future of HEI is a multifaceted task that requires
a comprehensive understanding of the intricacies in-
volved in the integration of SSI wallets.
As (Katini et al., 2023) highlights in their work,
the role of mobile wallets in not only reducing CO2
emissions. Inspired by their methodology in measur-
ing outcomes, for future work we contemplate con-
ducting a survey to gather qualitative feedback on
how the SSI wallet is benefiting educational users in
context of the aforementioned use cases in HEI.
Currently the BIRD project progresses on the pro-
totypical implementation and there will be an open
beta testing phase for the NBP, more steps can be
taken towards measuring the actual impact on sustain-
ability.
5 CONCLUSION
Governments and societies need to equip their cit-
izens with necessary competencies, knowledge and
values crucial for creating a sustainable future to-
gether (UNESCO, 2024). One of the five main focus
areas of UNESCO’s Education for Sustainable Devel-
opment is transforming learning environments in or-
der to promote sustainability. That is precisely what
the BIRD Lab is trying to achieve: providing new
application scenarios for federated learning environ-
ments through innovation and prototypically imple-
menting those.
The publication at hand outlines the BIRD Lab’s
proposal on unveiling the whole potential of what SSI
Wallets offer and how their usage can promote the
sustainability within federated learning environments.
Hereby, the contribution is twofold, on the one hand,
it helps enhancing the digital infrastructure for a sus-
tainable university and, on the other hand, possible
use cases for interoperability are provided. Moreover,
this paper presents how SSI Wallets can be integrated
within BIRD platform and University system land-
scapes in general, thus, providing the foundation for
further research.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
BIRD is funded by the European Union – NextGen-
erationEU through a grant from the Federal Ministry
of Education and Research. The views and opinions
expressed are solely those of the authors and do not
necessarily reflect the views of the European Union
or the European Commission. Neither the European
Union nor the European Commission can be held re-
sponsible for them. The project is conducted in co-
operation with: University of Potsdam, Deutscher
Akademischer Austauschdienst, Technical University
of Berlin, Otto-von-Guericke University of Magde-
burg, Gesellschaft f
¨
ur wissenschaftliche Datenverar-
beitung mbH G
¨
ottingen, Gesellschaft f
¨
ur Akademis-
che Studienvorbereitung und Testentwicklung, edu-
sharing Network, FernUniversit
¨
at in Hagen, B
¨
undnis
f
¨
ur Bildung e.V., Mathplan GmbH and T-Systems.
REFERENCES
Abad-Segura, E., Gonz
´
alez-Zamar, M.-D., Infante-Moro,
J. C., and Ruip
´
erez Garc
´
ıa, G. (2020). Sustain-
able management of digital transformation in higher
education: Global research trends. Sustainability,
12(5):2107.
Alshuwaikhat, H. M. and Abubakar, I. (2008). An inte-
grated approach to achieving campus sustainability:
assessment of the current campus environmental man-
agement practices. Journal of cleaner production,
16(16):1777–1785.
Amaral, L. P., Martins, N., and Gouveia, J. B. (2015).
Quest for a sustainable university: a review. Interna-
tional Journal of Sustainability in Higher Education,
16(2):155–172.
Benta, D., Bologa, G., Dzitac, S., and Dzitac, I. (2015).
University level learning and teaching via e-learning
platforms. Procedia Computer Science, 55:1366–
1373.
BMBF (2024). Erstes pilotprojekt f
¨
ur
nationale bildungsplattform startet.
https://www.bmbf.de/bmbf/de/home/ documents/er-
stes-pilotprojekt-fuer-nationale-bildungsplattform-
startet.html. Accessed: 2024-01-15.
CSEDU 2024 - 16th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
508

BMI (2024). Onlinezugangsge-
setz(ozg): German online access act.
https://www.onlinezugangsgesetz.de/Webs/OZG/EN-
/home/home-node.html. Accessed: 2024-01-15.
BMZ (2023). Sdg4: Hochwertige bildung.
https://www.bmz.de/de/agenda-2030/sdg-4. Ac-
cessed: 2024-01-15.
Bock, S. and Jelinski, J. (2023). Der digitale campus–
unterst
¨
utzung internationaler studieninteressierter und
studierender neu gedacht. Zeitschrift f
¨
ur Hochschu-
lentwicklung, 18(1):131–149.
Brundtland, G. H. (1987). Our common future world com-
mission on environment and developement.
DAAD (2024). Bird: Bildungsraum digital.
https://www.daad.de/en/the-daad/what-we-
do/digitalisation/bird/. Accessed: 2024-01-15.
Enmeshed (2024). Enmeshed app. https://enmeshed.eu/.
Accessed: 2024-01-15.
eSALSA (2024). e-service-agentur der hochschulen in
sachsen-anhalt. https://esalsa.de/. Accessed: 2024-
01-15.
Guo, S. and Zeng, D. (2020). Pedagogical data federation
toward education 4.0. In Proceedings of the 6th In-
ternational Conference on Frontiers of Educational
Technologies, pages 51–55.
Katini, K., Amalanathan, S., and Hriizhiinio, K. (2023).
Can mobile wallet usage contribute towards environ-
mental sustainability? evidence from a moderated me-
diation approach. Universal Access in the Information
Society, pages 1–17.
Kavassalis, P. (2020). Designing an academic electronic
identity management system for student mobility us-
ing eidas eid and self-sovereign identity technologies.
EUNIS.
Kortemeyer, G. (2022). Self-sovereign user scenarios in the
educational domain.
Neumann, K., Walia, D. S., Staegemann, D., H
¨
ausler, R.,
Weidner, S., and Turowski, K. (2023). Towards a
german national education platform. In 2023 In-
ternational Conference on Software, Telecommunica-
tions and Computer Networks (SoftCOM), pages 1–6.
IEEE.
SDSN (2020). Accelerating education for the sdgs in uni-
versities: a guide for universities, colleges, and ter-
tiary and higher education institutions.
Staegemann., D., Degenkolbe., R., Weidner., S., H
¨
ausler.,
R., Lange., V., and Turowski., K. (2022). Possi-
ble application scenarios for a german national ed-
ucation platform. In Proceedings of the 14th Inter-
national Conference on Computer Supported Educa-
tion - Volume 1: CSEDU, pages 361–368. INSTICC,
SciTePress.
Strack, H., Gollnick, M., Karius, S., Lips, M., Wefel, S.,
Altschaffel, R., Bacharach, G., Gottlieb, M., Pon-
gratz, H., Radenbach, W., et al. (2022). Digitization
of (higher) education processes: Innovations, security
and standards. EPiC Series in Computing, 86:22–33.
Tobin, A. and Reed, D. (2016). The inevitable rise
of self-sovereign identity. The Sovrin Foundation,
29(2016):18.
UNESCO (2024). Education for sustainable de-
velopment. https://www.unesco.org/en/sustainable-
developmen/education. Accessed: 2024-01-15.
United Nations (2015). Transforming our
world: the 2030 agenda for sustain-
able development. https://documents-dds-
ny.un.org/doc/UNDOC/GEN/N15/291/89/PDF/N1-
529189.pdf?OpenElement. A/RES/70/1.
van Dijk, N. and Rikken, M. (2023). Ssi wal-
let for education and research - a technical
exploration. https://www.surf.nl/files/2023-
05/technical-exploration-ssi-wallet-for-education-
and-research.pdf. Accessed: 2024-01-15.
Verhoef, A. H. and Du Toit, J. (2018). Embodied digi-
tal technology and transformation in higher education.
Transformation in Higher Education, 3(1):1–8.
Vora, P. and Ingram, G. (2023). A pact to sustain digital
public infrastructure for the sdgs.
Walt.id (2024). Walt.id ssi: Self-sovereign identity.
https://docs.walt.id/v/ssikit/ssi-kit/what-is-ssi. Ac-
cessed: 2024-01-15.
Unveiling the Potential: Assessing the Role of SSI Wallets in Promoting Sustainability in Federated Learning Environments
509
