
Evaluating the Impact of Generative Adversarial Network in Android
Malware Detection
Fabio Martinelli
1
, Francesco Mercaldo
2,1
and Antonella Santone
2
1
Institute for Informatics and Telematics, National Research Council of Italy (CNR), Pisa, Italy
2
Department of Medicine and Health Sciences “Vincenzo Tiberio”, University of Molise, Campobasso, Italy
Keywords:
Malware, Deep Learning, GAN, Android, Security.
Abstract:
The recent development of Generative Adversarial Networks demonstrated a great ability to generate images
indistinguishable from real images, leading the academic and industrial community to pose the problem of
recognizing a fake image from a real one. This aspect is really crucial, as a matter of fact, images are used in
many fields, from video surveillance but also to cybersecurity, in particular in malware detection, where the
scientific community has recently proposed a plethora of approaches aimed at identifying malware applications
previously converted into images. In fact, in the context of malware detection, using a Generative Adversarial
Network it might be possible to generate examples of malware applications capable of evading detection
by antimalware (and also able to generate new malware variants). In this paper, we propose a method to
evaluate whether the images produced by a Generative Adversarial Network, obtained starting from a dataset of
malicious Android applications, can be distinguishable from images obtained from real malware applications.
Once the images are generated, we train several supervised machine learning models to understand if the
classifiers are able to discriminate between real malicious applications and generated malicious applications.
We perform experiments with the Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network, a type of Generative
Adversarial Network, showing that currently the images generated, although indistinguishable to the human
eye, are correctly identified by a classifier with an F-Measure greater than 0.8. Although most of the generated
images are correctly identified as fake, some of them are not recognized as such, they are therefore considered
images generated by real applications.
1 INTRODUCTION AND
RELATED WORK
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a class
of neural networks utilized in unsupervised machine
learning. They consist of two opposing components:
a generator, responsible for producing synthetic data,
and a discriminator (or cost network), tasked with dis-
cerning real data from the generated fakes. The gener-
ator and discriminator engage in a competition where
the generator aims to deceive the discriminator with
realistic data, while the discriminator seeks to iden-
tify the real from the fake.
This adversarial interplay fosters the learning of
a generator that can create remarkably authentic data
samples. Once the GAN is trained on a specific
dataset, it becomes capable of tasks like future pre-
diction or image generation with high fidelity. How-
ever, GANs find broader applications across vari-
ous domains, including style transfer, data augmenta-
tion, text generation, and video synthesis(Goodfellow
et al., 2020).
Recently, there has been a growing interest in
the application of GANs in the field of cybersecu-
rity. The rationale behind this interest is quite appar-
ent: by generating deceptive data that closely resem-
bles authentic information, GANs offer a way to ex-
ploit vulnerabilities in security systems. This process
is known as ”evasion,” wherein the security system
fails to detect the falsified data, leading to a success-
ful breach. Biometric authentication systems, among
others, can be particularly susceptible to such attacks.
The danger posed by adversarial technologies pri-
marily lies in their ability to bypass alarms and ac-
cess control mechanisms that have been trained using
available data. Consequently, they pose a significant
threat to defensive systems. However, it’s worth not-
ing that these very same adversarial technologies can
also be used as a defensive tool. By leveraging GANs
and related techniques, security experts can design
590
Martinelli, F., Mercaldo, F. and Santone, A.
Evaluating the Impact of Generative Adversarial Network in Android Malware Detection.
DOI: 10.5220/0012699000003687
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE 2024), pages 590-597
ISBN: 978-989-758-696-5; ISSN: 2184-4895
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

anomaly detection and authentication systems that are
more resilient against such attacks. In this context,
GANs serve as a valuable asset in fortifying cyberse-
curity measures.
Lately, with the advancement of deep learning and
its capacity to construct models proficient in image-
related tasks (Mercaldo et al., 2022; Huang et al.,
2024a; Huang et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2023; Huang
et al., 2021), various approaches have emerged to de-
tect malware using deep learning techniques. These
methodologies leverage the power of deep learning
to achieve effective classification performance (Sun
et al., 2021; Mercaldo et al., 2021; Huang et al.,
2024b), especially when dealing with image-based
data in the context of malware detection(Iadarola
et al., 2021).
Starting from these considerations, in this paper
we propose a method aimed to understand whether
GANs can represent a threat to image-based malware
detection. In particular, we consider a Deep Convolu-
tional Generative Adversarial Network (DCGAN) to
generate a set of images starting from a dataset of im-
ages obtained from Android malware. To the best of
the author’s knowledge, this paper represents the first
attempt to generate images related to Android mal-
ware. As a matter of fact, only the paper published by
Nguyen et al.(Nguyen et al., 2023) proposes the eval-
uation of malware images generated by a GAN, but
relating to PC malware and not to mobile ones. With
the aim to evaluate the quality of the fake images, we
build several machine learning models aimed to dis-
criminate between real and fake images.
The paper proceeds as follows: in Section 2 we
describe the method we designed and implemented to
understand whether DCGAN is able to generate im-
ages related to Android malware applications that are
indistinguishable from the real ones; the results of the
experimental analysis are shown in Section 3 and, fi-
nally, conclusion and future works are drawn in the
last section.
2 THE METHOD
In this section, we introduce our devised method to
accomplish two objectives: (i) generating images as-
sociated with Android malware applications and (ii)
distinguishing these synthetic images from images
obtained from real-world Android malware instances.
To generate an image from an application, we
have developed a Python script that focuses on ex-
tracting byte values from a binary executable and sub-
sequently creating the corresponding grayscale im-
age.
Figure 1 shows the image generation workflow.
To transform a binary into an image, we inter-
pret the sequence of bytes (Bit Vectors in Figure 1)
that represents the binary as the bytes of a grayscale
PNG image (Greyscale Pixel in Figure 1). For this
conversion, we adopt a predetermined width of 256
and a variable length based on the size of the binary.
To achieve this, we have designed a script capable
of encoding any binary file into a lossless PNG for-
mat(Mercaldo and Santone, 2020).
In essence, the script operates through the follow-
ing steps:
• the binary file’s individual bytes are converted
into numerical values (ranging from 0 to 255),
which will subsequently determine the pixel
color(Greyscale Pixel in Figure 1);
• each byte corresponds to a grayscale pixel in the
resultant PNG image (Application Image in Fig-
ure 1).
After obtaining the images from real-world An-
droid applications, the subsequent step in the pro-
posed method involves employing DCGAN to gen-
erate fake images associated with Android applica-
tions: this second step related to the proposed method
is shown in Figure 2.
In every GAN, there is a minimum of one gen-
erator (Generator in Figure 2) and one discrimina-
tor (Discriminator in Figure 2). As the generator and
discriminator engage in their adversarial competition,
the generator refines its capacity to produce images
that closely align with the distribution of the training
data, thanks to the feedback received from the dis-
criminator.
The DCGAN introduced a GAN architecture that
utilizes CNNs to define the discriminator and genera-
tor.
DCGAN offers several architectural guidelines
aimed at improving training stability(Radford et al.,
2015):
1. substituting pooling layers with strided convolu-
tions in the discriminator and fractional-strided
convolutions in the generator;
2. incorporating batch normalization (batchnorm) in
both the generator and discriminator;
3. removing fully connected hidden layers in deeper
architectures;
4. employing ReLU activation for all generator lay-
ers except the output, which utilizes Tanh;
5. employing LeakyReLU activation in all discrimi-
nator layers.
Evaluating the Impact of Generative Adversarial Network in Android Malware Detection
591
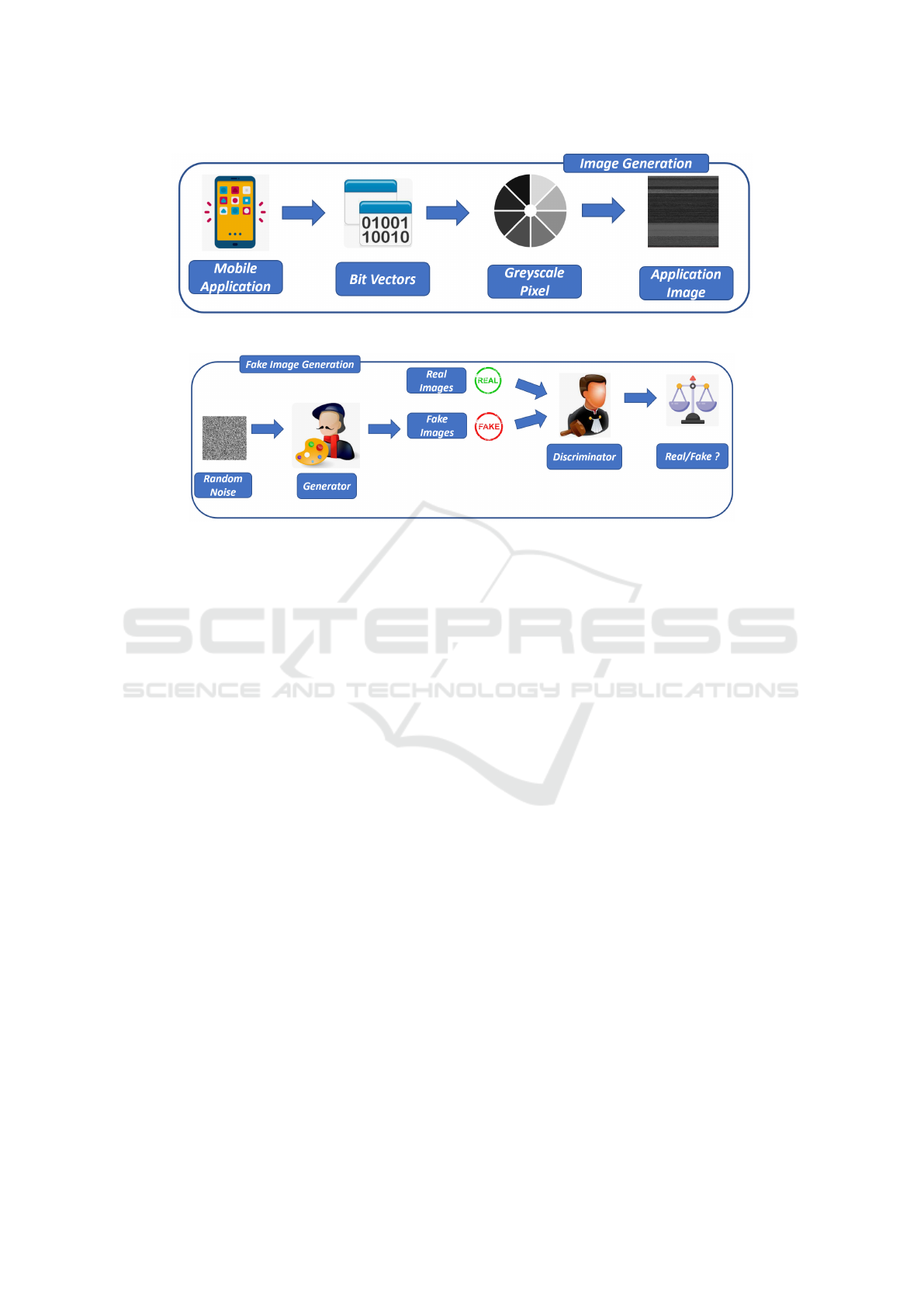
Figure 1: The Image Generation step.
Figure 2: The Fake Image Generation step.
In DCGAN, we make use of batch normalization
(batchnorm) in both the generator and the discrimina-
tor to enhance the stability of GAN training. Batch-
norm operates by standardizing the input layer, ensur-
ing it has a mean of zero and a variance of one. Typi-
cally, batchnorm is inserted after the hidden layer and
before the activation layer.
Within the DCGAN generator and discriminator,
four frequently utilized activation functions are: sig-
moid, tanh, ReLU, and LeakyReLU.
We conduct the training of the generator and dis-
criminator networks concurrently.
The initial stage involves preparing the data for
training. In the case of training a DCGAN, there is no
need to divide the dataset into training, validation, and
testing sets since we are not employing the generator
model for a classification task. A set of images ob-
tained from real-world Android malware are obtained
with the procedure shown in Figure 1.
The generator necessitates input images in the for-
mat (60000, 28, 28), which signifies that there are
60,000 training grayscale images with dimensions of
28x28. The loaded data possesses the shape (60000,
28, 28) since it is in grayscale format.
In order to ensure compatibility with the genera-
tor’s final layer activation, which uses tanh, we nor-
malize the input images to fall within the range of [-1,
1].
The main objective of the generator is to create
realistic images and trick the discriminator into per-
ceiving them as authentic.
The generator takes random noise as input and
generates an image that closely resembles the train-
ing images. Given that we are generating grayscale
images with dimensions of 28x28, the model archi-
tecture must ensure that the generator’s output has a
shape of 28x28x1.
To accomplish this, the generator undertakes the
following steps:
1. it transforms the 1D random noise (latent vector)
into a 3D shape using the Reshape layer;
2. the generator repeatedly upsamples the noise
by employing the Keras Conv2DTranspose layer
(also known as fractional-strided convolution in
the paper) to achieve the desired output image
size, which, in our case, is a grayscale image with
dimensions of 28x28x1.
The generator comprises several crucial layers
that serve as its fundamental building blocks:
1. Dense (fully connected) layer: primarily used for
reshaping and flattening the noise vector.
2. Conv2DTranspose: employed to upscale the im-
age during the generation process.
3. BatchNormalization: utilized to enhance training
stability, positioned after the convolutional layer
and before the activation function.
Within the generator, ReLU activation is applied
to all layers, excluding the output layer, which utilizes
tanh activation.
ENASE 2024 - 19th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
592

We developed a function for building the gen-
erator model architecture, which model summary is
shown in Table 1.
To construct the generator model, we utilized the
Keras Sequential API. Initially, we added a Dense
layer to facilitate reshaping the input into a 3D for-
mat. It is crucial to specify the input shape within this
initial layer of the model architecture.
Afterward, we incorporated the BatchNormaliza-
tion and ReLU layers into the generator model. Sub-
sequently, we reshaped the preceding layer from 1D
to 3D and performed two upsampling operations us-
ing Conv2DTranspose layers with a stride of 2. This
process enabled us to progress from a 7x7 size to
14x14 and finally to 28x28, achieving the desired im-
age dimensions.
Following each Conv2DTranspose layer, we in-
cluded a BatchNormalization layer, followed by a
ReLU layer.
Lastly, we utilized a Conv2D layer with a tanh ac-
tivation function.
The generator model comprises a total of
2,343,681 parameters, out of which 2,318,209 are
trainable, while the remaining 25,472 are non-
trainable parameters.
Next, we delve into the implementation of the dis-
criminator model.
The discriminator functions as a simple binary
classifier, responsible for discerning whether an im-
age is real or fake. Its primary goal is to precisely
classify the provided images.
Nevertheless, there are a few differences between
a discriminator and a typical classifier:
1. we employ the LeakyReLU activation function in
the discriminator;
2. the discriminator deals with two categories of in-
put images: real images sourced from the training
dataset labeled as 1, and fake images generated by
the generator labeled as 0.
It is worth noting that the discriminator network is
usually smaller or simpler in comparison to the gener-
ator. This is due to the fact that the discriminator has a
relatively easier task than the generator. In fact, if the
discriminator becomes too powerful, it may impede
the progress and improvement of the generator.
Table 2 shows the model summary related to the
discriminator model.
To build the discriminator model, we will once
more define a function. The input to the discrimi-
nator comprises either real images (from the training
dataset) or fake images generated by the generator.
These images have a size of 28x28x1, and we pass
the arguments (width, height, and depth) to the func-
tion accordingly.
During the construction of the discriminator
model, we implement Conv2D, BatchNormalization,
and LeakyReLU layers twice for downsampling. Sub-
sequently, we incorporate the Flatten layer and apply
dropout. Finally, in the last layer, we employ the sig-
moid activation function to produce a single value for
binary classification.
The discriminator model consists of 213,633 pa-
rameters, with 213,249 being trainable parameters
and 384 being non-trainable parameters.
Calculating the loss is a crucial aspect of training
both the generator and discriminator models in DC-
GAN (or any GAN).
In the context of the DCGAN being considered,
we adopt the modified minimax loss, which involves
utilizing the binary cross-entropy (BCE) loss func-
tion.
We need to compute two distinct losses: one for
the discriminator and another for the generator.
Concerning the Discriminator Loss, as the dis-
criminator receives two sets of images (real and fake),
we will compute the loss for each group indepen-
dently and then merge them to obtain the overall dis-
criminator loss.
TotalDloss = loss f rom real images +
loss f rom f ake images
With regard to the generator loss, rather than
training G to minimize log(1 − D(G(z)) i.e., to en-
hance the probability of the discriminator, D, cor-
rectly classifying fake images as fake, we focus on
training the generator, G, to maximize this probabil-
ity logD(G(z)) i.e., the probability that D incorrectly
classifies the fake images as real: this the modified
minimax loss we exploit.
To enhance the probability of the discriminator, D,
correctly classifying fake images as fake, we focus on
training the generator, G, to maximize this probabil-
ity.
The training process consists of 50 epochs.
Once generated the images with the DCGAN, the
last step of the proposed method, shown in Figure 3
is devoted to build models aimed to discriminate be-
tween real and fake images related to Android mal-
ware applications.
As shown in the third step of the proposed method
in Figure 3, to build a model aimed to discern between
generated and real images we need two datasets: the
first one is composed by images obtained from An-
droid malware (Real Images in Figure 3), the second
one composed by images generated from the DGCAN
shown in Figure 2 (Generated Images in Figure 3).
The real images are the same we exploited in step two
of the proposed method (i.e., fake image generation
in Figure 2). From the two sets of images, we extract
Evaluating the Impact of Generative Adversarial Network in Android Malware Detection
593

Table 1: Model Generator.
# Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
1 dense (Dense) (None, 12544) 1266944
2 batch normalization (BatchNormalization) (None, 12544) 50176
3 re lu (ReLU) (None, 12544) 0
4 reshape (Reshape) (None, 7, 7, 256) 0
5 conv2d transpose (Conv2DTranspose) (None, 14, 14, 128) 819328
6 batch normalization 1 (BatchNormalization) (None, 14, 14, 128) 512
7 re lu 1 (ReLU) (None, 14, 14, 128) 0
8 conv2d transpose 1 (Conv2DTranspose) (None, 28, 28, 64) 204864
9 batch normalization 2 (BatchNormalization) (None, 28, 28, 64) 256
10 re lu 2 (ReLU) (None, 28, 28, 64) 0
11 conv2d (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 1) 1601
Table 2: Model Discriminator.
# Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
1 conv2d 1 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 64) 1664
2 batch normalization 3 (BatchNormalization) (None, 14, 14, 64) 256
3 leaky re lu (LeakyReLU) (None, 14, 14, 64) 0
4 conv2d 2 (Conv2D) (None, 7, 7, 128) 204928
5 batch normalization 4 (BatchNormalization) (None, 7, 7, 128) 512
6 leaky re lu 1 (LeakyReLU) (None, 7, 7, 128) 0
7 flatten (Flatten) (None, 6272) 0
8 dropout (Dropout) (None, 6272) 0
9 dense 1 (Dense) (None, 1) 6273
Figure 3: The Fake Image Detection step.
a set of numeric features using the Simple Color His-
togram Filter. This filter is designed to compute the
histogram representing the pixel frequencies of each
image. By applying this filter, we extract 64 numeric
features from each image.
After obtaining the feature set from both the gen-
erated and real images, we use these features as inputs
to a supervised machine learning algorithm. The pur-
pose is to create a model capable of detecting whether
an image is related to a fake or real application (i.e.,
Fake Detection in Figure 3).
Obviously, if the classifiers exhibit optimal per-
formance, the generated images will be significantly
different from the original ones, otherwise, the ma-
chine learning models will not be able to distinguish
the original images from the generated ones.
Considering that we train the GAN for 50 epochs,
we build a model for each epoch, to understand if
during the various phases of GAN training images
more similar to the originals are gradually generated.
For this reason, considering that for conclusion valid-
ity we exploit four different machine learning algo-
rithms, we consider 50 x 4 = 200 different models in
the experimental analysis.
3 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS
In this section, we present and analyze the results of
the experimental analysis.
ENASE 2024 - 19th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
594
This experiment aims to show whether GANs can
currently be considered a threat to mobile malware
detector deep learning based. For this reason, af-
ter having appropriately generated a series of images
through a DCGAN, we trained several classifiers, in
order to understand if they are able to distinguish be-
tween malware and trusted applications. Since the
DCGAN generates a series of images at each epoch,
the performance of the models to distinguish between
images of real applications and fake images is shown,
in order to understand whether as the epochs increase,
given that images are presumably generated more
similar to the real ones, the performance of the classi-
fiers (aimed to distinguish between real and fake ap-
plication image) should decrease in case the classifier
fails to correctly identify the real images from the fake
ones.
With the aim to generate images related to An-
droid malware, we exploit a dataset composed by
1000 real-world Android malicious applications (and,
thus, we generated 1000 images related to real-world
applications), among 71 malware families with the
aim to cover the current landscape of Android mal-
ware(Li et al., 2017).
The DCGAN is trained for 50 epochs and each
epoch requires approximately 25 seconds in the ex-
perimental analysis (where we exploited the NVIDIA
T4 Tensor Core GPU). We set the DCGAN to gener-
ate, for each epoch, 1000 fake images.
Four different widespread supervised machine
learning classifiers are exploited with the aim to en-
force conclusion validity: J48, SVM, RandomForest,
and Bayes. For each algorithm, we built a model for
each epoch, for a total of 4 models x 50 epochs = 200
different models. Each model is built with the im-
ages obtained from real-world applications and with
the image generated for a certain epoch.
We consider a cross-validation value of k=10 for
model training and testing.
Table 3 shows the experimental analysis results
obtained with the procedure previously explained.
For each epoch, we obtain 1000 images generated
by the GAN, we generate a model (with the 1000 fake
images and the 1000 real ones) and we report for the
model the Precision, Recall, and F-Measure values.
In Table 3 we show the experimental analysis re-
sults: for the reason of space we report the results
related to three epochs: the first one (i.e., 0 in the
column Epoch), the middle one (i.e., 25 in the col-
umn Epoch) and the final one (i.e., 49 in the column
Epoch), with the aim to understand the general trend.
From the results shown in Table 3 we can ob-
serve that the performances of Precision, Recall, and
F-Measure are quite similar for all the epochs (as
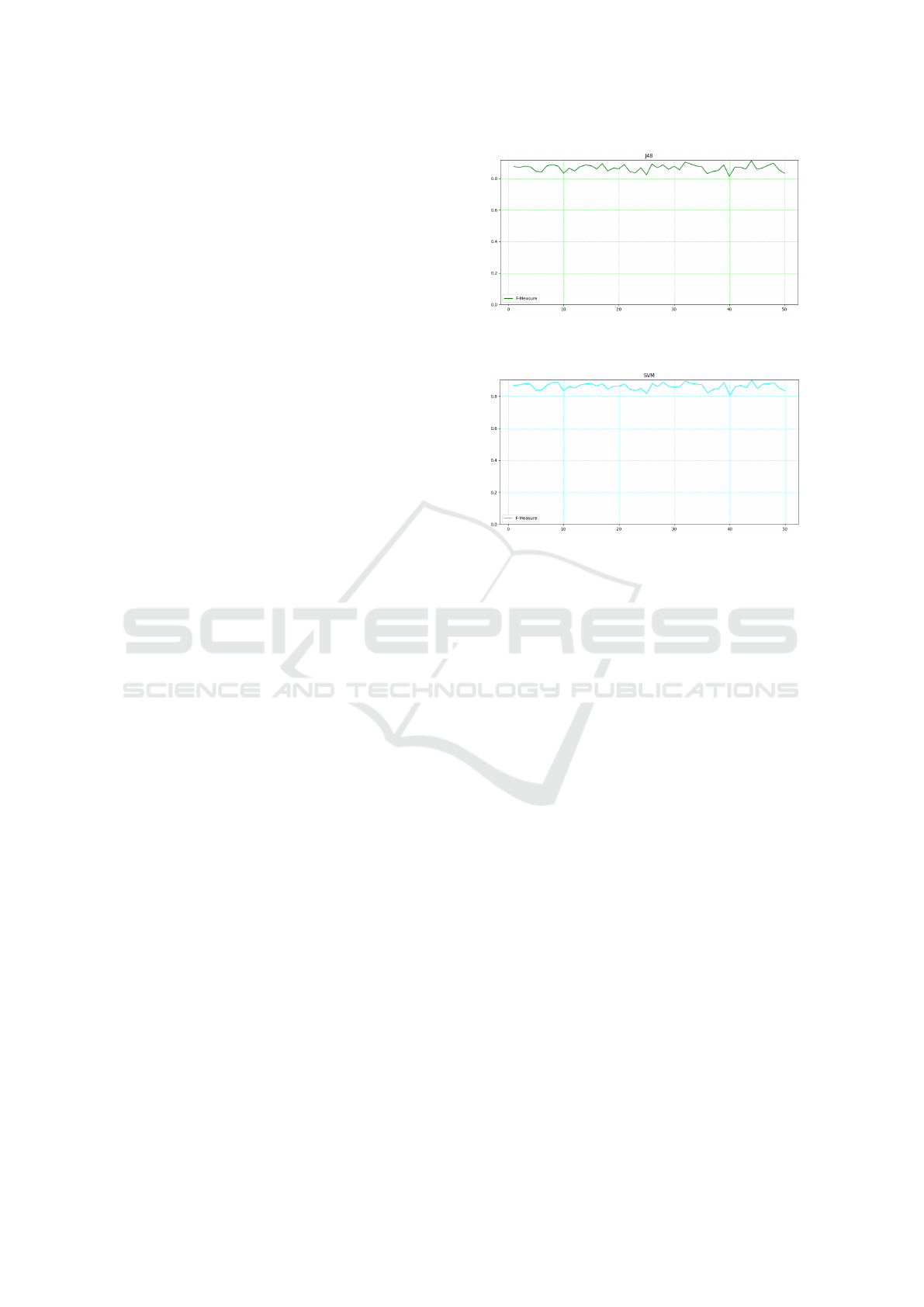
Figure 4: The F-Measure trend, obtained with the J48
model,for the 50 epochs.
Figure 5: The F-Measure trend, obtained with the SVM
model, for the 50 epochs.
a matter of fact, all the values are great than 0.8):
there are no substantial differences between the per-
formances obtained with the models trained with im-
ages obtained with the 25 epoch exams or the 50-th.
This behavior is symptomatic of the fact that the
images generated during the various epochs are no
longer similar to the real ones as the epochs increase.
Furthermore, the values of Precision, Recall, and F-
Measure obtained in any case leave it understood that
a part of fake applications is not correctly recognized
by the various classifiers, even when they are gener-
ated in the initial epochs.
To better understand the trend of the classifiers
during the several epochs, in Figures 4, 5, 6, 7 we
show the plot of the F-Measure trend for the 50
epochs, respectively, for the J48 model (shown in Fig-
ure 4), the SVM model (shown in Figure 5), the Ran-
domForest one (shown in Figure 6) and the Bayes
model (shown in Figure 7)
From the plots shown in Figures 4, 5, 6, 7 we can
observe that there is no presence of a particular trend,
as a matter of fact, the F-Measure, for all the models
involved in the experiment, is stable to value greater
than 0.8 and this happens regardless of the epoch.
From the machine learning model point of view, as the
epochs increase, images that are more similar to the
real ones are not generated, and this aspect is noted
by F-Measure values which are extremely similar in
all epochs (both the initial and the final ones). This
behavior is found in all four models used, so we can
Evaluating the Impact of Generative Adversarial Network in Android Malware Detection
595
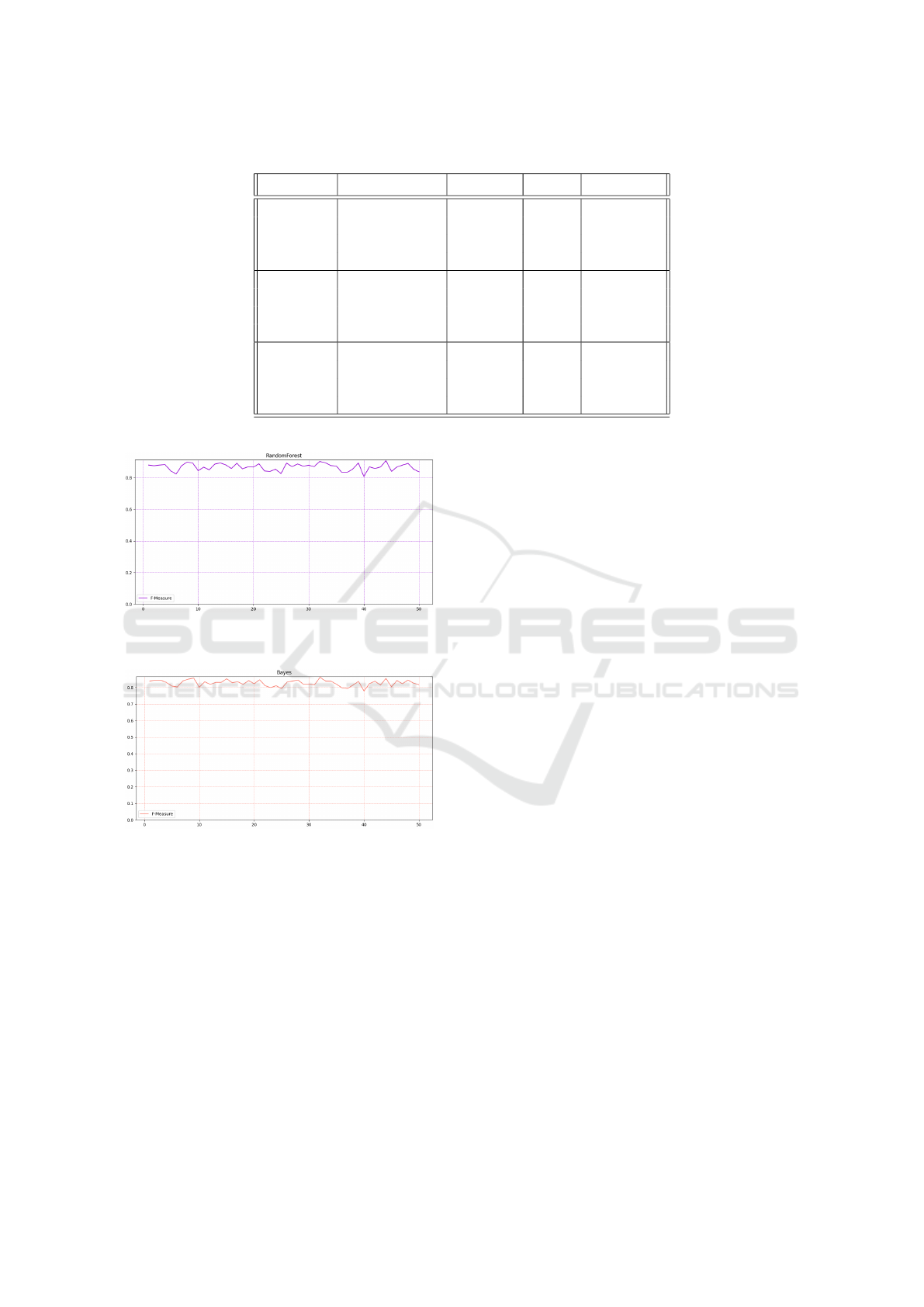
Table 3: Experimental analysis results for the 0, 25, and 49 epochs.
Epoch Algorithm Precision Recall F-Measure
0
J48 0,877 0,876 0,876
SVM 0,870 0,869 0,869
RandomForest 0,880 0,880 0,880
Bayes 0,839 0,838 0,838
25
J48 0,892 0,892 0,892
SVM 0,880 0,879 0,879
RandomForest 0,892 0,892 0,892
Bayes 0,832 0,832 0,832
49
J48 0,835 0,833 0,833
SVM 0,836 0,835 0,835
RandomForest 0,837 0,837 0,837
Bayes 0,816 0,816 0,816
Figure 6: The F-Measure trend, obtained with the Random-
Forest model, for the 50 epochs.
Figure 7: The F-Measure trend, obtained with the Bayes
model, for the 50 epochs.
conclude that this is a general trend and not specific
to a single classification algorithm. For this reason,
it is possible to conclude that, due to the current state
of the art of GANs, they do not currently represent a
threat, as a classifier is able to discriminate between
real images and fake images with quite good perfor-
mances. On the other hand, however, we highlight
that a small percentage of images manage to evade the
controls and, for this reason, to elude detection, and
this aspect in the future could actually pose a threat in
the context of image-based malware detection.
4 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
Considering the ability of GANs to generate images
that are indistinguishable from the human eye, the
need arises to understand if they can pose a threat
to image recognition-based systems, including mal-
ware detection that analyzes suitably converted ap-
plications through deep learning in images. We pro-
posed a method aimed to evaluate whether the im-
ages (related to Android malware applications) gener-
ated by a DCGAN can be discriminated by real ones.
Once we generated the images we resort to four dif-
ferent supervised machine-learning algorithms to un-
derstand whether it is possible to build a model aimed
to discriminate between real images (obtained from
Android malware) and fake images. The experimen-
tal analysis showed that all the supervised models
we considered are able to discriminate real images
from fake ones with an F-Measure greater than 0.80,
therefore on the one hand demonstrating that most of
the fake images are recognized, but with the aware-
ness that several images related to Android malware
manage to evade the fake detection models. In fu-
ture work, we plan to consider other kinds of im-
ages obtained, for instance, from the malware sys-
tem call trace and we will evaluate other GANs, for
instance, the conditional generative adversarial net-
work and the cycle-consistent generative adversarial
network to compare the obtained results with the one
shown by the DGCAN exploited in this paper.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially supported by EU DUCA,
EU CyberSecPro, SYNAPSE, PTR 22-24 P2.01 (Cy-
ENASE 2024 - 19th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
596

bersecurity) and SERICS (PE00000014) under the
MUR National Recovery and Resilience Plan funded
by the EU - NextGenerationEU projects.
REFERENCES
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B.,
Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., and Ben-
gio, Y. (2020). Generative adversarial networks. Com-
munications of the ACM, 63(11):139–144.
Huang, P., Li, C., He, P., Xiao, H., Ping, Y., Feng, P., Tian,
S., Chen, H., Mercaldo, F., Santone, A., et al. (2024a).
Mamlformer: Priori-experience guiding transformer
network via manifold adversarial multi-modal learn-
ing for laryngeal histopathological grading. Informa-
tion Fusion, page 102333.
Huang, P., Tan, X., Zhou, X., Liu, S., Mercaldo, F., and
Santone, A. (2021). Fabnet: fusion attention block
and transfer learning for laryngeal cancer tumor grad-
ing in p63 ihc histopathology images. IEEE Journal
of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 26(4):1696–
1707.
Huang, P., Xiao, H., He, P., Li, C., Guo, X., Tian, S.,
Feng, P., Chen, H., Sun, Y., Mercaldo, F., et al.
(2024b). La-vit: A network with transformers con-
strained by learned-parameter-free attention for in-
terpretable grading in a new laryngeal histopathol-
ogy image dataset. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and
Health Informatics.
Huang, P., Zhou, X., He, P., Feng, P., Tian, S., Sun, Y., Mer-
caldo, F., Santone, A., Qin, J., and Xiao, H. (2023).
Interpretable laryngeal tumor grading of histopatho-
logical images via depth domain adaptive network
with integration gradient cam and priori experience-
guided attention. Computers in Biology and Medicine,
154:106447.
Iadarola, G., Martinelli, F., Mercaldo, F., and Santone, A.
(2021). Towards an interpretable deep learning model
for mobile malware detection and family identifica-
tion. Computers & Security, 105:102198.
Li, Y., Jang, J., Hu, X., and Ou, X. (2017). Android mal-
ware clustering through malicious payload mining. In
Research in Attacks, Intrusions, and Defenses: 20th
International Symposium, RAID 2017, Atlanta, GA,
USA, September 18–20, 2017, Proceedings, pages
192–214. Springer.
Mercaldo, F., Martinelli, F., and Santone, A. (2021). A pro-
posal to ensure social distancing with deep learning-
based object detection. In 2021 International Joint
Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pages 1–5.
IEEE.
Mercaldo, F. and Santone, A. (2020). Deep learning
for image-based mobile malware detection. Jour-
nal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques,
16(2):157–171.
Mercaldo, F., Zhou, X., Huang, P., Martinelli, F., and San-
tone, A. (2022). Machine learning for uterine cervix
screening. In 2022 IEEE 22nd International Confer-
ence on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE),
pages 71–74. IEEE.
Nguyen, H., Di Troia, F., Ishigaki, G., and Stamp, M.
(2023). Generative adversarial networks and image-
based malware classification. Journal of Computer
Virology and Hacking Techniques, pages 1–17.
Radford, A., Metz, L., and Chintala, S. (2015). Unsu-
pervised representation learning with deep convolu-
tional generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1511.06434.
Sun, X., Li, L., Mercaldo, F., Yang, Y., Santone, A., and
Martinelli, F. (2021). Automated intention mining
with comparatively fine-tuning bert. In Proceedings
of the 2021 5th International Conference on Natu-
ral Language Processing and Information Retrieval,
pages 157–162.
Zhou, X., Tang, C., Huang, P., Tian, S., Mercaldo, F., and
Santone, A. (2023). Asi-dbnet: an adaptive sparse
interactive resnet-vision transformer dual-branch net-
work for the grading of brain cancer histopathological
images. Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational
Life Sciences, 15(1):15–31.
Evaluating the Impact of Generative Adversarial Network in Android Malware Detection
597
