
Security Analysis for BB84 Key Distillation
Sara Nikula
1 a
, Anssi Lintulampi
1 b
and Kimmo Halunen
2 c
1
VTT Technical Research Center of Finland, Oulu, Finland
2
University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
fi fi fi
Keywords:
Quantum Key Distribution, BB84, Classical Post-processing, Key Distillation, Security Analysis.
Abstract:
Key distillation, also referred to as classical post-processing, plays a pivotal role in Quantum Key Distribution
(QKD) protocols. Key distillation encompasses numerous subroutines, making the analysis of its overall
security implications potentially challenging for those outside the research community. In this paper, we
elucidate the role of the key distillation phase in QKD from a security standpoint. We begin by analyzing the
different components of the key distillation phase individually, followed by an examination of the process as
a whole. We then calculate the bit strength of the produced key, assuming that an attacker is executing an
intercept and resend attack. For our analysis, we employ a practical key distillation implementation linked to
a decoy state BB84 protocol as a case study. Our findings suggest that the security of the final key, post the
key distillation phase, hinges on several factors. These include the theoretical security of the implemented
subroutines, the total information leakage throughout the process, and the choices of subroutine parameters.
Given these assumptions, we can distill 287 secure bits for every 1000 bits that undergo the key distillation
procedure.
1 INTRODUCTION
To facilitate confidential communication between two
parties, an encryption key is required. Traditionally,
this encryption key is agreed upon using asymmet-
ric public-key cryptographic protocols, such as RSA
(Moriarty et al., 2016) or elliptic curves (Nir et al.,
2018). However, these algorithms are vulnerable to
the algorithm presented by Shor (1994), which can
be executed on a cryptographically relevant quantum
computer. This implies that future key agreement pro-
tocols will need to be updated to be resistant to quan-
tum computing.
One solution to this issue is quantum-safe pub-
lic key cryptography (also known as post-quantum
cryptography, PQC), which is based on mathemati-
cal problems that are not easily solvable even with
quantum computing. Another quantum-safe method
for establishing secret encryption keys between two
parties is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD). The pri-
mary advantage of QKD over classical post-quantum
key agreement schemes is that the security of QKD is
grounded in the laws of quantum physics, rather than
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2299-8030
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-7361-054X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1169-5920
on the assumption that certain mathematical problems
are computationally difficult to solve. The first QKD
protocol, BB84, was introduced in 1984 by Bennett
and Brassard (2014). The security of the BB84 proto-
col is based on encoding bit information in the polar-
ization of a single photon, with a randomly selected
basis. Measuring the photon will destroy its original
state, ensuring that any potential eavesdropping will
be detected as an increased error rate.
Therefore, in theory, QKD should provide uncon-
ditionally secure encryption keys, as it cannot be com-
promised by any computational algorithms, whether
classical or quantum. However, in practice, the situ-
ation is more complex due to imperfect implementa-
tions and the necessity for the classical key distillation
phase.
The BB84 protocol is composed of two distinct
phases: the quantum phase and the classical phase.
The quantum phase alone is insufficient for the deriva-
tion of an encryption key. To ensure the encryption
key is both secure and error-free, a key distillation
procedure must be executed over the classical chan-
nel. The classical key distillation process encom-
passes the following sub-procedures: authentication,
bit error estimation, error correction, and privacy am-
plification. These procedures collectively ensure the
Nikula, S., Lintulampi, A. and Halunen, K.
Security Analysis for BB84 Key Distillation.
DOI: 10.5220/0012717500003767
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT 2024), pages 407-415
ISBN: 978-989-758-709-2; ISSN: 2184-7711
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
407

integrity and security of the encryption key.
In this paper, we present a comprehensive anal-
ysis of the key distillation implementation of the
BB84 protocol from an information security perspec-
tive. Several publications already exist that focus on
specific aspects of the key distillation process. For
instance, the works of Dupuis (2023), Shen et al.
(2023), and Li et al. (2023) emphasize privacy am-
plification, while Lizama-Perez (2023) concentrates
on error correction. The general vulnerabilities of
practical quantum channel implementations have also
been explored, as evidenced by the studies of Sun and
Huang (2022) and Reutov et al. (2023). However,
there is a noticeable lack of comprehensive security
analyses of QKD key distillation implementations in
the existing literature.
This paper addresses the considerations that must
be taken into account when integrating theoretically
secure subroutines of the classical key distillation
phase into a QKD system. We propose a model for
estimating the robustness of the key distillation phase,
factoring in the imperfect realization of a quantum
channel. We believe this contribution provides valu-
able insights that bridge the knowledge gap between
the scientific community and technology providers,
thereby enhancing the practical implementation of
QKD systems.
The primary contributions of our paper are
twofold. First, we provide a straightforward exam-
ple model for estimating the security of a complete
BB84 key distillation procedure. Second, we present
an analysis of how the various components of this pro-
cess influence the security of the final distilled key.
These insights offer a comprehensive understanding
of the key distillation process and its impact on the
overall security of QKD systems.
The organization of the paper is as follows. In
Section 2, we distinguish among the various security
aspects of classical post-processing and make refer-
ences to established QKD standards and tools. Sec-
tion 3 is dedicated to presenting our findings. Here,
we allocate specific subsections to detail each key dis-
tillation subroutine, culminating in a comprehensive
security analysis. The implications of our analysis
and the practicality of our proposed methodology are
deliberated in Section 4. Finally, Section 5 encapsu-
lates our conclusions drawn from the research.
2 METHODOLOGY
In this section, we introduce the prevailing standards
and tools associated with QKD protocols and provide
a synopsis of the BB84 key distillation process. Sub-
sequently, we highlight crucial security perspectives
pertinent to key distillation.
The recently introduced ISO/IEC (2023) standard
on QKD delineates security requirements for both the
quantum and classical phases of QKD, taking into
consideration various types of threats. The Interna-
tional Telecommunication Union (ITU) has also is-
sued recommendations concerning various aspects of
QKD, such as the resilience of QKD networks (ITU,
2023) and key management (ITU, 2020). Further-
more, the European Telecommunications Standards
Institute (ETSI) hosts a working group dedicated to
QKD (ETSI, 2024b), which is actively preparing doc-
uments on various aspects of QKD, including the se-
curity of implementation (ETSI, 2024a).
2.1 General Overview of BB84 Key
Distillation
In the process of key distillation, the classical channel
is not intended to be encrypted. However, it requires
authentication to confirm that the key is being shared
with the correct party. The initial step, known as sift-
ing, involves selecting only those photons that were
prepared and measured in the same basis. As a result,
the outcome of the measurement should be determin-
istic (Bennett and Brassard, 2014). Nonetheless, the
sifted bit string is typically not perfect due to channel
imperfections causing some bits to flip. To estimate
the error rate, a subset of the sifted key bits is revealed
and compared with the corresponding bit sequence of
the other party.
Error correction is a process that eliminates bit er-
rors induced by channel noise. During the error cor-
rection phase, parity checks are transmitted over a
public channel. However, these checks inadvertently
disclose some information about the secret key. The
privacy amplification step is designed to counteract
this leakage. It reduces the length of the key bit string
to its final size.
2.2 Security Implications of Key
Distillation
The security of the key distillation phase is consid-
ered to stem from the protocol’s capacity to miti-
gate information leakage during the quantum phase,
as well as its ability to limit its own information leak-
age, thereby ensuring the output of secure key mate-
rial. Consequently, the combined imperfections of the
quantum protocol and classical post-processing algo-
rithms determine the theoretical security level of the
final key.
SECRYPT 2024 - 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography
408

The objective of the key distillation phase is to
generate a secret key from the information exchanged
during the quantum phase. Therefore, it is neces-
sary to establish certain security assumptions for the
quantum phase. This ensures that the key distilla-
tion process is sufficiently efficient to counter poten-
tial threats, such as eavesdropping.
On the one hand, if our focus is solely on the prac-
tical software security of the key distillation phase,
we can be assured that the key distillation process it-
self will not introduce any new security threats. On
the other hand, we will lack information about the se-
curity level of the keys produced by the protocol, as
the security of the keys is dependent on the quantum
phase.
The overall security of the final output from the
key distillation process hinges on the assumption that
the information leakage during both quantum and
classical protocols can be accurately quantified. The
key distillation protocol itself does not interact with
any quantum phenomena. However, if we aim for it
to produce practically secure keys, we must be cog-
nizant of potential limitations in the quantum phase.
For instance, key information can be obtained by tam-
pering with the phase or wavelength of the signal (Sun
et al., 2015; Li et al., 2011), through Trojan horse at-
tacks (Jain et al., 2014), blinding attacks (Weier et al.,
2011), photon number splitting attacks (Hong et al.,
2016), or by exploiting information about the timing
or duration of the signals (Huang et al., 2018; Sun
and Huang, 2022). Countermeasures that mitigate or
expose some of the attacks directed at the quantum
phase have been proposed, for example, by Huang
et al. (2018) and Yoshino et al. (2018).
In this paper, we focus solely on the intercept and
resend attack model as a potential threat emanating
from the quantum channel. This approach is justified,
as the intercept and resend attack model can be de-
tected or mitigated using key distillation subroutines.
Moreover, a comprehensive discussion of all possible
threat types falls outside the scope of this paper.
An intercept and resend attack involves an eaves-
dropper capturing each individual photon, measuring
it, and then retransmitting it to the intended receiver.
This type of attack can provide the eavesdropper with
substantial information about the secret key, but it also
introduces errors into the resulting key bit string. By
calculating the probability of this attack, we derive
a parameter that represents the likely number of bits
eavesdropped during the quantum phase.
In more complex cases, this parameter could be a
combination of effects of several attack types, cover-
ing all possible leaked bits during the quantum phase.
Each subprocess involved in the key distillation
phase influences the security level of the protocol’s
final output. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the
final output meets our criteria for a secure encryption
key. This implies that merely proving the security of
the individual subprocesses is insufficient. Instead,
we need to have a comprehensive understanding of
the entire process.
3 RESULTS
In this section, we scrutinize our key distillation im-
plementation using the security aspects outlined in the
previous section. Each step of the key distillation
phase is examined individually: we first present the
implementation of the specific subprocess, followed
by an analysis of its security.
The key distillation software we implemented re-
ceives a bit-sifted noisy key from the quantum layer
and executes steps that result in a distilled secure en-
cryption key. Figure 1 provides an overview of the
classical key distillation steps. It is important to note
that while the messages on the classical channel are
authenticated, they are not encrypted.
The key distillation software that has been imple-
mented is connected to the control interface, the key
management interface, and the quantum channel in-
terface. The control interface signals when a new key
exchange process is about to be initiated. The quan-
tum channel transmits the bit-sifted raw key to the key
distillation software, and the final product, a distilled
secure encryption key, is then forwarded to the key
management interface.
3.1 The Quantum Channel
Our QKD system implements the discrete-variable
BB84 protocol (Bennett and Brassard, 2014) with
phase modulation and decoy states. The photons are
transmitted from the preparation device to the mea-
surement device via an optical fiber.
The error rate of the implemented quantum chan-
nel is approximately 10% caused by the optical trans-
mitters and receivers. This value is obtained via em-
pirical tests on our quantum channel.
At both ends of the quantum channel, a laptop is
connected to either the preparation device or the mea-
surement device. The Alice side manages the prepa-
ration, while the Bob side handles the measurements.
Once the quantum phase is complete, the laptops re-
ceive the raw bit strings from their respective quantum
interfaces.
In our setup, the bit-sifting process is executed di-
rectly on the laptops that control the quantum proto-
Security Analysis for BB84 Key Distillation
409
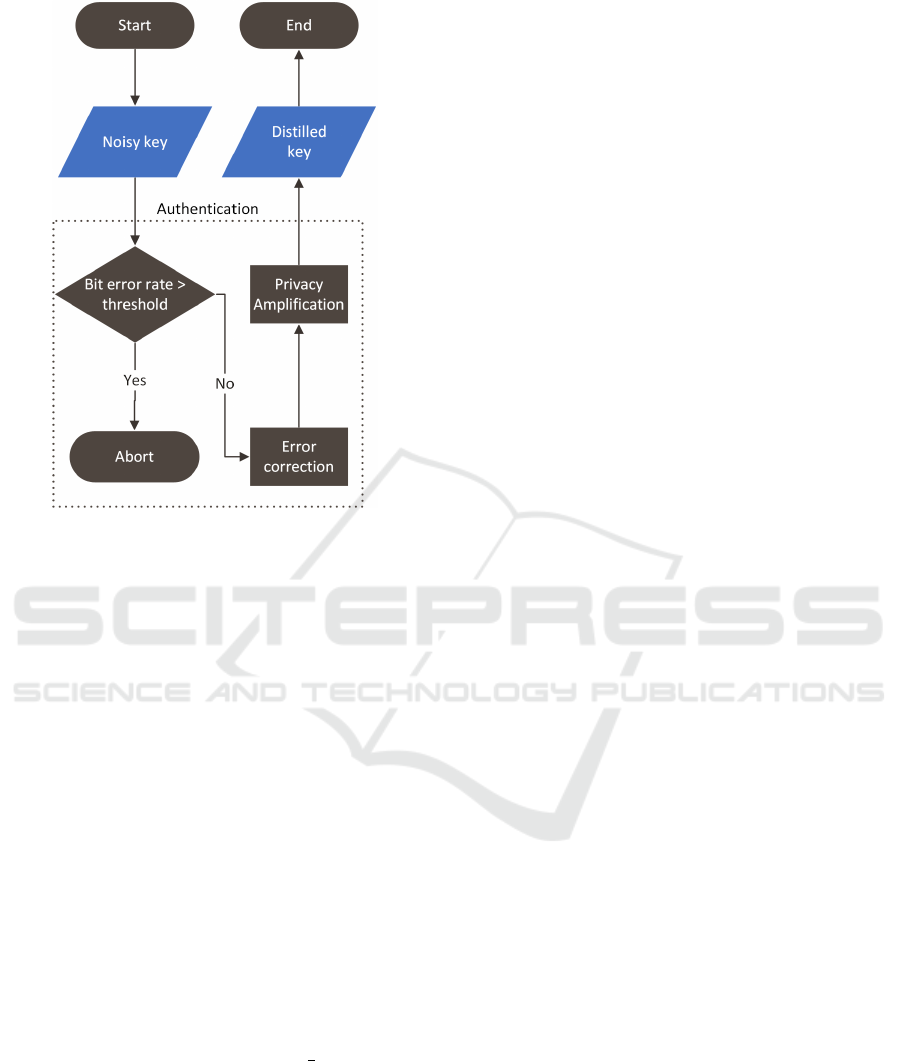
Figure 1: The diagram illustrates the steps involved in the
key distillation software. The process commences when the
noisy key is received from the quantum channel.
col. Consequently, the input received by our key dis-
tillation software is the bit-sifted raw key. Given that
the basis choices of Alice and Bob are public, we ex-
clude the bit-sifting phase from our security analysis.
Each execution of the quantum phase results in 1000
raw bits that are prepared and measured in the same
basis.
3.1.1 Security Analysis: Quantum Channel
The security of the BB84 protocol is predicated on
the assumption that each pulse contains a single pho-
ton (Bennett and Brassard, 2014). Our quantum layer
employs a decoy-state protocol to identify potential
photon-number splitting attacks (Mi et al., 2022).
Consequently, there are two potential sources of er-
ror: natural errors resulting from imperfections in the
quantum channel, and errors induced by intercept-
and-resend attacks. If an attacker intercepts a photon
and subsequently retransmits it, the probability of in-
ducing an error in that specific bit is
1
4
(Bennett and
Brassard, 2014). Given that each intercepted photon
is independent of the others, the number of erroneous
bits in this scenario follows a binomial distribution
with p = 0.25.
In this regard, we have three possible alternatives:
1. assuming that every error is caused by eavesdrop-
ping,
2. assuming that every error is caused by errors in
the quantum channel, or
3. trying to calculate the distribution between these
two, relying on our knowledge about the quantum
channel.
3.2 Authentication
Authenticated steps are delineated in Figure 1. We
have implemented authentication using symmetric
message authentication codes (MACs) and a post-
quantum key encapsulation method to disseminate the
symmetric authentication session key. Specifically,
our method employs the CRYSTALS–Kyber key en-
capsulation algorithm (Bos et al., 2018) to generate a
confidential authentication session key for Alice and
Bob. We utilized the CRYSTALS–Kyber implemen-
tation and certificate management functions of the
OpenSSL provider, developed by the Open Quantum
Safe Project (Stebila and Mosca, 2016). Following
the exchange of authentication keys, Alice and Bob
can utilize this session key to generate message au-
thentication codes using a specified MAC algorithm.
Our implementation employs the HMAC algorithm
(NIST, 2008) to generate secure message authentica-
tion codes using the symmetric key.
3.2.1 Security Analysis: Authentication
The security prerequisites for authentication meth-
ods are as follows: The final distilled encryption key
remains uncompromised even if the authentication
method fails after the completion of the QKD. There-
fore, it is sufficient to employ a transiently secure
authentication method. However, the authentication
method in use should maintain its security through-
out the key distillation process. In practice this means
that to obtain more security the parties that are ex-
changing secret keys using QKD should renew their
authentication session key from time to time.
The implemented authentication method seems
like a viable option from the security perspective.
The threat posed by Shor’s algorithm (1994) excludes
classical public key authentication methods and key
encapsulation methods from being used in the authen-
tication. The resilience against quantum computing
is justified as QKD protocols are considered to be a
secure key exchange method in the era of quantum
computing.
The key encapsulation algorithm CRYSTALS-
Kyber was chosen from the list of algorithms that Na-
tional Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
has chosen to be included in the post-quantum pub-
lic key cryptography standard (Alagic et al., 2022).
SECRYPT 2024 - 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography
410

HMAC is a secure and efficient keyed hashing algo-
rithm and thus was selected.
CRYSTALS–Kyber is still going through stan-
dardization process. First version of the NIST’s
post-quantum public key cryptograhpy standard is ex-
pected in 2024 (NIST, 2017b). Future security of the
authentication method is directly affected if vulner-
abilities are found during the standardization. This
affects also the security promise of QKD key distilla-
tion if vulnerable method is used for authentication.
Security level of the authentication method is
given by security strength categories that NIST has
defined for PQC algorithms in their call for propos-
als (NIST, 2017a). Standardized algorithms should
fulfill the security definitions of these categories. De-
pending on the chosen parameter size, CRYSTALS–
Kyber should correspond to at least the same cryp-
tographic strength as AES128 against both classical
and quantum attacks (CRYSTALS Team, 2023). We
consider this to be sufficient minimum strength for
QKD authentication method. Most security would be
achieved using parameters for security level 5, which
corresponds to security of AES256 (NIST, 2017a).
Security of any authentication method that uses
public key cryptography depends on securely dis-
tributing the public keys of participants. In order to
trust the security of the key encapsulation method we
have to assume that a secure public key infrastructure
exists.
3.3 Error Rate Estimation
In the error estimation phase, Alice randomly selects a
10% portion of the raw bit string. Bob compares these
bits to his respective bits and calculates how many bits
are changed. The error rate estimate is the ratio be-
tween flipped bits and all bits. This step is referred to
as bit error rate estimation or sometimes as parameter
estimation (Wolf, 2021). The sample used for error
rate estimation is removed from the raw bit string to
ensure it does not become part of the final secure key.
If the error rate is in acceptable limits, which in
our case is ≤ 12%, Bob will send his error rate es-
timate to Alice. Otherwise, he only sends a signal to
interrupt the distillation process and start the quantum
phase again.
3.3.1 Security Analysis: Error Rate Estimation
Error rate estimate of the raw bit string is needed for
two purposes:
1. High error rate refers to interference on the chan-
nel, which can be caused by intercept and resend
attack. In this case, the parties abort the process
and try again later. Errors can also occur due
to natural factors like photon loss, detection and
misalignment errors, background noise, and dark
counts (Bennett et al., 1992).
2. Error rate estimate is needed when conducting
CASCADE error correction protocol in the error
correction phase.
Estimating the error rate consists of several steps:
(1) one must choose acceptable threshold λ
max
for the
error rate of the bit string, (2) one must choose the
proper size k for the subset of the noisy key that is
revealed, (3) one must calculate the error rate Λ
k
of
this subset and (4) in order to continue the execution
of the protocol, the subset must pass a check Λ
k
≤
λ
max
(Wolf, 2021).
The size k of the subset has to be decided. The
reliability of the estimate depends on the relative size
of the subset: the smaller the subset, the more unre-
liable is the estimate (Lu et al., 2017). Let
X
k
denote
the fraction of errors in the k-sized subset, with mean
µ = 0.1. Each X
i
is a Bernoulli trial with p = 0.1 and
X
k
concentrates around µ = E(X
k
) = p = 0.1 as k in-
creases. The size of k can be estimated, e.g., by max-
imizing the probability P(0.1 − ε ≤ X
k
≤ 0.1 +ε).
Generally, the proportion of errors Λ
k
in the sam-
ple S is Λ
k
=
E
k
, where E is the hamming weight of the
string S
Alice
⊕ S
Bob
(i.e., the number of erroneous bits)
and k is the size of the sample (Wolf, 2021). For ex-
ample, if E = 36 and k = 360 it means that Λ
k
= 0.1.
High estimate of Λ
k
requires action: if Λ
k
> λ
max
the key should be discarded. We define λ
max
= 0.1 +
ε, where ε is the maximum allowed deviation from the
error rate of the implemented quantum channel.
When the condition Λ
k
≤ λ
max
is satisfied, we in-
put Λ
k
as the estimated quantum bit error rate to the
CASCADE error correction protocol.
All error rate estimation methods based on the
sample error rate include some amount of uncertainty.
However, during the error correction process, Bob
will get the error rate Λ
n
of the whole bit string as
he will have a copy of the noisy key and the error
corrected key. At this point, the protocol can still be
aborted if Λ
n
> Λ
k
. Thus, the accuracy of Λ
k
will be
more of a efficiency than a security aspect: the eaves-
dropping attempt will be noticed after the error cor-
rection, but this approach will lower the secure key
generation rate.
Defining an exact upper bound for the tolerable
error rate after BB84 protocol is a challenging
question. We must rely on the assumption that with a
high enough probability, if an eavesdropper has been
listening the quantum channel, either the protocol
will abort or the eavesdropper will end up with a small
Security Analysis for BB84 Key Distillation
411

enough amount of information (Gottesman and
Lo, 2001).
We treat the quantum channel here as a binary
symmetric channel, which means that each bit is
flipped with probability p, and the total amount of
flipped bits follows a binomial distribution. We strive
to set the highest tolerable error rate and raw key size
so that it seems highly unlikely to get a key with this
error rate in case that the eavesdropper would actually
have eavesdropped each bit in our quantum phase.
As stated earlier the natural error rate in our quan-
tum channel is 0.1 and the maximum accepted error
rate is 0.12. In our setup, the amount of raw bits com-
ing to the distillation process is 1000. The probabil-
ity for getting a sample of 1000 bits with error rate
of 0.12 or less from a binomial distribution with ac-
tual p = 0.25 is ≈ 9.445 · 10
−25
, which we consider
small enough to rely that the eavesdropper has not
measured all bits in the quantum phase. On the other
hand, probability for getting this error rate or less, i.e.,
probability of the raw bit string passing the error rate
test when there is no eavesdropping activity, is 0.983.
Above we calculated the probability for each pho-
ton in the quantum phase being measured by an eaves-
dropper, so that p = 0.25. The other scenario is that
only some portion of the quantum phase has been
eavesdropped. If we know the error probability of the
channel and we can compute the error in the received
binary string, it is possible to estimate the number of
bits that have been eavesdropped. Let p denote the
probability of an error if a bit is eavesdropped and q
the probability of an error for a bit that is not eaves-
dropped. We will assume q < p and that the prob-
ability of error due to the channel and the probabil-
ity induced by eavesdropping are independent of each
other. We will also assume that the errors for each bit
are independent events.
We denote by n the number of bits received and by
k the number of eavesdropped bits. Now the observed
error R is
R =
k
n
× p +
n − k
n
× q.
Solving for k gives
k =
n(R − q)
p − q
.
Now if we have the error probability after eaves-
dropping at E
e
= 0.25 and the error for the channel
at E
c
= 0.1, we can compute p and q. Obviously,
q = E
c
= 0.1, but for p we have to note, that both
eavesdropping AND channel error can happen inde-
pendently and thus both possibilities need to be calcu-
lated. Thus p = (1 − E
e
) × E
c
+ E
e
× (1 − E
c
), which
gives p = 0.3 with the values of E
e
and E
c
given
above.
Now we can compute (under the assumptions
given above) the value for k once R has been com-
puted from the received binary string. If we take
R = 0.12 as suggested by the earlier analysis and
n = 1000 we get k = 100, which would mean that 100
bits were eavesdropped. Of course, this being a prob-
abilistic system, this level of accuracy and certainty is
not necessarily warranted. However, this gives some
indication on the likeliest number of eavesdropped
bits, which can then be adjusted with some error mar-
gin to make a good guess on the amount of eaves-
dropped bits.
3.4 Error Correction
For error correction, we utilized the Cascade-Python
library (Rijsman Revision, 2020), a Python-based im-
plementation of the CASCADE protocol (Brassard
and Salvail, 1994). The CASCADE protocol is based
on iterative parity checks: the party with the noisy
version of the key shuffles the key bits and requests
parity information for these blocks, while the party
with the original version of the key provides the par-
ity information. This process is repeated until all bit
errors are corrected with a high probability. CAS-
CADE is a probabilistic procedure, meaning it does
guarantee the removal of 100% of the bit errors each
time. However, based on our software tests, CAS-
CADE performed very well when removing bit errors
with an error rate of 0.1.
3.4.1 Security Analysis: Error Correction
The primary security aspect related to the error cor-
rection phase is our ability to quantify the amount of
information leakage during this phase.
Due to the probabilistic nature of CASCADE, the
actual amount of information leakage is only known
after the protocol has concluded. In practice, a re-
sponse to a single parity query leaks one bit of in-
formation (Martinez-Mateo et al., 2015; Mehic et al.,
2020). Our error correction software tracks the num-
ber of leaked bits by counting the responses to parity
queries.
After removing the 10% error rate estimation sub-
set from the 1000 raw key bits, we are left with 900
bits in the error correction phase. Correcting errors
from a 900-bit raw key with CASCADE leaks approx-
imately 513 bits (averaged over 100 test runs using
our software). This leaves us with 387 secret bits af-
ter error correction, assuming that the quantum phase
has not been eavesdropped on.
SECRYPT 2024 - 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography
412

3.5 Privacy Amplification
In our implementation, we conduct privacy amplifi-
cation by multiplication with a Toeplitz matrix. We
construct an n × m sized Toeplitz matrix (where n is
the number of final key bits and m is the number of
bits in the error corrected bit string) from a random
seed and multiply the raw bit string with this matrix.
The resulting bit string then becomes the final secure
key. Due to the cyclic nature of the Toeplitz matrix,
the length of the seed must be n + m − 1.
3.5.1 Security Analysis: Privacy Amplification
The purpose of privacy amplification is to mitigate
the information leaked during quantum or classical
protocols. The main security aspects of the privacy
amplification steps are: the seed of the hash function
is selected randomly (Bennett et al., 1995; ISO/IEC,
2023); the length of the secure key after privacy am-
plification is at most n − t (where n = amount of all
bits and t = amount of bits known to an eavesdrop-
per) (Bennett et al., 1995); and following from the
previous point, we must have a good enough approx-
imation about the maximum number of bits leaked to
a potential eavesdropper. In practice, we will need
to have some extra raw bits to cover situations where
more than the average number of bits are leaked.
For choosing the seed of the Toeplitz matrix, we
have used the function os.urandom in the Python
standard library (Python Software Foundation, 2023).
According to the documentation, this function should
provide enough entropy for cryptographic purposes,
so the randomness aspect should be satisfied. Bit
leaks in the quantum phase and the error correction
phase are addressed in the previous sections. The fi-
nal point, the length of the resulting bit string, is ad-
dressed in the next section.
3.6 The Security Level of the Final Key
Let us denote the number of raw bits that enter the
key distillation phase as X. Furthermore, let us de-
note the size of the error rate estimation subset as a,
the amount of leaked information in the error correc-
tion phase as b, and the maximum number of poten-
tially eavesdropped bits as c. After the privacy ampli-
fication step, as claimed by Bennett et al. (1995), the
length of the distilled key should be at most:
δ = X − a − b − c. (1)
Earlier, we calculated that correcting errors from
a bit string consisting of 900 bits leaks approximately
513 bits, which leaves us with 387 secret bits, assum-
ing that the quantum phase has not been eavesdropped
on. We also calculated that when using the maxi-
mum tolerable error rate of 0.12, the estimated num-
ber of eavesdropped bits in the quantum phase would
be 100.
In our implementation, the final secure key was
used as a 256-bit AES key (Dworkin, 2023). A length
of 256 bits was chosen because it is expected to of-
fer a security level of 128 bits in the era of computa-
tionally relevant quantum computers, taking into ac-
count the algorithm by Grover (1996), which achieves
a quadratic speedup in unstructured search.
In our experiments, we obtained the following val-
ues for the maximum tolerable error rate: X = 1000,
a = 100, b = 513 and c = 100. Now, following Equa-
tion 1:
δ = 1000 − 100 − 513 − 100 = 287.
Thus, our key distillation process can distill 287
secure bits for every 1000 raw bits from the quantum
layer. Because 287 > 256, we have obtained enough
secure bits to generate a 256-bit secret key. The ex-
cess bits serve as a security parameter which should
cover unexpected bit leaks in the quantum or classical
phase.
4 DISCUSSION
The conventional method of measuring the security of
encryption algorithms is based on key length; differ-
ent key lengths offer varying levels of security, typi-
cally such that more key bits equate to increased se-
curity against attacks. Consequently, the length of the
distilled encryption key impacts the level of security
it can provide during encryption.
Another factor to consider is the potential for
eavesdropping during the key-establishment process,
which could result in a potential attacker gaining
some knowledge about the key. In our paper, we focus
on the intercept and resend attack, estimate its proba-
bility using statistical means, and collect its probable
effects into a single parameter when defining the se-
curity level of the key.
However, numerous other attacks may threaten
the security of the quantum phase. Thus, in practi-
cal implementations, this parameter must be defined
more comprehensively, taking into account all pos-
sible threats that have not been mitigated with ef-
fective countermeasures. Defining such a parameter,
which collects information about the quantum phase
as a whole, is a topic for further research. Our paper
provides an example of defining and using such a pa-
rameter in conjunction with other parameters derived
from the classical phase.
Security Analysis for BB84 Key Distillation
413

Measuring the exact security level of the produced
key might be impossible because quantum protocols,
such as BB84 used here, are not deterministic in na-
ture but include some random aspects. For instance,
we can calculate the average number of pulses that
may be eavesdropped given the error rate of the bit
string, but this is only an estimate and the actual num-
ber may differ. Thus, the only viable option, in the
case of imperfect devices, appears to be to decide
on a maximum number of eavesdropped bits that can
be tolerated. Evidently, the more secure we want to
be, the more raw bits are needed and the more time-
consuming the key establishment phase will be.
Another important factor is the extent to which
the security countermeasures during key distillation
affect the key generation rate of the protocol. The se-
curity of the distilled keys can always be enhanced
by demanding lower error rates and using more raw
bits, but when implemented in real-life use cases,
a key distillation process must meet certain perfor-
mance requirements, and thus excessive security mea-
sures could render it practically useless.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We have conducted a comprehensive security analysis
of a key distillation phase of a practical QKD based
on the BB84 protocol. We have assumed that cer-
tain security limitations, such as the probability of a
specific number of photons being eavesdropped, re-
sult from the protocol’s quantum phase, and we have
acknowledged these limitations in our analysis. To
simplify the analysis, we have considered only the in-
tercept and resend attack as a possible source of in-
formation leakage, although we note that many other
attacks threaten practical QKD implementations.
With the help of existing standards and literature,
we have examined every subroutine in the key dis-
tillation phase – authentication, error rate estimation,
error correction, privacy amplification – and analyzed
their effects on the security level of the final key.
Our analysis contributes to the collection of gen-
eral frameworks that can be used to evaluate QKD key
distillation implementations.
The security level of the final key is influenced by
several parts of the system, and a single unambiguous
measure for this security level should not be consid-
ered sufficient. Instead, due to the non-deterministic
nature of the quantum phase, we propose that the se-
curity level should be considered as a combination of
the bit length of the key and the probability that a cer-
tain portion of these bits is eavesdropped. The secu-
rity level can be enhanced either by increasing the bit
length or by adding safety procedures to the key dis-
tillation phase, such as using more raw bits to produce
the final key. As the final use case of the secret key is
left open, the final computational strength of the key
must be determined separately for each case.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by the National
Quantum Communication Infrastructure in Finland
(NaQCI.fi) project (Grant Agreement 101091479),
which is part of the European Union’s The European
Quantum Communication Infrastructure (EuroQCI)
initiative.
REFERENCES
Alagic, G., Apon, D., Cooper, D., Dang, Q., Dang, T.,
Kelsey, J., Lichtinger, J., Miller, C., Moody, D., Per-
alta, R., et al. (2022). Status report on the third round
of the NIST post-quantum cryptography standardiza-
tion process. US Department of Commerce, NIST.
Bennett, C. and Brassard, G. (2014). Quantum cryptogra-
phy: Public key distribution and coin tossing. The-
oretical Computer Science, 560:7–11. Theoretical
Aspects of Quantum Cryptography – celebrating 30
years of BB84.
Bennett, C. H., Bessette, F., Brassard, G., Salvail, L., and
Smolin, J. (1992). Experimental quantum cryptogra-
phy. Journal of cryptology, 5:3–28.
Bennett, C. H., Brassard, G., Cr
´
epeau, C., and Mau-
rer, U. M. (1995). Generalized privacy amplifi-
cation. IEEE Transactions on Information theory,
41(6):1915–1923.
Bos, J., Ducas, L., Kiltz, E., Lepoint, T., Lyubashevsky, V.,
Schanck, J. M., Schwabe, P., Seiler, G., and Stehl
´
e, D.
(2018). CRYSTALS-Kyber: a CCA-secure module-
lattice-based KEM. In 2018 IEEE European Sympo-
sium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), pages 353–
367. IEEE.
Brassard, G. and Salvail, L. (1994). Secret-key reconcil-
iation by public discussion. In Helleseth, T., editor,
Advances in Cryptology — EUROCRYPT ’93, pages
410–423, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin Heidel-
berg.
CRYSTALS Team (2023). CRYSTALS–Kyber web-
site. https://pq-crystals.org/kyber/. Last accessed
14.2.2024.
Dupuis, F. (2023). Privacy Amplification and Decoupling
Without Smoothing. IEEE Transactions on Informa-
tion Theory, 69(12):7784–7792.
Dworkin, M. J. (2023). Advanced Encryption Standard
(AES). https://doi.org/10.6028/NIST.FIPS.197-upd1.
ETSI (2024a). ETSI GS QKD 016 V2.1.1 (2024-01).
ETSI (2024b). Industry Specification Group (ISG) on
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD). https://www.etsi.
org/committee/qkd. Last Accessed 25.1.2024.
SECRYPT 2024 - 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography
414

Gottesman, D. and Lo, H.-K. (2001). Proof of security of
quantum key distribution with two-way classical com-
munications. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, 49:457–475.
Grover, L. K. (1996). A fast quantum mechanical algorithm
for database search. In Proceedings of the twenty-
eighth annual ACM symposium on Theory of comput-
ing, pages 212–219.
Hong, K., Foong, O.-M., and Low, T. (2016). Challenges in
quantum key distribution: A review. In ICINS ’16:
Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on
Information and Network Security, pages 29–33.
Huang, A., Sun, S.-H., Liu, Z., and Makarov, V. (2018).
Quantum key distribution with distinguishable decoy
states. Phys. Rev. A, 98:012330.
ISO/IEC (2023). ISO/IEC 23837-1:2023 - Information se-
curity — Security requirements, test and evaluation
methods for quantum key distribution — Part 1: Re-
quirements.
ITU (2020). ITU-T Recommendations/ ITU-T Y.3803
(12/2020). Last Accessed 25.1.2024.
ITU (2023). ITU-T Recommendations/ ITU-T Y.3815
(09/2023). Last Accessed 25.1.2024.
Jain, N., Anisimova, E., Khan, I., Makarov, V., Marquardt,
C., and Leuchs, G. (2014). Trojan-horse attacks
threaten the security of practical quantum cryptogra-
phy. New Journal of Physics, 16(12):123030.
Li, H.-W., Wang, S., Huang, J.-Z., Chen, W., Yin, Z.-
Q., Li, F.-Y., Zhou, Z., Liu, D., Zhang, Y., Guo,
G.-C., Bao, W.-S., and Han, Z.-F. (2011). Attack-
ing a practical quantum-key-distribution system with
wavelength-dependent beam-splitter and multiwave-
length sources. Phys. Rev. A, 84:062308.
Li, K., Yao, Y., and Hayashi, M. (2023). Tight exponential
analysis for smoothing the max-relative entropy and
for quantum privacy amplification. IEEE Transactions
on Information Theory, 69(3):1680–1694.
Lizama-Perez, L. (2023). Reverse reconciliation for optimal
error correction in quantum key distribution. Symme-
try, 15(3).
Lu, Z., Shi, J.-H., and Li, F.-G. (2017). Error rate estima-
tion in quantum key distribution with finite resources.
Communications in Theoretical Physics, 67(4):360.
Martinez-Mateo, J., Pacher, C., Peev, M., Ciurana, A., and
Martin, V. (2015). Demystifying the information rec-
onciliation protocol cascade. Quantum Info. Comput.,
15:453–477.
Mehic, M., Niemiec, M., Siljak, H., and Voznak, M. (2020).
Error reconciliation in quantum key distribution pro-
tocols. In Ulidowski, I., Lanese, I., Schultz, U. P.,
and Ferreira, C., editors, Reversible Computation:
Extending Horizons of Computing: Selected Results
of the COST Action IC1405, pages 222–236, Cham.
Springer International Publishing.
Mi, S., Dong, S., Hou, Q., Wang, J., Yu, Y., Wei, Z., and
Zhang, Z. (2022). Joint photon-number splitting at-
tack on semi-quantum key distribution. Frontiers in
Physics, 10.
Moriarty, K., Kaliski, B., Jonsson, J., and Rusch, A. (2016).
PKCS #1: RSA Cryptography Specifications Version
2.2. RFC 8017.
Nir, Y., Josefsson, S., and P
´
egouri
´
e-Gonnard, M. (2018).
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) Cipher Suites for
Transport Layer Security (TLS) Versions 1.2 and Ear-
lier. RFC 8422.
NIST (2008). The Keyed-Hash Message Authentication
code (HMAC). Federal Information Processing Stan-
dards Publication 198-1.
NIST (2017a). Post-quantum cryptography: Call for
proposals. https://csrc.nist.gov/CSRC/media/
Projects/Post-Quantum-Cryptography/documents/
call-for-proposals-final-dec-2016.pdf. Last accessed
14.2.2024.
NIST (2017b). Post-quantum cryptography:
Workshops and timeline. https://csrc.nist.
gov/Projects/post-quantum-cryptography/
workshops-and-timeline. Last accessed 14.2.2024.
Python Software Foundation (2023). os, Miscellaneous op-
erating system interfaces. https://docs.python.org/3/
library/os.html. Last accessed 14.2.2024.
Reutov, A., Tayduganov, A., Mayboroda, V., and Fat’yanov,
O. (2023). Security of the decoy-state BB84 pro-
tocol with imperfect state preparation. Entropy,
25(11):1556.
Rijsman Revision, B. (2020). The Cascade informa-
tion reconciliation protocol. https://cascade-python.
readthedocs.io/en/latest/protocol.html. Last accessed
14.2.2024.
Shen, Y.-C., Gao, L., and Cheng, H.-C. (2023). Privacy am-
plification against quantum side information via reg-
ular random binning. In 2023 59th Annual Allerton
Conference on Communication, Control, and Com-
puting (Allerton), pages 1–8.
Shor, P. W. (1994). Algorithms for quantum computation:
discrete logarithms and factoring. In Proceedings 35th
annual symposium on foundations of computer sci-
ence, pages 124–134.
Stebila, D. and Mosca, M. (2016). Post-quantum key ex-
change for the internet and the open quantum safe
project. In International Conference on Selected Ar-
eas in Cryptography, pages 14–37. Springer. https:
//openquantumsafe.org/.
Sun, S. and Huang, A. (2022). A review of security eval-
uation of practical quantum key distribution system.
Entropy, 24(2).
Sun, S.-H., Xu, F., Jiang, M.-S., Ma, X.-C., Lo, H.-K., and
Liang, L.-M. (2015). Effect of source tampering in
the security of quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. A,
92:022304.
Weier, H., Krauss, H., Rau, M., F
¨
urst, M., Nauerth, S., and
Weinfurter, H. (2011). Quantum eavesdropping with-
out interception: an attack exploiting the dead time
of single-photon detectors. New Journal of Physics,
13(7):073024.
Wolf, R. (2021). Quantum Key Distribution - An Introduc-
tion with Exercises, volume 988 of Lecture Notes in
Physics. Springer.
Yoshino, K.-i., Fujiwara, M., Nakata, K., Sumiya, T.,
Sasaki, T., Takeoka, M., Sasaki, M., Tajima, A.,
Koashi, M., and Tomita, A. (2018). Quantum key
distribution with an efficient countermeasure against
correlated intensity fluctuations in optical pulses. npj
Quantum Information, 4(1).
Security Analysis for BB84 Key Distillation
415
