
Generative AI Risk Management in Digital Economy
Victor Chang, Leigh Draper and
Simin Yu
Department of Operations and Information Management, Aston Business School, Aston University, Birmingham, U.K.
Keywords: Generative AI, Risk Management, Mitigation Strategies.
Abstract: In Healthcare Procurement, This Study Delves into the Integration of Generative AI, Focusing on Its
Application within HealthTrust Europe's marketing and communication frameworks. By analyzing the
interplay between innovative AI-driven content personalization and the associated ethical, security, and
operational risks, the research offers a nuanced perspective on leveraging technology for enhanced efficiency
and engagement. The study employs qualitative research methods to assess risks and propose mitigation
strategies, advocating for best practices in AI governance and risk management. It emphasizes the importance
of maintaining network security, data integrity, and ethical standards in deploying AI solutions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) has sparked
considerable interest at both the human and corporate
levels. This is because generative AI has many
potential applications where it can be used to create
personalized and engaging marketing and
communications materials for healthcare
procurement companies (Ooi et al., 2023). These
technologies, such as Chat GPT and Copilot, can
generate new content and have many possible
applications (Preiksaitis & Rose, 2023). However,
generative AI poses significant challenges that may
be addressed effectively, ethically, and equitably
(Preiksaitis & Rose, 2023). However, more
organizations may still need to fully explore the long-
term implications of AI integration on outcomes and
services, so the gap points towards longitudinal
studies assessing the enduring effects of AI-driven
innovations. Thus, this study aims to identify
generative AI risks and mitigations to launch a
protected generative AI to create marketing and
communications content that considers and mitigates
potential pitfalls and threats.
The significance of this study is to identify the
risks of novel technology and risk management to
consider the best approaches for organizations. This
study will provide overviews and recommendations
for HealthTrust Europe and healthcare procurement
companies on development.
This study aims to identify novel generative AI
risks and mitigations and investigate the risks and
benefits of using best practice approaches to maintain
network security.
This study's objectives were stated as follows:
• exploring the risks, feasibility, and benefits of
developing a pilot scheme
• identifying and analyzing novel technology
risks and mitigations
• considering best practice approaches to
maintain network security
This study is categorized into several sections to
deal with the research question. The introduction
demonstrated the generative background and found
research significance. The literature review
introduced the risk of novel technologies and
generative AI models. Meanwhile, this study's
research method adopts qualitative research using
interpretivism theory. Result and recommendation
conducted mitigations. Finally, the last section
presented the conclusion and recommendation.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Healthtrust Europe Scenario
Health Trust Europe, which is the leading provider of
healthcare products and services to NHS Trusts,
private healthcare providers, and public sector
organizations, has a large and diverse customer base
and a network of suppliers, including market leaders
and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) the
120
Chang, V., Draper, L. and Yu, S.
Generative AI Risk Management in Digital Economy.
DOI: 10.5220/0012729800003717
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business (FEMIB 2024), pages 120-127
ISBN: 978-989-758-695-8; ISSN: 2184-5891
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

organization aims to deliver high-quality, cost-
effective, innovative solutions that meet its
customers' and suppliers' needs and expectations.
Health Trust intends to use generative AI solutions to
improve its marketing and communication strategy,
resulting in personalized and engaging content for its
target audiences. According to the Gartner
Organisation, expects that by 2026, more than 80% of
enterprises will have used or deployed generative AI-
enabled app. In contrast, Harvard Business Review
recently shared that a recent McKinsey survey
revealed that only 10% to 14% of companies
consistently deploy generative AI in their marketing
and sales initiatives (Lamarre et al., 2023). Thus,
there are risks to enterprises' declining to deploy
generative AI, which states that generative AI is
unreliable for customers.
2.2 Implementation of Health Trust
Europe
HealthTrust Europe aspires to deploy a secure
generative AI solution that will facilitate attaining
several strategic objectives. These objectives
encompass augmenting customer loyalty and
retention by delivering pertinent and timely
information, promotions, and suggestions
(Khennouche et al., 2024). Additionally, the
organization aims to attract new clientele and enlarge
its market presence by effectively communicating its
unique value proposition, domain expertise, and
distinctive competencies through generative AI.
Lastly, HealthTrust Europe seeks generative AI to
bolster its reputation and credibility by exemplifying
a steadfast commitment to quality, innovation, and
environmental sustainability (Archer, 2021).
2.3 Novel Technologies
2.3.1 Office 365 Co-Pilot
Given the existing utilization of Office 365 within
HealthTrust Europe's technological framework, the
integration of Office 365 Co-Pilot emerges as the
favored alternative. Office 365 Co-Pilot, a novel
enhancement, leverages Natural Language
Processing (NLP) and transformers (Hadi et al.,
2023b). The core of NLP and transformers lies in their
capacity to enable computational systems to
comprehend and produce human language,
encompassing both text and speech. Co-Pilot employs
these technologies to scrutinize the user's input and
contextual cues, generating pertinent and constructive
recommendations. These include, but are not limited
to, sentence completion, summary creation,
information retrieval, and query resolution.
Furthermore, Co-Pilot is designed to evolve by
assimilating user feedback and preferences, tailoring
its functionality to align with individual user styles
and requirements. A comprehensive evaluation is
imperative to cement this choice (Balk et al., 2021).
Therefore, this study focuses on harnessing
generative AI technologies to optimize healthcare
procurement processes.
2.3.2 Novel Generative AI Technologies
The generative AI sector is rapidly evolving, driven
by significant advancements and investments from
leading tech companies such as Google, Microsoft,
and Amazon. Notably, Large Language Models
(LLMs) like Microsoft 365 Copilot, Google Bard, and
OpenAI's GPT-4 are at the forefront, offering
capabilities that range from code generation to
multilingual customer support and marketing content
creation (Hadi et al., 2023a). Furthermore, tools such
as Amazon Bedrock and Google's Vertex AI Platform
democratize AI access and enhance project
management for professionals. Meanwhile, the trend
towards using LLMs trained on an organization's data
aims to produce content that reflects its unique brand
identity and meets the nuanced demands of its
audience (Budhwar et al., 2023). Consequently, this
dynamic landscape is shaped by tech giants and
invigorated by innovative AI startups like Anthropic,
signaling a vibrant and expanding field (Pasquero &
Poletto, 2023). Thus, the generative AI industry is
innovative and emerging in the world
(Badrinarayanan et al., 2017).
2.4 Generative AI Model
2.4.1 Encoder-Decoder Architecture
The encoder is a neural network that encodes the
input prompt into a vector representation in the latent
space. The latent space is a high-dimensional space
that captures the semantic and syntactic features of
the input prompt and the data (Zermatten et al., 2023).
The decoder is another neural network that decodes
the vector representation into the output text. The
output text is the generated content that matches the
input prompt and the data. The diagram below shows
the basic structure of the generative AI model, which
is based on an encoder-decoder architecture.
Figure 1: Basic structure of the generative AI model.
Input Encoder State Decoder Output
Generative AI Risk Management in Digital Economy
121
2.4.2 Generative AI: End-to-End Process
The data acquisition methodology involves gathering
diverse sources such as procurement contracts,
business and market intelligence, and other relevant
data. This data is then pre-processed and cleansed to
meet the generative AI model's requirements,
ensuring its compatibility and effectiveness
(Mourtzis, 2021).
Central to the solution is the generative AI model,
which is capable of producing textual content based
on the processed data and input prompts. This content
undergoes thorough evaluation and refinement by
human editors or automated systems to maintain
quality and relevance (Bandi et al., 2023). The
dissemination phase involves distributing the
polished content to targeted audiences via various
channels, including email, social media, and
websites, to maximize reach and engagement. This
process encapsulates the core components and steps
of the comprehensive solution (Nagy et al., 2023).
Figure 2: End-to-End Process AI model.
This paper showed that generative AI has many
applications; Health Trust Europe organizations
adopted generative AI to create customized and
engaging marketing and communications materials
for healthcare procurement organizations. In addition,
this study also summarized novel technology and
generative AI models, which help researchers explore
risks and mitigations.
3 METHODS
Our research methodology adopted the qualitative
research method; we observed that Health Trust
Europe acknowledges that the generative AI solution
presents significant dangers to digital and cyber
privacy and security and designed a full Risk
Assessment matrix for analysis and result mitigation.
Moreover, this study's philosophy adopts social
action theory. Social action theory focuses on how
people take actions that hold personal significance
and how these interactions impact societal norms
(Coleman, 1986). This study also identifies and
analyses novel technology risks and mitigations to
consider best practice approaches to maintain
network security. Additionally, interpretivism theory,
as the research approach in this study, interpretive
approach delves into understanding events in society
based on the specific value system of the society
(Ryan, 2018). This study interpreted generative AI
risk and mitigations to contribute to a risk-based
approach. The study applied an inductive approach
across the whole study; we analyzed generative AI
risk and management using variables to make risk
assessments for analysis and get results.
3.1 Definition of Variables
HealthTrust Europe is aware of the significant risks
of generative AI, including digital and cyber privacy,
security, reputational, financial, regulatory, ethical,
and legal challenges. In utilizing generative AI for
external communications and marketing, the
organization may address various risk categories as
variables:
Table 1: Full Risk Assessment matrix.
Potential Consequences
L6 L5 L4 L3 L2
Not
Si
g
nificant
Minor Moderate Major Severe
Likelihood
Expected to occur
regularly under normal
Circumstances
Almost
Certain
5 Moderate 10 Major 15 Major 20 Severe
25 Very
Severe
Expected to occur at
some time
Likely
4 Moderate 8 Moderate 12 Major 16 Major 20 Severe
It may occur at some
time.
Possible
3 Minor 6 Moderate 9 Moderate 12 Major 15 Major
It is not likely to occur in
normal circumstances.
Unlikely
2 Minor 4 Moderate 6 Moderate 8 Moderate 10 Major
Could happen but
p
robabl
y
never will
Rare 1 Minor 2 Minor 3 Minor 4 Moderate 5 Moderate
Define
Objecti
ve
Gather and
Pre Process
Data
Choose
appropri
ate
model
Train
the
Model
Evaluat
e and
Refine
Test and
Validate
Deploy
and
Iterate
FEMIB 2024 - 6th International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
122
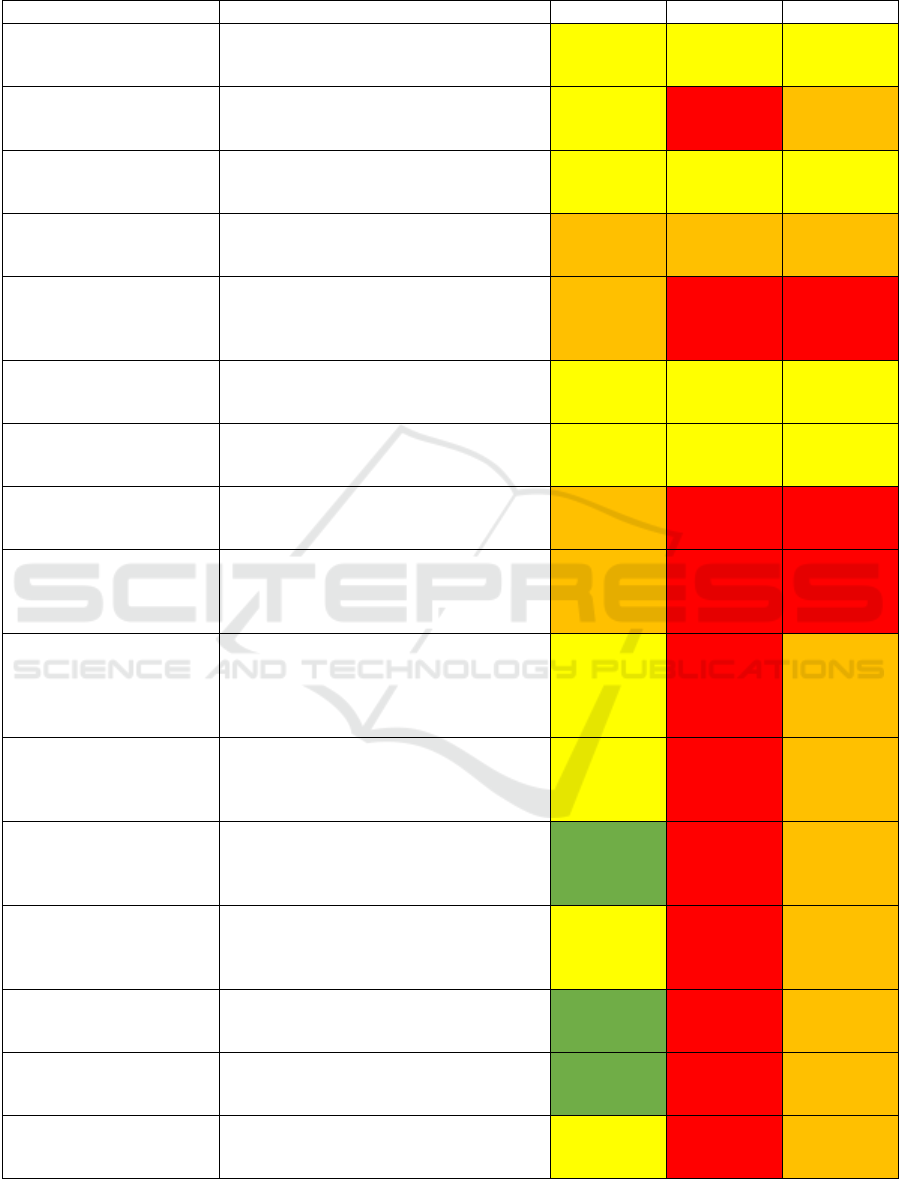
Table 2: Organization's risk assessment result.
Step Risk Likelihood Impact Risk Level
Generic - Conduct a
thorough risk assessment
and impact analysis
Incomplete or inaccurate identification and
assessment of risks and impacts
Possible (3) Medium (3) Moderate (9)
Generic - Establish clear
policies, guidelines, and
b
est practice
Non-compliance or inconsistency with
relevant laws, regulations, standards, and
guidelines
Possible (3) Severe (5) Major(15)
Generic - Manage the
project budget, timeline,
and scope
The project exceeds the budget due to
unexpected costs of data acquisition, model
development, or content generation
Possible( 3) Moderate (3) Moderate (9)
Generic - Manage the
project budget, timeline,
and sco
p
e
The project is delayed due to technical
issues, stakeholder feedback, or content
a
pp
roval
Likely (4) Major (4) Major (16)
Generic - Engage with
customers, suppliers, and
other stakeholders.
Lack of trust, confidence, or consent from
the customers, suppliers, or other
stakeholders due to insufficient or
ineffective communication or engagement
Likely (4) Severe (5) Severe (20)
Generic - Manage the
project budget, timeline,
and sco
p
e
The project scope changes due to new
requirements, features, or content types
Possible (3) Medium (3) Moderate (9)
Technology - Incorporate
human oversight and
intervention
Human bias, error, or manipulation
affecting the content quality, accuracy,
authenticit
y
, and accountabilit
y
Possible (3) Medium (3) Moderate (9)
Technology- Ensure the
project quality
The project quality is compromised due to
poor data, model, or output quality and
reliabilit
y
Likely (4) Severe (5) Severe (20)
Technology- Ensure the
data quality and reliability
The data is incomplete, inaccurate,
outdated, biased, or irrelevant, affecting the
quality and reliability of the generated
content
Likely (4) Severe (5) Severe (20)
Technology - Ensure the
model's complexity and
explainability
The model is complex and difficult to
understand, explain, or debug, posing
challenges for the development,
deployment, and maintenance of the
g
enerative AI technolo
gy
Possible (3) Severe (5)
Major
(15)
Technology - Ensure the
model scalability and
performance
The model requires high computational
resources and costs, hindering the
scalability and performance of the
g
enerative AI technolo
gy
Possible (3) Severe (5)
Major
(15)
Technology - Ensure the
output ethics and social
impact
The output is misused, manipulated, or
stolen, causing legal and security problems,
such as plagiarism, fraud, identity theft,
etc.
Unlikely (2) Severe (5) Major (10)
Cyber - Implement robust
technical and
organisational measures
Data breach, loss, or corruption due to
cyberattacks, human errors, or system
failures technical and organisational
measures
Possible (3) Severe (5)
Major
(15)
Cyber - Ensure data
protection and privacy
The data is breached, leaked, or accessed
by unauthorised parties, violating data
p
rotection and privacy laws and regulations
Unlikely (2) Severe (5) Major (10)
Cyber - Ensure the model's
integrity and functionality
The model is hacked, corrupted, or
tampered with, compromising the integrity
and functionalit
y
of the
g
enerative AI
Unlikely (2) Severe (5) Major (10)
Cyber - Ensure the output
authenticity and
accountabilit
y
The output is spoofed, impersonated, or
falsified, deceiving or harming the target
audience or stakeholders
Possible (3) Severe (5)
Major
(
15
)
Generative AI Risk Management in Digital Economy
123

Generic Risks: Common to all projects,
including budget, schedule, scope, and quality
concerns.
Technology-Specific Risks: Unique to
generative AI, such as data integrity, model
reliability, and output accuracy.
Cyber Risks: Related to the security and privacy
of AI technology, including threats like hacking,
phishing, and spoofing.
3.2 Risk Assessment Matrix
A full Risk Assessment matrix has been attached in
Table 1. This study explores the risks, feasibility, and
benefits of developing a pilot scheme in likelihood
form. These investigations have potential
consequences from L2 to L6. According to the
organization, various risk categories, Generic,
Technology-specific, and cyber risks, analyze
likelihood, impact, and risk level to get results.
4 RESULT
According to the organization's various risk variables:
Generic risks, Technology-specific risks and cyber
risks, this study created several criteria like
likelihood, impact and risk level to get results.
Through the whole risk assessment matrix to get
results. Pertinent risks associated with content
generation and security through generative AI
encompass:
Data Privacy and Security: The necessity for
generative AI solutions to access sensitive data
mandates stringent protective measures, including
encryption and access controls, to mitigate data
breaches and misuse risks in adherence to regulations
like GDPR.
Content Quality and Accuracy: There exists a
potential for generative AI to yield content that may
be inaccurate or misleading. It is imperative for
organizations to implement rigorous verification and
editorial processes, supplemented by human
oversight, to ensure content integrity and address any
resultant feedback or grievances.
Content Authenticity and Accountability: The
indistinguishability of AI-generated content from
human-produced content necessitates clear labeling
and attribution to the originating organization,
alongside verification methods such as digital
signatures, to uphold content authenticity.
Content Ethics and Legality: Generating
content that could be deemed unethical or illegal
poses significant concerns. Organizations may ensure
that AI-generated content is congruent with their
ethical standards and complies with applicable legal
frameworks and industry
5 DISCUSSION
In light of the risks identified, adopting a
comprehensive and forward-looking strategy for the
ethical and responsible deployment of generative AI,
as proposed in the detailed Risk Mitigation Report
found in Appendix 1, emerges as a prudent approach.
This strategy advocates for a thorough risk
assessment, engaging various stakeholders to explore
potential risks and their implications rigorously. It
echoes the holistic perspectives emphasized in the
academic literature reviewed. The formulation of
Policy and Governance Frameworks, rooted in the
principles of transparency, accountability, fairness,
and safety, is crucial, reflecting the scholarly
consensus on the ethical governance of AI
technologies (Birkstedt et al., 2023). Adopting
stringent Data Management and Security measures,
including data cleansing, anonymization, and
encryption, alongside robust authentication and
auditing protocols, aligns with the best practices
identified in the existing literature (Ooi et al., 2023),
underscoring the importance of safeguarding data
integrity.
The integration of Human Oversight through
approaches like human-on-the-loop or human-in-
command is vital for ensuring accountability and
maintaining content integrity, resonating with the
recommendations by Birkstedt et al., (2023) and
paralleling discussions in the literature on human-AI
collaboration. Utilizing both qualitative metrics,
continuous monitoring, and evaluation is imperative
for continually refining the AI system's effectiveness
and societal impact, mirroring the iterative evaluation
processes highlighted in the academic discourse.
Engaging Stakeholders in ongoing dialogues about
the AI solution's benefits, potential risks, and
limitations is essential for establishing a foundation
of transparency and trust, reflecting the existing
literature's emphasis on stakeholder inclusivity in AI
deployments (Khennouche et al., 2024). This
multifaceted strategy aligns with the academic
literature. It encourages a more measured and
nuanced interpretation of the findings, avoiding
definitive judgments and fostering a balanced
understanding of AI's potential and challenges in
organizational contexts.
FEMIB 2024 - 6th International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
124

6 RECOMMENDATION
Based on the existing literature and frameworks, I
have reviewed best practice approaches/models for
generative AI risk analysis and selected two for this
project:
6.1 The NIST AI Risk Management
Framework (AI RMF)
This is a voluntary set of standards, guidelines, and
best practices to help organizations manage
cybersecurity risks. The AI RMF can help
HealthTrust Europe design, develop, use, and
evaluate trustworthy and responsible AI solutions by
following the four core functions: Govern, map,
measure, and manage. It can help identify, protect,
detect, respond to, and recover from cyber threats that
may affect the generative AI solution, such as data
breaches, adversarial attacks, or system failures
(Tabassi, 2023).
6.2 AI Trust Risk and Management
Framework (AI TRiSM)
Gartner defines AI TRiSM as “a framework that
supports AI model governance, trustworthiness,
fairness, reliability, robustness, efficacy, and data
protection.” (Gartner, 2016)
The AI TRiSM Index covers six dimensions of
trust: transparency, reliability, usability, security,
ethics, and robustness. The model can help
HealthTrust Europe to identify and address the key
factors that influence the trustworthiness of its
generative AI solution, such as the AI system itself,
the data, the environment, the stakeholders, and the
governance. These factors are interrelated and affect
each other so that they may be considered holistically
and dynamically.
HealthTrust Europe can map out the solution's
architecture, design, and functionality, such as the AI
model, the data pipeline, the user interface, and the
output generation. It can also identify the data
sources, data types, data quality, data processing, and
data storage for its generative AI solution, as well as
the use cases, scenarios, and user groups for its
generative AI solution, such as marketing,
communication, customer service, and supplier
management.
Utilizing both NIST and AI TRiSM for generative
AI risk analysis offers distinct advantages:
Complementary Frameworks: NIST's
comprehensive risk management process synergizes
with AI TRiSM's succinct trustworthiness
framework, offering varied perspectives and
granularity.
Holistic Analysis: Together, they foster a
balanced evaluation of generative AI, weighing
potential impacts on diverse stakeholders and societal
implications.
Standardized Communication: These
frameworks facilitate transparent, consistent
reporting on AI risks and trustworthiness, employing
a unified language and structure.
Stakeholder Engagement: NIST and AI TRiSM
enhance the clarity and accessibility of generative AI
risk analyses for a broad audience, including
developers, users, regulators, and the general public.
6.3 Best Practice Approaches
The following scenarios are examples of how both
Best Practice approaches can be used to support the
analysis and mitigation of identified risks associated
with the proposed solution:
In the first scenario, the National Institute of
Standards and Technology (NIST) framework is
employed to meticulously guide the identification,
assessment, and management of potential technical,
ethical, legal, and social risks associated with the AI
solution, including challenges related to data quality,
privacy, model explainability, transparency,
cybersecurity, adversarial attacks, and issues
stemming from human bias, error, or manipulation.
Concurrently, the AI Trust, Risk, and Security
Management (TRiSM) Index is instrumental in
measuring and enhancing the solution's
trustworthiness by utilizing indicators and metrics
focused on transparency, reliability, usability,
security, ethics, and robustness.
In the second scenario, the creation of external
articles and social media posts is envisioned as a
means to communicate and report the performance
and impact of the AI solution to a diverse array of
stakeholders, including regulators, investors,
partners, and the general public. Utilizing the NIST
framework, the generative AI risk analysis's rationale,
methodologies, and outcomes are meticulously
documented and disclosed, ensuring that the
addressed potential risks and impacts are
transparently conveyed. Furthermore, the AI TRiSM
framework is leveraged to provide clear, accessible
information regarding the source and nature of the
generative AI content, alongside evidence and
verification mechanisms. Employing both
frameworks consistently and transparently to
communicate and report on the generative AI risk
Generative AI Risk Management in Digital Economy
125

analysis significantly contributes to building trust,
confidence, and a positive reputation for the
organization and its solution.
In the third scenario, the evaluation of generative
AI solutions for crafting presentations and emails
involves a comparative analysis to select the most
superior options based on quality, reliability, and
trustworthiness. The NIST framework is utilized to
conduct a thorough and systematic risk assessment
for each potential solution, evaluating its efficacy in
addressing anticipated risks and impacts.
Additionally, the AI TRiSM framework is applied to
compare and rank the alternatives based on their
trustworthiness scores, enabling the identification of
each option's strengths and weaknesses, thereby
facilitating a more informed decision-making
process.
7 CONCLUSION
This research elucidates the substantial opportunities
and advantages of generative AI in marketing and
community engagement for HealthTrust Europe,
alongside a set of strategic recommendations to
navigate and alleviate the inherent risks. The study
outlines a comprehensive AI governance strategy by
adopting frameworks like the NIST AI RMF and AI
TRiSM model, emphasizing collaboration with legal
and data protection entities to define clear roles,
responsibilities, and risk boundaries. This includes a
detailed examination of the AI system's structure, risk
evaluation, and performance measurement against
predefined metrics, coupled with implementing risk
mitigation tactics to ensure data integrity and uphold
the principles of transparency, fairness, and
accountability.
However, the study acknowledges certain
limitations, such as the potential for evolving
technological landscapes to outpace current
governance frameworks, and the challenge of fully
anticipating the social implications of generative AI.
Future research directions should focus on dynamic
governance models that can adapt to technological
advancements, and deeper inquiries into the long-
term societal impacts of AI integration, ensuring that
the organization's commitment to social
responsibility remains at the forefront of its
technological adoption strategy.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research is partly supported by VC Research
(VCR 0000230) for Prof Chang.
REFERENCES
Archer, M. S. (2021). The mess we are in: How the
Morphogenetic Approach helps to explain it: IACR
2020 Warsaw. Journal of Critical Realism, 20(4), 330–
348. https://doi.org/10.1080/14767430.2022.1984698
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., & Cipolla, R. (2017).
Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder
architecture for image segmentation. IEEE
Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, 39(12), 2481–2495.
Balk, A. D., Hernandez, T. R., Lennan, K. J., Martinez, C.
E., Olbricht, N. M., & Wimberly, B. D. (2021).
Taxonomy of Situational Awareness Information for the
Future Long-Range Assault Aircraft (FLRAA) Medical
Evacuation (MEDEVAC) Co-Pilot. https://apps.dtic.
mil/sti/citations/trecms/AD1164209
Bandi, A., Adapa, P. V. S. R., & Kuchi, Y. E. V. P. K.
(2023). The power of generative ai: A review of
requirements, models, input–output formats, evaluation
metrics, and challenges. Future Internet, 15(8), 260.
Birkstedt, T., Minkkinen, M., Tandon, A., & Mäntymäki,
M. (2023). AI governance: Themes, knowledge gaps
and future agendas. Internet Research, 33(7), 133–167.
Budhwar, P., Chowdhury, S., Wood, G., Aguinis, H.,
Bamber, G. J., Beltran, J. R., Boselie, P., Lee Cooke, F.,
Decker, S., DeNisi, A., Dey, P. K., Guest, D., Knoblich,
A. J., Malik, A., Paauwe, J., Papagiannidis, S., Patel, C.,
Pereira, V., Ren, S., … Varma, A. (2023). Human
resource management in the age of generative artificial
intelligence: Perspectives and research directions on
ChatGPT. Human Resource Management Journal,
33(3), 606–659. https://doi.org/10.1111/1748-8583.12
524
Coleman, J. S. (1986). Social Theory, Social Research, and
a Theory of Action. American Journal of Sociology,
91(6), 1309–1335. https://doi.org/10.1086/228423
Gartner, W. B. (2016). Entrepreneurship as organizing:
Selected papers of William B. Gartner. Edward Elgar
Publishing. https://books.google.co.uk/books?hl=zh-
CN&lr=&id=A3ONCwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR1&
dq=(Gartner&ots=KWc8LhO6Bu&sig=OTf7OTJ2i6y
40lBChqxUpPW47X4
Hadi, M. U., Tashi, Q. A., Qureshi, R., Shah, A., Muneer,
A., Irfan, M., Zafar, A., Shaikh, M. B., Akhtar, N., Wu,
J., & Mirjalili, S. (2023a). A Survey on Large Language
Models: Applications, Challenges, Limitations, and
Practical Usage [Preprint]. https://doi.org/10.36227
/techrxiv.23589741.v1
Hadi, M. U., Tashi, Q. A., Qureshi, R., Shah, A., Muneer,
A., Irfan, M., Zafar, A., Shaikh, M. B., Akhtar, N., Wu,
J., & Mirjalili, S. (2023b). Large Language Models: A
Comprehensive Survey of its Applications, Challenges,
FEMIB 2024 - 6th International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
126

Limitations, and Future Prospects [Preprint].
https://doi.org/10.36227/techrxiv.23589741.v4
Khennouche, F., Elmir, Y., Himeur, Y., Djebari, N., &
Amira, A. (2024). Revolutionizing generative pre-
traineds: Insights and challenges in deploying ChatGPT
and generative chatbots for FAQs. Expert Systems with
Applications, 246, 123224.
Lamarre, E., Smaje, K., & Zemmel, R. (2023). Rewired:
The McKinsey guide to outcompeting in the age of
digital and AI. John Wiley & Sons. https://books.
google.co.uk/books?hl=zh-CN&lr=&id=DjDFEAAA
QBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&dq=(McKinsey,+2023)&ots
=YHxpIC13Jf&sig=MNhupEewOtBtlos86d3Ohfip51s
Mourtzis, D. (2021). Towards the 5th industrial revolution:
A literature review and a framework for process
optimization based on big data analytics and semantics.
Journal of Machine Engineering, 21(3).
https://bibliotekanauki.pl/articles/1833773.pdf
Nagy, P., Frey, S., Sapora, S., Li, K., Calinescu, A., Zohren,
S., & Foerster, J. (2023). Generative AI for End-to-End
Limit Order Book Modelling: A Token-Level
Autoregressive Generative Model of Message Flow
Using a Deep State Space Network. 4th ACM
International Conference on AI in Finance, 91–99.
https://doi.org/10.1145/3604237.3626898
Ooi, K.-B., Tan, G. W.-H., Al-Emran, M., Al-Sharafi, M.
A., Capatina, A., Chakraborty, A., Dwivedi, Y. K.,
Huang, T.-L., Kar, A. K., Lee, V.-H., Loh, X.-M., Micu,
A., Mikalef, P., Mogaji, E., Pandey, N., Raman, R.,
Rana, N. P., Sarker, P., Sharma, A., … Wong, L.-W.
(2023). The Potential of Generative Artificial
Intelligence Across Disciplines: Perspectives and
Future Directions. Journal of Computer Information
Systems, 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/08874417.2023
.2261010
Pasquero, C., & Poletto, M. (2023). Biodesign in the Age of
Artificial Intelligence: Deep Green. Taylor & Francis.
https://books.google.co.uk/books?hl=zh-
CN&lr=&id=2sXDEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT8&d
q=this+dynamic+landscape+is+shaped+by+tech+giant
s+and+invigorated+by+innovative+AI+startups+like+
Anthropic,+signalling+a+vibrant+and+expanding+fiel
d.&ots=eql9u1-y7S&sig=vE88-
MbQY5AMZgp60Ak1ItbHXVg
Preiksaitis, C., & Rose, C. (2023). Opportunities,
challenges, and future directions of generative artificial
intelligence in medical education: Scoping review.
JMIR Medical Education, 9, e48785.
Ryan, G. (2018). Introduction to positivism, interpretivism
and critical theory. Nurse Researcher, 25(4), 41–49.
Tabassi, E. (2023). Artificial Intelligence Risk Management
Framework (AI RMF 1.0). https://www.nist.gov/
publications/artificial-intelligence-risk-management-
framework-ai-rmf-10?trk=public_post_comment-text
Zermatten, V., Navarro, J. C., Hughes, L., Kellenberger, T.,
& Tuia, D. (2023). Text as a richer source of
supervision in semantic segmentation tasks. IGARSS
2023-2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote
Sensing Symposium, 2219–2222. https://ieeexplore.
ieee.org/abstract/document/10282398/?casa_token=rI
wWKhBvi5YAAAAA:GT1viBA2JPi8Kg2K1b4NXU
-9g_fr0DnG_QwSNbUTsEB-eMAaOp2Y5xBOG6Nu
g40khhrgLNMw7A
Generative AI Risk Management in Digital Economy
127
