
Generative AI for Productivity in Industry and Education
Ferenc H
´
ejja
1,3 a
, Tam
´
as Bart
´
ok
3 b
, Roy Dakroub
3 c
and Gergely Kocsis
2 d
1
University of Debrecen, Doctoral School of Informatics, Hungary
2
University of Debrecen, Faculty of Informatics, Department of Informatics Systems and Networks, Hungary
3
EPAM Systems, Hungary
Keywords:
Generative Artificial Intelligance (GenAI), Large Language Models (LLM), Industry, Education, Productivity.
Abstract:
Generative AI tools are the cutting edge solutions of complex AI related problems. While investigating state-
of-the-art results related to the effect of GenAI in the literature, one can note that the trends most likely lead to
the expectation of a positive effect on the middle and long run. Based on these findings we define 4 productivity
gain related hypotheses that we study using two types of methodologies. Namely we perform a survey research
related to university-industry collaboration and quantitative studies mainly based on industrial productivity
metrics. We have partnered with a major IT services provider - EPAM Systems - to be able to track, validate
and analyze the key productivity metrics of software development projects, with and without using GenAI
tools. This evaluation is being performed on various stages of the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC)
and on several project roles. Our goal is to measure the productivity increase provided by GenAI tools.
Although this research has just started recently, considering that the area has extremely high attention we
present some initial findings.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to a recent note published by IMF ”Al-
most 40 percent of global employment is exposed to
AI” (Cazzaniga et al., 2024). Even though the ab-
solute impact of this exposure is not uniform, indus-
try and especially IT ecosystem has to stay up to date
with the emerging changes implied by AI and more
precisely LLM models. The same note emphasizes
that ”Workers with a college education have histori-
cally shown a greater ability to transition into what
are now jobs with high AI-complementarity poten-
tial.” underlining the well-known fact that the key of
making Industries able to adopt to these changes is
education (Cazzaniga et al., 2024).
Research by Cecilia Ka Yuk Chan, Wenjie Hu,
and Faming Wang’s team unveils that students’ per-
ceptions of GenAI significantly influence their learn-
ing outcomes, and that a carefully planned AI educa-
tion policy, like the proposed AI Ecological Education
Policy Framework, can help manage AI integration in
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-5770-5577
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-3384-1919
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7767-1107
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0018-4201
university settings, align actions with their policy, im-
prove AI literacy and thereby, prepare students for an
AI-driven future. (Chan, 2023; Chan and Hu, 2023)
(Wang et al., 2023).
Not surprisingly one of the areas of industry that
is the most affected by the revolution of Generative
AI is the IT industry. While the last revolution of
this field was the widespread application of agile soft-
ware development methodologies about a decade ago,
it seems that nowadays we are at the rise of another
revolution. Even though the exact productivity gain of
using AI at different phases of the Software Develop-
ment Life Cycle (SDLC) is not known, and there are
even voices saying that in some cases the use of AI
can even hinder the production, it seems that accord-
ing to the common voices the use of LLM Generative
AI (GenAI) can improve productivity. The questions
we pose in this current research aim to find some ex-
act measures of this productivity gain so that one can
decide that according to the recent state of the tech-
nology at what phases of SDLC does it worth to apply
the new tools.
In the meantime we try to apply our results from
three different points of view. i.) The first and most
important aspect is of course the industrial one since
this is the field that can benefit the most in the short
128
Héjja, F., Bartók, T., Dakroub, R. and Kocsis, G.
Generative AI for Productivity in Industry and Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0012736200003708
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Complexity, Future Information Systems and Risk (COMPLEXIS 2024), pages 128-135
ISBN: 978-989-758-698-9; ISSN: 2184-5034
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

run from applying AI. ii.) The second aspect is from
the perspective of industry management. It may be
a question how AI can improve productivity on high
level management of industries. This connection ap-
pears to be less trivial. iii.) The third aspect is the
side of education. More precisely university and col-
lege education. The main questions here is if these
actors can effectively prepare students to the appli-
cation of GenAI in their work and even it would be
good to know what effects GenAI has on the learn-
ing experience itself. It is also an open questionn
how the high education can integrate the industrial re-
sults and tasks into their programme as new special-
izations (e.g. How to prepare students to be suitable
for new job types like prompt engineering or GenAI
aided software development?).
Since these three fields and questions cover a re-
ally broad area of research we aim to focus our stud-
ies the exact case IT industry and related studies in
the early phase of our work.
In this paper the next section presents our find-
ings based on reviewing related state-of-the-art pub-
lications. After that we pose our hypotheses we aim
to answer in our research, while in section 4 we show
the two forms of studies we would like to use we also
present our first findings that may prove our hypothe-
ses. The paper closes with a short discussion.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Generative AI in the IT Industry
Although the application of Generative AI in indus-
trial processes does not have a broad scientific liter-
ature yet, leading IT companies has started to pub-
lish their related findings in the industrial environ-
ment (including white papers, technical reports and
business journals). These publications predict that we
are before fundational productivity changes in the re-
lated fields of industry.
According to EPAM’s report, ”A Call to Ac-
tion for Generative AI” (Burkitt et al., 2023), 80%
of the workforce could have at least 10% of their
tasks affected, 19% of the workforce may see at least
50% of their tasks impacted, 300 million full-time
jobs could potentially be automated globally, Genera-
tive AI could eventually increase annual global GDP
by 7%, Productivity gains for a range of tasks and
processes may be greater than 50%, The combined
impact of productivity gains and revenue growth
may increase the enterprise value of successful early
adopters by up to 20%+ (see also (Eloundou et al.,
2023) and (Hatzius et al., 2023)).
A study conducted by William Harding and
Matthew Kloster from GitClear suggests that AI pro-
gramming assistants such as GitHub Copilot could
decrease code quality and increase redundancy. The
study reveals AI tools are proficient at adding new
code but fail to update, delete, or move existing ones,
resulting in an alarming increase in code churn and re-
dundancy. Additionally, concerns about AI-generated
code’s security have also surfaced in other studies.
Despite these concerns, its positive impact on pro-
ductivity is acknowledged, contingent upon task com-
plexity and developer skill. Nevertheless, a consensus
seems to indicate humans are irreplaceable in coding,
as AI tools are still error-prone. (Harding and Kloster,
2024)
In recent research conducted by Thomas Dohmke,
Marco Iansiti, and Greg Richards, generative AI, in-
cluding GitHub Copilot, has been found to signif-
icantly increase developer productivity. The tool
was shown to help developers implement solutions
faster, leading to improved productivity and satisfac-
tion. GitHub Copilot’s impact only grows over time,
with users accepting an average of 30% of code sug-
gestions and less experienced developers benefiting
the most. The researchers argue that as developers
become more proficient in AI-prompting and interac-
tion, approximately 80% of code will be AI-written
in the future — a trend which could democratize soft-
ware development and boost developers’ innovative
potential. Like previous groundbreaking technolo-
gies, generative AI may lead to new business mod-
els and a shift towards higher-order work. (Dohmke
et al., 2023)
In this study by Alok Mishra and Yehia Ibrahim
Alzoubi, Agile and Waterfall methodologies were
compared and analyzed for software development.
The researchers discovered that both methodologies
have their strengths: Agile for its flexibility and Wa-
terfall for its stability. They concluded that there is
no one-size-fits-all approach; instead, firms may need
to use a hybrid framework combining aspects of both
Agile and Waterfall methods to meet different project
requirements. The study also suggested that future re-
search could focus on real-world applications of these
hybrid methodologies. Ultimately, the researchers ad-
vocated for firms to incorporate Agile principles into
their existing systems, especially in the digital era.
(Mishra and Alzoubi, 2023)
In his book ”Generative AI - Navigating the
Course to the Artificial General Intelligence Future”,
Martin Musiol invites readers on a journey into the
new world of generative AI and artificial general in-
telligence (AGI), arguing that we are on the precipice
of a transformative epoch in technology. He believes
Generative AI for Productivity in Industry and Education
129

that advancements in AI like ChatGPT mark a point
of no return, underscoring the vast potential of gener-
ative AI across a variety of fields. Musiol maintains
that the swift progression and adoption of generative
AI surpasses the growth arc of preceding technolo-
gies. Believing that this technology has the potential
to redefine the future, he asserts that generative AI can
empower individuals to become significantly more ef-
fective humans. Musiol concludes that mastering AI
will offer a distinct advantage in the realm of tomor-
row, endorsing AI as a tool for striving towards a bet-
ter future rather than a replacement for human intel-
lect and innovation. (Musiol, 2023)
2.2 Generative AI in Universities
In contrary to the industrial era, educational related
research has already a notable amount of scientific
surces in connection to the use of Generative AI tools
by students.
The research conducted by Cecilia Ka Yuk Chan
and Wenjie Hu reveals that students’ views on Gen-
erative AI (GenAI) technologies significantly impact
their learning processes and results. By getting to
know students’ readiness and apprehensions about
GenAI tools, educators can incorporate such tech-
nologies into the teaching process more efficiently.
This step enhances educational outcomes and culti-
vates a comprehensive approach to learning. More-
over, understanding students’ perspectives helps in
assessing AI literacy, enabling the educators to iden-
tify and bridge the knowledge gaps, thereby prepar-
ing students for an imminent AI-driven future. (Chan,
2023; Chan and Hu, 2023).
Faming Wang and his team aimed to devise an
AI education policy targeted at university teaching
and learning. The AI Ecological Education Policy
Framework was proposed to manage the varied as-
pects of AI integration in university settings, divided
into three dimensions – Pedagogical, Governance,
and Operational. This structure aims to help stake-
holders better understand the implications of AI for
teaching and learning and ensure that they are aware
of their responsibilities. If this framework is adopted,
educational institutions can ensure the responsible
and ethical use of AI and augment potential benefits.
Nonetheless, further study is necessary to fully under-
stand the potential benefits and risks associated with
AI in academic settings. Rather than simply push-
ing for AI implementation, stakeholders must care-
fully consider which AI technologies to use, how best
to use them, and fully grasp their capabilities. (Wang
et al., 2023).
In a recent research study, Ramteja Sajja and
Ibrahim Demir developed an automated system, Vir-
tualTA, designed to answer logistical questions on on-
line course discussion boards and educational plat-
forms. The researchers aimed to enhance the qual-
ity of course content and individualized student ad-
vising as well as mitigate inequality amongst students
in terms of knowledge accessibility. The virtual assis-
tant system is also designed to ease transitions for stu-
dents changing degree programs or disciplines. While
the system was developed and tested under controlled
circumstances, the research offers valuable insights
into the potential of VirtualTA in enhancing student
learning and engagement. The researchers acknowl-
edge that while chatbots can reduce the workload for
teachers, they cannot entirely replace human interac-
tion. Future studies could explore improvements to
the AI-augmented educational assistance framework
to better cater to students’ diverse needs and complex-
ities in their academic journeys.(Sajja et al., 2023)
Jeya Amantha Kumar’s research study explores
the impact of Embodied Conversational Agents (ECs)
on project-based learning activities. The study aimed
to evaluate learning outcomes and found that ECs
positively influenced learning performance and team-
work. However, the study found no significant dif-
ferences in the need for cognition, motivational be-
lief, creative self-efficacy, and perception of learning.
The research concluded that while ECs did not signif-
icantly impact cognitive and motivational processes,
they did not create any barriers to project-based learn-
ing either. Interestingly, the study found that the in-
troduction of ECs contributed to a sense of ”team
spirit”. Going forward, further research could explore
the transformational potential of ECs as digital assis-
tants in educational settings.(Kumar, 2021)
While the above results clearly show that when ap-
plied properly GenAI tools can significantly improve
productivity even in high complexity cases we also
have to point out some possible limitations. In their
detailed review Tayyba Rasool et. al. has shown that
technological overload may have a negative effect on
productivity (Rasool et al., 2022). This fact may also
be the reason of the quantitatively slightly different
results of the previously mentioned sources.
3 RESEARCH QUESTIONS
Based on the above findings we posed 4 hypotheses
among 3 main areas related to productivity gain im-
plied by the use of GenAI.
COMPLEXIS 2024 - 9th International Conference on Complexity, Future Information Systems and Risk
130

3.1 The Relevance of Generative AI in
Productivity
While the exact level of the gain implied by the ap-
plication of GenAI proven to be different in different
sources, is seems that a consensus is forming declar-
ing that the use of GenAI has a positive impact on
productivity. Thus we formed our first hypothesis as
below:
Hypothesis 1. The application of GenAI tools can in-
crease the productivity in certain areas.
According to the actual state of our studies we have a
limited number of sources to underly this finding but
even now there are some industrial fields where ex-
act tools can be identified for several tasks. A good
example of this is again software development. Ta-
ble 3 in the appendix section presents a collection of
usable GenAI tools for different phases of the Agile
SDLC (See (Sommerville, 2010) - Chapter 3). In the
table classical and Agile SDLC phases are listed non-
necessarily in their time order. We have collected the
related deliverables and successfully identified the ap-
plicable GenAI tools.
3.2 Measuring Productivity in AI Aided
Software Development and
Education
For different fields like Software Development, In-
dustrial Management or University Education there
are well-known metrics of productivity with which
it is possible to show the effect of the use of some
new technologies or tools. An interesting questions is
however if we can define a uniform way of measuring
productivity in these related but in the mean time dif-
ferent areas. According to our review we would like
to underline the following two related hypotheses:
Hypothesis 2. There might exist a uniform metric of
the objective productivity gain.
Hypothesis 3. There should be a methodology which
can be used for measuring the productivity gain.
Our aim in this work is to find the uniform metric re-
ferred in Hypothesis 2 and also describe the way how
this metric can be measured in order to provide a pos-
sibility for researchers of this field to make a com-
parison to their findings. And this implies our last
hypothesis related to the uniform property of produc-
tivity.
3.3 Comparison of Productivity Gains
in Industry and Education
Closely related to our previous topic we defined in a
separate hypothesis that according to our expectations
productivity itself measured in different fields (indus-
try and education) is a comparable measure, so we can
decide where the use of GenAI has more effect.
Hypothesis 4. Productivity/efficiency is a universal
measure, that can be applied in both fields (Indus-
try/Education).
To underline this hypothesis we need to compare the
related findings of ours and others from the two areas.
As an outcome we would also like to declare in which
area the gain may be bigger.
In order to reach our goals we base our work on
two methods, survey research and analysis of produc-
tivity metrics. While the first method can underly our
first hypothesis, the others can be revealed by the use
the latter one.
4 METHODOLOGY
In order to have first-hand data about the effect of
the use of GenAI tools we base our research on two
sources. i.) At first we sent out surveys to three dif-
ferent groups of users of GenAI tools to get a picture
about their subjective opinion and impression about
these. ii.) At second we measured well known pro-
ductivity metrics of the IT industry to have objective
data about the effect.
4.1 A Survey About the Use of GenAI
Tools
Our surveys are being sent out to three different
groups of users of GenAI tools. Namely i.) to uni-
versity Students, ii.) to Academic Lecturers and Pro-
fessors with Executive roles and iii.) Managerial-level
Innovation consultants in Industry.
As a short summary of the structure of all the sur-
veys, in them we define 5 main topics that we are in-
terested in from three different aspects. By the use of
the results we get from these we expect to be able to
answer questions from Students, Academic lecturers
and IT Industrial Consultants related to
• Section 1: the overall opinion on the productivity
implied by the use of GenAI tools
• Section 2: the aspects of Adoption and Integration
of GenAI
Generative AI for Productivity in Industry and Education
131
• Section 3: the key challenges and opportunities
during the adoption and integration
• Section 4: the possible (and likely uniform) ways
of measuring productivity
• Section 5: the future of GenAI areas.
Technically we have created a ”master survey” that
has been altered in different ways to fit the special
aspects of the different target audiences. As a re-
sult, our findings coming from different target groups
will become comparable and commonly processable.
In relation with our hypotheses, we suppose that the
GenAI related productivity gain (Section 1) depends
on the other four factors (i.e. the level of integration,
the faced challenges, the way how we measure and
the related expectations).
4.1.1 Identifying SDLC Phase Related GenAI
Enabled Key Use Cases
While results of the surveys may give us an over-
all picture of the use of GenAI in the above men-
tioned fields, the scope of this survey would be also to
identify the GenAI enabled key use cases within the
SDLC phases including the Requirements Gathering,
Design, Development, Testing, Deployment and Sup-
port such as the key uses cases listed in the Table 1.
4.2 IT Industrial Productivity Metrics
Table 2 presents those agile productivity metrics that
can be used within agile software development lifecy-
cle. We have categorized the metrics into team and in-
dividual level ones and also estimated their expected
importance during the quantitative analysis.
Based on business inside preliminary findings we
have identified agile productivity metrics by SDLC
phases and job roles that may potentially be good
measurements for our quantitative analysis. On Table
4 of the appendix section one can note that for each
role we have identified at least 2 metrics, while for
pure software development related roles several mea-
surable indicators are available.
5 DISCUSSION
In this work we focus on the investigation of produc-
tivity gain implied by the use of GenAI from the as-
pects of industry and education. At the current stage
we have performed a review of the state-of-the-art
findings to get a picture of the expected effect of it
and also the possible limitations.
Based on them we stated 4 hypotheses, declaring
that according to our expectations i.) GenAI tools can
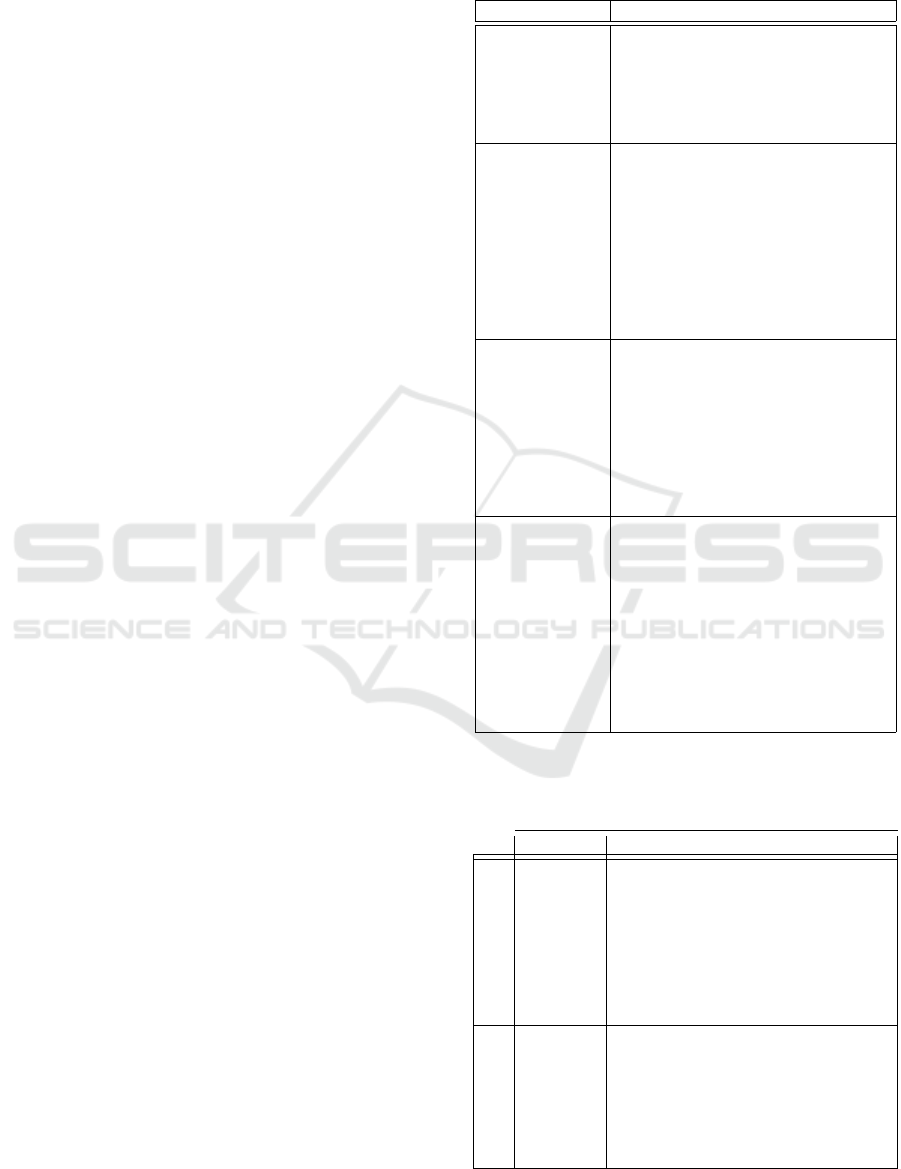
Table 1: GenAI enabled SDLC Key Use Cases - One aim
of our study is to find those use cases that show the most
possible productivity gain when applying GenAI.
Areas Key Use Cases
Key Product
Management
Use Cases
- Ideation and Intake
- Define and Design
- Develop (linking to SDLC)
- Launch and GoToMarket Planning
- Measure
- Retire
Key Business
Analysis
Use Cases
- Domain and Competitor Analysis
- Requirements Elicitation and Anal-
ysis
- Backlog Creation: Epic, User Story
and Acceptance Criteria Writing
- Process and Data Modelling
- Communications and Stakeholder
Management
- Knowledge Management and Train-
ing
Key Enginee-
ring Use Cases
- API/3rd Party Integration
- Business/Application Logic Imple-
mentation
- Unit Test Coverage
- Code Refactoring
- Code Explanation and Documenta-
tion
- Programming Language Conver-
sion
Key Testing
Use Cases
- Test Case Design and Development
- Test Code Generation and Mainte-
nance
- Test Planning, Execution and Re-
sults Analysis
- Test Case Maintenance and Man-
agement
- Test Data Generation and Manage-
ment
- Test Result Analysis and Defect
Management
Table 2: Proposed agile metrics for measuring the GenAI
productivity gain during software development on team’s
and on individulas’ level.
Priority Metric
Team metrics
High Velocity (Avg. velocity by sprints)
Medium Cycle time
High Lines of Code by Developers (Avg)
High Changed Lines of Codes
High Rework Time
Medium Average Code Review Time
Medium Code Review Failure Rate
Individual metrics
Medium Time in Requirements
Medium Requirement quality
Medium Time in Grooming
High Average Code Review Time
Medium Test Cases Creation
Medium Defect Rate
COMPLEXIS 2024 - 9th International Conference on Complexity, Future Information Systems and Risk
132

boost productivity and ii-iii.) the productivity gain
can be measured by a uniform metric or set of met-
rics. We also state that iv.) productivity itself is a
comparable universal metric that can be used across
these less closely related fields.
To reason our hypotheses we will perform a sur-
vey based study and quantitative analysis based on in-
dustrial productivity related metrics.
This position paper on the one hand presented the
structure, scope and target of the survey to be used.
On the other hand we have successfully identified
the investigatable industrial roles, use cases and tools
with their related metrics.
As a next step of our work we will send out the
surveys for our industrial and educational partners.
Meanwhile at our partner comparable projects are
started with and without the use of GenAI tools. Ac-
cording to our expectations we get enough data in the
next 3 − 4 months to be able to start the analytical in-
vestigation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors acknowledge EPAM for making the
project metrics data available which was essential to
show results based on analysis.
Gergely Kocsis was supported by the project TKP
2021 NKTA of the University of Debrecen Project
no TKP 2021 NKTA 34 has been implemented with
the support provided from the National Research, De-
velopment and Innovation Fund of Hungary, financed
under the TKP 2021 NKTA funding scheme.
REFERENCES
Burkitt, F., Zhukov, A., and Razorionov, D. (2023). A call
to action for generative ai. Technical report, EPAM.
Cazzaniga, M., Jaumotte, F., Li, L., Melina, G., Panton,
A. J., Pizzinelli, C., Rockall, E. J., and Tavares, M. M.
(2024). Gen-ai: Artificial intelligence and the future
of work. IMF Staff Discussion Notes, pages 1–42.
Chan, C. K. Y. (2023). A comprehensive ai policy education
framework for university teaching and learning. Inter-
national Journal of Educational Technology in Higher
Education, 20(1):38.
Chan, C. K. Y. and Hu, W. (2023). Students’ voices on
generative ai: perceptions, benefits, and challenges
in higher education. International Journal of Educa-
tional Technology in Higher Education, 20(1):43.
Dohmke, T., Iansiti, M., and Richards, G. (2023). Sea
change in software development: Economic and pro-
ductivity analysis of the ai-powered developer lifecy-
cle.
Eloundou, T., Manning, S., Mishkin, P., and Rock, D.
(2023). GPTs are GPTs: An Early Look at the Labor
Market Impact Potential of Large Language Models.
Papers 2303.10130, arXiv.org.
Harding, W. and Kloster, M. (2024). Coding on copilot -
2023 data shows downward pressure on code quality.
Technical report, GitClear - visited at 15.02.2024.
Hatzius, J. et al. (2023). The potentially large ef-
fects of artificial intelligence on economic growth
(briggs/kodnani). Goldman Sachs.
Kumar, J. A. (2021). Educational chatbots for project-based
learning: investigating learning outcomes for a team-
based design course. International Journal of Educa-
tional Technology in Higher Education, 18(1):65.
Mishra, A. and Alzoubi, Y. I. (2023). Structured soft-
ware development versus agile software develop-
ment: a comparative analysis. International Journal
of System Assurance Engineering and Management,
14(4):1504–1522.
Musiol, M. (2023). Generative AI: Navigating the Course
to the Artificial General Intelligence Future. Wiley,
Hoboken, New Jersey.
Rasool, T., Warraich, N. F., and Sajid, M. (2022). Ex-
amining the impact of technology overload at the
workplace: A systematic review. SAGE Open,
12(3):21582440221114320.
Sajja, R., Sermet, Y., Cwiertny, D., and Demir, I. (2023).
Platform-independent and curriculum-oriented intel-
ligent assistant for higher education. International
Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Educa-
tion, 20(1):42.
Sommerville, I. (2010). Software Engineering. Addison-
Wesley, Harlow, England, 9 edition.
Wang, F., King, R. B., Chai, C. S., and Zhou, Y.
(2023). University students’ intentions to learn ar-
tificial intelligence: the roles of supportive environ-
ments and expectancy–value beliefs. International
Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Educa-
tion, 20(1):51.
Generative AI for Productivity in Industry and Education
133
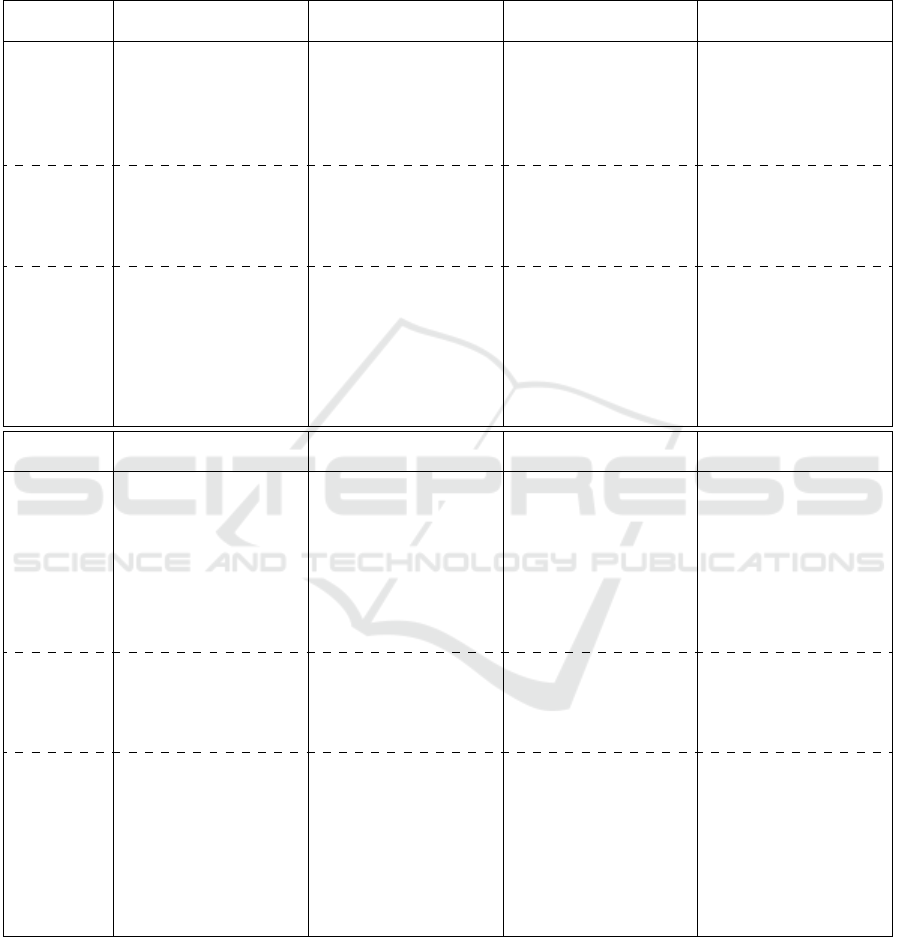
APPENDIX
Table 3: GenAI enabled activities, deliverables and tools related to the phases of the Agile SDLC. In the table classical and
Agile SDLC phases are listed non-necessarily in their time order. We have collected the related deliverables and successfully
identified the appliable GenAI tools.
I. Reqs. Gathering II. UX Design III. Architecture Design IV.Delivery Plan
GenAI
accelerated
activity
Personas & Journeys
Stakeholders Interviews
Epics and User Stories
Domain
& General Research
Documents Analysis
Personas & Journeys
Wireframes
Prototyping
Define design guidelines
& code structure
Define non-
functional requirements
Define Quality
Attributes
Generate Delivery Plan
GenAI
assisted
deliverable
Epics & User Stories
High Fidelity Mockup
Application Prototype
Design and
Coding Guidelines
Solution Architecture
Document
Delivery Plan
(tasks, grouping,
sequencing)
Project Risks
& Mitigation Plan
GenAI tool
Azure Open AI GPT
FaceBook LLAMA-2
Amazon Titan
Anthropic’s Claude 2.1
Midjourney
Stable Fusion
DALL-E 2
Hostinger
Durable
Visily AI
WIX
Uizard
Azure Open AI GPT
FaceBook LLAMA-2
Amazon Bedrock
AmazonQ
Amazon Titan
Anthropic
´
s Claude 2.1
Azure Open AI GPT
Amazon Titan
Anthropic’s Claude 2.1
V. Development VI. Testing VII. Deployment
VIII. Support
& Maintenance
GenAI
accelerated
activity
Translate User Stories
into Gherkin Scenarios
Generate Unit Tests
Coding with Copilot
Code Review
Translate User Stories
into Test Requirements
Generate Test
Specification
Generate Functional
tests
Generate Automated
Tests
Test Results Analysis
Update Build
& deployment Scripts
Proactive Monitoring
& Recovery
Bugs Troubleshoo
Proactive Tests Coverage
Refactoring
GenAI
assisted
deliverable
Unit Tests
Source Code
Integration
& Regression Test
Documentation
Test Plan
Test Specification
Manual and autoamted
E2E Test
Documentation
CI Scripts
Deployment Scripts
Bug Fixes
Increased Tests Coverage
Refactored Code
Enhanced Maintainability
GenAI tool
Azure Open AI GPT
Google Codey
GitHub Copilot
Amazon CodeWhisperer
Copilot X (Copilot Chat)
Copilot Enterprise
Copilot Workspace
Anthropic’s Claude 2.1
Amazon Titan
Azure Open AI GPT
Google Codey
GitHub Copilot
Amazon CodeWhisperer
Duet AI
Phind
Codeium (Plugin)
Anthropic
´
s Claude 2.1
Amazon Titan
Azure Open AI GPT
GitHub Copilot
StarCoder
Amazon CodeWhisperer
Duet AI
Phind
Codeium (Plugin)
Anthropic
´
s Claude 2.1
Amazon Titan
ChatGPT
GitHub Copilot
StarCoder
Amazon CodeWhisperer
Duet AI
Phind
Codeium (Plugin)
Anthropic
´
s Claude 2.1
Amazon Titan
COMPLEXIS 2024 - 9th International Conference on Complexity, Future Information Systems and Risk
134
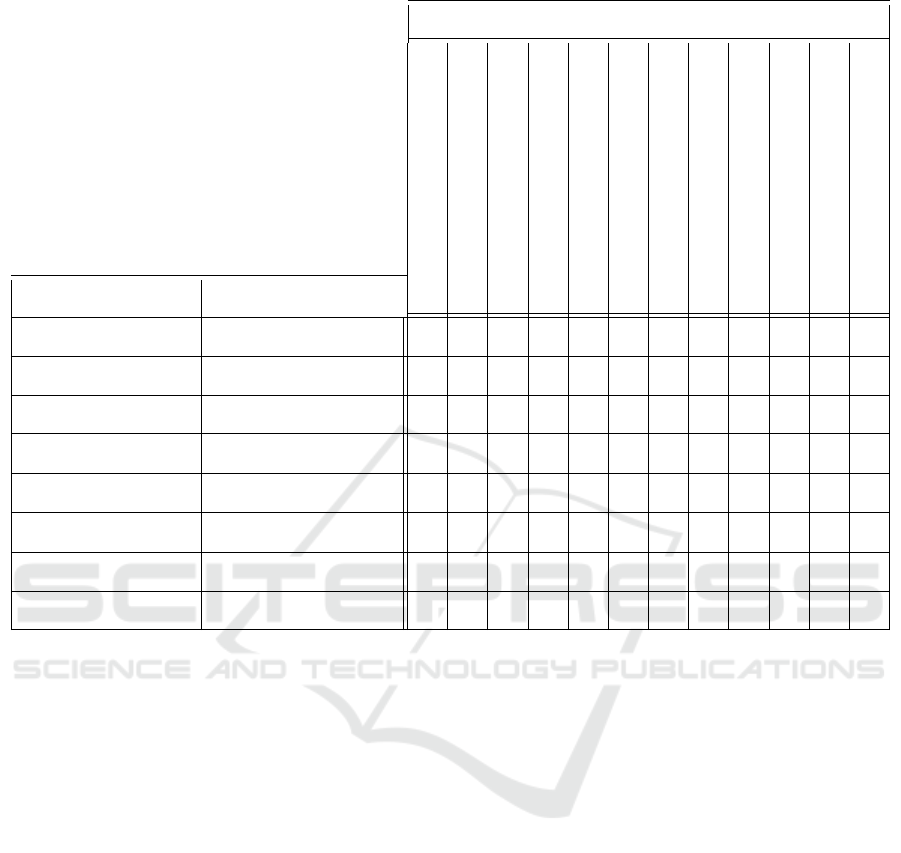
Table 4: Identified Agile productivity metrics by SDLC phases and Job roles.
Agile productivity metric
Velocity (Average velocity by sprints
Cycle time
Time in Requirements
Requirement quality
Time in grooming
Lines of Code by Developers (Avg)
Changed Lines of Codes
Rework Time
Average Code Review Time
Code Review Failure Rate
Test Cases Creation
Defect Rate
SDLC Phase Job role
Requirements Gathering Business analyst X X X X
UX Design UX Designer X X
Architecture Design Software Architect X X
Delivery Plan
Project manager, Delivery
manager, Scrum master
X X X
Development Developer X X X X X X X
Testing
Test automation engineer,
Manual test engineer
X X X
Deployment DevOps engineer X X X X X X X X
Support DevOps engineer X X
Generative AI for Productivity in Industry and Education
135
