
Industry 4.0: Wearable IoT Device Applied to Warehouse Management
Lucas Samaniego Vicente
a
, Saul Delabrida
b
, Mateus Coelho Silva
c
,
Adrielle de Carvalho Santana
d
and Ricardo Augusto Rabelo Oliveira
e
Programa de P
´
os-Graduac¸
˜
ao em Instrumentac¸
˜
ao, Controle e Automac¸
˜
ao de Processos de Minerac¸
˜
ao, Universidade
Federal de Ouro Preto e Instituto Tecnol
´
ogico Vale, Ouro Preto, Minas Gerais, Brazil
Keywords:
Warehouse, Raspberry Pi, IoT, Node-Red, Wearable, RFID.
Abstract:
Companies in the retail sector need proper control of their stock to avoid financial waste and guarantee the
effectiveness of their operations. A more detailed analysis of this problem reveals the complexity of imple-
menting a management methodology that enables optimal control of all stock, since human errors occur during
operations and various scenarios depend on different variables. Therefore, to solve the problem of efficient
warehouse stock management and the resulting inefficiency of operations, this study proposes the implemen-
tation of a wearable, developed using a Raspberry Pi 4B with IoT and Node-Red, in conjunction with a mobile
device, which assists operators during the processes of stocking, searching for and removing material from
the warehouse more efficiently. As a result, the proposed system can identify, by reading an RFID tag with
a mobile device, the characteristics of the equipment in question, showing all this information on an OLED
display, as well as directing what will be done with this equipment via an app. Among the metrics that demon-
strate the effectiveness of the proposed system is the time taken to stock and remove the material, since all the
procedures are managed in real-time on the app and updated in its inventory control.
1 INTRODUCTION
The purpose of having a stock in a company is based
on the notion that certain products or materials are
expected to be used later, to meet market demand
or internal demand. Among its many functions, the
following can be mentioned: Increased scale in the
retail and transport sectors, protection against price
increases, as well as safeguarding the organization
against uncertainties in demand and replenishment
times. In a nutshell, stockpiling provides a better bal-
ance in terms of the organization’s operations, mak-
ing it possible to reduce labor costs and maximize
installed capacity. (Bertaglia, 2012) To have access
to these functionalities, it is often necessary to spend
a lot of money, but stocks guarantee safety levels in
complex and uncertain environments. (Gonc¸alves,
2013)
In this context, efficient stock management is es-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-3526-2454
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8961-5313
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3717-1906
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1457-8930
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5167-1523
sential, and there are alternatives to help this complex
process. Among them, the use of technology, lever-
aged by the advent of Industry 4.0, has become in-
creasingly attractive. This is justified by its potential
to be used on a large scale, at an increasingly afford-
able cost, and because it incorporates challenges that
are on the frontier of human knowledge, with the po-
tential to revolutionize sectors in the field of logistics.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the proposal architecture.
The fourth industrial revolution, or industry 4.0,
seeks to increasingly integrate various productive sec-
tors, with machinery and devices connected, forming
a complex and robust system. In this context, this in-
532
Vicente, L., Delabrida, S., Silva, M., Santana, A. and Oliveira, R.
Industry 4.0: Wearable IoT Device Applied to Warehouse Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0012736300003690
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2024) - Volume 2, pages 532-539
ISBN: 978-989-758-692-7; ISSN: 2184-4992
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

dustry has six important attributes in terms of project
management: The Internet of Things, cyber-physical
systems, Big Data, automation, artificial intelligence,
and cloud computing. (Borges et al., 2022)
From the current market reality, one case worth
highlighting concerns order picking, since it is seen
as a laborious, arduous, time-limited, repetitive, error-
prone, and expensive process in warehouses. These
characteristics put a significant strain on the human
worker, creating fatigue and feelings of monotony,
as well as dissatisfaction, generally leading to poor
performance and employee demotivation.(Ponis et al.,
2020) (Rejeb et al., 2020)
Because of this reality, one of the most promi-
nent technologies in Industry 4.0 has begun to be used
when it comes to manufacturing and logistics opera-
tions, which is Augmented Reality. It uses computer-
generated displays, sound, text, and effects to en-
hance the user experience in the real world and sup-
port workers in their daily tasks, such as assembly,
order picking, and maintenance. (Plakas et al., 2020)
This article aims to present a proposal for a sys-
tem that uses an IoT wearable device to optimize op-
erations within a warehouse, using a low-coast system
to read RFID tags within an smartphone, and provide
essential data to the wearable. To this end, this arti-
cle is divided into related works, the state of the art
in wearables in Industry 4.0, an overview of the pro-
posed system, the methodology used, and, finally, the
respective results and discussions.
2 RELATED WORKS
This section presents the related works in the litera-
ture, providing an overview of how Industry 4.0 tech-
nologies can be applied in a warehouse scenario.
Recent works in the literature include (Hamdy
et al., 2022), which aimed to propose a system that
uses the Node-Red platform to apply the Internet of
Things in a warehouse scenario. Based on a database,
it was possible to manage inventory and forecast stock
demand, using both quantitative and qualitative meth-
ods. In this context, the system could not be tested in
a real warehouse, nor did it implement a user interface
with a dashboard linked to Node-Red for real-time vi-
sualization of all inventory, which the author suggests
as an opportunity for application in future work.
For the entire warehouse to communicate with the
internet, it is necessary to have middleware that is
also capable of receiving information from the ma-
terials and interacting with the user. Among the var-
ious devices that have this potential, the Raspberry
Pi 4 Model B was an option used in the (Silapunt
et al., 2022) study. Using this middleware, an in-
telligent manual pallet truck was created, whose in-
stalled Raspberry Pi processed and uploaded the data
received on the server via the local Wi-Fi network
and, with the web application developed, analyzed
this data and carried out specific warehouse activities.
Based on (Peri
ˇ
sa et al., 2018), it can be seen
that wearable devices are applicable to warehouse
management. Through this study, a smart wearable
bracelet was created, which had RFID tag readers,
NFC, and a Bluetooth connection. When wearing the
smart wristband, the user receives all the relevant in-
formation collected from the smart warehouse envi-
ronment and can read barcode information from prod-
ucts and pallets. In addition, the user obtains the in-
formation needed to determine the location of specific
pallets of products.
3 STATE OF THE ART IN
WEARABLES FOR INDUSTRY
4.0
3.1 Augmented Reality in Warehouses
A use case is presented in a study on the possibili-
ties of augmented reality in warehouse management.
In this study, the global supply chain of the logis-
tics company DHL is evaluated, which is one of the
first companies to introduce augmented reality tech-
nology. The entire system runs on a platform, where
a worker uses a smart glasses, like Vuzix, and a ring
scanner to collect goods.
These devices provide the operator with various
functions and information, starting with the operator’s
login, and visual aids displayed graphically through
the glasses, where the user will see on the graphi-
cal tool the exact location of the goods, the quantity
they should select and the next item. This information
guides the worker precisely, quickly, and efficiently to
a particular order item.
Therefore, this method of picking goods is much
more efficient than the classic form of paper picking.
Finally, about worker training and integration into the
work process, it can be said that this technology is
not difficult to use and can be quickly learned by the
worker.(Hus
´
ar and Knap
ˇ
c
´
ıkov
´
a, 2021)
3.2 Wearable Devices in Inventory
Management
The use of digital resources has proven to be a facilita-
tor inefficient inventory management, which enables
Industry 4.0: Wearable IoT Device Applied to Warehouse Management
533

it to even be a crucial requirement in the market, since
dealing with large-scale data is not a simple task, and
through its use, new insights can be investigated for
improvements in the supply chain process, as noted
by (Anusha et al., 2022).
In this context, in a world of scarce resources, the
use of information converted into knowledge is essen-
tial not only today but also for the future of human-
ity. Thus, this creation and utilization of knowledge
is a basic condition in the supply chain, and inventory
management must be supported by intelligent algo-
rithms and modern heuristics that use this knowledge
to avoid overstocking while combating stock short-
ages or losses (Cimen et al., 2021) (Manuel Vera,
2021).
3.3 Communication Between Hardware
and RFID Sensors
Well-known logistics companies such as Amazon use
sensors to optimize processes in which it is necessary
to identify several items simultaneously, which would
be too slow and error-prone without this implementa-
tion. Its application can extend even to the food indus-
try since there are studies in which RFID tags are in-
tegrated with chip-free sensors to measure humidity,
temperature, gas concentration, and pH. (Fathi et al.,
2020)
The way it is applied varies according to need
since this technology can be molded for different
types of use. Analyzing the behavior and monitor-
ing the movement of a visitor in a museum, for ex-
ample, can be done using a set of mobile antennas
and passive RFID tags. The embedded system was
made up of an RFID reader, a 10-axis inertial man-
agement unit, and a logger that allows internal local-
ization based on the detection of multiple tags located
in known positions along the visitor’s route. This ap-
proach was tested in simulation and in real museum
practice.(Vena et al., 2021)
However, the biggest challenge that discourages
the implementation and full benefits of Industry 4.0
technologies are the costs involved with the technol-
ogy. In the supply chain, the implementation of RFID
technology is hampered by the cost of RFID tags and
adoption problems. The costs involved with the use-
ful life of the systems tend to make organizations re-
luctant to implement these Industry 4.0 technologies
and, in the case of organizations that have already im-
plemented the technology, they tend to fall behind in
maintaining these systems due to the costs and the
inaccuracies of the system, since the lack of main-
tenance makes the systems unreliable.(Tikwayo and
Mathaba, 2023)
3.4 Wearable Device Apple Vision Pro
The Apple Vision Pro is a wearable device with sig-
nificant potential to transform human interaction with
the digital world. This device can provide real-time
access to information and detailed guidance for the
execution of complex tasks, enhancing operational ef-
ficiency across various contexts.
In daily life, the Apple Vision Pro can have a sub-
stantial impact on user health and well-being. The
device can monitor user health, providing alerts when
rest is needed or if a position could cause injury. Fur-
thermore, real-time feedback allows users to quickly
correct errors and learn new skills more efficiently.
In industry, the Apple Vision Pro has the poten-
tial to improve both operational efficiency and prod-
uct quality. Workers can use the device to inspect
products on a production line, identifying defects that
may be difficult to detect with the naked eye.
4 OVERVIEW OF THE
PROPOSED SYSTEM AND
VALIDATION TESTS
This section presents the architecture of the proposed
system. Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the
desired architecture and its functionalities.
Generally speaking, the proposed system includes
RFID tags, whose identifications will be read by a
mobile application, which interacts with the tag via its
NFC sensor, and publishes the tag’s identification ID
via MQTT communication, according to the task to
be performed. The tasks are divided into three forms:
1. Stocking: Once the material has been identified,
you want to store it in a suitable place in the ware-
house. Thus, according to the item’s ID, Rasp-
berry Pi 4B will process this data, and, depend-
ing on the material’s characteristics, the cloud
database will indicate the appropriate storage ad-
dress on the display.
2. Pickup: Once a material is to be withdrawn, it
can be updated in the database system by reading
the relevant tag and clicking on the ”withdraw”
button in the application.
3. Detail and Search: Within the mobile applica-
tion, the user will enter the material they want
to search for or have its detailed information
and, according to the information contained in the
database, the display will be informed of the ad-
dress where the item is located and its respective
characteristics. Among the information returned
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
534
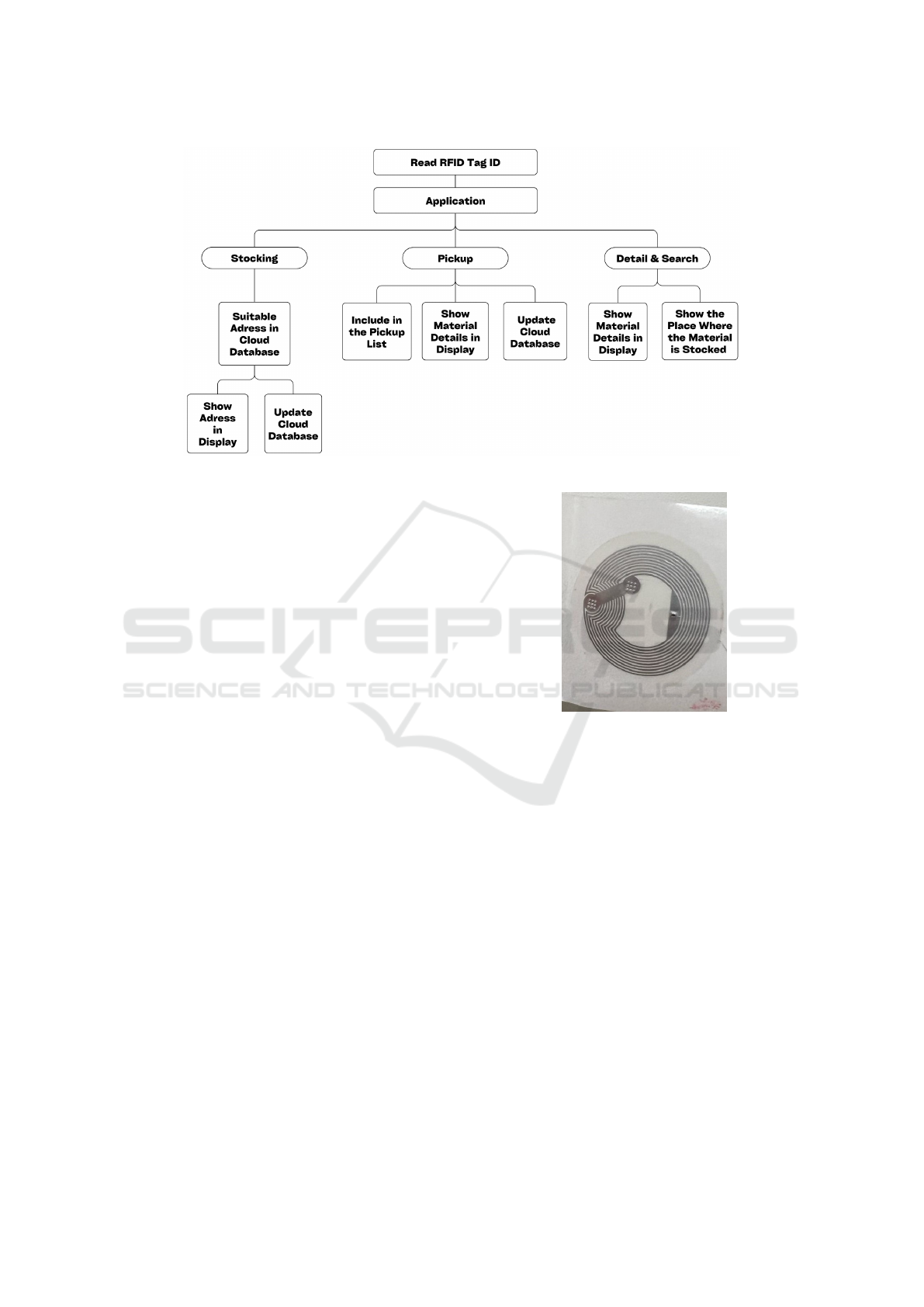
Figure 2: System Flowchart.
is material location data, name, part number, se-
rial number, and status, among others. As a result,
the operator can see all the desired information
about a particular item in an up-to-date display.
In more detail, the system can be divided as shown
in Figure 2.
4.1 RFID Tags
Passive RFID tags, which store unique identifications
(IDs), function as passive antennas that receive radio
frequency signals and can be attached using labels to
materials that require stricter control.
RFID tags, employing Radio-Frequency Identi-
fication technology, have emerged as indispensable
tools for optimizing and automating processes across
various domains. Equipped with microchips and an-
tennas, these tags facilitate data transmission through
radiofrequency, enabling efficient identification and
tracking of objects, animals, or even individuals. This
technology represents an evolution compared to con-
ventional barcodes, offering the capability of remote
reading, resulting in faster and more precise data col-
lection in diverse environments.
The distinctive advantage of RFID tags lies in
their ability to store and transmit unique informa-
tion associated with each label. This feature not only
streamlines logistical operations but also contributes
to product authentication and ensures the integrity of
the supply chain.
4.2 Smartphone Application
To read RFID tags and then enable the user to per-
form tasks based on the ID of the tag read, a smart-
Figure 3: RFID Tag.
phone application was developed that has an interface
for interaction with the user, as well as a backend that
directs the application’s MQTT communications with
the broker.
In the Figure 4, it’s show that the smart phone ap-
plication is able to help the operator to search any
good, pick up the item, update the database and stock,
using the NFC reader in the smart phone for identify
the ID number of the RFID tag.
Among the ways to use the functionalities of the
mobile application is the possibility of turning on or
off the device’s NFC sensor, using a button. When
a RIFD tag is identified, its respective ID number is
shown on the smart phone screen. Based on this iden-
tification, the operator specifies what he wants to do
with that material.
We will assume that the indoor location is associ-
ated with the Smartphone Application and the Cloud
Server communication.
Industry 4.0: Wearable IoT Device Applied to Warehouse Management
535

Figure 4: Smartphone application layout.
4.3 Wearable Device
A Raspberry Pi 4B, with a Linux-based operating
system, will be responsible for running code which,
when connected to the internet via Wi-Fi, will be able
to receive specific information from the requested
sensors and send it to a server in the cloud. Once this
data has been processed, the microprocessor receives
it and uses it to help the operator through augmented
reality visualization on the OLED display.
The Figure 5 illustrates how the wearable device
is used. The OLED display is supported by a sup-
port made by 3D printing, which was developed to
be viable as a wearable device and be suitable for the
display fittings and their respective connections to the
Raspberry Pi.
Figure 5: Wearable Device with display.
4.4 Cloud Server
A server hosted in the cloud can have a variety of
resources to meet the demands of software or stor-
age services. Working as a complement to the mi-
croprocessor, which has limited resources due to its
structure, the server is capable of storing, processing,
and managing a large amount of data, and can inte-
grate applications such as MySQL, i.e. a structured
database that helps control data and can be presented
in the form of a dashboard.
In practice, the server receives the RFID tag iden-
tifications checks its database for the information re-
lating to these requested identifications, and sends an
action back to the microprocessor. Also it is responsi-
ble for managing the client’s physical location in the
indoor environment. This feedback provides the nec-
essary information for the Raspberry Pi to transmit
the data requested by the operator to an OLED display
so that the operator can interact with the environment
and this information can be linked to the material in
the form of augmented reality. This form of interac-
tion constitutes an Internet of Things mechanism and
helps make the system lean.
4.5 OLED Display
The component in which the operator can interact
with the environment, with augmented reality, to
identify relevant information about a material, be it its
location, part number, serial number, material status,
and status of said item.
The transparent OLED display has the capability
to allow the wearer to see the surrounding environ-
ment, even if information is being shown on the dis-
play.
4.6 Validation Tests
Validation tests for a wearable device in a warehouse
environment should indeed focus on critical aspects
such as accurate identification of materials. The de-
vice must be capable of accurately recognizing and
differentiating between various materials and prod-
ucts in the warehouse.
In addition, the device’s ability to provide clear
guidance to the operator is crucial. For instance, the
device could use arrows or other visual indicators to
guide the operator to the exact location of the ma-
terial. This must involve testing the accuracy of the
device’s navigation system and its ability to integrate
with the warehouse’s inventory management system.
These tests help ensure that the device not only
improves the efficiency of warehouse operations but
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
536
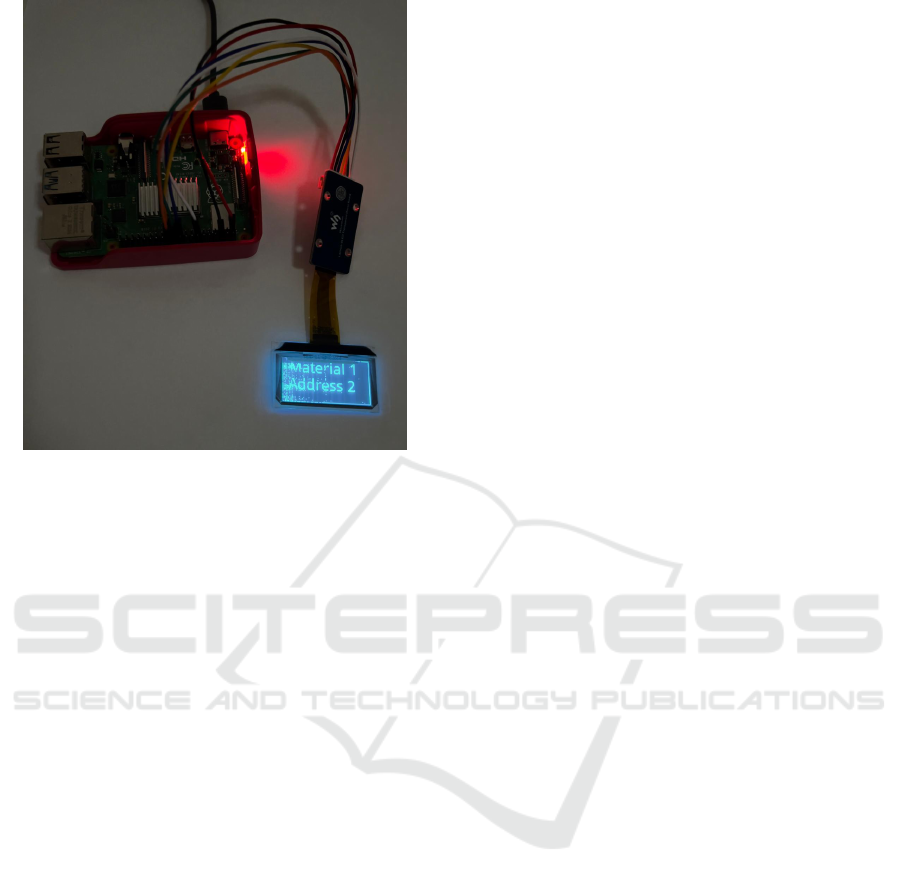
Figure 6: Raspberry Pi with OLED display.
also minimizes errors, thereby enhancing the accu-
racy and reliability of the material handling process.
5 METHODOLOGY
5.1 Internet of Things
The Internet of Things is becoming one of the main
foundations of Industry 4.0, helping companies and
organizations to strengthen their level of competitive-
ness in the market. In this context, linked to the pop-
ularization of embedded systems with Wi-Fi connec-
tivity, wireless communication and exchange of infor-
mation between devices has proved to be an alterna-
tive for guaranteeing the security of this information
and its scalability.
5.2 Node-Red Development
Environment
The Node-Red programming tool has been widely
used in the context of research and industry when it
comes to developing programs for automation, mak-
ing it possible to connect devices, APIs, and online
services. (Node-Red Site, 2023)
Unlike other types of development environments,
Node-Red is a browser-based editor, built in Node.js,
which is capable of connecting flows via nodes. Be-
cause it has vast libraries of nodes, Node-Red can per-
form various functions, such as communicating be-
tween devices using the MQTT protocol, connecting
a system to a database hosted in the cloud, performing
logical-mathematical operations, and executing code
locally.
5.3 Interaction Between Devices via
MQTT Protocol
The operator needs to perform actions that indicate to
the device its need for information. To do this, the
operator can interact with the device using buttons
which, when pressed, help to select the correct item
to be evaluated.
Once the desired item has been selected, commu-
nication takes place between the smartphone applica-
tion and the display, and for this, we chose to build
communication via the MQTT (Message Queuing
Telemetry Transport) protocol. This protocol is based
on the transport of messages in a client/server format,
enabling communication between (MQTT Site, 2023)
machines, which, in the case of this work, is the com-
munication between the Raspberry Pi and the OLED
Display integrated with augmented reality.
As an alternative to setting up MQTT communica-
tion, we chose to implement a code in the Node-Red
development environment. Through this code, the mi-
croprocessor can send requests arising from the oper-
ator’s handling of the wearable device, which, in re-
turn, receives information relevant to warehouse man-
agement. Once the item data is returned to the device,
the operator can see the exact location of the material
or its particular characteristics.
6 RESULTS
As a result of implementing the system, it was pos-
sible to demonstrate its operation and functionality.
Figure 4 illustrates the layout of the mobile applica-
tion.
The layout of the app shows the connection status
of the smartphone’s NFC sensor and the connection
between the app and the MQTT broker. In addition,
the app has buttons that act sending the ID of the iden-
tified item. Although all the buttons send the ID, they
send it via a specific topic, which tells the wearable
device what kind of information it should pass to the
display.
As a result of processing the tag ID read, the dis-
play was able to show the following results for each
task:
As a way of measuring the impact of this device
on a real warehouse application, a qualitative compar-
ison was made of the average time taken to update the
system and the database of a warehouse that does not
Industry 4.0: Wearable IoT Device Applied to Warehouse Management
537

Figure 7: Raspberry Pi Flow in Node Red.
(a) Go ahead (b) Go back
(c) Turn left (d) Turn right
Figure 8: Illustration of arrows for operator direction.
have this type of infrastructure. In this context, for
the user to write off materials that have been stored
and removed from the system, it is necessary to fill
in a lot of information and, the more materials that
need to be processed, the longer it takes to complete
all the write-offs, especially if the warehouse has few
employees available to carry out the write-offs. In
the case of the proposed system, the material write-
off is carried out automatically by the system in the
database, making the user’s routine more productive
and with less manual work.
In the Figure 8, it’s shown an illustration of arrows
for operator direction when it’s needed to find some
materials. Like a GPS guide, the display guide the
operator to the correct position of an especific good.
The position of the good is saved in the cloud database
and track the position of the operator by the GPS in-
side the smartphone e show how to go to the item.
In addition, the proposed system offers greater se-
curity in the process of identifying material for stor-
age and withdrawal, since each item has a unique
identification, which reduces the chance of human er-
ror when carrying out the collection.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this work, a wireless communication system was
developed and implemented between an embedded
device, i.e. a Raspberry Pi 4B, and a smartphone ap-
plication, using the MQTT protocol. The system aims
to provide information about items in a warehouse to
an operator via a transparent OLED display connected
to the Raspberry Pi, generating a user experience with
the environment. In addition, the system has been
integrated with RFID tags and a smartphone’s NFC
reader, which allow items in the warehouse to be iden-
tified, facilitating stock control and monitoring and
providing low-cost identification of rfid tags using a
smartphone..
The system can be tested in a real scenario, with
different types and quantities of items. The pro-
posed system is applicable in various contexts involv-
ing inventory management, warehousing, and logis-
tics, helping to improve the efficiency and safety of
processes. In future work, we suggest integrating the
system with other technologies, such as cameras and
robots, to expand the functionalities and possibilities
for operator interaction with the environment.
ICEIS 2024 - 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
538

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank FAPEMIG, CAPES,
CNPq, Instituto Tecnol
´
ogico Vale, and the Federal
University of Ouro Preto for supporting this work.
This study was partially funded by the Coordenac¸
˜
ao
de Aperfeic¸oamento de Pessoal de N
´
ıvel Superior
- Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001, the Con-
selho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cient
´
ıfico e Tec-
nol
´
ogico (CNPq) finance code 306101/2021-1 and
308219/2020-1, FAPEMIG - Finance Code APQ-
01331-18.
REFERENCES
Anusha, D. J., Panga, M., Fauzi, A. H., Sreeram, A., Iss-
abayev, A., and Arailym, N. (2022). Big data an-
alytics role in managing complex supplier networks
and inventory management. International Conference
on Sustainable Computing and Data Communication
Systems, ICSCDS 2022 - Proceedings, pages 533–
538.
Bertaglia, P. R. (2012). Log
´
ıstica e gerenciamento da
cadeia de abastecimento. Saraiva.
Borges, I. B., Alves, J. L., de Lima, L. K. A., and de Nadae,
J. (2022). Ind
´
ustria 4.0: impactos das novas tecnolo-
gias no gerenciamento de projetos. Exacta, 20:832–
860.
Cimen, E. B., Kurban, I., Selmanoglu, O., Sahin, M., and
Kilinc, D. (2021). A hybrid stock optimization ap-
proach for inventory management. HORA 2021 - 3rd
International Congress on Human-Computer Inter-
action, Optimization and Robotic Applications, Pro-
ceedings.
Fathi, P., Karmakar, N. C., Bhattacharya, M., and Bhat-
tacharya, S. (2020). Potential chipless rfid sensors for
food packaging applications: A review. IEEE Sensors
Journal, 20:9618–9636.
Gonc¸alves, P. S. (2013). Administrac¸
˜
ao de Materiais. Else-
vier.
Hamdy, W., Al-Awamry, A., and Mostafa, N. (2022). Ware-
housing 4.0: A proposed system of using node-red for
applying internet of things in warehousing. Sustain-
able Futures, 4:100069.
Hus
´
ar, J. and Knap
ˇ
c
´
ıkov
´
a, L. (2021). Possibilities of us-
ing augmented reality in warehouse management: A
study. Acta logistica, 8:133–139.
Manuel Vera, J. (2021). Inventory control under unobserved
losses with latent state learning. In 2021 7th Interna-
tional Conference on Computer and Communications
(ICCC), pages 1594–1599.
MQTT Site (2023). Mqtt oficial site. Available at: https:
//mqtt.org/. Accessed in September 13th, 2023.
Node-Red Site (2023). Site oficial da node-red. Acessado
em 15 de novembro de 2023.
Peri
ˇ
sa, M., Sente, R. E., Cviti
´
c, I., and Kolarovszki, P.
(2018). Application of innovative smart wearable de-
vice in industry 4.0. EAI.
Plakas, G., Ponis, S. T., Agalianos, K., Aretoulaki, E., and
Gayalis, S. P. (2020). Augmented reality in manu-
facturing and logistics: Lessons learnt from a real-
life industrial application. Procedia Manufacturing,
51:1629–1635.
Ponis, S. T., Plakas, G., Agalianos, K., Aretoulaki, E.,
Gayialis, S. P., and Andrianopoulos, A. (2020). Aug-
mented reality and gamification to increase productiv-
ity and job satisfaction in the warehouse of the future.
Procedia Manufacturing, 51:1621–1628.
Rejeb, A., Keogh, J. G., Wamba, S. F., and Treiblmaier, H.
(2020). The potentials of augmented reality in supply
chain management: a state-of-the-art review. Man-
agement Review Quarterly 2020 71:4, 71:819–856.
Silapunt, R., Panpanyatep, W., and Boonsothonsatit, G.
(2022). Design and development of the smart object
for the iot-enabled smart warehouse. In 2022 Inter-
national Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON),
pages 1–4.
Tikwayo, L. N. and Mathaba, T. N. D. (2023). Applica-
tions of industry 4.0 technologies in warehouse man-
agement: A systematic literature review. Logistics,
7(2).
Vena, A., Illanes, I., Alidieres, L., Sorli, B., and Perea, F.
(2021). Rfid based indoor localization system to ana-
lyze visitor behavior in a museum. 2021 IEEE Inter-
national Conference on RFID Technology and Appli-
cations, RFID-TA 2021, pages 183–186.
Industry 4.0: Wearable IoT Device Applied to Warehouse Management
539
