
Secure Audio Watermarking for Multipurpose Defensive Applications
Salma Masmoudi
1 a
, Maha Charfeddine
1 b
and Chokri Ben Amar
2 c
1
REGIM: REsearch Groups on Intelligent Machines, National Engineering School of Sfax (ENIS), University of Sfax,
Sfax 3038, Tunisia
2
Department of Computer Engineering, College of Computers and Information Technology, Taif University,
Taif 21944, Saudi Arabia
Keywords:
Audio Watermarking, Tamper Detection, Authenticity, Integrity Control, Recovery.
Abstract:
Audio recordings contain very sensitive content, such as historical archival material in public archives that
protects and conserves our cultural heritage, digital evidence in the context of law enforcement, the online
formats of sensitive digital Holy Quran, etc. Such audio content is vulnerable to doctoring and falsification of
its origin with malicious intent. One tool to solve several multimedia security difficulties facing this sensitive
content is to tag it with a message before the distribution process. This technique is called watermarking.
Hence, this paper aims to present a scheme of tamper detection and integrity control based on multipurpose
and secure audio watermarking. To treat the integrity control application, we suggested embedding in the
digital audio signal the tonal components resulting from the Human Psychoacoustic Model masking study,
which are extracted as features from the relevant low-frequency band of the original audio signal. In addition,
a Multilayer perceptron-based denoising autoencoder was executed after learning robust representation from
corrupted audio features to correct the watermarked frequencies, thereby restoring the original ones. Conse-
quently, blind tamper detection and blind invertibility were guaranteed. The detailed results indicated that the
suggested scheme achieved higher performance at the integrity control and tamper detection level, as well as
at the watermarking and reversibility properties.
1 INTRODUCTION
Audio recordings contain very sensitive content such
as historical material in public archives that conserve
our cultural heritage, digital evidence in the context of
law enforcement, the online formats of sensitive digi-
tal Holy Quran, etc. Such audio content is vulnerable
to falsification of its origin. Henceforth, the reliability
and provenience of such digital audio content and the
sureness about its origin are very serious factors.
To address this issue, it become essential to use a
mechanism protecting and verifying the authenticity
and the integrity of digital sound recordings. Ordi-
nary watermarking techniques produced an alteration
in the signal to protect that causes loss of data. Ac-
cordingly, watermarking schemes controlling the in-
tegrity of the digital content becomes compulsory. In
these particular schemes, the alterations can be lo-
cated in the watermarked content. However, if a sig-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4827-2158
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2996-4113
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0129-7577
nal is watermarked with an ordinary scheme for in-
tegrity control and is opposed to attacks, then its sig-
nificant parts or/and the hidden watermark can disap-
pear, and it is not possible to reconstruct it.
For this reason, it is interesting to conceive sophis-
ticated versatile watermarking techniques for copy-
right protection (Masmoudi et al., 2020), integrity
control, blind tamper detection (Masmoudi et al.,
2024) and blind-recovering recovery that are also ro-
bust enough to compensate for the drawbacks of ordi-
nary watermarking schemes. The blindness concept
signifies that the original audio signal isn’t needed ei-
ther in the detection process or in the tamper detec-
tion and reversibility ones. In this paper, we introduce
a multipurpose defensive audio watermarking tech-
nique based on different NN (Neural Networks) archi-
tectures and exploiting HPM (Human Psychoacoustic
Model) properties with LPC (Linear Prediction Cod-
ing) envelope estimation of the audio spectral, which
is original reversible, robust and blind.
This paper is planned as follows: section two
presents a literature review of the recent works. Sec-
tion 3 presents the multipurpose audio watermarking
Masmoudi, S., Charfeddine, M. and Ben Amar, C.
Secure Audio Watermarking for Multipurpose Defensive Applications.
DOI: 10.5220/0012739400003687
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE 2024), pages 743-751
ISBN: 978-989-758-696-5; ISSN: 2184-4895
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
743

system. In addition, Section 4 illustrates the experi-
ments and results. Finally, the conclusion is presented
in the last section, along with perspectives for future
research.
2 RELATED WORKS
Sometimes it is indispensable to verify the authentic-
ity of input content, i.e., to decide whether the data
are original, fake, or a modified version of the origi-
nal one.
Authentication techniques are the solutions to
these problems. They are conceived for integrity
verification and source origin authentication. They
are implemented using digital signature (Romney and
Parry, 2006) or digital watermarking.
The digital signature is a non-repudiation en-
crypted message digest extracted from the digital con-
tent. It is generally stored as a separate file which can
be attached to the data to attest integrity and origi-
nality. In contrast, digital watermarking techniques
insert a watermark into the digital content so that the
watermark is residing in protection of this content.
In this context, fragile watermarking has been em-
ployed in the few past years to counter the dilemma of
content authentication and tamper localization of im-
age (Awasthi and Nirmal, ) and video (El’Arbi et al.,
2011; Tarhouni et al., 2023) hosts. The main intend
of such schemes is to be fragile in content manipula-
tion attacks; i.e. good detection performance on tam-
per localization while robust to conventional signal
processing operations (e.g. resampling, adding noise,
and filtering). But, in many application fields, such as
criminal execution, the court and news, recorded au-
dio files could be unkindly falsified or removed during
transmission.
As a result, these digital signals should be checked
to decide whether they are authentic or changed (Li
et al., 2014; Tong et al., 2013). As the Human Au-
ditory System (HAS) is more sensible than the Hu-
man Visual System (HVS) (Ali et al., 2022), fragile
audio watermarking schemes for content authentica-
tion and tamper detection are more defiant than those
for image and video. Hence, research on audio wa-
termarking in tampering detection and recovery has
been suggested in recent years.
In (Hu and Lee, 2019), the authors introduced
multi-purpose audio watermarking found on Lifting
Wavelet Transform LWT decomposition to fulfill au-
thentication and copyright protection. Following the
3-level Lifting Wavelet Transform (LWT) decomposi-
tion of the audio signal, the coefficients in chosen sub-
bands are partitioned into frames for embedding. To
enlarge applicability, the robust watermark including
proprietary information, synchronization code, and
frame-related data was principally hidden in the ap-
proximation subband using perceptual-based rational
dither modulation (RDM) and adaptive quantization
index modulation (AQIM). The fragile watermark is
a highly compressed version of the embedded audio.
Hashing comparison and source-channel coding make
it possible to recognize tampered frames and restore
affected regions. Experimentation indicates that the
inserted robust watermark can endure common at-
tacks, and the fragile watermark is very operational
in tamper detection and recovery. The integration of
a frame synchronization mechanism makes the sug-
gested system endure cropping and replacement at-
tacks. The perceptual evaluation shows that the wa-
termark is inaudible and the scheme is appropriate for
content authentication applications.
Moreover, to guarantee the requirements of the
International Federation of Phonographic Industry
(IFPI) for robustness, imperceptibility, payload, and
audio integrity, the paper (Narla et al., 2021) proposes
a robust and blind digital audio watermarking (DAW)
scheme. The suggested method uses quantization in-
dex modulation to include a pre-processed watermark
picture into singular values of audio signal coeffi-
cients. To detect audio tampering, such as deletion,
copy-move, and substitute attacks, a hash produced
using the SHA-512 method is put in watermarked au-
dio frames. Audio is split, and then each segment
is turned into a matrix to achieve tamper detection.
Audio is split, and then each segment is turned into
a matrix to achieve tamper detection. Each matrix
segment is subjected to singular value decomposition
(SVD), and the median is computed. To create the
secret key, these values are logically XOR with the
encrypted watermark.
In addition, (Liu et al., 2024) suggests a new au-
thentication and recovery watermarking scheme for
encrypted audio. The authors present the relative en-
ergy (RE) feature and analyze the characteristics of
the feature. In the inserting process, the host audio is
firstly encrypted. Then the resulting encrypted audio
is split into frames. The embedding of watermark bits
into each frame is done by quantifying the RE fea-
ture. At the decoding stage, the receivers locate the
attacked frames based on the watermark extraction
and substitute the attacked frames using 0 amplitude
signals, which are scattered over different segments
after anti-scrambling transformation and do not influ-
ence the expressed meaning of watermarked signal.
Experimental evaluation results demonstrate that the
scheme improves the security of audio signals stored
on third-party servers.
ENASE 2024 - 19th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
744

3 PROPOSED METHOD
In this section, we depict an enhanced secure mul-
tipurpose audio watermarking scheme based on two
different Neural Network architectures in the fre-
quency domain able to assure very high impercepti-
bility, robustness, security, integrity, blind detection,
blind tamper localization and blind recovering (re-
versibility) proprieties.
In general, robust watermarks are not affected
when the watermarked data is attacked. These water-
marks are often used in copyright protection applica-
tions. However, fragile watermarks can be destroyed
by data manipulation, and these are also called a
tamper-proof watermark. The fragile watermark can
detect the modifications in the signal and also recog-
nize the place where the modifications have occurred
and also the signal before the change. Therefore,
these watermarks are used for content authentication,
integrity control, and tamper localization. Hence, to
conceive a multipurpose audio watermarking we use
a fragile-content watermarking approach (Steinebach
and Dittmann, 2003) combining robust-watermarking
and fragile-content features.
The adopted watermarking scheme is presented in
(Charfeddine et al., 2022). It inserts imperceptibly
the watermark and assures a good robustness to var-
ious attacks by exploiting BPNN architecture in the
embedding and extraction processes and by studying
some HPM proprieties with the LPC envelope esti-
mation of the PSD (Power Spectrum Density). This
watermarking scheme is denoted DCT-NNS-MPH.
We then explain the importance of selecting rel-
evant features from the audio signal as watermark
to ensure integrity control and after that tamper de-
tection and recovery. We present an MLP-based de-
noising autoencoder (Charte et al., 2018) adopted to
train the chosen original and watermarked attacked
features with their indexes and positions to perform
then adequately their content (feature-frequencies or
features-values) reversibility.
We achieve blind frame-resynchronization in the
detection process in the case of particular de-
synchronization attacks. This re-synchronization
mechanism is blind when the proposed watermarking
scheme is robust and promises then reversibility.
In the case of unrobustness, the re-
synchronization mechanism is semi-blind and
only the indexes of the original features in the audio
frame (and the original frame numbers, when the
attack is very destructive) are needed by the receiver
to assure then reversibility and the original feature
frequencies recovering.
Effectively, neither the original audio signal nor
the real feature values are transmitted to the receiver
to perform detection, tamper localization and recov-
ery. In both types of reversibility, simulating the
MLP-based denoising autoencoder DAE on the ex-
tracted features from the watermarked and attacked
audio signal permits to recover of particularly relevant
original frequencies by removing tampered informa-
tion (denoising).
Figure 1 illustrates the general proposed audio wa-
termarking scheme: from an audio file, a feature vec-
tor (W1) is extracted. W1 encloses W1-frames, W1-
indexes and W1-values (frequencies). The embed-
ded watermark is the concatenation of W1-frames and
W1-indexes only. The watermarked audio signal is
then transferred via a noisy channel. Next, the water-
mark (W2-frames and W2-indexes) is extracted and
a newly generated feature vector (W3-frames, W3-
indexes and W3-values) is extracted from the water-
marked and attacked file.
If W1-frames and W2-frames are equal and W1-
indexes and W2-indexes too, then robustness is
achieved. If W2-frames and W3-frames are equal and
W2-indexes and W3-indexes also, then authenticity is
reached and integrity is preserved.
However, if W2-frames and W3-frames are differ-
ent or/and W2-indexes and W3-indexes are distinct,
then authenticity and integrity are not achieved. Thus,
based on re-synchronization mechanism depending
on the robustness of our scheme, we can perform
blind tamper detection and blind invertibility by cor-
recting tampered relevant frequency parts after sim-
ulating the MLP-based denoising autoencoder on the
extracted features and without using the original au-
dio nor W1-values.
3.1 HPM Based Relevant Features
Extraction
We need to yield a binary representation of the audio
content that is small enough to be hidden as a wa-
termark and significant enough to identify alterations.
To maintain audio content’s semantic integrity, only a
part of its full spectrum is regularly required.
For our scheme, we select a low-frequency band
to collect suitable and relevant features since this band
defines the most significant contents of the audio sig-
nal. Specifically, we choose pertinent tonal compo-
nents resulting from the fifth step of the Global Mask-
ing Threshold Ltg algorithm of the HPM (Pan, 1995)
and discard noise frequencies.
In reality, these tonal components constitute the
decimated maskers that do not affect the audio qual-
ity if they are inserted later in the middle frequency
Secure Audio Watermarking for Multipurpose Defensive Applications
745
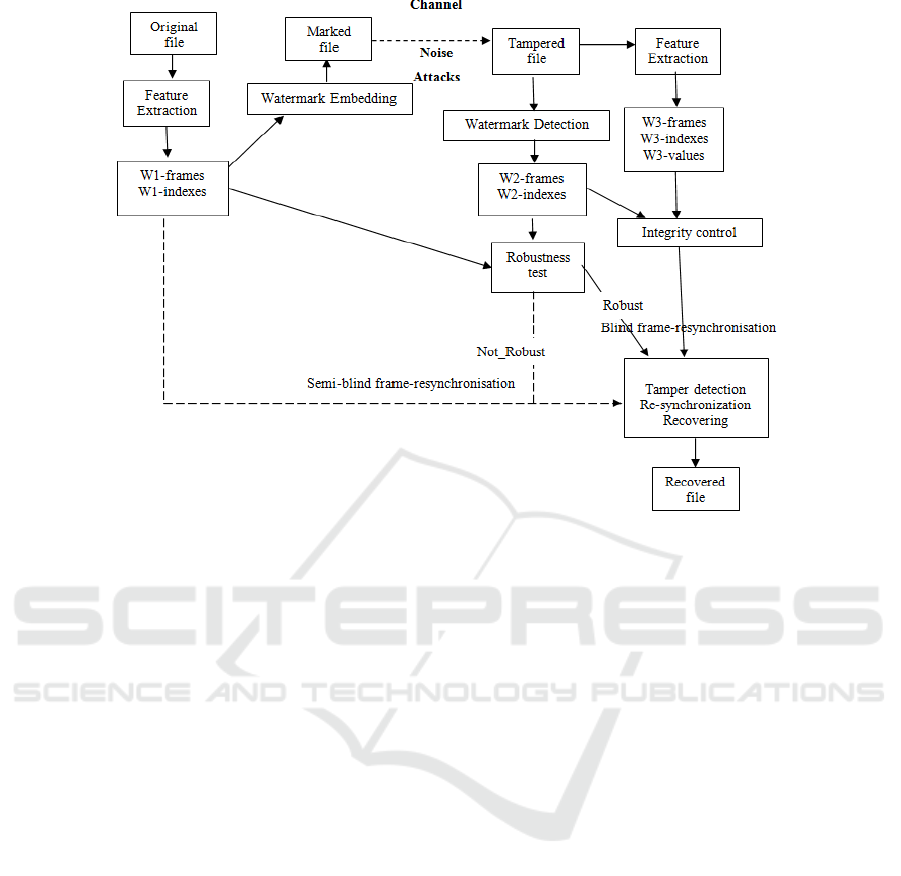
Figure 1: General scheme of the proposed tamper detection system based on DCT-NNS-MPH watermarking.
since they are situated under the Ltg curve. In ad-
dition, decimation constitutes the adopted feature re-
duction approach in our proposed scheme permitting
to diminish the amount of data embedded as water-
mark. After separating the sampled audio signal into
slighter frames and dividing the signal into 32 sub-
bands by a time-frequency mapping filterbank using
a pseudo-Quadrature mirror filter QMF filter (Cruz-
Roldan et al., 2000), the fifth step prompting to re-
trieve the relevant tonal features is computed:
1. FFT is calculated for the conversion from time to
frequency.
2. Sound pressure level is determinated in each sub-
band.
3. Threshold in quiet is determinated (absolute
threshold of hearing).
4. Tonal or sinusoid-like components only of the au-
dio signal are found (not considering the non-
tonal ones).
5. Tonal maskers are decimated and constitute the
searched pertinent features.
It is important to distinguish between tonal and non-
tonal components as shown in figure 3.
For computing the global masking threshold, it
is necessary to derive the tonal and non-tonal com-
ponents from the FFT spectrum. This stage be-
gins with the localization of local maxima after ex-
tracting tonal components (sinusoids-like) from low-
frequency band (4Khz) in a bandwidth of a critical
band.
In our case, we don’t consider the non-tonal com-
ponents since they are noisy parts of the audio signal
and therefore they are less significant in point of view
integrity and authentication of the audio signal. In ad-
dition, ignoring them permits adequate reduction of
the features.
We finally generate a vector W1 containing rele-
vant tonal features. Each is identified by a frame num-
ber ”W1-frame”, an index within this frame ”W1-
index”, and the frequency ”W1-value”.
3.2 Used MLP-Based Denoising
Autoencoder for Tamper Detection
and Reversibility
An autoencoder can be seen as the composition of an
encoding map f which projects inputs onto a different
feature space, and a decoding map g which operates
inversely.
The main objective of the autoencoder is to re-
cover as much information as possible from the orig-
inal input, so it will attempt to minimize the distance
between the inputs and the outputs. The distance
function used in the cost function is usually the Mean
Squared Error MSE (Charte et al., 2018), the output
units should use an unbounded activation function.
The quality of learned features can be evaluated by the
ENASE 2024 - 19th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
746
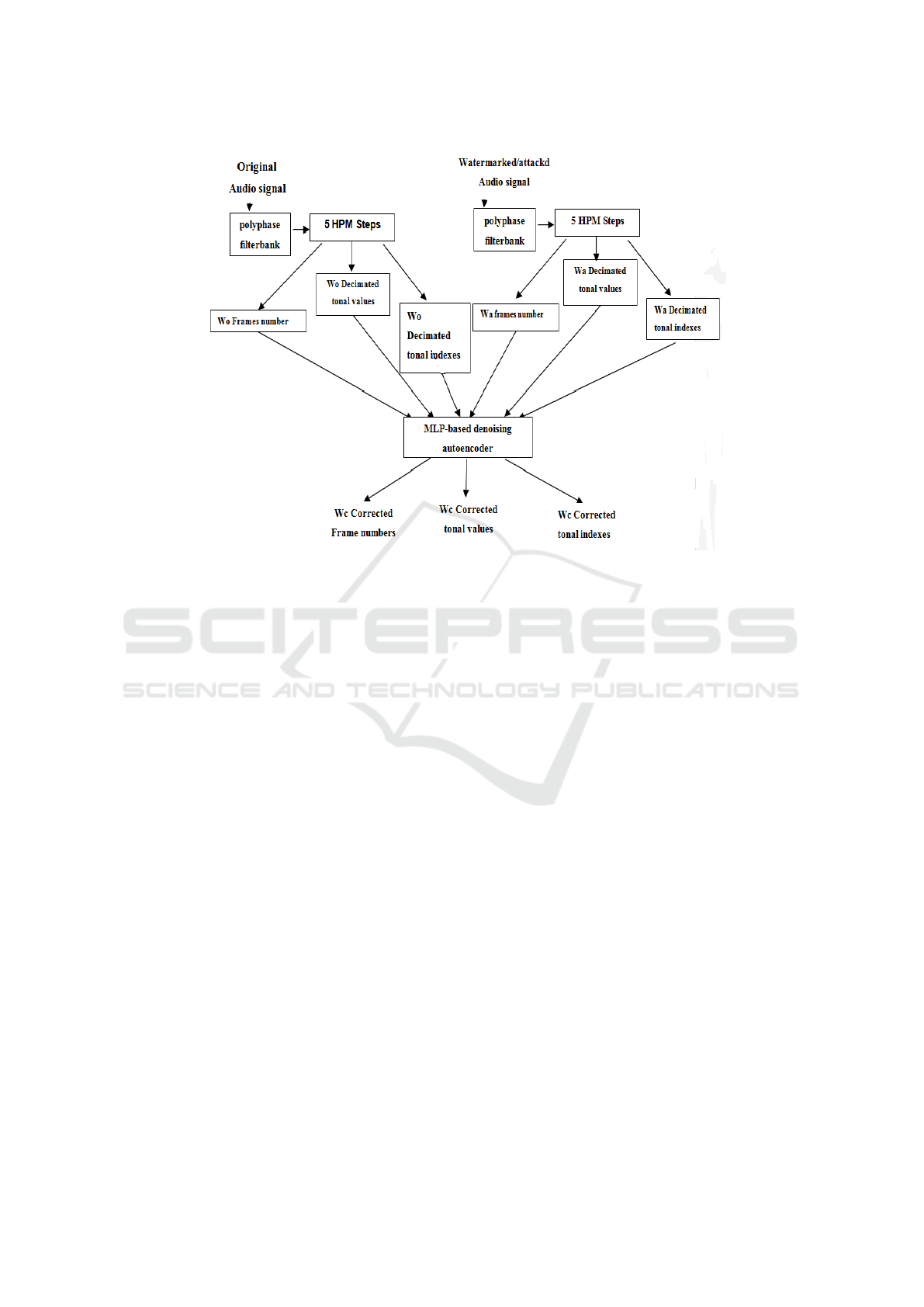
Figure 2: MLP-based denoising autoencoder training process.
model’s ability to project instances back to the origi-
nal feature space.
For this purpose, regression metrics can be used.
Some common metrics that serve to assess the useful-
ness of the learned features are Mean squared error,
Root Mean Squared Error, Mean absolute error and
Mean absolute percentage error (Charte et al., 2018).
The proposed audio watermarking scheme uses
the decimated tonal features extracted from real-life
audio examples, their indexes in a selected frame, and
the frame number of both the original and attacked au-
dio signals as inputs to the DAE during the insertion
process. The objective is to recover original infor-
mation from tampered audio signals by removing the
attacked information. The idea was inspired by the
behavior of the denoising DAE (Charte et al., 2018),
which attempts to learn a robust representation from
corrupted data. Similarly, we consider the attacked
features as input to the DAE and it is trained to re-
cover original ones by correcting altered data as illus-
trated in figure 2.
In the detection process, we simulate the trained
MLP-based denoising DAE with the extracted fea-
tures from the watermarked attacked audio signals.
We obtain as output a correction of the extracted fea-
tures. Thus, we substitute the tampered content values
in the low-frequency band with the corrected content
values in the correspondent frames and the adequate
tonal indexes (which are already re-synchronized if
destructive attacks cause de-synchronization prob-
lems in addition to tampers).
Thanks to this MLP-based denoising DAE archi-
tecture with consideration of the re-synchronization
process, we adequately locate the tampering and en-
sure the invertibility and recovery of the audio signal.
We considered sparse autoencoder by activity regu-
larization to explicitly seek an efficient learned repre-
sentation (Charte et al., 2018). It is handled through
an L1 penalty on the activations with a coefficient λ1
added to the cost function during training to increase
the amount of sparsity in the learned representations.
Additionally, an L2 regularization or weight decay
technique is used by adding a penalty term with co-
efficient λ2 to the cost function.
The training is based on the backpropagation algo-
rithm using the Adam optimizer with an initial learn-
ing rate 0.005 and 3500 epochs. During the train-
ing phase, a learning rate scheduler was considered
to reduce with drop-based technique the learning rate.
This prevents the gradient descent from sticking into
local minima.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
This section is dedicated to presenting several experi-
ments carried out to test the performance characteris-
tics of this proposed audio watermarking method.
Secure Audio Watermarking for Multipurpose Defensive Applications
747
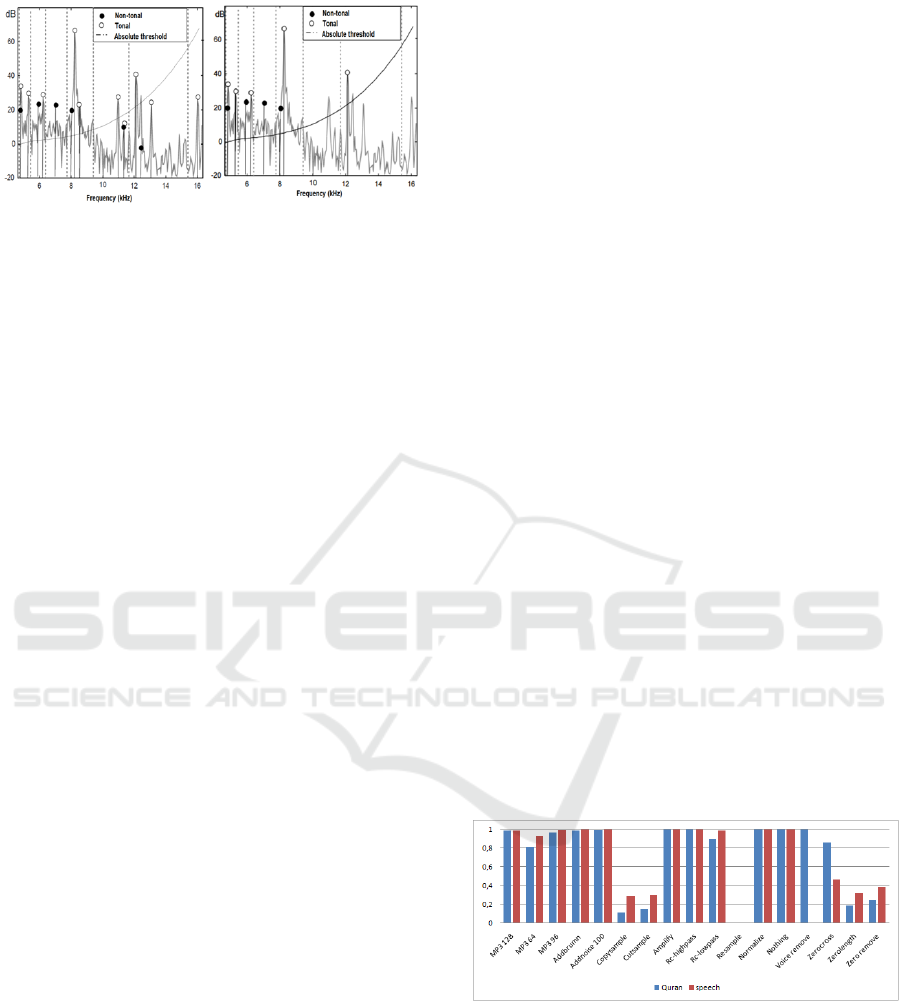
Figure 3: Discrimination between tonal and non-tonal com-
ponents.
4.1 Testing Environment
In this work, different MATLAB simulations are per-
formed. MP3 compression and audio StirMark at-
tacks are common transformations used in the litera-
ture by scientific researchers, which can have a signif-
icant impact on the robustness of the watermark, the
integrity of the audio signal, and the precision of the
detection process. For the compression operation, we
used standard tools such as the lame Audio Encoder.
For other audio manipulations, we used the standard
StirMark Benchmark for Audio (SMBA) tool with de-
fault parameters (WVL, 2006) and Audacity 2.3.3.
Experimental tests are performed on original WAVE
audio files of type music and Quranic-sensitive audio
signals. Owing to the sensitivity of Quranic verses,
there is a crucial need to incessantly monitor Quranic
verses dispatched through Internet websites to make
sure that they are not changed or fraudulent and are
authenticated.
All audio signals have 44.1 KHz as the sampling
rate, 16 bps as several bits per sample, and a duration
of around 20 s. We present the result of a selection of
some audio signals which each one is threatened to 49
Stirmark attacks and three MP3 compression attacks
with three different bitrates. The selected WAVE au-
dio files are musical audio and Quranic-sensitive sig-
nals.
The average length of the extracted features con-
stituting the watermark is about 2100 bits depending
on the sound duration. NC and BER are calculated
to evaluate the similarity between the extracted origi-
nal features and the inserted ones (or between the de-
tected watermark and the attacked extracted features).
4.2 Inaudibility Results
Transparency performance ensures that the water-
marking scheme does not degrade the host signal sig-
nificantly. Otherwise, the watermark embedding pro-
cess did not introduce distinguishable noise in the
host carrier. The objective difference grade (ODG)
(Acevedo, 2006) measure is used. ODG can take a
value between −4 and 0. The closer the value of ODG
to 0, the more degradation is imperceptible.
Table 1 shows the inaudibility results of the pro-
posed scheme.
Due to the exploitation of the frequency percep-
tual masking associated with the LPC estimation of
the digital audio signal, SNR values are significantly
higher than the designed value by the IFPI (20 dB)
(Eya et al., 2013).
In addition, we observe that all the ODG values
are less than −1. Thus, the proposed scheme satisfies
the inaudibility requirements of optimal audio water-
marking techniques.
4.3 Robustness Results
Figure 4 exhibits the MP3 and Stirmark robustness
results. From this figure and the results presented in
the paper (Charfeddine et al., 2022), we observe very
good MP3 robustness results (even, with 64Kbps as
compression rate which is a very destructive attack).
Thus, we realize that using the HPM in the frequency
domain assures not only perfect inaudibility but also
good robustness to MP3 compression.
When observing figure 4 and based on the results
in the paper (Charfeddine et al., 2022), we deduce that
the DCT-NNS-HPM scheme has good robustness re-
sults except for some destructive attacks with highly
damaging perceptive effects.
Experimental results have revealed that the ex-
ploitation of frequency perceptual masking studied in
HPM with the spectral envelope concern in the fre-
quency domain is very interesting with very good in-
audibility and robustness results.
Figure 4: Robustness results of the DCT-NNS-HPM water-
marking scheme.
4.4 Comparison
Inaudibility and robustness comparison results with
the previous scheme (Maha et al., 2010) and other
published audio watermarking schemes are presented
in (Charfeddine et al., 2022) and in tables 2 and 3.
ENASE 2024 - 19th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
748
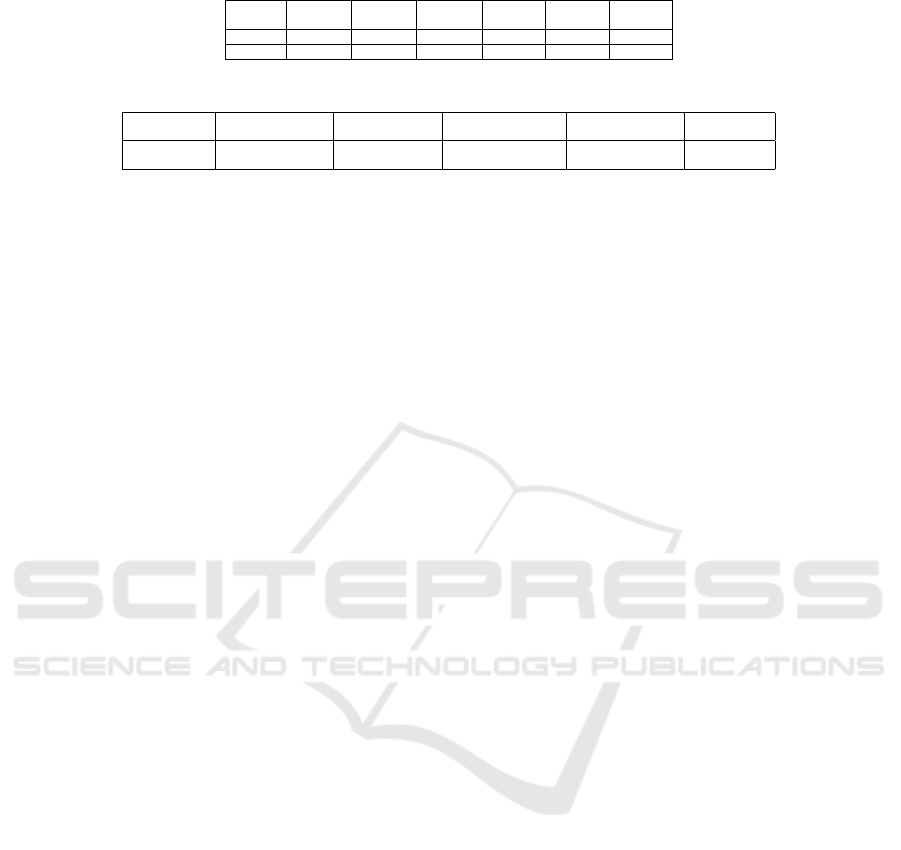
Table 1: Inaudibility results of the DCT-NNS-HPM scheme.
File\
Metrics
Speech1 Speech2 Speech3 Quran 1 Quran 2 Quran 3
SNR 38,0132 45,8644 39,368 42,1998 44,3242 42,2308
ODG -0,9249 -0,9512 -0,3992 -0,7589 -0,4725 -0,6626
Table 2: Average ODG comparison with other watermarking methods.
Inaudibility (Xiang et al., 2015) (Xue et al., 2019) (Korany et al., 2023) (Hu and Lee, 2019)
The proposed
Method
Absolute
Average ODG
1.1623 0.6175 0.245 [0.56, 0.79] 0.43
4.5 Integrity Control Results
To check whether the watermarked audio signal is
tampered or not after Stirmark attacks, we verify in-
tegrity by comparing the original content features and
the extracted content of the attacked watermarked au-
dio file.
If no attack occurs, the bit rate error (BER) is
equal to zero. When observing table 4, we show test
results after performing MP3 attacks with different bit
rates and Stirmark attack also.
For example in table 4, the attacks MP3 with
128Kbps, invert, extra stereo and adbrumn superior to
5100 present results BER equal or inferior to the no-
operation attack “nothing”. An error rate equal or be-
low the bit error of the nooperation attack can be seen
as a threshold for verifying integrity. Content signal
processing like the removal of voice and removal of
samples has higher error rates than the nooperation
attack as they are very destructive.
4.6 Tamper Detection Results
In the tamper localization experimental results, we
begin by verifying the integrity of the audio signal. As
we explained previously, tamper detection can be pre-
ceded also by a re-synchronizing mechanism to ad-
just the frame positions or/and corresponding indexes
of the extracted features from tampered audio signals.
Attacks can cause de-synchronization problems in ad-
dition to tampers.
Consequently, we can deduce when observing ta-
ble 5, that if integrity is OK (BER equal or infe-
rior to the nooperation attack “nothing”), neither re-
synchronization nor tamper localization, DAE denois-
ing and recovering are needed. However, if integrity
fails (NO), then it is important to check the robustness
propriety to decide on the re-synchronization mecha-
nism type. In effect, if the robustness is achieved but
the integrity fails, so blind re-synchronization is exe-
cuted.
Thus, tamper localization constitutes the frame
positions or/and their corresponding indexes of the
detected watermark (due to the robustness propriety)
and is followed by the DAE simulation and the re-
covery of the real value features. However, when
robustness failed and integrity also, then semi-blind
re-synchronization is compulsory depending on only
the received frame positions or/and corresponding in-
dexes (without needing the original real value fea-
tures) which constitute the tampered parts of the audio
signal that will be after that recovered thanks to DAE
denoising.
4.7 Reversibility Results
The same tamper localization conditions are applied
to the recovery process and depend on the robustness
and then the re-synchronization process type. Thus
after simulating the DAE on the tampered features,
this system proceeds to perform denoising and cor-
recting the altered data. Getting the denoised features
as the output of the DAE, we compare them with the
original features by calculating the BER:
- If BER is equal or inferior to the nooperation at-
tack “nothing”, then perfect recovering is achieved,
we obtain consequently similar audio file to the wa-
termarked signal without attacks.
- If BER equal or inferior to 0.2, then satisfactory re-
covering is accomplished, we obtain partially compa-
rable audio signal to original one.
Finally if BER superior to 0.2 then recovering is
failed and it is not possible to attain even a partially
similar audio signal to the original file.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we have introduced a reversible, robust
and blind NNS-based audio watermarking scheme ex-
ploiting HPM masking proprieties of MPEG audio
standard and benefiting from the advantages of LPC
envelope estimation of the audio spectral density. Im-
perceptibility and robustness are accomplished thanks
to the exploitation of a BPNN architecture in the in-
sertion and detection processes with consideration of
HPM masking benefits and also LPC envelope esti-
mation advantages.
Secure Audio Watermarking for Multipurpose Defensive Applications
749
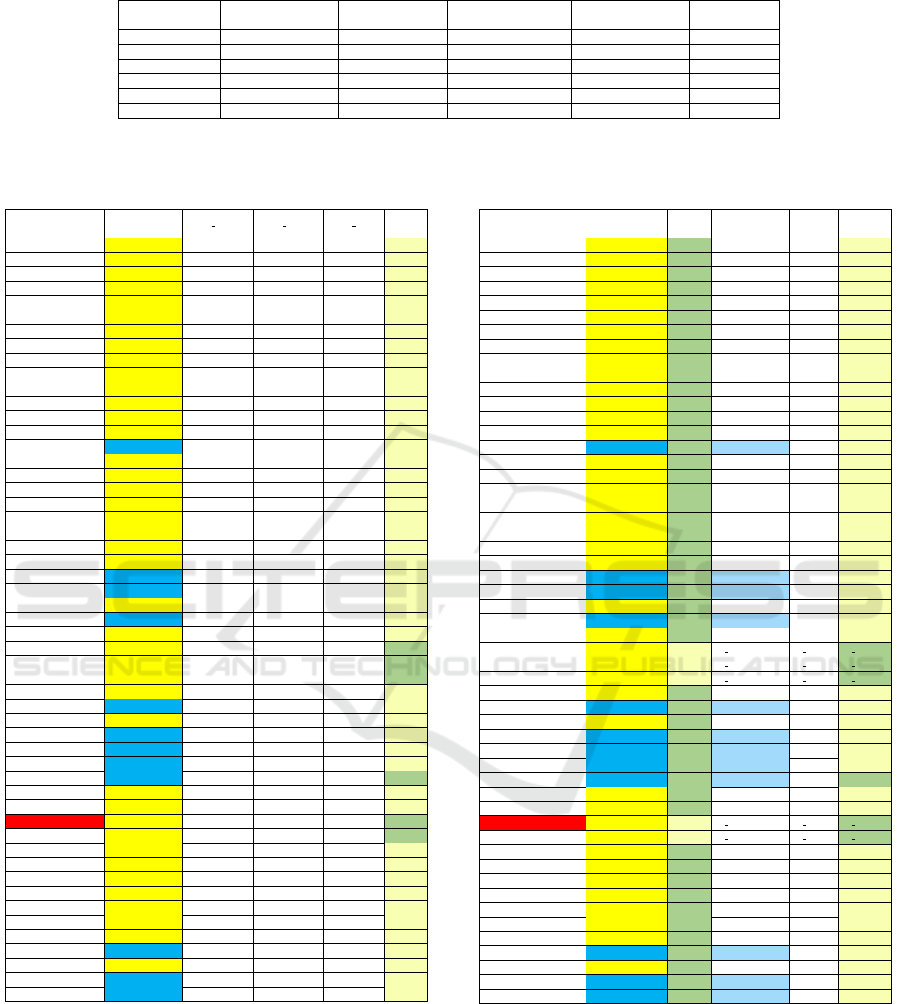
Table 3: Average BER comparison with other watermarking methods.
Attacks (Xiang et al., 2015) (Xue et al., 2019) (Korany et al., 2023) (Hu and Lee, 2019)
The proposed
Method
Resampling 0,53 0,5913 0,4676 0 0
AddNoise 3,4835 5,0429 2 0.61 0
Amplify 0,0184 0,0398 0,0199 — 0
MP3 (128 kbps) 0,0184 0,0797 0,017 0.06 0,013
HighPassFilter 0,0184 0,0398 0,0376 — 0
LowPassFilter 0,0184 0,0398 0,039 0 0,01
Table 4: Integrity results of the proposed tamper detection
based on DCT-NNS-HPM watermarking for a sensitive sig-
nal.
Attack
Integrity
Rob
Dec
Ber frame Ber index Ber reel
Int
Dec
MP3 128 Robust 0,007 0,040 0,087 NO
MP3 64 Robust 0,040 0,040 0,120 NO
MP3 96 Robust 0,020 0,013 0,093 NO
Addbrumn 1 Robust 0,013 0,053 0,120 NO
Addbrumn 2 Robust 0,100 0,100 0,233 NO
Addbrumn 3 Robust 0,533 0,427 0,253 NO
Addbrumn 4 Robust 0,013 0,000 0,167 NO
Addbrumn 5 Robust 0,020 0,007 0,220 NO
Addbrumn 6 Robust 0,033 0,007 0,233 NO
Addbrumn 7 Robust 0,033 0,007 0,233 NO
Addbrumn 8 Robust 0,053 0,020 0,233 NO
Addbrumn 9 Robust 0,053 0,033 0,233 NO
Addbrumn 10 Robust 0,073 0,047 0,233 NO
Addbrumn 11 Robust 0,100 0,053 0,233 NO
Addfftnoise Non Robust 1,000 0,913 0,000 NO
Addnoise 1 Robust 0,013 0,060 0,100 NO
Addnoise 2 Robust 0,033 0,080 0,133 NO
Addnoise 3 Robust 0,047 0,060 0,127 NO
Addnoise 4 Robust 0,100 0,040 0,153 NO
Addnoise 5 Robust 0,107 0,047 0,160 NO
Addsinus Robust 0,007 0,073 0,120 NO
Amplify Robust 0,000 0,000 0,107 NO
Compressor Robust 0,173 0,033 0,167 NO
Copysample Non Robust 0,713 0,120 0,213 NO
Cutsample Non Robust 0,647 0,187 0,200 NO
Dynnoise Robust 0,147 0,027 0,147 NO
Echo Non Robust 0,613 0,067 0,253 NO
Exchange Robust 0,007 0,053 0,100 NO
Extrastereo 30 Robust 0,000 0,000 0,033 OK
Extrastereo 50 Robust 0,000 0,000 0,033 OK
Extrastereo 70 Robust 0,000 0,000 0,033 OK
FFT hipass Robust 0,027 0,060 0,127 NO
FFt Invert Non Roust 0,000 0,000 0,027 NO
FFt Real reverse Robust 0,007 0,073 0,120 NO
FFt Stat1 Non Robust 0,380 0,087 0,187 NO
FFt test Non Robust 0,380 0,087 0,200 NO
Flippsample Non Robust 0,287 0,067 0,167 NO
Invert Non Robust 0,000 0,000 0,033 OK
Lsbzero Robust 0,007 0,073 0,107 NO
Normalize Robust 0,007 0,073 0,087 NO
Nothing Robust 0,000 0,000 0,033 OK
Original Robust 0,000 0,000 0,033 OK
Rc-highpass Robust 0,227 0,040 0,207 NO
Rc-lowpass Robust 0,007 0,053 0,107 NO
Resample Robust 1,000 0,000 0,767 NO
Smooth Robust 0,027 0,047 0,080 NO
Smooth 2 Robust 0,060 0,067 0,153 NO
Stat1 Robust 0,000 0,000 0,040 NO
Stat2 Robust 0,007 0,053 0,100 NO
Voice remove Non Robust 1,000 0,000 0,767 NO
Zerocross Robust 0,040 0,080 0,147 NO
Zerolength Non Robust 0,480 0,060 0,173 NO
Zero remove Non Robust 0,240 0,067 0,173 NO
In addition, authentication and integrity are ade-
quately controlled thanks to the appropriate choice of
the extracted features to be hidden in the audio sig-
nal. These features constituting the relevant tonal
coefficients are extracted from the significant low-
frequency band of the cover audio signal after HPM
study.
Concerning blind detection, blind tamper detec-
tion, and blind-recovery processes, they are accom-
Table 5: Tamper detection results of the proposed tamper
detection based on DCT-NNS-HPM watermarking for sen-
sitive signals.
tamper detection
Attack
Rob
Dec
Int
Dec
Sync
DAE
Tamp
detect
MP3 128 Robust NO Blind OK OK
MP3 64 Robust NO Blind OK OK
MP3 96 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addbrumn 100 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addbrumn10100 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addbrumn 1100 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addbrumn 2100 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addbrumn 3100 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addbrumn 4100 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addbrumn 5100 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addbrumn 6100 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addbrumn 7100 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addbrumn 8100 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addbrumn 9100 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addfftnoise Non Robust NO Semi-blind OK OK
Addnoise 100 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addnoise 300 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addnoise 500 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addnoise 700 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addnoise 900 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Addsinus Robust NO Blind OK OK
Amplify Robust NO Blind OK OK
Compressor Robust NO Blind OK OK
Copysample Non Robust NO Semi-blind OK OK
Cutsample Non Robust NO Semi-blind OK OK
Dynnoise Robust NO Blind OK OK
Echo Non Robust NO Semi-blind OK OK
Exchange Robust NO Blind OK OK
Extrastereo 30 Robust OK
Extrastereo 50 Robust OK
Extrastereo 70 Robust OK
FFT hipass Robust NO Blind OK OK
FFt Invert Non Roust NO Semi-blind OK OK
FFt Real reverse Robust NO Blind OK OK
FFt Stat1 Non Robust NO Semi-blind OK OK
FFt test Non Robust NO Semi-blind OK OK
Flippsample Non Robust NO Semi-blind OK OK
Invert Non Robust OK Semi-blind OK OK
Lsbzero Robust NO Blind OK OK
Normalize Robust NO Blind OK OK
Nothing Robust OK
Original Robust OK
Rc-highpass Robust NO Blind OK OK
Rc-lowpass Robust NO Blind OK OK
Resample Robust NO Blind OK OK
Smooth Robust NO Blind OK OK
Smooth 2 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Stat1 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Stat2 Robust NO Blind OK OK
Voice remove Non Robust NO Semi-blind OK OK
Zerocross Robust NO Blind OK OK
Zerolength Non Robust NO Semi-blind OK OK
Zero remove Non Robust NO Semi-blind OK OK
plished by using an MLP-based denoising autoen-
coder associated with a re-synchronization mecha-
nism. The DAE based-re-synchronization mecha-
nism permits during simulation in the detection stage
to delete noises and correct tampers even after de-
synchronization problems, attacks or audio signal ma-
nipulations. Copyright protection, authentication, in-
tegrity control, blind tamper detection and blind in-
vertibility are reached efficaciously. A comparable
ENASE 2024 - 19th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
750

MLP-based denoising DAE training architecture can
be performed on the original frequencies and those
enclosing the watermark (with possible alterations
due to some attacks) which permits to correcting
the watermarked frequencies after DAE simulation in
the detection process and reconstructing the original
ones. The goal here is to reconstruct completely the
host signal, either its significant parts from which we
have extracted the features and also its recovered orig-
inal coefficients that are modified after watermarking.
This total recovery can be very interesting in some
applications where the cover signal must be entirely
recuperated.
REFERENCES
Acevedo, A. G. (2006). Audio watermarking quality eval-
uation. In E-business and Telecommunication Net-
works, pages 272–283. Springer.
Ali, B. Q. A., Shahadi, H. I., Kod, M. S., and Farhan, H. R.
(2022). Covert voip communication based on audio
steganography. International Journal of Computing
and Digital Systems, 11(1):821–830.
Awasthi, A. and Nirmal, M. L. Multiple image watermark-
ing approach based on anfis for copyright protection
and image authentication: A review.
Charfeddine, M., Mezghani, E., Masmoudi, S., Amar, C. B.,
and Alhumyani, H. (2022). Audio watermarking for
security and non-security applications. IEEE Access,
10:12654–12677.
Charte, D., Charte, F., Garc
´
ıa, S., del Jesus, M. J., and Her-
rera, F. (2018). A practical tutorial on autoencoders
for nonlinear feature fusion: Taxonomy, models, soft-
ware and guidelines. Information Fusion, 44:78–96.
Cruz-Roldan, F., Lopez-Ferreras, F., Amo-Lopez, P., and
Maldonado-Bascon, S. (2000). Pseudo-qmf fil-
ter banks for audio signals subband coding. In
2000 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,
Speech, and Signal Processing. Proceedings (Cat. No.
00CH37100), volume 1, pages 237–240. IEEE.
El’Arbi, M., Charfeddine, M., Masmoudi, S., Koubaa, M.,
and Amar, C. B. (2011). Video watermarking algo-
rithm with bch error correcting codes hidden in audio
channel. In IEEE symposium series in computational
intelligence, pages 164–17.
Eya, M., Maha, C., and Chokri, B. A. (2013). Audio silence
deletion before and after mpeg video compression. In
2013 International Conference on Computer Applica-
tions Technology (ICCAT), pages 1–5. IEEE.
Hu, H.-T. and Lee, T.-T. (2019). Hybrid blind audio water-
marking for proprietary protection, tamper proofing,
and self-recovery. IEEE Access, 7:180395–180408.
Korany, N. O., Elboghdadly, N. M., and Elabdein, M. Z.
(2023). High capacity, secure audio watermarking
technique integrating spread spectrum and linear pre-
dictive coding. Multimedia Tools and Applications,
pages 1–24.
Li, J., Wang, R., Yan, D., and Li, Y. (2014). A multipurpose
audio aggregation watermarking based on multistage
vector quantization. Multimedia tools and applica-
tions, 68:571–593.
Liu, Z., Cao, Y., and Lin, K. (2024). A watermarking-
based authentication and recovery scheme for en-
crypted audio. Multimedia Tools and Applications,
83(4):10969–10987.
Maha, C., Maher, E., Mohamed, K., and Chokri, B. A.
(2010). Dct based blind audio watermarking scheme.
In 2010 International conference on signal processing
and multimedia applications (SIGMAP), pages 139–
144. IEEE.
Masmoudi, S., Charfeddine, M., and Ben Amar, C. (2020).
A semi-fragile digital audio watermarking scheme for
mp3-encoded signals using huffman data. Circuits,
Systems, and Signal Processing, 39:3019–3034.
Masmoudi, S., Charfeddine, M., and Ben Amar, C. (2024).
Mp3 audio watermarking using calibrated side infor-
mation features for tamper detection and localization.
Multimedia Tools and Applications, pages 1–26.
Narla, V. L., Gulivindala, S., Chanamallu, S. R., and Gang-
war, D. (2021). Bch encoded robust and blind audio
watermarking with tamper detection using hash. Mul-
timedia Tools and Applications, 80(21-23):32925–
32945.
Pan, D. (1995). A tutorial on mpeg/audio compression.
IEEE multimedia, 2(2):60–74.
Romney, G. W. and Parry, D. W. (2006). A digital sig-
nature signing engine to protect the integrity of dig-
ital assets. In 2006 7th International Conference on
Information Technology Based Higher Education and
Training, pages 800–805. IEEE.
Steinebach, M. and Dittmann, J. (2003). Watermarking-
based digital audio data authentication. EURASIP
Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2003:1–
15.
Tarhouni, N., Masmoudi, S., Charfeddine, M., and Amar,
C. B. (2023). Fake covid-19 videos detector based on
frames and audio watermarking. Multimedia Systems,
29(1):361–375.
Tong, X., Liu, Y., Zhang, M., and Chen, Y. (2013). A novel
chaos-based fragile watermarking for image tamper-
ing detection and self-recovery. Signal Processing:
Image Communication, 28(3):301–308.
WVL, D. (2006). Audio benchmarking tools and steganal-
ysis. Technical report, Technical report, ECRYPT-
European Network of Excellence in Cryptology.
Xiang, Y., Natgunanathan, I., Rong, Y., and Guo, S. (2015).
Spread spectrum-based high embedding capacity wa-
termarking method for audio signals. IEEE/ACM
transactions on audio, speech, and language process-
ing, 23(12):2228–2237.
Xue, Y., Mu, K., Li, Y., Wen, J., Zhong, P., and Niu,
S. (2019). Improved high capacity spread spectrum-
based audio watermarking by hadamard matrices. In
Digital Forensics and Watermarking: 17th Interna-
tional Workshop, IWDW 2018, Jeju Island, Korea, Oc-
tober 22-24, 2018, Proceedings 17, pages 124–136.
Springer.
Secure Audio Watermarking for Multipurpose Defensive Applications
751
