
Views of Administrators on the Use of Social Media Networks and
Tools in School Management Processes
Murat Taşdan
1a
, Ali İbrahim Can Gözüm
2b
, Michail Kalogiannakis
3c
and Stamatios Papadakis
4d
1
Department of Educational Management, Dede Korkut Faculty of Education, Kafkas University, Kars, Turkey
2
Department of Early Childhood Education, Dede Korkut Faculty of Education, Kafkas University, Kars, Turkey
3
Department of Special Education, Faculty of Education, University of Thessaly, Volos, Greece
4
Department of Early Childhood Education, Faculty of Education, University of Crete, Crete, Greece
Keywords: School Administration, School Principal, Social Media, Management Processes, Digital Communication.
Abstract: This study explores school administrators' perspectives regarding integrating social media networks and tools
into school management processes, assessing their impact on decision-making, planning, coordination,
communication, and evaluation. The research was conducted through a phenomenological design and
involved 29 administrators from various schools in Kars City, selected via maximum diversity sampling. Data
was collected using a custom "Administrator Interview Form on the Use of Social Media Networks and Tools
in School Management Processes" and analyzed through content and descriptive analysis methods. Findings
revealed that administrators heavily utilize social media personally and institutionally, citing benefits like
enhanced communication efficiency, speed, security, resource sharing, manageability, and guidance
effectiveness. While social media aids decision-making, planning, communication, and coordination,
administrators noted limitations and advantages in these processes. They acknowledged social media's
influence on decision dissemination but highlighted its underutilization in evaluation and recognizing its
potential for positive contributions. Recommendations include enhancing administrators' proficiency in
leveraging social media for effective school management and their awareness of its implications.
1 INTRODUCTION
Social media enables individuals and organizations to
express themselves and communicate with others by
creating profiles. This evolution has impacted various
aspects of daily life, from personal to professional
spheres, facilitating two-way communication and the
rapid transfer of information (Urhan et al., 2023;
Korkmaz & Ünal, 2019).
As defined by Kaplan (2010), social media
networks are dynamic platforms that rapidly
disseminate vast amounts of information to millions
of devices worldwide. These platforms provide an
accessible and cost-effective means for publishing,
sharing, and connecting with others (Prykhodkina &
Makhynia, 2020). Various social media platforms,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8675-6068
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7765-4403
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9124-2245
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3184-1147
including Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Weibo,
Flickr, Instagram, Pinterest, YouTube, Vimeo,
WordPress, and Blogger, offer diverse ways for users
to engage (Daly, 2019). Social media is widely
utilized by students, teachers, administrators, and
parents as a primary information source (Şahin &
Üstüner, 2018). School administrators harness social
media for educational decision-making, communica-
tion with teachers and students, sharing teachers'
achievements and projects, and educating parents
about its benefits (Harb & Al-Zou’bi, 2022). Their
usage patterns typically include information/research,
entertainment, recognition, and personal development.
Educational leaders must lead comprehensive
technological integration to equip individuals with the
skills needed for the knowledge-based economy of the
Ta¸sdan, M., Gözüm, A., Kalogiannakis, M. and Papadakis, S.
Views of Administrators on the Use of Social Media Networks and Tools in School Management Processes.
DOI: 10.5220/0012744200003693
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2024) - Volume 1, pages 585-592
ISBN: 978-989-758-697-2; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright © 2024 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
585

21st century (McLeod & Richardson, 2011).
Administrators also utilize social media to bolster their
institutional image, enhance community relations, and
engage with stakeholders (Yusuf et al., 2020).
Accessing quality information on social media
influences perception, comprehension, decision-
making, and actions in personal and professional
domains, fostering active engagement among users as
creators, disseminators, and consumers of information
and knowledge (Daly, 2019).
Social media networks and tools empower school
staff to engage in decision-making processes and
regularly highlight their accomplishments to
stakeholders. They serve as potent instruments for
schools to actively shape their public image and
establish a positive brand identity. Stakeholders can
conveniently access general and specific school
information through various tools such as frequent
blog posts, regular tweets, interactive social
networking platforms, and consistent podcasts and
online videos, all at minimal cost. This enhanced
communication fosters a stronger brand image (Cox
& McLeod, 2014). Social media tools provide
effective channels for school leaders to address
crucial matters among staff or stakeholders and build
consensus before making final decisions.
Additionally, they enable leaders to articulate a vision
for academic success, inspire academic staff, and
extend support through direct communication with
parents and the community (Yusuf et al., 2020). In a
study by Korkmaz and Ünal (2019), administrators
and teachers expressed that establishing a two-way
dialogue between teachers and students/parents
within the school through new communication
technologies could enhance the education network.
Social media is widely utilized by various
educational stakeholders, including students,
educators, academic staff, and school administrators.
Recognizing its significance, educators emphasize
exploring its educational applications to keep pace
with advancing technologies (Özmen et al., 2011).
School principals who overlook social media risk
missing out on a powerful communication tool (Harb
& Al-Zou’bi, 2022). Establishing a robust social
media strategy for school administrators is essential
for effective content management and transparent
communication (Yusuf et al., 2020). Studies
emphasize the importance of conscious social media
usage skills for school administrators (Bayram,
2017). Social media enables administrators to engage
with stakeholders, but proper management is crucial
to avoid chaotic situations. Given its role in
expediting workflow and crisis communication,
practical social media training for administrators is
imperative (Urhan et al., 2023).
The rapid evolution of social media prompts
various perspectives on its integration. While existing
literature often focuses on students or teachers,
administrators, as vital stakeholders, receive less
attention (Šliogerienė et al., 2014). Administrators
must possess the knowledge and skills to utilize social
media effectively in schools. Assessing their effective
use of social media lies primarily in school
management processes, encompassing decision-
making and other stages. In the digital age,
administrators' proficiency in using social media
directly influences school management.
This research aims to elucidate school
administrators' views regarding using social media
networks and tools in school management processes.
Within this framework, the aim is to determine, based
on administrators' experiences, how social media
influences decision-making, planning, coordination,
communication, and evaluation processes in schools'
management processes. In this context, the two
research questions are:
1. What are school administrators' perceptions,
challenges, and opportunities regarding using
social media?
2. How does integrating social media networks
and tools into school management processes
affect the decision-making processes of school
administrators?
2 METHOD
2.1 Research Model
This research is a qualitative study conducted to
describe the use of social media networks and tools in
school management processes. The study was carried
out with a phenomenological design. Phenomenology
is a qualitative research type that examines the nature
of human events related to using social media
networks and tools in school management processes.
It focuses on the events individuals directly
experience in real-world contexts (Yin, 2011). In
phenomenological research, the focus is on how
individuals make sense of their experiences using
social media networks and tools, attempting to
identify common characteristics of these experiences
(Creswell & Poth, 2018).
CSEDU 2024 - 16th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
586

2.2 Study Group
The study group consists of 29 school administrators
serving in schools in the centre of Kars province.
These participants were determined using a
maximum variation sampling technique. This
sampling aims to bring together differences arising
from heterogeneity to create a typical pattern and to
explore standard dimensions or fundamental
experiences related to the subject (Patton, 2002;
Creswell & Poth, 2018). A maximum variation
sample consists of cases intentionally selected to be
as dissimilar from each other as possible.
The study group includes 11 principals, two vice
principals, and 16 assistant principals. Age
distribution analysis revealed that 4 participants are
aged 25-30, 2 are aged 31-35, 2 are aged 36-40, 8 are
aged 41-45, 8 are aged 46-50, and 5 are aged 50 and
above. Additionally, 9 participants rated the
socioeconomic level of their school as "low," 15 as
"medium," and five as "high."
2.3 The Data Collection Instrument
The research utilized the "Administrator Interview
Form Regarding the Use of Social Media Networks
and Tools in School Management Processes,"
developed by the researcher. Initially, a literature
review on social media use in education was
conducted, followed by an examination of
administrators' research on social media use. Ten
semi-structured questions were planned based on
these reviews, covering school management
processes. The draft form was reviewed by four
academics specializing in educational management
and qualitative research, resulting in the removal of
two questions, the addition of two new questions, and
the revision of three questions. The finalized draft,
including basic personal information questions,
underwent a pilot interview with two administrators.
Adjustments were made based on the pilot study,
resulting in the final version of the interview form. An
example of a semi-structured interview question is
provided below:
"How do administrators utilize social media
networks and tools in decision-making?"
2.4 Data Collection
Data collection occurred in October 2023, during the
first semester of the academic year 2023-2024.
Administrators were given the choice of audio, video,
or written interviews but preferred the written format.
They were contacted by phone, briefed on the
interview, and scheduled based on availability.
Interviews were recorded with consent and later
transcribed for accuracy. Participant files were
renamed and coded (Y1-Y29) to ensure
confidentiality.
2.5 Data Analysis
The study data were analyzed using MAXQDA
software. In this research, qualitative data were
thematized through content analysis. The
fundamental process in content analysis involves
organizing similar data into specific concepts and
themes and interpreting them in a way the reader can
understand. In this context, interviews with school
administrators regarding their views on social media
and tools were first segmented into codes, and then
similar codes were grouped under common themes.
The opinions of administrators were presented with
frequency distribution under specific themes.
Participant quotations were included in the findings
to interpret the meaning of the obtained themes
(Patton, 2002).
As part of the validity and reliability assessments
of the research, efforts were made to ensure
credibility, transferability, and consistency, as
emphasized by Merriam (2009).
3 FINDINGS
Under this heading, the views and experiences of
school administrators obtained through qualitative
data analysis techniques relevant to the research
objective are presented.
Table 1: Social Media Networks and Tools Most Used by
School Administrators.
Social Media Platfor
m
f
Whatsa
pp
19
Insta
g
ra
m
13
Twitte
r
12
Faceboo
k
10
Telegra
m
1
As seen in Table 1, school administrators
primarily use "WhatsApp" among social media tools,
followed by Instagram, Twitter, Facebook, and
Telegram, respectively.
Views of Administrators on the Use of Social Media Networks and Tools in School Management Processes
587
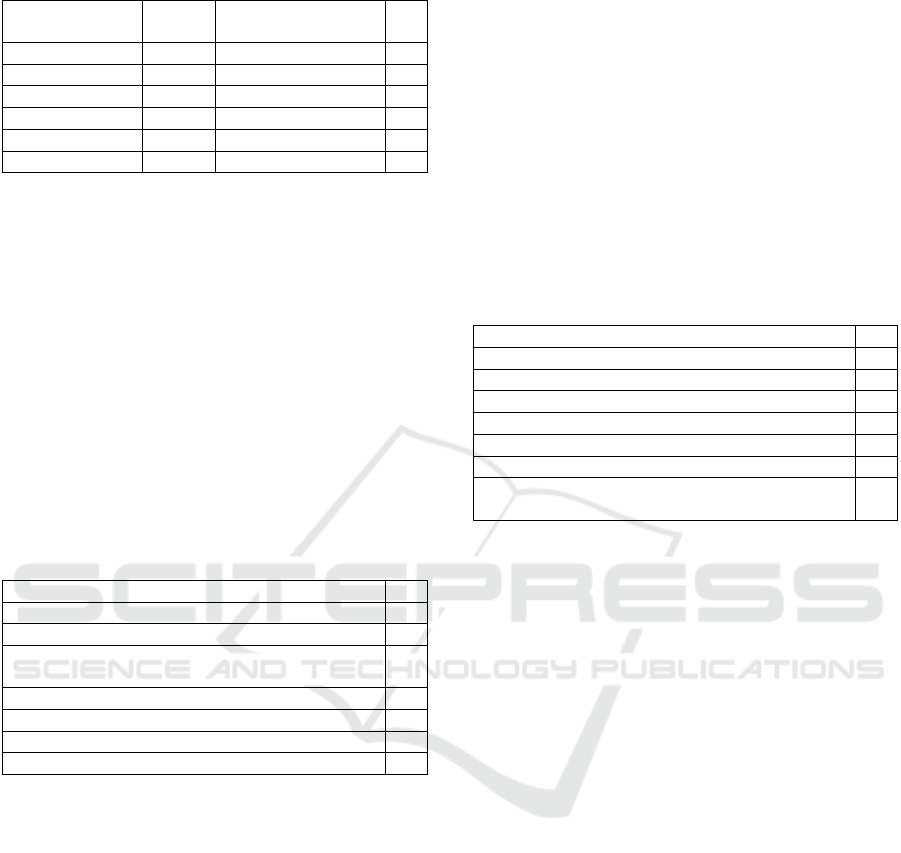
Table 2: Management of School Social Media Accounts.
Social Media
Platforms
f Managed by Whom f
Website 19 Administration 18
Instagra
m
13 IT Teachers 2
Twitte
r
12 Teachers 1
Whatsa
pp
10
Faceboo
k
1
None 4
As shown in Table 2, in the schools included in
the research, school administrators primarily use
"Instagram, Twitter, WhatsApp, and Facebook" as
social media platforms. While school websites are
utilized for communication and information in 10
schools, four schools do not use social media
accounts. Although school administrators mostly
manage school social media accounts, IT teachers and
other teachers occasionally manage them. Most
school administrators need to have training related to
the use of social media (f=25).
3.1 Contribution of Social Media to the
School
Table 3: Contribution of Social Media to the school.
Contribution f
Effective in
p
romotion an
d
attracting attention 7
A necessit
y
of the digital age 2
Facilitates communication between school,
p
arents, an
d
students 2
Information dissemination 2
Meets evolving an
d
changing needs 2
More harmful than
b
eneficial 2
Contribute to advertisin
g
an
d
p
romotion 2
According to Table 3, school administrators utilize
social media for various management purposes,
including promotion, communication facilitation,
information dissemination, and meeting evolving
needs. While some acknowledge its positive impact,
others express concerns about its potential
drawbacks. Participants emphasize social media's
effectiveness in promotion and communication,
noting its importance in reaching wider audiences and
adapting to the digital age. However, they also raise
concerns about negative impacts, cautioning against
misuse and its potential to disrupt social structures.
For instance, one administrator states, "I believe its
contribution is significant... having an effective social
media page for the school will yield successful
results. (Y2) " Another participant finds “social
media useful for showcasing school activities” (Y4).
Despite acknowledging social media's positive
role in enhancing knowledge and skills, participants
warn against its misuse, which could lead to time
wastage and disruption of social structures.
Additionally, they highlight the potential risks of
encountering positive and negative opinions from
broader audiences, particularly regarding
“thoughtless comments” undermining intended
promotion(Y5).
3.2 State of Adequate Knowledge of
Social Media Networks and Tools
Table 4: State of Adequate Knowledge about Social Media
Networks and Tools.
Contribution f
Insufficient in-service trainin
g
3
Dislikin
g
the use of social media 2
Lac
k
of develope
d
interest sensitivit
y
2
Beingmerelya use
r
2
Limite
d
time available 2
Absence of le
g
alit
y
an
d
ethics 2
Belief in insufficient societal awareness of the
topic 2
According to Table 4, one-third of the interview
school administrators consider themselves
"knowledgeable" about social media, while two-
thirds do not. Reasons cited for the lack of knowledge
include insufficient training, personal preference
against social media, limited interest, time
constraints, and ethical concerns. Some
administrators attribute their knowledge deficiency to
inadequate training and personal disinterest in social
media. One administrator mentions, "Yes, I consider
the lack of knowledge and experience about using
social media networks as a deficiency... However, I
gained sufficient knowledge and experience about
using social media networks in school or daily life.
(Y8)" Others emphasize using social media to
promote the school's brand and values to a broader
audience. One administrator states, "We aim to share
our school's brand, mission, values, and philosophy
and reach a wider audience. (Y12)" Additionally,
some administrators prioritize legal and ethical
considerations in social media usage, ensuring
privacy and obtaining consent before sharing student
or staff information. One administrator mentions, "I
try to comply with legal and ethical issues, ensuring
privacy... I do not publish the visuals and information
of any of my students or staff members without
obtaining explicit consent. (Y14)"
CSEDU 2024 - 16th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
588
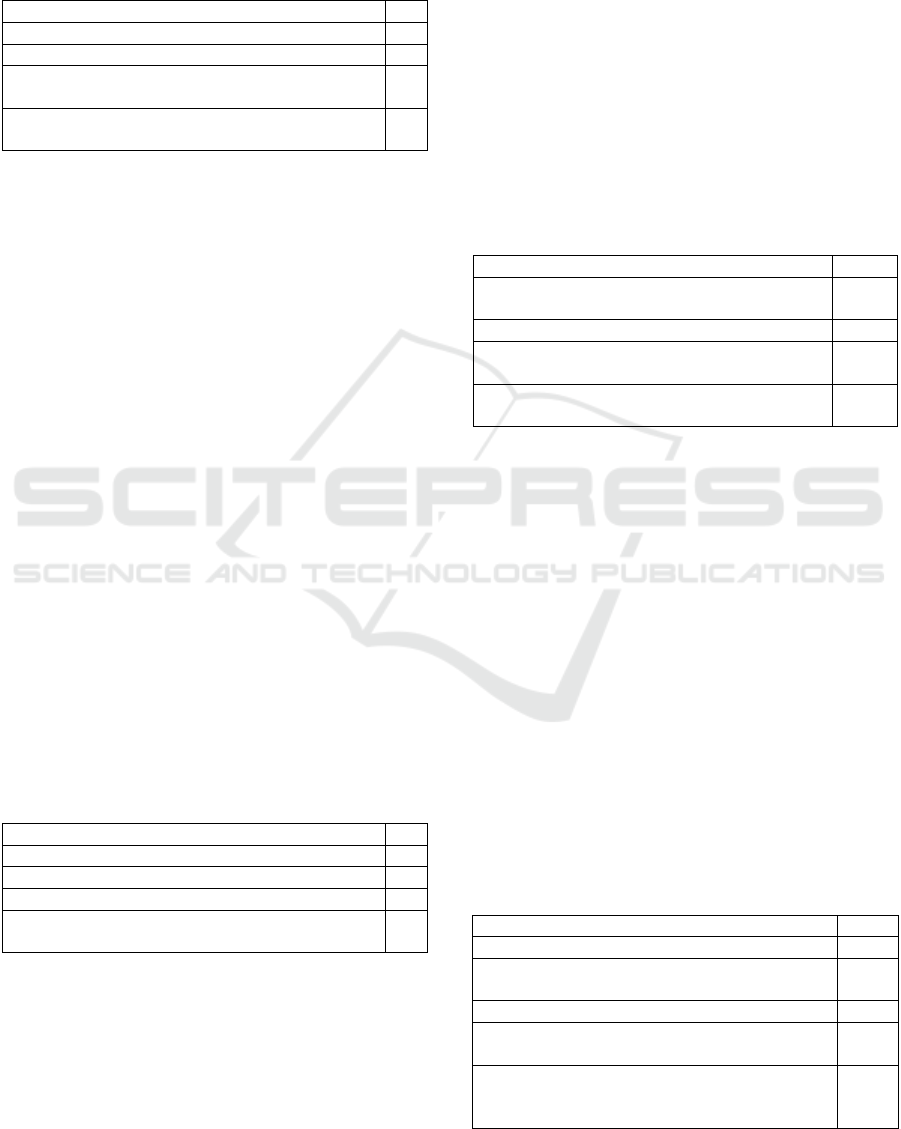
3.3 Use of Social Media Networks and
Tools in Decision-Making Processes
Table 5: Use of social media networks and tools in decision-
making processes.
Usa
g
e Status f
Usin
g
9
Not Using 11
We conducted a social media survey to give
teachers a sa
y
in an a
pp
lication to ou
r
school. 2
We consulted and decided on a meeting day for
teachers to use these tools. 2
As shown in Table 5, about half of the school
administrators utilize social media networks and tools
in their decision-making processes. They have
employed methods such as conducting surveys via
social media to involve teachers in decisions
regarding school applications. "We had surveyed
social media to give teachers a say in an application
to be made at our school. (Y17) " This indicates a
participatory approach to decision-making. Some
administrators are cautious about personal sharing on
social media platforms, focusing instead on deriving
mutual benefits from shared content. "I prefer not to
share, but I look for mutual benefit in other people's
shares. (Y18)" Moreover, administrators use social
media as a resource for decision-making, drawing
insights from the practices of other schools. "I have
partially made decisions by looking at the work of
other schools on social media... For example, I had
requested that an event shared by a school during
celebrations be discussed with our teachers. (Y20) "
This highlights the role of social media in inspiring
and informing decisions by adapting successful
strategies from other schools.
3.4 Publishing Decisions on Social
Media
Table 6: Publishing Decisions on Social Media.
Statement f
Desiring the Sprea
d
of Decisions 2
I do not share on social media 2
Concerns about the Publication of Decisions 2
Standing Behind Decisions and Recognizing
Positive Effects 2
The statements in Table 6 indicate that participants
express desires for the spread of decisions on social
media, reluctance to share, concerns about the
publication of decisions, and emphasis on standing
behind decisions and acknowledging their positive
effects. These different attitudes among participants
reflect various aspects of decision dissemination
through social media. A group of participants
expressed their reluctance to share on social media. "I
prefer not to share; I look for mutual benefit in others'
sharing." (Y111). Some participants, on the other
hand, found it appropriate for decisions to be
disseminated through social media. "We use the
process of sharing decisions with stakeholders. For
instance, we also announce upcoming trial exams to
students and parents through social media." (Y17)
3.5 The Impact of Social Media
Networks and Tools on the
Planning Process
Table 7: The impact of social media networks and tools on
the planning process.
Ex
p
ression f
Utilizing Social Media for School
Mana
g
ement
9
Does not affect 10
Flexibility and Convenience in Administrative
Wor
k
2
Impact of Sharing on Parents, Students, and
Administration
2
Table 7 reveals that approximately half of the school
administrators believe social media usage impacts
school management plans. Administrators view
social media as a planning tool, considering accurate
and reliable information for favourable decisions.
"Social media can be used as an effective tool for
schools to share content, interact, learn about current
situations, and communicate between schools."
(Y13). These statements emphasize the positive
impacts of integrating social media into school
management practices, highlighting benefits such as
improved communication, greater accessibility, and
increased efficiency in administrative tasks. "You do
not necessarily have to be present at the school to do
administrative work. (Y9)"
3.6 Use of Social Media Tools in School
Planning
Table 8: Use of social media tools in school planning.
Positive impact f
Fast an
d
reliable communication 5
Accelerates communication and decision-
makin
g
4
We use
d
it
b
ecause it appeals to a large audience 2
We used social media, networks, and tools in
ou
r
school.
3
Yes, the school's corporate accounts provide
information about the school and contribute to
the school's advertisement.
3
Views of Administrators on the Use of Social Media Networks and Tools in School Management Processes
589
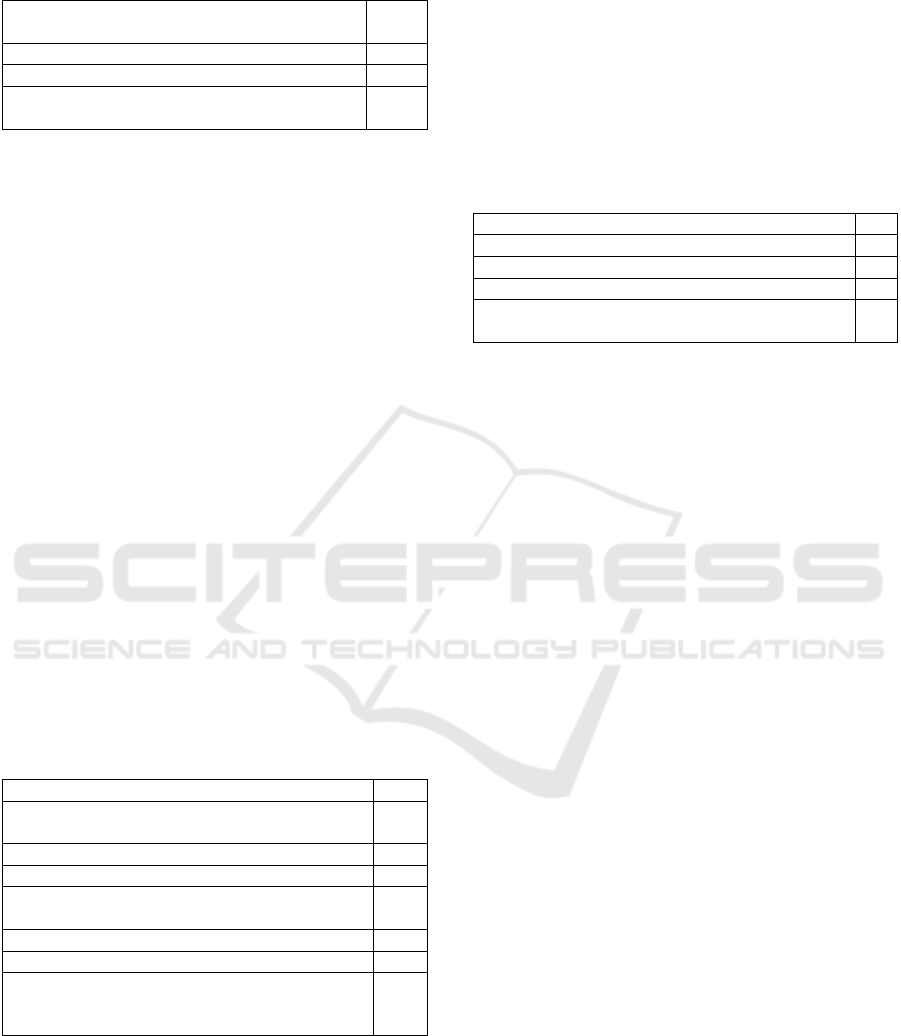
Table 8: Use of social media tools in school planning
(cont.).
It is essential because many who follow the
school follow social media.
2
Ne
g
ative im
p
act f
Fo
r
le
g
al reasons. 2
It is not wrong to create a perception through
social media.
1
Table 8 indicates that social media usage in school
management affects the planning process positively
and negatively. Administrators generally believe that
social media networks and tools positively influence
school planning. Some reasons include more
accessible access to "announcements and appealing
to a larger audience". (Y12) Some participants
reported positive impacts, stating, "Yes, we used
social media, networks, and tools for our school,
(Y10)" reflecting active utilization for school
purposes, enhancing communication and
engagement. However, some participants cited
negative impacts, such as refraining from social
media use due to legal concerns, indicated by
statements like "No, for legal reasons. (Y7)"
Additionally, concerns about manipulating
perceptions through social media raise ethical
considerations, as reflected in the statement, "I do not
think it is wrong to create perception through social
media. (Y9)."
3.7 The Impact of Social Media
Networks and Tools on in-School
Communication
Table 9: The impact of social media networks and tools on
in-school communication.
In-school communication f
Perfect for more efficient and instant
communication
3
I thin
k
it speeds things up 2
I can get feedbac
k
on this." 2
I can reach the announcements more
efficientl
y
."
2
Relations are not
b
reaking 2
Socialization 2
It offers a significant opportunity, especially in
reaching and communicating with higher
authorities
2
As seen in Table 9, school administrators find social
media networks and tools functional in in-school
communication as "one-to-one for more efficient and
instant communication" (Y17), "it speeds up the
work", "I can get feedback about it" (Y8), "it is
effective, I can reach announcements more easily",
"relationships are not broken" and "socialization"
(Y15). These expressions indicate that social media
speeds up communication, provides easier access to
announcements, facilitates receiving feedback, and
helps strengthen relationships. Additionally, some
statements highlight that social media enables
collaboration and enhances interaction.
3.8 Communication Outside School
Table 10: Communication outside school.
Communication outside school f
Does not affect 17
Impacts 8
We hea
r
about the a
g
enda 3
Events can be organized simultaneously with
civil societ
y
organizations."
2
In Table 10, school administrators said social media
tools will not only impact communication within the
school. However, some noted effects like staying
informed about current events and coordinating
activities with external groups. "Social media allows
us to see the thoughts, ideas and activities of these
groups, but it does not affect any communication."
(Y1). "Sometimes when we like their posts, it has a
negative impact. But we try not to go beyond ethical
principles." (Y3)
4 CONCLUSIONS AND
DISCUSSION
In this study, aimed at exploring school
administrators' views on using social media networks
and tools in school management, it was found that
"WhatsApp" was the most preferred platform,
followed by "Instagram," "Twitter," "Facebook," and
"Telegram" respectively. However, it is worth noting
that "WhatsApp" is primarily a messaging app, not a
social media platform. This suggests that
administrators may need more social media
categorization and usage.
School administrators preferred "Instagram,
Twitter, WhatsApp, and Facebook" as their primary
institutional social media accounts. Notably,
WhatsApp was mentioned among corporate social
media accounts. In Turkey, the most used social
media tools in 2022 were YouTube, Instagram,
Facebook, TikTok, and Twitter, respectively (Digital
2022: Global Overview Report). This suggests that
administrators may perceive platforms like YouTube
and TikTok as less suitable for educational
institutions. In a study in Lebanon, administrators
CSEDU 2024 - 16th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
590

preferred Facebook, Skype/Google, and YouTube
among 33 listed social media sites (Harb & Al-Zou'bi,
2022), similar to trends observed in Turkey.
However, differences were noted in Skype/Google
and YouTube use between Lebanese and Turkish
administrators. In another study, only two primary
schools had YouTube accounts, while platforms like
Instagram and Facebook were widely used (Köseoğlu
& Aydın, 2022). Texas school principals primarily
preferred YouTube, followed by Pinterest, and one-
third mentioned observing student blogs (Powers &
Green, 2016). In Ekiti State, secondary school
principals found social media highly effective, with
WhatsApp, Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube
commonly used for information dissemination
(Olowo et al., 2020). Administrators utilize social
media extensively in schools' personal and
organizational contexts.
School administrators recognize the multifaceted
contributions of social media networks and tools to
school management processes. They highlight the
effectiveness of these platforms in promotion,
information gathering, and facilitating
communication among stakeholders. Some
administrators, however, express concerns about the
negative impacts of social media tools. In a study by
Çetinkaya (2019), all school principals utilized
WhatsApp for communication, emphasizing benefits
such as overcoming communication barriers and
efficient resource sharing. Despite these benefits,
one-third of administrators in this study reported
being "informed" about social media networks and
tools, while two-thirds indicated they were "not
informed". The majority lacked formal training in
social media usage, attributing their lack of
knowledge to insufficient training opportunities,
personal preferences, and legal/ethical concerns.
School administrators primarily manage schools'
social media accounts, with minimal involvement
from IT teachers and other educators. Research by
Köseoğlu and Aydın (2022) reveals that those
overseeing public primary school social media
accounts often lack expertise and receive minimal
training in managing these platforms. Şahin and
Üstüner (2018) note that school principals are
moderately familiar with media education and using
social networks in their management practices.
Integrating social media into school management
correlates positively with principals' familiarity with
media education, benefiting all stakeholders.
Köseoğlu and Aydın (2022) further highlight that
school social media accounts are typically managed
by principals, vice principals, or teachers, sometimes
leading to post control and account security
challenges.
Approximately half of the school administrators
use social media networks and tools in decision-
making processes, emphasizing the importance of
involving teachers in decision-making and
acknowledging the impact of publishing decisions on
social media. Advances in technology, especially
during the pandemic, underscore the necessity of
practical technology usage among school
administrators (Cox & McLeod, 2014). Social media
tools are perceived as valuable aids in school
management planning, providing access to a broad
audience, facilitating fast and reliable
communication, and enhancing transparency. While
some administrators’ express concerns about legal
implications and the potential for misperceptions
through social media, others highlight its efficiency
in enhancing in-school communication, speeding up
work processes, and fostering relationships (Olowo et
al., 2020).
A study from Israel stressed the need to balance
parental involvement in school management and
social media communication to avoid disrupting
cooperation within the school community. While
social media tools benefit administrative
communication, they also pose challenges. Some
teachers find administrative communication outside
school hours acceptable, while others see it as
disruptive. Concerns about data reliability and
potential misuse, as well as addiction to social media
leading to communication breakdowns and
psychological issues, were highlighted (Ferster,
2020; Çetintürk & Balyer, 2021).
Research indicates that using social media tools in
school managerial communication offers
convenience and speed. Baruah (2012) highlights
how social media provides simple and cost-effective
communication, organizing, and information
dissemination methods. Similarly, Billington and
Billington (2012) note the demand for social media
tools for business communication and
announcements. Conversely, Akıncı-Vural and Bat
(2010) argue that social media encourages participant
communication. However, using social media tools in
schools has positive and negative outcomes.
Çetintürk and Balyer (2021) found that using social
media tools in school administrative communication
reduces face-to-face interaction, leading to
communication errors and disruptions between
school administration and teachers. While teachers
appreciate the speed and convenience of
administrative communication via social media, some
Views of Administrators on the Use of Social Media Networks and Tools in School Management Processes
591

express concerns about communication errors and
disruptions caused by its use.
In conclusion, school administrators' perceptions
of social media usage indicate that these platforms are
effective communication tools and can offer various
opportunities in school management processes.
However, some challenges are associated with social
media usage, particularly concerning security,
privacy, and time management, which can raise
significant concerns. How does integrating social
media networks and tools into school management
processes affect the decision-making processes of
school administrators? Integrating social media
networks and tools into school management
processes can positively influence the decision-
making processes of school administrators. This
integration can enhance decision-making by enabling
faster communication, information sharing, and
participant interaction. However, it should be noted
that this integration may also face specific challenges,
especially regarding data security, ethics, and
accuracy. Future studies should further investigate the
impacts of social media on school administrators, its
role in education, and best practices.
REFERENCES
Baruah, Trisha Dowerah. (2012). Effective of Social Media
as a tool of communication and its potential for
technology enabled connections: A micro-level study
Bayram, A. (2017). A qualitative study on the contribution
of educational administrator’s use of social media to
educational administration. European Journal of
Education Studies, 3(9), 456–469.
Billington, M. G., & Billington, P. J. (2012). Social media
tools for leaders and managers. Journal of Leadership,
Accountability and Ethics, 9(6), 11-19
Cox, D., & McLeod, S. (2014). Social media marketing and
communications strategies for school superintendents.
Journal of Educational Administration, 52(6), 850-868.
Creswell, J. W., & Poth, C. N. (2018). Qualitative Enquiry
and Research Design: Choosing Among Five
Approaches, 4th Edn. Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Çetintürk, N. ve Balyer, A. (2021). Yönetsel iletişimde
sosyal medya araçlarının kullanımına ilişkin öğretmen
görüşleri. Jass Studies-The Journal of Academic Social
Science Studies, 14(85): 107-121.
Daly, A. J., Liou, Y. H., Fresno, M. D., Rehm, M., &
Bjorklund Jr, P. (2019). Educational leadership in the
Twitterverse: Social media, social networks, and the
new social continuum. Teachers College Record,
121(14), 1-20.
Digital (2022) Global Overview Repor https://datareportal.
com/reports/digital-2022-global-overview-report
Ferster, I. (2020). The influence of parents’ activities in the
school and parents’ communication through social
media on educational management in Israeli schools.
Zeszyty Naukowe UPH seria Administracja i
Zarządzanie, 51(124).
Harb, A., & Al-Zou’bi, R. (2022). School Principals’
Familiarity with Media Education and its Correlation
with Their Use of Social Networks in School
Administration.
Korkmaz, E. V., & Ünal, Ş. G. A. (2019). Örgütsel iletişim
aracı olarak sosyal medya kullanımı, beyşehir eğitim
sektörü örneği. The Journal Of Academic Social
Science, 53(53), 668-681.
Köseoğlu, Ö., & Aydın, İ. (2022). Devlet ilkokullarında
sosyal medya politikası ve yönetimine ilişkin nitel bir
araştırma. Journal Of Political Administrative And
Local Studies, 5(1), 1-25.
Merriam, S. B (2009). Qualitative research: A guide to
design and implementation. San Francisco: John Wiley
& Sons
Olowo, B. F., Fashiku, C. O., Adebakin, A. B., & Ajadi, O.
T. (2020). Social Media: A Modern Tool to Enhance
Communication Skills of the Secondary School
Principals in Ekiti State. International Journal of
Education and Development using Information and
Communication Technology, 16(2), 97-108.
Özmen, F., Aküzüm, C., & Sünkür, M. (2012). Sosyal ağ
sitelerinin eğitsel ortamlardaki işlevselliği. Education
Sciences, 7(2), 496-506.
Patton, M. Q. (2002). Qualitative research and evaluative
methods (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage
Publications
Prykhodkina, N., & Makhynia, T. (2020). Using of social
media in school management: experience of Ukraine
and United States of America. Educational Dimension,
3, 181-198.
Powers, K., & Green, M. (2016). Principals’ perspectives
on social media in schools. The Journal of Social Media
in Society, 5(2), 134-168.
Šliogerienė, J., Oleškevičienė, G. V., Fotheringham, J., &
Palfreyman, K. J. (2014). Social Media Adoption in
Adult Education–Administrators’ Experience. Public
Policy and Administration, 13(4), 690-703.
Şahin, M. ve Üstüner, M. (2018). Sosyal Medyaya İlişkin
Okul Yöneticilerinin Görüşleri, İnönü Üniversitesi
Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi 19(1), 335-355. DOI:
10.17679/inuefd.334250
Urhan, B., Yeniçıktı, NT, Şimşek, G., Albayrak, ES,
Güdekli, İ. A., Hoştut, S. ve Çelik, BBA (2023).
Sosyal medya kullanımı ve sosyal sermaye:
Okul yöneticilerinin sosyal medya kullanım
alışkanlıkları ve algıları. Heliyon . journal homepage:
www.cell.com/heliyon
Vural-Akıncı Z. B. & Bat, M. (2010). Yeni bir iletişim
ortamı olarak sosyal medya: ege üniversitesi iletişim
fakültesine yönelik bir araştırma. Yaşar Üniversitesi E-
Dergisi, 5(20), 3348-3382. https://doi.org/10.19168/
jyu.65130
Yin, R. K. (2011). Qualitative research from start to finish.
New York: Guilford Press
Yusuf, B., Walters, L. M., & Mohamed, A. H. (2020).
Social Media and School Leadership Efficiency. In
Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Education
CSEDU 2024 - 16th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
592
