
A Secure and Privacy-Preserving Authentication Scheme with a
Zero-Trust Approach to Vehicle Renting in VANETs
Mahdi Akil
1
, Leonardo Martucci
1
and Jaap-Henk Hoepman
1,2
1
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Karlstad University, Universitetsgatan 2, Karlstad, Sweden
2
Institute for Computing and Information Sciences (ICIS), Radboud University Nijmegen, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
Keywords:
Zero-Knowledge Proofs, Delegatable Anonymous Credentials, Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks, Authentication
Scheme.
Abstract:
Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs) enable communications between vehicles and infrastructure and are
a key part of future Intelligent Transportation Systems. Significant advancements have been made in ensur-
ing anonymous and secure communication within VANETs; however, integrating privacy-preserving vehicle
rentals in VANETS is an unsolved problem. Existing protocols do not address the unique challenges posed by
vehicle sharing and rentals, particularly regarding vehicle owners’ and renters’ privacy. This paper proposes a
novel rental protocol within VANETs. Our solution is based on delegatable anonymous credentials and Non-
Interactive Zero-Knowledge (NIZK) proofs. It allows drivers to securely delegate credentials to vehicles. This
approach ensures that each vehicle broadcasts authenticated messages, verified through NIZK proofs, while
the identity of the actual driver is verifiably escrowed to an inspector that can lift driver privacy in case of
abuse. The latter property implements accountability into the system. Our protocol addresses the trust issues
inherent in previous systems by providing a robust mechanism for privacy-preserving, accountable vehicle
rentals in VANETs, enhancing the overall security and functionality of these networks.
1 INTRODUCTION
Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs) represent a
significant advancement in Intelligent Transportation
Systems, enhancing communication among vehicles,
infrastructure, and pedestrians. These networks play
an important role in improving road safety, traffic ef-
ficiency, and overall driver experience. Integrating
VANETs into transportation infrastructure represents
a big step towards utilizing technology for safer, more
efficient, and responsive road systems.
The field of VANETs has progressed to ensure
anonymity in vehicle communications. The state-
of-the-art in this field prioritize privacy and security,
employing encryption techniques, pseudonymization,
and mix-zone frameworks (Engoulou et al., 2014)
(Petit et al., 2014). These strategies are crucial
for protecting sensitive information, including vehi-
cle identities, locations, and driving patterns, against
unauthorized access.
Despite these developments, one often neglected
area in VANETs is vehicle renting. This oversight is
concerning given the increasing prevalence of vehicle
sharing and rental services. The absence of a dedi-
cated privacy-preserving protocol for vehicle rentals
in VANETs poses privacy risks for both vehicle own-
ers and renters, especially when vehicles are operated
by individuals other than their registered owners.
To address this issue, previous protocols, as in
(Akil et al., 2023b), provided each driver with a cer-
tificate containing the driver’s identity. This iden-
tity was shared with the vehicle and subsequently en-
crypted for inclusion in all transmitted messages, aim-
ing to ensure driver accountability. However, this sys-
tem relied heavily on the vehicle’s use of the cor-
rect driver identity, with no verification methods to
confirm the authenticity of the encrypted identity.
This reliance has potential security vulnerabilities and
placed trust in the vehicle for the protocol to succeed.
This paper proposes a novel rental protocol to
overcome the limitations of previous systems. Our
approach issues anonymous credentials to drivers.
When a driver (either an owner or a renter) operates a
vehicle, they delegate this credential to the vehicle, in-
cluding their driver unique identity within the creden-
tial. Just like in (Akil et al., 2023a), our system allows
vehicles to exchange messages non-interactively. As
the vehicle broadcasts messages, it concurrently gen-
114
Akil, M., Martucci, L. and Hoepman, J.
A Secure and Privacy-Preserving Authentication Scheme with a Zero-Trust Approach to Vehicle Renting in VANETs.
DOI: 10.5220/0012759600003767
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT 2024), pages 114-127
ISBN: 978-989-758-709-2; ISSN: 2184-7711
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

erates a Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge (NIZK)
proof of the delegated credential ownership. The en-
crypted identity of the driver is always escrowed in
the NIZK broadcasted to nearby vehicles guarantee-
ing driver accountability and also completely removes
trust on the vehicle’s use of the correct driver identity.
The remainder of this paper is structured as fol-
lows. The background and a short description of
Zero-knowledge proofs, attribute based credentials as
well as delegatable anonymous credentials, and de-
tails about inspection and certificates are presented
in Section 2. Section 3 describes the system archi-
tecture, its privacy requirements and the adversary
model. and Section 4 outlines the detailed explana-
tion of our proposed scheme. Section 5 provides secu-
rity and privacy analysis, as well as the performance
analysis of our protocol. In section 6 we present the
related work, its limitations and compare it to ours.
Section 7 discusses the flexibility of our model and
its extensions. The conclusions, limitations, and fu-
ture directions are summarized in Section 8.
2 BACKGROUND
In this section we give a high level overview about
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs), discuss Attribute-
based Credentials (ABCs), Delegatable Anonymous
Credentials (DACs) and the delegation process.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: The groundwork of the
proof of knowledge concept was first done in (Fiege
et al., 1987). For interactive proofs, the notation from
(Camenisch et al., 2009) (Camenisch and Stadler,
1997) is commonly adopted. This notation is used
such that ZPK{(α,β,δ) : y = g
α
h
β
, ˜y = ˜g
α
˜
h
δ
} denotes
a ZKP of integers α,β and δ such that y = g
α
h
β
and
˜y = ˜g
α
˜
h
δ
holds where y,g,h, ˜y, ˜g and
˜
h are publicly
known elements of some groups G = ⟨g⟩ = ⟨h⟩ and
˜
G = ⟨ ˜g⟩ = ⟨
˜
h⟩ that have the same order. Here, the
variables within the parentheses, (α, β, δ), are the se-
cret quantities being proved, while all other variables
are known to the verifier.
A Signature Proof of Knowledge on a message m,
denoted as SPoK{...}(m), represents a non-interactive
proof achieved via the Fiat-Shamir heuristic (Fiat and
Shamir, 1986). Such a SPoK proves to the recipient
that the sender knows the values of the secret quan-
tities and intended to send the message m (whose in-
tegrity is protected by this signature).
Attribute-Based Credentials (ABCs): Enable users
to securely authenticate with service providers while
maintaining their privacy (Chaum, 1985). This
method reveals only the essential information re-
quired for a transaction. An ABC is a collection of
user-verified attributes signed by an issuer I. Each
time a user present their credential, they generate a
new token. This token is a zero-knowledge proof,
confirming their ownership of the credential in a
privacy-preserving way. While generating this token,
users have the choice to disclose specific attributes
from their credential or to reveal only certain con-
ditions related to these attributes. To verify a token,
only the public key of the issuer is needed.
We write C
I
(a
0
,..,a
L
) for an ABC issued by I to
user U with private key k
U
= a
0
and containing at-
tributes a
1
,..,a
L
. Users can prove ownership of a se-
lection of attributes in the ABCs they possess to a ver-
ifier through a ZKP. The proof discloses the values of
the revealed attributes A
d
, while maintaining the con-
fidentiality of the hidden attributes A
h
. This confiden-
tiality includes the private key a
0
= k
U
, which is kept
secret. Such a selective disclosure proof can include
a signature over a message m chosen by the user, in-
dependent of the attributes contained in the ABC.
We write PK{A
h
: C
I
(A
h
;A
d
)}(m) for the ZKP
over message m proving ownership of a credential is-
sued by I containing revealed attributes A
d
and hidden
attributes A
h
. This proves that the message m was sent
by a user owning attributes A
h
issued by I.
ABCs allow users to generate domain specific
pseudonyms, derived from their secret key, in such
a way that:
• A user can only generate only one valid
pseudonym for a specific domain (specified by its
unique string or number).
• Users can prove validity of a pseudonym to a ver-
ifier while showing a credential, and
• given two different pseudonyms for two different
domains, it is impossible to tell whether they be-
long to the same user.
We write N(a
0
,dom) for the domain specific
pseudonym of user U with private key a
0
= k
U
for
the domain specified by dom (typically a string).
A selective disclosure proof of a credential issued
by I, over a message m, revealing attributes A
d
and a
domain specific pseudonym N for domain dom is rep-
resented as PK{A
h
|C
I
(A
h
;A
d
)∧N = N(a
0
,dom),a
0
∈
A
h
}(m,N).
Delegatable Anonymous Credentials (DAC): Are
an advanced form of anonymous credentials that al-
low an owner of a credential to pass on a credential
containing specific permissions or rights derived from
the original credential to other users (Belenkiy et al.,
2009). This delegation process ensures that each del-
egated credential retains its integrity and traceability
back to the original issuer. Such credentials are par-
ticularly useful in scenarios where authority or access
A Secure and Privacy-Preserving Authentication Scheme with a Zero-Trust Approach to Vehicle Renting in VANETs
115

needs to be shared or transferred temporarily, like in
corporate environments for accessing restricted data,
or in healthcare settings for sharing patient records
among multiple practitioners. The key advantage of
delegatable credentials is their flexibility in allowing
the original credential holder to control the extent of
access and permissions granted to the delegatees, all
while maintaining a high level of security and privacy.
Delegation Process: The high-level process of dele-
gation, including the presentation and verification of a
token, involves the following steps (Camenisch et al.,
2017):
• The issuer I (also known as the root delegator)
generates a public key pair (pk
i
,sk
i
).
• User A , generates a public key pair (pk
A
,sk
A
).
• A sends the public key pk
A
and a set of attributes
a = {a
1
,a
2
,...,a
L
} to the root delegator.
• Using sk
i
, I signs A’s public key along with the
set of attributes and sends the generated signature
σ
1
back to A.
• A now has a first level (Level-1) credential which
is issued by I , C
A
: {sk
A
,σ
1
,a, pk
A
}
• A can then delegate her credential to another user,
say User B who shares her public key pk
B
with A ,
• Using sk
A
, A signs B’s public key and a set of
attributes a
′
where (a
′
⊂ a) with A’s secret key sk
A
which results in σ
2
.
• A , sends {σ
2
, a
′
, σ
1
, a} to B.
• Consequently, B now has a Level-2 credential
comprised of two signatures with the correspond-
ing attribute sets, and credential public keys of
both A and B
C
AB
: {(σ
1
,a, pk
A
),(sk
B
,σ
2
,a
′
, pk
B
)}
• B can then use her credential secret key sk
B
to fur-
ther delegate her credential as described above, or
to sign a message m by generating a presentation
token.
• B can present a token that is essentially a non-
interactive zero-knowledge (NIZK) proof of pos-
session of the signatures and the corresponding
public keys from the delegation chain, without re-
vealing their actual values over a message m as
follows:
PK{(σ
1
,σ
2
, pk
A
,sk
B
, pk
B
,a
′
) : C
AB
{(σ
1
,a, pk
A
),
(sk
B
,σ
2
,a
′
, pk
B
)}}(m)
• Verification of the token requires only the public
key of the issuer pk
i
, thereby hiding the identities
of both A and B , as well as their non-disclosed
attributes, selectively.
Note that, if B wants to further delegate a level-2
credential, she can only delegate from attributes a
′
.
As seen above, the delegated credential C
AB
in-
cludes {(σ
1
,a, pk
A
)}, indicating that the identity of
the delegator is not concealed from the delegatee.
This could potentially pose a privacy concern for the
delegator. However, in real-world scenarios where an
ABC is delegated, it is common for the delegator and
delegatee to already know each other. Therefore, we
argue that concealing identities is more crucial dur-
ing the presentation phase, which is the approach we
adopt.
Inspection: In our system, accountability is ensured
through an inspection process that is achieved using
verifiable encryption (Camenisch and Shoup, 2003).
This process allows message recipients to report any
instances of misbehavior by senders to an inspec-
tor. Misbehaviour is defined later in the paper. Each
message transmitted is verifiably escrowed with the
sender’s unique identifier id encrypted as a cipher
ψ. In the event of misbehavior, recipients forward
ψ to the inspector. The inspector is the only entity
in our system capable of decrypting ψ, to retrieve
the sender’s id. This decryption process employs
the Elliptic Curve ElGamal (ECElGamal) encryption
scheme, (Appendix A). Ensuring a robust and secure
method of inspection. The inspector’s public-key pair
denoted as (pk
in
,sk
in
), where:
• The encryption of an identifier id by any
user within the system is represented as ψ ←
enc(pk
in
,id).
• The decryption process, enabling the inspector
to recover the id from ψ, is denoted as id ←
dec(sk
in
,ψ).
Of course inspection is only useful if the verifier
can check that the encryption it receives is indeed the
encryption of one of the hidden attributes in the del-
egated credential C
AB
. Therefore the proof of a dele-
gated credential C
AB
owned by a user B can be pre-
sented as follows:
PK{(σ
1
,σ
2
, pk
A
,sk
B
, pk
B
,a
′
) :
C
AB
{(σ
1
,a, pk
A
),(σ
2
,a
′
,sk
B
, pk
B
)}
∧ψ = enc(pk
in
,id),id ∈ a
′
}(m,ψ)
This mechanism ensures that accountability is main-
tained within the system, allowing for the identifica-
tion and reporting of misbehaving participants in a se-
cure and efficient manner.
Certificate Signing and Verification: In our system,
the integrity and authenticity of certificates are en-
sured through cryptographic signatures. These sig-
natures are generated using a private key and can be
SECRYPT 2024 - 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography
116

verified by any party using the corresponding pub-
lic key, without access to the private key. We em-
ploy the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm
(ECDSA), which is built upon the principles of El-
liptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) (Appendix B). This
choice leverages the efficiency and security of ECC
within a public key infrastructure.
The process of signing a certificate, denoted as
Cert, by a user u with the public-key pair (pk
u
,sk
u
)
is represented as:
σ ← sign(sk
u
,Cert)
This notation indicates that the signature σ is pro-
duced by applying the signing function sign to the
certificate Cert using the private key sk
u
.
Verification of this signature ensures the certifi-
cate’s validity. The verification process is denoted as:
{⊤,⊥} ← verify(pk
u
,Cert,σ)
This expression signifies that the verification function
verify takes the public key pk
u
, the certificate Cert,
and the signature σ as inputs, and outputs a boolean
value indicating the validity of the signature.
3 SYSTEM MODEL
This section describes our system components that are
used to design our VANET as well as the privacy and
security requirements that are needed to be fulfilled
and the adversary model.
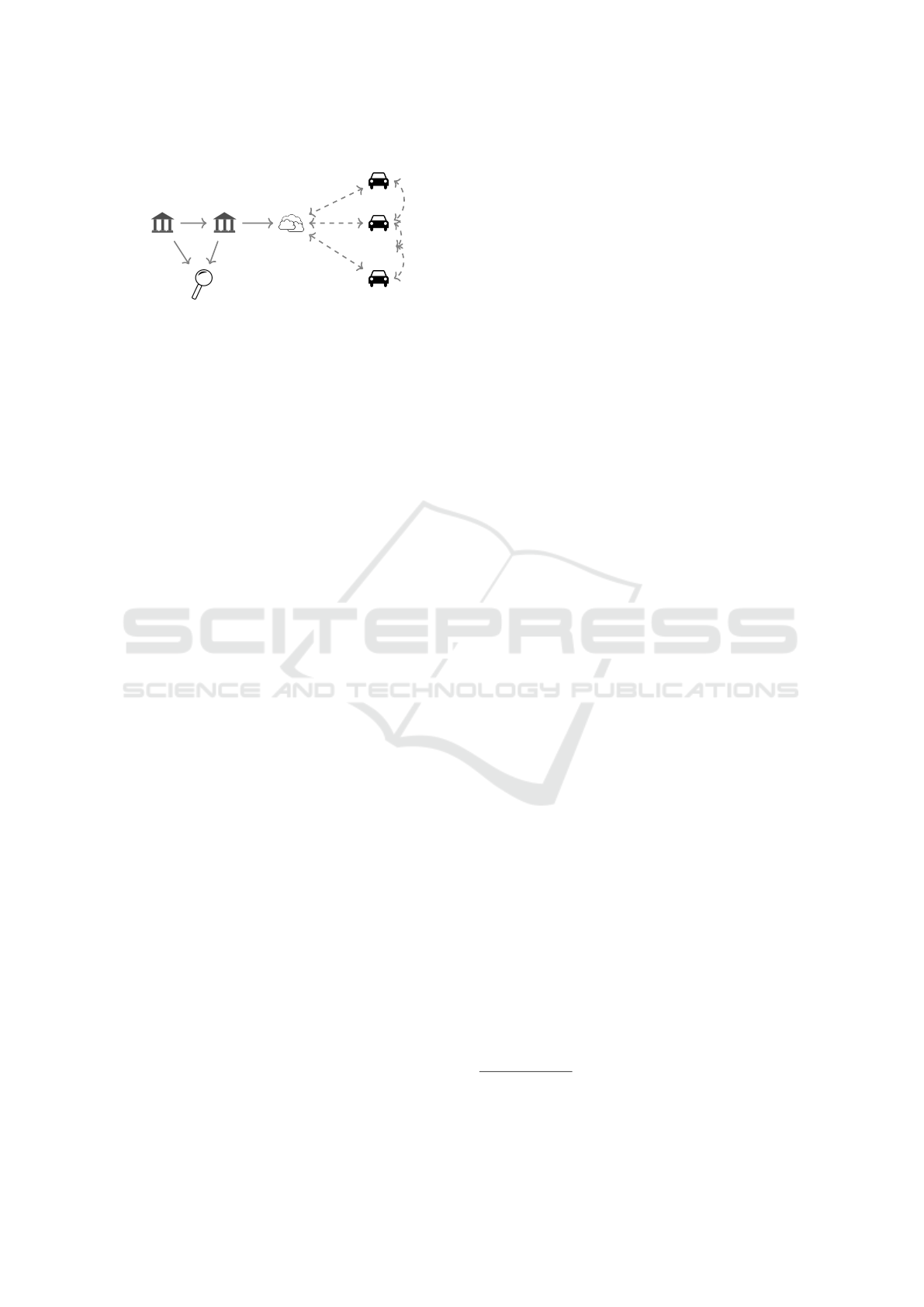
The designed system model includes various system
entities with different roles (figure 1). The main goal
of our protocol is to allow vehicles to exchange verifi-
able authenticated messages, i.e., we require the iden-
tity of the current driver of the vehicle to be escrowed
in the messages sent. Drivers in our system contact
the CA only once to register themselves, and all other
communication between drivers and vehicles is done
without any intervention from the CA. In our sys-
tem, we use a synchronous system-wide epoch mech-
anism, denoted as ε, which is uniformly refreshed for
all entities. This epoch serves many purposes:
• used to establish links between messages, ensur-
ing the linkability within a specific timeframe,
and,
• acts as a mechanism to prevent the system from
being flooded by an excessive number of mes-
sages.
• overcomes problems with the CSMS where ve-
hicles are preloaded with pseudonyms from a
Pseudonym Authority (Brecht et al., 2018). The
problems are outlines in (Akil et al., 2023a).
This approach is effective against potential message
flooding, maintains the system’s manageability and
efficiency (Akil et al., 2020).
3.1 System Components
Our VANET consist of the following entities:
• The scheme authority (SA) is responsible for gen-
erating and publishing the public parameters of
the system and the registration of the certificate
authorities and inspectors. The role of the SA
could be fulfilled by a sufficiently trusted global
authority.
• The certificate authority (CA) is responsible for
issuing credentials and certificates to the drivers.
The CA is usually a transportation authority.
• The inspector is the only entity that can
deanonymize drivers. Note that the inspector is
not monitoring the VANET communication, only
receiving reports of misbehaving vehicles.
• Vehicles are equipped with only one On Board
Unit (OBU) that contains their private key and a
certificate of the owner. Only the part of the OBU
where the private key and the owner certificate are
stored is considered tamper-proof. Vehicles in our
system can act as:
– senders, vehicles that send authentic messages,
– receivers, vehicles that verify the received mes-
sages.
• Drivers d, have valid driver certificate and a cre-
dential from the CA. A Driver can be:
– an owner (o), who owns a vehicle
– a renter (r), who rents vehicles.
• A communication network is used to transport
messages and divided into:
– local area broadcast network: between vehi-
cles and vehicles,
– wide area communication network: between
vehicles and CA.
3.2 Requirements
The Security and privacy requirements of our system
are as follows:
• verifiable broadcasting, broadcast messages are
only accepted by vehicles if they were sent by a
vehicle, driven by a registered driver,
• conditional anonymity, id
d
of a driver is always
anonymous to other vehicles and can only be re-
vealed by the inspector,
A Secure and Privacy-Preserving Authentication Scheme with a Zero-Trust Approach to Vehicle Renting in VANETs
117
network
SA CA
inspector
vehicles
.
.
.
Figure 1: Our of VANET architecture.
• no replay-attacks, a vehicle can not replay a re-
ceived message after a time threshold δt where
δt defines the maximum allowed delay between
sending and receiving a message. δt is typically
smaller than the length of an epoch ε,
• privacy-preserving accountability, a driver can
not deny being the source a message sent by a car
she was driving, based on received reports, the in-
spector can deanonymize the driver of a vehicle
without involving the owner in case the vehicle
was rented,
• linkability within epochs, messages sent by a ve-
hicle are linked within ε,
• unlinkability outside epochs, messages sent by the
same vehicle are unlinkable across epochs,
• sybil-free, the same vehicle can neither have more
than one OBU nor can it pretend to be multiple
vehicles at the same time on the road,
• no renter framing, an owner should not be able to
convince a vehicle that she owns a renting agree-
ment without the consent of a renter.
• zero vehicle trust: a vehicle cannot send a valid
proof containing an id belonging to someone other
than the current driver.
3.3 Adversary Model
Our adversary model is designed to include a range of
threats that jeopardize the privacy and integrity of the
network. These threats include, eavesdropping, mes-
sage injection, impersonation, replay attacks, and the
exploitation of rogue vehicles using counterfeit iden-
tities for message broadcasting.
• Network Layer Attacks: the adversary aims
to intercept and analyze traffic to steal sensitive
information (eavesdropping) or inject malicious
data packets to disrupt communication flow (mes-
sage injection).
• Vehicle Layer Attacks: the adversary may at-
tempt to impersonate legitimate vehicles to broad-
cast false information or replay old messages to
create confusion and distrust among network par-
ticipants.
Despite these capabilities, we assume that the adver-
sary cannot break the underlying cryptographic prim-
itives used to secure communications.
4 HIGH LEVEL DESCRIPTION
OF THE PROTOCOLS
In here we discuss how our protocols are designed.
Our cryptographic settings closely follow the dele-
gatable credential system (Camenisch et al., 2017) to
develop a non-interactive authentication scheme for
VANETs and to achieve the goals listed in 3.2.
4.1 Initialization Protocol
At the very beginning, the scheme authority publishes
all public parameters pp (Camenisch et al., 2017)
(Camenisch and Shoup, 2003) to registered CAs and
car manufacturers. The CA and inspector generate
their public key-pair (pk
CA
,sk
CA
), (pk
CA
1
,sk
CA
1
) and
(pk
in
,sk
in
) respectively during this protocol as well
1
.
During initialization, the CA specifies that a creden-
tial can only be delegated once so in our system we
can have a Level-2 credential at most.
For all the next protocols, we assume that all entities
have access to all pp published by the SA.
4.2 Registration Protocol
During this protocol, drivers interact with the CA to
get a unique id id
d
, a driver certificate Cert
d
and a
driver credential C
d
:
• d generate her public key pair (pk
d
,sk
d
),
• d sends a list of attributes a : {a
1
,a
2
,...,a
L
} to the
CA where a
1
is the public key pk
d
, other attributes
could include (name, birth date, address, . . . ),
• the CA verifies the list of attributes,
• the CA generates a unique id for the driver id
d
,
• the CA uses sk
CA
to sign the set of attributes
σ
CA
1
← sign(sk
CA
,{a
0
,a
1
,...,a
L
}) where a
0
is
id
d
,
• the CA also generates a certificate for the driver
Cert
d
: {PII
d
, pk
d
,id
d
,start
t
,end
t
}, where PII
d
1
While multiple CAs would typically operate within
each country in reality, our protocol for the sake of sim-
plicity assumes a single CA.
SECRYPT 2024 - 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography
118

are the driver’s attributes, start
t
and end
t
indicate
the start and end date of the certificate,
• the CA then uses sk
CA
1
to sign the certificate Cert
d
σ
CA
2
← sign(sk
CA
1
,Cert
d
)
• the CA sends σ
CA
1
, Cert
d
and σ
CA
2
to the driver,
• d now has a signed certificate Cert
d
and a Level-1
credential from the CA
C
d
: {σ
CA
1
,sk
d
, pk
a
,a}
After completing the driver’s registration process, the
driver communicates with the vehicle she owns to
transmit {Cert
d
, pk
d
, pk
CA
, pk
CA
1
, and pk
in
}, which
are then stored in the vehicle’s OBU. Among these,
{Cert
d
, pk
d
, pk
CA
1
} are used in the unlocking proto-
col, whereas {pk
in
, pk
CA
} are used in the sending and
receiving protocols.
4.3 Renting Protocol
A vehicle owner can rent out their vehicle to a valid
renter by signing a rental agreement A
or
. The pro-
cess begins when the renter presents a signed digital
certificate, Cert
d
, to the vehicle owner from whom
they wish to rent. The owner then checks the va-
lidity of this certificate to ensure it’s legitimate. If
⊤ ← (pk
CA
1
,σ
CA
1
,Cert
d
), the owner drafts a rental
agreement, A
or
, which includes the renter’s unique id
{id
r
, the terms of the rental, the start date, and the
end date of the lease}. The agreement is first signed
by the renter σ
r
← sign(sk
r
,A
or
) then by the owner
σ
o
← sign(sk
o
,A
or
). The agreement serves as a veri-
fiable document enabling the vehicle’s systems to rec-
ognize the validity of the rental contract. At the end
of this protocol the renter gets {A
or
,σ
r
,σ
o
}.
4.4 Unlocking Protocol
In this process, a vehicle owner must demonstrate to
the vehicle that they are the legitimate owner by refer-
encing a certificate stored within the vehicle’s OBU.
Likewise, a renter must show that they possess a valid
rental agreement to be granted access to the vehicle.
The system uses a challenge-response protocol to
verify identities, with the procedure differing slightly
depending on whether the driver is an owner or a
renter. To simplify, we denote an owner’s digital
certificate and their corresponding public and private
keys as {Cert
o
, pk
o
,sk
o
}, while for a renter, these are
represented as {Cert
r
, pk
r
,sk
r
}. This notation helps
to distinguish between the credentials used by owners
and renters during the verification process.
• if the owner o is unlocking her own vehicle v:
– o initiates the unlocking protocol as an owner,
– v generates a random string c, saves c and then
sends it to o to sign,
– o uses her private key sk
o
to sign the challenge
as σ ← sign(sk
o
,c), and sends the resulting sig-
nature σ and c to v,
– v verifies the signature σ using pk
o
:
{⊤,⊥} ← verify(pk
o
,c,σ),
– if ⊤ ← verify, then v signals to the owner to ini-
tiate the delegation process to generate a Level-
2 credential:
*
The vehicle v starts by generating a fresh
public key pair (pk
v
,sk
v
) and shares pk
v
with
o,
*
o starts the delegation process by signing pk
v
and a set of attributes from the Level-1 creden-
tial a
′
where a
′
⊂ a using sk
o
, resulting in σ
o
where id
o
∈ a
′
.
*
{σ
o
, a
′
, σ
CA
1
, a}, are all sent back to v where
σ
o
is the owner’s signature, a
′
are the signed
attributes from the owner which include the
unique id of the owner id
o
, σ
CA
1
is the signa-
ture of the CA for the Level-1 credential, a are
the attributes of the Level-1 credential,
*
So Level-2 credential is a
chain of 2 credential links C
ov
:
{
(σ
CA
1
,a, pk
o
),(σ
o
,a
′
,sk
v
, pk
v
)
}
,
*
v can now prove that it owns Level-2 creden-
tial C
ov
using its secret key sk
v
.
• if a renter r is unlocking a rented vehicle v:
– r initiates the unlocking protocol and sends
renting agreement A
or
, her certificate Cert
r
, the
signatures σ
r
, σ
o
, and public key pk
r
to v,
– v checks the owner’s signature on A
or
using
the public key of the owner pk
o
as {⊤,⊥} ←
verify(pk
o
,A
or
,σ
o
),
– v uses pk
r
to verify: {⊤,⊥} ←
veri f y(pk
r
,A
or
,σ
r
),
– v checks if the current date is between the start
and end date from the rental agreement A
or
,
– v generates a random string c, saves c and then
sends it to r to sign,
– r uses her private key sk
r
to sign the challenge
as σ ← sign(sk
r
,c), and sends the resulting sig-
nature σ and c to v,
– v verifies the signature σ using pk
r
: {⊤,⊥} ←
verify(pk
r
,c,σ
r
),
– if ⊤ ← verify, then v send OK to the driver to
initiate the delegation process,
– r delegates a credential C
vr
to the vehicle con-
taining id
r
by following the same steps from
before as the owner. v ends up with C
rv
:
A Secure and Privacy-Preserving Authentication Scheme with a Zero-Trust Approach to Vehicle Renting in VANETs
119
{
(σ
CA
1
,a, pk
r
),(σ
r
,a
′
,sk
v
, pk
v
)
}
, where a
′
in-
cludes the id of the renter id
r
.
Note that:
• the vehicle does not know the secret key of the
owner/renter sk
o
or sk
r
, therefore, it is impossi-
ble for the vehicle to present or delegate a Level-1
credential,
• when a vehicle is turned off, we assume that the
vehicle’s freshly generated public key pair and the
credential saved in the OBU are deleted, and
• every time a driver initiates the unlocking proto-
col, the vehicle has to generate a new public key
pair so a new credential will also be delegated by
the driver.
4.5 Sending Protocol
Requires a system wide epoch, which is a time inter-
val ε. Once an epoch ε
i
is over, it is immediately fol-
lowed by the next epoch ε
i+1
. To broadcast a message
m, a vehicle v needs to convince the verifier vehicle
that it:
1. possesses a delegated credential from a valid
driver without revealing its attributes,
2. can encrypt a hidden attribute id
d
using the veri-
fiable encryption scheme (Camenisch and Shoup,
2003),
3. can generate a valid signature on m to demonstrate
possession of a valid secret.
Every vehicle v has a delegated creden-
tial from the driver represented as C
dv
:
{
(σ
CA
1
,a, pk
d
),(σ
d
,a
′
,sk
v
, pk
v
)
}
where pk
d
is
the public key of the driver and the rest are as defined
in the unlocking protocol. C
dv
consists of two creden-
tial links. The first link (σ
CA
1
,a, pk
d
) which proves
that the driver has a level-1 credential containing
attributes a. The second link (σ
d
,a
′
,sk
v
, pk
v
) proves
that the driver has issued attributes a
′
where id
d
∈ a
′
to the owner of the public key pk
v
. The secret key sk
v
allows the vehicle to prove that it is the owner of the
level-2 credential C
dv
.
To broadcast a message m, the vehicle v:
• extracts the current timestamp ts,
• appends ts to the message m, so m
′
= m ∥ ts,
• encrypts the current driver id
d
as ciphertext ψ =
enc(pk
in
,id
d
) using the inspector’s public key
pk
in
(Camenisch and Shoup, 2003),
• uses the current sk
v
to generate an epoch based
pseudonym N
ε
= N(sk
v
,ε) = g
sk
v
ε
, where g
ε
is the
hash of ε, i.e., g
ε
= H(ε)
(Γ−1)/ρ
mod Γ, and H
Algorithm 1: Send a ZKP over message m (PK).
Input: {ε, C
dv
, ts, m}
1 if new ε
i
is starting then
2 Generate N
(ε
i
)
3 while ε
i
is not finished do
4 m
′
= m||ts
5 encrypt driver id id
d
: ψ = enc(pk
in
,id
d
)
6 calculate
PK : {(σ
CA
1
,σ
d
, pk
d
,sk
v
, pk
v
,a
′
) :
C
dv
{(σ
CA
1
,a, pk
d
),(σ
d
,a
′
,sk
v
, pk
v
)
∧ N
ε
i
= N(sk
v
,ε),sk
v
∈ C
dv
∧ ψ = enc(pk
in
,id
d
),id
d
∈ a
′
}
(m
′
,N
ε
i
,ψ)
send PK to nearby vehicles
is a hash function mapping {0,1}
∗
→ Z
Γ
(Ca-
menisch et al., 2010).
• v generates NIZK proof signature on {m
′
,N
ε
i
,ψ}
which outputs:
PK : {(σ
CA
1
,σ
d
, pk
d
,sk
v
, pk
v
,a
′
) :
C
dv
{(σ
CA
1
,a, pk
d
),(σ
d
,a
′
,sk
v
, pk
v
)
∧ N
ε
i
= N(sk
v
,ε),sk
v
∈ C
dv
∧ ψ = enc(pk
in
,id
d
),id
d
∈ a
′
}(m
′
,N
ε
i
,ψ)
• PK including (m
′
,N
ε
i
,ψ) is then broadcasted to
neighbouring vehicles.
Note that:
• ψ is randomized in every message transmitted to
ensure unlinkability.
• all public keys in the credential remain hidden in
the zero-knowledge proof so the identities of all
delegators are not revealed.
4.6 Receiving Protocol
The recipient vehicle starts by checking if (ts
′
− ts ≤
δt), where ts
′
is the exact time of receiving the mes-
sage and δt is the maximum allowed delay threshold
(3.2). If this checks out the verifier is convinced that
the message is not replayed and then proceeds to ver-
ify the received PK using the public key of the CA
pk
CA
non-interactively, i.e., without the need to con-
tact the CA. If True ← veri f y(pk
CA
,PK) proves that
the NIZK is constructed by a vehicle that owns a valid
delegated credential (Camenisch et al., 2017), so the
recipient accepts the message and saves N
ε
i
until the
end of the epoch ε
i
to link all messages from the same
SECRYPT 2024 - 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography
120

Algorithm 2: Verify a ZKP over message m (PK).
Input: {PK,ε}
Output: {True, False}
1 if ε
i+1
started then
2 Discard all saved pseudonyms
3 if PK received then
4 extract ts from m
5 if ts
′
−ts ≤ δt then
6 verify PK
7 if True ← veri f y(pk
CA
,PK) then
8 Read m
9 N
ε
is valid
10 ψ is valid
11 Save N
ε
12 else if False ← veri f y(pk
CA
,PK)
then
13 discard PK and m
14 else if ts
′
−ts > δt then
15 message is replayed discard PK
vehicle. An overview about the process is shown in
algorithm 2.
Note that:
• The verifier only sees (m
′
,N
ε
,ψ) in clear text and
everything else is hidden in the Zero-knowledge
proof.
• When we move to ε
i+1
, all saved pseudonyms are
removed.
4.7 Inspection Protocol
In our inspection protocol, a verifier vehicle has the
capability to report another vehicle that misbehaves
by transmitting the received encrypted identifier ψ,
directly to the inspector. Upon receiving this en-
crypted data, the inspector will then deanonymize
the driver’s identity, by employing the decryption al-
gorithm, id
d
→ dec(sk
in
,ψ) (Camenisch and Shoup,
2003). This decryption outputs the unique identifier
id
d
that is linked to the driver, for more details about
how the decryption process is done check (Appendix
A). This step is crucial in our system, which aims
to protect privacy of the driver and ensure privacy-
preserving accountability. With this inspection proto-
col, our system achieves privacy-preserving account-
ability, making the VANET more trusted and secure.
5 SECURITY, PRIVACY &
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
This section examines the security and privacy system
goals established in 3.2 and assesses the implementa-
tion of our model with these goals. We also conduct
a computational performance evaluation of our model
based on the number of operations required to execute
the algorithms used in V2V communication.
5.1 Security and Privacy Evaluation
Our protocol employs credential delegation to achieve
our goals.
• Verifiable Broadcasting: In our system, the au-
thenticity of broadcasted messages is ensured
through the verification of a proof of knowledge
PK. This PK is only valid if it originates from
a vehicle in possession of a legitimate delegated
credential from the current driver. To illustrate the
robustness of this mechanism, consider the sce-
nario where a malicious vehicle, denoted as v
m
,
which knows the current epoch ε attempting to
fake a PK
f
and a pseudonym N
ε
, v
m
might gener-
ate a vehicle credential C
v
. This fake credential in-
cludes attributes not signed by the Certificate Au-
thority (CA) with the private key sk
CA
. Due to the
lack of CA’s signature on these attributes, the ver-
ification process against the CA’s public key pk
CA
will result in the failure of PK
f
, effectively pre-
venting the malicious attempt to send messages
from an unregistered vehicle or by using a fake
credential.
• conditional anonymity: our system ensures the
anonymity of drivers under normal circumstances,
revealing identities of the drivers only when they
misbehave. Each message broadcasted by a ve-
hicle v incorporates the encrypted driver identity
id
d
, denoted as ψ. This encryption ensures that
id
d
remains confidential, as only entities with the
secret inspection key sk
in
can decrypt ψ. Addi-
tionally, the owner’s public key, embedded within
the delegated credentials C
ov
or C
vr
, is hidden
within the zero-knowledge proof, safeguarding
the owner’s anonymity as well.
In the event of a vehicle’s misbehaviour, a report
containing ψ is sent to the inspector. Using sk
in
,
the inspector decrypts ψ to retrieve the actual id
d
,
where id
d
← dec(pk
in
,ψ) to identify the misbe-
having driver. This approach maintains driver pri-
vacy until a misbehaviour requires identity disclo-
sure.
A Secure and Privacy-Preserving Authentication Scheme with a Zero-Trust Approach to Vehicle Renting in VANETs
121

• no replay attacks: each vehicle appends the cur-
rent timestamp, denoted as ts, into every message
sent. When a message is received, vehicles assess
its freshness by verifying if ts
′
− ts ≤ δt, where
ts
′
represents the message reception time, and δt
is a threshold established by the scheme authority
based on experimentations of message transmis-
sion durations. This mechanism ensures that any
delayed attempt to replay a message will fail this
freshness check. Furthermore, the integrity and
authenticity of the timestamp, and by extension
the entire message, are safeguarded through digi-
tal signatures. Consequently, any alteration to ts
by a malicious entity will be detected, causing the
message verification to fail at the recipient’s end,
thereby preventing replay attacks.
• privacy-preserving accountability: during vehic-
ular communication, each message broadcasted
by a vehicle is escrowed with the driver’s id
d
,
irrespective if the driver is the vehicle owner or
a renter. To attribute accountability to the cur-
rent driver, the inspector can employ a decryp-
tion algorithm id
d
← dec(sk
in
,ψ) (Camenisch and
Shoup, 2003), to retrieve and map the id
d
to its
corresponding driver. This mechanism guarantees
that the individual behind the wheel is held re-
sponsible for their actions, regardless if they are
the owners or renters of the vehicle. Given that
id
d
is included in the delegated credential, any at-
tempt to use an fake id
d
will lead to the unsuccess-
ful verification of the proof of knowledge PK. Ad-
ditionally, this mechanism guarantees that the cur-
rent driver owns id
d
associated with every trans-
mitted message without any reliance on the trust
of the OBU as they do in (Akil et al., 2023b).
• linkability within epochs: Within a given epoch
ε, for all its transmitted messages, a sender vehi-
cle will have a consistent pseudonym, N
ε
, which is
guaranteed because the secret key sk
v
used to gen-
erate the pseudonym is part of the delegated cre-
dential. This allows a receiver vehicle to link all
messages originating from the same sender within
the epoch, using the pseudonym N
ε
as the identi-
fier. This ensures message traceability.
• unlinkability outside epochs: to ensure unlinka-
bility between different epochs, vehicles generate
a new pseudonym every different epoch. For any
two distinct epochs, ε
1
and ε
2
, the corresponding
pseudonyms N
ε
1
and N
ε
2
, created by the same ve-
hicle, are defined as N
ε
1
= N(sk
v
,ε
1
) = g
sk
v
ε
1
and
N
ε
2
= N(sk
v
,ε
2
) = g
sk
v
ε
2
, respectively. Given that
g
ε
1
and g
ε
2
represent two unique hash values de-
rived from a cryptographically reliable hash func-
tion H, it is ensured that N
ε
1
and N
ε
2
are dis-
tinct and unrelatable for any two epochs ε
1
and
ε
2
, thus preserving the unlinkability of a vehicle’s
pseudonyms across different epochs.
• sybil-free: Our protocol is designed to mitigate
Sybil attacks through the following mechanisms:
– Each vehicle is equipped with only one On-
Board Unit (OBU), and the CA conducts a thor-
ough verification of the driver’s attributes prior
to credential issuance. The unlocking protocol
further enforces that a vehicle cannot possess
more than one credential simultaneously, thus
preventing the concurrent use of multiple iden-
tities.
– During any given epoch ε, a sender ve-
hicle is restricted from generating multiple
pseudonyms N
ε
, as these are linked to the epoch
itself and the vehicle’s secret key sk
v
. Given
that ε only transitions upon the completion of
the current epoch and sk
v
remains unchanged,
the generation of multiple pseudonyms within
the same epoch is effectively impossible.
These safeguards collectively ensure that ve-
hicles are unable to produce multiple distinct
pseudonyms within the same epoch, thereby pre-
venting any attempt by a vehicle to pretend to be
multiple vehicles and initiate a Sybil attack.
• no renter framing: the driver’s id
d
is hidden un-
less the driver activates the unlocking protocol
where she needs to include id
d
in the delegated
credential to the vehicle. A renter owns the rental
agreement A
or
which contains the end date of the
renting period, and needs to be validated every
time a renter unlocks the car. The owner can only
reuse the id of the renter if the vehicle doesn’t re-
move the delegated credential after it is turned off
and since we trust the vehicle to remove all infor-
mation about the driver after the car is turned off
then the owner is prevented from reusing the id
d
of the renter.
• zero vehicle trust: at the end of the unlocking
protocol, a driver (owner or renter) delegates a
credential to the vehicle containing the id of the
driver, if a vehicle tries to broadcast a message
containing an id that belongs to a driver other
than the current driver, the verification process
will fail. Unlike the protocol from (Akil et al.,
2023b) where there was no way to detect if the
broadcasted id belongs to the current driver or not.
SECRYPT 2024 - 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography
122
5.2 Performance Analysis
Our protocol is based on delegatable credentials and
non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs (Camenisch
et al., 2017).
Bilinear Groups: Let G be a bilinear group gener-
ator that takes an an input a security parameter 1
k
and outputs the descriptions of multiplicative groups
∧ = (q,G
1
,G
2
,G
t
,e,g
1
,g
2
) where G
1
, G
2
and G
t
are groups of prime order q, e is an efficient, non-
degenerating bilinear map e : G
1
× G
2
→ G
t
, g
1
and
g
2
are generators of the groups G
1
and G
2
respec-
tively.
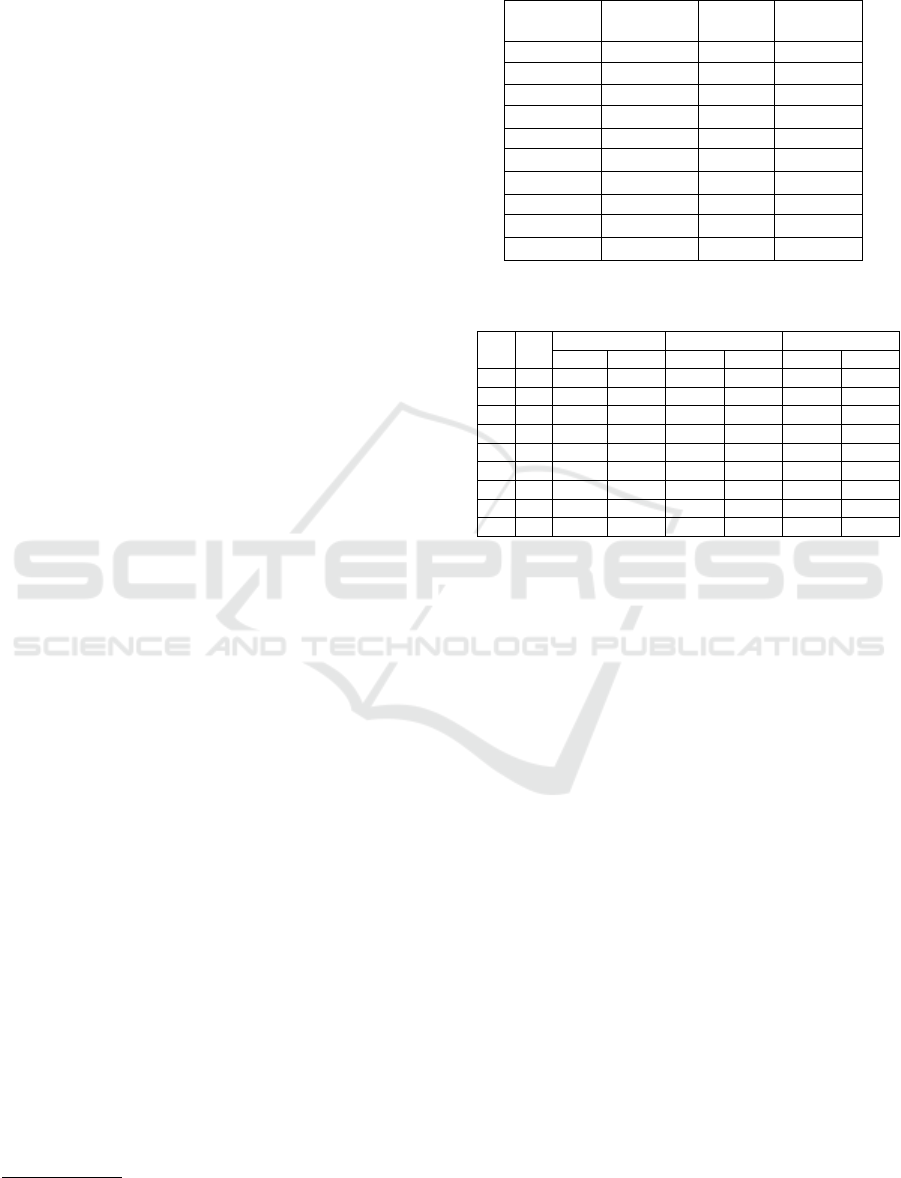
Basic Operations: Table 1 shows the time it takes
to perform each cryptographic operation, our tests are
based on the MIRACL library
2
. We have tested using
3 machines:
1. Apple M1 Pro 8 cores running macOS 14.3.1 with
16GB RAM
2. Intel i7−6700 @4.0GHZ 8 cores running Ubuntu
20.04.4 with 16GB RAM
3. Intel(R) Xeon(R) Silver 4214R @2.4GHZ 8 cores
running Ubuntu 20.04.4 with 16GB RAM
The sending and receiving protocols of the system are
time-critical as they allow vehicles to send and receive
traffic-related data while driving. On the other hand,
renting, unlocking, and inspection protocols can be
considered less time-critical.
To count the number of operations required to com-
pute and verify proofs. We use the following no-
tation; X{G
j
1
}, X{G
j
2
}, and X {G
j
t
} to denote X j-
multi-exponentiations in the respective group; j = 1
means a simple exponentiation. We denote as E
k
a
k-pairing product that we can compute with k Miller
loops and a single shared final exponentiation. We
use d
i
and u
i
to represent the number of disclosed
and undisclosed attributes respectively at level-i and
n
i
= d
i
+ u
i
.
Operations Required to Send and Verify a Proof:
• Generating a proof for a level-2 delegated creden-
tial:
– for level-1:
1G
2
+ (n
i
+ 2)G
1
+ (1 + d
i
)G
2
t
+
(1 + u
i
)G
3
t
+ (2 + n
i
)G
2
1
– for level-2:
1G
1
+ (n
i
+ 2)G
2
+ (1 + d
i
)G
2
t
+
(1 + u
i
)G
3
t
+ (2 + n
i
)G
2
2
• Verifying a proof for a level-2 credential:
2
https://github.com/miracl/core/tree/master/c
Table 1: Computation cost (in ms) for different crypto-
graphic operations.
Crypto Apple M1 Intel i7 Intel(R)
Operation Pro 6700 Xeon(R)
G
1
0,10 0,15 0,23
G
2
1
0,12 0,19 0,28
G
2
0,23 0,39 0,57
G
2
2
0,35 0,55 1,05
G
t
0,28 0,47 0,79
G
2
t
0,38 0,62 0,96
G
3
t
0,53 0,90 1,73
E 0,75 1,22 1,52
E
2
1,13 1,87 2,23
E
3
1,52 2,54 2,92
Table 2: Computation cost (in ms) for sending and receiving
using different numbers of undisclosed attributes.
u
1
u
2
Apple M1 Intel i7 Intel(R)
Send Ver Send Ver Send Ver
0 0 3.75 5.26 6.14 8.71 10.44 11.73
1 0 4.50 6.67 7.38 11.05 12.68 14.75
2 0 5.25 8.08 8.62 13.57 14.92 17.77
0 1 4.86 6.78 7.98 11.25 13.79 14.65
0 2 5.97 8.30 9.82 13.79 17.14 17.57
1 1 5.61 8.19 9.22 13.59 16.03 17.67
2 1 6.36 9.60 10.46 15.93 18.27 20.64
1 2 6.72 9.71 11.06 16.13 19.38 20.59
2 2 7.47 11.12 12.30 18.47 21.60 23.61
– for level-1:
(1 + d
i
)E + (1 + u
i
)E
2
+ (2 + n
i
)G
t
– for level-2 (last level)
(2 + d
i
)E
2
+ u
i
E
3
+ (2 + d
i
)G
t
Refer to Table 2 for the execution times associ-
ated with the sending and receiving protocols, which
varies according to the number of hidden attributes
employed. In the table, u
1
denotes the number of hid-
den attributes in level-1, and u
2
the number in level-2.
More information about this could be found in (Ca-
menisch et al., 2017).
The execution times presented in Table 2 were ob-
tained using the MIRACL C library and a 254-bit
Barreto-Naehrig curve (Barreto and Naehrig, 2005).
The table indicates that generating a level-2 creden-
tial proof without any undisclosed attributes is accom-
plished in only 3.75 ms, whereas the verification pro-
cess takes 5.26 ms. Furthermore, the table demon-
strates the impact of hidden attributes on computation
time: each additional undisclosed attribute in the first
credential link (u
1
) results in an increase of 0.75 ms in
generation time, and each attribute added to the sec-
ond link (u
2
) is an additional 1.1 ms. In terms of ver-
ification, the introduction of each hidden attribute in-
curs an additional time cost of 1.41 ms for the first
credential link and 1.52 ms for the second.
A Secure and Privacy-Preserving Authentication Scheme with a Zero-Trust Approach to Vehicle Renting in VANETs
123

Our evaluations, conducted across three distinct
machines as shown in Table 2, reveal a direct cor-
relation between machine specifications and execu-
tion times for cryptographic operations. Specifically,
the data illustrates an increase in execution times for
both the generation and verification of cryptographic
proofs as the hardware capabilities of the test ma-
chines becomes lower. This phenomenon not only
highlights the dependency of cryptographic computa-
tion efficiency on underlying hardware but also aligns
with the principles of Moore’s Law. According to
Moore’s Law, first articulated by Gordon Moore in
1965, the number of transistors on a microchip dou-
bles approximately every two years, suggesting a cor-
responding increase in computational power. This
exponential growth in hardware efficiency implies
that future advancements in computing hardware are
likely to lead to significant reductions in execution
times for cryptographic operations. As such, in line
with the historical trajectory of computing technol-
ogy marked by Moore’s Law, we anticipate that future
iterations of hardware and computational strategies
will continue to expedite cryptographic processes, en-
hancing their feasibility and efficiency for a broad
spectrum of applications.
6 RELATED WORK
This section provides a review of existing research in
the field, highlighting contributions and identifying its
limitation.
Akil et al. present a novel privacy-preserving au-
thentication protocol in (Akil et al., 2023b), ensur-
ing secure message exchanges between vehicles. Ad-
ditionally, they introduce a vehicle rental protocol,
enabling owners to rent out their vehicles to other
drivers. However, the proposed system inherently
relies on the trustworthiness of the On-Board Unit
(OBU) to accurately utilize the correct driver identity
(id) during message exchanges. The current design
lacks mechanisms to prevent or detect the misuse of
an id that may be attributed to a driver who is not cur-
rently driving the vehicle. This gap highlights a po-
tential vulnerability in ensuring the integrity of driver
identification within their protocol.
The paper (Liu et al., 2023) targets the enhance-
ment of security and privacy within VANETs, ad-
dressing the limitations of existing authentication
mechanisms. The proposed PTAP protocol elim-
inates the dependence on trusted third parties and
minimizing computational overhead. PTAP assures
anonymity of identity and privacy of location, while
still enabling traceability when necessary. The pro-
tocol demonstrates resilience against both passive
and active attacks under certain security assump-
tions. A notable aspect of PTAP, as discussed in
(Pfitzmann and Hansen, 2010), is its adoption of
transaction pseudonyms, where a new, non-linkable
pseudonym is generated for each message exchange.
This approach, while enhances privacy, raises con-
cerns within VANET contexts, particularly regarding
the continuity of environmental awareness among ve-
hicles (Akil et al., 2020).
(Shao and Piao, 2023) present a novel authenti-
cation scheme for VANETs. This scheme utilizes
elliptic curve signcryption to ensure secure and ef-
ficient communication between vehicles. The pro-
posed system is designed to be lightweight, aiming
to reduce computational and communication over-
head in VANETs. It emphasizes on achieving a bal-
ance between security and performance, focusing on
the unique requirements of vehicle-to-vehicle com-
munication. A key feature of the proposed system is
the generation of pseudo identities (pseudonyms), de-
rived from vehicle-produced random numbers. How-
ever, the scheme’s current design does not have re-
strictions on the quantity of random numbers a vehi-
cle can generate within a certain period, allowing for
the creation of multiple pseudonyms. This leaves the
system vulnerable to Sybil attacks, undermining its
security.
(Zhou et al., 2023) propose an enhanced certifi-
cateless aggregated signature (CLAS) scheme for se-
cure identity authentication within VANETs. This
scheme is particularly designed to mitigate vulnera-
bilities in existing VANET authentication protocols,
with a special focus on public key replacement at-
tacks. A distinctive aspect of this protocol is its re-
liance on a pseudonym that is assigned by the cer-
tificate authority at the time of vehicle registration to
achieve anonymity. This pseudonym is used through-
out all the vehicle lifetime for vehicular communica-
tions. However, this design choice introduces a po-
tential risk for linkability attacks, as the persistent use
of a single pseudonym could allow for the tracking
of vehicle movements over time, compromising the
anonymity that is crucial for user privacy in VANETs.
In Table 3, only our paper achieves all the neces-
sary security and privacy requirements needed to con-
struct a vehicular network suitable for the real world.
A notable gap is observed in addressing the privacy
issues associated with vehicle renting or sharing in
VANETs. Other than our work only one of the papers
addresses the complexities that arise when a vehicle’s
identity is tied not just to the owner but to multiple
users, such as renters or borrowers. This oversight
is important because it involves a different set of se-
SECRYPT 2024 - 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography
124
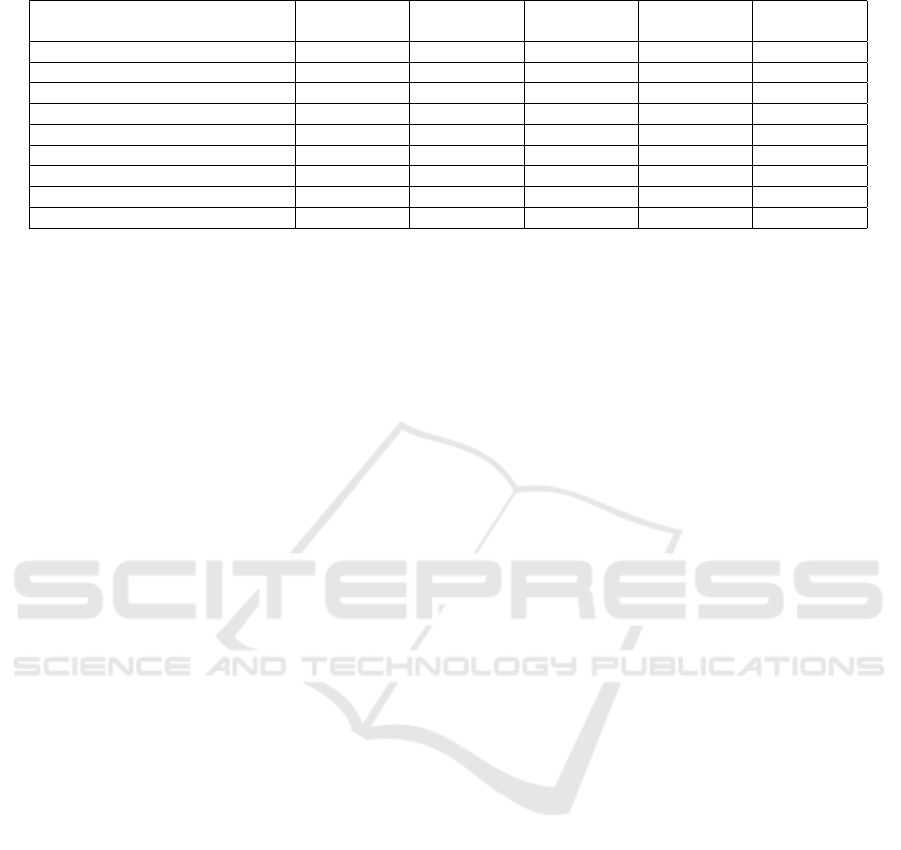
Table 3: Comparison between our proposed scheme and the related work.
`
`
`
`
`
`
`
`
`
`
Properties
Paper
Ours Scheme Akil et al. Liu et al. Shao and Piao Zhou et al.
Verifiable broadcasting ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓
Conditional anonymity ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓
No replay-attacks ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓
Privacy-preserving accountability ✓ ✓ - - -
Linkability within epochs ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ -
Unlinkability outside epochs ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ -
Sybil free ✓ ✓ - - -
No-renter framing ✓ ✓ - - -
Zero vehicle trust ✓ - - - -
curity and privacy challenges. For instance, when a
vehicle is rented, there’s a need to ensure the privacy
of both the owner and the renter, and to manage how
identity and usage data are handled to prevent mis-
use or unauthorized access to personal information.
Addressing this gap would enhance the applicability
of VANET security protocols in real-world scenarios
where vehicle sharing and rental are common.
7 DISCUSSIONS
In this section we discuss the adaptability of our sys-
tem, define misbehaving and illustrate how our sys-
tem safeguards against Sybil attacks.
Adaptability of Our Model: Our system’s architec-
ture flexibility could be used to facilitate provers in
not only verifying their possession of known certified
attributes but also in securely sharing these attributes
with various entities. This capability is particularly
beneficial in scenarios where access to specific ar-
eas is restricted and contingent upon vehicles meet-
ing certain predefined characteristics. For instance, in
urban environments striving for reduced carbon foot-
prints, areas might be designated where only electric
vehicles (EVs) are permitted entry. Here, our sys-
tem can enable provers, such as vehicle owners or
operators, to demonstrate their vehicle’s compliance
with such environmental standards, encompassing at-
tributes like electric vehicle status, fuel type compati-
bility, emission levels, or other eco-friendly certifica-
tions.
The extension of our model to include such
functionalities can leveraged using advanced crypto-
graphic techniques, ensuring that the attribute veri-
fication and sharing processes are not only tamper-
proof but also respect the privacy and data protection
needs of the entities involved. Furthermore, this ap-
proach can facilitate a dynamic and real-time verifi-
cation process, thereby enhancing the operational ef-
ficiency of restricted area management and contribut-
ing to the overarching objectives of sustainable urban
mobility and environmental conservation.
Misbehaving Vehicles: In our system, vehicles that
engage in non-compliant behavior with traffic rules or
manipulate the network for personal gains are classi-
fied as misbehaving vehicles. Such behaviors include,
but are not limited to, violations of traffic laws such as
running red lights, exceeding designated speed limits,
and engaging in network manipulation activities. An
example of the latter includes the strategic flooding
of nearby vehicles with an overwhelming volume of
messages in a short timeframe. This tactic is often
employed with the intention to congest certain routes,
thereby misleading other vehicles to alternative paths.
To address these issues, our system employs a spe-
cialized entity known as the inspector. The inspec-
tor’s primary function is to receive reports of misbe-
having vehicles. Upon receiving of such reports, the
inspector takes a real-world approach to issue fines
to the misbehaving vehicles rather than revoking their
operational credentials outright.
This decision to impose fines, rather than creden-
tial revocation, is based on real-world scenarios. The
inspector recognizes that while certain actions may
disrupt the orderly flow of traffic or the integrity of
the network, but not all transgressions could lead to
a severe consequence of revocation, which would ef-
fectively exclude the vehicle from the network. By
implementing a system of fines, our model ensures
that penalties are directly correlated to the nature and
severity of the misbehavior.
Sybil Resistance: To simultaneously safeguard
against Sybil attacks and preserve the privacy bene-
fits of pseudonyms, the issuance of pseudonyms must
be restricted to a single pseudonym per vehicle per
epoch. This can be achieved either by limiting the
generation of pseudonyms or by implementing de-
tection mechanisms to identify multiple pseudonyms
associated with a single vehicle. While both ap-
proaches are viable, restricting pseudonym genera-
tion is the more effective strategy as it eliminates the
need for detection, which can be a challenge in cer-
tain Sybil-resistant pseudonym schemes (Andersson
A Secure and Privacy-Preserving Authentication Scheme with a Zero-Trust Approach to Vehicle Renting in VANETs
125

et al., 2008) (Martucci et al., 2008) . Our proposed
solution avoids these complexities by enforcing the
limitation of one pseudonym per vehicle per epoch,
binding it to the current epoch and the vehicle’s se-
cret key which is included in the delegated creden-
tial. Consequently, only one valid pseudonym can be
generated per epoch, and verifiers can readily validate
and ensure the Sybil-freeness of received pseudonyms
without relying on third-party interactions.
8 CONCLUSIONS & FUTURE
WORK
This paper addresses the complex privacy and secu-
rity challenges in VANETs, particularly in vehicle
renting scenarios. It successfully bridges a signif-
icant gap in existing research by proposing a non-
interactive, privacy-preserving authentication scheme
that ensures the privacy of both vehicle owners and
renters. This work not only enhances the security
framework of VANETs but also adapts to the evolv-
ing landscape of vehicle sharing and renting, marking
a considerable step forward in the practical applica-
tion of VANET technologies. The paper fulfills all the
privacy and security requirements listed in 3.2. The
performance evaluation shows that the time taken to
send and verify proofs in this system is feasible, mak-
ing it possible to adopt in real-world transportation
systems. This authentication scheme also holds po-
tential for broader applications beyond VANETs, par-
ticularly in smart environments and IoT ecosystems,
where similar privacy and security concerns exist. As
future work, we plan to address the limitation of this
system, where we need to trust the vehicle to remove
credentials after it is turned off every time. We can
circumvent this by setting an end time for each dele-
gated credential or changing the delegation process to
include a signature from the driver, which would only
be valid for the duration of the drive.
REFERENCES
Akil, M., Islami, L., Fischer-H
¨
ubner, S., Martucci, L. A.,
and Zuccato, A. (2020). Privacy-preserving identifiers
for iot: a systematic literature review. IEEE Access,
8:168470–168485.
Akil, M., Martucci, L., and Hoepman, J.-H. (2023a). Non-
interactive privacy-preserving sybil-free authentica-
tion scheme in vanets. In Network and DistributedSys-
tem Security (NDSS) Symposium.
Akil, M., Naskar, S., Martucci, L., and Hoepman, J.-
H. (2023b). A privacy-preserving approach to vehi-
clerenting and driver accountability in vanets. In 18th
IFIP Summer School on Privacy and Identity Manage-
ment 2023-Sharing (in) a Digital World. OSLO August
7-13, 2023.
Amara, M. and Siad, A. (2011). Elliptic curve cryptogra-
phy and its applications. In International workshop
on systems, signal processing and their applications,
WOSSPA, pages 247–250. IEEE.
Andersson, C., Kohlweiss, M., Martucci, L. A., and
Panchenko, A. (2008). A self-certified and sybil-
free framework for secure digital identity domain
buildup. In Information Security Theory and Prac-
tices. Smart Devices, Convergence and Next Genera-
tion Networks: Second IFIP WG 11.2 International
Workshop, WISTP 2008, Seville, Spain, May 13-16,
2008. Proceedings 2, pages 64–77. Springer.
Barreto, P. S. and Naehrig, M. (2005). Pairing-friendly el-
liptic curves of prime order. In International work-
shop on selected areas in cryptography, pages 319–
331. Springer.
Belenkiy, M., Camenisch, J., Chase, M., Kohlweiss, M.,
Lysyanskaya, A., and Shacham, H. (2009). Random-
izable proofs and delegatable anonymous credentials.
In Advances in Cryptology-CRYPTO 2009: 29th An-
nual International Cryptology Conference, Santa Bar-
bara, CA, USA, August 16-20, 2009. Proceedings,
pages 108–125. Springer.
Brecht, B., Therriault, D., Weimerskirch, A., Whyte, W.,
Kumar, V., Hehn, T., and Goudy, R. (2018). A secu-
rity credential management system for v2x communi-
cations. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transporta-
tion Systems, 19(12):3850–3871.
Camenisch, J., Drijvers, M., and Dubovitskaya, M. (2017).
Practical uc-secure delegatable credentials with at-
tributes and their application to blockchain. In Pro-
ceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on
Computer and Communications Security, pages 683–
699.
Camenisch, J. et al. (2010). Specification of the identity
mixer cryptographic library, version 2.3.1, 2010.
Camenisch, J., Kiayias, A., and Yung, M. (2009). On the
portability of generalized schnorr proofs. In Annual
International Conference on the Theory and Appli-
cations of Cryptographic Techniques, pages 425–442.
Springer.
Camenisch, J. and Shoup, V. (2003). Practical verifiable
encryption and decryption of discrete logarithms. In
Annual International Cryptology Conference, pages
126–144. Springer.
Camenisch, J. and Stadler, M. (1997). Efficient group signa-
ture schemes for large groups. In Annual international
cryptology conference, pages 410–424. Springer.
Chaum, D. (1985). Security without identification: Trans-
action systems to make big brother obsolete. Commu-
nications of the ACM, 28(10):1030–1044.
Engoulou, R. G., Bella
¨
ıche, M., Pierre, S., and Quintero, A.
(2014). Vanet security surveys. Computer Communi-
cations, 44:1–13.
Fiat, A. and Shamir, A. (1986). How to prove your-
self: Practical solutions to identification and signature
SECRYPT 2024 - 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography
126

problems. In Conference on the theory and appli-
cation of cryptographic techniques, pages 186–194.
Springer.
Fiege, U., Fiat, A., and Shamir, A. (1987). Zero knowledge
proofs of identity. In Proceedings of the nineteenth an-
nual ACM symposium on Theory of computing, pages
210–217.
Johnson, D., Menezes, A., and Vanstone, S. (2001). The
elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ecdsa). In-
ternational journal of information security, 1:36–63.
Liu, X., Wang, Y., Li, Y., and Cao, H. (2023). Ptap: A novel
secure privacy-preserving & traceable authentication
protocol in vanets. Computer Networks, 226:109643.
Martucci, L. A., Kohlweiss, M., Andersson, C., and
Panchenko, A. (2008). Self-certified sybil-free
pseudonyms. In Proceedings of the first ACM con-
ference on Wireless network security, pages 154–159.
Petit, J., Schaub, F., Feiri, M., and Kargl, F. (2014).
Pseudonym schemes in vehicular networks: A sur-
vey. IEEE communications surveys & tutorials,
17(1):228–255.
Pfitzmann, A. and Hansen, M. (2010). A terminol-
ogy for talking about privacy by data minimization:
Anonymity, unlinkability, undetectability, unobserv-
ability, pseudonymity, and identity management.
Shao, H. and Piao, C. (2023). A provably secure lightweight
authentication based on elliptic curve signcryption for
vehicle-to-vehicle communication in vanets. IEEE
Transactions on Industrial Informatics.
Zhou, Y., Wang, Z., Qiao, Z., Yang, B., and Zhang, M.
(2023). An efficient and provably secure identity au-
thentication scheme for vanet. IEEE Internet of Things
Journal.
APPENDIX A
In here we represent the cryptographic building
blocks of the Elliptic Curve ElGamal (ECElGamal)
encryption scheme. key generation: In the Ellip-
tic Curve ElGamal (ECElGamal) encryption scheme,
the key generation process involves creating a public-
private key pair for the participating parties. Here is
a step-by-step guide for generating the keys in ECEl-
Gamal:
• Select a base point G of prime order n over a se-
cure elleptic curve defined over a finite field.
• Choose a random integer sk
in
in the range of
[1,n − 1], sk
in
is the private key.
• Calculate the corresponding public key pk
in
= G∗
sk
in
Encryption: To encrypt a message M by a user with
the public key pk
in
:
• Generate a random number rwhere(1 < r < n).
• Compute C
1
= r ∗ G
• Compute C
2
= M + r ∗ pk
in
• Send ψ = (C
1
,C
2
)
Decryption: The holder of the secret key sk
in
can de-
crypt ψ by calculating:
M = C
2
− sk
in
∗C
1
APPENDIX B
In here we present the elliptic curve digital signature
algorithm (ECDSA).
ECDSA (Johnson et al., 2001) follows the elliptic
curve cryptography (ECC) primitives with a public
key pair-based encryption. For a prime field F
p
, where
p is a large prime, an elliptic curve E
p
is defined by
the equation E
p
(a,b) : y
2
= x
3
+ ax + b mod p with
a,b ∈ F
p
. For a given point P ∈ E
p
, and any in-
teger x, a scalar multiplication in ECC is given by
x.P = P + P + ... + P(x-times). Any point P with the
smallest order z in ECC is called a base point if it
can generate all the points in the curve, i.e for z is
the smallest positive integer for which zP = O; O is
the order of the elliptic curve. The security of ECC
comes from the elliptic curve discrete logarithm prob-
lem: given two points P,Q ∈ E
p
, it is computationally
infeasible to compute x ∈ F
p
such that Q = x.P in a
polynomial time (Amara and Siad, 2011).
A high-level overview of the ECDS algorithm is
as follows:
• Key Generation: ECC can be used to generate
digital signatures on any message using a public
key pair p
k
,s
k
where s
k
is a secret integer from
F
p
and the public key p
k
is generated by using a
base-point of the ECC P such that p
k
= x.P. To
sign a certificate the signer uses its secret key s
k
which then can be verified using the public key p
k
and the public parameter P
• Signature Generation: the signer selects a ran-
dom integer k ∈ [1,z − 1] and compute a point
Q : (x,y) = k.P such that (r = x mod z) ̸= 0, (t =
k
−1
mod z) and s = k
−1
(e + s
k
r) mod z where
e = H(c) is a hashed value of the certificate (c) to
be signed. Finally, the signature is the pair (r,s).
• Signature Verification: to verify the signature,
the verifier first computes w = s
−1
mod z, u
1
=
ew and u
2
= rw. Then it generates the point X :
(x
1
,y
1
) = u
1
P +u
2
P and the value v = x
1
mod z.
If the value v = r then it confirms the signature.
A Secure and Privacy-Preserving Authentication Scheme with a Zero-Trust Approach to Vehicle Renting in VANETs
127
