
Six-Layer Industrial Architecture Applied to Predictive Maintenance
Fernanda Pereira Guidotti
1 a
, Jesimar da Silva Arantes
2 b
, M
´
arcio da Silva Arantes
3 c
,
Albeiro Espinosa Bedoya
4 d
and Claudio Fabiano Motta Toledo
1 e
1
Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of S
˜
ao Paulo, S
˜
ao Carlos, Brazil
2
Institute of Exact and Technological Sciences, University of Lavras, Lavras, Brazil
3
SENAI Institute for Innovation in Embedded Systems, ISI-SE, Florian
´
opolis, Brazil
4
Department of Computer Science and Decision, University of Colombia, Medellin, Colombia
fl
Keywords:
Systems Architecture AI, Industry 4.0, AI Industry Framework, Digital Transformation.
Abstract:
In the context of digital transformation defining Industry 4.0, the integration of Industrial Artificial Intelli-
gence (I-AI) emerges as a transformative element, promoting the development, validation, and deployment of
machine learning algorithms in industrial applications. As sensor technologies advance, reducing costs and
expanding the capability for direct data collection from machines, there arises a need for system architectures
that not only support but also optimize these data collection and analysis processes. This paper introduces an
innovative reference architecture for I-AI, which stands out by advancing beyond the traditional 5-layer (5C)
framework through the addition of a sixth layer, named ”Consciousness”. This innovative layer is designed
to retroactively feed the knowledge acquired back to the previous layers, significantly enhancing control and
optimization through AI systems. The proposed architecture, termed 6C, comprises the layers of Connec-
tion, Conversion, Cyber-Physical, Cognition, Configuration, and finally, Consciousness. The introduction of
the Consciousness layer marks a significant innovation in the literature, offering a mechanism by which the
architecture is capable of autonomously perceiving the state and needs of the industrial system. Validated
in an industrial case study, the 6C architecture demonstrated performance improvement by incorporating the
Consciousness layer, highlighting its effectiveness in enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making
within complex industrial contexts.
1 INTRODUCTION
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has profoundly impacted
industrial production, revolutionizing work environ-
ments and production chains. This transformation is
driven by technological advancements that facilitate
the integration of diverse features, such as embedded
systems, cloud resources, big data processing, and
AI techniques (Van Kranenburg, 2008). Such inte-
gration empowers industrial systems with autonomy,
enabling them to make informed decisions through
knowledge-based reasoning.
Access to information has been crucial for en-
hancing productivity and quality in the production
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5913-9371
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1776-1514
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9309-7678
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7292-987X
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4776-8052
process, achieved through intelligent machine adjust-
ments. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) exem-
plifies this by bridging the digital and physical worlds
in factories, utilizing advances in local sensing and
reliable communication protocols.
As a result, we are witnessing the 4th Indus-
trial Revolution, Industry 4.0, characterized by en-
hanced communication between equipment and com-
puter systems. This communication facilitates im-
proved production management through the genera-
tion of valuable information. The growing recogni-
tion of AI’s critical role in smart industries is evi-
denced by numerous national AI initiatives (Lee et al.,
2020a).
In this evolving landscape, industries are reeval-
uating their approaches and exploring new possibili-
ties. However, the challenge remains to develop in-
telligent systems capable of addressing complex and
varied problems. This has led to the emergence of In-
dustrial Artificial Intelligence (I-AI), which focuses
Guidotti, F., Arantes, J., Arantes, M., Bedoya, A. and Toledo, C.
Six-Layer Industrial Architecture Applied to Predictive Maintenance.
DOI: 10.5220/0012767000003753
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Software Technologies (ICSOFT 2024), pages 123-130
ISBN: 978-989-758-706-1; ISSN: 2184-2833
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
123

on the development, validation, and deployment of
machine learning (ML) algorithms for industrial ap-
plications, as noted by (Lee et al., 2018).
Industries seeking technological advancements
have begun leveraging ML solutions to optimize pro-
cesses. However, a significant gap exists between
constructing ML systems that function in a develop-
ment environment, such as notebooks, and creating
ML solutions robust enough for deployment in indus-
trial production environments (Ng, 2021). Address-
ing this gap necessitates a systematic framework for
I-AI.
This paper introduces a reference architecture for
I-AI that builds upon the 5C layers described by (Lee
et al., 2020b), with the addition of a novel Con-
sciousness layer. This layer enhances the architecture
by feeding acquired knowledge back to the previous
layers and improving the auto-tuning of AI systems
as a whole. Termed the 6C-layer, this architecture
has been validated in an industrial case study, show-
ing improved performance with the integration of the
Consciousness layer, aligning with the proposed 6C
architecture.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 re-
views related works; Section 3 describes the proposed
software architecture; Section 4 reports on the case
application; and Section 5 presents our conclusions.
2 RELATED WORK
We review studies related to AI in industry address-
ing software architecture projects, development of AI
solutions and their application in an industrial setting
as show in Table 1.
The article by (Liu et al., 2018) introduced a
framework for industrial AI applied in high-speed rail
networks using a 5C architecture. This framework
creates digital twins to monitor and optimize real-time
performance, predicting potential failure anomalies
and supporting maintenance decisions. The authors
reported a case study to monitor train traction, en-
gine condition, and railway line using sensors. They
highlighted the versatility of applying industrial AI
beyond railway transportation, suggesting an iterative
process. This article is directly related to our work
due to its innovative approach in applying industrial
AI to optimize cyber-physical systems, a methodol-
ogy we also employ to address similar challenges in
our study. The use of the 5C architecture and the em-
phasis on scalable and predictive solutions for opera-
tions and maintenance resonate with the goals of our
own framework, underscoring the relevance of this
work as a valuable precedent in related literature.
(Guo et al., 2019) presents an AI framework tai-
lored for the manufacturing sector to facilitate the de-
velopment and operation of AI models, especially for
device health management. This framework, known
as I-AI DevOps, addresses challenges such as predic-
tive maintenance, lifecycle management, and uncer-
tainty in AI models. The authors highlight three ma-
jor engineering challenges in predictive maintenance
applications: data scarcity, real-world uncertainties,
and interdisciplinary collaboration difficulties. The I-
AI DevOps framework follows a cyclical model that
encompasses requirements understanding, data col-
lection, exploratory analysis, model training, valida-
tion, and seamless integration with software during
the operations stage. Continuous monitoring ensures
users receive valuable insights. The authors empha-
size the importance of model forecast updates due to
inevitable long-term structural changes. This study’s
focus on the AI model life cycle in industry resonates
with our research objectives.
In their study, (Lee et al., 2020b) explore Indus-
trial AI and predictive analytics for smart manufac-
turing systems. They highlight how AI techniques
enable pattern recognition, learning from past expe-
riences, and making informed predictions to enhance
decision-making processes. The authors identify key
challenges faced by factories in the Industry 4.0 era,
including issues with transmission, storage, security,
connectivity, standardization, integration complexity,
and context awareness. They present a case study on
an intelligent bandsaw system using a 5C architec-
tural model. Data is collected and processed in a fog
layer before being analyzed in the cloud using analyti-
cal models. This process updates the cyber twin mod-
els of the bandsaw machines, providing insights into
blade integrity. Finally, the optimized operational pa-
rameters are sent to the machine, enabling the blade to
self-configure to improve or predict its lifespan. Lee
et al.’s (2020) study aligns with our research on AI-
driven solutions for industry. Their emphasis on pre-
dictive analytics and use of a 5C model offer insights
for designing AI architectures in manufacturing.
(Peres et al., 2020) conduct a systematic litera-
ture review on artificial intelligence in the industry,
proposing an adapted framework from (Lee et al.,
2020b). The purpose of this adaptation is the addition
of a Human-Machine Technology (HT), expanding
the 4 enabling technologies of the 5C architecture to
5. The HT technology aims to facilitate system inter-
action with people. The goal of such interaction is to
assist maintenance and diagnostic operations through
virtual or augmented reality means. The authors also
outline future challenges in three areas: data, mod-
els, and infrastructure. This study contributes to the
ICSOFT 2024 - 19th International Conference on Software Technologies
124

Table 1: Comparison with related works.
Autor Software architecture AI deployment Application case
(Liu et al., 2018) 5C ✔ Prognostics and Health Management for Rail
(Guo et al., 2019) I-AI DevOps ✗ Prognostic model lifecycle management
(Lee et al., 2020b) 5C ✗ Intelligent bandsaw system
(Peres et al., 2020) Adapted 5C ✗ ✗
(Calabrese et al., 2020) Big Data Architecture ✔ Predictive Maintenance
(Granlund et al., 2021) ✗ ✔ Medical scenario
Our proposal 6C ✔ Predictive Maintenance
proposed research by considering the analysis of ap-
plication context.
The study by (Calabrese et al., 2020) introduces an
application that employs a data-centric approach uti-
lizing machine learning in industrial machinery. They
present a three-step architecture involving data acqui-
sition from machine logs through sensors, followed
by data processing, analysis, and predictive model-
ing, and finally, information display on a dashboard.
The authors illustrate a case study in a woodwork-
ing shop, demonstrating the prediction of potential
machine failures based on historical log data. Em-
phasizing the need for intelligent systems to compre-
hend machine integrity status, they focus on devel-
oping a computational pipeline for predictive mainte-
nance. This study significantly contributes to research
in constructing a pipeline for predictive maintenance,
addressing one of the major challenges in the indus-
try.
The authors (Granlund et al., 2021) conduct a case
study on AI systems deployment, focusing on chal-
lenges faced in a medical scenario. They employ De-
vOps and MLOps to integrate organizations and de-
scribe a pipeline involving data scientists, software
developers, and experts. Oravizio software provides
risk information regarding hip and knee surgery, uti-
lizing three prediction models for infection, revision,
and mortality risks. Challenges included dataset or-
ganization, model definition, and training. This study
contributed to the proposed research concerning the
construction of pipelines and system integration.
In Table 1, it’s observed that out of the related
studies, 6 employ some form of software architecture,
with three of them utilizing the 5C architecture (Liu
et al., 2018; Lee et al., 2020b). The study by (Peres
et al., 2020), although not directly using the 5C archi-
tecture, is based on it to propose a new framework
with Humana technology. Meanwhile, (Guo et al.,
2019) introduces a DevOps cycle in the industry, and
(Calabrese et al., 2020) describes a pipeline architec-
ture for data acquisition, processing, and monitoring.
Most of the studies present industrial application
cases, except for (Peres et al., 2020), which conducts
a systematic review of AI challenges and prospects in
the industry. However, none of the studies compre-
hensively address the interaction between layers. In
contrast, our study proposes a 6-layer architecture, in-
cluding the ability to acquire domain consciousness.
The reviewed studies indicate a growing adop-
tion of AI frameworks to optimize industrial opera-
tions. Our proposed 6C architecture represents a pro-
gression beyond existing architectures, enabling au-
tonomous knowledge acquisition and smarter interac-
tion between layers. This pioneering approach aims
to fill gaps in the literature on assertive implemen-
tation of AI models in industry, establishing a new
paradigm for intelligent industrial systems.
3 PROPOSED ARCHITECTURE
The 5C architecture provides a solid foundation for
integrating Artificial Intelligence into the industry, es-
tablishing a structured framework for data process-
ing and analysis through its five layers: Connection,
Conversion, Cyber-Physical, Cognition, and Config-
uration. These layers facilitate everything from data
acquisition to the self-configuration of machines, pro-
moting efficient interaction between physical and dig-
ital systems. However, to fully embrace the dy-
namic challenges of the modern industrial environ-
ment, there is a recognized need to evolve beyond
these fundamentals. This work proposes an evolution
of the 5C architecture by incorporating an innovative
sixth layer: Consciousness. This new layer not only
compiles all relevant information generated in the pre-
vious stages but also employs knowledge-based rea-
soning, providing active feedback to the preceding
layers. The addition of the Consciousness layer ex-
pands the system’s ability to learn autonomously, en-
abling a deeper understanding and adaptation to in-
dustrial scenarios. This evolution does not diminish
the importance of the 5C architecture; on the contrary,
it builds upon its robust structure, integrating enabling
technologies and promoting synergy that elevates in-
dustrial AI to a new level of effectiveness. By retain-
ing the original five layers, our framework expands
its functionalities to include a continuous and interac-
tive learning cycle, where the generated intelligence
is used not only for diagnostics and configurations but
Six-Layer Industrial Architecture Applied to Predictive Maintenance
125

also to constantly enhance the system based on oper-
ational insights.
The present paper advances from the 5C architec-
ture in (Lee et al., 2015; Lee et al., 2020a; Lee et al.,
2020b) by adding the Consciousness layer and the en-
abling knowledge technologies as shown by Figure
1. We keep the previous 5C-levels described in (Lee
et al., 2015):
• Connection identifies equipment and mechanisms
for acquiring data.
• Conversion decodes the collected data into mean-
ingful information.
• Cyber integration analyses the information
through the digital twin concept.
• Cognition provides diagnostic information to
identify failures.
• Configuration executes auto-tunning becoming
the machines self-configurable.
Figure 1: Industry AI architecture with 6 layers.
We introduce the Consciousness layer that assem-
bles all relevant information generated through the
previous step, reasoning from the acquired knowledge
and sending feedback to the previous layers. The idea
is to allow a whole self-learning that goes beyond
those addressed by the configuration level.
Figure 2 illustrates the overlap between the 6C-
levels and the respective enabling technologies in our
architecture.
The 6C architecture states a pipeline to guide the
development process: development, validation, and
deployment at each layer. In this context, we con-
sider the four enabling technologies from (Lee et al.,
2020b) and include the Knowledge Technology as de-
scribed next:
• The Platform layer provides the framework for
selecting, organizing, and integrating hardware
and software at each level, tailored to specific in-
dustrial scenarios where I-AI is required. This en-
ables device connections, data analysis, and inte-
grated knowledge acquisition reliably.
• DT - Data Technology is linked to the Connec-
tion layer, defining the technology for data ac-
quisition and communication, and its relation to
databases, tables, sensors, or cloud storage.
• AT - Analytical Technologies encompass three
other layers: in the Connection layer, data adjust-
ments and conversion into information occur; in
the cyber-physical layer, the concept of a digital
twin is utilized to create a reliable virtual model of
the industrial process or machine; and in the cog-
nition layer, machine learning methods are em-
ployed to predict failures or changes, leading to
self-configuration of machine behaviors.
• OT - Operation Technology enables the configu-
ration layer, allowing control and optimization of
the industrial process based on findings from ana-
lytical technologies.
• KT - Knowledge Technology covers the con-
sciousness layer, monitoring the entire process
and utilizing learning and decision-making mod-
els to evaluate feedback and adjustments, en-
abling continuous optimization of the I-AI pro-
cess in the industry.
Our proposal of a Consciousness layer, enabled
by KT, includes some OT duties as previously stated
in (Lee et al., 2015), which now will help to reason
from acquired knowledge through the development
process. The authors in (Lee et al., 2015) mention
feedback following a closed-loop to redesign the life-
cycle or manage the manufacturing system. However,
our proposal sees the self-adjust, self-configure, and
self-optimize features in (Lee et al., 2015) working
here as a more immediate adjustment tool from ana-
lytic outcomings. The KT will lead such analysis to
another baseline at the knowledge level by employ-
ing a fusion of information and deeper analysis. The
complete information will be evaluated based on, e.g.,
some time series from data and result profiles, and the
knowledge learned will feedforward the other layers.
The knowledge learned can be sent back consider-
ing three categories, representing the level of consci-
entiousness reached by the system. The first category
is the production estimation and evaluation, which
share relevant information for connection and conver-
sion levels. The second is the evaluation and moni-
toring that feed cyber and cognition levels. Finally,
life cycle monitoring makes fine-tuning adjustments
for machines, methods, and monitoring systems.
The 6C architecture represents a significant ad-
vancement in the integration of Artificial Intelligence
in the industry, surpassing the limits previously es-
tablished by the 5C architecture. By introducing the
Consciousness layer and associating it with enabling
ICSOFT 2024 - 19th International Conference on Software Technologies
126

Figure 2: Industry AI architecture highlighting the six layers.
knowledge technologies, our proposal establishes a
new paradigm for autonomous and adaptive systems.
This innovation not only enhances operational effi-
ciency and predictive capabilities but also opens new
avenues for research and technological development,
fostering a deeper integration between AI and indus-
trial processes.
4 APPLIED CASE STUDY
The case study considers a vegetal oil production in-
dustry with machines and sensors generating thou-
sands of daily data. We extend the approach proposed
by (Arantes et al., 2021) for the same industry, which
was the first attempt to include an intelligent system in
its production process. The industry still needs strate-
gies to efficiently manage all devices and sensors to
take advantage of the information available. How-
ever, the mentioned industry has software technolo-
gies for production control and management, such
as Manufacturing Execution System (MES), Super-
visory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA), and
Systems Applications and Products (SAP). However,
the company does not use such systems to create an
I-AI environment.
A relevant issue for the industry is machine main-
tenance, where there was no predictive or intelligent
system to detect or avoid failures besides the amount
of available data. The authors in (Arantes et al., 2021)
addressed the predictive issue, and we advanced from
them by deploying our 6C architecture in the produc-
tion process. The problem of predictive maintenance
seeks to identify potential failures in machines even
before they show an apparent signal. When minimal
signs of an eventual failure are neglected, severe dam-
ages to the company’s assets can cause the stop of ac-
tivities that leads to financial losses.
The model proposed by the authors (Arantes et al.,
2021) detects whether the machine is operating in
a degraded state and, if necessary, interrupts its op-
eration before a critical condition arises. The main
idea of such a method is to use time-series data for
anomaly detection. Figure 3 illustrates the previous
intelligent system flow developed for the industry,
with three main modules:
• Data: performs data acquisition from sensors,
store in the database, and create a fault history.
• Analytics: performs the predictive maintenance
by monitoring, diagnosis, and prediction.
• Interface: displays the results of alerts, reports,
and register of information about detected faults.
Data
sensors
database
historic
Analytics
monitoring
diagnosis
prediction
Interface
alerts
report
register
Figure 3: The conceptual flow of predictive maintenance.
The data from the sensors and maintenance his-
tory provided by the SAP system feed an account of
the monitored equipment. From these and other infor-
mation sources, Analytics can carry out the processes
to determine the information required to predict a fail-
ure. This integration occurs through an API, and the
information becomes available to the user through a
dashboard. Thus, the system allows us to keep track
of the equipment, proactively executing preventive
maintenance measures. From this current pipeline,
we make changes with Figure 4 illustrating the 6C ar-
chitecture adaptation to the vegetal oil industry under
study.
The connection layer executes the data acquisi-
tion and communication by the machine’s sensors
through ethernet communication. We obtain the elec-
trical current, temperature, vibration, and pressure
data, among other features, from machine sensing.
Six-Layer Industrial Architecture Applied to Predictive Maintenance
127
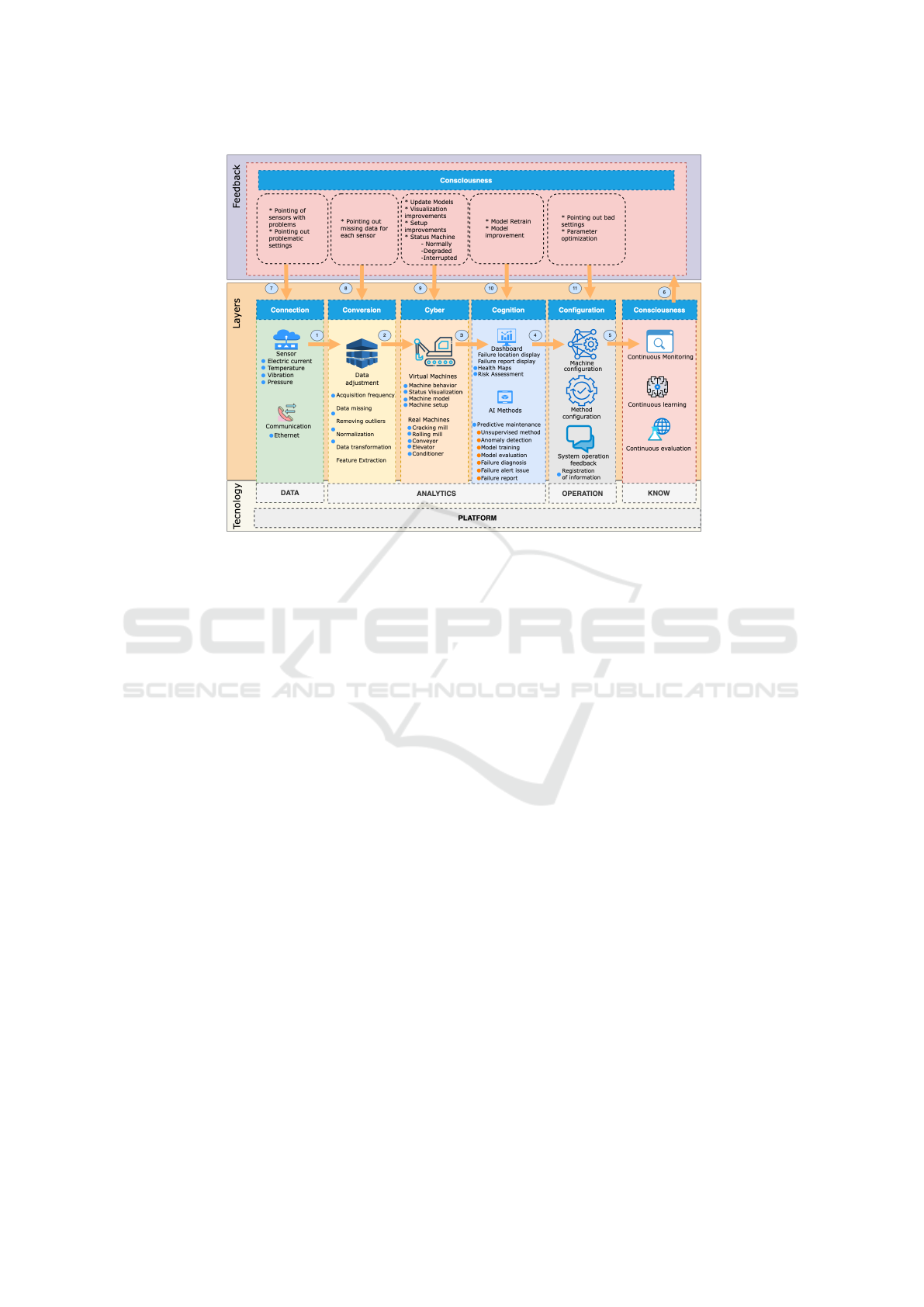
Figure 4: 6C Architecture of AI in vegetal oil industry.
Next, the database adjustments take place in the con-
version layer, where standardization of the sensor fre-
quency during data acquisition occurs, as well as the
treatment of missing data, the removal of outliers, and
the normalization of the input data for the next level.
In cyber-physics, we have a virtual representation
of the machine that allows adjusting its configuration.
We have the prediction model developed in (Arantes
et al., 2021) extended for the following machines in
the industry: cracking mill, rolling mill, conveyor,
elevator, and conditioner. The cognition layer han-
dles previously processed data by applying the un-
supervised method for predictive maintenance from
(Arantes et al., 2021). At this layer, it is possible to
train and validate the model, providing the fault di-
agnosis through a dashboard for the user. Such vi-
sualization of results allows the user to find the fault
location and access the machine-related fault report.
Thus, the failure detection and prediction happen in
the cognition layer, where the prediction model spec-
ifies the probability (%) of the current failure. The
operator access such evaluation through the Dash-
board, learning about what happened to the sensor or
machine and being able to make decisions for more
proactive maintenance, saving resources. In the con-
figuration layer, the eventual changes to the configu-
ration parameters happen based on the models’ pre-
diction results.
Finally, the Consciousness layer becomes possi-
ble to monitor data and machines, map the system’s
health, and enable continuous learning. We can now
iterate among the previous layers, estimate the pro-
duction, and determine if the devices are operating
normally or in a degraded state. All the reasoning
over such information leads to more robust adjust-
ments in the previous levels.
The Consciousness layer is where the understand-
ing of the process as a whole takes place. In the
configuration layer, there is feedback to the process
whenever the operator modifies the industrial rele-
vant features, either because the AI warned or because
the operator may have done preventive maintenance.
The operator informs the system, which learns from
such changes in the production process. Moreover,
the next time the same pattern of behavior occurs, the
algorithm will notice and be more assertive about it.
The Figure 5 illustrates a general flow in which the
system identifies possible anomalies. If the system
does not identify anomalies, it takes no action, but
when it does, a failure signal is issued, and the dash-
board is updated, reporting the failure in the dash-
board. When the operator visualizes the failure on
the dashboard, she/he opens a maintenance call, the
maintenance team goes to the machine, performs cor-
rective actions, and reports to the operator the action
taken at the end. If the failure occurs, the operator
informs the system about the corrective action; other-
wise, the operator adds false positive feedback to the
system. However, the system learns in both cases by
retraining the related models.
We state four scenarios of our applied case study
based on Figure 5:
ICSOFT 2024 - 19th International Conference on Software Technologies
128

Figure 5: General system flow.
Scenario I - False Negative. In this case, the sys-
tem does not find any anomalies and does not take
any action, which means do not inform the opera-
tor. However, let’s suppose that the operator identi-
fies a strange noise in the engine when next to the
machine. The operator decides to schedule mainte-
nance and verifies a problem in the machine, e.g., the
maintenance team changes the engine’s bearing belt.
It informs the operator, who feeds the system, about
the problem and the corrective action taken. The sys-
tem learns by receiving a time window with the data
related to the problem, which allows learning by ad-
justing the weights or other parameters in the system
model during the retraining. Next time, the system be-
comes more sensitive to the sensors and metrics that
led to this problem, thus increasing the chance of de-
tection.
Scenario II - True Negative. The system does not
find any anomalies and does not take action to no-
tify the operator. When passing through the machine,
the operator does not notice anything abnormal, and
she/he does not give any feedback to the system,
which understands that everything is right. As the
forecast was correct and the information is complete,
nothing needs to be done in the Consciousness layer.
Scenario III - False Positive. The system identifies
an anomaly, triggers a failure signal, and updates the
Dashboard to show the failure. As soon as the oper-
ator checks the Dashboard and sees the fault, she/he
goes to the machine but does not identify anything
wrong with it. The operator decides to open a call for
maintenance anyway. The maintenance team checks
the machine and does not identify anything wrong
with it, informing the operator that it works correctly.
The operator tells the system that the machine does
not have a failure at that period, allowing the system
to learn from this operator’s feedback by adjusting the
weights and parameters of the prediction models.
Scenario IV - True Positive. The system identifies
an anomaly and issues a failure signal, updating the
Dashboard. The operator visualizes the failure in the
Dashboard, but he doe not identify the problem at the
machine. She/he opens a call for maintenance, and
the maintenance team identifies a problem. For in-
stance, the team changes the bearing and replaces it,
informing the operator later about the action taken.
The operator updates the system with such informa-
tion about the failure and the corrective action done.
In the Consciousness layer, the system learns by ad-
justing the weights and other parameters to identify
such failures regarding the corrective actions. When
a similar fault happens again, the system will inform
about the most likely fault type and the related ac-
tions.
To visualize the cases, refer to Table 2, which
demonstrates the results where machine failures oc-
curred. A total of 17 lines report favorable conditions,
which makes sense once we have 14 true positives
(TP) and three false negatives (FN).
Table 2: Results obtained in the case study.
time
ID
did the
problem
happen?
did the
model
predict?
failure
intensity
failure
classifi-
cation
10 yes yes 28.89% light
12 yes yes 95.98% warning
14 yes yes 89.12% warning
15 yes yes 64.55% warning
16 yes yes 30.34% light
18 yes yes 30.93% light
20 yes yes 15.47% light
37 yes yes 34.23% light
54 yes no - -
56 yes no - -
57 yes no - -
66 yes yes 40.74% light
73 yes yes 41.25% light
110 yes yes 23.66% light
135 yes yes 19.00% light
136 yes yes 16.50% light
141 yes yes 27.08% light
We employed the same metrics defined in
(Arantes et al., 2021) as shown in Table 2 for eval-
uation of the results achieved by the machines’ mod-
els. Table 3 presents the confusion matrix with the re-
sults obtained in the experiments. These results show
the great precision of the method that, in this context,
was able to predict all the failures that occurred. The
recall was 82.4 %, precision 100%, accuracy 98.1%,
F1-score 90.3%, and the Area Under the Receiver Op-
erating Characteristic Curve (AUC) was 91.2%.
Table 3: Confusion matrix with the results.
Total population Cond. positive Cond. negative
Predicted positive [TP] 14 [FP] 0
Predicted negative [FN] 3 [TN] 141
The implementation of the 6C architecture not
only addressed specific challenges in the vegetable
Six-Layer Industrial Architecture Applied to Predictive Maintenance
129

oil industry but also showcased a model applicable
to other domains, providing valuable insights for the
adoption of intelligent practices across various sectors
of Industry 4.0.
This interactive and visual approach to data man-
agement not only streamlines the maintenance pro-
cess but also significantly contributes to the preven-
tion of unexpected downtimes and associated costs of
emergency repairs. This case study confirms the fea-
sibility and effectiveness of the 6C architecture in op-
timizing predictive maintenance in industrial environ-
ments. The implementation of this innovative archi-
tecture not only overcame challenges identified with
previous approaches but also demonstrated a signif-
icant improvement in the accuracy of fault detection
and prediction.
5 CONCLUSION
This article introduced an innovative AI architecture
for the industry, based on the 5C framework described
in (Lee et al., 2015), and advanced by adding a sixth
layer called Consciousness. A case study in the
vegetable oil production industry, which already im-
plemented an intelligent system for fault prediction,
served to evaluate the proposed 6C architecture. The
6C architecture facilitated interaction across all layers
of the process, promoting the exchange of discoveries
from the Consciousness layer and enabling compre-
hensive monitoring of the system’s lifecycle, as well
as continuous learning and evaluation. Applications
of AI in industry are vast and diverse, covering differ-
ent processes and sectors. Further validation in new
industrial scenarios is essential to reinforce the ver-
satility of the 6C architecture. While this study fo-
cused on predictive maintenance, the proposed archi-
tecture has the potential to be implemented in any AI
application in the industry, underscoring industrial AI
as a promising approach to overcoming operational
and maintenance challenges. The 6C architecture,
with its continuous iterations and ability to acquire
domain consciousness, promises to revolutionize in-
dustrial systems, offering a path to enhanced innova-
tion and efficiency.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank SENAI Institute for Innovation in
Embedded Systems for supporting the research.
REFERENCES
Arantes, J., Arantes, M., Fr
¨
ohlich, H. B., Siret, L., and
Bonnard, R. (2021). A novel unsupervised method
for anomaly detection in time series based on statisti-
cal features for industrial predictive maintenance. In-
ternational Journal of Data Science and Analytics,
12(4):383–404.
Calabrese, M., Cimmino, M., Fiume, F., Manfrin, M.,
Romeo, L., Ceccacci, S., Paolanti, M., Toscano, G.,
Ciandrini, G., Carrotta, A., Mengoni, M., Frontoni,
E., and Kapetis, D. (2020). Sophia: An event-based
iot and machine learning architecture for predictive
maintenance in industry 4.0. Information, 11(4).
Granlund, T., Kopponen, A., Stirbu, V., Myllyaho, L., and
Mikkonen, T. (2021). Mlops challenges in multi-
organization setup: Experiences from two real-world
cases. In 2021 IEEE/ACM 1st Workshop on AI Engi-
neering - Software Engineering for AI (WAIN), pages
82–88.
Guo, Z., Bao, T., Wu, W., Jin, C., and Lee, J. (2019).
Iai devops: A systematic framework for prognostic
model lifecycle management. In 2019 Prognostics
and System Health Management Conference (PHM-
Qingdao), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Lee, J., Bagheri, B., and Kao, H.-A. (2015). A cyber-
physical systems architecture for industry 4.0-based
manufacturing systems. Manufacturing Letters, 3:18–
23.
Lee, J., Davari, H., Singh, J., and Pandhare, V. (2018). In-
dustrial artificial intelligence for industry 4.0-based
manufacturing systems. Manufacturing Letters, 18.
Lee, J., Singh, J., Azamfar, M., and Keyi, S. (2020a). In-
dustrial ai:a systematic framework for ai in industrial
applications. Zhongguo Jixie Gongcheng/China Me-
chanical Engineering, 31:37–48.
Lee, J., Singh, J., Azamfar, M., and Pandhare, V. (2020b).
Industrial ai and predictive analytics for smart man-
ufacturing systems. In Smart Manufacturing, pages
213–244. Elsevier.
Liu, Z., Jin, C., Jin, W., Lee, J., Zhang, Z., Peng, C., and Xu,
G. (2018). Industrial ai enabled prognostics for high-
speed railway systems. In 2018 IEEE International
Conference on Prognostics and Health Management
(ICPHM), pages 1–8.
Ng, A. (2021). A chat with andrew on mlops: From
model-centric to data-centric ai. Available in:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=06-AZXmwHjo.
Peres, R. S., Jia, X., Lee, J., Sun, K., Colombo, A. W., and
Barata, J. (2020). Industrial artificial intelligence in
industry 4.0 - systematic review, challenges and out-
look. IEEE Access, 8:220121–220139.
Van Kranenburg, R. (2008). The Internet of Things: A
critique of ambient technology and the all-seeing net-
work of RFID. Institute of Network Cultures.
ICSOFT 2024 - 19th International Conference on Software Technologies
130
