
Multi-Method Approaches for Simulation Modelling of Warehouse
Processes
Pietro De Vito
a
, Umberto Battista
b
, Anna Bolognesi
c
and Stefano Sanfilippo
d
STAM S.r.l., Engineering Solutions, Via Lorenzo Pareto 8 Rosso A, Genoa, Italy
Keywords: Warehouse Optimization, Multi-Method Simulation, Agent-based Modelling, Discrete Event Simulation,
Resource Allocation, Intralogistics Optimization.
Abstract: Efficient warehouse management is essential for business-to-business (B2B) operations, ensuring timely
delivery, cost minimization, and operational efficiency. To meet these challenges, advanced modelling and
simulation techniques are increasingly adopted. This paper shows the application of multi-method simulation
approaches, specifically agent-based and discrete event simulation, applied to optimize warehouse processes
and resource allocation for a leading sport brand retailer in the B2B sector. By combining these approaches,
we aimed to capture the complexity of warehouse operations and identify opportunities for improvement. The
simulation model developed using AnyLogic software, integrated agent-based modelling to represent entities
such as packages, articles, orders, warehousemen, and trucks, along with discrete event simulation to model
key events like order arrival and truck departure. The developed model has been used to optimize the resource
allocation ensuring order fulfilment. Scenario analyses revealed varying resource requirements across
different demand scenarios, highlighting the challenges posed by increasing demanded volumes. The study
underscores the importance of strategic resource planning and proactive measures to address capacity
limitations and ensure warehouse efficiency in meeting future demand. Our findings contribute to informed
decision-making in warehouse management, guiding strategies for optimization and adaptation to evolving
market demands.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Context
In modern commerce, two primary transactional
models prevail: Business-to-Consumer (B2C) and
Business-to-Business (B2B), representing distinct
paradigms for goods and services exchange. B2C
transactions involve direct interactions with
individual consumers, focusing on personalized
experiences and brand loyalty. On the other hand,
B2B transactions occur within corporate ecosystems,
involving complex networks and multiple
stakeholders to meet supply chain needs. Efficient
warehouse management is crucial for B2B
operations, ensuring timely delivery, cost reduction,
and operational efficiency. To address these
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7353-2011
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5479-684X
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-2762-3703
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-0547-6222
challenges, businesses increasingly employ advanced
modelling and simulation techniques to optimize
warehouse processes.
This paper discusses the use of multi-method
simulation approaches, including agent-based and
discrete event simulation, for modelling and
optimizing B2B warehouse processes for a leading
sport brand retailer. Through a detailed case study, we
demonstrate the efficacy of simulation models in
analysing and optimizing key processes, such as order
fulfilment and inventory management, to improve
overall efficiency in serving B2B clientele.
The main objective of this study was to create a
simulation model to understand the warehouse's
capacity to manage predicted volumes and identify
opportunities for productivity enhancement and so to
provide strategic decision-making support for
De Vito, P., Battista, U., Bolognesi, A. and Sanfilippo, S.
Multi-Method Approaches for Simulation Modelling of Warehouse Processes.
DOI: 10.5220/0012771700003758
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH 2024), pages 305-312
ISBN: 978-989-758-708-5; ISSN: 2184-2841
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
305

resource allocation, workflow optimization, and
infrastructure investments in the warehouse
environment. The study conducted scenario analyses
to identify potential capacity constraints and
opportunities for process improvement, providing
actionable recommendations for mitigating risks and
enhancing resilience.
Ultimately, this study aimed to empower
stakeholders with the tools and information needed to
make informed decisions aligning with the
organization's strategic goals, while laying the
foundation for future-proofing the operation and
positioning for long-term success and growth.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Warehouse optimization is a topic of significant
interest in both academia and industry, with
numerous studies exploring various approaches to
enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of
warehouse operations. In this section, we review the
existing literature on simulation modelling in
warehouse optimization, with a particular focus on
multi-method approaches and their application in the
context of B2B operations. Simulation modelling has
emerged as a powerful tool for analysing, predicting,
and optimizing warehouse operations. By replicating
the behaviour of a real-world system within a model,
simulation enables researchers and practitioners to
experiment with different scenarios, test alternative
strategies, and evaluate the performance of various
configurations without disrupting actual operations.
In the context of warehouse optimization, simulation
models can highlight the intricate interactions
between different processes, resources, and
constraints.
Discrete Event Simulation (DES), System
Dynamics, and Agent-Based Modelling (ABM) are
three simulation methods commonly used in
warehouse-oriented environments. DES (Rana, D. S.,
2018, Gagliardi, J.-P., Renaud, J., & Ruiz, A. 2007,
Saderova, J., Rosova, A., Behunova, A., Behun, M.,
Sofranko, M., & Khouri, S. 2022) allows for the
modelling of discrete events, such as order entry,
order processing, transport, and delivery, providing
detailed insight into warehouse dynamics. System
Dynamics (Ramirez-Malule, D., Jaén-Posada, J. S., &
Villegas, J. G. 2021) analyses the interdependencies
and feedback loops within a warehouse system,
helping to understand its behaviour over time. Agent-
based (Maka, A., Cupek, R., & Wierzchanowski, M.
2011) modelling is a methodology that focuses on
modelling the behaviour of individual agents within a
warehouse. This enables the analysis of emergent
properties and the optimisation of warehouse
operations. These methodologies are essential tools
for improving efficiency, optimising resource
utilisation, and addressing warehouse management
challenges.
DES has several advantages in warehouse-
oriented environments. Firstly, it helps to analyse
system behaviour, identify bottlenecks, evaluate
trade-offs, and optimize processes in logistics and
supply chain management. Moreover, DES enables
decision-makers to test multiple tactics in a virtual
system without disrupting operations, thereby
optimizing inventory management, transportation
routing, and warehouse operations. However, while
DES models can be useful, they often rely on
simplified assumptions that may not fully capture the
dynamics of real-world systems.
In contrast, System Dynamics offers valuable
insights into complex warehouse systems by
capturing the interactions between various actors and
processes. Decision-makers can use System
Dynamics to assess the impact of different variables
on system performance and optimize procedures for
increased efficiency. However, accurately modelling
all variables in System Dynamics models can be
challenging due to their complex interrelationships,
which poses a limitation.
ABM provides a more realistic representation of
how agents interact within the warehouse
environment and adapt dynamically to changing
conditions. This approach assists decision-makers in
comprehending emergent behaviours, optimising
resource allocation, and enhancing overall efficiency
in warehouse operations. However, creating precise
agent-based models can be a challenging and time-
consuming task due to the requirement for detailed
data and behavioural rules for individual agents.
2.1 Multi-Method Approaches in
Simulation Modelling
Multi-method simulation approaches have gained
popularity for their ability to provide a
comprehensive understanding of complex systems.
While traditional simulation methods like DES focus
on system-level behaviours and resource utilization
(Law and Kelton, 2018; Rossetti et al., 2019), they
may overlook nuanced interactions among individual
entities within warehouses. To overcome this
limitation, researchers integrate multiple simulation
methods, such as ABM and DES, to better understand
warehouse dynamics (Macal and North, 2010). ABM
models individual entities and their interactions,
SIMULTECH 2024 - 14th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
306

allowing for detailed analysis of decision-making
processes (Bonabeau, 2002), while DES excels in
representing system-level processes and events,
facilitating the analysis of resource utilization
(National Aeronautics and Space Administration,
1995). Integrating ABM and DES enables researchers
to capture the complexity of warehouse operations,
providing insights into system-level behaviours and
individual agent interactions (Klügl and Bazzan,
2019). Studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of
multi-method simulation approaches in optimizing
warehouse processes (Heath et al., 2012).
In warehouse optimization, traditional simulation
approaches like DES are widely used for modelling
system-level behaviours (Law and Kelton, 2018).
However, in complex warehouse systems, DES alone
may not provide a complete understanding of
dynamics due to pivotal interactions between
individual entities (Rossetti et al., 2019; Meredith et
al. 2023). To address this limitation, researchers
integrate multiple simulation methods, such as ABM
and DES, enhancing modelling capabilities. ABM
focuses on modelling individual entities and their
interactions within a system, allowing for a granular
analysis of the system's complexity. This integration
enables researchers to capture both macroscopic
system-level behaviours and microscopic agent-level
interactions, providing a comprehensive
understanding of complex warehouse systems.
Several studies have demonstrated the effectiveness
of multi-method simulation approaches in warehouse
optimization, highlighting the importance of
considering both macroscopic and microscopic
factors for achieving operational efficiency (Macal
and North, 2010, Hafezalkotob et al., 2016).
2.2 Challenges and Opportunities
Multi-method simulation approaches offer promise in
addressing the complexities of warehouse
optimization, yet they present challenges and
opportunities that require careful consideration.
Integrating ABM and DES introduces complexity,
requiring meticulous attention to model assumptions,
data capture, and computational resources. Scaling
the model amplifies these challenges in development
and implementation. Parameter estimation in multi-
method simulations demands sophisticated
techniques, necessitating a deep understanding of
system dynamics and iterative refinement for
accuracy.
Validation of multi-method simulation models is
inherently complex due to the stochastic nature of
warehouse operations and the interplay between
macroscopic and microscopic dynamics. Extensive
validation against empirical data is essential to ensure
accurate representation and reliable results, often
involving comparisons with operational metrics and
sensitivity analyses.
Despite challenges, multi-method simulation
offers significant opportunities for advancing
warehouse optimization by providing a
comprehensive understanding of B2B operations.
This holistic perspective uncovers inefficiencies,
identifies optimization opportunities, and evaluates
strategic interventions. Multi-method simulation
facilitates scenario analysis and decision support,
enabling stakeholders to explore alternative
strategies, assess outcomes, and make informed
decisions.
In conclusion, while multi-method simulation
presents challenges in model complexity, parameter
estimation, and validation, its benefits in capturing
the intricacies of B2B warehouse operations justify
further research and exploration. Leveraging the
strengths of agent-based and discrete event
simulation, multi-method approaches offer a
powerful toolset for optimizing warehouse operations
and enhancing efficiency in B2B supply chains.
3 SIMULATION MODEL
DEVELOPMENT
Figure 1: Warehouse environment.
The aim of developing the model was to simulate the
flow of items through packaging, storage, picking,
and delivery to trucks after preparation by warehouse
staff. The process depends on the arrival of customer
orders and the departure of trucks. When a customer
order is received, the storekeeper prepares it for
delivery by lorry. The preparation of orders involves
organizing items into package, each containing a
specific set of articles. The shop aims to maintain a
stock of the majority of articles in the warehouse to
Multi-Method Approaches for Simulation Modelling of Warehouse Processes
307

ensure prompt fulfilment of most orders. All of these
aspects must be managed accurately within the
operation to ensure effective matching of demand and
supply. The development has been done in the
AnyLogic commercial software.
3.1 Overview of Anylogic
AnyLogic is a versatile simulation software that
offers support for various modelling paradigms,
including agent-based (Agent-Based Modelling),
discrete event (Event-Based ), and system dynamics.
Its graphical interface and Java-based modelling
language provide flexibility and ease of use, making
it well-suited for complex simulation projects such as
warehouse optimization. AnyLogic was chosen for its
capabilities, which allowed us to craft a thorough
multi-method simulation model proficient in
capturing the complexities of both individual entities
within the warehouse environment and overall
warehouse operations. Our approach utilizes ABM to
represent various elements within the warehouse
environment, including packages, articles, orders,
warehousemen involved in different processes, and
trucks. Additionally, we incorporate discrete event
simulation to model events that occur at different
moments during the simulation, such as the arrival of
orders and the departure of trucks.
3.2 Agent-Based Modelling
ABM forms the cornerstone of our simulation
approach, allowing us to represent individual entities
(agents) within the warehouse environment with high
granularity. Each agent is endowed with specific
properties, behaviours, and decision-making
capabilities to accurately simulate their interactions
within the warehouse ecosystem. The implemented
agents include:
Packages and Articles, packages represent the
containers in which articles are stored and
transported within the warehouse. Each package
agent is characterized by properties such as size,
weight, destination, and contents. Articles, on the
other hand, represent the individual items
stocked in the warehouse and objects of the
orders.
Orders represent the requests placed by
customers for specific articles. Each order agent
contains information such as customer details,
order quantity, truck and the related warehouse
bay. Orders may consist of multiple articles and
packages, depending on the customer's
requirements.
Trucks represent the vehicles used for
transporting goods to and from the warehouse.
Each truck agent is characterized by properties
such as capacity and destination. Trucks are
responsible for transporting packages and orders
between the warehouse and customer locations.
Warehousemen represent the workers
responsible for performing various tasks within
the warehouse, such as inbound receiving,
stocking shelves, picking items for orders, and
loading/unloading trucks. Each warehouseman
agent is associated with properties related to their
productivity capacity, such as articles processed
per hour. By modelling warehousemen with
different productivity capacities, we can
accurately simulate the impact of workforce
variability on overall warehouse performance.
Figure 2: Agents of the model.
3.3 Event-Based Modelling
In integration and support to the ABM approach, our
simulation model incorporates event-based
simulation to capture key events that occur at
different moment of the simulation. ABM enables the
simulation of the behaviours and interactions of
individual entities within the warehouse environment.
Event-based simulation, in contrast, allows the
modelling of the occurrence of specific events and the
subsequent impact on workflow dynamics.
Order Arrival: one of the key events we model in
our simulation is the arrival of orders from
customers. Orders arrive at the warehouse
according to predefined arrival patterns or
distribution functions. The timing, quantity, and
characteristics of incoming orders influence
warehouse workload, resource utilization, and
order fulfilment processes. By simulating order
arrival events, we can replicate the dynamic
nature of customer demand and evaluate the
warehouse's ability to meet service level
agreements and customer expectations.
Truck Departure: another key event we capture
in our simulation is the departure of trucks
transporting goods to delivery destinations. Once
orders are picked and packaged, trucks are
dispatched from the warehouse to deliver the
goods to customer locations. By simulating truck
SIMULTECH 2024 - 14th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
308

departure events, we can assess the efficiency of
delivery operations, optimize routing decisions,
and minimize transportation costs. Additionally,
truck departure events may trigger subsequent
events within the simulation, such as updating
inventory levels and initiating replenishment
processes.
Therefore, by integrating event-based simulation
with agent-based modelling, we create a dynamic
simulation environment that accurately reflects the
real-world dynamics of warehouse operations. Events
drive changes in system state, trigger agent
behaviours, and influence decision-making
processes, resulting in emergent behaviours and
system-wide effects. This integrated approach allows
us to capture the complexity and uncertainty inherent
in warehouse operations and provides valuable
insights into system performance under various
conditions.
4 WAREHOUSE PROCESSES
SIMULATION
4.1 Warehouse Processes
The warehouse chain can be divided into 4 main
phases: inbound, stocking, picking, and outbound.
Inbound operations include receiving, sorting, and
storing incoming goods at a warehouse or distribution
centre. Stocking involves arranging and organizing
items within the warehouse for easy accessibility
during subsequent picking. Picking involves
retrieving individual items or specific orders from
warehouse shelves in preparation for shipment or
delivery. Outbound encompasses all operations
related to shipping the stocked items from the
warehouse to customers, stores, or other final
destinations. These processes are essential for
ensuring efficient inventory management and timely
delivery of goods.
Figure 3: Warehouse intralogistics processes.
This section provides an overview of the
simulation model developed to replicate the key
processes within the warehouse environment. The
model aims to replicate the real-world workflows and
interactions observed in the warehouses of the sport
brand retailer.
The inbound process begins with the arrival of
trucks carrying packages containing goods destined
for the warehouse. Upon arrival, packages are
unloaded, and goods with standard-sized packages
are directed to an intricate conveyor system for
distribution to the shelves. Warehousemen stationed
at this destination sector receive these packages and
proceed to stock them on the shelves, recording their
positions in the Warehouse Management System
(WMS). This process ensures accurate inventory
management and facilitates efficient retrieval during
order fulfilment.
In the stocking process, warehousemen retrieve
packages from the conveyor system and place them
on designated shelves according to product categories.
The WMS guides warehousemen to the appropriate
shelf locations, ensuring optimal storage organization
and minimizing retrieval times during picking
operations. Warehousemen record the stocking of
packages in the WMS, updating inventory levels and
ensuring real-time visibility of available stock.
The picking process starts when an order is
received on the WMS. The warehousemen in charge
of order processing go through the shelves to pick the
individual items needed to fulfil the order. In contrast
to traditional bulk picking, in which entire parcels are
dispatched, in this area, packages filled with a few
units of heterogeneous items are prepared (generally
the contents correspond to about 20 items). Then the
warehousemen systematically retrieve the articles
and place them in the new packages until the order is
completed.
Finally, in the outbound process, completed
orders are conveyed to the outbound area where
packages are collected and palletized for loading onto
trucks. Warehousemen ensure that packages are
correctly labelled, sealed, and prepared for shipment.
Once palletized, packages are loaded onto trucks for
transportation to customer destinations.
4.2 Integration of Processes
The simulation model integrates these warehouse
processes to replicate the dynamic flow of goods and
activities within the warehouse environment. We
adopted a high-level approach to modelling each
process for standard packages, encompassing
inbound, stocking, picking, and outbound operations.
To ensure accuracy, we created a 2D model based on
the warehouse plans and the structure of conveyors.
This enabled us to account for distances and the time
Multi-Method Approaches for Simulation Modelling of Warehouse Processes
309

required to move packages between different areas of
the warehouse.
In addition, we developed a detailed microscopic
model for the picking area to analyse operations in
relation to the number of warehousemen present. This
microscopic analysis was crucial for identifying
inefficiencies and understanding the impact of
workforce allocation on overall performance, a topic
that will be explored further in the Results chapter.
By simulating the intricate details of the picking
process, such as the movement of warehousemen, the
retrieval of individual items, and the organization of
packages, we were able to capture the complexities of
real-world operations and assess the effectiveness of
different staffing levels and strategies.
To implement the logic of the models, we utilized
flowcharts made available by the logical blocks
present in AnyLogic libraries. These blocks were
customized to incorporate functions capable of
replicating the algorithms and logic adopted by the
WMS.
Through the integration of these processes, our
simulation model provides valuable insights into
system performance, resource utilization, and
operational efficiency, facilitating informed decision-
making and strategic planning for warehouse
management. The comprehensive nature of our model
allows to explore various scenarios, experiment with
different strategies, and identify opportunities for
improvement. By leveraging simulation technology,
businesses can optimize warehouse operations,
improve customer service, and adapt to changing
market demands with confidence and agility.
4.3 Model Validation
The validation phase played a crucial phase of our
work and involved a thorough comparison of
simulation results with real-world and well-known
situations occurred in the past. The validation
procedure involved gathering real-world data and
outlining reference scenarios that encompassed
various operational conditions and challenges
typically encountered. The available real-world data
was leveraged to input the parameters into the model
to generate output data comparable with the reference
scenarios. This process was iterative in order to
recalibrate the model and minimize the error degree.
These scenarios provided valuable insights into
the complexities of warehouse operations, allowing to
validate the performance of the simulation model
under various conditions.
We specifically focused on historical data
representing both off-peak and peak conditions in the
sport brand retailer's warehouse, respectively the
scenarios n. 0a and 0b reported in Table 1. Executing
the simulation involved closely mimicking real-world
parameters and configurations. This included
replicating staffing levels, equipment capacities,
order volumes, and workflow processes to accurately
simulate the operational dynamics.
Comparing simulation results to real-world
observations involved a meticulous analysis of key
performance metrics such as throughput, order
fulfilment rates, inventory levels, and resource
utilization.
Through this validation process, we were able to
estimate the magnitude of model error and identify
specific components or processes within the model
that contributed to inaccuracies. This iterative
refinement process allowed to adjust parameters,
refine algorithms, and incorporate additional details
or complexities into the model to minimize
discrepancies and improve alignment with real-world
observations. The validation campaign performed on
the latest version of the model returned the results
shown in the table below. The model's error shows
high reliability overall. On the peak scenario in
particular, the model has a lower average error (2,8%)
than the off-peak scenario (5,6 %). With the use case,
it was determined that the error obtained is still
acceptable. In fact, there are several factors, external
and psychological, which the model does not take into
account and which play a non-negligible role on
resource efficiency. For example, when the workload
is not particularly high, people tend to work not to
their full capacity, which slows down operations. In
addition, there may be unexpected events that often
slow down the smooth running of warehouse
operations, which means that at such times there is a
surplus of resources to make up for lost time.
Table 1: Comparison of simulation results with real
implementation.
Scen.
n.
Volumes
[packages/
day]
Total number
of resources
(real)
Total Number
of Resources
(simulated)
Error
0a 5.828 28 26,5 5,6%
0b 7.576 35 34 2,8%
Therefore, the validation process provided
valuable insights into the accuracy and reliability of
our simulation model. By ensuring that simulation
results were comparable to real-world situations and
configurations encountered in the sport brand
retailer's warehouses, we enhanced the reliability of
the model and gained confidence in its predictive
capabilities.
SIMULTECH 2024 - 14th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
310
5 RESULTS
Following the rigorous validation process aligning
the simulation model with real-world warehouse
performances, the study delved into various scenario
analyses to assess the warehouse's capacity to handle
forecasted volumes over the coming years, as
outlined in Section 1. The primary focus was on
optimizing the allocation of resources to effectively
meet the increasing demand while maintaining
operational efficiency.
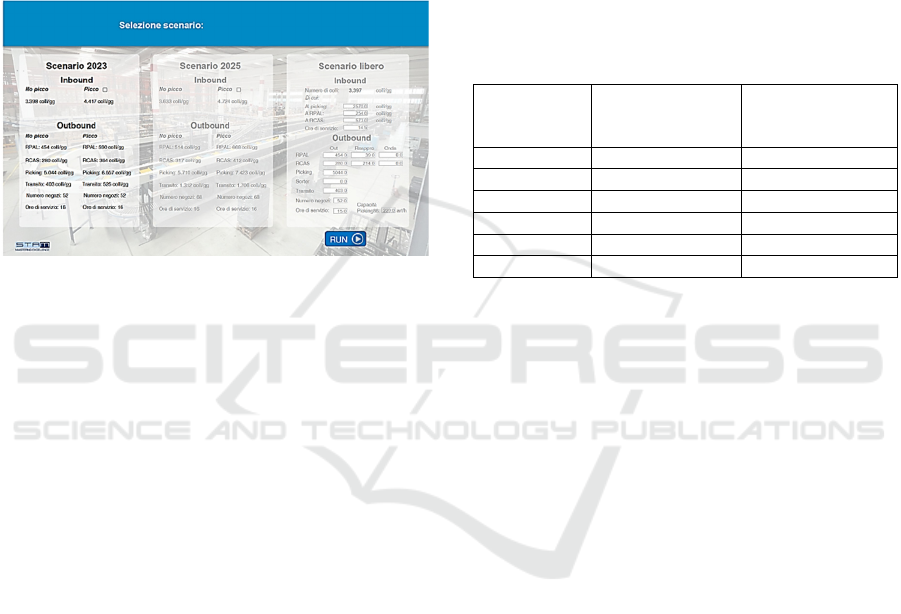
Figure 4: Model UI for scenario setting.
The simulation model was subjected to multiple
scenario tests based on different demand projections
and operational conditions. These scenarios were
categorized into optimistic and pessimistic scenarios,
each with variations in peak and off-peak demand
conditions. The aim was to evaluate how the
warehouse performed under various demand
scenarios and to identify resource requirements for
each scenario.
The simulation model analysed the number of
warehousemen and machines needed in different
sectors to handle the projected volumes effectively.
This optimization process involved fine-tuning
resource allocation to ensure efficient workflow
management while meeting customer demands. By
identifying the optimal number of resources required
in each scenario, the model provided valuable
insights for strategic resource planning and
allocation.
Results from the scenario analyses revealed
varying resource requirements across different
demand scenarios. In the optimistic off-peak scenario
(1a), which corresponds to the average demand for
the year, volumes increased by 6% compared to the
baseline (0a). The resource requirement in this case
has already increased significantly compared to the
current operating set-up (+66%).
In the peak optimistic scenario (1b), where
demand surged during peak periods, the model
indicated a notable increase in resource requirements,
particularly in manpower compared to 0b (+176%).
The challenges intensified in scenarios 2a and 2b,
the pessimistic off-peak and peak scenarios,
respectively. In these scenarios, characterised by
significantly higher demand than at present, the
simulation model predicted a significant increase in
resources. In particular, the most drastic increase was
in the number of warehousemen.
The Table 2 shows the key results on which the
assessments were made, i.e. for each scenario, the
volumes and the corresponding required resources are
indicated.
Table 2: Simulation campaign results.
Scenario n. Volumes
[packages/day]
Total Number of
Resources
(simulated)
0a 5.828 26.5
0b 7.576 34
1a 6.181 44
1b 11.434 94
2a 7.853 54
2b 15.495 128
Our study emphasizes the critical role of strategic
resource planning and allocation in warehouse
management. While our simulation model provided
valuable insights into resource requirements under
varying demand scenarios, it also highlighted the
imperative for proactive measures to overcome
capacity limitations and ensure the warehouse's
resilience in meeting future demand effectively.
Integrating simulation results with practical
considerations and strategic decision-making enables
the sport retailer to devise robust strategies for
optimizing warehouse operations and navigating
evolving market demands adeptly.
However, discussions with sport retailer
management revealed a crucial consideration
regarding the feasibility of implementing the
recommended resources. The projected volumes
could potentially strain the warehouse, particularly in
the picking process, due to space constraints and
congestion issues. The warehouse's physical
limitations, including limited space and
infrastructure, pose challenges to scaling up resources
beyond a certain threshold.
In response, it is essential to explore additional
measures beyond resource allocation to mitigate
potential crises in warehouse operations. Strategies
such as layout optimization, process redesign,
automation implementation, and facility expansion
offer promising avenues to enhance the warehouse's
capacity to handle increasing volumes while
Multi-Method Approaches for Simulation Modelling of Warehouse Processes
311

sustaining operational efficiency. These proactive
measures are essential for ensuring the warehouse's
adaptability and competitiveness in an ever-evolving
business landscape.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Warehouse management is crucial for supply chain
operations, ensuring efficient goods movement and
order fulfilment. This study explores warehouse
optimization using advanced modelling and
simulation techniques, focusing on challenges faced
by B2B businesses. We aimed to develop a simulation
model to forecast warehouse capacity and provide
strategic insights to the sport brand retailer for
managing increasing demand. Integrating agent-
based and discrete event simulation methodologies
enabled us to capture both macroscopic and
microscopic aspects of warehouse operations.
Challenges encountered included model
development, estimation, and validation, particularly
in integrating simulation methods and parameter
estimation. Validation was rigorous but essential,
comparing simulation outputs with empirical data to
ensure accuracy. Scenario analyses identified
resource allocation strategies for different demand
scenarios, aiding strategic decision-making. Our
study highlights the significance of strategic decision-
making and proactive planning in B2B warehouse
management. Multi-method simulation approaches
offer promising opportunities for optimizing
operations and adapting to market demands.
Future work involves developing new models to
analyse the automatic systems that will be
implemented in the warehouses, enhancing the
capability to predict and optimize operations further.
This will enable businesses to stay ahead of evolving
market trends and maintain competitiveness in the
dynamic landscape of warehouse management.
REFERENCES
Law, A. M., & Kelton, W. D. (2018). Simulation Modeling
and Analysis. McGraw-Hill Education.
Rossetti, M. D., Hill, R. R., Johansson, B., Dunkin, A., &
Ingalls, R. G. (2019). Proceedings of the 2019 Winter
Simulation Conference. Winter Simulation Conference.
Macal, C. M., & North, M. J. (2010). Tutorial on agent-
based modelling and simulation. In Proceedings of the
2010 Winter Simulation Conference (pp. 2-15). IEEE.
Bonabeau, E. (2002). Agent-based modelling: Methods and
techniques for simulating human systems. Proceedings
of the National Academy of Sciences, 99 (suppl 3),
7280-7287.
Klügl, F., & Bazzan, A. L. C. (2019). Multiagent-based
simulation XIX. Springer.
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (1995),
Systems Engineering Handbook, URL: https://www.
nasa.gov/reference/systems-engineering-handbook/).
Heath, Brian & Ciarallo, Frank & Hill, Raymond. (2012).
An agent-based modelling approach to analyze the
impact of warehouse congestion on cost and
performance. The International Journal of Advanced
Manufacturing Technology. 67. 10.1007/s00170-012-
4505-5.
Meredith, E.; Papakostas, N. and Hargaden, V. (2023).
Impact of Inventory Management Policies on Supply
Chain Resilience at RiRiShun Logistics. In Proceedings
of the 13th International Conference on Simulation and
Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and
Applications - SIMULTECH; ISBN 978-989-758-668-
2; ISSN 2184-2841, SciTePress, pages 159-168. DOI:
10.5220/0012146800003546
Rana, D. S. (2018). Discrete event simulation for logistics
and supply chain management. International Journal of
Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET),
9(2), 974-985.
Gagliardi, J.-P., Renaud, J., & Ruiz, A. (2007). A
simulation model to improve warehouse operations.
*Proceedings - Winter Simulation Conference*, 2012-
2018. https://doi.org/10.1145/1351542.1351899
Saderova, J., Rosova, A., Behunova, A., Behun, M.,
Sofranko, M., & Khouri, S. (2022). Case study: the
simulation modelling of selected activity in a
warehouse operation. *Wireless Networks, 28*(1),
431-440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02574-6
Ramirez-Malule, D., Jaén-Posada, J. S., & Villegas, J. G.
(2021). A System Dynamics Model for Warehouse
Performance Measurement with Highly Seasonal
Demand and with Long and Short Life Products. In
Proceedings of the International Conference on
Industrial Engineering and Operations Management
(pp. 1-6).
Maka, A., Cupek, R., & Wierzchanowski, M. (2011).
Agent-based Modeling for Warehouse Logistics
Systems. In “2011 UkSim 13th International
Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation”
(pp. 151-155). Cambridge, UK. doi:
10.1109/UKSIM.2011.37.
Hafezalkotob, A., & Farahani, R. Z. (2016). An integrated
simulation-optimization framework for supply chain
network design under uncertainty. Computers &
Industrial Engineering, 100, 1-12.
SIMULTECH 2024 - 14th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
312
