
Research on the Application and Management of Shared Bikes in
Smart Cities
Weiqing Liu
EDP School of Intelligent Engineering, Hubei Enshi College, Enshi, Hubei, 45000, China
Keywords: Shared Bike Management, Smart Cities, Urban Air Quality, Sustainable Transportation.
Abstract: As a typical means of shared transportation, the application and management of shared bikes face some
challenges. Therefore, the application and management of shared bikes in smart cities have been studied
indepth in this paper. This study founds that an effective management system and policies are needed to ensure
the healthy development of the bike-sharing industry. In addition, the relationship between bike-sharing and
urban air quality. The use of a large number of motor vehicles has led to increasingly serious air pollution
problems, and shared bikes, as a low-carbon and environmentally friendly mode of transportation, can reduce
vehicle exhaust emissions and improve air quality. In summary, Shared cycling in the wisdom of city
application and management is facing some problems, but through the optimization measures, intelligent
control methods and air quality improvement strategy related research, can effectively solve these problems,
the government, Shared cycling enterprises and related departments of cooperation and regulation is a key
factor in the management of Shared bicycle therefore, Shared cycling managers and policy makers need to
pay attention to these research results, formulate corresponding policies and measures to promote the
sustainable development of Shared cycling industry.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid growth of the urban population and the
aggravation of traffic congestion problems, sharing
traffic and emerging transportation modes have
become one of the important means to reduce the
traffic pressure. The development of shared
transportation and emerging transportation modes in
smart cities is becoming a focus of research. As a low-
carbon, environmentally friendly and convenient way
of transportation, shared bikes have gradually
attracted people's attention. However, the chaos
caused by the excessive number of shared bikes or
mismanagement has brought considerable problems
to city managers. Therefore, it is necessary for the
application and management of shared bikes in smart
cities.
In recent years, many studies have deeply
explored the application and management of shared
bikes. By analyzing the use data of shared bikes,
Zhang et al. proposed some optimization measures,
such as reasonably adjusting the distribution of
vehicles and setting up parking spots, to reduce traffic
congestion and improve user experience (Lei et al
2017). Zhang discusses the intelligent control method
to realize the shared bikes in the smart city
environment class human beings (Wang et al 2018).
Burda Studying the strategy of implementing public
bike sharing in Dhaka City, Bangladesh (Zhang and
Zhou 2019). Shaheen et al. studied early operator
understanding and trends of public bike sharing in
North America (Burda and Hakim 2017). Sun studied
the relationship between shared bikes and urban air
quality by analyzing the use of shared bikes and urban
air quality data and proposed some strategies to
improve air quality, such as encouraging the use of
shared bikes instead of motor vehicles (Shaheen et al
2015). To sum up, sharing transportation and
emerging transportation modes are of great
significance in smart cities. As one of its
representatives, shared bikes have management
problems, but reasonable management and technical
means can give full play to their advantages and bring
convenience and environmental benefits to urban
transportation. Therefore, it is of great practical
significance to strengthen the research and
management of shared transportation and emerging
transportation modes.
This paper aims to make a comprehensive
analysis of the application and management of shared
234
Liu, W.
Research on the Application and Management of Shared Bikes in Smart Cities.
DOI: 10.5220/0012815600004547
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Data Science and Engineering (ICDSE 2024), pages 234-241
ISBN: 978-989-758-690-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

bikes in smart cities. This paper adopts the scientific
data collection method, collects a large number of
data, including user data, vehicle data and traffic data,
and uses the statistical principle to make a
comprehensive analysis and processing of the data.
Finally, this paper makes an in-depth analysis of the
cases of shared bike management in different cities
and different enterprises and summarizes the
problems and solutions existing in the management of
shared bikes. The results of this paper can provide
valuable reference and suggestions for bike-sharing
managers and policy makers, and promote the healthy
development of the bike-sharing industry.
2 METHODS AND DATA
2.1 Data Source
The data source of this article is the Washington, D.
C. Bike sharing system is a way of renting bikes, the
process of automatic membership, renting and
returning bikes through the network of kiosks
locations throughout the city. Using these systems,
people can rent a bike from one place and return it
elsewhere as needed. Currently, there are more than
500 bike-sharing programs worldwide. The data
generated by these systems make them attractive to
researchers by explicitly recording the duration of
travel, departure location, arrival location, and
elapsed time. Thus, bicycle-sharing systems serve as
sensor networks that can be used to study urban
mobility. Combine historical usage patterns with
weather data to predict bike rental demand in the
Capital Bike Sharing program in Washington, DC.
2.2 Application of Time Series Analysis
in Bike-Sharing Research
Time series analysis is an important statistical method
that can dig deep into patterns and trends over time
from data points. In the field of bike-sharing research,
time series analysis plays a key role, helping us to
fully understand the dynamic trends and patterns of
the use of shared bikes.
Through sophisticated time series analysis, this
paper can predict the amount of shared bikes used in
different periods (for example, different time periods
of the day, different days of the week, etc.). This
predictive ability is crucial to the effective
management and scheduling of bike-sharing
companies. It can help companies better plan vehicle
distributions and optimize scheduling algorithms to
meet user needs and improve operational efficiency.
Furthermore, time series analysis can also reveal
seasonal and cyclical changes in bike-sharing use.
These findings help companies better understand user
needs and develop targeted operational strategies.
Moreover, time series analysis can also detect
abnormal usage behavior, such as a sudden increase
in usage in a short period or a prolonged sustained
trough. These abnormalities may mean the
occurrence of certain special events, such as bad
weather, holidays, large events, etc. With this
information, companies can adjust their operational
strategies promptly to address possible challenges.
2.3 Selection and Suitability of the
ARIMA Model
ARIMA model was used for time series prediction.
The model is particularly suitable for non-stationary
time series data and enables efficient analysis of the
changes in shared bike usage over time. By studying
past data trends and patterns, the ARIMA model
predicts the use trend in the future and provides a
scientific basis for the effective management of
shared bikes.
To be more accurate, this study also involves the
analysis of autocorrelation and partial
autocorrelations. These analyses help to determine
the parameters in the ARIMA model, such as lag
order (lag) and differential order. By analyzing the
autocorrelation and partial autocorrelation of shared
bike use data, this paper can have a deeper
understanding of the change law of bike use over
time, to predict the future use trend more accurately.
3 TIME SERIES ANALYSIS OF
SHARED BIKE USAGE DATA
3.1 Analysis of Autocorrelation and
Bias Toward Autocorrelation
In this paper, SPSS 25 and ARIMA models were used
for time series analysis and prediction in hours. The
analysis of autocorrelation and partial autocorrelation
revealed sequences with significant and partial
autocorrelation, especially in a 1 to 6 h delay (Figure
1). This suggests that the past values of these
sequences have significant effects on the future
values and that this effect diminishes over time. This
analysis is important for understanding changes in
time series data and for predicting future trends.
Research on the Application and Management of Shared Bikes in Smart Cities
235
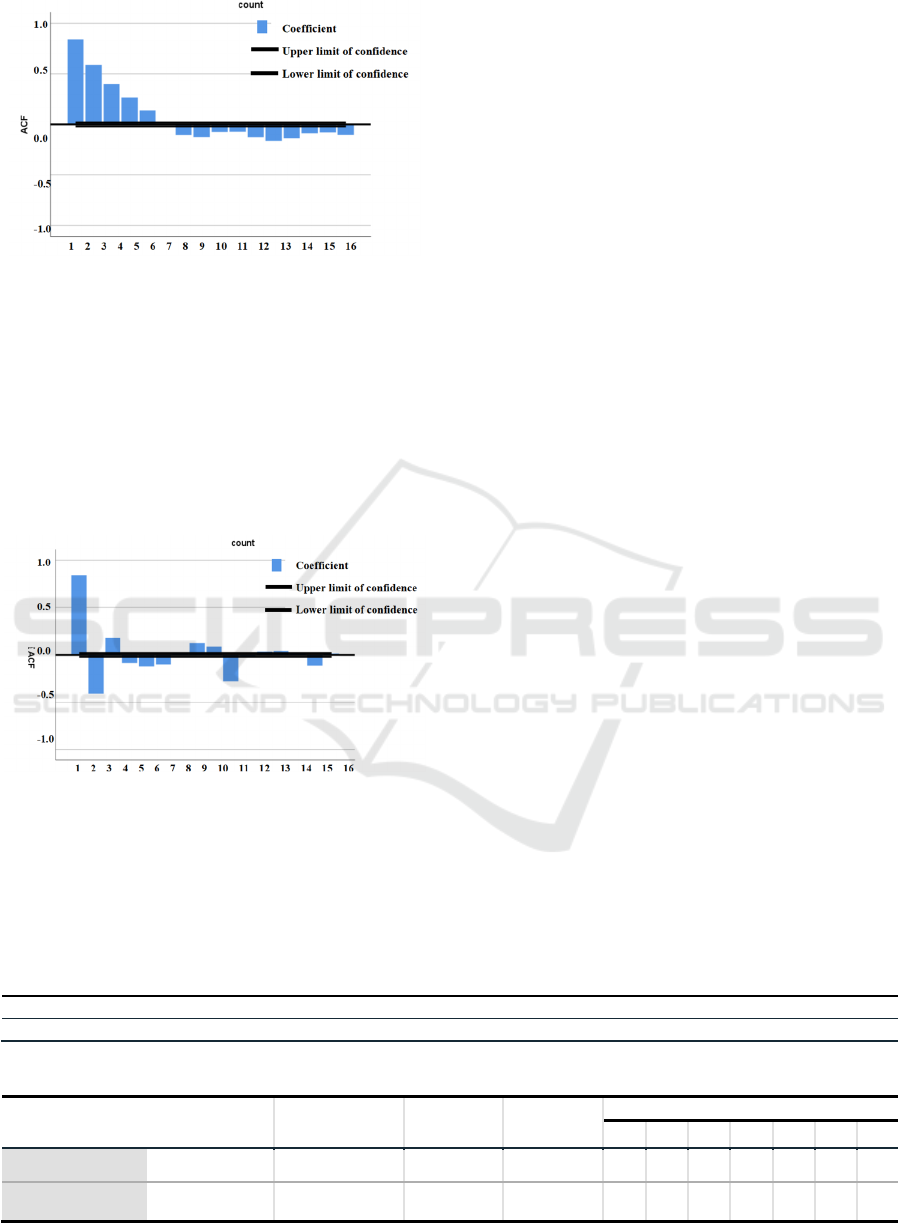
Figure 1: Time series analysis (Picture credit: Original).
Autocorrelation (ACF) and partial autocorrelation
(PACF) are commonly used in time series analysis. A
sequence autocorrelation diagram is a (linear)
diagram between a sequence and its lag. Figure 2
shows the hysteresis weights as a function of
hysteresis. How the correlation between individual
time steps decrease or disappear with increasing time
steps. Sequence autocorrelation graph is a method to
test the presence of sequences.
Figure 2: The hysteresis weights (Picture credit: Original).
The partial autocorrelation coefficient plot shows
the partial autocorrelation coefficient as a function of
hysteresis. The partial autocorrelation coefficient can
be seen as the remaining effect after removing some
of the effects that have been explained by the previous
lag value. Thus, the partial autocorrelation coefficient
plot can be used to determine the number of periods
p in the autoregressive AR model. The p-value of this
model is 1.
This indicates that there is a time series
association of shared bike usage, that is, there is a
mutual correlation between the previous period and
the latter period.
3.2 Non-Simulated Sequence and the
ARIMA Model
The instability of the time series means that the
statistical characteristics of the data such as the mean
and variance will change significantly at different
time points. Therefore, the overall characteristics of
the time series cannot be described by a fixed model,
but the model needs to be adjusted according to the
time change. The effective analytical method for non-
stationary sequences is the ARIMA (1,0,1) model.
This model captures the dynamic changes of the time
series by combining the differential and moving
average terms and can fit the non-stationary time
series data relatively well. Where "1" indicates the
order of the difference, "0" indicates the order of the
autoregressive part, and "1" indicates the order of the
moving average part. By tuning these parameters, the
ARIMA model can adapt to different time-series data
features (Table 1). The purpose of this study is to use
the ARIMA (1,0,1) model to conduct an in-depth
analysis of non-stationary time series data, to better
understand the internal laws and trends of time series
data and provide strong support for subsequent data
analysis and prediction.
As shown in Table 2, the parameter display,
autoregressive (AR), and moving average (MA)
terms of the ARIMA model all have significant
effects on the model, which reveals the complexity
and dynamics of the usage patterns of shared bikes.
Table 1: Model description.
types of models
model ID count model _1 ARIMA(1,0,1)(0,0,0)
Table 2: Model fit.
Fitting statistics average value standard error least value crest value
centile
5 10 25 50 75 90 95
Stable R square .764 . .764 .764 .764 .764 .764 .764 .764 .764 .764
R square .764 . .764 .764 .764 .764 .764 .764 .764 .764 .764
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
236

3.3 Model Size and Prediction Accuracy
After the statistics of the output degree of the model,
a series of indicators, such as stationary R square,
RMSE and MAPE, are obtained(Table 3). They
provide an important basis for us to evaluate the
accuracy and stability of the selected model in the
actual data prediction. From these statistics, this paper
can see the validity of the model in predicting the use
of shared bikes.
Specifically, the stationary R square value is
0.764, which is quite high, meaning that the model
can explain 76.4% of the variation in the real data.
This result fully demonstrates the powerful ability
and accuracy of the model in capturing and predicting
the usage of shared bikes, indicating that the model
can effectively apply the patterns and trends in
historical data to predict the future usage of shared
bikes.
In addition, other indicators such as RMSE (root
mean squared error) and MAPE (average absolute
percentage error) also further confirm the superiority
of the selected model in the output of actual data.
These statistics provide us with a more
comprehensive perspective, allowing us to more
accurately evaluate the predictive performance of the
model.
In conclusion, based on the output degree
statistics of the model, this paper can conclude that
the selected model is valid and reliable in predicting
the usage of shared bikes. This conclusion provides
strong support for decision-makers to enable them to
make rational decision making and planning based on
these prediction data.RMSE and MAPE values were
87.928 and 164.601, and these statistical measures
further verified the accuracy of the model predictions.
Figure 3 shows the fitting and measured results,
which show that the effect is better.
Figure 3: The fitting results (Picture credit: Original).
4 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
AND REGRESSION ANALYSIS
4.1 Descriptive Statistical Analysis
In this analysis, this paper used the correlation
coefficient to quantify the relationship between the
analyzed terms (Table 4). First, by calculating the
correlation coefficient, this paper assessed whether
these relationships were present. Then, by positive
and negative symbols, this paper determined the
direction of these relationships. Moreover, the
magnitude of the correlation coefficient also reflects
the strength of the linear relationship between the
variables.
The Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC)and the
Spearman correlation coefficient are two commonly
used correlation coefficients, both of which can be
used to describe the degree of correlation. The basic
criteria for these two coefficients are consistent.
Generally, when the absolute value of the correlation
coefficient is greater than 0.7, this paper can that a
strong correlation is greater than 0.4, and when the
absolute value is less than 0.2.
In the previous section, this paper performed a
descriptive statistical analysis of the sample data and
found that the data used had a certain degree of rigor
and rationality. Next, this paper will initially judge
the degree of correlation between the variables
through the correlation analysis.
Table 3: Model statistics.
model Number of
predictive
variables
Model fit degree statistics Young-Box Q (18) The
number of
outliers
Stable R
square
R square normalization BIC statistics DF conspicuousness
count-
model _1
0 .764 .764 8.956 2287.039 16 .000 0
Research on the Application and Management of Shared Bikes in Smart Cities
237
Table 4: Descriptive statistics.
N
least value crest value mean standard deviations
season 10886 1 4 2.51 1.116
holida
y
10886 0 1 .03 .167
workin
g
da
y
10886 0 1 .68 .466
weathe
r
10886 1 4 1.42 .634
temp 10886 .82 41.00 20.2309 7.79159
atemp 10886 .760 45.455 23.65508 8.474601
humidit
y
10886 0 100 61.89 19.245
windspee
d
10886 .0000 56.9969 12.799395 8.1645373
casual 10886 0 367 36.02 49.960
re
g
istere
d
10886 0 886 155.55 151.039
coun
t
10886 1 977 191.57 181.144
N
umber of valid cases
(
in a column
)
10886
Table 5: Relativity.
season holiday workingday weather temp atemp humidity windspeed casual registered count
season PCC 1 .029* -.008 .009 .259* .265* .191* -.147* .097* .164* .163*
holiday PCC .029* 1 -.250* -.007 .000 -.005 .002 .008 .044* -.021* -.005
workin
g
da
y
PCC -.008 -.250* 1 .034* .030* .025* -.011 .013 -.319* .119* .012
weather
PCC .009 -.007 .034* 1 -.055* -.055* .406* .007 -.136* -.109* -.129*
temp
PCC .259* .000 .030* -.055* 1 .985* -.065* -.018 .467* .319* .394*
atemp
PCC .265* -.005 .025* -.055* .985* 1 -.044* -.057* .462* .315* .390*
humidit
y
PCC .191* .002 -.011 .406* -.065* -.044* 1 -.319* -.348* -.265* -.317*
winds
p
ee
d
PCC -.147* .008 .013 .007 -.018 -.057* -.319* 1 .092* .091* .101*
casual
PCC .097* .044* -.319* -.136* .467* .462* -.348* .092* 1 .497* .690*
registered
PCC .164* -.021* .119* -.109* .319* .315* -.265* .091* .497* 1 .971*
count
PCC .163* -.005 .012 -.129* .394* .390* -.317* .101* .690* .971* 1
*. At the 0.01 level (two-tailed), the correlation was significant.
*. At the 0.05 level (two-tailed), the correlation was significant.
Table 6: Model summary.
model R R s
q
uare Ad
j
uste
d
R s
q
uare Error in the standard estimation
1 .743
a
.552 .551 121.325
a. Predictor variables: (constants), casual, holiday, windspeed, weather, season, workingday, attemp, humidity, temp
In this section, the Pearson coefficient and Spearman
coefficient were used for correlation. Among them,
the Pearson coefficient was used in this analysis.
After testing, the results are shown in the Table 5.
According to the descriptive statistical analysis,
the use of shared bikes was significantly associated
with factors such as season, holidays, weekdays,
weather and temperature. Specifically, the season has
a particularly significant impact on the shared usage
of bikes, which reflects users' concern about the
weather conditions in different seasons.
4.2 Regression Analysis
The R side, also known as the determination
coefficient, is an indicator of quantifying the
goodness of fit of the model (Sun et al 2018). Its
explanatory ability is crucial because it can show the
degree to which the model interprets the data. The
closer the R square value is to 1, the higher the
goodness of fit of the model is. In this case, the R
square value is 0.551, indicating that the model is a
good fit (Table 6).
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
238
Table 7: ANOVAa.
model
q
uadratic su
m
free de
g
ree mean s
q
uare F cons
p
icuousness
1 regression 197079673.678 9 21897741.520 1487.632 .000
b
residual 160093239.998 10876 14719.864
amount to 357172913.676 10885
a. Dependent variable: coun
t
b
. Predictor variables: (constants), casual, holiday, windspeed, weather, season, working day, attempt, humidity, temp
Table 8: Coefficient.
model
Unstandardized coefficients Standardization coefficient
t cons
p
icuousnessB Standard erro
r
Beta
1 (constant) 13.454 6.938
1.939
.053
season 17.453 1.113 .108 15.683 .000
holiday 23.985 7.230 .022 3.317 .001
workingday 95.916 2.829 .247 33.909 .000
weather -2.765 2.042 -.010 -1.354 .176
temp -1.622 .890 -.070 -1.821 .069
atemp 1.908 .819 .089 2.329 .020
humidity -.680 .077 -.072 -8.775 .000
windspeed .626 .156 .028 4.017 .000
casual 2.611 .031 .720 84.010 .000
a. Dependent variable: coun
t
As shown in Table 7, F (1487.632), significance
p(0.00) is less than 0.05, indicating that the
correlation coefficient of the regression equation is
not 0, indicating that the regression equation is
meaningful.
According to the regression coefficient in Table 8,
the significance of all the variables except weather
temp is less than 0.05, indicating that all the other
variables have a significant impact on the count.
Regression analysis revealed the extent of
different factors on the use of shared bikes. For
example, there are significant differences in the
effects of weekdays and holidays on usage, which
may be related to the travel habits and daily activity
patterns of urban residents.
4.3 Discussion and Management
Suggestions Combined with Data
Analysis
Data-driven management decision-making: The data
analysis results of this paper highlight the importance
of using data-driven decision-making methods when
implementing bike-sharing management in smart
cities. By analyzing the time series data of shared bike
use, city managers can more effectively predict and
respond to changes in the demand for shared bikes
(Sun et al 2019 & Li et al 2020).
Scheduling strategy for weather forecast:
regression analysis and correlation analysis reveal
key factors affecting the use of shared bikes, such as
weather, temperature, and urban activity. These
findings could guide city managers to develop
scheduling strategies for more weather forecasting,
such as adjusting the allocation of shared bikes under
specific weather conditions or holidays.
Standardized management system: Combined
with the prediction results of the ARIMA model, a
smart cities can develop a standardized bike-sharing
management system, which can adjust the allocation
of shared bikes in real time, optimize user experience,
and alleviate traffic congestion.
5 CHALLENGES AND
OPPORTUNITIES
Bike-sharing has played an important role in relieving
urban traffic pressure, but it also brings new
challenges. Due to the rapid growth of shared bikes,
some cities have experienced problems such as
excessive concentration and parking in disorder,
affecting the urban landscape and traffic order.
In addition, the peak use period of bike-sharing
often coincides with the commuting rush hour in the
city, which strengthens the traffic congestion in the
city to some extent.
In the context of smart cities, shared bikes
provide an environmentally friendly and fast way to
Research on the Application and Management of Shared Bikes in Smart Cities
239

make short trips, which helps to reduce urban carbon
emissions and improve residents' travel efficiency
(Zhang et al 2020).
The popularity of bike-sharing also provides
valuable data sources for data collection and analysis
in cities, helping city managers to better understand
urban traffic patterns and residents' travel needs.
In the future, the bike-sharing industry may be
further developed through technological innovation,
such as the use of more advanced positioning and
navigation technologies, to improve the utilization
rate and management efficiency of the bikes (Zhang
and Qi 2018).
With the development of Internet of Things
technology, shared bikes can be more customized,
such as real-time data analysis to automatically adjust
the allocation of bikes to better meet user needs.
To better manage and develop bike-sharing, city
managers need to develop reasonable strategies and
policies, such as optimizing the urban traffic layout,
providing more special bicycle lanes, and
establishing reasonable charging and weak
mechanisms.
At the same time, the government and enterprises
should strengthen cooperation to jointly promote the
sustainable development of shared bikes and provide
more convenient, efficient, and environmentally
friendly travel options to urban residents.
6 CONCLUSION
This paper studies the challenges and opportunities of
bike-sharing management through data analysis, and
puts forward corresponding management
suggestions. As a convenient and environmentally
friendly means of transportation, shared bike has
developed rapidly in cities in recent years. However,
with the increasing number of shared bikes, a series
of management problems have also emerged. This
paper first analyzes the imbalance between supply
and demand faced by shared bikes. Due to the uneven
distribution of shared bikes, there may be a surplus in
some areas, while others may have insufficient bikes.
In addition, shared bikes are also prone to excessive
aggregation of bikes, making it difficult for users to
find available bikes. To address these problems, this
paper proposes a data-driven management decision
strategy. Through the data analysis of user behavior
and demand, the demand change of shared bikes can
be predicted, and the allocation of vehicles can be
adjusted in advance to achieve the goal of supply and
demand balance. Secondly, this paper also studies the
impact of the weather on the use of shared bikes.
Weather is one of the most important factors for
people to choose their travel tools. For example, in
bad weather, people prefer to use public transport or
taxis rather than ride shared bikes. Therefore, this
paper believes that weather factors need to be taken
into account when formulating scheduling strategies
to better allocate shared bikes and improve their
utilization rate and management efficiency.
Finally, this paper puts forward some suggestions
for the management of shared bikes. First of all, a
standardized bike-sharing management system
should be established. Through unified management
and scheduling, the balanced distribution of bikes can
be realized and the user experience can be optimized.
Secondly, the government can formulate
corresponding strategies and policies to support the
development of shared bikes, such as optimizing the
transportation layout, establishing special bicycle
lanes, and formulating charging and weak
mechanisms. For future studies, this paper suggests
that the sustainability of shared bike management can
be further explored. For example, how to achieve a
balanced allocation of shared bikes, improve
utilization and management efficiency, and how to
optimize the user experience. In addition, the
coordinated development of shared bikes and other
vehicles, and the impact of shared bikes on the urban
environment and traffic conditions can also be
studied. The significance of these studies is to provide
a scientific basis for the management of shared bikes
and promote the intelligent and sustainable
development of urban traffic.
In conclusion, this paper studies the challenges
and opportunities of bike-sharing management.
Further research can provide more profound
theoretical and practical guidance for the
management of bike-sharing, and promote the
sustainable development of the bike-sharing industry.
Through continuous exploration and innovation,
bike-sharing can truly become an important part of
urban transportation and provide residents with more
convenient, efficient, and environmentally friendly
travel options.
REFERENCES
Z. Lei, T. Liu, L. Yang, et al. Urban traffic research based
on shared bicycle data. Urban Transportation, 14(2),
123-132, (2017).
H. Wang, T. Xu, X. Jia, & W. Li. Shared bicycle
management in a smart city: A case study of
Hangzhou, China. Transportation Research Part C:
Emerging Technologies, 90, 58-71,. (2018).
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
240

Y. Zhang & J. Zhou. Intelligent control of shared bike in
smart city environment. Communications in Computer
and Information Science, 1048, 287-296,. 2019.
J. M. Burda & S. Hakim. Shared bikes and the city:
Strategies for implementing public bike-sharing in a
city of Dhaka. IATSS Research, 41(2), 102-109,. 2017.
S. Shaheen, E. Martin, N. Chan, A. Cohen, & J. M.
Pogodzinski.. Public bikesharing in North America:
early operator understanding and emerging trends.
Transportation Research Record: Journal of the
Transportation Research Board, 2534(1), 78-87, 2015.
L. Sun, Y. Zhang, X. Wang, et al.. Research on the
relationship between shared bicycles and urban air
quality. Transportation and Transportation Research,
17(4), 65-71, (2018).
L. Sun, Y. Chen, C. Liu, & P. Yang.. Optimizing docking
station allocation in bike-sharing systems. IEEE
Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,
20(10), 3950-3961, (2019).
M. Li, K. Chen, T. Wang, et al. Research on the layout
model of shared bicycle parking areas. Transportation
Planning and Management, 39(5), 94-100,(2020). .
J. Zhang, Z. Gui, S. Wang, & Y. Xu.The Application of
Shared Bicycles in Smart Cities. In International
Conference on Data Mining and Big Data (pp. 776-
783). Springer, Singapore. (2020).
Y. Zhang & S. Qi. A Research on Management of Shared
Bike in Smart City Based on Internet of Things. In
2018 13th International Conference on Computer
Science & Education (ICCSE) (pp. 897-902).
IEEE.(2018).
Research on the Application and Management of Shared Bikes in Smart Cities
241
