
The Contradiction of Social Media at Stage: Study on the Use of
Social Media in Hong Kong
Peiyang Ding
School of Science and Technology, Hong Kong Metropolitan University, 518031 Hong Kong, China
Keywords: Information Cocoon, Statistics, Big Data.
Abstract: In the process of the public's use of social media, social media will use internal algorithms to guide and record
the masses to obtain their inner preference content, to make "personalized" recommendations. In addition, the
information disseminated through social media in the new century has strong timeliness and good
dissemination. However, at the same time, the particularity of the use of social media is limited by the
relatively short period, and it has not been possible to form regulations and countermeasures that can be widely
used and have strong binding force. Given the above descriptions, this paper starts from the contradictions
existing in social media, through the analysis of a wide range of public data, to understand the group trend
and provide ideas for the questionnaire survey, and then through the collection of a variety of questionnaire
data research methods, the use of descriptive statistics and the calculation of scores for special topics to make
the scores and the proportion of respondents and other factors complex, and then according to the final results
of statistics and classification, and finally to obtain that social media has different advantages and
disadvantages in different use environments, and has a certain warning effect on individuals. This research is
helpful for users to improve their abilities.
1 INTRODUCTION
As society grows, people have more social media
options to choose from. In recent years, people have
become more easily able to access information
through social media, and in-depth research has been
conducted on how social media can help people
optimize their lifestyles (Cao 2011). A subset of
adolescents believe that social media broadens their
horizons and gives them access to resources and
information about different cultures (Wang 2023).
Another segment believes that social media promotes
mutual understanding among students in terms of
acculturation, and they are all willing to use social
media to make friends. In this environment, the
contradictions between several groups around social
media are gradually emerging. The main
contradiction and motivation is that the function of
social media is to a certain extent related to the means
of communication and communication between
individuals, attracting people to spend more time.
However, when people are immersed in social media
and have similar social purposes, their attention to
real social storage will be diverted, and the
contradictions between the two will seriously affect
the development of the individual (Gong and Fu
2020). Social media is diverse, and it is easy to access
information in many ways, such as entertainment,
communication, shopping, eating, etc., providing a
variety of choices and enriching life (Li and Xie
2020). However social media tends to be
homogeneous in terms of functionality, and
developers are failing to deliver effective modern
features. In this regard, research uses data to help
media weaken the contradiction between diversity
and uniformity, and help build an advantage to stand
out from the crowd of social media.
From ancient times to the present, the timeliness
of information has been widely valued (Xiao 2023).
Social media is a leader in information dissemination,
through which the public can obtain first-hand
information, which is convenient for timely response
and processing (Shahbaznezhad et al 2021).
However, the contradiction between the spread of
false information can confuse the public, and in
severe cases, it will have an impact on the facts under
objective conditions, and the contradiction between
the two can be assisted by the study of data to
formulate the norms for the use of social media.
When people use social media, they will
subconsciously obtain their inner preference content,
58
Ding, P.
The Contradiction of Social Media at Stage: Study on the Use of Social Media in Hong Kong.
DOI: 10.5220/0012820900004547
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Data Science and Engineering (ICDSE 2024), pages 58-63
ISBN: 978-989-758-690-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
and the vast majority of social media will choose to
use internal algorithms to record content to optimize
the user's push content, which is a manifestation of
personalization. Under the influence of individuation,
there is a contradiction between the growth of the
individual and the establishment of an information
cocoon.
This paper constructs a new type of questionnaire
to collect people's daily attitudes and related opinions
on the use of social media, uses the scoring
mechanism to study multiple respondents, judges the
practicality of social media according to the theory,
deeply analyzes the psychological activities and
states of the respondents, and discusses and
researches them.
2 OVERVIEW
The information cocoon is a theoretical hypothesis for
the network information age put forward by the
American scholar Keith Sunstein (Keith 2008).
Network information brings more information and
choices while allowing people to selectively obtain
information, and only under the guidance can some
information be included in the scope of the collection,
people who obtain the same information are stuck in
a circle, and different circles are isolated from each
other or even opposed, so that people's lives are
shackled in a "cocoon" (Zhu and Li 2021).
Under the influence of the information cocoon,
individuals and groups have a tendency to be
polarized, and they will choose and obtain
information that individuals are relatively more
interested in in the way of a large number of
existences, and let this kind of information exist in a
large number of individual lives. This will solidify
one's way of thinking, resulting in a strong way of
acting exclusively and paranoidly. At the same time,
individuals interfere with public opinion or
irrationally attack zero individuals who do not agree
with each other. When there is a lack of sharing and
discussion of key information, one's sensitivity to
important information from the outside world
decreases, reducing the stickiness between oneself
and society, and lacking the understanding of social
diversity, which has an obstructive effect on the
improvement of one's level and disconnects with the
normal way of social operation.
The increased effectiveness of information and
the ease of information exchange makes social media
the choice of most individuals. At the same time,
changing the way of communication across
geographical restrictions and broadening the channels
for the masses to obtain information can enable
individuals to better understand the world and
improve the knowledge level of the masses (Esteban
2019). At the same time, the way of receiving
information according to the senses is fixed, and there
is no higher communication outcome while having a
way to obtain more information, the use of social
media will give up the action information and attitude
carried by the other party during offline
communication, and simple text descriptions online
need more descriptions to express the inner meaning
of words, which often has lower efficiency than
offline communication methods.
Under the influence of personalization,
individuals can easily obtain the information they
want, avoid missing relevant information, increase
user loyalty, improve the competitiveness of the
media, and generate good word-of-mouth marketing
(Lv and Yang 2021). The acquisition of long-term
personalized information will solidify the thinking
mode, easy to produce a strong exclusive, and
paranoid personality and way of doing things, lack of
sharing and discussion of diverse information, reduce
the stickiness between oneself and society,
disconnect with the normal social operation mode,
produce social anxiety, and build an "information
cocoon".
2.1 Current Situation
Figure 1 shows that 92.0% of the respondents like the
function of image content, 61.33% like to read text-
related functions, and 57.33% and 57.78% are willing
to use horizontal video and vertical short video,
respectively. But when faced with the live streaming
feature, only 9.78% of people said they liked it.
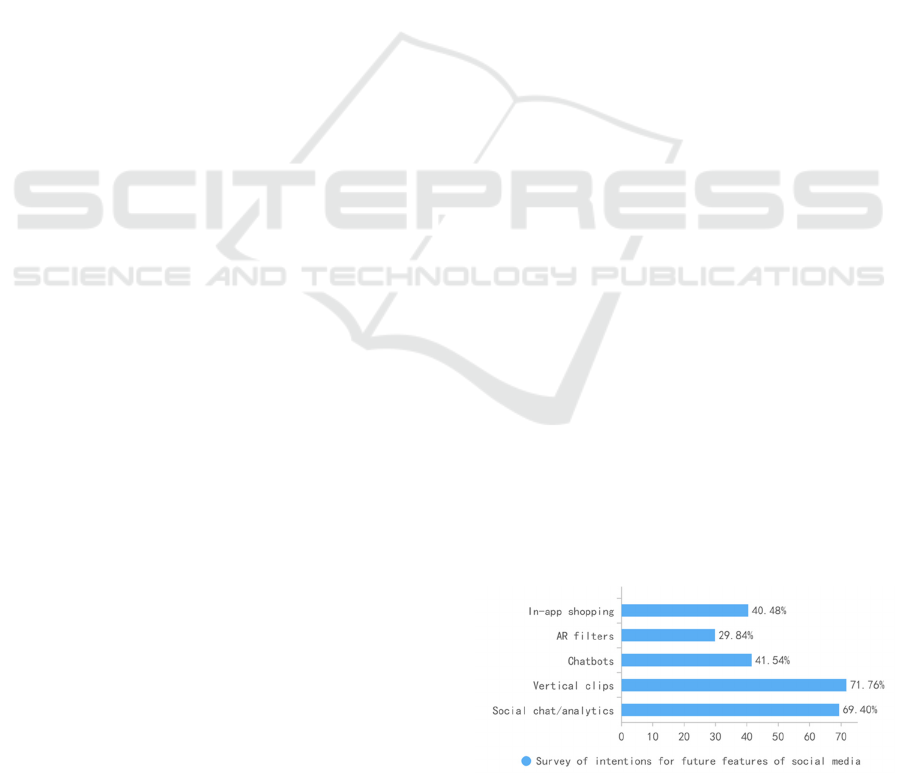
According to the survey on the intention to use social
media functions, 69.40% of people have the intention
to use social chat functions, 71.76% have the
intention to use the vertical short video function, and
41.54% and 40.48% have the intention to use the
chatbot and in-app shopping function, respectively.
For AR filters, 29.84% of people are willing to use
them.
Figure 1: Survey of intentions for future features of social
media (Picture credit: Original)
The Contradiction of Social Media at Stage: Study on the Use of Social Media in Hong Kong
59
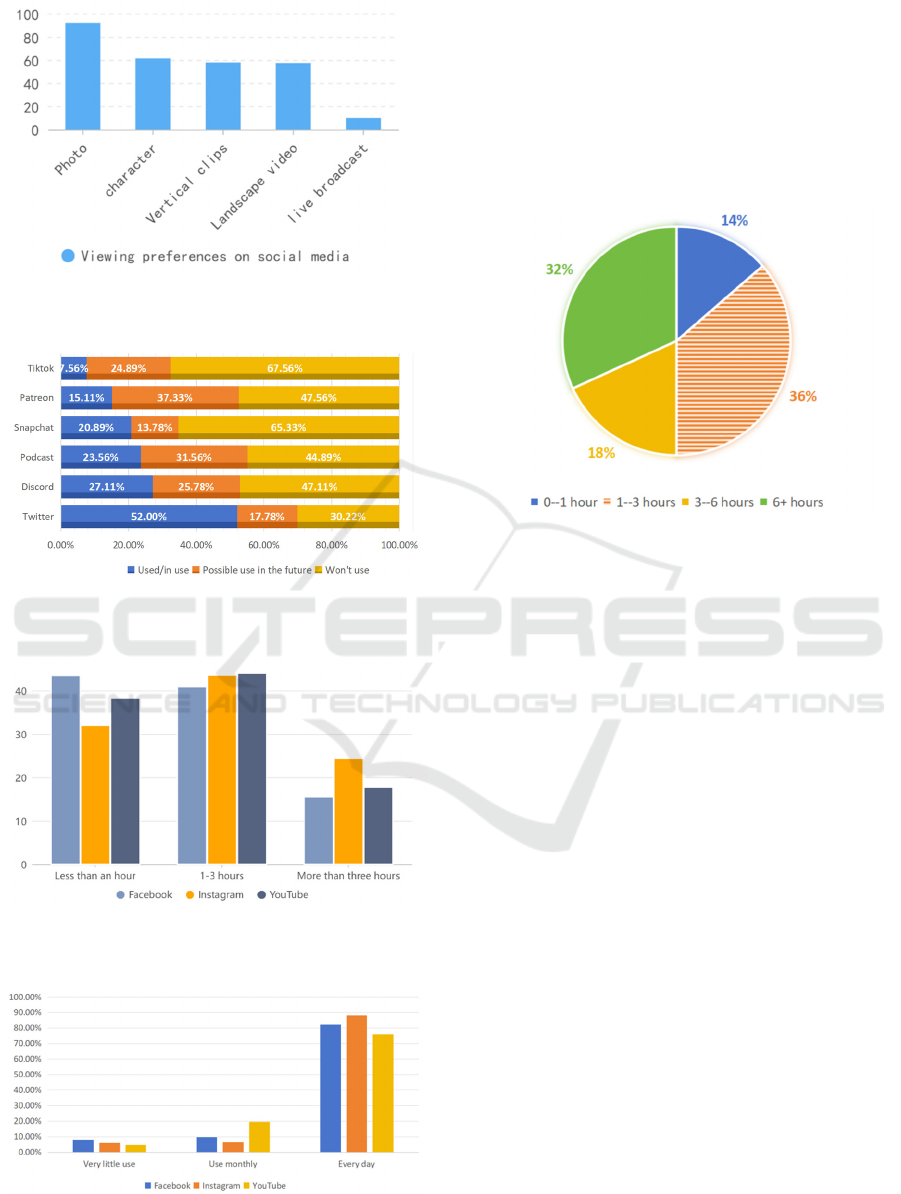
Figure 2: Viewing preferences on social media (Picture
credit: Original)
Figure 3: Whether or not social media has been used
(Picture credit: Original)
Figure 4: Average percentage of time spent on social media
(Photo/Picture credit: Original)
Figure 5: Percentage of users are intimate with social media
(Picture credit: Original)
Survey data on how much time is spent on social
media daily (Figure 2 - Figure 5). Whether it's
Facebook, Instagram, or YouTube, nearly 7 out of 10
people spend more than an hour a day on social
media. At the same time, more than 80 percent of
respondents use this social media daily. With a fixed
total time, more time spent on social media means
less time spent on other daily activities (Figure 6).
Figure 6: Average daily social media usage (Picture credit:
Original)
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This study looks at social media users under the
guidance of social media personalization. This
research is of great significance to open up a new
direction, whether it is to adjust the social style of
individuals in daily life or to be able to behave more
effectively in the face of special situations. This study
mainly focuses on the contradictions existing in social
media and uses literature analysis to search and read
relevant materials and literature, mainly through
questionnaire surveys, supplemented by score
calculation. The advantage of this method is that it
can analyze the authenticity of the questionnaire
content and the validity of data collection, which is
conducive to the conduct of research. The ultimate
goal of this study is to provide a favorable basis for
the relevant regulations and countermeasures to be
specified by professional departments.
3.1 Questionnaires
This study designed several questionnaires to collect
data on users' perceptions of the impact of social
media on traditional social methods and the direction
of social media use, data on the frequency of users'
use of social media, data on social media information
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
60
acquisition tendency, and data on the judgment of the
authenticity of social media information acquisition,
personalized treatment, and information cocoon
perception. On this basis, the scores of individual
special topics are assigned, the questionnaire scores
are finally calculated, the characteristics of the
respondents are analyzed according to the theory, and
effective conclusions are finally drawn.
3.2 Analysis of Results
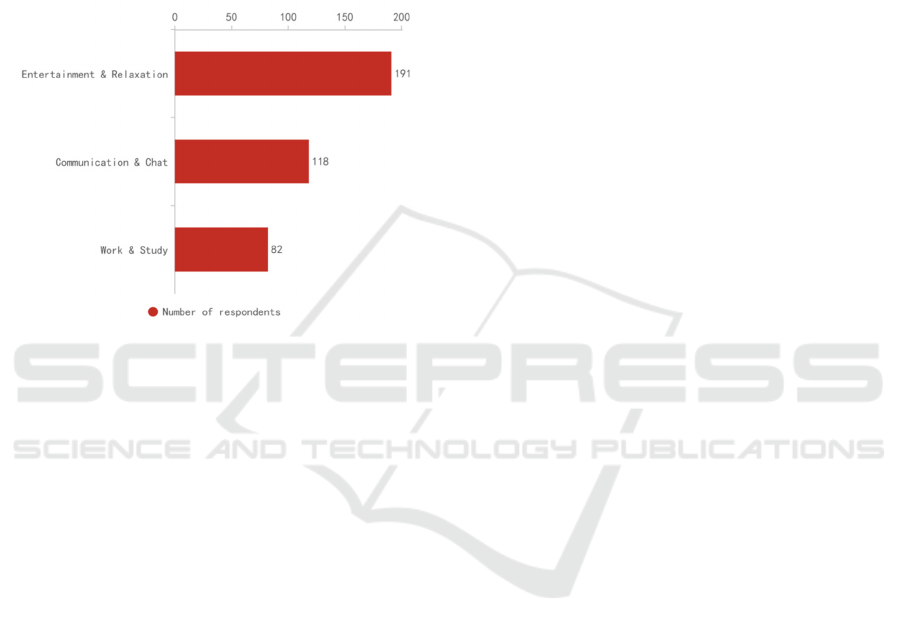
Figure 7: Purpose of using social media (Picture credit:
Original)
According to the survey results, 183 respondents in
the survey on the impact of social media on their daily
lives felt that using social media avoided spending
useless social time offline. Among them, 154
respondents believe that the function of social media
is enough to replace offline social networking, 96
people think that using social media is more attractive
to them than offline social networking, and 53
respondents believe that offline social networking has
too many limitations and it is better to use social
media. The remaining 17 respondents believe that the
use of social media will not encroach on offline social
time, of which 7 respondents believe that using both
can give full play to the advantages of social media
and offline social networking at the same time, and
10 respondents believe that they have higher
efficiency in offline social networking. In addition, 9
respondents felt that they lacked experience in using
social media and were more willing to socialize
offline. This type of data is scored separately based
on weighting and selection and is used to determine
how well respondents feel good about social media.
According to the calculation, 37 respondents have a
very high degree of favorability towards social media,
and they believe that the use of social media can
minimize the time consumption of offline social
networking and improve the quality of life and time
utilization. The 156 respondents believe that the use
of social media can simplify communication, but in
exceptional cases, it is still necessary to communicate
offline to achieve the best results. Seven respondents
believe that social communication in person
maximizes the quality of communication and is more
effective than social media.
As shown in Figure 7, 82 respondents were the
most judgmental when judging the authenticity of
social media content, followed by 63 respondents
who believed that whether the information had been
disseminated by the intimate people around them
should be the main criterion for whether it was
authentic. When used as an auxiliary basis for
judgment, 70 respondents believed that they should
judge whether it is true from their subjective
perspective, and 56 respondents believed that they
should listen to the opinions of those around them.
This type of data assigns a score to each type of
response based on a ranking order, and then calculates
it, and these scores are used to determine respondents'
attitudes towards social media and messaging. After
calculation, the author believes that 47 respondents
have a strong ability to distinguish the authenticity of
information on social media and can effectively
distinguish the truth from the false in the face of
diversified information and filter out content that is
beneficial to them. The 133 respondents have a
relatively general ability to distinguish the
authenticity of information, and it is usually easy to
distinguish the authenticity of information, but it is
easy to lose direction in the face of complex
situations. The 20 respondents have poor
discrimination skills and are easily influenced by
various information in the process of using social
media.
In terms of social media personalization, 64
respondents supported social media personalization,
while 136 respondents did not. Of the 64 respondents
who support social media personalization, 35 believe
that it is convenient to obtain information about their
preferences, while the other 29 believe that they can
block inappropriate content such as ads. Of the
remaining 136 respondents who do not support
personalization, 41 prefer diverse information, and 63
believe that personalization leads to their association
with social media. Thirty-two respondents believe
that social media personalization leads to fewer ways
to get information. In this type of analysis, each
respondent's score is calculated based on the total
proportion of each type of person in the group, and
the stickiness between the respondent and social
media is determined. After calculation, 46
The Contradiction of Social Media at Stage: Study on the Use of Social Media in Hong Kong
61

respondents have a good stickiness to the social
media they are using, 133 respondents have a normal
level of stickiness to the use of social media, which is
not easy to get away from and is not easy to be tied to
social media, and 21 respondents have a poor
stickiness to the social media they are using.
In terms of the impact of information cocooning
on themselves, 110 respondents believed that
information cocooning would lead to more subjective
thinking about problems was the biggest impact, 105
respondents believed that information building
reduced their communication with the outside world
was a secondary impact, and 80 respondents believed
that solidifying the way and content of information
obtained by themselves was the least impact of
information cocooning on themselves. The
respondents' understanding of information building is
arranged in order, according to a certain proportion,
and calculated according to the set score, to judge the
degree to which the respondents are affected by the
information cocoon. After calculation, 23
respondents can fully face up to the information
cocoon and have a better strategy to avoid being
affected, 144 respondents can realize the impact of
the information cocoon on themselves and make
certain measures, 30 respondents have a certain
understanding of the impact of the information
cocoon, but there is no better way to deal with it, and
3 respondents are seriously affected by the
information cocoon and have not been able to make
effective responses.
4 DISCUSSION
Based on the results of the questionnaire survey,
offline social networking can allow individuals to get
to know each other better because individuals can
communicate face-to-face in real life, and in this
process, both parties usually carry certain emotions
and body movements, which will improve
communication efficiency to a certain extent. At the
same time, it can be limited by time and space, as
people need to communicate at specific times and
places. When using social media, individuals can
more easily obtain the information they need, and at
the same time, social media has the characteristics of
fragmentation and strong virtuality, which is
convenient for individuals to use and has a higher
tolerance for negative attitudes and evaluations,
maintaining and expanding relationship networks,
establishing individual image and strengthening
community status.
By publishing real-time information and
professional reviews on social media, supplemented
by data obtained from observations or experiments,
institutions can attract more traffic and attention,
improve their visibility and authority, and individuals
will have a deeper trust in them, and once there is a
mistake, it will cause greater losses. In this regard,
individuals can effectively avoid judgment errors and
avoid disturbing their thinking through multi-faceted
and multi-angle verification.
Personalization can shorten the distance between
supply and demand, the two sides can form a good
cooperative relationship, and timely and targeted
services can help individuals to obtain the satisfaction
of expected benefits or make unreasonably expected
benefits have been corrected and improve efficiency.
However, at the same time, it is easy to lead to the
gradual narrowing and radicalization of individual
ideological vision, which can improve the stickiness
of individuals and groups in the short term, so that
individual satisfaction can be greatly improved, but in
the long term, it is easy to bind both sides, limit each
other's development and lose the opportunity to
improve blind vision.
5 CONCLUSION
The results of this study are that both sides of social
media, both positive and negative, can be effective. In
daily life, it can enrich the means of communication
and communication between individuals and provide
a space for individuals to display. In the face of
special situations, a variety of social media can create
new ideas, provide reliable and effective ideas and
solutions to solve problems and alleviate social
pressure. In the face of the problem of "information
cocoon" and personalization, it is necessary to obtain
diversified information, strive to understand and try
new things, broaden the scope of individual
information and refuse to blindly follow the opinions
and opinions of others, so as to help individuals grow
better. This study provides a lot of valuable reference
significance for future research in this direction,
mainly for the impact of social media personalization
on people's daily life, the use and practicality of social
media in the process of information dissemination,
and the relevant regulations and countermeasures that
can provide a favorable basis for professional
departments.
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
62

REFERENCES
B. L. Cao, J Hunan Radio Television University 3, 65-69
(2011)
Y. Y. Wang, J Hebei Open University 06, 89-92 (2023)
Y. P. Gong, J. J. Fu, Press Com Review 3, 67-75 (2020)
Y. Li, Y. Xie, J Marketing Res 1, 1-19 (2020)
R. B. Xiao, Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems
12, 4215 (2023)
H. Shahbaznezhad, R. Dolan, M. Rashidirad, J Interact
Mark 1, 47-65 (2021)
R. Keith, China: Law Press 2, 47 (2008)
H.T. Zhu, S.X. Li, Library Infor Service 18, 141-149 (2021)
O. Esteban, Our World Data 2, 14 (2019)
W. Lv, Y. Yang, Y.B. Management Science 5, 44-57 (2021)
The Contradiction of Social Media at Stage: Study on the Use of Social Media in Hong Kong
63
