
The Impact of Education Input on China's Economic Growth
Lei Ge
1
and Haoran Xu
2
1
Business School of Hohai University, Hohai University, Nanjing, China
2
Faculty of Social Science, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada
Keywords: Education, Economic, Regional diparities
Abstract: This study examines the correlation between education investment and economic growth in China, with a
focus on regional differences. The study aims to shed light on the positive impacts of education investment
on a country's economic development and emphasizes the importance of understanding these dynamics for
policymakers and stakeholders. The motivation behind this study is to recognize the critical role that education
plays in shaping a country's economic landscape. As China continues to undergo rapid economic
transformation, understanding the delicate relationship between education investment and economic growth
becomes imperative. This paper reveals the different impacts of education spending through a comprehensive
analysis of education spending patterns and economic indicators in different regions. The results of the study
show that education investment has a positive and substantial impact on China's overall economic growth. In
addition, the study identifies regional differences, emphasizing that the extent of this impact varies across
different regions of the country. This differential effect can be attributed to different levels of educational
infrastructure, government policies, and economic activities in each region. Influenced by factors such as
geographic location, resource conditions, and policy advantages, China's industrial structure exhibits
developmental differences in the spatial economic pattern. The significance of this study is that it has the
potential to sensitize policymakers, educational institutions, and investors on the strategic importance of
promoting education for sustained economic development. Recognizing the impact of different regions
requires targeted policies to address the specific educational challenges and opportunities in different regions
of China.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since China's reform and opening, China's
modernization has entered a rapid growth, in the past
decades of China's becoming the world's factory, due
to the demographic dividend brought about by the
economic growth of the population after the number
of people brought by the benefits of a slightly
exhausted economy. The quality of the labor force has
become particularly important. The contradiction
between the development needs of late-developing
countries such as China and the layout of the global
industrial chain is the root cause of the long-standing
problem of the imbalance between human capital and
industrial structure. Therefore, to solve this problem,
we can not only take short-term measures to catch up
with the other side but also focus on the dynamic
process of China's sustainable economic development
and promote the long-term coordination of human
capital accumulation and industrial structure
upgrading (Ni & Ding, 2022). At the beginning of the
21st century, China's working-age population had an
average of 7.18 years of education, and the figure rose
to 10.9 years by 2021, which is enough to show that
the structure of China's human capital has undergone
a great change (Zhang, 2022). It is undeniable that the
human capital dividend will replace the demographic
dividend as the new engine of China's economic
growth. Higher education is regarded as an important
support for economic and social progress, and the
relationship between higher education concentration,
human capital, scientific and technological R&D, and
economic growth has attracted a lot of attention and
become a focus of discussion in all walks of life (Cai
& Tan, 2024).
Education is one of the key determinants of a
country's economic well-being, as it can increase the
human capital of the country's labor force, thereby
promoting economic development and improving
people's living standards (A, 2010). Stable economic
growth and development in the long term can only be
achieved through three main factors: the development
of science and technology, the growth of the various
capital factors, and the development of the education
86
Ge, L. and Xu, H.
The Impact of Education Input on China’s Economic Growth.
DOI: 10.5220/0012823800004547
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Data Science and Engineering (ICDSE 2024), pages 86-90
ISBN: 978-989-758-690-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

system. Education is the means to raise the national
average level of professional skills and knowledge by
training and attracting the necessary resources.
Defining the dynamic evolution of low educated and
low skilled primary human capital towards high
skilled and highly educated advanced human capital
as the process of advanced human capital structure
(Zhang, 2023). The International Bureau of Education
(IBE) is the only international organization that has a
mandate to promote and protect human rights in the
field of education. With the improvement of national
education level, well educated individuals are more
likely to have innovative abilities, problem-solving
skills, and flexibility to adapt to changes. At the same
time, educated people are more likely to engage in
research and development and innovation activities,
thereby contributing to the technological level of the
economy. Human capital accumulation acts as a
powerful catalyst, providing a constant source of
motivation and support in the process of technological
innovation (Zhang, 2022). In addition, human capital
has other positive effects, including a decrease in
crime rates or an improvement in health conditions,
which are expected by society (Valero). With the
accumulation of human capital, it will also have
further positive effects, such as an increase in the
moral level of the entire society. Education has a
tremendous power to trigger change. By providing
knowledge, developing skills, and shaping values, it
can improve individual health and livelihood
conditions, contribute to social stability, and
effectively promote economic growth in the long term
(Brooks). Education, to a certain extent, improves the
quality of individuals and thus has a sense of social
responsibility, which can work together to maintain
social stability and ensure stable economic
development (Liu, 2023).
Therefore, how to better understand the impact
mechanism of human capital on economic growth is
of great significance to implementing the innovation-
driven development strategy and promoting high-
quality development (Ni & Ding, 2022).
The research on human capital can be traced back
to Schultz, who is the founder of human capital theory
and the main practitioner of human capital investment
today (Zhang, 2023).
This thesis analyzes the correlation between
education investment and local economic growth in 21
provincial administrative regions, including Liaoning,
Heilongjiang, Tianjin, Beijing, Shanghai, and Jiangsu.
The relationship between education investment and
GDP changes in each region is analyzed while
controlling for four constant variables: investment
(real utilized foreign capital), the number of tertiary
education students (university plus postgraduate
students), the urbanization rate, and the level of per
capita consumption.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The theory of human capital holds that in the process
of economic growth, the importance of human capital
exceeds that of material capital. Human capital
investment is directly proportional to national
income, and compared to material resources, the
growth rate of human capital is faster. The core of
human capital is to improve population quality, and
education investment is the main component of
human capital investment. The human capital theory
originated from economic research. American
economists Schultz and Becker explored the reasons
for the rapid economic growth and productivity
improvement in some developed countries after
World War II, and found that the main reason was the
increase in high-quality talents who received
education in these countries (Cai & Tan, 2024). The
human capital possessed by high-quality talents is
demonstrated through higher education, which in turn
leads to an increase in social output (Cai & Tan,
2024). Since the introduction of the human capital
theory, several empirical studies have emerged in
academia on the role of education in economic
growth, such as Schultz's residual method of
measuring national income growth through education
investment, and Denison's growth accounting method
of linking factor investment with economic growth.
Chen Zhao (2004) studied the differences in
human capital and education development among
regions in China and found that balanced
development of higher education will help to narrow
the income gap between regions (Zhang, 2022).
Higher education is usually accompanied by
economic benefits. A study by economist and global
human development professor George
Psacharopoulos and World Bank advisor Harry
Patrinos found that for every additional year of
education, a person's income increases by
10%(Brooks). Therefore, higher education is
considered an important support for economic and
social progress, and the relationship between the
concentration of higher education and economic
growth has received much attention, becoming a
focus of discussion in various sectors of society.
According to a recent study by the National Bureau
of Economic Research (NBER) in the United States,
learning institutions have found that more education
investment has an impact on national and state
The Impact of Education Input on China’s Economic Growth
87
economies of over $200 billion. Therefore, it is
evident that education plays a crucial role in the
economic development of a country (Brooks).
Existing literature usually defines the core
connotation of economic growth as the growth of
gross domestic product (GDP). Many existing studies
use per capita GDP or the growth rate of per capita
GDP as a proxy variable to represent economic
growth. This study uses each province's regional
gross domestic product as a proxy variable for
economic growth.
How to leverage the economic growth effect of
human capital based on the regional industrial
structure differences in China has always been a focus
of academic research point. Early literature formed a
consensus view that in the regional industrial
environment, the role of human capital in the central
and western regions is not significant, and the
efficiency of human capital investment in the service
industry is relatively high. This paper further explores
the impact of education investment on economic
growth in different regions based on this.
In summary, this article proposes the following
hypothesis: the increase in education investment has
a positive impact on China's economic growth, and
the impact of education investment on China's
economic growth varies in different regions.
3 THE IMPACT OF EDUCATION
INPUT ON CHINA'S
ECONOMIC GROWTH
3.1 Model Building
In this paper, the following linear regression model is
used for empirical analysis:
𝐺
=𝛼+𝛽𝐸
+𝑦𝐻
+𝜕𝐼
+𝛿𝐶
+𝜀 (1)
Wherein, i represents the city and t represents the
year. The dependent variable Git represents the
economic growth situation, for which the GDP of
each province is selected as an indicator. Eit stands
for the education expenditure for each province.;
Following the research in existing literature, this
paper incorporates other factors that may affect
economic growth as control variables into the model,
including the human capital level Hit. The metrics in
this study include the local higher education
graduates, investment (actual utilization of foreign
capital) Iit, and urbanization rate (urban
population/total population) Cit. In addition, ε
represents the random disturbance term, and α is the
constant of the model.
This paper conducts empirical analysis based on
data from 22 provinces in China, including Jiangsu,
Anhui, Shanghai, Hubei, etc., for the years 2012-
2021. All data were obtained from the statistical
yearbooks of each province and directly administered
municipality each year. For a small amount of
missing data, interpolation or extrapolation methods
were employed for supplementation.
3.2 Data Analysis
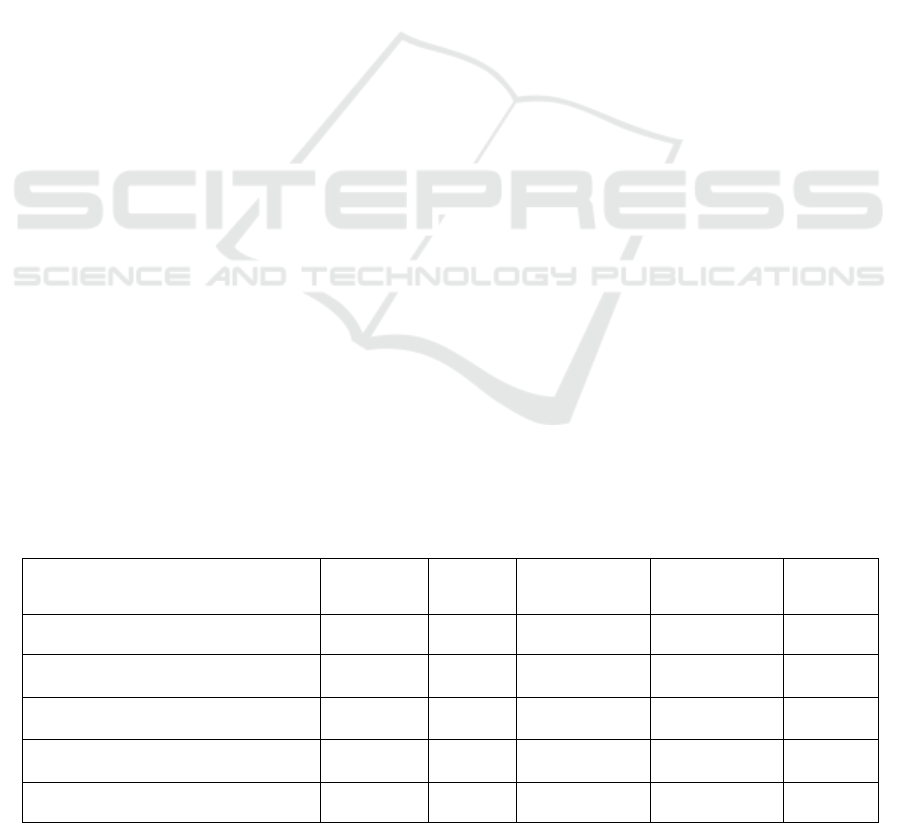
Table 1 reveals significant variations in the maximum
and minimum values of each variable, indicating
substantial fluctuations in variables such as regional
gross domestic product (GDP), education
expenditure, human capital level, actual utilization of
foreign capital, and urbanization rate across
provinces. This paper conducts empirical analysis
based on data from 22 provinces in China, including
Jiangsu, Anhui, Shanghai, Hubei, etc., for the years
2012-2021. All data were obtained from the statistical
yearbooks of each province and directly administered
municipality each year. For a small amount of
missing data, interpolation or extrapolation methods
were employed for supplementation.
Table 1. Descriptive statistics of variables.
Variable Name Max Min Mean
Standard
Deviation
Median
GDP(in hundred million CNY) 124369.67 828.2 27937.444 23910.462 21499.28
Education Expenditure
(
in ten thousand CNY
)
37966900 1071776 9363447.233 5867674.779 8085153
Foreign Direct Investment
(in ten thousand USD)
18400200 321 1180908.298 2255023.056 719749.5
Higher Education Enrollment
(in people)
1178402 33500 412398.838 221547.547 393658
Urbanization rate/% 93.768 23.93 60.383 13.471 59.771
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
88
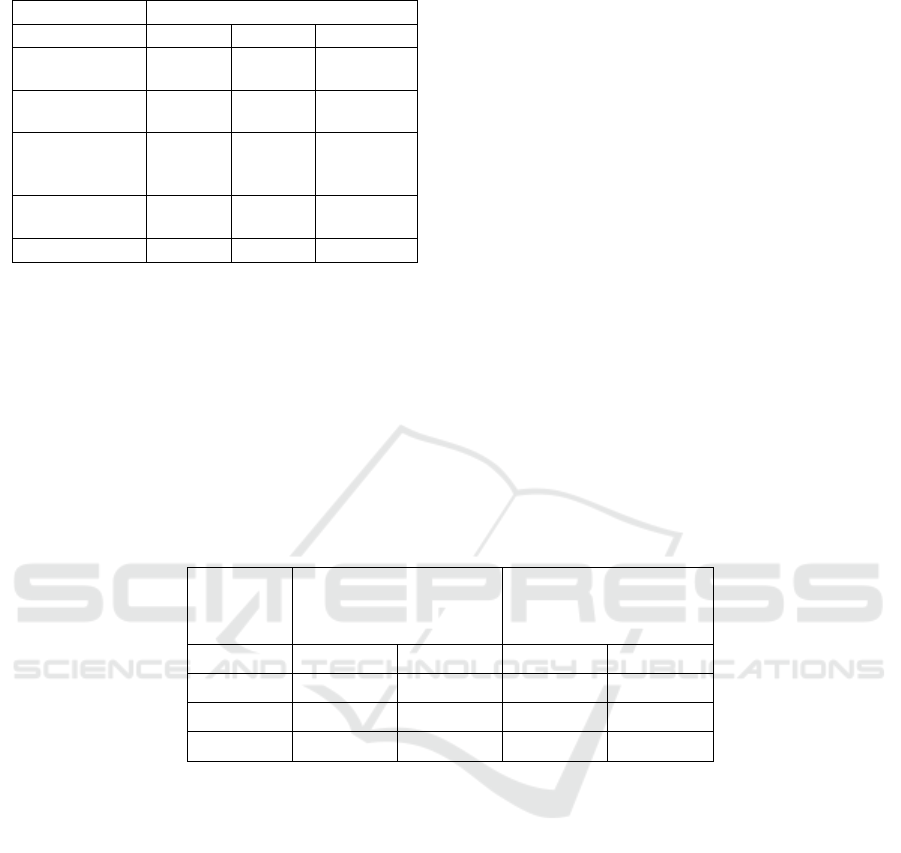
Table 2. Analysis of regression result.
Standardized Coefficients
(1) (2) (3)
Education
Expenditure
0.937 0.891
Foreign Direct
Investment
0.637 -0.001
Higher
Education
Enrollment
-0.063 -0.014
Urbanization
rate
0.251 0.166
R
2
0.877 0.537 0.899
The paper adopts the method of controlling
variables. Specifically, in columns (1) and (2),
education expenditure and control variables are
individually added to the regression model, while
column (3) includes all variables simultaneously in
the regression model. In multivariate analysis, the
value of the normalization coefficient represents the
standardized change of the dependent variable when
the unit standard deviation of the independent
variable changes. This aids in a more comprehensive
understanding of the impact of each independent
variable on the dependent variable and allows for a
better comparison of their relative influences.
Therefore, Table 2 selects the standardized
coefficients of each independent variable for analysis.
The results indicate that, in the three models, the
fit is higher for models (1) and (2) which include the
independent variable of education expenditure, while
the fit is lower for the model that includes only
control variables. Moreover, the standardized
coefficients for education expenditure are
consistently around 0.9%. These findings strongly
support the hypothesis proposed in the paper,
indicating that an increase in education expenditure in
various provinces leads to positive GDP growth.
Specifically, a 1% increase in education expenditure
is associated with approximately a 0.9% increase in
GDP.
Next, the collected data will be segmented into
three regions: East, Central, and West. Linear
regression analysis will be conducted again to explore
the varying impact of education expenditure on
economic growth in different regions.
Table 3. The impact of education expenditure in different regions
Normalization
Coefficients
R
2
(1) (2) (1) (2)
Eastern 0.974 1.029 0.948 0.976
Central 0.920 0.825 0.843 0.850
West 0.895 0.547 0.798 0.955
The eastern region comprises eight provinces,
including Beijing, Tianjin, Liaoning, Shanghai,
Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, and Guangdong. The
central region includes six provinces: Jilin,
Heilongjiang, Anhui, Jiangxi, Hubei, and Hunan. The
western region encompasses eight provinces: Inner
Mongolia, Guangxi, Sichuan, Guizhou, Gansu,
Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang. In column (1),
education expenditure is individually added to the
regression model, while column (2) includes all
variables simultaneously for analysis.
From the results in Table 3, it is observed that the
model has a high fit, and the single independent
variable, education expenditure, positively influences
economic growth. Additionally, it is noted that the
influence of education expenditure on GDP growth
decreases gradually from the eastern to the western
regions. After incorporating control variables,
changes in the standardized coefficients of education
expenditure are observed. A comparative analysis of
the data reveals that the eastern region, with stronger
economic strength and better infrastructure, shows
higher values for all variables compared to both the
central and western regions. Consequently, education
expenditure in the eastern region is significantly
correlated with economic growth, with a 1% increase
capable of driving approximately a 1.029% increase
in GDP. Despite lower data values in the central
region, education expenditure still exhibits a
considerable impact on economic growth, with a 1%
increase associated with approximately 0.825% GDP
growth. In the western region, where economic
development is slower compared to the eastern and
central regions, and with the lowest data values, the
The Impact of Education Input on China’s Economic Growth
89

impact of education expenditure on economic growth
shows the greatest variation.
4 CONCLUSION
From an overall analysis of the results, it can be
observed that the growth in education expenditure
effectively drives economic growth in China. In
addition, there are significant differences in the
impact of education expenditure on different regions
of China. For the eastern region, an increase in
education expenditure significantly stimulates
economic growth. Higher education expenditure in
the central region plays an important role in
promoting economic growth. However, compared to
other regions, the impact of education expenditure on
economic growth is less pronounced in the western
region.
Therefore, this article proposes the following
suggestions for China's economic growth: firstly,
increasing education investment in various regions is
crucial to drive economic growth. Secondly, from the
data, it can be seen that the infrastructure construction
in some provinces is not yet developed enough, and
the urbanization rate is relatively low. With the
increase of urbanization rate, cities usually pay more
attention to investment in infrastructure and
educational resources. Therefore, it is necessary to
vigorously promote infrastructure construction in
various regions, increase urbanization rates, and
create more favorable conditions for promoting
economic growth through education investment.
Finally, considering the significant regional
economic disparities and imbalanced development,
the effectiveness and focus of education investment
should vary among different regions. It is necessary
to strategically allocate resources in each region in
order to maximize the effectiveness of education
investment under limited economic conditions.
AUTHORS CONTRIBUTION
All the authors contributed equally and their names were
listed in alphabetical order.
REFERENCES
N. Ni, N. Ding, Human Capital and Economic Growth 6,
46-58 (2022).
Y. Zhang, The influence of human capital structure and
R&D input on economic growth 116, 38-41 (2022).
W. Cai, M. Tan, Technological research and development
358, 67-75 (2024).
E. A, Education and economic growth (2010).
H. Zhang, Research on the contribution rate of human
capital accumulation to economic growth 119, 55-32
(2023).
H. Zhang, Chinese economy Study of the impact of growth
368, 18-24 (2022).
A. Valero, Education and economic growth. Department of
Education. chrome-
extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://
files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED614082.pdf
R. Brooks, What is the relationship between education and
economy. Wrexham.
https://online.wrexham.ac.uk/what-is-the-relationship-
between-education-and-the-economy/
S. Liu, Shangzhan Economic 218, 112-118 (2023).
S. Zhang, Background of Low Fertility 113, 58-72 (2023).
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
90
