
Energy Efficiency Analysis of China Based on DEA Methods Under
Dual Carbon Target
Jingqi Wang
College of Science, North China University of Technology, Beijing, 100043, China
Keywords: DEA Methods, Energy Efficiency, Energy Consume, Low Carbon, Environment
Abstract: With the increasingly serious environmental problems, the realization of low-carbon energy transformation
in China's energy system has been promoted to the national strategic height. It has certain practical
significance and necessity to investigate its production efficiency scientifically and accurately and analysis
its improvement path. In this paper, the Data envelopment analysis (DEA) method is utilized to measure the
energy of 30 provinces and municipalities in China from 2010 to 2020 using deep2.1 software, from a
temporal and spatial perspective. According to the data analysis, this paper makes suggestions: pay attention
to the important role of technological innovation in improving energy efficiency, strengthen the scientific
research investment of new energy enterprises, cultivate internationally competitive energy talents; strengthen
regional energy cooperation, promote clean energy to replace traditional energy, increase the research on
clean coal utilization technology, improve coal utilization efficiency and reduce carbon emissions, and further
improve environmental protection policies, and increase the punishment of polluting enterprises. At the same
time, encourages enterprises to trade carbon emission rights, increase carbon emission costs, promote
enterprises to improve energy efficiency. In the production process, Chinese companies should try their best
to energy conservation and emission reduction, and reduce energy consumption. In energy consumption,
popularize energy-saving products and improve energy efficiency; strengthen regional energy cooperation
and promote the rational allocation of energy resources. Through regional coordination, the improvement of
energy efficiency can be realized, reduction of national energy consumption level can be promoted.
1 INTRODUCTION
Energy plays a crucial role in supporting human
survival and facilitating social development. With the
increasing energy demand, environmental problems
caused by energy shortage and excessive energy
consumption have gradually attracted people's
attention. How to effectively improve energy
efficiency is crucial for the sustainable development
of China's economy. Therefore, it is of great
theoretical and practical significance to scientifically
evaluate the energy efficiency situation and the major
influencing factors in China to provide reliable
suggestions and empirical data reference for
improving energy efficiency.
Through theoretical induction, the Data
envelopment analysis (DEA) model is widely used in
energy efficiency measurement. Yao et al. proposed
a methodology that decomposes total factor
productivity change into two distinct elements,
technological progress and changed in technical
efficiency (Yao et al, 2023). Guo et al. investigated
how entry and innovation affect total factor
productivity growth (Guo et al, 2023). Yang et al.
observed Significant effects that persist over time
(Yang et al, 2023). Jin et al. developed a framework
to evaluate China's agricultural research investment
trends and its impact on total factor productivity (Jin
et al, 2002). Chen examined heterogeneous total
factor productivity (TFP) (Chen & Moore, 2009).
Asche analyzed total factor productivity change
(Liang & Wang, 2023).
With the gradual improvement of DEA models
and the increasingly prominent problem of the
product of environment, domestic scholars also began
to study green total factor productivity. Li utilized the
Malmquist index and a spatial Durbin model to
analyze the impact of the effect on green total factor
productivity (Asche, 2013, Li & Wu, et al, 2017). Li
used the Super-SBM model to calculate China's
agricultural green total factor productivity according
to carbon emissions (Li & Lin, 2017). The carbon
Wang, J.
Energy Efficiency Analysis of China Based on DEA Methods Under Dual Carbon Target.
DOI: 10.5220/0012825500004547
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Data Science and Engineering (ICDSE 2024), pages 91-97
ISBN: 978-989-758-690-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
91

emissions are usually used to calculate green total
factor production efficiency (Liu et al, 2021).
The main body of this paper is energy efficiency.
Through the literature research, the author
understands the variety of testing methods for energy
efficiency, combined with the knowledge that has
been learned.
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Data Source and Description
For the construction of energy efficiency index
system, most scholars choose to consider energy,
labor, technology, capital input, economic output
interaction and alternative relationship of the total
factor energy efficiency index. This paper refers to
the actual research, and chooses capital input, labor
input, technology input three indexes as input
elements, with local fiscal revenue to measure capital
input, with the end of employment to measure labor
input. Research and experimental development
personnel collaborated to measure the impact of
technology, using per capita GDP as the desired
output and the carbon dioxide emissions as the
undesired output. The specific input-output index
system is shown in the following table.
𝐸𝐶 =
∑
𝐸𝐶
=
∑
𝐸
×𝐶𝐹
×𝐶𝐶
×𝐶𝑂𝐹
×3.6
(1)
Among them, represents the estimated total
carbon dioxide emissions of various energy
consumption; 𝑖 represents energy consumption,
including coal, coke, gasoline, kerosene, fuel oil and
natural gas. 6 is the total energy consumption of each
province: represents the heat value of energy:
represents the carbon content: represents the
oxidation factor of energy in i. It's called carbon
dioxide emission.
2.2 Index Selection
Most researchers prefer to consider the interaction
between energy, labor, science and technology,
capital input, economic output, and the substitution
relationship of the total factor energy efficiency index
when constructing the energy efficiency index
system. Drawing on the actual research, this paper
selects three indicators including capital input, labor
input, and technology input as input elements. Local
fiscal revenue is used to calculate capital input,
employment termination is used to measure labor
input, and research and development personnel are
counted for technology input. Per capita GDP is used
as the desired output, and carbon dioxide emissions
serve as the undesired output. The specific input-
output index system is shown in the following Table
1.
Table 1: Index selection and unit.
Indicator t
yp
e name of index Index unit
Investment index
Local fiscal revenue 100 million
N
umber of people emplo
y
ed at the end of the
y
ea
r
human bein
g
Research and trial development personnel human bein
g
Expect output indicators Per capita GDP firs
t
Undesired output indicators Carbon dioxide emissions Ten thousand tons
2.3 Research Method
DEA-BCC Model measures the pure technical
efficiency by assuming a variable return of scale, it is
also called the variable return of scale (VRS) model.
BCC The model is shown as follows:
When σ =1, then the pure technical efficiency of
DMU is DEA effective. If the comprehensive
technical efficiency is θ and the pure technical
efficiency is σ, then the scale efficiency of DMU = θ
/ σ (Yang et al, 2023).
Malmquist Model: The Malmquist Index method
is a helpful tool for analyzing efficiency changes
across multiple samples. It can show the relationship
between comprehensive efficiency, technical
efficiency, and total factor production efficiency
index. This method can dynamically track the
changes in efficiency values of sample data over
different time periods. The Malmquist index was first
proposed in 1953 to solve the problem of variations
in the consumption bundle in the consumption
function. CAVES applied the Malmquist index to
analyze energy production efficiency (Asche, 2013).
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
92
𝑀
𝑦
,𝑥
,𝑦
,𝑥
=
,
,
∗
,
,
(2)
Where
𝑥
,𝑦
𝑥
,𝑦
𝐷
𝐷
For input and
output variables in 𝑡+1 and 𝑡; for decision unit
distance function in 𝑡+1 and 𝑡.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Energy plays a crucial role as a material foundation
for human survival and social progress. With the
increasing energy demand, environmental problems
caused by energy shortage and excessive energy
consumption have gradually attracted people's
attention.
3.1 Descriptive Statistics
Based on previous data comparing energy
consumption and carbon emissions. In this research,
the DEA-Malmquist method is applied to measure the
energy efficiency of China from 2010-2020 from both
static and dynamic perspectives, and to compare the
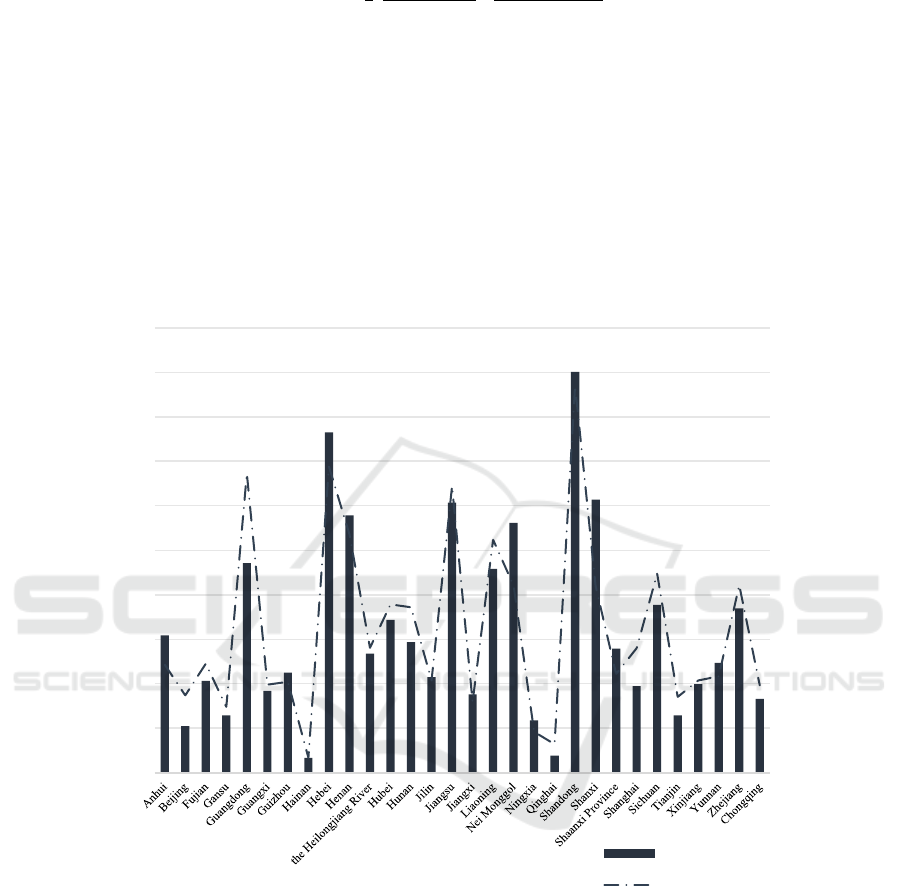
efficiency differences of the seven regions (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Comparing energy consumption and carbon emissions plot (Picture credit: Original)
Using the original input and output data and
Deap2.1 software, the total energy factor productivity
and decomposition index were calculated for the 30
provinces in China. and municipalities from 2010 to
2020. Combined with the Malmquist index, the total
factor production efficiency is used to evaluate it
dynamically. As shown in Table 2., the average total
factor production efficiency of 30 provinces and
municipalities in China from 2010 to 2020 is 0.951,
indicating that the energy efficiency of these 30
provinces and municipalities has not yet reached the
effective state. From 2010 to 2014, tfp increased year
by year, with a significant decrease in 2014-2015.
From 2015 to 2016, it recovered to the level of 2013-
2014 and probably decreased from 2016 to 2019.
From 2010 to 2020, the development of energy
efficiency in all regions of China will be divided into
three phases: the first from 2010 to 2014, the second
from 2014 to 2016, and the three from 2016 to 2019.
(Table 2).
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
25000
30000
35000
40000
0.00
10000.00
20000.00
30000.00
40000.00
50000.00
60000.00
70000.00
80000.00
90000.00
100000.00
Carbon dioxide emissions
Total energy consumption
Carbon dioxide emissions
Total energy consumption
Energy Efficiency Analysis of China Based on DEA Methods Under Dual Carbon Target
93

Table 2: Malmqusit index decomposition of energy efficiency.
y
ear eff tech
p
eh sec tf
p
2010-2011 1.027 0.870 1.015 1.012 0.894
2011-2012 1.021 0.910 1.023 0.998 0.928
2012-2013 1.000 0.961 1.005 0.996 0.962
2013-2014 1.016 0.962 1.016 1.000 0.977
2014-2015 0.994 0.932 0.995 0.999 0.927
2015-2016 1.022 0.958 1.033 0.989 0.979
2016-2017 0.972 0.995 0.960 1.012 0.967
2017-2018 1.010 0.961 1.006 1.003 0.970
2018-2019 1.035 0.929 1.105 0.936 0.961
mean 1.011 0.941 1.017 0.994 0.951
According to the principle of the Malmquist index
method, the total factor production efficiency is the
product of the comprehensive technical efficiency
change index and the technical change index.
In the first stage, the contribution to the growth
of total factor production efficiency is technological
changes. The sudden decline of total factor
production efficiency in the second stage is mainly
due to the decline of technological changes, while the
scale also decreases in efficiency. Combined with the
literature research, environmental protection was
valued in 2014.31 provinces and the Ministry of
Environmental Protection signed the "Target
Responsibility Letter for Air Pollution Prevention and
Control", and the policy had a great impact on the
technical change index, thus affecting the total factor
productivity. In the third stage, the total factor
productivity index continued to decline, but from
2018 to 2019, the technical change index increased.
The scale efficiency index decreased, indicating that
the development of new energy technology in China
is effective. The technology application is in scale,
and it is in the stage of energy technology
transformation and development after the
environmental protection policy.
In general, technical changes play a leading role
in the total factor efficiency of production. In
contrast, the change is relatively flat at present, which
may require further optimization of resource
allocation and scale expansion strategy.
3.2 Regional Trend
Without the influence of environmental effects and
random factors, the total factor growth rate decreased
by 1% annually from 2010 to 2020 (table 3). Surgical
efficiency (TECH) increased by 2.4% annually;
technological progress level. TCH decreased by 3.2%
annually. This shows that the decline in the
productivity of environmental service enterprises is
mainly caused by the relative decline of technology.
From the perspective of segmentation, only the
average annual productivity of environmental
monitoring enterprises has seen a small improvement,
and the main driving force is the obvious
improvement in the technical efficiency of
enterprises. However, the productivity of enterprises
in the other five categories showed a small downward
trend, with a decline rate of 0.56% ~2.25%.
Between, the main reason is the negative impact
of the technological relative regression on
productivity. The results of the first stage show that,
without considering the influence of environmental
factors and random factors, the improvement of
correct management decisions is not enough to offset
the adverse impact of the relative decline of
technology level on the production efficiency of
enterprises.
From the perspective of regional analysis, the
results under environmental constraints energy
efficiency and overall technology progress level are
low (only 0.94) has not reached the equilibrium
degree. The efficiency difference between provinces,
regions, in the study period of Beijing, Shanghai
province energy efficiency mean is 1, every year
reached the effective state, and the average energy
efficiency in Guizhou is only 0.87.
Energy efficiency in North China and Eastern
China is significantly higher than in other regions. In
this regard, the differences in resource endowment of
different regions, as well as the supply and demand of
different resources and the development degree of
utilization, and relevant policies should be formulated
according to local conditions.
From a dynamic point of view, between 2010-
2020 our country's energy total factor productivity
changed overall downward trend, and gradually in the
good direction in recent years, the technological
progress is the main factor of driving energy
efficiency growth, should adhere to resource
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
94

orientation and science and technology, and attach
importance to technology research and development,
actively develop clean coal utilization technology,
unconventional oil and gas exploration and
development technology, but also to promote the
development of energy conservation and emissions
reduction technology, intensify mining environment
monitoring, increase the proportion of clean energy
consumption, under the condition of low carbon
environmental protection improve energy efficiency
(table 4).
Table 3: Static index analysis of energy efficiency.
area firm crste vrste scale
Sichuan 25 0.135 0.135 1.000
Henan 10 0.165 0.165 1.000
Guan
g
don
g
5 0.169 0.169 1.000
Shandon
g
21 0.196 0.196 1.000
Jian
g
su 15 0.207 0.207 1.000
Hebei 9 0.209 0.209 1.000
Hunan 13 0.212 0.212 1.000
Anhui 1 0.221 0.221 1.000
Hubei 12 0.243 0.243 1.000
Yu nn an 28 0.251 0.251 1.000
Liaonin
g
17 0.265 0.291 0.913
the Heilon
gj
ian
g
Rive
r
11 0.268 0.268 1.000
Shaanxi Province 23 0.271 0.271 1.000
Guan
g
xi 6 0.287 0.287 1.000
Shanxi 22 0.289 0.289 1.000
Jian
g
xi 16 0.299 0.299 1.000
Zhe
j
ian
g
29 0.314 0.314 1.000
Guizhou 7 0.349 0.349 1.000
Xin
j
ian
g
27 0.351 0.351 1.000
Chon
g
qin
g
30 0.365 0.365 1.000
Jilin 14 0.387 0.474 0.816
Gansu 4 0.393 0.393 1.000
N
ei Mon
gg
ol 18 0.430 1.000 0.430
Fu
j
ian 3 0.479 0.479 1.000
Shan
g
hai 24 0.672 1.000 0.672
Bei
j
in
g
2 1.000 1.000 1.000
Hainan 8 1.000 1.000 1.000
N
in
g
xia 19 1.000 1.000 1.000
Qin
g
hai 20 1.000 1.000 1.000
Tian
j
in 26 1.000 1.000 1.000
Table 4: Total factor energy efficiency.
area firm effch techch pech sech tfpch
Anhui 1 1.01 0.89 1.02 7.00 0.90
Bei
j
in
g
2 1.00 1.08 1.00 1.99 1.08
Fu
j
ian 3 1.04 0.95 1.08 0.97 0.99
Gansu 4 1.02 0.88 1.02 2.00 0.90
Guan
g
don
g
5 1.01 0.97 1.03 0.98 0.97
Guan
g
xi 6 1.01 0.89 1.01 2.00 0.89
Guizhou 7 0.98 0.88 0.98 1.10 0.87
Hainan 8 1.00 0.96 1.00 2.00 0.96
Hebei 9 0.99 0.92 0.99 1.09 0.91
Henan 10 1.01 0.90 1.01 2.00 0.91
Energy Efficiency Analysis of China Based on DEA Methods Under Dual Carbon Target
95

Table 4: Total factor energy efficiency (cont.).
area firm effch techch
p
ech sech tf
p
ch
The Heilon
gj
ian
g
Rive
r
11 1.03 0.92 1.03 2.00 0.94
Hubei 12 1.03 0.95 1.04 9.98 0.98
Hunan 13 1.01 0.93 1.01 7.00 0.94
Jilin 14 1.02 0.96 1.00 1.92 0.98
Jian
g
su 15 1.05 0.95 1.09 8.96 0.99
Jian
g
xi 16 0.99 0.89 0.99 1.01 0.88
Liaonin
g
17 1.01 0.96 1.01 1.10 0.97
N
ei Mon
gg
ol 18 0.99 1.00 1.00 0.99 0.99
N
in
g
xia 19 1.00 0.98 1.00 1.90 0.98
Qin
g
hai 20 1.00 0.99 1.00 2.00 0.99
Shandon
g
21 1.00 0.96 1.01 9.99 0.96
Shanxi 22 1.01 0.91 1.01 1.10 0.91
Shaanxi Province 23 1.03 0.95 1.04 10.00 0.98
Shan
g
hai 24 1.02 1.04 1.00 1.18 1.06
Sichuan 25 1.03 0.89 1.03 1.99 0.92
Tian
j
in 26 0.98 0.97 1.00 6.98 0.96
Xin
j
ian
g
27 1.01 0.94 1.02 9.99 0.95
Yu nn an 28 1.01 0.88 1.01 1.09 0.89
Zhe
j
ian
g
29 1.01 0.95 1.05 9.97 0.96
Chon
g
qin
g
30 1.04 0.96 1.06 0.98 0.99
mean 1.01 0.94 1.02 9.99 0.95
3.3 Discussion
According to the above studies, the paper puts
forward the following suggestions:
Chinese energy enterprises should increase their
investment in new energy technology innovation, and
attach importance to the important role of
technological innovation in improving energy
efficiency, to improve China's energy efficiency. The
government and enterprises should increase their
investment in technological innovation, increase the
allocation of research and development funds and
human resources, and cultivate internationally
competitive energy technologies.
China needs to work on optimizing its energy mix
by promoting the use of clean energy in place of
traditional energy sources, and increasing the
proportion of clean energy in the total energy
consumption. It is also important for enterprises to
focus on researching clean coal utilization technology
to improve the efficiency of coal utilization and
reduce carbon emissions. Strengthening
environmental protection policies. The Chinese
government will further improve environmental
protection policies, increase penalties for polluting
enterprises, and guide them to take the path of green
development. At the same time, enterprises are
encouraged to carry out carbon emission rights
trading, increase the cost of carbon emission, and
promote enterprises to improve energy efficiency.
Strengthen the training of energy talents. China
aims to provide comprehensive training for a diverse
pool of energy professionals, equipping them with a
global perspective and enhancing their expertise in
areas such as energy technology research and
development, as well as energy management.
Simultaneously, the Chinese government will
prioritize the enhancement of professional
development programs for individuals already
employed within the energy industry, thereby
elevating the overall quality standards across the
sector.
Strengthen regional coordination. The Chinese
government should strengthen energy cooperation
among regions and promote rational allocation of
energy resources. Through regional coordination,
China can improve energy efficiency and reduce
national energy consumption.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the measurement of energy data from
various regions in China from 2010 to 2020, this
paper finds that China's energy efficiency has not yet
reached its overall effective state, and there are
significant fluctuations in energy efficiency from
2014 to 2016. Under this premise, this paper puts
forward policy suggestions such as increasing
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
96

investment in technological innovation, optimizing
energy structure and strengthening environmental
protection policies to provide reference for improving
energy efficiency and green and low-carbon
development in China. Through the implementation
of these policies, China's energy enterprises can help
to improve production efficiency, reduce carbon
emissions, and achieve sustainable development. At
the same time, the government, enterprises and
scientific research institutions should make joint
efforts to contribute to improving energy efficiency
and green and low-carbon development in China.
REFERENCES
S. C. Yao, J. Q. Zhi, J. B. Fu, et al. Journal of South China
University of Technology: Natural Science Edition
51(6), 97-108 (2023).
A. Guo, L. Niu, P. J. Liu, et al. Economic Geography 43(9),
172-178 (2023).
H. Yang, Y. H. Pan and G. W. Cai, China Industrial
Economy 7, 46-65 (2023).
S. Q. Jin, J. K. Huang, R. F. Hu and S. Rozelle, International
Political Economy, (2002).
M. X. Chen and M. O. Moore, Journal of International
Economics, (2009).
Y. W. Liang and M. L. Wang, Agricultural Economic
Issues 10, 101-115 (2023).
F. Asche, G. Atle and R. Nielsen, Aquaculture, (2013).
B. Li and S. S. Wu, Journal of Clean Production, (2017).
K. Li and B.Q Lin, Applied Energy, (2017).
D. D. Liu, X. Y. Zhu and Y. F. Wang, Journal of Clean
Production, (2021).
Energy Efficiency Analysis of China Based on DEA Methods Under Dual Carbon Target
97
