
Convolutional Neural Network's Stacking Classifier on
Cardiovascular Disease
Chuhong Zhou
Jinan University-University of Birmingham Joint Institute, Jinan University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 511443, China
Keywords: Ensemble Learning, Classification, Prediction, Machine Learning
Abstract: Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. To diagnose cardiovascular disease, multiple
risk indicators need to be combined, which is a challenge for limited medical resources. To reduce
misdiagnosis, machine learning is being used to predict cardiovascular disease. Due to the inherent defect of
algorithms, the results of a single model will produce certain errors. To improve prediction accuracy,
Ensemble Learning combines several machine learning algorithms. However, Convolutional Neural Network
(CNN), as an algorithm of machine learning, is not sufficiently applied in predicting problems of
cardiovascular disease. Part of the data collected by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in
2022 was used in this experiment, and pre-processing operations such as feature selection, Undersampling,
and Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) were performed. This experiment tested the
accuracy of using a CNN as the base learner and meta-learner for the stacking model and compared it with
traditional algorithms. The results show that the accuracy of the ensemble learning model that integrates CNN
is 91.13, which is higher than the traditional algorithm compared to it.
1 INTRODUCTION
Heart disease is a disease involving the heart and
blood vessels, including coronary heart disease,
cerebrovascular disease, rheumatic heart disease, and
other related diseases. The heart is second only to the
brain as an important organ of the human body, and
cardiovascular diseases have a huge impact on
patients. According to the World Health Organization
(WHO) estimating, in 2019, heart disease accounted
for 32% of global deaths, totaling approximately 17.9
million people (World Health Organization 2021).
Research has shown that using a wide range of
intervention measures to prevent cardiovascular
disease is cost-effective in both low - and middle-
income areas (Shroufi et al. 2013).
However, there are problems in the diagnosis of
cardiovascular disease. The risk indicators related to
cardiovascular disease include blood pressure,
myocardial enzymes, low-density lipoprotein
cholesterol, and other indicators. Personal lifestyle
also has an impact on the incidence rate, such as
smoking, diet, obesity, and lack of exercise (Tsao et
al. 2023). Doctors need to identify, quantify, and
explain the relationships between variables. To
accurately diagnose heart disease, skilled and
experienced doctors and excellent medical equipment
are required, which is a challenge for both society and
the economy.
Therefore, when predicting cardiovascular
diseases, it is necessary to introduce the excellent
information processing ability and computing speed
of the computer. Machine learning is a branch of
computers. With the increasing amount and
complexity of available data and the improvement of
computer computing power, machine learning can
learn from the ever-increasing data, and it is possible
to use artificial intelligence to accelerate and enhance
the research and clinical application of heart disease
(Jone et al. 2022).
In the past few years, scholars and researchers
have attempted to apply machine learning to disease
prediction and have tried various algorithms, such as
Decision Tree, k-nearest neighbor algorithm, and
Random Forests, and achieved good experimental
results (Sudheer et al. 2021).
However, a single machine learning model may
produce some errors in predicting results when facing
complex problems due to the differences in algorithm
logic and computational methods. Ensemble learning
is a method of combining multiple foundational
models to form a more powerful predictive model.
116
Zhou, C.
Convolutional Neural Network’s Stacking Classifier on Cardiovascular Disease.
DOI: 10.5220/0012827800004547
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Data Science and Engineering (ICDSE 2024), pages 116-121
ISBN: 978-989-758-690-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
Research has shown that applying ensemble learning
to cardiovascular disease prediction can leverage the
complementarity between different models and
provide more reliable decision-making results
(Ahmed et al. 2022).
In addition, cardiovascular disease is not a single
disease, and there is a certain correlation between
various complications. The interconnection of
parameters may change the prediction results (Zhou
et al. 2023). In actual prediction, it is necessary to
make comprehensive judgments and extract features.
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is a deep
learning algorithm widely used in image processing
and pattern recognition. It has a strong feature
extraction ability and can capture local structures in
images. However, the application in data analysis is
insufficient.
Therefore, the objective of this project is to use
CNN as a base learner and a meta-learner to test the
accuracy of ensemble learning models containing
CNN in predicting cardiovascular diseases and
compare the prediction accuracy with ensemble
learning models composed of other classifiers.
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Dataset
The data for this experiment was initially obtained
from the Behavioral Risk Factors Monitoring System
(BRFSS), which is an annual telephone survey
conducted by its subsidiary, the Centers for Disease
Control and Prevention (CDC) (Kaggle 2023). Select
246022 samples and 40 health indicators from
approximately 400000 samples and 300 health
indicators. Among them, 232587 had no or no history
of heart disease, and 13435 had a history of heart
disease.
2.2 Pre-Processing
Features that have little or no relevance to
classification results in the data set will reduce the
model performance and increase the computational
cost. Therefore, feature selection is required before
training the model (Abdollahi & Nouri-Moghaddam
2022). In this experiment, Relief and FCBF
algorithms were used to screen valuable
characteristics of heart disease. In addition, as shown
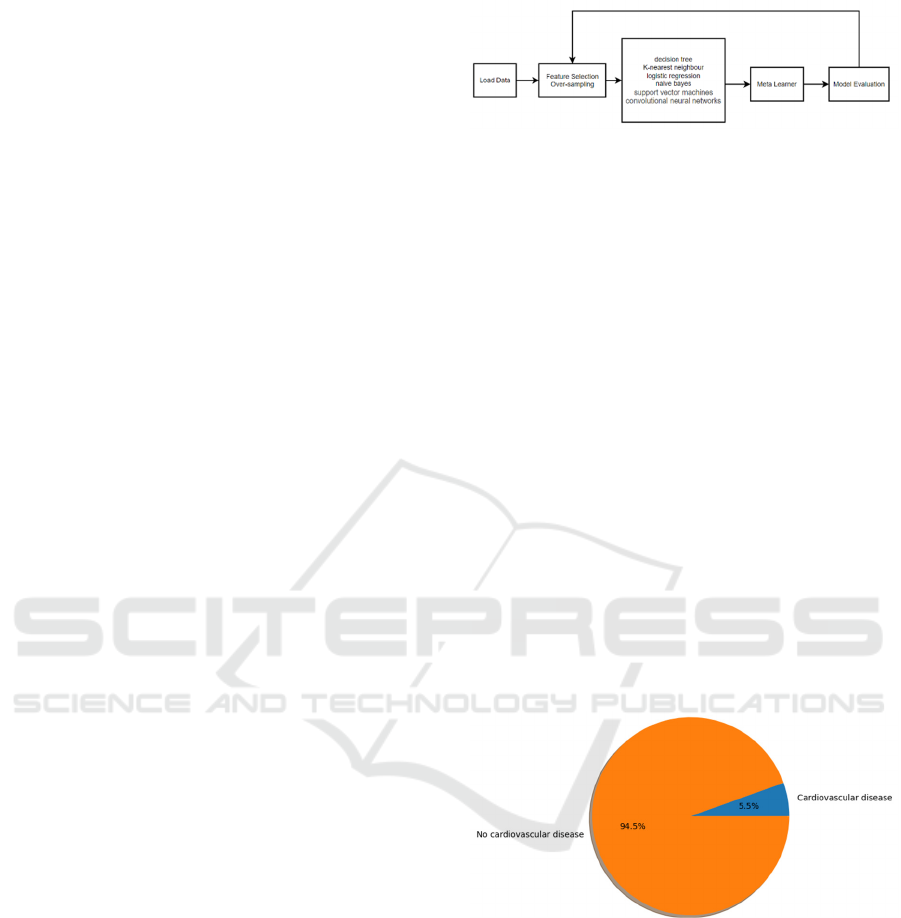
in Figure 1, the model structure will be re-selected
after each training round based on the training results.
Figure 1. The structure of the experimental model (Photo
credit: Original)
Figure 2 shows the distribution of samples. The
number of samples suffering from heart disease is
higher than the number of samples without heart
disease. There is a class-imbalance in this dataset.
When training a model, the model may be more
inclined to predict classes with a larger sample size,
resulting in classification errors for classes with a
smaller sample size. To solve this problem, the
experiment adopts Undersampling to randomly delete
most of the samples in the dataset. Synthetic Minority
Over Sampling Technique (SMOTE) is also used to
balance the datasets. The general steps of SMOTE are
as follows:
1. Find the k nearest neighbor samples for
each minority class sample.
2. Randomly select a sample from the k
samples as the nearest neighbor sample.
3. Make a copy of the nearest neighbor
sample to generate a new composite sample.
4. Repeat Steps 2-3 until a preset number of
synthetic samples are generated.
Figure 2. The distribution of the data set (Photo credit:
Original).
2.3 Stacking Classifier
Figure 3 briefly illustrates the process of the stacking
algorithm. Stacking uses a meta learner to integrate
the prediction results of multiple base models, which
can compensate for the shortcomings of a single
model, further explore features, and better classify
data.
Convolutional Neural Network’s Stacking Classifier on Cardiovascular Disease
117
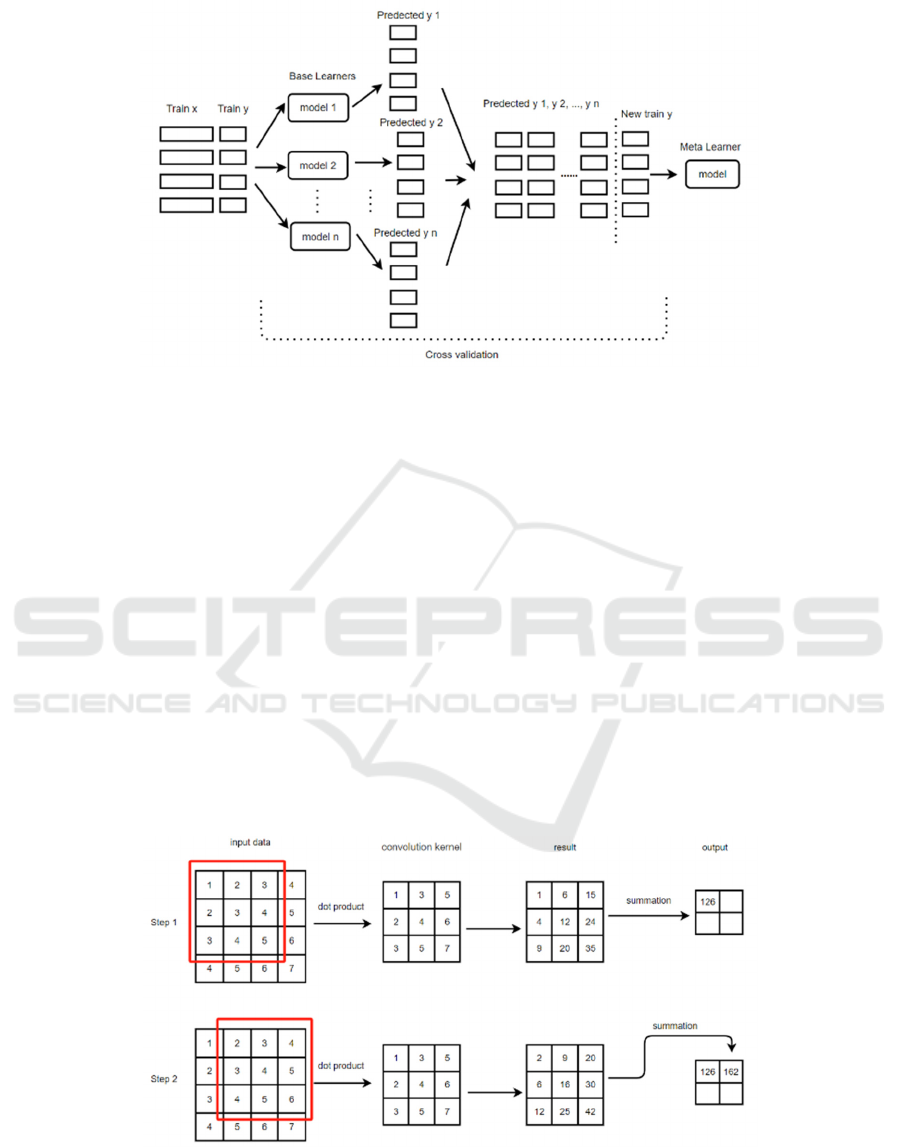
Figure 3. The structure of the stacking (Photo credit: Original).
1. The first layer is base learners, which use the
same or different training sets to train multiple base
learners. Each base learner can use the same or
different classifiers, parameters, or training sets.
2. Use all base learners of the first layer to predict
the new sample set and record the prediction results.
It is best to use the cross-validation method in
practical applications.
3. Combine the predictions of all the base learners
in the first layer and use the predictions as a new data
set.
4. Train the meta-learner using the dataset
obtained in the previous step.
2.4 Base Learners
2.4.1 Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
The convolutional Layer, Pooling Layer, and Fully
Connected Layer constitute the basic unit of CNN
(Sudha & Kumar 2023). The core idea of CNN is to
mine the features of data by using convolution
operations. Then, reduce the dimensionality of the
feature space through pooling operations, and finally
combine advanced features through fully connected
layers to produce the final classification or regression
results.
Convolutional Layer: Figure 4 shows the process
of convolutional layer operation. The convolutional
kernel calculates the inner product of the window
corresponding to the convolutional kernel by sliding
on the input data and generating a feature map. This
feature mapping will be conveyed to the next layer.
The weights can be learned through training.
Figure 4. The working process of the convolution layer (Photo credit: Original).
Pooling Layer: Convolutional layers often mine
numerous features, which need to be appropriately
reduced through pooling operations. Common
pooling operations include Max Pooling and Average
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
118
Pooling, which take the maximum or average value
from multiple features.
Fully Connected Layer: Merge all the features in
the previous layer together to convert into the final
classification or regression result.
2.4.2 Decision Tree (DT)
The samples to be trained start from the root node, and
each internal node contains a decision rule that can
gradually classify the samples. The final samples will
be divided into multiple subsets and form a tree like
structure.
2.4.3 K-nearest neighbour (KNN)
KNN is a simple and intuitive supervised learning
algorithm. The basic principle is to compare K
training samples with the closest similarity to the
predicted sample. The most commonly used decision-
making method is to select the category that appears
most frequently among the K nearest neighbor
samples.
2.4.4 Support Vector Machines (SVM)
The principle of SVM is to set a hyperplane in the
sample space, which maximizes the distance between
the hyperplane and the different class sample points
closest to the hyperplane so that the sample points can
be effectively segmented. The support vectors are the
points closest to the hyperplane, which determines the
decision boundary.
The accuracy of SVM may suddenly decrease as
the number of training samples increases (Deng
2023). Therefore, the training set size of the base
learners composed of SVM in this experiment is
smaller than that of other base learners.
2.4.5 Logistic Regression (LP)
Logistic regression is a classic algorithm that uses the
sigmoid function to establish a relationship between
input features and output features, and its results
directly reflect the probability of the sample
belonging to a certain category.
2.4.6 Naive Bayes (BY)
Naive Bayes is based on the Bayesian theorem, where
the prior probability of a certain feature is known, the
posterior probability is calculated, and then the
sample is classified with the maximum Posterior
Probability.
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
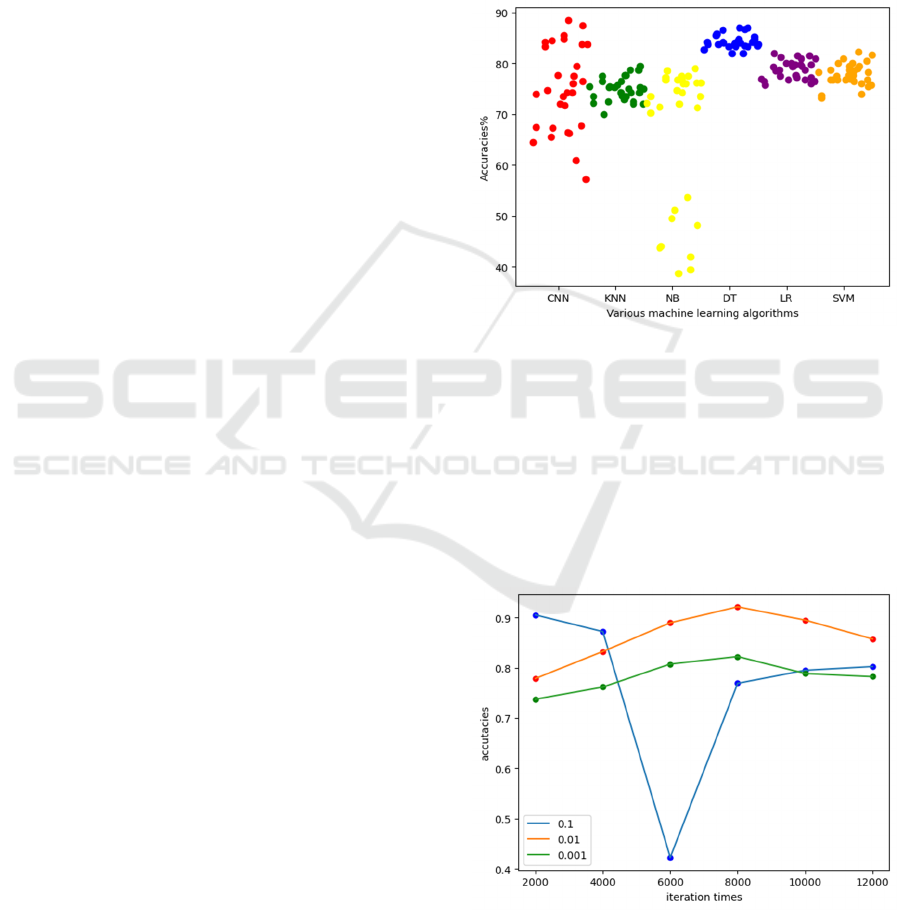
In this experiment, a total of six base learners were
introduced, including DT, KNN, LR, NB, SVM, and
CNN, with a total of 30 models per model. Figure 5
shows the accuracy of all base learners in the
experiment. Among them, the average accuracy of the
CNN classifiers is 74.81%, and the highest accuracy
is 86.75%.
Figure 5. The accuracies of the base learners (Photo credit:
Original).
Figures 6 and 7 respectively show the changes in
accuracy and loss function with increasing iteration
times, and compare them with different learning rates.
When the learning rate is 0.001, the overall
performance of the model is the best, with the highest
accuracy of 91.13. And the loss is lower than other
learning rates.
Figure 6. The accuracies of different learning rates (Photo
credit: Original).
Convolutional Neural Network’s Stacking Classifier on Cardiovascular Disease
119
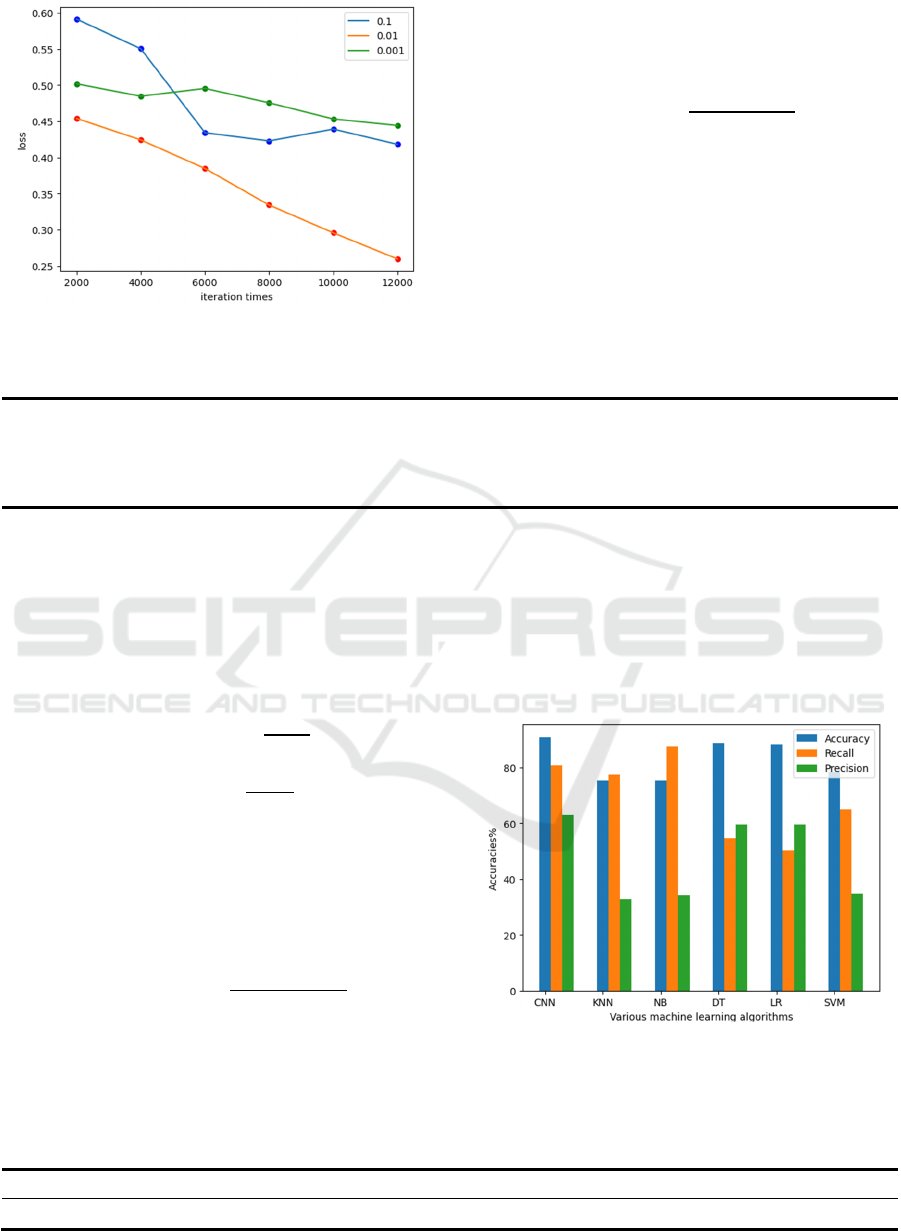
Figure 7. The loss of different learning rates (Original)
Accuracy represents the ratio between the
correctly classified number and the sample size. The
formula is
𝑎𝑐𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑎𝑐𝑦
(1)
Table 1 is the fusion matrix, which defines
parameters in formula (1), where True and False
represent whether the predicted and accurate results
of the model are the same. Positive and Negative
represent the categories of predicted results.
Table 1. The confusion matrix (Table credit: Original).
Actual class
Have cardiovascular disease No cardiovascular disease
Predicted class
Have cardiovascular disease True Positive (TP) False Positive (FP)
No cardiovascular disease False Negative (FN) True Negative (TN)
However, when there is a class ambiguity issue in
the dataset, i.e. the model may perform well in overall
accuracy, but its accuracy may decrease when
predicting minority categories (Amalia et al. 2019).
That is to say, there is bias in the model. Therefore,
when comparing the performance of the model,
Precision and recall were introduced as evaluation
criteria, and the formula is:
𝑝𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛
(2)
𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑙
(3)
F1 score can better measure the overall
performance of the classifier on imbalanced datasets
by comprehensively considering accuracy and recall,
providing a more comprehensive and accurate
performance evaluation. The formula is:
𝐹
2
(4)
Figure 8 and Table 2 show the performance of the
CNN classifier as a meta-learner and compare it with
the other 5 classifiers. CNN achieved an accuracy of
90.9, with the F1 score being the highest among the
six classifiers. The higher the F1 score, the better the
balance between Precision and Recall achieved by the
classifier, and the more accurate its predictive ability
for positive and negative class samples. Therefore,
CNN models have good performance in predicting
cardiovascular disease problems.
Figure 8. The comparison of different meta-learners
(Photo credit: Original).
Table 2. The F1 score of different meta-learners (Table credit: Original).
Algorithm CNN KNN NB DT LR SVM
F1-score 0.7080 0.4608 0.4930 0.5600 0.5462 0.4528
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
120

4 CONCLUSION
Cardiovascular disease is the disease that causes the
highest number of deaths and has a huge impact on
human health. To accurately predict cardiovascular
diseases, ensemble learning has been widely applied
in this field.
In this experiment, CNN was incorporated into
ensemble learning as a base learner and a meta-
learner. When performing feature selection, Relief,
and FCBF algorithms were used, combined with
model prediction accuracy. Undersampling and
SMOTE algorithms were used to solve the class
balance problem of data. The experiment also tested
the performance of DT, KNN, LR, NB, SVM and
CNN as base learners and meta-learners, and
compared them. The results show that CNN has
excellent performance in processing cardiovascular
disease data, with a prediction accuracy of 91.13. It
also outperforms other traditional algorithms in the F1
score.
About suggestions for further research, CNN can
be used in the diagnosis of more diseases in the future,
such as cancer, diabetes, respiratory diseases, etc.
REFERENCES
A. Shroufi, R. Chowdhury, R. Anchala, BMC Public
Health, 13(1), 1-1, (2013).
C. W. Tsao, A. W. Aday, Z. I. Almarzooq, Circulation,
147(8), e93-e62, (2023).
D. Sudheer, A. Potti, N. Anjali Devi, et al, International
Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, 9(8):
27-29, (2021).
D. Zhou, H. Qiu, M. Shen, et al, BMC Medical Informatics
and Decision Making, 23(1), 99. (2023).
J. Abdollahi, B. Nouri-Moghaddam, Iran Journal of
Computer Science, 5(3), 229-246, (2022).
J. Deng, Engineering and Technology, 38, 187-198, (2023).
Kaggle, Indicators of Heart Disease (2022 UPDATE),
2023, available at
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/kamilpytlak/personal
-key-indicators-of-heart-disease
L. Amalia, C. Alejandro, M. Alejandr, et al, Pattern
Recognition, 91, 216-231, (2019).
P. N. Jone, A. Gearhart, H. Lei, et al, JACC: Advances,
1(5), 100153, (2022).
S. Ahmed, S. Shaikh, F. Ikran, et al, Journal of Sensors,
(2022).
V. K. Sudha, D. Kumar, Engineering and Technology, 38,
187-198, (2023).
World Health Organization, Cardiovascular diseases
(CVDs), 2021, available at
https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-
sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
Convolutional Neural Network’s Stacking Classifier on Cardiovascular Disease
121
