
Behavioral Responses to Health Anxiety in Different Populations
Were Analyzed Based on Social Media Platform Data
Chenxiao Yang
Faculty of Hospitality and Tourism Management, Macau University of Science and Technology, 999078 Macau, China
Keywords: User Behaviour, Health Anxiety, Social Media Network Data Analysis, Analysing the Relationship between
Social Media and Public Health Perceptions.
Abstract: As an emerging field of social media platforms in recent years, the public has been paying more and more
attention to their health issues, and at the same time, the problems of distorted information, varying quality of
information, and public health anxiety have emerged one after another. Based on the questionnaire on
"public's behavior towards obtaining health information on the internet" designed in this study, statistical
correlation analysis and regression analysis were used to obtain the behavioral characteristics of social media
users, and it was found that the negative emotions triggered by the public's access to the health information
on the Internet tended to correlate significantly with the topic of the information they were concerned about,
the type of publisher, and the subsequent behavior of the users after they had accessed the information and
that the users' different demographic and behavioral characteristics correlated significantly with their
behavioral characteristics before and after accessing the health information. This study suggests that these
user behavioral characteristics are significantly related to the topic of the information, the publisher type, and
the subsequent behavior after accessing the information. This study suggests that these user behavioral
characteristics are important for social media managers to develop more.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid development of science and
technology and the continuous change of society,
social media has gradually integrated into people's
daily lives and become the main channel of
information dissemination and social interaction. In
this digital era, social media not only influences the
way people communicate but also affects people's
knowledge, concerns, and behaviors about health and
fitness to a great extent. Globally, health and fitness
are highly valued, not only in terms of individual
quality of life but also in the overall health of the
country and the sustainable development of society
("14th Five-Year" National Health Plan 2022). In
2022, the General Office of the State Council issued
the “14th Five-Year Plan for National Health”,
making the popularisation of health knowledge,
participation in health activities, and provision of
health services key tasks in the future to promote the
construction of “Healthy China” (American
Psychiatric Association 2013). As an important
health resource, health information plays an
important role in improving citizens' health literacy
and promoting public health. Social media, as an
emerging platform for information dissemination, has
attracted attention in the health field due to its unique
characteristics and wide audience. In the past, the
promotion of health information mainly relied on
traditional publicity channels, such as television,
radio, and print media (Jourard and Lasakow 1958).
However, with the rise of social media, the way to
promote health information has been revolutionized.
People can use social media platforms to popularise
health-related knowledge, share health-related
experiences, and search for relevant professional
information.
According to the 2022 National Health Insight
Report, the epidemic brought about a rapid increase
in health literacy of 23%, which shows that the
public's health awareness is increasing nowadays, and
they pay more and more attention to their health status
(Lebel et al 2020). However, while social media
disseminates a large amount of health information,
information of varying quality has emerged in large
quantities, triggering problems such as distorted
information and users' inability to accurately judge
the information. At the same time, the public's
318
Yang, C.
Behavioral Responses to Health Anxiety in Different Populations Were Analyzed Based on Social Media Platform Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0012836000004547
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Data Science and Engineering (ICDSE 2024), pages 318-325
ISBN: 978-989-758-690-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

excessive concern for health and reduced tolerance
for disease have led to an increasing prevalence of
health anxiety. “Health anxiety refers to the worry
and concern about one's health status, which is
manifested in the preconceived notion of having a
serious disease and excessive health-related
behaviors in the absence of physical symptoms”
(Bayrak 2020).
The purpose of this paper is to explore in depth
the behavioral characteristics of public access to
health information in the social media era and analyze
its correlation with health anxiety. Taking TicTok,
Xiaohongshu, and Weibo as the data collection
platforms and their main user groups - youth and
middle-aged groups - as an example, this paper adopts
statistical research methods to explore the influencing
factors of the behavioral characteristics of the public's
access to health information and health anxiety and
puts forward corresponding countermeasures and
suggestions for mitigating the problem of health
anxiety triggered by the social media platforms, and
at the same time, enables the management of the
social network platforms to better understand” the
users' self-disclosure behaviors”, to further
optimizing the operation and service model (Landi et
al 2020).
2 METHODOLOGIES
2.1 Research Method
The questionnaire "Survey on the Behaviour of Users
in Obtaining Health Information" was developed in
conjunction with the actual survey. The questionnaire
includes the following four parts: First,
demographics: including gender, age, education,
spousal status, geography, family income, 6 topics.
Second, the frequency and motivation of acquiring
online health information: the frequency was divided
into 5 levels from low to high, and the motivation was
mainly application motivation. Third, the content
tendency of acquiring online health information: the
information content classification includes medical
disease-related prevention and treatment, health care,
fitness and healthy weight loss, and mental health,
and the information type includes graphic
information and video information. Fourth, the
subsequent behaviour of acquiring online health
information, including how the information is
processed after reading, the application behaviour,
and whether it is too much to produce health anxiety
(Nikčević et al 2021).
2.2 Statistical Methods
SPSS 27. 0 was used to conduct statistical analysis to
descriptively analyze the demographic
characteristics, health information acquisition
behaviors, and emotional feedback (Axelsson et al
2020). The Spearman correlation coefficient was
used to analyze the correlation between information
acquisition behaviors and users' demographic
characteristics, the cross-tabular chi-square test was
used to test the correlation between the tendency to
acquire information content and whether or not to
overproduce health anxiety, the subsequent behaviors
of acquiring information and whether or not to
overproduce health anxiety, and the correlation
between the users' behaviors were analysed by
Pearson correlation coefficient (Wheaton and
Messner 2021). The factors influencing the emotional
tendency produced by users were analyzed by binary
logistic regression, and the regression relationship
between user behaviors was examined by linear
regression (Rumker et al 2020). This study was
performed using a test level of α = 0. 05.
3 DATA RESULTS AND
ANALYSES
3.1 Demographic Characteristics
The questionnaire was sent to 196 people and
contained demographic characteristics in six latitudes:
gender, age, education, spousal status, city level, and
household income. The age group was divided into
four age groups: 18-25, 26-35, 35-45, and 46-55 years
old; education was divided into four subgroups: high
school and below, undergraduate, postgraduate, and
doctorate and above; and household income was
divided into five income levels ranging from less than
$150,000 to more than $1.05 million. The survey
results show that the ratio of men to women is about
1:1, and the age of the respondents is mainly
distributed between 18-25 years old and 46-55 years
old, reaching 36.22% and 30.10% respectively. 56.63
percent of the respondents have attained the level of
bachelor's degree. 60.71 percent of the respondents are
married, and 39.29 percent of the respondents are
unmarried. 60.71% of the respondents are married,
39.29% are unmarried, and 60.63% of the respondents
have a bachelor's degree. 60.71% of the respondents
are married. The proportion of respondents with a
household income of less than 150,000 yuan was
55.10 percent, and the proportion of respondents with
Behavioral Responses to Health Anxiety in Different Populations Were Analyzed Based on Social Media Platform Data
319

a household income of 160,000-250,000 yuan was
20.41 percent.
3.2 Current Status of Online Health
Information Behavior
Descriptive statistics on the frequency of access to
health information, motivation, content, and user
follow-up behavior of the respondents. Included
among these, the Frequency of access was divided
into Never, Rarely, Occasionally, Often, and
Frequently.
Application motivation was divided into Access
based on own needs, Substitute for others, and No
access behavior. Information content was divided
into Medical disease prevention and treatment,
Health Care, Fitness and weight loss, and Mental
health. User follow-up behavior was divided into
Netroots, celebrities' recommendation behaviors, and
products, Explanation of principles shared by
ordinary accounts, Real-life health information works
shared by ordinary accounts, and works of health
bloggers. The type of information was divided into
Graphic and Video. Information processing methods
were divided into Like or favorite and no repeat
viewing, like or favorite and will read again when
needed, like or favorite or forward to people around
you and there are multiple readings, only viewed and
no subsequent behavior. Emotional feedback was
divided into Negative (increases health anxiety) and
Positive (helps health).
The results show that the frequency of their access
to the most "often access" or "occasionally pay
attention to ", reached 41.33% and 27.04%
respectively. Access to health information according
to their own needs is the main application of user
access to motivation, reaching 65.82%. Health care is
the most frequently accessed content, reaching
52.55%. More than half of the users will have to mark
behavior for health information and read it twice.
71.43% of the users' emotional feedback presents a
positive state, and 28.57% of the users' emotional
feedback presents a negative state.
About the user behavior using a Likert scale way
to count the distribution of different behavioral
characteristics, the specific average of the user scores
is shown in Table 1.
3.3 Correlation between Information
Access Behavior and Demographic
Characteristics
The results of Spearman correlation coefficient
analysis show that users' behaviours vary according
to different demographic characteristics. Among
them, the user's education, family income, and the
city level they belong to are all significantly
positively correlated with the user's belief in the
health information obtained from the Internet (P <
0.05), in which the more flourishing the city, the
higher the degree of belief in the health information,
which is analysed for the following two reasons, the
first is that the Internet habits are different between
different city levels, and some underdeveloped cities
may not be so dependent on the Internet, so their
degree of belief will be lower, and the second reason
is that the developed cities are less dependent on the
Internet. The second reason is that the overall
acceptance of developed cities is higher, so the public
will be more willing to accept some new types of
information, while the acceptance of less developed
cities will be lower. There is a significant positive
correlation between users' education and family
income and their willingness to buy the health
products recommended in the work. There is no
significant correlation between the users' education,
family income, and the city level they belong to, and
the frequency of obtaining health information, and the
frequency of forwarding the information after
obtaining it, and the degree of belief (P > 0. 05), see
Table 2.
Table 1: Average distribution of user behavior characteristics.
Behavior Mean score (Likert matrix scale)
Make relevant adjustments in lifestyle habits 2.75
Direct purchase of health products recommended in the work 3.24
Investigate further or seek professional advice on issues of interest 3.14
Frequency of forwarding health-related information obtained from
social media networks to
p
eo
p
le around me.
3.16
Level of trust in health information obtained from the internet 3.99
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
320
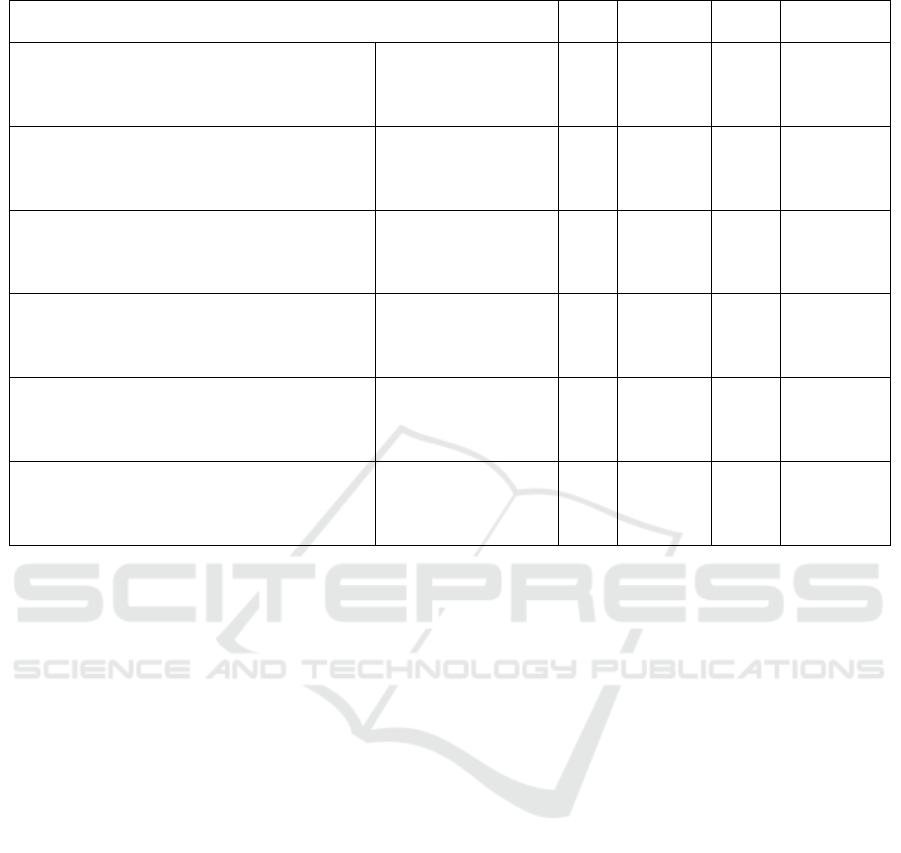
Table 2: Formatting sections, subsections and subsubsections.
Age Education
City
Level
Household
income
Frequency of access to health information
Pearson Correlation
Significance (two-
tailed
)
.070
.329
.014
.846
.042
.558
.008
.907
How often do I forward the health information
I get from social media networks to the people
around me?
Pearson Correlation
Significance (two-
tailed)
-.033
.649
.002
.973
.078
.279
-.028
.699
How much do I trust the health information I
get from social media networks?
Pearson Correlation
Significance (two-
tailed)
-.151
.058
.213
.007
.176
.026
-.196
.013
The extent to which I have made adjustments
to my lifestyle habits based on health
information obtained from social media
networks.
Pearson Correlation
Significance (two-
tailed
)
-.080
.266-
.032
.658
.045
.530
-.031
.668
My willingness to buy the products
recommended in health information works
directly.
Pearson Correlation
Significance (two-
tailed
)
.117
.102
.191
.007
.183
.010
-.079
.273
My willingness to conduct further research or
consult a professional to find out more about a
problem.
Pearson Correlation
Significance (two-
tailed)
-.039
.585
.068
.347
.067
.354
-.010
.891
3.4 Correlation Between Information
Acquisition and Processing
Behaviors and Health Anxiety
The cross-tab chi-square test was used to investigate
the correlation between the motivation for access, the
type of information accessed, and the demographic
characteristics with subsequent emotions. Analysis of
the data shows that there is a significant difference in
the emotions generated by the different topics of
health information that users pay attention to (P <
0.05), where the main body of health information is
divided into four categories, including prevention and
treatment of medical diseases, health care, fitness and
weight loss, and mental health, in which the
proportion of negative emotions generated by users
paying attention to the topic of prevention of medical
diseases is significantly higher than that of the other
three groups, as shown in Table 3. This study suggests
that the reason may be that the information in this area
is more serious, and the possibility of exaggeration is
also higher, more likely to make users feel fearless.
There is a significant difference between the different
publisher types that users tend to follow in terms of
their emotions (P < 0.05), with publisher types
divided into health information shared by netroots
and celebrities(stars), ordinary accounts with
explanations of the principles of information,
ordinary accounts with real-life experience, and
professional health bloggers, in which the proportion
of negative emotions generated by users who tend to
follow health information shared by celebrities and
Internet celebrities is significantly higher than that of
the other three groups. significantly higher than the
other three groups. There is a significant difference in
the emotions generated by users of different age
groups (P < 0.05), and this paper divides age into four
groups: 18-25 years old, 26-35 years old, 36-45 years
old, and 46-55 years old. Among them, the proportion
of negative emotions generated by users in the age
group of 26-35 years is significantly higher than that
of the other three groups, which may be analyzed as
this age group is often in the stage of the greatest
pressure of work and life, and also in the stage of
some significant changes in the state of the body, so
it may be easier for users in this age group to pay too
much attention to their health and thus more prone to
generate negative emotions of health anxiety. In this
study, the degree of users' willingness to buy works
was divided into five measures according to the
Likert scale, and the data showed that the degree of
users' willingness to buy works had a significant
difference in the emotions generated by users (P < 0.
05).
Behavioral Responses to Health Anxiety in Different Populations Were Analyzed Based on Social Media Platform Data
321
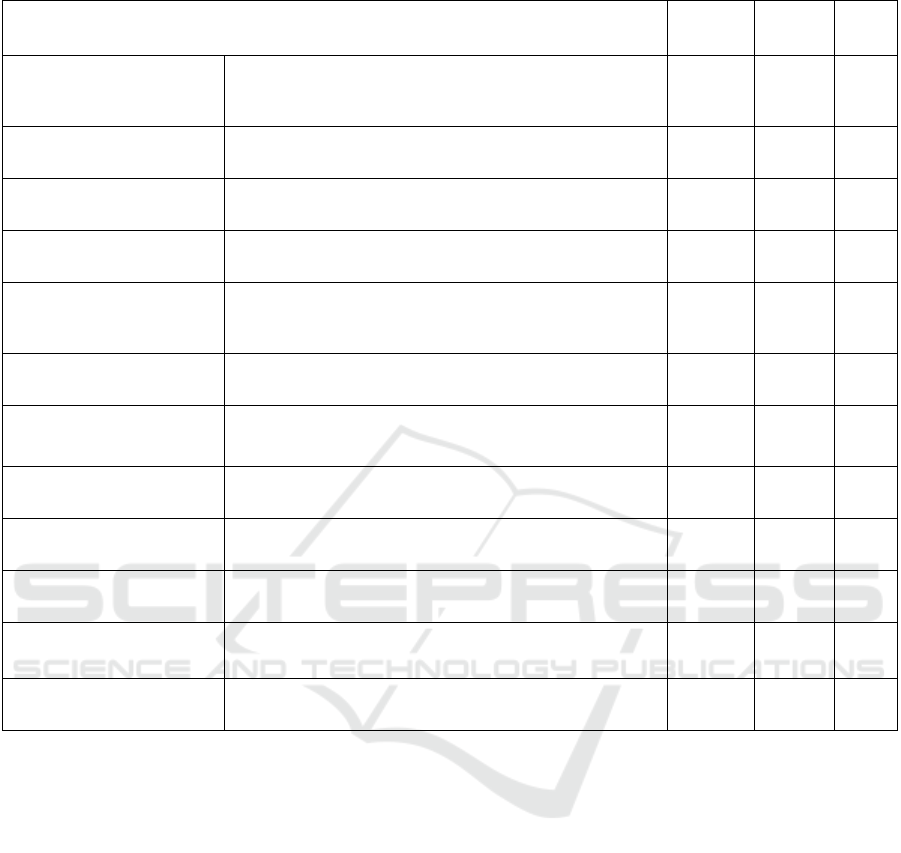
Table 3: Emotional feedback --whether or not to overproduce health anxiety.
Negative Positive Total
Information content Medical disease prevention and treatment 47.7% 52.3% 100%
Health Care 22.3% 77.7% 100%
Fitness and weight loss 25.6% 74.4% 100%
Mental health 20.0% 80.0% 100%
User follow-up behaviour
of the respondents
Netroots, celebrities' recommendation behaviours and
products
69.2% 30.8% 100%
Explanation of principles shared by ordinary accounts 29.2% 70.8% 100%
Real-life health information works shared by ordinary
accounts.
19.6% 80.4% 100%
Works of health bloggers 19.7% 80.3% 100%
Age 18-25years old 31.0% 69.0% 100%
26-35years old 46.7% 53.3% 100%
36-45years old 16.7% 83.3% 100%
46-55years old 23.7% 76.3% 100%
However, there is no significant difference (P > 0.
05) between the users' initiative and passivity in
acquiring health information, the users' way of
dealing with health information after acquiring it, the
users' gender, marital status, education level, family
income status, and the level of the city line of life on
the emotions generated by the users.
3.5 Correlation Between Information
Acquisition and Processing
Behaviour
The Likert scale is used to classify user behaviours
into degrees, including the frequency of acquiring
health information, the frequency of forwarding the
information after acquiring it, the degree of making
relevant adjustments to lifestyle habits after acquiring
health information, the degree of willingness to buy
the products recommended in the health-related
works, the degree of willingness to conduct further
investigation or consult with relevant professionals
after acquiring the information, and the degree of
belief in the health-related information acquired
through the Internet. Pearson correlation coefficient
was used to analyze the correlation between users'
health information acquisition behaviours, and the
data showed that there was a significant positive
correlation between users' health information
acquisition behaviours (P < 0.05), see Table 4.
3.6 Regression Analysis of Information
Access and Health Anxiety
Negative emotions after acquiring online health
information were assigned as 0, and positive
emotions after acquiring online health information
were assigned as 1. Gender, marital status, the
initiative of acquiring health information, the
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
322
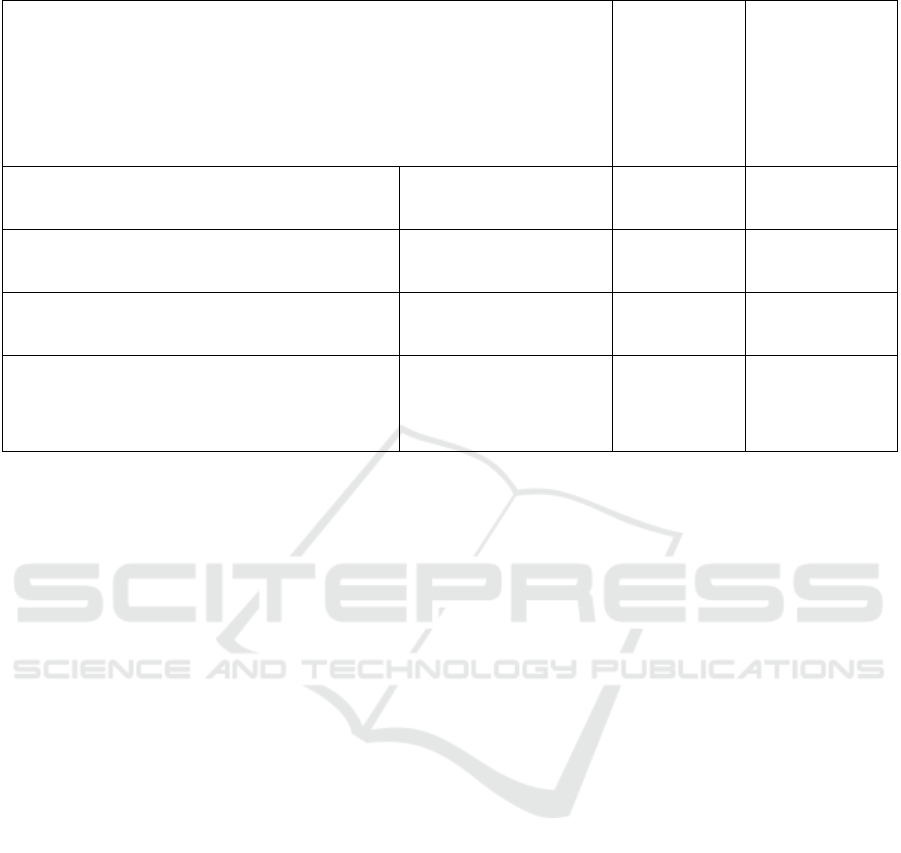
Table 4: Formatting sections, subsections and subsubsections.
Frequency of
access to
health
information
How often I
forward the
health
information I get
from social media
networks to the
people around
me.
The extent to which I have made adjustments to my
lifestyle habits based on health information
obtained from social media networks.
Pearson Correlation
Significance (two-tailed)
.582
.000
.618
.000
My willingness to buy the products recommended
in health information works directly.
Pearson Correlation
Si
g
nificance
(
two-tailed
)
.379
.000
.611
.000
My willingness to conduct further research or
consult a professional to find out more about a
p
roblem.
Pearson Correlation
Si
g
nificance
(
two-tailed
)
.445
.000
.584
.000
How much I trust the health information I get from
social media networks.
Pearson Correlation
Significance (two-tailed)
.235
.003
.433
.000
motivation to apply it, the topic of the information,
the type of information, the type of publisher, the
user's subsequent processing behaviours, and the six
user behaviours of the survey respondents were used
as the independent variables in the biclassified
logistic regression analysis, using the direct entry
method to screen the independent variables, with a
test level of 0. 05, in which gender, marital status, the
initiative to obtain health information, application
motivation, information topics, information types,
publisher types, and user follow-up processing
behaviour were set up as dummy variables, with the
following categories: female, married, equal
frequency of active searching and passive obtaining
of information, no application motivation, mental
health category topics, short video category works,
health category works, and user behaviours, short
video type works, health bloggers, and no follow-up
processing behaviour as reference.
Among them, there is a significant difference for
the four different treatments after obtaining health
information, with Treatment 1 (the behaviour that
users will only like or favorite and will not read it
twice) generating 0.209 times more positive
sentiment for each additional unit. Treatment 2
(behaviours where users will only like or favorite and
read twice if necessary) produced 1.191 times more
positive sentiment per unit increase. Treatment 3
(behaviours where users will like, favorite, and
retweet) produces 1.277 times more positive
sentiment per unit increase. For the degree of users'
willingness to purchase products recommended in
health information works and the emotions generated
by them, each unit increase in the level of willingness
to make relevant adjustments in lifestyle habits after
accessing health information produces 3.351 times
more positive sentiment.
3.7 Regressivity Between Information
Acquisition and Processing
Behaviour
Each of the five subsequent behaviours of users'
access to health information was taken as the
independent variable, and the frequency of public
access to health information was selected as the
dependent variable, where the standardized
coefficient Beta indicates the correlation between the
dependent variable and the independent variable, and
the constant denotes the longitudinal intercept
between the dependent variable and the y-axis when
the dependent variable is zero. The results show a
primary linear regression relationship between all
user behaviours. Among them, the frequency of users'
attention to health information only shows a
significant linear relationship with the frequency of
users' willingness to forward health information to
people around them and the degree of users'
willingness to make adjustments to their lifestyle
habits after obtaining health information, with linear
regression equations of Y=0.202X+1.681 and
Y=0.365X+1.681, respectively, and the linear
regression equations of Y=0.202X+1.681 and
Y=0.365X+1.681, respectively. The three behaviours
Behavioral Responses to Health Anxiety in Different Populations Were Analyzed Based on Social Media Platform Data
323
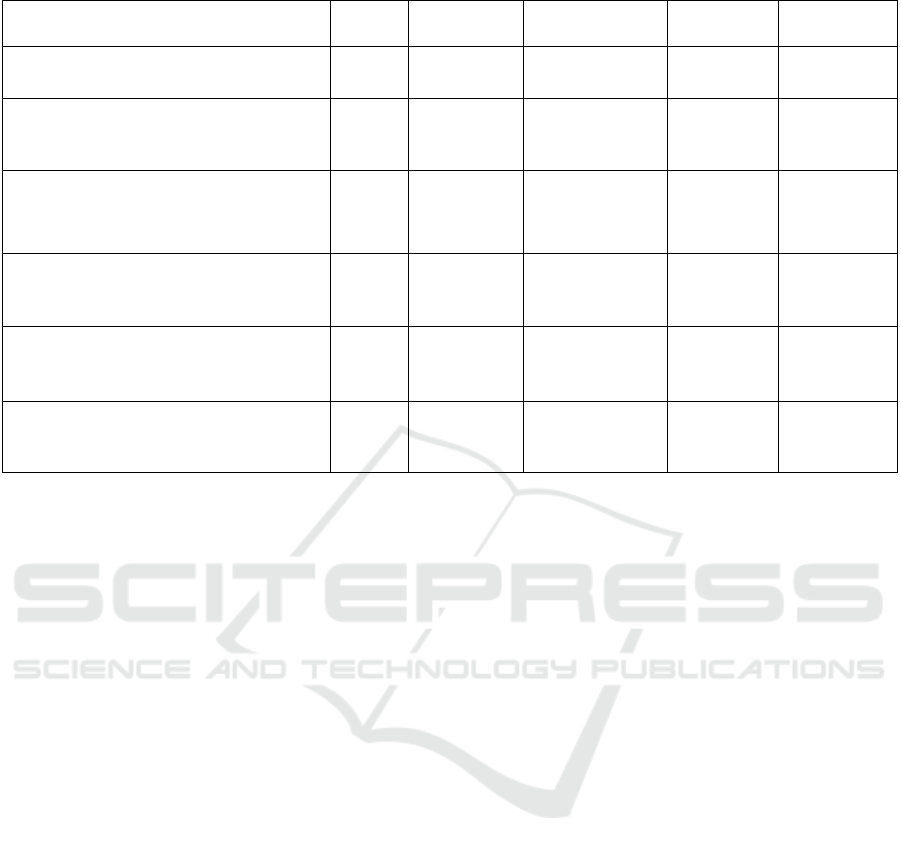
Table 5: Frequency of access to health information.
B
Standardised
Error
Standardized
coefficient Beta
Significance numbering
Constant 1.681 .266 .000 1, 2, 3, etc.
How often do I forward the health
information I get from social media
networks to the people around me?
.202 .090 .201 .027
1.1, 1.2, 1.3,
etc.
The extent to which I have made
adjustments to my lifestyle habits based
on health information obtained from
social media networks.
.365 .085 .374 .000
1.1.1, 1.1.2,
1.1.3, etc.
My willingness to buy the products
recommended in health information
works directly.
-.034 .090 -.035 .705
My willingness to conduct further
research or consult a professional to find
out more about a problem.
.053 .080 .059 .512
How much do I trust the health
information I get from social media
networks?
-.011 .074 .014 .878
of the degree of users' willingness to recommend
health products, the degree of users' willingness to
further investigate or consult professionals who want
to understand the problem, and the frequency of users'
attention to health information and the degree of
users' belief in health information do not have a
significant linear regression relationship with the
frequency of users' attention to health information, as
shown in Table 5.
4 DISCUSSION
The commercial nature of social media brings
confusion to the public's health needs is the objective
background of this study, and it is important to
consider whether the information that social media
users pay attention to is the initial needs of the users
themselves or the information environment that the
corresponding managers and publishers of social
media want the users to receive. Based on these
unchangeable objective phenomena, in-depth
research on the information acquisition and
processing behaviour of social media users and the
impact of acquired online health information on their
behaviour is the focus of subsequent research.
5 CONCLUSION
This study found that there are corresponding
behavioural patterns in users' access to health
information. Users' frequency of accessing health
information, education level, family income, and city
level are all significantly correlated with the degree
of belief in the health information they obtain online.
Users' frequency of accessing health information,
education level, and family income are all
significantly related to their willingness to use the
health products recommended in the work. The
emotions generated by users after accessing health
information on the Internet are an important influence
on health anxiety, and user behaviour has a certain
degree of relevance to the generation of related
emotions. Among them, the subject of the
information that the user pays attention to, the type of
publisher that the user follows, the degree of
willingness to buy the products recommended in the
health-related works, and the age of the user
significantly influence the generation of the related
emotions. Therefore, the current situation of health
information acquisition under different demographic
characteristics should be further promoted according
to the corresponding behavioural characteristics, and
since the behaviour of users in acquiring health
information significantly affects the emotions
generated by users, managers of social media
ICDSE 2024 - International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
324

platforms should appropriately guide the behaviour of
social media users to reduce the occurrence of health
anxiety.
REFERENCES
The Central People's Government of the People's Republic
of China, Circular of the General Office of the State
Council on the Issuance of the "14th Five-Year"
National Health Plan (2022)
https://www.wenhuasd.com/document/875.html.
American Psychiatric Association, American Psy Publish
(2013)
S. M. Jourard, P. Lasakow, J Abnormal Soci Psychology 1,
91-98 (1958)
S. Lebel, B. Mutsaers, C. Tomei, Measure Course Cor Plos
One 15(7), e0234124 (2020).
S. Bayrak, Int J Soc Psychiatr 5, 504-511 (2020)
G. Landi, K. I. Pakenham, G. Boccolini, S. Grandi, E.
Tossani, Front Psychol 11, 2195 (2020)
A. V. Nikčević, C. Marino, D. C. Kolubinski, J Affect
Disorders 279, 578-584 (2021)
E. Axelsson, E. Andersson, B. Ljótsson, D. Björkander,
Jama Psychiatry 9, 915-924 (2020)
M. G. Wheaton, G. R. Messner, J Obsess-Compuls Rel 28,
100605 (2021)
L. Rumker, L. Talkar, J. Torous, J Medical Inter Res
22(10), e22635 (2020).
Behavioral Responses to Health Anxiety in Different Populations Were Analyzed Based on Social Media Platform Data
325
