
BlueDoS: A Novel Approach to Perform and Analyse DoS Attacks on
Bluetooth Devices
Poonam Namdeo Shelke
a
, Saurav Gupta
b
and Sukumar Nandi
c
Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati, India
Keywords:
Bluetooth, Bluetooth Low Energy, DoS Attack, Bluez, l2ping, hcitool, Packet Flooding.
Abstract:
The use of Bluetooth devices is surging across the digital landscape. As the diversity and quantity of these de-
vices increase, so does the focus on security within Bluetooth technology. Our research primarily concentrates
on DoS attacks on Bluetooth devices. We discovered that existing tools rely on the Linux Bluetooth drivers
and utilities provided by the Bluez protocol stack. Because of this reliance, these tools require full command
over Bluetooth communication as they are confined to the functionalities offered by the underlying protocol
stack. To address this limitation, we developed a Bluetooth driver binary using Bluez Linux protocol stack, our
testbed named ”Bluedos”. As Bluedos is developed using C, similar to other Linux drivers, it provides more
flexibility in packet creation and handling Bluetooth connections at the operating system level. With ”Blue-
dos”, we extensively analysed DoS attacks on various Bluetooth devices, using headphones from reputable
brands to illustrate potential attack vectors. We also analysed the ramifications of DoS attacks on different
connection parameters, such as response time, and introduced a novel l2connect and an l2connect flooding
attack against Bluetooth devices. We validated our findings using a Bluetooth sniffer and drew conclusions
based on our analyses.
1 INTRODUCTION
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard designed
for short-range data transfer among supported de-
vices and the creation of Wireless Personal Area Net-
works(WPANs). Operating between 2.402 and 2.480
GHz in unlicensed yet regulated ISM bands, Blue-
tooth offers two mechanisms, which are Classic Blue-
tooth, mainly employed for continuous data trans-
mission, such as headsets and Bluetooth Low En-
ergy, which is used for periodical bursty data trans-
missions, such as smartwatches or fitness bands. The
simpler security mechanisms BLE devices use to con-
serve energy can inadvertently compromise commu-
nication security and provide an advantage to adver-
saries (C
¨
asar et al., 2022) (Kwon et al., 2016).
BLE and Classic Bluetooth connections are estab-
lished via a single key exchange mechanism(Phan and
Mingard, 2012). If compromised, it opens the door
to various attacks (Jakobsson and Wetzel, 2001), in-
cluding passive attacks, where the attacker gains con-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-8177-5882
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-3014-6929
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5869-1057
nection access and listens to the data; Man-In-The-
Middle attacks, where the attacker impersonates an
authorised user and intercepts information; and DoS
attacks, which can prevent an authorised user from
accessing data or connecting to the devices.
Our research primarily focuses on Denial of Ser-
vice (DoS) and User De-authentication attacks (Has-
san et al., 2018). In DoS attacks, we aim to flood the
connection to prevent authorised users from connect-
ing to the intended devices. In User De-authentication
attacks, we attempt to disconnect a user already con-
nected to a device, rendering the device and technol-
ogy unusable.
We use headsets from reputed brands such as One-
plus and BoAt for DoS attack experiments. We em-
ploy a system with Linux as the underlying OS to
send Bluetooth packets to these devices. We devel-
oped our testbed to execute the DoS attacks on Blue-
tooth devices and collected the statistics of the attack,
including a comprehensive analysis of the attack’s im-
pact on the devices’ response time. We also analyse
the exchange of Bluetooth packets between currently
connected devices using the nrf52840 Bluetooth snif-
fer and Wireshark (NORDIC, 2021).
838
Shelke, P., Gupta, S. and Nandi, S.
BlueDoS: A Novel Approach to Perform and Analyse DoS Attacks on Bluetooth Devices.
DOI: 10.5220/0012845700003767
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT 2024), pages 838-843
ISBN: 978-989-758-709-2; ISSN: 2184-7711
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

2 RELATED WORK
As Bluetooth devices become increasingly integral to
our daily routines, the study of Bluetooth security
has emerged as a compelling research area. A sub-
stantial body of research is dedicated to the security
facets of Bluetooth technology. Given the ubiquity of
Bluetooth across numerous devices and the growing
adoption of BLE, the security standards for BLE de-
vices are continually evolving. To secure Bluetooth
connections, devices employ various strategies, in-
cluding using randomized MAC addresses to conceal
the original MAC address during connection adver-
tisement. Bluetooth devices also utilise Frequency
Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS)(Wang, 2001) to
periodically switch frequencies within a single con-
nection, thereby safeguarding against eavesdropping.
Additionally, encryption is used to maintain the con-
fidentiality of data shared between devices (Barua
et al., 2022).
Despite these security measures, Bluetooth de-
vices remain vulnerable to a range of attacks, in-
cluding Man-In-The-Middle attacks, DoS attacks via
l2ping, and various strategies to predict the original
MAC address of the Bluetooth device.
In the context of DoS attacks on Bluetooth de-
vices, the majority of research employs standard
l2ping request packets (Y
¨
uksel et al., 2022) (Ditton
et al., 2020). l2ping uses l2cap internally to transmit
ping echo requests. These requests are sent continu-
ously and at a high rate, leaving the receiving device
with insufficient capacity to manage them. This leads
to a deluge of l2ping packets at the receiver’s end, ren-
dering the receiver incapable of handling additional
requests and resulting in a DoS attack (Barua et al.,
2022). However, the research must thoroughly anal-
yse the different request parameters on the attack’s
success.
Another common security measure implemented
by all Bluetooth devices is the concealment of the de-
vice’s MAC address. Bluetooth devices use random
MAC addresses to transmit advertising packets and
employ the read MAC address at the time of connec-
tion establishment. All attacks, including the l2ping
DoS attack, require the device’s original MAC ad-
dress to proceed. The original MAC address serves
as the device’s unique identity for sending packets.
Tucker et al., in their study titled ”Blue’s Clue,”
demonstrated that the original MAC address can be
obtained for every discoverable and non-discoverable
device (Tucker et al., 2023). Considering this re-
search, we assume that we have access to the original
MAC addresses of the devices, and our focus is on
executing DoS attacks on the devices.
3 OUR CONTRIBUTIONS
The primary objective of our research is to scrutinise
the effects of DoS attacks on Bluetooth devices. Our
contributions are as follows:
• We have developed a unique Bluetooth testbed,
”Bluedos”, designed to execute and examine var-
ious Bluetooth attacks.
• Our testbed boasts several unique features absent
in all other online instruments for analysing Blue-
tooth DoS attacks. These features include:
– Compatibility with all basic features fine-tuned
to support l2ping and hcitool, which are crucial
for DoS attack analysis.
– Support for sending l2connect requests.
– Capability to send flood of l2connect requests.
– Support executing flooding attacks using vari-
ous commands of hcitools, a feature not sup-
ported by the standard hcitool or other tools.
– Ability to perform all the Bluetooth DoS at-
tacks sequentially and automatically, then gen-
erating a summary of potential attacks on spe-
cific Bluetooth devices.
• We have introduced a novel connection flooding
attack that can be deployed against Bluetooth de-
vices. This attack disconnects the Bluetooth de-
vices and maintains the disconnection by sending
a deluge of requests.
• We have conducted an in-depth analysis of ad-
vertising packets using the Bluetooth sniffer
nrf52840 BLE sniffer.
4 METHODOLOGY
Our research primarily focuses on analysing the im-
pact of DoS attacks on various Bluetooth devices,
specifically headphones from renowned brands such
as Oneplus and BoAt. We initially attempted to utilise
available tools for the attack (Y
¨
uksel et al., 2022).
However, they only met our requirements to a lim-
ited extent. This is because most Bluetooth tools are
built on top of the utilities provided by Bluez protocol
stack, limiting their functionality to what is provided
by the utility code they employ.
To overcome these limitations, we developed our
testbed, ”Bluedos”, specifically designed to test Blue-
tooth DoS attacks. Bluedos is built using Linux as the
operating system and Bluez (Qualcomm, 2000), an
open-source Bluetooth protocol stack for Linux. Hav-
ing direct access to the protocol stack and the binaries
made it feasible to create this testbed. Most of the
BlueDoS: A Novel Approach to Perform and Analyse DoS Attacks on Bluetooth Devices
839
tools used by Bluetooth attack scripts, such as l2ping
and hcitool, are part of the Bluez protocol stack.
Our testbed, Bluedos, is publicly available on
GitHub
1
for Bluetooth DoS attack analysis. It can
also be distributed as a binary executable, eliminat-
ing the need for building and installation, which can
be directly used for analysis. Notably, our testbed
supports various attack mechanisms, including sup-
port for l2ping and hcitool attacks. We have also in-
troduced a new attack for l2connect, where we send
a flood of connect requests. It also supports various
flooding attacks with hcitool, which are not part of
the standard hcitool.
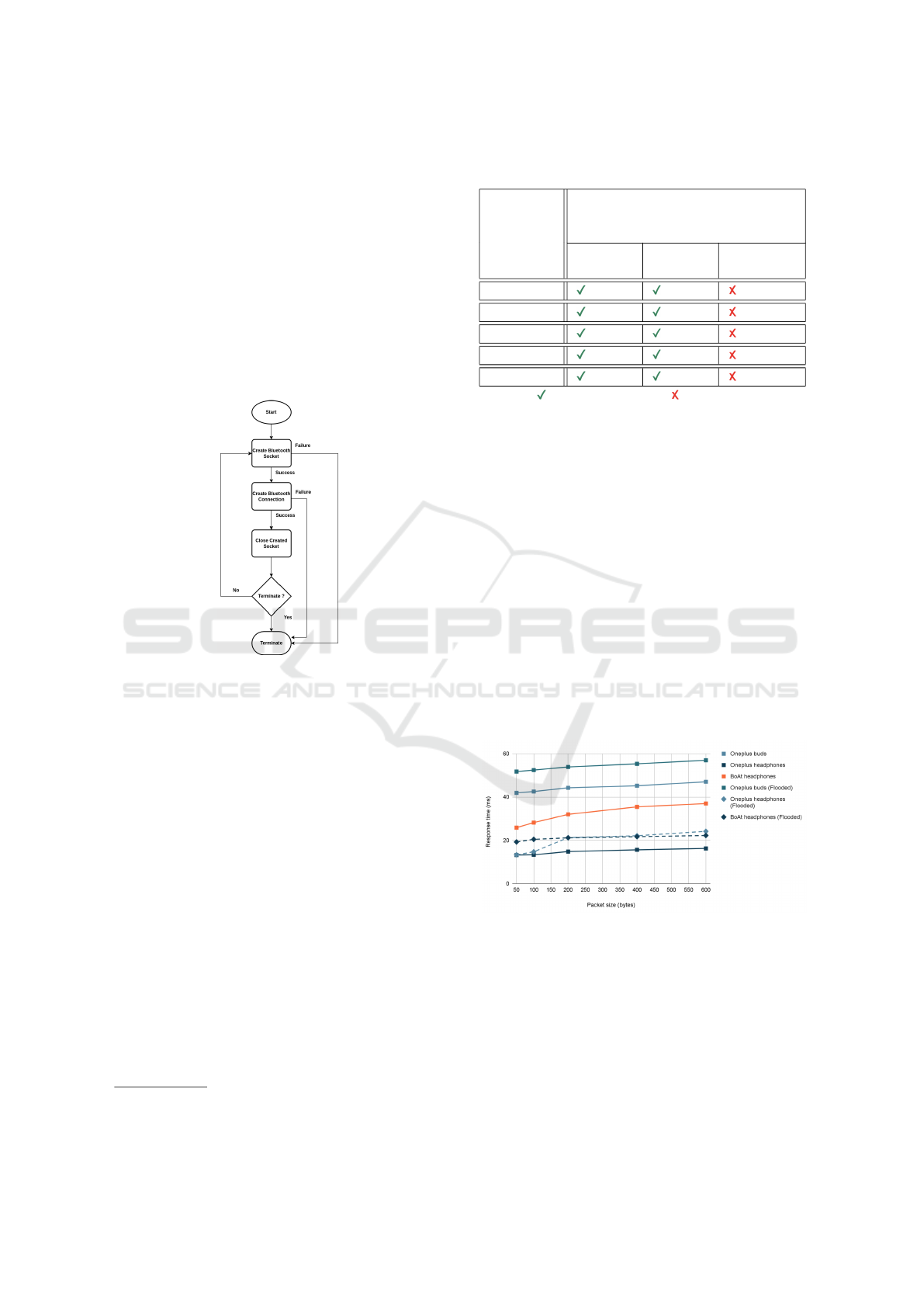
Figure 1: Connection Flooding Attack Flowchart.
The attack methodology for the disconnection at-
tack has been shown in Figure 1. First, we create a
Bluetooth socket, then establish a Bluetooth connec-
tion and close the socket. This process is performed
repeatedly until we decide to terminate it.
5 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
We comprehensively analysed DoS attacks on Blue-
tooth devices from various recognised brands. We
employed l2ping and hcitool to send request pack-
ets to the target devices. However, these tools proved
insufficient for DoS attack experimentation because
they were utility tools meant to support basic Blue-
tooth operations. Bluedos using the Bluez protocol
stack in Linux and used it to conduct extensive exper-
iments on headphones(OnePlus and BoAt) and ear-
buds(OnePlus). The device we’re using for the attack
is equipped with a single Bluetooth adapter, running
the Kali Linux OS and Bluez Linux protocol stack.
1
Bluedos: A Bluetooth test bed, https://github.com/
poonamshelke1712/bluez/pull/1/files
Table 1: l2ping packet size on disconnection of the Blue-
tooth device.
Packet
Size
(Bytes)
Impact on disconnection of the de-
vice for normal and flooded flow
Oneplus
buds
Oneplus
headsets
BoAt
headsets
50
100
200
400
600
Note: ‘ ’ disconnected and ‘ ’ not disconnected
5.1 Experiments with Vanilla l2ping
Vanilla l2ping supports transmitting ping requests to
check the status of a device. We executed a series of
experiments to test the efficacy of this feature using
packets of varying lengths. Additionally, we carried
out tests targeting Bluetooth devices with flooding at-
tacks. The results of these experiments are presented
in Table 1.
We observed that the vanilla l2ping attack was
successfully able to disconnect Oneplus buds and
Oneplus headsets but failed to disconnect Boat head-
sets for different packet sizes. We carried out experi-
ments to measure the packets’ response time. Figure 2
illustrates the response times for various packet sizes
under normal and flooding conditions. The results in-
dicated that the average response is proportional to the
packet size.
Figure 2: Analysis of response time and packet size for
l2ping packets.
We conducted multi-threaded flooding on Blue-
tooth devices to assess the impact of l2ping flooding.
Figure 3 illustrates the impact on response time as the
number of threads used to simulate the flooding attack
increases. Our observations indicate that the devices’
response time is directly proportional to the number
of threads used to send the packets.
SECRYPT 2024 - 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography
840
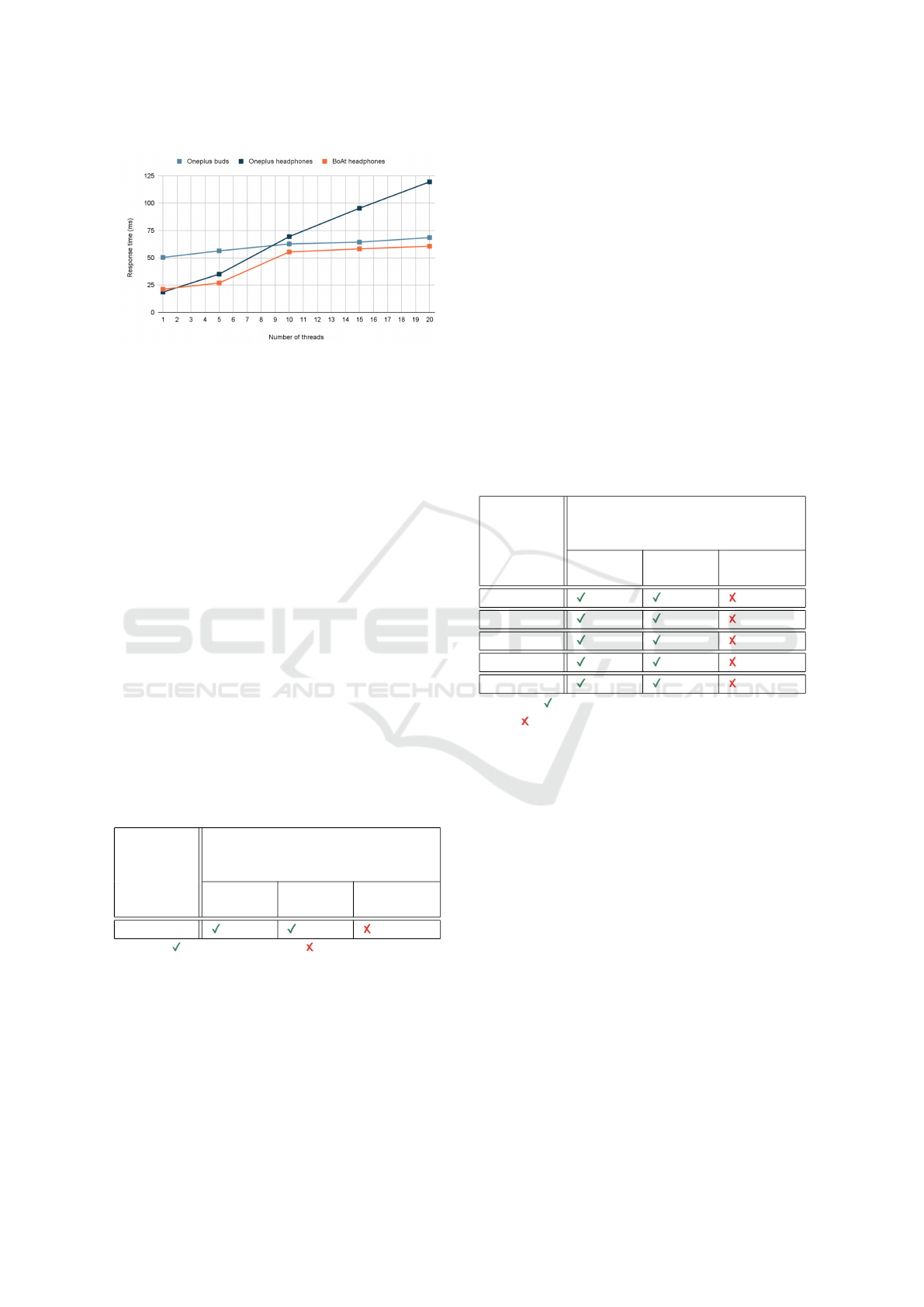
Figure 3: Analysis of response time and number of threads
for l2ping.
5.2 Experiments with Modified l2ping
We modified the l2ping tool to use it for analysing
DoS attacks since the vanilla version is not designed
for this purpose. We reviewed its source code to un-
derstand how l2ping works. l2ping is a component of
the Bluez Linux protocol stack, an open-source distri-
bution under General Public License. Vanilla l2ping
is sufficient to perform a disconnection attack on One-
plus buds and headsets. However, we intended to
determine which code section is responsible for the
disconnection. Our analysis revealed that the afore-
mentioned devices disconnected before transmitting
the packets of the l2ping. We found that an l2cap
socket connection is initiated with the Bluetooth de-
vice before the l2ping request packets are transmit-
ted, which caused the disconnection of the devices.
To confirm our findings, we created an executable bi-
nary that only sends l2cap socket connection requests
to the target device. Our findings are presented in Ta-
ble 2.
Table 2: l2cap connect request on disconnection of Blue-
tooth devices.
Request
type
(l2cap)
Impact on disconnection of the de-
vice
Oneplus
buds
Oneplus
headsets
BoAt
headsets
connect
Note: ‘ ’ disconnected and ‘ ’ not disconnected
During our experiment, we successfully discon-
nected Oneplus buds and headsets. However, we
could not perform a disconnection attack on BoAt
headsets. Similar to Oneplus and BoAt headsets also
respond to connection requests, but they do not re-
lease the existing connection. Upon further study, we
observed that Oneplus does not allow multiple con-
nections simultaneously, but BoAt headsets do allow
them to connect to multiple central devices simulta-
neously. While it is possible to disconnect the device
using ”l2cap” connect requests, the device can recon-
nect upon reconnection.
5.3 l2cap Connection Flooding Attack
l2cap can disconnect a device; however, the attack
is not persistent, and devices can establish a connec-
tion again. To overcome this limitation, we developed
a connection flooding attack that continuously sends
connection requests to keep the device disconnected.
We also experimented with sending these requests at
periodic intervals instead of a flood to analyse the at-
tack’s performance on different devices at different
flooding intervals.
Table 3: l2capconnect request flooding on continuous dis-
connection of the Bluetooth devices.
Request
interval
(sec)
Impact on continuous disconnec-
tion of the device
Oneplus
buds
Oneplus
headsets
BoAt
headsets
10
5
2
1
0 (flood)
Note: ‘ ’ remains disconnected;
and ‘ ’ Connection re-established
The result of connect request flooding for differ-
ent intervals on continuous disconnection of the de-
vice is shown in Table 3. Connect request flooding
keeps Oneplus devices disconnected. Table 4 shows
the time devices take to reconnect and remain con-
nected before the subsequent disconnection. Lower
time signifies that the devices remain connected for a
shorter time before they are disconnected again. This
analysis helps us learn the interval a device remains
disconnected before re-initiating its connection. We
can use this information to optimise the attacks better.
Since BoAt headphones have been impervious to
all our previous attacks, we used multiple devices ca-
pable of performing all forms of l2ping and l2connect
attacks, including flooding attacks, to disconnect the
headphones. We also opened multiple connections
and kept them open. However, our attempts failed
to achieve any consistent disconnects. We believe
that BoAt devices allow connections with multiple de-
vices(3 or more) simultaneously. We would require
more attacking devices to compensate for the same.
BlueDoS: A Novel Approach to Perform and Analyse DoS Attacks on Bluetooth Devices
841
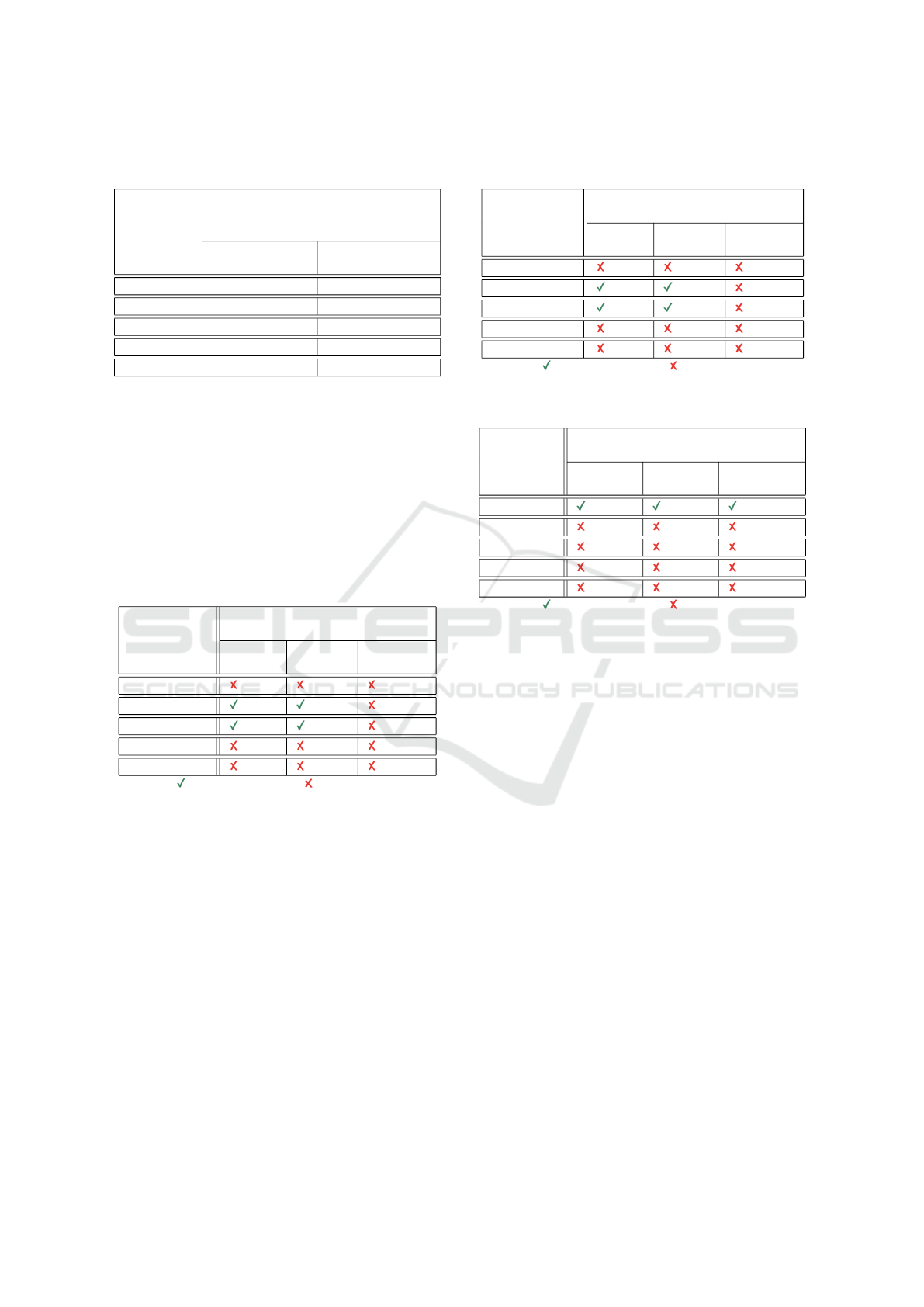
Table 4: Connect request interval on time-period before the
next disconnection.
Request
Interval
(sec)
Impact on the average time for which
connection is established before next
disconnection
Oneplus buds Oneplus
headsets
10 7 0
5 3 0
2 3 0
1 3 0
0 (flood) 3 0
5.4 Experiments with Vanilla hcitool
We experimented with hcitool, which performs utility
functions with Bluetooth devices. It is far from be-
ing fabricated precisely to perform attacks on devices.
However, we use name, info, connect (cc), reconnect
(lecc) and leinfo features of hcitool to test attacks. Ta-
ble 5 shows the impact of various hcitool commands
on the disconnection of Bluetooth devices.
Table 5: hcitool commands on successful disconnection of
the Bluetooth device.
hcitool com-
mand
Impact on disconnection of the
device for normal flow
Oneplus
buds
Oneplus
headsets
BoAt
headsets
name
info
connect (cc)
lecc
leinfo
Note: ‘ ’ disconnected and ‘ ’ not disconnected
5.5 Experiments with Modified hcitool
Vanilla hcitool is not designed to analyse DoS attacks.
As a result, it lacks essential features such as flood-
ing and periodic request analysis. To overcome these
limitations, the functionalities of hcitool have been
incorporated into our testbed, complete with support
for flooding and periodic requests. The results of hci-
tool flooding attacks on various Bluetooth devices are
shown in Table 6.
5.6 D-DoS Connection Flooding Attack
We have performed D-DoS attacks on Bluetooth
headsets. We used two attacking devices to carry out
the D-DoS attack. We also executed attacks that have
been discussed earlier using multi-device D-DoS.
Table 6: Results of hcitool commands on successful discon-
nection of the Bluetooth device with flooded flow.
hcitool com-
mand
Impact on disconnection of the
device for flooded flow
Oneplus
buds
Oneplus
headsets
BoAt
headsets
name
info
connect (cc)
lecc
leinfo
Note: ‘ ’ disconnected and ‘ ’ not disconnected
Table 7: D-DoS attacks on successful continuous discon-
nection of the Bluetooth device.
command
name
Impact for flooded flow for D-DoS
Oneplus
buds
Oneplus
headsets
BoAt
headsets
connection
ping
name
info
cc
Note: ‘ ’ disconnected and ‘ ’ not disconnected
According to the data presented in Table 7, the D-
DoS connection flooding attack successfully discon-
nected the BoAt headsets, which failed previously.
6 EXPERIMENTS WITH SNIFFER
Bluetooth packet sniffing is a method of intercepting
Bluetooth communication in its vicinity. We use the
nrf52840 Bluetooth packet sniffer (NORDIC, 2021).
As shown in Figure 4. We used an attacker machine
equipped with our ”Bluedos” testbed, a Linux-based
computer. We used Android mobiles and headsets of
popular brands such as Oneplus and BoAt for target
devices.
The sniffer listens to the advertisement packets in
the vicinity. Once the target devices have established
a connection, we direct the sniffer to intercept the spe-
cific connection’s packets. Using the attacker’s ma-
chine, we initiate a DoS attack using our method de-
fined earlier. The sniffer can capture all the packets
exchanged during the connection, revealing flags and
parameters for each packet. We use this information
to analyse the Bluetooth communication.
SECRYPT 2024 - 21st International Conference on Security and Cryptography
842

Figure 4: Experimental setup for sniffer for packet analysis.
6.1 Observations with Bluetooth Sniffer
Using the Bluetooth sniffer, we have made the follow-
ing key observations:
• Oneplus headsets and buds respond to adver-
tisement requests and cease transmission once a
connection is established. This observation led
to the development of our l2connect attack and
l2connect flooding attack. Detailed findings are
presented in Table 4.
• BoAt headsets behave differently, sending adver-
tising requests and accepting connections from
other devices even after a connection. This be-
haviour suggests that the l2connect attack is inef-
fective on the BoAt headsets. Detailed results are
presented in Table 2 and Table 4.
7 CONCLUSIONS
Our work analyses various DoS attack mechanisms
on Bluetooth devices. DoS attacks generally utilize
the basic version of l2ping. However, it lacks com-
prehensive DoS attack analysis capabilities. We de-
veloped our testbed, ”Bluedos”, to address this limi-
tation using the Bluez Linux protocol stack. Our ex-
periments involve sending l2ping requests and l2ping
request flooding to target devices and studying the at-
tack’s impact on various parameters like device re-
sponse time.
Observing the device’s behaviour, we introduced
two novel attacks, the l2connect attack and the
l2connect flooding attack. We successfully demon-
strated the attack’s efficacy against the Bluetooth de-
vices under study. The flooding attack disconnected
devices and prevented them from connecting to any
other device, rendering them unusable. We also exe-
cuted a D-DoS attack to analyse the impact of mul-
tiple attacking devices, which successfully discon-
nected the Boat headset, previously impervious to dis-
connection by a single attacking device. We attribute
this behaviour to a feature that allows devices to con-
nect with multiple devices simultaneously.
Finally, the Bluetooth sniffer allowed us to cross-
validate all observations and provide reasoning for the
behaviour of the Bluetooth devices in response to var-
ious packets and attack mechanisms used for the DoS
attack analysis.
REFERENCES
Barua, A., Al Alamin, M. A., Hossain, M. S., and Hossain,
E. (2022). Security and privacy threats for bluetooth
low energy in iot and wearable devices: A compre-
hensive survey. IEEE Open Journal of the Communi-
cations Society, 3:251–281.
C
¨
asar, M., Pawelke, T., Steffan, J., and Terhorst, G. (2022).
A survey on bluetooth low energy security and pri-
vacy. Computer Networks, 205:108712.
Ditton, S., Tekeoglu, A., Bekiroglu, K., and Srinivasan, S.
(2020). A proof of concept denial of service attack
against bluetooth iot devices. In 2020 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Pervasive Computing and Com-
munications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), pages
1–6.
Hassan, S. S., Bibon, S. D., Hossain, M. S., and Atiquzza-
man, M. (2018). Security threats in bluetooth technol-
ogy. Computers & Security, 74:308–322.
Jakobsson, M. and Wetzel, S. (2001). Security weaknesses
in bluetooth. In Cryptographers’ Track at the RSA
Conference, pages 176–191. Springer.
Kwon, G., Kim, J., Noh, J., and Cho, S. (2016). Blue-
tooth low energy security vulnerability and improve-
ment method. In 2016 IEEE International Conference
on Consumer Electronics-Asia (ICCE-Asia), pages 1–
4. IEEE.
NORDIC (2021). NRF52840 bluetooth sniffer. https:
//www.nordicsemi.com/products/nrf52840.
Phan, R. C.-W. and Mingard, P. (2012). Analyzing the se-
cure simple pairing in bluetooth v4. 0. Wireless Per-
sonal Communications, 64:719–737.
Qualcomm (2000). BlueZ bluetooth protocol stack. https:
//github.com/bluez/bluez.
Tucker, T., Searle, H., Butler, K., and Traynor, P. (2023).
Blue’s clues: Practical discovery of non-discoverable
bluetooth devices. In 2023 IEEE Symposium on Secu-
rity and Privacy (SP), pages 3098–3112.
Wang, H. (2001). Overview of bluetooth technology. State
College, PA: Department of Electrical Engineering,
Pennsylvania State University.
Y
¨
uksel, T., AYDIN,
¨
O., and DALKILIC¸ , G. (2022). Per-
forming dos attacks on bluetooth devices paired with
google home mini. Celal Bayar University Journal of
Science, 18(1):53–58.
BlueDoS: A Novel Approach to Perform and Analyse DoS Attacks on Bluetooth Devices
843
