
Modelling of an Untrustworthiness of Fraudulent Websites Using
Machine Learning Algorithms
Kristína Machová
a
and Martin Kaňuch
Department of Cybernetics and Artificial Intelligence, Technical University of Košice, Letná 9, Košice, Slovakia
Keywords: Untrustworthy Content, Fraudulent Websites, Detection Models, Machine Learning, Neural Networks.
Abstract: This paper focuses on learning models that can detect fraudulent websites accurately enough to help users
avoid becoming a victim of fraud. Both classical machine learning methods and neural network learning were
used for modelling. Attributes were extracted from the content and the structure of fraudulent websites, as
well as attributes derived from the way of their using, to generate the detection models. The best model was
used in an application in the form of a Google Chrome browser extension. The application may be beneficial
in the future for new users and older people who are more prone to believe scammers. By focusing on key
factors such as URL syntax, hostname legitimacy, and other special attributes, the app can help prevent
financial loss and protect individuals and businesses from online fraud.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Internet gives us many advantages, but there are
also disadvantages and threats to this wonderful tool.
Hacker attacks, stolen personal data and whitewashed
accounts are often mentioned in the media. Many
people still fall into the trap of scammers even though
there is a huge effort by the authorities to stop these
scams. What do these scams look like? Can they be
stopped? How can such scams be avoided and how
can internet users be alerted using a smart app? This
article offers answers to these questions and possible
solutions.
Phishing attacks have become a major concern in
the digital age, posing significant threats to users'
online security. Detecting and preventing phishing
websites is crucial to protect individuals and
organizations from falling victim to cybercrimes.
The Australian Government's website
(scamwatch.gov.au) shows how the number of
reports of fraud and the amount of money lost has
evolved. In 2019, Australians lost more than $142
million to scammers. In 2020 it was $175 million in
2021 - $323 million and in the first 3 months of 2022
alone people lost $167 million to scams, more than in
the whole of 2019. As we can see, this problem is only
getting worse.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7741-4039
Large companies are also falling victim to internet
fraud. For example, if a hacker gains access to an
employee's email of a company and sends a phishing
page that looks like a company login sent to the
employee from a supervisor, the hacker can gain
access to sensitive company information and the
company can suffer major financial losses. Or the
fraudster will spread a link to a page that looks like a
legitimate news site and inform the public about a
false event, which in turn will negatively affect stock
growth (Ciampaglia, 2018).
The results of our research into the ability to
model fraudulent behaviour on the web have been
used to develop an application that can detect that a
user is on a fraudulent website and inform the user if
the application service is activated. We think that this
application will be especially helpful for new Internet
users and older people, who are most often victims of
such scams and are the most vulnerable.
2 FRAUDULENT WEB SITES
The Internet has always been relatively secure in the
realm of websites run by large companies, well-
known brands and other technology giants. Payment
gateways on online stores are very well secured with
218
Machová, K. and Ka
ˇ
nuch, M.
Modelling of an Untrustworthiness of Fraudulent Websites Using Machine Learning Algorithms.
DOI: 10.5220/0012886700003838
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2024) - Volume 1: KDIR, pages 218-225
ISBN: 978-989-758-716-0; ISSN: 2184-3228
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

two/three and multi-factor authentication. But
sometimes it happens that we get to a website that
pretends to be trustworthy but a fraudster has created
an exact copy of the site. We want to log in to our
account but logging in doesn't work and our password
and email have just been sent to the scammer. This
method of creating a fraudulent site is called spoofing
in English. Nowadays, DDoS attacks became a real
problem. The number of DDoS attacks in 2021 has
been recorded as high as 9.75 million (Vermer, 2021).
Although DDoS attacks are more frequent, modern
servers can handle them more easily than in the past.
In 2021, hackers managed to obtain just one
single password to the system of the US oil pipeline
company Colonial Pipeline (Turton, 2021). The
hackers gained access to the system after an employee
entered the password to a fraudulent website posing
as the company's VPN. The hackers then locked down
the entire system using ransomware and demanded a
ransom of 75 bitcoins ($4.4 million at the time).
In July 2020, Twitter employees were the target
of a phishing attack, and hackers managed to gain
access to the accounts of many celebrities as Elon
Musk, Bill Gates, and shared the message that if you
send Bitcoin to a certain Bitcoin address, your deposit
will be doubled (Leswing, 2021). The scam was also
shared by hacked accounts of well-known financiers
such as Mike Bloomberg and Warren Buffet. This
was an example of a scam called a Ponzi scheme.
Factors such as page load time, SSL protocol and
contact details play an important role in identifying a
fraudulent site (Fedorko, 2020). If the loading time of
a web page is longer than 5 seconds, it causes a
decrease in the credibility of the page. According to
the latest rules, all websites should have SSL. It is the
"https:" at the beginning of the URL. The presence of
SSL increases the credibility of the website. Also,
visibly accessible contact information - phone
number, e-mail address, brief information about the
company, for example, physical address, ID number,
etc. increase the credibility of the website.
2.1 Related Works
Several studies have focused on what fraudulent sites
have in common and how big the differences are
between phishing sites, fraudulent payment gateways,
fraudulent online stores and sites that pretend to be
legitimate news organizations. For example, one of the
common features that fraudulent sites have in common
are invalid certificates and many buttons with broken
links (Fedorko, 2020). In this study a descriptive
statistic, multiple linear regression and structural
equation modelling were used.
Other research, which worked with a dataset of
phishing websites (Hannousse, 2021), discusses an
importance of the syntax of URLs, i.e., how many
special characters are in a link, how long the link is,
how many times the www subdomain is in the link,
whether the link contains the name of a globally
known brand, and also whether the domain is
registered at all and if so what is its age. These are
features that we can more easily extract and
preprocess for machine learning models. In this study,
following machine learning were used for detection
models training: logistic regression, random forest
and support vector machines. The best performing
model was learned using random forests method.
In 2013, research was conducted where 2046
participants decide whether or not the website
displayed is trustworthy on a scale of 1-5. Those
participants who very frequently ranked websites
with the number 5 or the number 1 were often the
most wrong in their decisions (Rafalak, 2014). In the
study, descriptive statistics were used for estimated
psychological traits levels. The results of this research
are helpful in designing a method to detect fraudulent
websites.
Nowadays, more and more user-generated
content is hosted on web servers that belong to a small
group of giant technology companies. This trend is
leading to a centralized web with many problems.
These could be addressed by decentralizing the web,
which has the potential to ensure that the end-user
always knows that the website they are currently on
is from a legitimate source or not. A study (Kim,
2021) proposes a blockchain-based way of operating
such a decentralized web.
Another way to prevent phishing and password
leaks is by using blockchain encryption of messages
and communications in companies between company
servers when logging into the system. If an employee
sends a login key or password to a corporate system,
the blockchain ensures through a stored hash that only
the target corporate server can read the content of the
message - i.e. the password (Cai, 2017). In this case,
it cannot happen that the content of the message - the
password to the system, can be read by a hacker who
sent a phishing website to the employee.
The study (Rutherford, 2022) demonstrates that
the machine learning approach is viable with
validation accuracy ranging from 49 to 86%. The
support vector machine was able to predict whether a
cadet would be compromised upon receipt of a
phishing attack with a 55% accuracy while a recall
score was 71%. On the other hand, logistic regression
model had the highest 86% accuracy while
maintaining a recall score only of 16%.
Modelling of an Untrustworthiness of Fraudulent Websites Using Machine Learning Algorithms
219

In the paper (Aljabri, 2022), in addition to the
classic machine learning methods, it was also used a
deep learning. For classification performance in
identifying phishing websites, random forest
algorithm achieved the highest accuracy.
The article (Alnemari, 2023) presents
experiments with phishing detection models learned
using artificial neural networks, support vector
machines, decision trees, and random forest
techniques. Their results show that the model based
on the random forest technique is the most accurate.
The analysis of related works in the field showed,
that blockchain encryption and descriptive statistic
are often used. From machine learning methods
mainly logistic regression, random forest and support
vector machines were used. So we have decided to
use logistic regression from statistical methods of
machine learning and random forests as very
successful method of ensemble learning, and two
other methods of ensemble learning - gradient
boosting and ADABoost. We also experimented with
neural networks, as they have recently been
successful in solving a wide range of problems.
3 USED METHODS
3.1 Classic Machine Learning
We have used one of methods of regression analysis
namely logistic regression (LR) as the classic statistic
machine learning method suitable for detection
models generation on numerical, non-text data. The
LR is a technique to estimate parameters of a logistic
model. Logistic model is a model where linear
combinations of independent variables are
transformed using a specific type of logistic function,
mostly a sigmoid function (Brownlee, 2023).
We also tested approaches based on ensemble
learning such as boosting (gradient boosting - GB and
XGBoost – extreme boosting) and random forest
(RF). The ensemble learning is based on the idea of
combination of several weak prediction models into
one stronger model for final decision.
The GB provide this by iterative minimizing the
loss function. The algorithm generates a set of
decision trees where each tree is trained to predict the
difference between the predicted and true values (i.e.,
residual values) of the previous tree. The algorithm
then calculates the residues of the predictions and
trains a new decision tree to predict these residues.
This process is repeated several times. The final
prediction is obtained by voting or averaging the
results of particular trees. One of the benefits of GB
regression is its ability to handle a wide variety of data
types. In addition, it is known for its high accuracy
and robustness, as well as its ability to process high-
dimensional data. However, it also has some
limitations. One is that it can be a computationally
complex, especially for large datasets. Another
limitation is that the model can be sensitive to the
choice of hyper parameters such as learning speed
and the number of trees in the file (Ke, 2017).
XGBoost (Extreme Gradient Boosting) is
designed to improve the performance of traditional
gradient boosting algorithms using a combination of
regularization and parallel processing techniques.
Regularization techniques such as L1 and L2 are used
to prevent overtraining and improve generalization
performance. XGBoost also uses a technique to trim
trees, further reducing overtraining and improving
model efficiency (Chen, 2016).
RF tries to minimize the variance by creating more
decision trees in different parts of the same training
data. Individual trees are de-correlated using a random
selection of a subset of attributes. The method achieves
the final classification by voting or averaging the
results of particular trees. RF method is used mainly in
cases where a limited amount of data is available,
which significantly reduces memory requirements
when generating many trees (Donges, 2024).
3.2 Neural Networks
We also experimented with very successful methods
for generating of artificial neural networks, namely
LSTM (long-short term memory), CNN
(convolutional neural network) and MLP (multi-layer
perceptron).
LSTM is the most known recurrent neural
network, which can re-store information a longer time
and that is why they can process longer sequence of
inputs. LSTM networks are composed of repeating
modules (LSTM blocks) in the form of a chain. The
basis of LSTM is a horizontal line through which a
vector passes between individual blocks. There are
three gates (input, forget and output gate) in
individual cells. These gates are used to remove or
add information to the state of the block. Information
passes through these gates, which are composed of
neurons with a sigmoidal activation function.
Depending on the value of the output on these
neurons, certain amount of information passes
through it (0 means that no information passes
through the gate and 1 means that everything passes
through the gate) (Ralf, 2019).
The basic building block of the CNN network is a
convolutional layer that applies a set of filters to the
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
220

input and extracts properties from it. Filters are
learned by training as weights and other parameters.
Filters are usually small in size to capture local
patterns in the data. The output from the
convolutional layer is then transmitted through a
nonlinear activation function such as ReLU
(Rectified Linear Unit) to insert nonlinearity into the
network. In addition to convolutional layers, CNN
networks typically include post-layer pooling, which
reduces dimensionality and helps prevent overfitting.
The most common type is max pooling, which selects
the maximum value in a certain local region of the
property map. The last layers of the CNN network are
usually fully interconnected layers. The output from
the last layer is used for prediction (He, 2016).
MLP consists of multiple layers of interconnected
neurons, each performing a nonlinear transformation
at its input. The basic building block of MLP is the
perceptron, which receives a set of input values and
produces a single output value. The output of a
perceptron is determined by the weighted sum of its
inputs that passes through a nonlinear activation
function such as a sigmoid or ReLU function. MLPs
are powerful models that can learn complex nonlinear
input-output relationships (Goodfellow, 2016).
4 MODELS TRAINING AND
TESTING
4.1 Dataset Description
We sourced data from (Hannousse, 2021). Dataset is
also available to download from (Kaggle, 2024). This
dataset contains 11 429 URL addresses, and has 87
attributes and information about its legitimacy; 50%
of URLs were legitimate and 50% of URLs were
linking to phishing websites. Dataset contains 3 types
of attributes: attributes extracted from syntax of URL,
attributes extracted from source code of a website and
attributes that were queried using APIs. Dataset was
split to 2 datasets. We also created 3rd dataset, which
contained URLs with 34 extracted attributes. These
URLs were of a browsing history of a simulated user.
All datasets were loaded and adjusted in python
programming environment – Spyder Anaconda using
library pandas.
Dataset 1 was full dataset with all 87 attributes.
This dataset was used to test the suitability of a
diverse group of models from simple ones that use
one function for classification to more complex ones
that use network of functions for classification.
Dataset 2 was reduced to 34 attributes. The rest
53 attributes were removed from the dataset 2
because we couldn’t reliably extract their values from
websites other than those in the kaggle dataset, so the
final model learned also from those 53 attributes
would not be sufficiently general while using for
phishing detection on a random website. The
methodology of filtering was based on indication of
missing values during the extraction process. The
reason for those extraction errors (missing values of
attributes) could be that many of phishing websites
are after some period blocked by internet provider,
blocked by firewall or antivirus software or simply no
longer exist. The chosen 34 attributes are detailed in
the Appendix. We expected that after attributes
reduction the performance of models could be
negatively impacted but extraction of attributes
values was much faster (from 30 seconds to less than
one second).
Dataset 3 was used to test the functionality of the
application. It contained 100 URLs of a simulated
user, every URL contained 34 attributes (same as in
dataset 2) and information of legitimacy of an URL.
4.2 Methodology
We chose a diverse type of models from the simplest
ones to models based on learning an artificial neural
networks. We have also used techniques of ensemble
learning as random forest, gradient boosting, and
XGBoost. All these different types of methods were
chosen to see how well they can classify target
attribute – phishing webpage. The above-mentioned
models were trained at first on Dataset 1 (first round).
Then three best methods were used for training on
Dataset 2 with reduced number of attributes (second
round) and only one best method was used for
training on Dataset 3 (final round). The process is
illustrated in Figure 1.
4.3 First Round of Training
Models were trained in python programming
environment – Spyder Anaconda using library scikit-
learn. Dataset 1 with 87 attributes was split into train
and test dataset (ratio 80:20). In both sets the ratio of
legitimate and phishing URLs was 50:50. Following
models were trained and tested on this dataset: LR,
GB, XGBoost, RF, LSTM, CNN, and MLP. The
number of models (for example trees in RF) was set
on 100. The same n_estimators=100 was set for GB
and XGBoost. The hyper-parameters of the various
NNs are presented in Table 3 and Table 4.
Modelling of an Untrustworthiness of Fraudulent Websites Using Machine Learning Algorithms
221
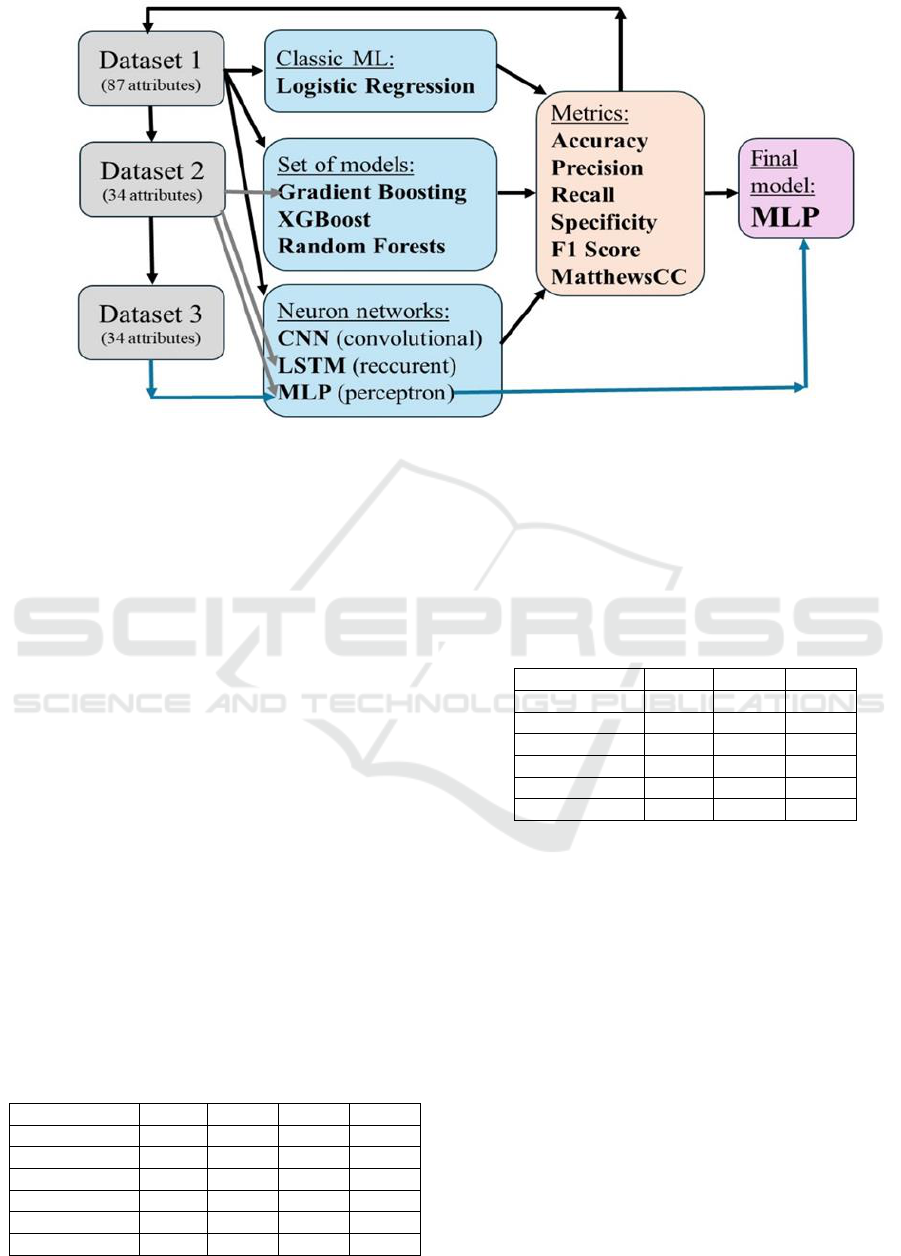
Figure 1: The methodology of models training.
After testing we evaluated the accuracy of every
model and for next training (second round) chose
only those, that achieved accuracy of more than 95%.
We chose accuracy as metric to compare models
because accuracy is most basic metric that evaluates
general performance of models. This metric is also
suitable for a balanced dataset.
Models that achieved expected accuracy were:
GB, LSTM and MLP Neural Network. Other Metrics
such as precision, recall, sensitivity, F1-score, and
Matthew’s correlation coefficient were calculated for
the tested models and are shown on Table 1 and 2.
The mentioned three best methods were used for
training on Dataset 2 with reduced number of
attributes. The reason for this was that we wanted to
see how much the accuracy of these models drops
when we train them on less complete and complex
data, but which are more suitable for use in real-world
conditions, since it is not necessary to extract all 87
attributes values considered at the beginning of
training process. In recognition of the phishing pages,
we need to extract for them all values of all attributes,
which were used in final model training.
Table 1: The results of experiments on Dataset 1 using LR,
GB, XGB (XGBoost) and RF. The shortcut Matthews CC
is Matthew’s Correlation Coefficient.
Method
LR
GB
XGB
RF
Accuracy
0.783
0.952
0.949
0.925
Precision
0.823
0.956
0.953
0.921
Recall
0.760
0.953
0.949
0.934
Specificity
0.810
0.951
0.948
0.915
F1 Score
0.790
0.954
0.951
0.927
Matthews CC
0.568
0.904
0.897
0.849
In Table1 and Table 2, there are bolded the results
in accuracy of three best models. In Table 1 it is GB
– gradient boosting, and in Table 2 they are LSTM –
long-short term memory, and MLP - multi-layer
perceptron.
Table 2: The results of experiments on Dataset 1 using
CNN, LSTM, and MLP.
Method
CNN
LSTM
MLP
Accuracy
0.942
0.954
0.963
Precision
0.951
0.954
0.952
Recall
0.939
0.958
0.974
Specificity
0.946
0.950
0.953
F1 Score
0.945
0.956
0.963
Matthews CC
0.884
0.908
0.927
4.4 Second Round of Training
We determined that going forward, we would only
train models on Dataset 2 that exceeded
accuracy=0.95 in the first round on Dataset 1, and
thus GB, LSTM and MLP were selected.
We used the scikit-learn library to train the GB
model. In the first step of testing, normalized data
entered the learning process. We defined the model as
follows:
▪ model=GradientBoostingClassifier
(n_estimators=100,
▪ learning_rate=0.1,
▪ max_depth=3).
We then trained and tested the model with the
functions:
▪ model.fit(X_train, y_train)
▪ tested y_pred=model.predict(X_test).
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
222
Finally, we displayed the confusion matrix with the
function cm=confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred).
The LSTM model was trained using the keras
library. In the first step, it was necessary to change the
shape of the input normalized data to make it suitable
for the LSTM model. This reshaping was done with
the following functions:
▪ X_train=np.reshape(X_train,(X_train.shape
[0],1,X_train.shape[1]));
▪ X_test=np.reshape(X_test,(X_test.shape[0],
1,X_test.shape[1])).
We defined the model architecture with the
following functions (see Table 3).
Table 3: The architecture of the LSTM model.
Method
LSTM
model
“sequential()”
model_add (LSTM)
128 neurons
input_shape
1
return_sequencies
False
dense
64, activation=”relu”
dense
1, activation=”sigmoid”
optimizer
Adam, lr=0.001
model_compile
loss=”binary_crossentropy”
optimizer_metrics
“accuracy”
For training the MLP model, we also used the
scikit-learn library. In the first step of training,
normalized data entered the learning process. We
defined the model as follows (see Table 4).
Table 4: The architecture of the MLP model.
Method
MLP
model
“MLPClassifier”
solver
“adam”
alpha
0,01
hidden_layer_sizes
100, 100, 100, 100, 100
max_iter
100
random_state
44
The results of testing of all the models trained on
Dataset 2 are shown in Table 5.
Table 5: The results of experiments on Dataset 2 using GB,
LSTM and MLP.
Method
GB
LSTM
MLP
Accuracy
0.925
0.933
0.948
Precision
0.927
0.940
0.935
Recall
0.929
0.932
0.960
Specificity
0.920
0.933
0.935
F1 Score
0.928
0.936
0.947
Matthews CC
0.850
0.865
0.895
The predicted reduction in accuracy in the second
round of training GB model was confirmed but the
reduction in accuracy was minimal from 95.22% to
92.5%. The reduction in accuracy of the LSTM model
in the training on Dataset 2 was also confirmed but
the reduction in accuracy was also minimal from
95.40% to 93.25%, and similarly for MLP model was
observed the reduction of accuracy, but the reduction
was the lowest - only 1.57%. The final best MLP
model has been retrained on Dataset 3 and used in our
application for phishing detection.
5 PHISHING DETECTION
APPLICATION
It is important for the proper functioning of the
application to ensure smooth operation. The
application cannot slow down the page load time and
at the same time it must evaluate the page fast enough
to inform the user about the threat. The threat
information should not block the website but rather
alert the user with a pop-up window, as an extension
for Google Chrome, not as a new browser window.
If a website is flagged as fraudulent, because
posing as a real news service or because this is a
satirical site such as babylonbee.com or
theonion.com, should the app block access to such
sites? We think not. We just want to inform the user
that what they are reading may not be true or the
website is not a legitimate news service. So, we would
like to stick to the principle of freedom of expression
and just warn the user.
This work introduces a functional web application
(Google Chrome extension) that can detect
fake/phishing/spoofing websites and is intended to
help people not to be fooled and robbed. Our
application consists of two parts.
The first part – Python script - is launched
automatically when browser is launched, user does
not interact with this part at all. Python script is coded
in a form of server that awaits input from browser –
from extension using REST – get method. When
script gets the URL sent from Chrome extension,
MLP model trained on dataset 2 extracts all 34
attributes from URL and URL is evaluated. If URL is
evaluated as phishing, number 1 is sent to extension,
if URL is evaluated as legitimate, number 0 is sent to
extension.
The second part – Google Chrome extension - is
part that user will see and can interact with it. The
application is situated on the top right corner of
browser for good visibility, as shown in Figure 2.
Modelling of an Untrustworthiness of Fraudulent Websites Using Machine Learning Algorithms
223
The extension automatically sends newly opened
URLs to Python script using REST method put. While
waiting for response, extension changes its colour to
yellow and text changes to “LOAD…” indicating that
extension is waiting for response (shown in Figure 2).
If 5 seconds passes and no response follows,
extension changes its colour to orange and text
changes to “ERR” indicating error message (shown in
left part of Figure 3). If extension receives number 0
in 5 seconds time, extension changes its colour to
green and text changes to “tick” symbol (shown in the
middle part of Figure 3). If extension receives number
1 (python script evaluated URL as phishing site), the
extension changes its colour to red and text changes
to “X” symbol (shown in right part of Figure 3).
Figure 2: The illustration of our application as Google
Chrome extension.
Figure 3: The illustration of different responses of the
application.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Our study demonstrates the effectiveness of machine
learning models in detecting phishing websites. We
have trained and tested all selected models on the
entire Dataset 1 - 87 attributes and expected accuracy
of at least 95%. The models that achieved the required
accuracy in the first round were MLP, LSTM and GB.
In the second round of training, we used Dataset 2
reduced to 34 attributes (attributes that we can
reliably extract from various websites outside the
dataset). We re-trained and tested the models that
advanced to this second round. We expected an
accuracy of at least 90% and this was achieved for all
three models in the second round. The highest
accuracy was achieved by the Multilayer Perceptron
(MLP) model at 94.75%. We used this model in
developing a web application for real-time phishing
detection. This solution can enhance online security
and provide users with instant alerts regarding the
legitimacy and trustworthiness of visited websites.
This approach offers a proactive solution to combat
phishing attacks and reduce the risk of cybercrimes.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Scientific Grant
Agency of the Ministry of Education, Science,
Research and Sport of the Slovak Republic, and the
Slovak Academy of Sciences under no. 1/0685/21
and by the Slovak Research and Development
Agency under the Contract no. APVV-22-0414.
REFERENCES
Aljabri, M., Mirza, S. (2022) Phishing Attacks Detection
using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models.
7th International Conference on Data Science and
Machine Learning Applications (CDMA), Riyadh,
Saudi Arabia, 2022, ps. 175-180.
Alnemari, S., Alshammari, M. (2023) Detecting Phishing
Domains Using Machine Learning. Applied Sciences,
Vol. 13, no. 8, 2023, ps. 4649-4649, ISSN 2076-3417.
Brownlee, J. (2023) Logistic regression for machine
learning [online] 2023, Accessible [August 5, 2024].
Cai, C., Yuan, X., Wang, C. (2017) Towards trustworthy
and private keyword search in encrypted decentralized
storage. In IEEE International Conference on
Communications (ICC17), 2017, ps. 1-7, DOI:
10.1109/ICC.2017.7996810.
Chen, T., Guestrin, C. (2016) Xgboost: A scalable tree
boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM
SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge
Discovery and Data Mining, 2016, ps. 785-794, ISBN
978-1-4503-4232-2.
Ciampaglia, G. et al. (2018). Research Challenges of
Digital Misinformation: Toward a Trustworthy Web.
AI Magazine [online]. Vol. 39, no. 1,2018, ps. 65-74,
ISSN 0738-4602.
Donges, N. (2024) Random forest: A complete guide for
machine learning [online] 2024, Accessible [August 5,
2024].
Fedorko, I., Gburová, J. (2020). Selected Factors of
Untrustworthiness during web pages using. [online].
2020, ISSN 2453-756X.
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A. (2016) Deep
learning. MIT press, 2016, captions 6-9, ISBN
9780262035613.
Hannousse, A. Yahiouche, S. (2021). Web page phishing
detection. [online]. V3. Mendeley Data, 2021, DOI:
10.17632/c2gw7fy2j4.3.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J. (2016) Deep residual
learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
224

IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition, 2016, ps. 770-778, DOI:
10.1109/CVPR.2016.90.
Kaggle (2024) Kaggle datasets [online] Accessible [May
25, 2024] <[https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/
shashwatwork/web-page-phishing-detection-dataset]>.
Ke, G. et al. (2017) Lightgbm: A highly efficient gradient
boosting decision tree”. In Advances in neural
information processing systems, Vol. 30, no.1., 2017,
ps. 1-9.
Kim, G.-H. (2021). Blockchain for the Trustworthy
Decentralized Web Architecture. International Journal
of Internet, Broadcasting and Communication [online].
Vol. 13, no. 1, ps. 26–36, 2021. ISSN 2233-7857.
Leswing, K. (2021). Hackers appear to target Twitter
accounts of Elon Musk, Bill Gates, others in digital
currency scam, CNBC [online] 2021, Accessible [May
25, 2024] <https://www.cnbc.com/2020/07/15/
hackers-appear-to-target-twitter-accounts-of-elon-
musk-bill-gates-others-in-digital-currency-
scam.html>.
Rafalak, M., Abramczuk, K., Wierzbicky, A. (2014)
Incredible: is (almost) all web content trustworthy?
Analysis of psychological factors related to website
credibility evaluation. In Proceedings of the 23rd
International Conference on World Wide Web (WWW
'14 Companion), New York, Association for
Computing Machinery, 2014, ps. 1117-1122, ISBN
9781450327459.
Ralf, C., Rothstein-Morris, E. (2019) Understanding LSTM
[online] 2019, Accessible [May 25, 2024]
https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.09586.
Rutherford, S., Lin, K., Blaine, R.W. (2022) Predicting
Phishing Vulnerabilities Using Machine Learning.
IEEE SoutheastCon Conference, IEEE345 E 47TH ST,
NEW YORK, NY 10017 USA, 2022, ps. 779-786.
Turton, W., Mehrotra, K. (2021). Hackers Breached
Colonial Pipeline Using Compromised Password,
Bloomberg [online] 2021-06-04, Accessible [May 25,
2024] https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/
2021-06-04/hackers-breached-colonial-pipeline-using-
compromised-password.
Vermer, B. (2021). Cybercriminals launched 9.75 million
DDoS attacks in 2021. (IN)SECURE Magazine,
Vol.70, ps. 54-55, 2021.
APPENDIX
The attributes in the Dataset 2 were following:
▪ length_url - is the length of the URL obtained by
the function len(url)
▪ length_hostname is the length of the hostname
obtained by len(urlparse(url).netloc)
▪ ip detects if the URL is in IP shape
▪ nb_dots detects the number of "." characters in
URL
▪ nb_hyphens detects the number of "-" in URL
▪ nb_at detects the number of "@" in URL
▪ nb_qm detects the number of "?" in URL
▪ nb_and detects the number of "&" in URL
▪ nb_or detects the number of "|" in URL
▪ nb_eq detects the number of "=" in URL
▪ nb_underscore detects the number of "_" in URL
▪ nb_tilde detects whether the character " ~ " is
present in the URL with the function
url.count('~')>0
▪ nb_percent detects the number of "%" in URL
▪ nb_slash detects the number of "/" in URL
▪ nb_star detects the number of "*" in URL
▪ nb_colon detects the number of " : " in URL
▪ nb_comma detects the number of " , " in URL
▪ nb_semicolumn detects the number of " ; " in
URL
▪ nb_dollar detects the number of "$" in URL
▪ nb_space detects the number of spaces in the
URL
▪ nb_www detects the number of strings "www" in
the URL with the function url.count('www')
▪ nb_com detects the number of "com" strings in
the URL with the url.count('com') function
▪ nb_slash detects the number of "//" in URL
▪ https_token detects whether the string "https" is
present in the URL
▪ ratio_digits_url detects the ratio between the
number of digits and the number of other non-
numeric characters in the URL
▪ abnormal_subdomain detects the abnormal
shape of the subdomain "www" with the function
re.search('(http[s]?://(w[w]?|\d))([w]?(\d|-
)))',url)
▪ nb_subdomains counts the number of
subdomains in the URL with the function
len(re.findall("\.",url))
▪ prefix_suffix finds out if there are
prefixes/suffixes in the URL with the function
re.findall(r "https?://[^\-]+-[^\-]+/",url)
▪ shortening_service detects if the URL is
shortened by services such as tinyurl, bit.ly,
bit.do, etc.
▪ phish_hints detects if there are strings in the link
that may point to a phishing link. Strings such as:
"wp", "login", "css", "plugins", etc.
▪ domain_in_brand detects if there is a name
string from the tag list in the URL. Tags like:
"Pepsi", "Adidas", "Adobe", "Amazon",
"Google", etc.
▪ website registered in WHOIS database,
▪ domain_registration_length
▪ websites PageRank
Modelling of an Untrustworthiness of Fraudulent Websites Using Machine Learning Algorithms
225
