
Generating Small Instances with Interesting Features for the Traveling
Salesperson Problem
Tianyu Liang
1 a
, Zhize Wu
1 b
, Matthias Th
¨
urer
2 c
, Markus Wagner
3 d
and Thomas Weise
1 e
1
Institute of Applied Optimization, School of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data, Hefei University, Jinxiu Dadao 99, Hefei,
230601, Anhui, China
2
Professur Fabrikplanung und Intralogistik, TU Chemnitz, Str. der Nationen 62, 09111 Chemnitz, Sachsen, Germany
3
Department of Data Science and AI, Faculty of Information Technology, Monash University, Wellington Road, Clayton,
Victoria 3800, Australia
Keywords:
Traveling Salesperson Problem, Instance Generation, Frequency Fitness Assignment, Local Optima.
Abstract:
The Traveling Salesperson Problem (TSP) is one of the most well-known N P -hard optimization tasks. A
randomized local search (RLS) is not a good approach for solving TSPs, as it quickly gets stuck at local
optima. FRLS, the same algorithm with Frequency Fitness Assignment plugged in, has been shown to be
able to solve many more TSP instances to optimality. However, it was also assumed that its performance will
decline if an instance has a large number M of different possible objective values. How can we explore these
more or less obvious algorithm properties in a controlled fashion, if determining the number #L of local optima
or the size BL of their joint basins of attraction as well as the feature M are N P -hard problems themselves?
By creating TSP instances with a small number of cities for which we can actually know these features! We
develop a deterministic construction method for creating TSP instances with rising numbers M and a sampling
based approach for the other features. We determine all the instance features exactly and can clearly confirm
the obvious (in the case of RLS) or previously suspected (in the case of FRLS) properties of the algorithms.
Furthermore, we show that even with small-scale instances, we can make interesting new findings, such as that
local optima seemingly have little impact on the performance of FRLS.
1 INTRODUCTION
Given a fully-connected graph of n nodes and the dis-
tances d(i, j) between each pair of nodes i and j, the
Travelling Salesperson Problem (TSP) asks us to find
the shortest round trip tour visiting each of the nodes
and finally returning back to the starting point (Lawler
et al., 1985; Gutin and Punnen, 2002; Weise et al.,
2014a; Weise et al., 2016). A tour can be represented
as permutation p of the first n natural numbers and the
objective function (subject to minimization) is defined
as
f (p) = d(p[n], p[1]) +
n−1
∑
i=1
d(p[i], p[i + 1]) (1)
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-3732-4831
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7416-5711
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2705-969X
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3124-0061
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9687-8509
We consider the symmetric TSP, where d(i, j) =
d( j, i) for all i, j ∈ 1..n. The problem of find-
ing the globally optimal tour minimizing f is N P -
hard (Gutin and Punnen, 2002). As a result, a variety
of metaheuristic algorithms like local searches (Hoos
and St
¨
utzle, 2005; Weise, 2009), Evolutionary Al-
gorithms (B
¨
ack et al., 1997; Chiong et al., 2012;
Weise, 2009, EAs) and simulated annealing (Kirk-
patrick et al., 1983;
ˇ
Cern
´
y, 1985, SA) have been
applied to the TSP. The state-of-the-art specialized
heuristics include LKH (Helsgaun, 2009) and oper-
ators like GAP by (Whitley et al., 2010) and EAX
by (Nagata and Soler, 2012).
The simplest randomized local search (RLS) can
only solve very small TSP instances (Liang et al.,
2022). It tends to quickly converge to local op-
tima, since it only accepts new tours that are bet-
ter or at least not worse than the current-best solu-
tion. In order to prevent the convergence to local op-
tima, Frequency Fitness Assignment (FFA) was de-
Liang, T., Wu, Z., Thürer, M., Wagner, M. and Weise, T.
Generating Small Instances with Interesting Features for the Traveling Salesperson Problem.
DOI: 10.5220/0012888800003837
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2024), pages 173-180
ISBN: 978-989-758-721-4; ISSN: 2184-3236
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
173

veloped (Weise et al., 2014b). It renders optimiza-
tion algorithms invariant under all injective transfor-
mations of the objective function value (Weise et al.,
2021b). A heuristic using FFA no longer prefers bet-
ter solutions over worse ones (Weise et al., 2023).
Plugging FFA into the RLS yielding the FRLS leads
to remarkable performance on several classical N P -
hard optimization problems such as Max-Sat (Weise
et al., 2021b; Weise et al., 2023), and the Job Shop
Scheduling Problem (Weise et al., 2021a; de Bruin
et al., 2023). (Liang et al., 2022; Liang et al., 2024)
showed that FRLS significantly improves the abil-
ity to reach globally optimal solutions on the TSP
compared to RLS, at the cost that it converges more
slowly. This slowdown seems to be related to the
number M of different objective values that exist for
a problem instance.
Whereas the scale n of a TSP instance is always
known, determining M is itself N P -hard. For the
common TSP benchmark instances, it can only be es-
timated and bound from below by m, the number of
different objective values actually encountered during
the search. We want to conduct a detailed analysis
of the impact of M on the performance of RLS and
FRLS. How can this be done if M cannot be deter-
mined for any of the benchmark instances available?
The first contribution of this work is a determinis-
tic method to create small benchmark instances with
a known number M. The upper bound
ˆ
M for M is the
number of unique nonsynonymous tours and we show
how to construct TSP instances having M =
ˆ
M.
It is not the problem scale n that determines what
solution quality a simple RLS without any means of
preventing it from getting stuck at local optima can
reach, but the number #L of these local optima and the
size BL of their corresponding joint basins of attrac-
tion. Determining these values, too, is N P -hard. The
second contribution of our work is a method of cre-
ating TSP instances with known values of #L and BL.
As the third contribution, we analyze the per-
formance of RLS and FRLS on these instances. We
confirm that RLS is sensitive to the presence of lo-
cal optima and BL, whereas FRLS is not. We con-
firm that FRLS is sensitive to M, whereas RLS is
not. The implementation of our instance generator,
all involved algorithms, the generated instances, and
their results are available at https://doi.org/10.5281/
zenodo.13324196.
2 BACKGROUND
On the TSP, the RLS starts by sampling an initial
tour p
c
uniformly at random (u.a.r.) from the space P
of all permutations (tours) of the first n natural num-
bers. It determines the tour length z
c
= f (p
c
) and then
performs a loop for the remainder of its computational
budget. In this loop, it samples a new slightly modi-
fied copy p
n
of p
c
with a unary operator move. The
resulting tour length z
n
= f (p
n
) is compared to z
c
and,
if it is less or equal, p
n
replaces p
c
.
Every unary search operator move spans a neigh-
borhood N(p) around each solution p that contains
all the possible solutions p
n
that could be the result
of move(p). Based on the acceptance criterion of the
RLS and this notion of the neighborhood, we can re-
cursively define the basin of attraction B(p) of a so-
lution p as the set of solutions from which p could
be reached by the RLS and become its new current
solution p
c
as follows:
B(p) = {p} ∪
[
p
′
∈N(p)∧ f(p
′
)≥ f(p)
B(p
′
) (2)
A solution p
′
is in the basin of attraction of a so-
lution p if there exists a path of non-worsening ob-
jective values from p
′
to p. We derive the predicate
optimal(p
⋆
) stating that a solution p
⋆
is an optimum
if it is not in the basin of attraction of a better solution:
optimal(p
⋆
) ⇔ ∄p ∈ P : f (p) < f (p
⋆
) ∧ p
⋆
∈ B(p) (3)
If a solution is not in the basin of attraction of a bet-
ter solution, then there exists no path in the search
space P along which the RLS could escape from it
to such a better solution. There could be a set P
⋆
of equally-good solutions that are interconnected and
form one optimum. A globally optimal solution is an
optimal solution with the smallest possible objective
value ˇz. All other optimal solutions are local optima.
None of this matters for the FRLS, which is
the RLS with Frequency Fitness Assignment (FFA)
plugged in. FFA is a module that prevents algorithms
from premature convergence to local optima by re-
placing the objective function value with its encounter
frequency in selection decisions. The FRLS for the
TSP therefore begins by initializing and filling a fre-
quency table H with zeros. It then samples the first
tour p
c
and evaluates its length z
c
. In its main loop,
it will sample a new tour p
n
and evaluate its length z
n
exactly in the same way as the RLS. Then, it will
increment the encounter frequencies H[z
c
] and H[z
n
]
of z
c
and z
n
. These incremented frequencies are then
compared instead of z
c
and z
n
when deciding whether
p
c
should be retained or replaced by p
n
. This means
that the algorithm will depart even from a better p
c
to a worse p
n
as long as the new tour length has
been seen less than or equally often than the current
one. This means that we need to preserve the best-
encountered tour and its length in additional variables
p
b
and z
b
in order to return them at the end.
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
174

If the algorithm reaches what would be a lo-
cal optimum p
⋆
under RLS, it will keep sampling
solutions from the neighborhood N(p
⋆
). In each
step, the encounter frequency H[ f (p
⋆
)] will increase
by 1, whereas the encounter frequency of only one of
the tour lengths in the neighborhood also increases.
Eventually, one of the neighboring solutions will have
a lower corresponding frequency value and the search
departs.
This increased exploration ability comes at the
cost of slower convergence, related to the number M
of different possible objective values of a problem
instance. Even when dealing with simple RLS and
FRLS, the question of when and why which algorithm
is the better choice is not trivial. We want to know
how the number #G of global optima, the number #L
of local optima, the sizes BG and BL of their respec-
tive joint basins of attraction, and the number M of
different objective values influence the algorithm per-
formance.
The most classical TSP benchmarks are the
TSPLIB (Reinelt, 1991) and the DIMACS 2008
TSP challenge (Johnson and McGeoch, 2008). How-
ever, the instances in these sets have either been ob-
tained from real-world problems or they are randomly
generated without aiming to construct specific val-
ues of the features discussed above. Many works try
to generate diverse TSP instances, including (Mers-
mann et al., 2012; Nallaperuma et al., 2012; Neumann
et al., 2018; Neumann et al., 2019; Bossek and Traut-
mann, 2016; Bossek et al., 2019; Bossek and Neu-
mann, 2022). However, they either produce instances
completely randomly, focus on the perspective of al-
gorithm performance, or use instance features that are
based mainly on statistics, or pursue a combination of
the above.
3 GENERATING SMALL
INTERESTING INSTANCES
Each permutation of the first n natural numbers repre-
sents a valid sequence of visiting the n cities of a TSP
instance. There are n! such permutations. With n = 14
we get |P| = 14! = 87 178 291 200 and thus probably
reach the limit at which a current machine can com-
fortably enumerate the complete search space P. If
we want to find the basins of attraction of the local
and global optima, we must evaluate Equation 2, i.e.,
construct a reachability matrix telling us which so-
lution can be reached from which other solution by
the RLS. This can be done using the Floyd-Warshall
Algorithm (Floyd, 1962; Warshall, 1962) in O(q
3
),
where q is the size of the entire search space, so we
get O(n!
3
) which becomes prohibitive at n = 8 with
8! = 40 320 and 8!
3
= 65 548 320 768 000.
Many solutions for the TSP are synonymous. It
does not really matter at which city a tour starts, so
we can reduce the search space size to (n−1)!, which
is 5040 for n = 8 and with 5040
3
= 128 024 064 000,
Equation 2 becomes manageable again.
We want to know all search space features, so we
focus on n = 8. We choose the typical 2-opt opera-
tor, also used in the studies (Liang et al., 2022; Liang
et al., 2024) that reverses a subsequence of the current
solution. It first chooses two indices 1 ≤ i < j < n
u.a.r., but ensures that either i ̸= 1 or j ̸= (n − 1).
The unary operator then computes rev(p,i, j) which
creates a copy of p with the sequence between and
including these two indices reversed. The neighbor-
hood N spanned by this operator is defined as:
N(p) =
rev(p, i, j) : ∀ 1 ≤ i < j < n,
i ̸= 1 ∨ j ̸= (n − 1)
(4)
The number M of different objective values was found
to have a major impact on the performance of FRLS
in previous studies (Liang et al., 2022; Liang et al.,
2024). These works used the TSPLIB instances and
approximated M using the actually discovered ob-
jective values as the lower bound m. The largest
observed m turned out to be less than ten million.
This is interesting because in a symmetric TSP with
n cities, there exist (n − 1)!/2 nonsynonymous tours
and, hence, there could be similarly many objective
values. For a scale n = 12, this already exceeds twice
the largest m value from these prior works – which
tackled problems with n up to 1400. Thus, at least in
the TSPLIB, the number M of different tour lengths
is much smaller than the theoretical maximum. For
n = 8, we get
ˆ
M = 5040/2 = 2520.
We now want to construct instances with the max-
imum possible M-value
ˆ
M. The inclusion or removal
of any edge in a tour must lead to a change in the tour
length that no other set of edge inclusions or removals
can achieve. In a symmetric TSP instance of scale n,
there are n(n − 1)/2 edges. At n = 8, this gives us
28 edges, which we number from 0 to 27. To achieve
maximum M, we assign the length 2
k
to edge k, i.e.,
the shortest edge has length 1 and the longest one has
length L
8
= 134 217 728. If instances with high M
are constructed at least partially like this, this explains
why the existing instances exhibit such small m: The
longest edge in such a TSP of scale n = 12 would have
length 2
11∗12/2−1
= 2
65
, which exceeds the range of a
64 bit integer variable.
We generate sequences of instances with n = 8
that iteratively approach the maximum M. The LO-k
series of instances begins with a distance matrix pop-
ulated by the value of the longest edge L
8
= 2
27
.
Generating Small Instances with Interesting Features for the Traveling Salesperson Problem
175

0 1 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2
27
2
27
0 2
27
0
0 1 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2
27
2
27
0 2
27
0
0 1 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 4 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2
27
2
27
0 2
27
0
0 1 128 2
13
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2 256 2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 4 512 2
27
2
27
2
27
0 8 2
10
2
27
2
27
0 16 2
11
2
27
0 32 2
12
0 64
0
LO-1 LO-2 LO-3 LO-14
0 1 128 2
13
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2 256 2
14
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 4 512 2
27
2
27
2
27
0 8 2
10
2
27
2
27
0 16 2
11
2
27
0 32 2
12
0 64
0
0 1 128 2
13
2
27
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 2 256 2
14
2
27
2
27
2
27
0 4 512 2
15
2
27
2
27
0 8 2
10
2
27
2
27
0 16 2
11
2
27
0 32 2
12
0 64
0
0 1 128 2
13
2
18
2
22
2
27
2
27
0 2 256 2
14
2
19
2
23
2
27
0 4 512 2
15
2
20
2
24
0 8 2
10
2
16
2
21
0 16 2
11
2
17
0 32 2
12
0 64
0
0 1 128 2
13
2
18
2
22
2
25
2
27
0 2 256 2
14
2
19
2
23
2
27
0 4 512 2
15
2
20
2
24
0 8 2
10
2
16
2
21
0 16 2
11
2
17
0 32 2
12
0 64
0
LO-15 LO-16 LO-25 LO-26
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 2
27
0 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 1 1 1 1 1
0 1 1 1 1
0 1 1 1
0 1 1
0 1
0
0 1 1 1 1 1 2
25
2
27
0 1 1 1 1 1 2
26
0 1 1 1 1 1
0 1 1 1 1
0 1 1 1
0 1 1
0 1
0
0 1 1 1 2
18
2
22
2
25
2
27
0 1 1 2
14
2
19
2
23
2
26
0 1 1 2
15
2
20
2
24
0 1 1 2
16
2
21
0 1 1 2
17
0 1 1
0 1
0
0 1 128 2
13
2
18
2
22
2
25
2
27
0 1 256 2
14
2
19
2
23
2
26
0 1 512 2
15
2
20
2
24
0 8 2
10
2
16
2
21
0 16 2
11
2
17
0 32 2
12
0 64
0
HI-1 HI-3 HI-14 HI-25
Figure 1: Selected instances of the LO and HI series.
For each such instance, we replace k elements with
a unique power of 2, starting with 1, 2, . . . , beginning
with those on the top-left of the first superdiagonal
moving towards the bottom-right and then continu-
ing with the next superdiagonal. This LO-k series de-
scribes a scenario where, initially, all edges are long
and most objective values are huge. Then the num-
ber M of different objective values is increasing with k
and the optimal objective value is decreasing. During
this process, local optima can emerge.
The HI-k series is the exact opposite, having its
distance matrices initially populated by the shortest
edge 1. In these instances, k unique higher powers
of 2, namely 2
27
, 2
26
, . . . , are then sorted into the dis-
tance matrix, in the reverse of the order used in the LO
series. In contrast to the LO-k series, most solutions
are short but more and more long solutions emerge
with rising k and, again, M grows with k. There can-
not be any local optima in this series. This allows
us to investigate M in total isolation from any other
factor that may impact algorithm performance. Both
series of instances are illustrated in Figure 1.
We now create the T-O, H-O, and K-O instance
groups with edge lengths sampled u.a.r. from the
ranges 1 to 10, 1 to 100, and 1 to 1000, respectively.
However, our goal is not to just create random matri-
ces. Instead, we repeatedly sample random instances
and preserve instances with O ∈ {2,4,6, 8, 10} op-
tima according to the optimal(·) definition from Equa-
tion 3, where O = #G + #L is the sum of the num-
bers #G and #L of global and local optima, respec-
tively. We thus obtain instance sets with different and
known numbers and sizes of optima. The M values for
these instances naturally differ significantly between
the groups. The greater the range for the edge lengths,
the greater the number M of different possible objec-
tive values.
We also manually design two TSP instances, V
and W, such that they have exactly one globally and
one locally optimal nonsynonymous tour. Each of
them can be traversed forwardly or backwardly, lead-
ing to four optima.
Our TSP instances, which violate the triangle
equation, are non-geometric. We aim to have in-
stances with specific properties, such as known num-
bers of optima and numbers of different objective val-
ues. In Table 1, we print the instance features. We
find that
ˆ
M = 2520 is indeed reached on the LO-k and
HI-k instances, but interestingly already for k ≥ 24 and
k ≥ 20, respectively.
We base our instance construction on the neigh-
borhood spanned by the unary operator from (Liang
et al., 2022; Liang et al., 2024), which reduces the
search space size to 5040 but does not prevent a
complete reversal of a given tour. This means that
both global and local optimal usually appear in pairs,
which is visible in the table. M grows with the in-
creasing ranges from which the edge lengths are sam-
pled in the T-O, H-O, and K-O sets, too. These in-
stances exhibit a variety of different combinations of
#G and #L values. The ranges of BG and BL show
that global and (if they exist) local optima can often
be reached from most points in the search space.
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
176

Table 1: The globally optimal tour length ˇz, the worse possible tour length ˆz, the total number M of different possible tour
lengths, the number #G of global optima and the number #g of globally optimal solutions, the number BG of solutions from
which RLS can reach a global optimum, the number #L of local optima that can trap RLS and the number BL from which RLS
can reach them. The total number of solutions in the search space P after symmetry removal is 5040.
inst ˇz ˆz M #G #g BG #L BL inst ˇz ˆz M #G #g BG #L BL
LO-1 939 524 097 2
30
2 1 1 440 5 040 0 0 T-6-3 21 61 37 2 2 5 030 4 5 034
LO-2 805 306 371 2
30
4 1 240 5 040 0 0 T-6-4 25 72 47 2 2 5 030 4 5 036
LO-3 671 088 647 2
30
8 1 48 5 040 0 0 T-6-5 11 64 54 2 2 5 036 4 5 016
LO-4 2
29
+ 15 2
30
16 1 12 5 040 0 0 T-8-1 21 66 46 2 2 5 024 6 5 016
LO-5 402 653 215 2
30
32 2 4 5 040 0 0 T-8-2 21 70 49 2 2 5 024 6 5 036
LO-6 2
28
+ 63 2
30
64 2 2 5 040 0 0 T-8-3 26 64 38 2 2 5 024 6 5 024
LO-7 2
27
+ 127 2
30
122 2 2 5 040 0 0 T-8-4 25 66 40 2 2 5 032 6 4 978
LO-8 2
27
+ 127 2
30
185 2 2 5 040 0 0 T-8-5 18 65 48 2 2 5 028 6 5 026
LO-9 2
27
+ 127 2
30
280 2 2 5 040 0 0 T-10-1 16 70 53 2 2 5 022 8 5 030
LO-10 2
27
+ 127 2
30
399 2 2 5 040 0 0 T-10-2 24 71 46 2 2 5 016 8 5 030
LO-11 2
27
+ 127 2
30
566 2 2 5 040 0 0 T-10-3 25 71 46 2 2 5 028 8 5 034
LO-12 2
27
+ 127 2
30
795 2 2 5 040 0 0 T-10-4 23 73 51 2 2 5 000 8 5 034
LO-13 8 129 2
30
997 2 2 4 862 2 5 038 T-10-5 21 65 43 2 2 5 022 8 5 014
LO-14 8 129 2
30
1 103 2 2 4 932 2 5 036 H-2-1 206 664 348 2 4 5 040 0 0
LO-15 8 129 939 540 480 1 311 2 2 4 946 2 5 032 H-2-2 161 528 298 2 2 5 040 0 0
LO-16 8 129 939 524 608 1 620 2 2 4 968 2 5 024 H-2-3 281 640 298 2 4 5 040 0 0
LO-17 8 129 939 524 104 1 930 2 2 5 004 2 5 012 H-2-4 290 636 285 2 2 5 040 0 0
LO-18 8 129 939 524 104 1 930 2 2 5 020 2 4 978 H-2-5 233 634 331 2 2 5 040 0 0
LO-19 8 129 805 568 520 1 930 2 2 5 028 2 4 944 H-4-1 224 606 313 2 2 5 038 2 5 034
LO-20 8 129 671 875 080 2 160 2 2 5 032 2 4 888 H-4-2 214 609 308 2 2 5 038 2 4 952
LO-21 8 129 671 137 800 2 400 2 2 5 032 2 4 792 H-4-3 136 590 345 2 2 5 038 2 4 932
LO-22 8 129 671 090 184 2 400 2 2 5 040 0 0 H-4-4 143 584 350 2 2 5 038 2 4 866
LO-23 8 129 541 066 760 2 400 2 2 5 040 0 0 H-4-5 179 648 378 2 2 5 028 2 5 012
LO-24 8 129 415 237 640 2 520 2 2 5 040 0 0 H-6-1 137 584 332 2 2 5 028 4 4 972
LO-25 8 129 404 227 592 2 520 2 2 5 040 0 0 H-6-2 182 501 275 2 2 5 008 4 5 038
LO-26 8 129 303 564 296 2 520 2 2 5 040 0 0 H-6-3 172 587 330 2 2 5 028 4 5 032
LO-27 8 129 236 455 432 2 520 2 2 5 040 0 0 H-6-4 168 567 322 2 2 5 030 4 5 008
HI-1 8 2
27
+ 7 2 1 3 600 5 040 0 0 H-6-5 197 663 352 2 2 5 034 4 4 944
HI-2 8 201 326 598 4 1 2 400 5 040 0 0 H-8-1 221 576 314 2 2 5 002 6 5 036
HI-3 8 234 881 029 8 1 1 632 5 040 0 0 H-8-2 263 522 228 2 2 5 030 6 5 000
HI-4 8 234 881 029 14 1 1 008 5 040 0 0 H-8-3 228 610 302 2 2 5 022 6 5 032
HI-5 8 234 881 029 27 1 648 5 040 0 0 H-8-4 145 627 374 2 2 5 032 6 5 026
HI-6 8 234 881 029 49 1 428 5 040 0 0 H-8-5 260 685 344 2 2 5 008 6 5 038
HI-7 8 234 881 029 79 1 248 5 040 0 0 H-10-1 141 544 328 2 2 5 016 8 5 038
HI-8 8 235 929 604 138 1 152 5 040 0 0 H-10-2 167 638 386 2 2 5 020 8 5 028
HI-9 8 236 453 891 246 1 96 5 040 0 0 H-10-3 101 621 416 2 2 5 030 8 4 890
HI-10 8 236 453 891 399 1 62 5 040 0 0 H-10-4 196 535 301 4 4 5 008 6 5 020
HI-11 8 236 453 891 544 2 28 5 040 0 0 H-10-5 270 667 329 2 2 5 008 8 5 030
HI-12 8 236 453 891 790 2 16 5 040 0 0 K-2-1 2 057 6 527 1 648 2 2 5 040 0 0
HI-13 8 236 453 891 1 135 2 8 5 040 0 0 K-2-2 2 349 7 140 1 668 2 2 5 040 0 0
HI-14 8 236 453 891 1 515 2 4 5 040 0 0 K-2-3 3 120 7 099 1 560 2 2 5 040 0 0
HI-15 8 236 453 891 1 821 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-2-4 1 918 6 339 1 713 2 2 5 040 0 0
HI-16 4 103 236 453 891 1 961 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-2-5 2 139 6 087 1 583 2 2 5 040 0 0
HI-17 6 150 236 453 891 2 112 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-4-1 1 485 5 822 1 559 2 2 5 038 2 4 950
HI-18 7 173 236 454 914 2 262 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-4-2 2 276 5 747 1 358 2 2 5 038 2 4 996
HI-19 7 684 236 455 425 2 400 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-4-3 2 021 5 878 1 486 2 2 5 038 2 4 954
HI-20 7 939 236 455 425 2 520 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-4-4 2 282 6 045 1 579 2 2 5 038 2 4 960
HI-21 8 066 236 455 425 2 520 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-4-5 1 986 6 389 1 605 2 2 5 036 2 5 030
HI-22 8 129 236 455 425 2 520 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-6-1 2 572 6 822 1 577 2 2 5 022 4 5 030
HI-23 8 129 236 455 425 2 520 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-6-2 1 096 5 677 1 609 2 2 5 026 4 5 034
HI-24 8 129 236 455 425 2 520 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-6-3 1 367 5 569 1 637 2 2 5 024 4 5 032
HI-25 8 129 236 455 432 2 520 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-6-4 1 638 6 434 1 657 2 2 5 018 4 5 034
HI-26 8 129 236 455 432 2 520 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-6-5 2 074 6 396 1 615 2 2 5 026 4 5 034
HI-27 8 129 236 455 432 2 520 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-8-1 2 398 6 387 1 530 2 2 5 028 6 5 028
T-2-1 27 59 33 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-8-2 1 624 6 329 1 663 2 2 5 008 6 5 038
T-2-2 28 69 42 2 8 5 040 0 0 K-8-3 1 721 5 762 1 596 2 2 4 982 6 5 000
T-2-3 18 60 42 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-8-4 2 142 5 845 1 521 2 2 5 032 6 4 918
T-2-4 16 59 44 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-8-5 1 369 5 746 1 594 2 2 5 014 6 5 030
T-2-5 23 70 48 2 2 5 040 0 0 K-10-1 1 530 6 416 1 659 2 2 5 028 8 4 978
T-4-1 31 68 38 2 4 5 032 2 5 010 K-10-2 1 379 5 217 1 649 2 2 5 020 8 5 034
T-4-2 14 58 45 4 4 5 040 0 0 K-10-3 2 491 6 830 1 582 2 2 5 008 8 5 014
T-4-3 17 74 58 2 2 5 038 2 4 862 K-10-4 3 062 6 266 1 475 2 2 5 024 8 5 004
T-4-4 20 70 49 2 2 5 036 2 5 032 K-10-5 1 850 6 334 1 651 2 2 5 012 8 5 028
T-4-5 28 69 42 2 4 5 036 2 5 002 V 9 656 18 882 229 2 2 5 038 2 5 000
T-6-1 19 62 43 2 2 5 036 4 5 034 W 9 680 18 892 696 2 2 5 038 2 5 000
T-6-2 27 57 31 6 12 5 040 0 0
Generating Small Instances with Interesting Features for the Traveling Salesperson Problem
177
5 10 15 20 25
10
0
10
2
10
4
10
6
10
8
LO-k
ert[FEs] (log-scaled)
RLS
FRLS
5 10 15 20 25
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
HI-k
ert[FEs] (log-scaled)
RLS
FRLS
2 4 6 8 10
10
0
10
2
10
4
10
6
T-O
ert[FEs] (log-scaled)
RLS
FRLS
2 4 6 8 10
10
0
10
2
10
4
10
6
H-O
ert[FEs] (log-scaled)
RLS
FRLS
2 4 6 8 10
10
0
10
2
10
4
10
6
K-O
ert[FEs] (log-scaled)
RLS
FRLS
4750 4800 4850 4900 4950 5000
10
0
10
2
10
4
10
6
BL (all instances)
ert[FEs] (log-scaled)
RLS
FRLS
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
10
0
10
2
10
4
10
6
10
8
M (log-scaled, all insts)
ert[FEs] (log-scaled)
RLS
FRLS
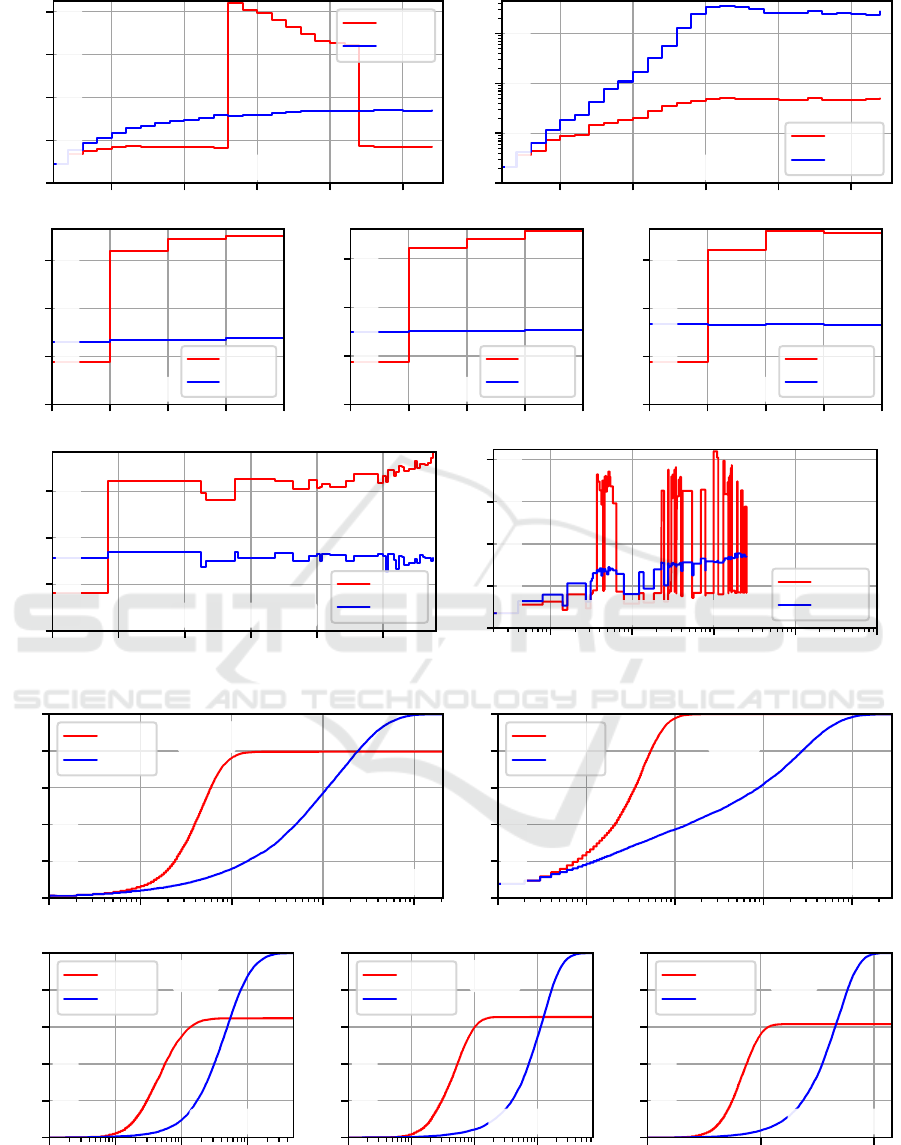
Figure 2: The empirically determined Expected Running Time (ERT) over different instance groups.
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
time in FEs
ECDF [f]
RLS
FRLS
LO-k
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
time in FEs
ECDF [f]
RLS
FRLS
HI-k
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
time in FEs
ECDF [f]
RLS
FRLS
T-O
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
time in FEs
ECDF [f]
RLS
FRLS
H-O
10
0
10
2
10
4
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
time in FEs
ECDF [f]
RLS
FRLS
K-O
Figure 3: The Empirical Cumulative Distribution Functions (ECDFs), i.e., the fraction of successful runs over time (measured
in FEs and log-scaled), aggregated over different instance groups.
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
178

4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
We now conduct 333 runs of the RLS and the FRLS on
each of our 131 instances, i.e., 43 623 runs per algo-
rithm. We use a maximum of 10
7
objective function
evaluations (FEs) for each run. The first observation
that we make is that all runs of FRLS always find an
optimal solution within the 10
7
FEs, whereas 11 036
(about 25%) of the RLS runs fail. On all instances
with #L > 0, at least some of the runs of RLS fail,
while it always succeeds in finding the global optima
on all instances without local optima.
In Figure 2, we plot the empirical Expected Run-
ning Time (ERT) over different instance groups and
parameters. The ERT is estimated as the ratio of the
sum of all FEs that all the runs consumed on a set of
problem instances until they either have discovered
a global optimum or exhausted their budget, divided
by the number of runs that discovered a global opti-
mum (Hansen et al., 2021).
The value of M increases for the LO-k and HI-k
instances until k reaches 24 and 20, respectively. The
diagrams in the first row of Figure 2 show that the run-
time that FRLS needs to solve an instance increases
with M.
1
RLS is much less affected by M. However,
we see an increased ERT for LO-13 to LO-21, which
happen to be the only instances with local optima in
this series.
The second row of diagrams shows that the ERT
of RLS grows steeply if the number O of optima in-
creases, as most of the T-O, H-O, and K-O instances
have local optima for O > 2. The ERT of FRLS is not
affected by the presence of local optima.
In the last row of Figure 2, we plot the ERT of both
algorithms with respect to the size BL of the basins
of attraction of the local optima (left) and over the
number of different objective values (right), aggre-
gated over all of our instances. The runtime of RLS is
strongly affected by BL, whereas it has no impact on
FRLS. A rising M slows down FRLS, whereas M has
no clear impact on RLS.
In Figure 3, we plot the Empirical Cumulative
Distribution Functions (ECDFs) over the different in-
stance groups. The ECDFs show the fraction of runs
that have solved their corresponding problem to op-
timality over the FEs (Hansen et al., 2021; Weise
et al., 2014a). FRLS can solve all instances to op-
timality and therefore always reaches the maximum
ECDF value of 1. The runs of RLS reach the optimal
solution either in the low hundreds of FEs or never,
1
For the HI-k instances, it stops increasing at k = 16,
which, interestingly, is when the first and second superdiag-
onal of the distance matrix begin to be filled with larger
powers of 2.
whereas FRLS may converge about one hundred times
slower but always finds an optimum.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We explored the performance of the RLS and
the FRLS on the symmetric TSP based on the num-
ber M of possible different objective values and the
number #L and size BL of the local optima. These
properties are unknown for the usual benchmark in-
stances and determining them itself would be N P -
hard. We created TSP instances with n = 8 cities for
which we can determine all such features exactly. We
designed instances in a deterministic way to produce
problems with different numbers M of tour lengths
and generated instances where M reaches its maxi-
mum possible value. We showed that the performance
of FRLS indeed deteriorates with increasing M and
that M has no tangible impact on the performance of
RLS. We also generated TSP instances with different
numbers O of optima, including both different global
and local optima structures. We confirmed that the
performance of RLS steeply declines if local optima
are present and if the size BL of their joint basins of
attraction increases. We found that the presence of lo-
cal optima does seemingly not have a tangible impact
on the FRLS performance. All of our code, instances,
and results are available in the immutable online
archive https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13324196.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors acknowledge support from the Project
of National Natural Science Foundation of China
62406095, the Project of Natural Science Foundation
of Anhui Province 2308085MF213, the Key Research
Plan of Anhui Province 2022k07020011, the Univer-
sity Scientific Research Innovation Team Project of
Anhui Province 2022AH010095, as well as the Hefei
Specially Recruited Foreign Expert program and the
Hefei Foreign Expert Office program.
REFERENCES
B
¨
ack, T., Fogel, D. B., and Michalewicz, Z., editors (1997).
Handbook of Evolutionary Computation. Oxford Uni-
versity Press.
Bossek, J., Kerschke, P., Neumann, A., and et al. (2019).
Evolving diverse TSP instances by means of novel and
creative mutation operators. In ACM/SIGEVO Conf.
Generating Small Instances with Interesting Features for the Traveling Salesperson Problem
179

on Foundations of Genetic Algorithms, pages 58–71.
ACM.
Bossek, J. and Neumann, F. (2022). Exploring the fea-
ture space of TSP instances using quality diversity. In
Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conf., pages
186–194. ACM.
Bossek, J. and Trautmann, H. (2016). Understand-
ing characteristics of evolved instances for state-of-
the-art inexact TSP solvers with maximum perfor-
mance difference. In Advances in Artificial Intelli-
gence (AI*IA’16), pages 3–12. Springer.
ˇ
Cern
´
y, V. (1985). Thermodynamical approach to the trav-
eling salesman problem: An efficient simulation algo-
rithm. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applica-
tions, 45(1):41–51.
Chiong, R., Weise, T., and Michalewicz, Z. (2012). Vari-
ants of Evolutionary Algorithms for Real-World Ap-
plications. Springer.
de Bruin, E., Thomson, S. L., and van den Berg, D. (2023).
Frequency fitness assignment on JSSP: A critical re-
view. In European Conf. on Applications of Evolu-
tionary Computation, pages 351–363.
Floyd, R. W. (1962). Algorithm 97: Shortest path. Commu-
nications of the ACM, 5(6):345.
Gutin, G. Z. and Punnen, A. P., editors (2002). The Travel-
ing Salesman Problem and its Variations. Springer.
Hansen, N., Auger, A., Ros, R., Mersmann, O., Tu
ˇ
sar, T.,
and Brockhoff, D. (2021). COCO: a platform for com-
paring continuous optimizers in a black-box setting.
Optimization Methods and Software, 36(1):114–144.
Helsgaun, K. (2009). General k-opt submoves for the Lin–
Kernighan TSP heuristic. Mathematical Program-
ming Computation, 1(2-3):119–163.
Hoos, H. H. and St
¨
utzle, T. (2005). Stochastic Local Search:
Foundations and Applications. Elsevier.
Johnson, D. S. and McGeoch, L. A. (2008). 8th DIMACS
Implementation Challenge: The Traveling Salesman
Problem. Rutgers University.
Kirkpatrick, S., Gelatt, Jr., C. D., and Vecchi, M. P. (1983).
Optimization by simulated annealing. Science Maga-
zine, 220(4598):671–680.
Lawler, E. L., Lenstra, J. K., Rinnooy Kan, A. H. G., and
Shmoys, D. B. (1985). The Traveling Salesman Prob-
lem: A Guided Tour of Combinatorial Optimization.
Wiley Interscience.
Liang, T., Wu, Z., L
¨
assig, J., van den Berg, D., Thom-
son, S. L., and Weise, T. (2024). Addressing the
traveling salesperson problem with frequency fitness
assignment and hybrid algorithms. Soft Computing.
doi:10.1007/s00500-024-09718-8.
Liang, T., Wu, Z., L
¨
assig, J., van den Berg, D., and Weise, T.
(2022). Solving the traveling salesperson problem us-
ing frequency fitness assignment. In IEEE Symposium
Series on Computational Intelligence, pages 360–367.
Mersmann, O., Bischl, B., Bossek, J., and et al. (2012).
Local search and the traveling salesman problem: A
feature-based characterization of problem hardness.
In Intl. Conf. on Learning and Intelligent Optimiza-
tion, pages 115–129. Springer.
Nagata, Y. and Soler, D. (2012). A new genetic algorithm
for the asymmetric traveling salesman problem. Ex-
pert Systems with Applications, 39(10):8947–8953.
Nallaperuma, S., Wagner, M., Neumann, F., Bischl, B.,
Mersmann, O., and Trautmann, H. (2012). Features of
easy and hard instances for approximation algorithms
and the traveling salesperson problem. In Works. on
Automated Selection and Tuning of Algorithms, Intl.
Conf. Parallel Problem Solving from Nature.
Neumann, A., Gao, W., Doerr, C., Neumann, F., and Wag-
ner, M. (2018). Discrepancy-based evolutionary diver-
sity optimization. In Genetic and Evolutionary Com-
putation Conf., pages 991–998. ACM.
Neumann, A., Gao, W., Wagner, M., and Neumann, F.
(2019). Evolutionary diversity optimization using
multi-objective indicators. In Genetic and Evolution-
ary Computation Conf., pages 837–845. ACM.
Reinelt, G. (1991). TSPLIB – a traveling salesman problem
library. ORSA Journal on Computing, 3(4):376–384.
Warshall, S. (1962). A theorem on boolean matrices. Jour-
nal of the ACM, 9(1):11–12.
Weise, T. (2009). Global Optimization Algorithms – The-
ory and Application. Institute of Applied Optimiza-
tion, Hefei University. http://iao.hfuu.edu.cn/images/
publications/W2009GOEB.pdf.
Weise, T., Chiong, R., Tang, K., L
¨
assig, J., Tsutsui, S.,
Chen, W., Michalewicz, Z., and Yao, X. (2014a).
Benchmarking optimization algorithms: An open
source framework for the traveling salesman problem.
IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 9(3):40–
52.
Weise, T., Li, X., Chen, Y., and Wu, Z. (2021a). Solving
job shop scheduling problems without using a bias for
good solutions. In Genetic and Evolutionary Compu-
tation Conf. Companion, pages 1459–1466. ACM.
Weise, T., Wan, M., Tang, K., Wang, P., Devert, A.,
and Yao, X. (2014b). Frequency fitness assign-
ment. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computa-
tion, 18(2):226–243.
Weise, T., Wu, Y., Chiong, R., Tang, K., and L
¨
assig,
J. (2016). Global versus local search: The impact
of population sizes on evolutionary algorithm perfor-
mance. Journal of Global Optimization, 66:511–534.
Weise, T., Wu, Z., Li, X., and Chen, Y. (2021b). Frequency
fitness assignment: Making optimization algorithms
invariant under bijective transformations of the objec-
tive function value. IEEE Transactions on Evolution-
ary Computation, 25(2):307–319.
Weise, T., Wu, Z., Li, X., Chen, Y., and L
¨
assig, J. (2023).
Frequency fitness assignment: Optimization without
bias for good solutions can be efficient. IEEE Transac-
tions on Evolutionary Computation, 27(4):980–992.
Whitley, L. D., Hains, D., and Howe, A. (2010). A hybrid
genetic algorithm for the traveling salesman problem
using generalized partition crossover. In Intl. Conf.
on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature, pages 566–
575. Springer.
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
180
