
Randomized Local Search vs. NSGA-II vs. Frequency Fitness
Assignment on The Traveling Tournament Problem
Cao Xiang
1 a
, Zhize Wu
1 b
, Daan van den Berg
2 c
and Thomas Weise
1 d
1
Institute of Applied Optimization, School of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data,
Hefei University, Jinxiu Dadao 99, Hefei, 230601, Anhui, China
2
Department of Computer Science, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, De Boelelaan 1111, Amsterdam, 1081 HV,
The Netherlands
Keywords:
Traveling Tournament Problem, NSGA-II, Randomized Local Search, Frequency Fitness Assignment.
Abstract:
The classical compact double-round robin traveling tournament problem (TTP) asks us to schedule the games
of n teams in a tournament such that each team plays against every other team twice, once at home and
once away (doubleRoundRobin constraint). The maxStreak constraint prevents teams from having more than
three consecutive home or away games. The noRepeat constraint demands that, before two teams can play
against each other the second time, they must at least play one other game in between. The goal is to find a
game plan observing all of these constraints and having the overall shortest travel length. We define a game-
permutation based encoding that allows for representing game plans with arbitrary numbers of constraint
violations and tackle the TTP as a bi-objective problem minimizing both the number of constraint violations
and the travel length by applying the well-known NSGA-II. We combine both objectives in a lexicographic
prioritization scheme and also apply the randomized local search RLS to this single-objective variant of the
problem. We realize that Frequency Fitness Assignment (FFA), which makes algorithms invariant under all
injective transformations of the objective function value, would also make optimization algorithms invariant
under all lexicographic prioritization schemes for multi-objective problems. The FRLS, i.e., the RLS with
FFA plugged in, would therefore solve both possible prioritizations of our TTP variants at once. We thus also
explore its performance on the TTP. We find that RLS performs surprisingly well and can find game plans
without constraint violations reliably until a scale of 36 teams, whereas FRLS and NSGA-II have an advantage
on small- and mid-scale problems.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Traveling Tournament Problem (TTP) is the com-
binatorial optimization problem of efficiently and
fairly organizing a tournament of n teams that play
against each other in a pairwise fashion (Easton et al.,
2001). The efficient part boils down to arranging the
games such that the total travel length
1
is short, which
is somewhat similar to the classical Traveling Sales-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-4811-7824
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7416-5711
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5060-3342
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9687-8509
1
Initially, each team is at its home location. On each
day, a team needs to travel if its scheduled game is not at
its present location. On the last day, each team may need
to travel back home unless their last game is a home game.
The total travel length sums up the lengths of all travels over
all teams.
person Problem (TSP). The fair part is represented in
several constraints. Compared to classical N P -hard
problems like the TSP, the Job Shop Scheduling Prob-
lem (JSSP), or Max-SAT, these constraints are what
make the TTP (more) challenging, as (Verduin et al.,
2023) pointed out at last year’s IJCCI. This problem
is indeed very hard and therefore, very interesting.
We focus on the classical compact double round
robin instances from the RobinX benchmark by (Van
Bulck et al., 2018; Van Bulck, 2024), where the fol-
lowing constraints apply (Van Bulck et al., 2020):
• doubleRoundRobin (2RR): Each team i plays
twice against every other team j, once at home
(home game) and once at the place of j (away
game). Therefore, there are g = n(n − 1) games
in the tournament.
• compactness: Each team has one game in ev-
ery slot and thus, the whole tournament lasts d =
38
Xiang, C., Wu, Z., van den Berg, D. and Weise, T.
Randomized Local Search vs. NSGA-II vs. Frequency Fitness Assignment on The Traveling Tournament Problem.
DOI: 10.5220/0012891500003837
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2024), pages 38-49
ISBN: 978-989-758-721-4; ISSN: 2184-3236
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

g/(n/2) = 2(n − 1) days.
• maxStreak: Each team has at most three away
and at most three home games in each consecu-
tive four time slots, i.e., the maximum lengths for
home and away streaks are both 3.
• noRepeat: Each pair of teams has at least one
different game between two consecutive mutual
games.
The first contribution of our work is to treat the TTP
as a bi-objective problem that can be approached with
metaheuristics. We define the two objective functions
f
e
(s), counting all constraint violations of a solution s
across the board, and f
t
(s), evaluating the total travel
length over all teams. If both objectives are mini-
mized, the result would be the game plan without any
constraint violation that also has the shortest possible
travel length among all such plans. The question is
how to achieve this goal.
An important ingredient to this end is to define a
proper search space P amenable to metaheuristic opti-
mization and a decoding decode which translates it to
the solution space S containing the game plans s. In
our work, we apply a game-based encoding where the
search space consists of permutations π of length g =
n(n − 1) where each element identifies one of the
g games. The decoding then processes such a permu-
tation π from beginning to end and places the games
into the earliest slot in the game plan s where both
involved teams do not yet have another game sched-
uled. Games that cannot be placed are omitted, so
the game plans can have so-called “byes” (Van Bulck,
2024; Thielen and Westphal, 2011; Brand
˜
ao and Pe-
droso, 2014), i.e., days at which a team does not have
a game scheduled, which, of course, are considered
in f
e
. With the exception of this last detail, which
makes the implementation more efficient, this encod-
ing is very similar to the one presented by (Choubey,
2010).
Having reduced the TTP to finding good permu-
tations π in the space P, we must now tackle the
question of how to go about conducting this search.
Since we consider the TTP as a multi-objective
problem with two objective functions, applying the
most famous multi-objective optimization algorithm,
NSGA-II (Deb et al., 2000; Deb et al., 2002) would be
an obvious approach. NSGA-II tries to push a popula-
tion of candidate solutions towards the Pareto frontier,
i.e., the trade-off curve where any further improve-
ment in f
e
would require an increase in f
t
and vice
versa. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first
to explicitly approach the TTP as a multi-objective
problem.
Then again, we are not really interested in obtain-
ing the Pareto frontier: The objective f
e
is more im-
portant than f
t
. Thus, we can turn the TTP into a
single-objective problem by defining a new objective
function
f (s) = (UB[ f
t
] + 1)∗ f
e
(s) + f
t
(s) (1)
where UB[ f
t
] is the upper bound of f
t
. In other words,
even an improvement or loss of 1 in terms of f
e
would
outweigh even the largest loss or improvement of f
t
(which could never be more than UB[ f
t
]), meaning
that the objectives are lexicographically ordered (An-
derson, 2000; George et al., 2015; Volgenant, 2002;
Zhang et al., 2023). This problem can then be ap-
proached by a single-objective technique. We pick
the randomized local search (RLS) for this purpose.
The question now arises whether RLS or NSGA-II
can find shorter error-free game plans. Will RLS get
trapped in local optima of f and the multi-objective
approach will pay off by finding a way around them?
Or will spreading out the search pressure over the
Pareto frontier consume more objective function eval-
uations (FEs) and the efficiency of RLS focusing all
FEs towards feasible game plans and then such with
short travel lengths lead to the better results? Answer-
ing this question is an interesting second contribu-
tion of our work.
In (Weise et al., 2014), a mechanism called Fre-
quency Fitness Assignment (FFA) was proposed.
FFA renders optimization processes invariant under
all injective transformations of the objective function
value (Weise et al., 2021b) and, as a result, removes
the bias towards better solutions (Weise et al., 2023).
By replacing the objective value f (s) of a solution s
with its encounter frequency H[ f (s)], an algorithm
that uses FFA does no longer prefer better solutions
over worse ones, i.e., FFA breaks with the most fun-
damental principle inherent in all metaheuristic opti-
mization methods.
The only iterative optimization algorithms that
have similar properties are random walks, random
sampling, and exhaustive enumeration. FFA has been
shown to improve the performance of RLS on clas-
sical N P -hard problems like the Max-SAT prob-
lem (Weise et al., 2021b; Weise et al., 2023), the
JSSP (Weise et al., 2021a; de Bruin et al., 2023), and
on TSP instances (Liang et al., 2022; Liang et al.,
2024). The third contribution is to also apply FFA
to the TTP, extending our comparison to RLS vs.
NSGA-II vs. FRLS, i.e., the RLS with FFA plugged
in.
But there is another reason for us to include FFA
into our experiments: We stated above that FFA ren-
ders algorithms invariant under injective transforma-
tions of the objective function value. What does this
mean in a multi-objective scenario? If we consider
our original multi-objective formulation of the TTP,
Randomized Local Search vs. NSGA-II vs. Frequency Fitness Assignment on The Traveling Tournament Problem
39

then f
e
and f
t
span a two-dimensional space O ⊂ N
2
.
Inspecting the construction of f in Equation 1, one re-
alizes that it is actually a bijective mapping of O 7→ N.
Indeed, each unique combination of a value of f
e
and
a value of f
t
will map to a unique value of f . Applying
the invariance transitively means that FRLS will be in-
variant – i.e., traverse the exactly same path through
the search space P – regardless of which of the two
original objectives is prioritized. If we would favor
travel length over game plan correctness instead, the
FRLS would still visit the same solutions. If FFA is
applied to one lexicographic prioritization scheme of
a k-objective problem, it will optimize all the k! possi-
ble orders of the objective functions at once. Finding
this puzzling property is the fourth contribution and
the deeper reason for us to explore what kind of re-
sults FRLS will yield on our TTP formulation.
Finally, as the fifth contribution, we publish not
just all of our results, but also all of the source code of
all involved algorithms, and all scripts for generating
the tables and figures in this paper in an immutable
archive at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13329107,
making our work fully reproducible.
The remainder of this paper is structured as fol-
lows. In Section 2, we will discuss the related works
on the TTP before introducing our approach and the
involved algorithms in detail in Section 3. We then
present our experiments and results in Section 4. We
conclude our paper in Section 5 with a summary and
outlook to future work.
2 RELATED WORK
(Anagnostopoulos et al., 2006) applied simulated an-
nealing to the TTP. Their five search operators work
directly on the game plans s ∈ S and thus, are more
complicated than the simple swap-2 unary operator
used in our work. Like in our work, the solutions may
violate the maxStreak and noRepeat constraints but
different from us, they always observe the doubleR-
oundRobin and compactness constraints. This forces
them to generate a starting solution that adheres to
these constraints as well, whereas we can just sample
a permutation uniformly at random (u.a.r.). Further-
more, like us when using the RLS and FRLS, they
construct a single summary objective function min-
imizing both constraint violations and travel length.
Different from us, this summary objective is not
a strict prioritization scheme but instead a penalty-
based method. They do not tackle problems larger
than n = 16.
(Chen et al., 2007) develop a hyper-heuristic
based on the ant colony optimization (ACO) where
ants travel through a graph whose nodes represent
heuristics. When visited, the heuristics correspond-
ing to the nodes are applied to the current solution
and transform it to a new game plan. The nodes can
be visited multiple times by the ants, allowing them
to better explore the solution space and try out differ-
ent combinations of heuristics. The article uses the
NLn instances in the experiment, i.e., does not inves-
tigate problems with more than 16 teams. While their
method cannot outperform the related works, this first
attempt to tackle the TTP with ACO did yield good
results on NL4 and NL6.
(Choubey, 2010) presents an encoding scheme for
tackling the TTP with GAs. The games to be sched-
uled are represented as symbols which are arranged in
a sequence and decoded to game plans. While some
details are not fully clear, it can be assumed that this
encoding will basically work like ours with some mi-
nor deviations: Games that cannot be scheduled due
to conflicts within the d tournament days are added to
the end of the game plan and thus expanding it, vio-
lating the compactness constraint. In our case, they
are simply omitted. In their work and ours, these
situations add to the number of errors. (Choubey,
2010) use a weighted sum as objective that penalizes
scheduling errors, but theirs is not a lexicographic pri-
oritization like ours. Their GA is applied to RobinX
instances with no more than n = 8 teams.
In (Khelifa and Boughaci, 2016), a harmony
search (HS) algorithm is hybridized with variable
neighborhood search (VNS) and applied to the mir-
rored TTP with reversed venues. The polygon
method (de Werra, 1988) is used to generate single-
round robin game plans and the encoding applied in
the HS maps teams to the abstract teams in this poly-
gon heuristic. The numerical results are limited to
instances with n ≤ 16.
(Khelifa et al., 2017) applied a Genetic Al-
gorithm (GA) whose initial population consists
of feasible game plans generated by the polygon
method (de Werra, 1988) The search operators work
directly on (feasible) game plans and minimizing f
t
.
As a result, they (and in particular, the binary
crossover operator), are much more complicated than
ours. No instance with more than n = 10 teams is
tacked in (Khelifa et al., 2017).
(Khelifa and Boughaci, 2018) finally apply a co-
operative search method for the TTP that handles the
constraints and travel length separately. They start by
generating a 2RR solution, similar to (Anagnostopou-
los et al., 2006). Then, however, they only search for
a feasible solution satisfying all constraints and ig-
nore the travel length using simulated annealing and
variable neighborhood search. Once a feasible solu-
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
40

tion is found, they apply a Stochastic Local Search
to minimize the travel length f
t
while only consid-
ering feasible solutions. The selection criterion used
in this last step is very similar to our prioritization
scheme f from Equation 1. We, however, always
only apply one algorithm (either only RLS or only
FRLS) to f , and the algorithm used is also much
simpler compared to those in (Khelifa and Boughaci,
2018). Different from (Khelifa and Boughaci, 2018),
we also do not work on the game plans directly but
on our game-permutation based representation, which
also allows for simpler search operators. Finally, the
largest instance used in (Khelifa and Boughaci, 2018)
has n = 24.
From this survey, we find that, to the best of
our knowledge, only (Choubey, 2010) applies an
encoding-based approach working directly on game
permutations. This is somewhat surprising, as such a
game-permutation based encoding has, at least from
the perspective of simplicity, several advantages. It
allows us to basically use all operators and algorithms
that work with permutations off-the-shelf. As a draw-
back, it permits solutions that violate any number of
constraints. Also, to the best of our knowledge, we
are the first to tackle the TTP explicitly as a multi-
objective problem, to apply a multi-objective algo-
rithm (NSGA-II) to it, and to apply a lexicographic
prioritization of the objectives in a weighted sum ap-
proach to let a local search sort out all types of con-
straint violations. Finally, we are the first to apply
FFA to the TTP, or, actually, to any multi-objective
problem, and to reveal its odd characteristics in this
domain.
3 OUR APPROACH
3.1 Algorithms
In our study, we apply three different algorithms,
RLS, FRLS, and NSGA-II. Let us begin by outlin-
ing the simplest one of them, the Randomized Lo-
cal Search (RLS), often also called Hill Climbing or
(1 + 1) EA (Russell and Norvig, 2002; Neumann and
Wegener, 2007; Johnson et al., 1988). As a black-box
metaheuristic, it allows us to choose a search space P
(in our case, permutations) and a unary search oper-
ator, a decoding function decode : P 7→ S that trans-
lates the points in the search space to game plans, and
an objective function f : S 7→ N rating the quality of
game plans (see Equation 1).
The blueprint of this metaheuristic is given in Al-
gorithm 1. The algorithm begins by sampling a ran-
dom point π
c
from the search space P, decoding it to
Algorithm 1: RLS(decode : P 7→ S, f : S 7→ N).
sample π
c
from P u.a.r.; s
c
← decode(π
c
);
z
c
← f (s
c
); ▷ see Equation 1
for 10
9
− 1 times do ▷ our termination criterion
π
n
← swap 2 values in π
c
u.a.r.;
s
n
← decode(π
n
); z
n
← f (s
n
);
if z
n
≤ z
c
then
π
c
← π
n
; s
c
← s
n
; z
c
← z
n
return s
c
, z
c
Algorithm 2: FRLS(decode : P 7→ S, f : S 7→ N).
H ← (0, 0,·· · ,0); ▷ H-table initially all 0s
sample π
c
from P u.a.r.; s
c
← decode(π
c
);
z
c
← f (s
c
); ▷ see Equation 1
s
b
← s
c
; z
b
← z
c
; ▷ best may otherwise get lost
for 10
9
− 1 times do ▷ our termination criterion
π
n
← swap 2 values in π
c
u.a.r.;
s
n
← decode(π
n
); z
n
← f (s
n
);
if z
n
< z
b
then s
b
← s
n
; z
b
← z
n
;
H[z
c
] ← H[z
c
] + 1; H[z
n
] ← H[z
n
] + 1;
if H[z
n
] ≤ H[z
c
] then
π
c
← π
n
; s
c
← s
n
; z
c
← z
n
return s
b
, z
b
▷ return preserved best
a game plan s
c
, and evaluating its objective value z
c
=
f (s
c
). In a loop, a new point π
n
is sampled as a
modified copy of π
c
using the unary operator, is de-
coded, and evaluated. If π
n
is not worse than π
c
, it re-
places it. When the computational budget of 10
9
FEs
is exhausted, both the best-so-far solution s
c
and its
quality z
c
are returned. In our experiments, the algo-
rithm terminates after 10
9
objective function evalua-
tions (FEs).
FFA is an algorithm module that prescribes re-
placing the objective values with their observed en-
counter frequencies in the selection decisions. Plug-
ging FFA into the RLS yields the FRLS sketched in
Algorithm 2. This algorithm starts like RLS, but ad-
ditionally initializes a frequency table H to be filled
with zeros. Where RLS compares the objective val-
ues z
n
and z
c
to decide whether π
n
should replace π
c
or be discarded, FRLS first increments the encounter
frequencies H[z
n
] and H[z
c
] of z
n
and z
c
and then com-
pares these instead of the objective values. As a re-
sult, it will accept π
n
if it corresponds to a solution
whose objective value has been seen less or equally
often than the one corresponding to π
c
. Since it no
longer matters whether z
n
is a better objective value
than z
c
or not, the algorithm may lose the best discov-
ered solution again and thus needs to remember it in
an additional variable s
b
.
(Weise et al., 2021b; Weise et al., 2023) showed
that the FRLS will be invariant under all injective
Randomized Local Search vs. NSGA-II vs. Frequency Fitness Assignment on The Traveling Tournament Problem
41

transformations of the objective function values. In
our case, f itself is a bijective transformation of the
space spanned by the possible pairs of return values of
the two original objective functions f
e
and f
t
. In fact,
any lexicographic/prioritization scheme implemented
as weighted sum is such a bijective transformation.
Therefore, the FRLS will be invariant, i.e., visit the
exact same candidate solutions in the exact same se-
quence, under all lexicographic approaches to solv-
ing the original problem (or any other multi-objective
problem). This baffling feature of such a simple algo-
rithm is worth exploring, which is what we will do in
this paper.
The third algorithm in our study, NSGA-II (Deb
et al., 2000; Deb et al., 2002), is the most well-known
multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. If the popu-
lation size is set to K, then this algorithm starts by
sampling a population containing 2K random initial
points in the search space and mapping them to game
plans, in the same way RLS and FRLS do. For each
solution, both objective functions f
e
and f
t
are evalu-
ated.
At the beginning of its main loop, NSGA-II will se-
lect K of the 2K points in the population and discard
the rest. This selection step proceeds in two phases.
Iteratively, the “fronts” of all solutions that are non-
dominated in the population are extracted from the
population. If the current front fits entirely into the
new population without exceeding K total solutions,
it is put into there and the selection continues. If it
does not fit entirely, then in the second phase, the new
population is filled up to size K by choosing the solu-
tions that have the farthest-away nearest neighbors to
both sides in each objective function (i.e., those with
the largest crowding distance).
It will then create K new points from the selected
ones. NSGA-II therefore uses a binary and a unary op-
erator, among which it chooses based on the crossover
rate cr. Each new solution is created by using, with
probability cr, a binary operator combining two per-
mutations. The solutions not created by the binary
operator are generated using the same unary search
operator as RLS and FRLS. Then, the K selected and
the K new solutions are put together to form the joint
population to undergo the selection at the beginning
of the next iteration.
3.2 Encoding, Objectives, and Search
Operators
A 2RR tournament involves n teams competing over
d = 2(n − 1) days. In our work, a game plan s ∈ S
therefore is a d × n matrix where the item s[i, j] ∈
−n..n denotes the opponent that team j plays on day i.
If s[i, j] > 0, then team j plays against team s[i, j] in the
home stadium of team j and if s[i, j] < 0, it has an away
game against team −s[i, j] at their stadium. s[i, j] = 0
indicates that no game is scheduled for team j on
day i, i.e., a “bye,” which constitutes a scheduling er-
ror.
The f
e
objective function counts all such byes (as
they imply violations of the compactness constraint),
as well as all violations of the doubleRoundRobin,
maxStreak, and noRepeat constraints mentioned in
the introduction. The f
t
objective computes the total
round trip travel length summed up over each team
(which start from and, finally, return to their home
location). If a team has a bye scheduled for a cer-
tain day, the travel length for this day can be con-
sidered as undefined
2
and is replaced by a penalty
value which equals 2Ω + 1, where Ω is the maxi-
mum distance between any two teams in the tour-
nament. This function can never exceed the upper
bound UB[ f
t
] = 2nd(2Ω + 1) used in Equation 1.
The search space P consists of the permutations π
of the first g = n(n − 1) natural numbers, correspond-
ing to the g games to be scheduled. Each number
in 1..g uniquely identifies a game with one home
team α and one away team β. The permutations π
are processed from front to end and are used to trans-
late a matrix s initially filled with 0 to a game plan.
When the element π[k] at index k of π is processed,
the decoding function decode first extracts the corre-
sponding α and β values. It will then find the smallest
index i such that s[i, α] = s[i,β] = 0. If such i exists, it
will set s[i, α] ← β and s[i,β] ← −α. This may violate
the maxStreak and noRepeat constraints, but we hope
that the search will correct such errors over time. If
no day exists where both teams α and β have byes,
the game is discarded, i.e., not scheduled. This will
always lead to an increase of f
e
and, eventually, re-
sult in a two byes somewhere in the game plan, also
causing an increase of f
t
.
It can immediately be seen that any feasible game
plan s can be represented as a permutation. One
would start with an empty permutation π and simply
translate s it iteratively from day i = 1 to i = d and,
for each day, process columns j = 1 to j = n. If the
team α = s[i, j] > 0 has a home game scheduled, one
would look for the necessarily existing other team β
playing against it on the same day i and append the
value identifying (α,β) to π. Eventually, one ends up
with a permutation π such that decode(π) = s. There-
fore, our encoding allows for representing and hope-
fully also finding the globally optimal solution.
2
If a team was not already at home, it would not be
a priori clear whether it would travel home or to the next
location.
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
42

The unary search operator used in all three op-
timization algorithms swaps two elements in a per-
mutation u.a.r. NSGA-II requires a binary crossover
operator which takes two permutations π
1
and π
2
as
input and produces another permutation π
n
as out-
put. Here we apply a generalized version of the Al-
ternating Position Crossover operator AP for the TSP
by (Larra
˜
naga et al., 1997; Larra
˜
naga et al., 1999).
The original AP operator creates π
n
by selecting al-
ternately the next element of π
1
and the next element
of π
2
, omitting the elements already present in the
offspring. For example, if π
1
= 12345678 and π
2
=
37516824, the AP operator gives π
n
= 13275468. Ex-
changing π
1
and π
2
results in π
n
= 31725468. Our
generalized version randomly decides, u.a.r., at each
step of filling π
n
, from which of the two parent permu-
tations a value should be copied. This should hope-
fully result in a greater variety of possible results. Our
operator also does not skip over a parent if its next el-
ement is already used, but instead picks the next not-
yet-used element from that parent.
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
4.1 Setup
We implement our algorithms in Python 3.10 on Win-
dows 10 using the moptipy (Weise and Wu, 2023)
framework, as well as numba just-in-time compila-
tion where possible. We use the 118 classical com-
pact 2RR instances from the RobinX benchmark by
(Van Bulck et al., 2018; Van Bulck et al., 2020; Van
Bulck, 2024):
• bra24 is based on the 24 teams in the main divi-
sion of the 2003 edition of the Brazilian soccer
championship,
• circn (Easton et al., 2001) with n ∈ 4, 6,8,. .., 40
where all teams are distributed equidistantly on a
circle,
• conn (Urrutia and Ribeiro, 2006) with n ∈
4,6,8,... ,40 where all distances are 1,
• galn (Uthus et al., 2013) with n ∈ 4, 6,8,. .., 40
uses the distances between Earth and exoplanets,
• incrn with n ∈ 4,6,8, ... ,40 has teams situated on
a straight line with the distance between teams i
and i + 1 being i
• linen with n ∈ 4, 6,8,...,40 has teams situated on
a straight line with neighbors being one distance
unit apart,
• nfln with n ∈ 16, 18,20,. .., 44 based on the on the
National Football League
• nln (Easton et al., 2001) with n ∈ 4,6,8,... ,16
based on the teams in the National League of the
Major League Baseball, and
• supn with n ∈ 4,6, 8,...,14
We investigate RLS and FRLS, which do not have
any parameters. We also apply the NSGA-II with a
crossover rate of cr = 1/16 and three different pop-
ulation sizes K ∈ {4,16,64}, which we refer to as
NSGA-II
4
, NSGA-II
16
, and NSGA-II
64
, respectively.
We conduct 7 runs per algorithm setup and problem
instance for at most 10
9
objective function evalua-
tions (FEs).
4.2 Results
Table 1 and Table 2 list the best f values found by the
different algorithms, averaged over the 7 runs per in-
stance. The best values are marked with bold face and
the last row, # best, counts how often each algorithm
reaches the best result. From this row, we immedi-
ately see that RLS performs best, yielding the best
result 72 times, followed by NSGA-II
64
(36 times),
and FRLS (21 times best). Among the NSGA-II se-
tups, larger populations are better as NSGA-II
64
beats
NSGA-II
16
beats NSGA-II
4
, so in future we will try
even larger populations. The NSGA-II and FRLS can
beat RLS on smaller problems. For example, FRLS
is best on circ4 to circ10, NSGA-II is best on circ12 to
circ20, whereas RLS is best on the remaining circn in-
stances. Interestingly, NSGA-II and FRLS also yield
the best results on all of the supn and nln instances
except for the smallest ones with n = 4, where RLS
wins. At this stage, we can summarize that the pop-
ulation of NSGA-II and the FFA component of FRLS
offer a clear advantage, but only if the instances are
not big.
If these best- f values are less than the upper
bound UB[ f
t
] of the travel length objective func-
tion f
t
, then this means that the discovered game
plans s have no error ( f
e
(s) = 0). In this case,
f (s) = f
t
(s), i.e., the printed values are actually the
travel lengths of the plans. The average solutions of
RLS are error-free on bra24, circ4 to circ36, con4 to
con38, gal4 to gal36, incr4 to incr34, on incr38, line4
to line36, and on all nfln, nln, and subn instances. We
therefore can conclude that, at least up to a scale n
of 36, RLS with our simple encoding and budget of
10
9
FEs can reliably find violation-free game plans
of the 2RR TTP. This means that given more time, it
would probably have found error-free game plans for
all of the RobinX instances used in our study. Recall
that the earlier studies usually use only instances with
n up the low twenties at most, usually in the middle-
tens.
Randomized Local Search vs. NSGA-II vs. Frequency Fitness Assignment on The Traveling Tournament Problem
43

Table 1: The best f values found by the different algorithms, averaged over the 7 runs per instance with 10
9
FEs each. We
also provide the upper bound UB[ f
t
] of f
t
and the upper bound UB-opt for the optimal tour length, taken from (Van Bulck,
2024) at the time of this writing. The best values are marked with bold face and counted in the last row (# best). Continued
in Table 2.
instance UB[ f
t
] UB-opt RLS NSGA-II
4
NSGA-II
16
NSGA-II
64
FRLS
bra24 7 093 200 538 866 688 630 81 904 796 35 246 018 703 411 537 039 600
circ4 120 20 20 20 20 20 20
circ6 420 64 65 69 66 66 64
circ8 1 008 132 146 163 144 146 135
circ10 1 980 242 286 329 280 285 276
circ12 3 432 400 491 591 482 494 501
circ14 5 460 616 793 923 805 782 863
circ16 8 160 898 1 186 10 750 1 231 1 159 1 445
circ18 11 628 1 268 1 684 33 608 6 844 1 676 5 645
circ20 15 960 1 724 2 353 62 145 20 851 2 340 110 399
circ22 21 252 2 366 3 171 173 883 55 141 3 214 368 743
circ24 27 600 3 146 4 159 513 812 83 573 8 136 853 588
circ26 35 100 3 992 5 355 502 946 211 752 15 475 1 642 139
circ28 43 848 4 642 6 790 991 604 346 019 69 524 2 740 632
circ30 53 940 5 842 8 401 1 682 421 679 980 139 661 4 527 256
circ32 65 472 7 074 10 443 2 575 350 666 393 300 591 6 972 901
circ34 78 540 8 042 12 539 3 291 243 1 438 983 439 302 10 114 965
circ36 93 240 9 726 15 153 4 680 108 1 908 173 774 723 14 698 709
circ38 109 668 11 424 378 500 5 739 472 2 385 512 1 115 263 20 594 348
circ40 127 920 12 752 459 834 8 906 144 3 513 490 1 867 497 27 822 677
con4 72 17 17 17 17 17 17
con6 180 43 43 43 43 43 43
con8 336 80 80 82 80 80 80
con10 540 124 124 133 126 126 127
con12 792 181 183 198 186 188 189
con14 1 092 252 254 274 262 261 266
con16 1 440 327 334 2 219 351 343 361
con18 1 836 416 428 7 820 719 439 474
con20 2 280 520 535 12 317 4 160 548 2 565
con22 2 772 626 653 20 920 6 645 668 20 159
con24 3 312 747 786 49 614 11 259 2 695 60 529
con26 3 900 884 928 79 045 29 979 5 407 114 757
con28 4 536 1 021 1 084 123 696 49 129 10 186 204 120
con30 5 220 1 177 1 256 183 371 59 516 14 712 305 013
con32 5 952 1 359 1 434 249 907 93 375 26 138 468 538
con34 6 732 1 512 1 634 296 112 122 935 47 846 665 550
con36 7 560 1 703 1 841 415 699 132 639 65 621 909 426
con38 8 436 1 918 2 062 543 426 186 582 98 547 1 232 937
con40 9 360 2 099 19 684 652 410 244 466 128 071 1 622 050
gal4 2 280 416 416 423 417 416 416
gal6 6 180 1 365 1 416 1 459 1 393 1 407 1 366
gal8 14 448 2 373 2 674 2 897 2 498 2 499 2 394
gal10 29 340 4 535 5 222 5 720 4 981 5 031 5 342
gal12 55 704 7 135 8 569 9 615 8 333 8 256 9 888
gal14 76 804 10 840 13 420 26 011 13 581 12 920 16 897
gal16 108 960 14 583 18 552 99 099 35 273 18 020 444 554
gal18 146 268 20 205 25 405 593 209 90 095 25 070 1 870 983
gal20 201 400 25 401 33 220 1 332 743 208 980 32 849 5 164 274
gal22 244 860 33 901 44 359 2 359 260 537 884 78 948 9 466 587
gal24 389 712 44 260 58 246 4 854 406 1 677 874 280 886 21 953 367
gal26 536 900 58 968 76 655 7 910 227 3 074 931 690 326 39 981 434
gal28 697 032 75 276 100 600 16 743 963 6 881 086 1 297 734 68 335 459
gal30 997 020 95 158 127 694 29 486 387 13 099 851 2 267 234 119 802 775
gal32 1 251 904 119 665 1 234 343 46 682 652 21 099 566 5 708 124 185 483 935
gal34 1 546 116 143 298 199 392 59 640 798 29 150 579 9 922 914 271 702 974
gal36 1 862 280 169 387 241 169 93 918 510 35 376 235 19 403 519 384 992 916
gal38 2 319 900 204 980 6 922 941 130 247 268 56 985 534 29 465 761 558 133 816
gal40 2 886 000 241 908 9 428 405 188 818 884 81 189 254 38 298 839 797 804 204
incr4 312 48 48 48 48 48 48
incr6 1 860 228 255 266 254 254 250
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
44

Table 2: Continued from Table 2.
instance UB[ f
t
] UB-opt RLS NSGA-II
4
NSGA-II
16
NSGA-II
64
FRLS
incr8 6 384 638 714 824 697 701 670
incr10 16 380 1 612 1 778 2 043 1 712 1 730 1 755
incr12 35 112 3 398 3 735 4 313 3 644 3 626 4 312
incr14 66 612 6 488 7 063 27 652 7 236 6 821 9 593
incr16 115 680 10 332 12 023 163 460 12 635 11 786 315 443
incr18 187 884 17 278 19 470 534 396 48 252 19 368 2 149 226
incr20 289 560 25 672 29 948 2 064 999 282 106 29 845 6 746 265
incr22 427 812 40 944 44 746 3 844 540 1 334 966 45 275 16 385 851
incr24 610 512 56 602 63 017 7 495 505 1 469 070 152 351 33 325 005
incr26 846 300 81 866 88 979 15 952 802 3 972 629 332 892 63 000 386
incr28 1 144 584 106 870 121 563 28 604 791 9 952 208 778 753 108 752 856
incr30 1 515 540 136 810 163 877 52 816 362 12 960 999 2 550 410 180 585 600
incr32 1 970 112 177 990 212 346 71 755 110 22 764 475 5 568 153 285 130 008
incr34 2 520 012 222 082 2 438 961 101 145 675 48 918 770 16 486 326 436 356 818
incr36 3 177 720 278 060 3 075 541 138 435 016 51 241 361 23 971 265 647 384 186
incr38 3 956 484 336 008 437 733 222 669 638 112 416 041 46 812 515 946 779 972
incr40 4 870 320 406 960 9 599 136 274 093 532 157 865 646 51 366 137 1 345 652 388
line4 168 24 24 24 24 24 24
line6 660 76 85 89 85 86 84
line8 1 680 162 183 203 175 182 167
line10 3 420 370 356 419 350 352 347
line12 6 072 584 618 729 602 615 640
line14 9 828 918 1 007 1 239 998 996 1 159
line16 14 880 1 320 1 503 16 751 3 703 1 485 1 981
line18 21 420 1 926 2 163 51 654 11 553 2 142 39 959
line20 29 640 2 548 2 988 228 273 16 077 3 008 313 491
line22 39 732 3 684 4 094 368 448 67 048 4 118 914 082
line24 51 888 4 732 5 331 770 377 147 056 5 468 1 868 418
line26 66 300 6 382 6 940 1 296 961 263 622 54 516 3 344 085
line28 83 160 7 778 8 762 1 876 289 865 566 56 562 5 810 457
line30 102 660 9 312 10 970 2 580 140 965 839 275 173 9 445 912
line32 124 992 11 234 13 422 4 302 373 1 443 644 370 949 13 768 626
line34 150 348 13 190 16 319 5 711 951 2 316 826 918 949 20 857 072
line36 178 920 15 536 19 657 8 893 440 3 191 630 1 349 717 29 804 800
line38 210 900 17 862 385 004 11 959 570 6 293 569 2 344 401 41 127 949
line40 246 480 20 546 978 543 14 223 932 7 108 618 3 761 441 56 340 615
nfl16 2 575 200 231 483 305 783 3 668 565 325 792 298 438 37 199 678
nfl18 3 283 380 282 258 385 630 9 831 069 1 817 916 377 761 82 614 298
nfl20 4 077 400 332 041 453 985 28 517 178 4 588 157 451 007 164 899 817
nfl22 4 957 260 400 636 554 380 21 185 780 14 068 063 553 708 281 914 620
nfl24 5 922 960 463 657 641 449 67 606 634 22 724 195 653 214 445 953 536
nfl26 6 974 500 536 792 760 150 119 472 514 34 729 015 1 777 608 658 635 398
nfl28 8 111 880 598 123 882 061 149 361 098 75 166 343 7 858 029 950 306 569
nfl30 9 509 100 739 697 1 094 695 258 024 414 97 663 698 20 136 400 1 347 689 293
nfl32 10 842 560 914 620 1 371 006 412 089 659 128 529 608 35 478 556 1 826 481 460
nl4 44 616 8 276 8 276 8 287 8 276 8 276 8 276
nl6 165 660 23 916 24 773 25 758 24 917 24 472 23 916
nl8 309 232 39 721 43 792 46 971 42 047 41 876 44 243
nl10 496 980 59 436 67 619 76 609 65 619 66 872 80 222
nl12 908 424 110 729 132 423 145 180 128 863 128 534 165 868
nl14 1 885 884 188 728 235 944 547 804 241 993 231 053 8 938 940
nl16 2 486 880 261 687 337 449 4 313 728 719 253 327 340 38 836 517
sup4 364 152 63 405 63 405 63 612 63 405 63 405 63 405
sup6 910 380 130 365 143 164 147 208 135 228 136 631 130 395
sup8 1 699 376 182 409 203 163 260 895 193 428 190 643 254 361
sup10 2 731 140 316 329 366 130 439 820 341 093 345 553 521 457
sup12 4 005 672 458 810 531 185 653 431 528 485 511 240 5 435 891
sup14 5 522 972 567 891 735 259 1 732 923 759 361 719 889 43 792 093
# best 72 3 14 36 21
Randomized Local Search vs. NSGA-II vs. Frequency Fitness Assignment on The Traveling Tournament Problem
45
10 20 30 40
10
0
10
2
10
4
10
6
10
8
mean life (log-scaled)
n
RLS
NSGA-II₄
NSGA-II₁₆
NSGA-II₆₄
FRLS
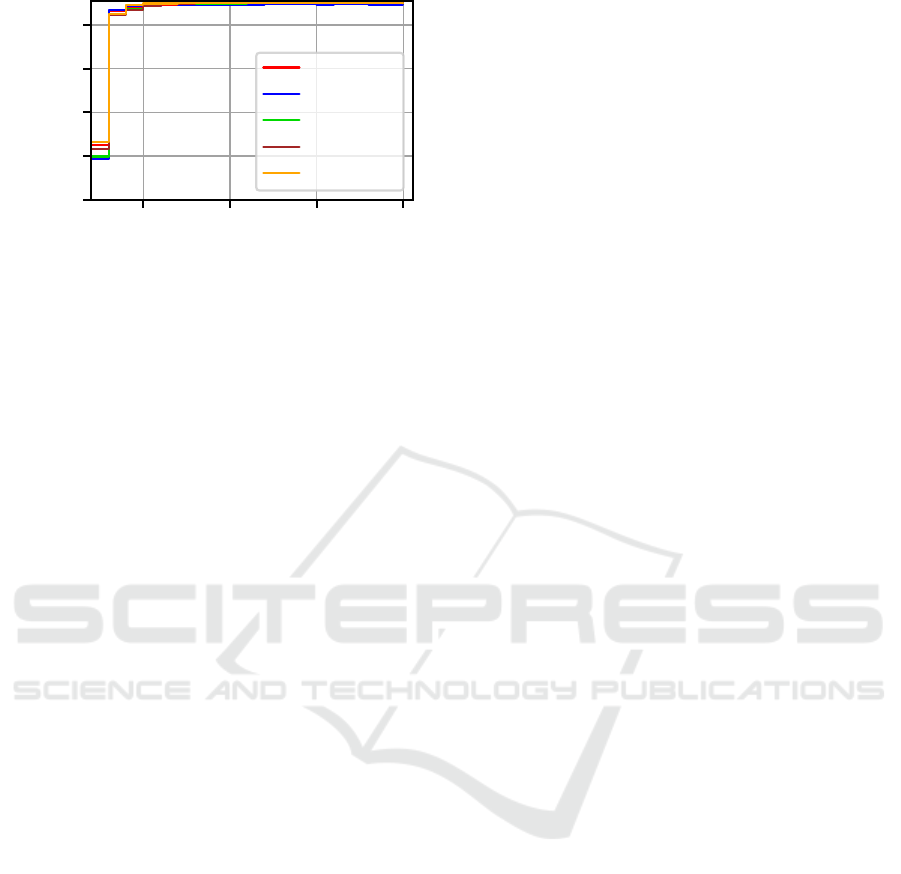
Figure 1: The average life index of the objective function
evaluation (FE) where the last improving move was made,
plotted in log-scale over the problem scale n.
From the RobinX website (Van Bulck, 2024), we
take the current upper bound UB-opt of the optimal
tour length for a feasible tour, i.e., the best result to
date delivered by any heuristic or exact method. We
find that the travel lengths delivered by our method
are not yet competitive. However, especially FRLS
can sometimes hit the upper bound UB-opt of the op-
timal travel length for a feasible tour. Most notably
on the instance line10, it dips below UB-opt of 370
by delivering a solution with travel length 347. Sadly,
while we were writing this text, the RobinX website
had been updated, moving the upper bound to 302.
Either way one question arises: Are these re-
sults the limit of what our algorithms and setups can
achieve?
The answer to this question is clearly No. In Fig-
ure 1, we plot the average life index of the objec-
tive function evaluation (FE) where the last improv-
ing move was made over the problem scale n. As-
tonishingly, all three algorithms keep improving until
the very end of the computational budget of 10
9
FEs
on all but the smallest problems. This means that, if
we had used a larger computational budget, we would
very likely have obtained better results.
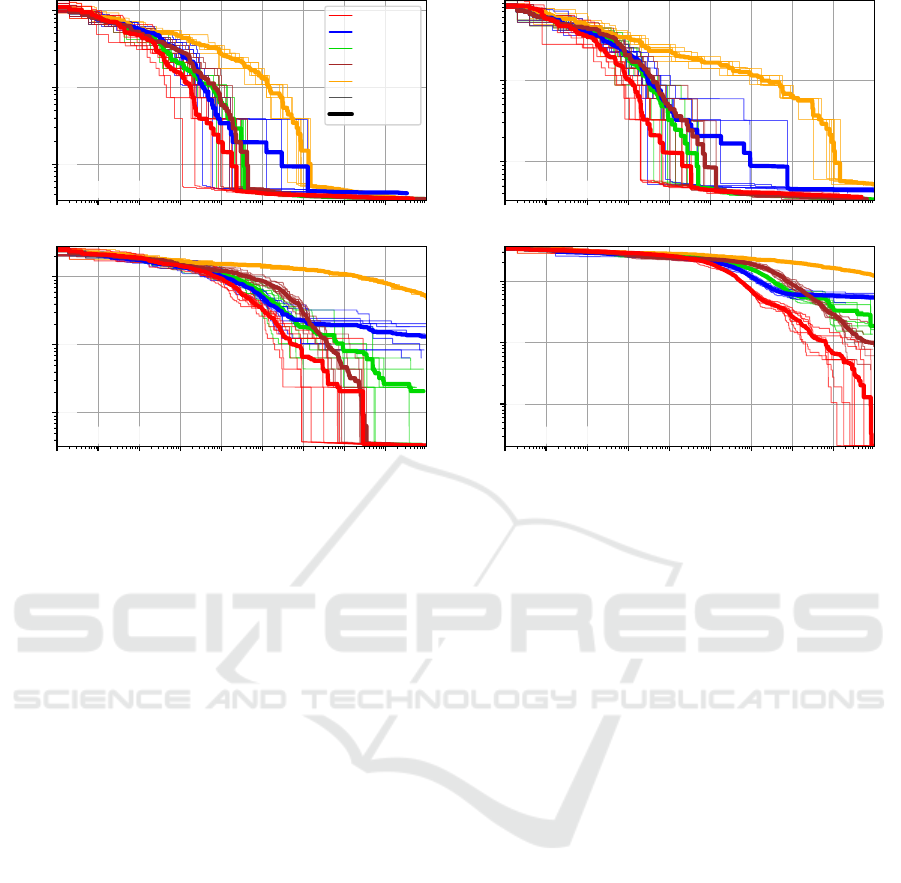
This is confirmed in Figure 2, where the progress
of the algorithm setups in terms of their best-so-far
f -value over time measured in FEs is illustrated on
four selected RobinX instances. On all four instances,
the initial larger improvements of the algorithms are
due to removing errors and the corresponding large
penalties in f . Once they cannot remove further er-
rors, their curves begin to flatten. Interestingly, the
curves for the two NSGA-II setups with smaller popu-
lations tend to become flatter more quickly than RLS.
NSGA-II
64
keeps improving long, but even it seem-
ingly begins to slow down at least on the large con38
instance before RLS. Despite these slowdowns, a
close inspection shows that all algorithms keep im-
proving until the very end of the budget, confirm-
ing the conclusions from Figure 1. FRLS is visibly
slower than the other algorithms, but the curves also
show that if more budget was given, it could have had
a good chance to outperform them. Notice that ear-
lier studies gave a computational budget of 10
10
FEs,
compared to the 10
9
used here (Weise et al., 2021b;
Weise et al., 2023; Liang et al., 2022; Liang et al.,
2024).
The two figures explain why RLS performs best:
The simple randomized local search has no means to
escape from local optima. The advantage of NSGA-II
with a large population, i.e., NSGA-II
64
, or of FRLS,
would be that they are probably much less likely to
get stuck at local optima, can keep improving long af-
ter RLS gets stuck, and will, hence, eventually find
better solutions. But it takes a long time until the
RLS stops improving, even on small problems. In-
deed, only on problems with up to six teams, it stops
improving before consuming 10
9
FEs in average! It
usually kept finding better solutions until the whole
budget was consumed. Interestingly, NSGA-II
4
and
NSGA-II
16
seem to not be better than RLS in their ex-
ploration ability. While NSGA-II
64
and FRLS may be
better in this respect, they pay for it by being slower in
exploitation, i.e., need longer to find solutions of the
same quality as RLS. Nevertheless, we expect that
had we used an even larger budget, FRLS and maybe
an NSGA-II setup with a bigger population would have
outperformed RLS eventually. On smaller and mid-
sized problems, they do find better results already.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The goal of solving the classical double-round robin
traveling tournament problem (2RR TTP) is to sched-
ule games in a fair and efficient way. Several meta-
heuristic approaches have been designed for it. The
majority of them work on the game plans directly and
only (Choubey, 2010) investigated an encoding based
on game permutations. We too, construct game plans
from permutations and search in the much simpler
space of permutations, allowing us to apply different
heuristics off-the-shelf.
We are, to the best of our knowledge, the first
to explicitly tackle the 2RR TTP as a bi-objective
problem, minimizing both constraint violations f
e
and
travel length f
t
as distinct objective functions. We
did this by applying the multi-objective NSGA-II al-
gorithm, as well as a randomized local search RLS
working on a lexicographical prioritization f of the
constraint violations f
e
over the travel length f
t
. We
furthermore plug frequency fitness assignment (FFA)
into the RLS, obtain the FRLS, and apply it to the
same prioritization scheme. This algorithm will opti-
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
46
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
10
6
10
7
10
8
10
3
10
4
10
5
time in FEs
best-so-far f on line10
RLS
NSGA-II₄
NSGA-II₁₆
NSGA-II₆₄
FRLS
single run
mean
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
10
6
10
7
10
8
10
6
10
7
time in FEs
best-so-far f on sup10
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
10
6
10
7
10
8
10
5
10
6
10
7
time in FEs
best-so-far f on gal20
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
10
6
10
7
10
8
10
4
10
5
10
6
time in FEs
best-so-far f on con38
Figure 2: The progress of the five algorithm setups in terms of f over time (measured in FEs) on line10, sup10, gal20, and
con38 (top-left to bottom-right). All axes use a log scale.
mize all possible prioritizations of a multi-objective
problem at once (which is a pleasing theoretically
property but otherwise of no relevance here).
Our experiments showed clearly that the encoding
we use is a feasible way to approach the 2RR TTP
even at larger scales and even if used in very dif-
ferent algorithms. The simple RLS can reliably find
game plans without errors for problem instances with
a scale n of 36 within our computational budget. This
is remarkable as most related works using metaheuris-
tics tackle problems of a smaller scale only.
We also found that RLS performed better than
NSGA-II and FRLS on larger problems while often
losing out on smaller scales. All algorithms can
keep improving during the complete computational
budget of 10
9
objective function evaluations that we
granted in the experiment (with the exception of re-
ally small problems). Unexpectedly, RLS did not con-
verge within this budget on all but the very smallest
instances but instead kept improving.
On the smaller instances, where RLS indeed con-
verged, both FRLS and NSGA-II could reach better
solutions. To be fair, what we refer to as “smaller
instances” are instances of scales n up to about 20,
which are already larger than what most related works
tackle. So had we limited our work to these scales,
we would probably have concluded that NSGA-II and
FRLS are better choices across the board. Therefore,
maybe a sixth contribution of our work is to find
that, while more sophisticated methods can beat crude
local search on small instances, big instances pose
a challenge so hard that even a primitive algorithm
can be competitive, even on a fairly large budget of
10
9
FEs.
In our future work, we will try to improve upon
the encoding scheme. If we can get it to produce
fewer constraint violations, we could probably reach
feasible solutions without error earlier in the search
and more search pressure would result on the travel
length f
t
. This would then also likely increase the im-
pact of the exploration power of FRLS and NSGA-II.
Of course, we also want to apply different metaheuris-
tics to the problem, but this only makes sense after
the encoding is improved: Any other method for pre-
venting convergence to local optima (e.g., in simu-
lated annealing) would currently likely not fare better
than FRLS or NSGA-II.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors acknowledge support from the Project
of National Natural Science Foundation of China
62406095, the Project of Natural Science Foundation
of Anhui Province 2308085MF213, the Key Research
Plan of Anhui Province 2022k07020011, the Univer-
sity Scientific Research Innovation Team Project of
Anhui Province 2022AH010095, as well as the Hefei
Specially Recruited Foreign Expert program and the
Hefei Foreign Expert Office program.
Randomized Local Search vs. NSGA-II vs. Frequency Fitness Assignment on The Traveling Tournament Problem
47

REFERENCES
Anagnostopoulos, A., Michel, L., Van Hentenryck, P., and
Vergados, Y. (2006). A simulated annealing approach
to the traveling tournament problem. Journal of
Scheduling, 9(2):177–193. doi:10.1007/S10951-006-
7187-8.
Anderson, J. (2000). A survey of multiobjective optimiza-
tion in engineering design. Technical Report LiTH-
IKP-R-1097, Link
¨
oping University, Department of
Mechanical Engineering, Link
¨
oping, Sweden. https:
//www.researchgate.net/publication/228584672.
Brand
˜
ao, F. and Pedroso, J. P. (2014). A complete search
method for the relaxed traveling tournament problem.
EURO Journal on Computational Optimization, 2(1-
2):77–86. doi:10.1007/s13675-013-0010-3.
Chen, P., Kendall, G., and Vanden Berghe, G. (2007). An
ant based hyper-heuristic for the travelling tournament
problem. In IEEE Symposium on Computational Intel-
ligence in Scheduling (CISched’07), April 2–4, 2007,
Honolulu, HI, USA, pages 19–26, Piscataway, NJ,
USA. IEEE. doi:10.1109/SCIS.2007.367665.
Choubey, N. S. (2010). A novel encoding scheme for travel-
ing tournament problem using genetic algorithm. In-
ternational Journal of Computer Applications (IJCA),
Special Issue on “Evolutionary Computation for Op-
timization Techniques” (ECOT’10)(2):79–82. https:
//www.ijcaonline.org/ecot/number2/SPE139T.pdf.
de Bruin, E., Thomson, S. L., and van den Berg, D.
(2023). Frequency fitness assignment on JSSP: A
critical review. In Correia, J., Smith, S. L., and
Qaddoura, R., editors, Proceedings of the 26th Eu-
ropean Conference on Applications of Evolutionary
Computation (EvoApplications’23), Held as Part of
EvoStar 2023, April 12-14, 2023, Brno, Czech Repub-
lic, volume 13989 of Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence, pages 351–363, Cham, Switzerland. Springer.
doi:10.1007/978-3-031-30229-9
23.
de Werra, D. (1988). Some models of graphs for scheduling
sports sompetitions. Discrete Applied Mathematics,
21(1):47–65. doi:10.1016/0166-218X(88)90033-9.
Deb, K., Agrawal, S., Pratab, A., and Meyarivan, T. (2000).
A fast elitist non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm
for multi-objective optimization: NSGA-II. In Schoe-
nauer, M., Deb, K., Rudolph, G., Yao, X., Lutton, E.,
Merelo-Guerv
´
os, J. J., and Schwefel, H., editors, Pro-
ceedings of the 6th International Conference on Paral-
lel Problem Solving from Nature (PPSN VI), Septem-
ber 18–20, 2000, Paris, France, volume 1917/2000
of Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), pages
849–858, Berlin, Germany. Springer-Verlag GmbH.
doi:10.1007/3-540-45356-3 83.
Deb, K., Agrawal, S., Pratap, A., and Meyarivan, T. (2002).
A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm:
NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Com-
putation, 6(2):182–197. doi:10.1109/4235.996017.
Easton, K., Nemhauser, G. L., and Trick, M. A. (2001).
The traveling tournament problem description and
benchmarks. In Walsh, T., editor, Proceedings
of the 7th International Conference on Principles
and Practice of Constraint Programming (CP’01),
November 26–December 1, 2001, Paphos, Cyprus,
volume 2239 of Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence, pages 580–584, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany.
Springer. doi:10.1007/3-540-45578-7 43.
George, A., Razak, A., and Wilson, N. (2015). The
comparison of multi-objective preference inference
based on lexicographic and weighted average mod-
els. In 27th IEEE International Conference on
Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI’15), Novem-
ber 9–11, 2015, Vietri sul Mare, Italy, pages 88–
95, Piscataway, NJ, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
doi:10.1109/ICTAI.2015.26.
Johnson, D. S., Papadimitriou, C. H., and Yannakakis,
M. (1988). How easy is local search? Jour-
nal of Computer and System Sciences, 37(1):79–100.
doi:10.1016/0022-0000(88)90046-3.
Khelifa, M. and Boughaci, D. (2016). Hybrid harmony
search combined with variable neighborhood search
for the traveling tournament problem. In Nguyen,
N. T., Manolopoulos, Y., Iliadis, L. S., and Traw-
inski, B., editors, Computational Collective Intel-
ligence - 8th International Conference (ICCCI’16),
September 28–30, 2016, Halkidiki, Greece, Part I,
volume 9875 of Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence, pages 520–530, Cham, Switzerland. Springer.
doi:10.1007/978-3-319-45243-2 48.
Khelifa, M. and Boughaci, D. (2018). A cooperative lo-
cal search method for solving the traveling tournament
problem. Computing and Informatics, 37(6):1386–
1410. doi:10.4149/CAI 2018 6 1386.
Khelifa, M., Boughaci, D., and A
¨
ımeur, E. (2017). An en-
hanced genetic algorithm with a new crossover oper-
ator for the traveling tournament problem. In 4th In-
ternational Conference on Control, Decision and In-
formation Technologies (CoDIT’17), April 5–7, 2017,
Barcelona, Spain, pages 1072–1077, Piscataway, NJ,
USA. IEEE. doi:10.1109/CODIT.2017.8102741.
Larra
˜
naga, P., Kuijpers, C. M. H., Murga, R. H., Inza, I.,
and Dizdarevic, S. (1999). Genetic algorithms for the
travelling salesman problem: A review of represen-
tations and operators. Artificial Intelligence Review,,
13(2):129–170. doi:10.1023/A:1006529012972.
Larra
˜
naga, P., Kuijpers, C. M. H., Poza, M., and Murga,
R. H. (1997). Decomposing bayesian networks:
Triangulation of the moral graph with genetic al-
gorithms. Statistics and Computing, 7(1):19–34.
doi:10.1023/A:1018553211613.
Liang, T., Wu, Z., L
¨
assig, J., van den Berg, D., Thom-
son, S. L., and Weise, T. (2024). Addressing the
traveling salesperson problem with frequency fitness
assignment and hybrid algorithms. Soft Computing.
doi:10.1007/s00500-024-09718-8.
Liang, T., Wu, Z., L
¨
assig, J., van den Berg, D., and
Weise, T. (2022). Solving the traveling salesper-
son problem using frequency fitness assignment. In
Ishibuchi, H., Kwoh, C., Tan, A., Srinivasan, D.,
Miao, C., Trivedi, A., and Crockett, K. A., edi-
tors, IEEE Symposium Series on Computational In-
telligence (SSCI’22), December 4–7, 2022, Singa-
pore, pages 360–367, Piscataway, NJ, USA. IEEE.
doi:10.1109/SSCI51031.2022.10022296.
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
48

Neumann, F. and Wegener, I. (2007). Randomized lo-
cal search, evolutionary algorithms, and the minimum
spanning tree problem. Theoretical Computer Sci-
ence, 378(1):32–40. doi:10.1016/j.tcs.2006.11.002.
Russell, S. J. and Norvig, P. (2002). Artificial Intelligence:
A Modern Approach (AIMA). Prentice Hall Interna-
tional Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2 edition.
Thielen, C. and Westphal, S. (2011). Complexity
of the traveling tournament problem. Theo-
retical Computer Science, 412(4-5):345–351.
doi:10.1016/J.TCS.2010.10.001.
Urrutia, S. and Ribeiro, C. C. (2006). Maximizing breaks
and bounding solutions to the mirrored traveling tour-
nament problem. Discrete Applied Mathematics,
154(13):1932–1938. doi:10.1016/j.dam.2006.03.030.
Uthus, D. C., Riddle, P. J., and Guesgen, H. W.
(2013). Solving the traveling tournament prob-
lem with iterative-deepening A*. In Borrajo, D.,
Kambhampati, S., Oddi, A., and Fratini, S., edi-
tors, Proceedings of the Twenty-Third International
Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling
(ICAPS’13), June 10–14, 2013, Rome, Italy, pages
488–489. AAAI. http://www.aaai.org/ocs/index.php/
ICAPS/ICAPS13/paper/view/6030.
Van Bulck, D. (2024). Minimum travel objective repos-
itory: Website of the RobinX benchmark. https:
//robinxval.ugent.be/RobinX/travelRepo.php, visited
on 2024-05-10.
Van Bulck, D., Goossens, D., Sch
¨
onberger, J., and Gua-
jardo, M. (2018). RobinX: An xml-driven classifi-
cation for round-robin sports timetabling. In Pro-
ceedings of the 12th International Conference on
the Practice and Theory of Automated Timetabling
(PATAT’18), August 28–31, 2018, Vienna, Aus-
tria, pages 481–484, Leuven, Belgium. EURO
Working Group on Automated Timetabling (EWG-
PATAT). https://patatconference.org/patat2018/files/
proceedings/paper39.pdf.
Van Bulck, D., Goossens, D., Sch
¨
onberger, J., and
Guajardo, M. (2020). RobinX: A three-field
classification and unified data format for round-
robin sports timetabling. European Jour-
nal of Operational Research, 280(2):568–580.
doi:10.1016/J.EJOR.2019.07.023.
Verduin, K., Thomson, S. L., and van den Berg, D. (2023).
Too constrained for genetic algorithms. Too hard
for evolutionary computing. The traveling tournament
problem. In van Stein, N., Marcelloni, F., Lam,
H. K., Cottrell, M., and Filipe, J., editors, Proceedings
of the 15th International Joint Conference on Com-
putational Intelligence (IJCCI’23), November 13-15,
2023, Rome, Italy, pages 246–257, Set
´
ubal, Portugal.
SciTePress. doi:10.5220/0012192100003595.
Volgenant, A. (2002). Solving some lexicographic
multi-objective combinatorial problems. European
Journal of Operational Research, 139(3):578–584.
doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(01)00214-4.
Weise, T., Li, X., Chen, Y., and Wu, Z. (2021a).
Solving job shop scheduling problems without us-
ing a bias for good solutions. In Genetic and
Evolutionary Computation Conference (GECCO’21),
July 10-14, 2021, Lille, France, Companion Vol-
ume, pages 1459–1466, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
doi:10.1145/3449726.3463124.
Weise, T., Wan, M., Tang, K., Wang, P., Devert, A.,
and Yao, X. (2014). Frequency fitness assignment.
IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation,
18(2):226–243. doi:10.1109/TEVC.2013.2251885.
Weise, T. and Wu, Z. (2023). Replicable self-documenting
experiments with arbitrary search spaces and algo-
rithms. In Genetic and Evolutionary Computa-
tion Conference Companion (GECCO’23 Compan-
ion), July 15-19, 2023, Lisbon, Portugal, New York,
NY, USA. ACM. doi:10.1145/3583133.3596306.
Weise, T., Wu, Z., Li, X., and Chen, Y. (2021b). Fre-
quency fitness assignment: Making optimization al-
gorithms invariant under bijective transformations
of the objective function value. IEEE Transac-
tions on Evolutionary Computation, 25(2):307–319.
doi:10.1109/TEVC.2020.3032090.
Weise, T., Wu, Z., Li, X., Chen, Y., and L
¨
assig, J. (2023).
Frequency fitness assignment: Optimization without
bias for good solutions can be efficient. IEEE Transac-
tions on Evolutionary Computation, 27(4):980–992.
doi:10.1109/TEVC.2022.3191698.
Zhang, S., Jia, F., Wang, C., and Wu, Q. (2023). Targeted
hyperparameter optimization with lexicographic pref-
erences over multiple objectives. In The Eleventh In-
ternational Conference on Learning Representations
(ICLR’23), May 1-5, 2023, Kigali, Rwanda, MA,
USA. OpenReview.net. https://openreview.net/pdf?
id=0Ij9 q567Ma.
Randomized Local Search vs. NSGA-II vs. Frequency Fitness Assignment on The Traveling Tournament Problem
49
