
Biomechanics of the Lower Extremity in Youth Football League:
FIFA 11+ One Leg Squat Analysis
Anna Davidovica
1a
, Sergejs Davidovics
1
, Guna Semjonova
1b
, Alexei Katashev
2c
,
Alexander Oks
3d
, Linda Lancere
4e
, Signe Tomsone
1f
and Maksims Zolovs
5g
1
Department of Rehabilitation, Riga Stradins University, 16 Dzirciema Street, LV-1007 Riga, Latvia
2
Institute of Mechanical and Biomedical Engineering, Riga Technical University, LV-1048 Riga, Latvia
3
Institute of Architecture and Design, Riga Technical University, LV-1048 Riga, Latvia
4
Department of Sociotechnical Systems Modelling, Vidzeme University of Applied Sciences, LV-4201, Valmiera, Latvia
5
Statistical Unit, Faculty of Medicine, Riga Stradins University, 16 Dzirciema Street, LV-1007 Riga, Latvia
Keywords: Lower Extremity, Biomechanical Variables, Youth Football League Players, One Leg Squat,
FIFA 11+, Wireless Sensor Systems, Smart Socks.
Abstract: Background: Football carries substantial injury risks, especially for youth players. Providing biofeedback of
lower limb motion during functional tasks is a crucial part of injury prevention programs such as FIFA 11+.
While the FIFA 11+ warm-up program providing individualised feedback remains challenging, wireless
sensor systems such as the DAid® Pressure Sock system, NOTCH® Inertial Sensor System, and PLUX
Wireless Biosignals (muscleBAN kit) System offer potential solutions. Aim: This study aims to explore the
correlation of lower limb biomechanical variables during the FIFA 11+ Part 2 exercise "One Leg Squat" in
youth football players using wireless sensor systems and video recordings. Methods: Using wireless sensor
systems and video recordings, we analysed lower limb biomechanics during the "One Leg Squat" exercise in
youth football players. Results: Strong positive correlations were identified between hip joint adduction and
the changes in the centre of pressure of the plantar surface of the foot (COP1y), as well as between hip joint
internal rotation and COP1y. COP2x correlated strongly with gluteus medius activity. Conversely, COP2y
showed a negative correlation with gluteus maximus activity. Conclusions: The results support the potential
of wireless sensor systems in monitoring the biomechanical changes of the lower extremity movements and
lay the groundwork for future biofeedback methods based on the DAid® smart socks system technology for
evaluating lower limb motion, especially the changes in the centre of pressure of the plantar surface of the
foot, during functional tasks in Football Youth League players.
1 INTRODUCTION
Football, a globally renowned sport boasting
approximately four hundred million players across
208 countries, carries a significant injury risk for
participants of all ages, both professional and
amateur. Injuries not only lead to player withdrawals
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3141-7998
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6554-0716
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8894-3748
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6925-1842
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0524-5106
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7836-2672
g
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9120-5869
but also impede team performance across various
levels (Sadigursky et al., 2017). Among youth aged
9-21, non-contact injuries account for 53% to 72% of
all injuries, with lower extremity injuries prevailing
in 72% to 93% of cases (Jones et al., 2019).
Today, the leading preventive exercise program
for correctness of the movement in football is the
Davidovica, A., Davidovics, S., Semjonova, G., Katashev, A., Oks, A., Lancere, L., Tomsone, S. and Zolovs, M.
Biomechanics of the Lower Extremity in Youth Football League: FIFA 11+ One Leg Squat Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0012894900003828
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support (icSPORTS 2024), pages 131-139
ISBN: 978-989-758-719-1; ISSN: 2184-3201
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
131

FIFA 11+ warm-up program, the application of which
reduces the risk of injuries by 30% (Sadigursky et al.,
2017), where the FIFA 11+ program 2nd Part’s task
“One Leg Squat” is targeted entirely at the
development of the correct lower limb motion pattern
and balance (Bizzini et al., 2015). Simultaneous
assessment by coaches of the entire team during
movement execution does not provide an individual
approach to each athlete, but an individual approach
is essential for the athlete to progress to the more
advanced set of exercises within the FIFA 11+
program and more intensive training (Bizzini et al.,
2015). The individualized objective approach could
be realized using objective motion capture
biofeedback systems (Kim et al., 2021; Hribernik et
al., 2022; Di Paolo et al., 2023).
Most golden standard objective biofeedback
methods for motion capturing, such as optical
systems, Microsoft Kinect camera systems (Bawa et
al., 2021), 3D kinematic analysis with optical motion
capture (OMCs) (Longo et al., 2022) and force plates
(Chen et al., 2021) have drawbacks that make them
challenging to implement in football players' daily
motion evaluation routines. Optical motion capture
systems, for example, are unsuitable for field
applications, requiring a stationary setup with a
limited spatial field of view (Suo et al., 2024). Force
plates used for measuring ground reaction forces and
foot plantar pressure are applicable only in laboratory
environments (Ahn et al., 2024), rendering them
impractical for daily football practice.
An alternative approach for providing
biofeedback of lower limb motion and biomechanical
parameters to athletes could be based on the use of
wireless smart sensor systems. For example, Inertial
Measurement Unit (IMU) systems measure a body's
specific force, angular rate, magnetic field, and
acceleration of a body in real-time (Khan et al., 2024).
Muscle activity capturing wireless sensors providing
real-time data on muscle performance and condition
based on electromyographic (EMG) signals (Tanaka
et al., 2022). For lower extremity distal segment
observation the smart insole systems (Khandakar et
al., 2022), such as Pedar (Brindle et al., 2022),
PODOSmart
®
(Ziagkas et al., 2021) and smart socks
such as the DAid® Pressure Sock systems could be
used, enabling the measurement of biomechanical
parameters of the foot, including the centre of
pressure (CoP) and pressure on various parts of the
foot plantar surface (Brindle et al., 2022; Oks et al.,
2020; Januskevica et al., 2020).
However, sensor systems present challenges,
particularly when multiple wireless devices are used
simultaneously. Synchronising data flow can be
complex and time-consuming, with potential signal
overlap leading to inaccuracies. Managing device
activation timing adds further complexity (Masalskyi
et al., 2024). The numerous sensors required for
comprehensive monitoring can restrict an athlete's
movement and impact biomechanics of lower
extremity. For instance, smart insoles, though useful
for gait analysis, are often rigid, causing discomfort
and limiting natural movement (Masalskyi et al.,
2024). So far DAid® smart socks, which incorporate
piezoresistive knitted textile pressure sensors
embedded in the sole, have demonstrated several
advantages to use them: enhanced comfort,
unobtrusiveness, accurate pressure measurement,
have no impact on foot biomechanics, and ease of use,
making them a promising tool for monitoring and
improving athletic performance (Oks et al., 2020;
Januskevica et al., 2020; Semjonova et al., 2022).
There is a correlation between lower limb
biomechanical variables during functional tasks
(Claiborne et al., 2006). For instance, increased hip
abductor (musculus gluteus medius) strength is
associated with reduced knee valgus angle during
functional exercises (Neamatallah et al., 2020). For
foot biomechanical variables there is a positive
correlation between greater foot pronation and
increased front to medial plantar pressure during
functional squat activities (Ahn et al., 2024).
Therefore, the aim of this study is to investigate
the correlation of biomechanical variables of the
lower extremity measured by separate wireless sensor
systems during the exercise “One Leg Squat” in a
population of youth league football players. We
hypothesised that by using three separate sensor
systems (DAid®, NOTCH® and PLUX®) during the
FIFA11+ Part 2 exercise “One Leg Squat”, strong
correlations will be observed among main
biomechanical variables: joint angles, muscular
activation and foot plantar pressure, supporting the
possibility of using smart socks as the sole
biofeedback system for evaluating lower limb
motion, during functional tasks.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Study Design and Participant
Recruitment
A cross-sectional correlation study involved 32 male
and female soccer players from the Latvian Youth
Soccer League (U-14 and U-15).
Participants met the following inclusion criteria:
at least 5 years of experience in the sport, no pain or
icSPORTS 2024 - 12th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
132

previous knee injuries or surgeries, no current knee
pain, no lower extremity injuries or surgeries in the
past six months, no lower extremity deformities, and
no vestibular dysfunction.
They performed the FIFA11+ Part 2 “One Leg
Squat” exercise using the DAid®, NOTCH® and
PLUX®, along with video analysis.
Informed consent was obtained, and the study was
approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Riga
Stradiņš University (approval received on 21 March
2023, No. 2-PĒK-4/294/2023).
Participants wore tight T-shirts or undershirts and
shorts that did not cover the knees and performed the
measurements in sports shoes with proper insoles.
Video recordings were made simultaneously with
the sensor data while participants performed the
FIFA11+ “One Leg Squat”. Three independent sports
physical therapists evaluated the correctness of the
movements, comparing their assessments with the
sensor data and verifying with video records.
2.2 Daid® Pressure Sock System
The DAid® Pressure Sock System consists of a pair
of socks, each with six pressure sensors in the sole:
two under the heel, two under the arch, and two under
the metatarsals, labelled as: (1) front medial, (2) front
lateral, (3) middle medial, (4) middle lateral, (5) heel
medial, and (6) heel lateral (Figure 1). This setup
monitors gait and detects supination/pronation.
Conductive pathways link the sensors to a data
acquisition unit that transmits data via Bluetooth to a
smartphone at up to 200 Hz per channel. For more
details see (Oks et al., 2019; Januskevica et al., 2020;
Semjonova et al., 2022).
Figure 1: DAid® smart socks sensor placement.
2.2.1 Calculating Centre of Pressure Using
Daid® Pressure Sock System Data
The data recorded from DAid® Pressure Sock
System provide monitoring of relative pressure
values under each sensor and calculation of
coordinates of centre of pressure (COP) for each foot
along mediolateral (COPx) and anteroposterior
(COPy) axes, as well as summarised COP position
(COPw).
Positive COPx values indicate a medial shift,
while negative values denote a lateral shift. Positive
COPy values signify an anterior shift, while negative
values indicate a posterior shift. COPw values
provide a general indication of COP location. The
COPx component on the X-axis (COPx) is crucial in
assessing the overpressure on the medial plantar
surface of the foot.
In this study, two methodologies COP1 and COP2
were used to calculate COP, where COP1x, COP1y,
COP1w and COP2x, COP2y, COP2w were obtained,
using DAid® Pressure Sock System data.
The socks generate a dataset consisting of the
resistances of sensors R1 to R6, measured in
kiloohms (kOhms) and recorded as ADC0 to ADC5
in the consolidated files. As applied pressure
increases, the sensor resistances decrease.
Therefore, two values were introduced for the
calculation of COP:
Ui = 100 – Ri (1)
Vi = 100 / Ri (2)
Values U and V increase when plantar pressure
increases.
The position of sensors over the foot were defined
by six vectors (see Figure 2):
x
1
= 0.26, y
1
= 0.97
x
2
= -0.26, y
2
= 0.97
x
3
= 0.26, y
3
= 0
x
4
= -0.26, y
4
= 0
x
5
= 0.26, y
5
= -0.97
x
6
= -0.26, y
6
= -0.97
where coordinates are defined in arbitrary units,
accounting the length of the foot is equal to 2 arbitrary
units. Therefore, the coordinates of COP are also
measured in arbitrary units.
The COP1 (COP
X
1, COP
Y
1, COP
W
1) are
calculated using values U
i
= 100 – R
i
as follows:
𝐶𝑂𝑃
∑
𝑈
𝑥
∑
𝑈
𝐶𝑂𝑃
∑
𝑈
𝑦
∑
𝑈
𝐶𝑂𝑃
∑
𝑈
6
The COP2 (COP
X
2, COP
Y
2, COP
W
2) are calculated
using values V
i
= 100 / R
i
as follows:
𝐶𝑂𝑃
∑
𝑉
𝑥
∑
𝑉
Biomechanics of the Lower Extremity in Youth Football League: FIFA 11+ One Leg Squat Analysis
133

𝐶𝑂𝑃
∑
𝑉
𝑦
∑
𝑉
𝐶𝑂𝑃
∑
𝑉
6
These two types of processing were used to determine
which method better distinguishes differences in COP
positions.
Figure 2: Nominal position of sensors over the foot plantar
surface.
2.3 Notch® Inertial Sensor System
The NOTCH ® IMUs system (Wearnotch by Notch
Interfaces, Inc., NJ, USA) used in this study features
wireless IMUs with nine-axis inertial sensors (three-
axis gyroscope, accelerometer, and magnetometer).
The Notch Pioneer app, installed on an iPhone 12
(iOS Version 1.7.1.1), processes data and sends it to
LabVIEW software, which computes average angles
and angular acceleration, then transfers the results to
an Excel sheet. Data recording occurs at 40 Hz.
During "One Leg Squat" recordings, the "Lower body
+ hip" configuration was selected in the app.
2.4 PLUX Wireless Biosignals
(MuscleBAN Kit) System
The wireless electromyography PLUX Wireless
Biosignals (muscleBAN kit) system was prepared to
monitor four muscles. The Plux application on a
computer captured muscle activity readings via
Bluetooth. Motor points were located using SENIAM
guidelines (Hermens et al., 2000). After electrode
placement, participants performed a maximum
voluntary contraction (MVC) to assess activities of
the musculus quadriceps femoris vastus lateralis,
musculus gluteus maximus, musculus gluteus medius
and musculus biceps femoris. In this study, the
normalisation of electromyographic (EMG) signals
(Halaki et al., 2012) from a specified muscle utilized
the EMG recorded from the same muscle during a
maximal voluntary isometric contraction (MVC) as
the reference value. Subsequently, the EMG signals
underwent processing by calculating the root mean
square from the rectified signal, the window for root
mean square calculation was 0.2 sec.
2.5 Task Description for Participants
Each participant was informed about the procedures
of the study (Bizzini et al., 2015). Before executing
the “One Leg Squat” exercise. Participants were
instructed to execute the "One Leg Squat", by
wearing a wireless DAid®, NOTCH®, PLUX® and
sports shoes (see Figure 3). Each participant executed
“One Leg Squat” 10 times 2 repetitions on both sides.
Figure 3: Study participants interact with the DAid®,
PLUX® and the NOTCH®, performing “One Leg Squat”.
2.6 Systems Synchronisation
The following steps were taken to synchronise the
three systems before starting “One Leg Squat'' task.
Each "One Leg Squat" was recorded by video camera.
The used data acquisition systems provided data
record at the sample rate 40 Hz (NOTCH® system)
and 140 Hz (socks data acquisition system). During
the measurement, all systems reported data together
with internal device time. The data from each system
were recorded in separated files. The all signal
processing was performed after recording, but not in
real time. The systems were not synchronised;
therefore, synchronisation was made at
postprocessing. The participants were asked to make
specific movement – bending the supporting leg knee,
the accelerometric and sock signal were aligned,
using the pattern of this movement as a marker. The
inaccuracy of time alignment does not exceed 25
milliseconds. The potential delay for output signals
was compensated by alignment procedure.
icSPORTS 2024 - 12th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
134
2.7 Expert Protocol
Each FIFA11+ "One Leg Squat" was analysed by
three certified physiotherapists with over five years of
experience working with athletes. They assessed the
performance by watching video recordings at 0.25x
slow motion. The experts determined whether an
adduction and internal rotation of the thigh, knee
abduction, lower leg external rotation, ankle eversion,
and excessive foot pronation was noted in 6 out of 10
squats, the full set was classified as incorrect. In total
of 32 videos from 32 participants were analysed.
2.8 Statistical Methods of Research
Leveraging LabView software, data synchronisation
was achieved from three systems. Each of the 32
participants yielded 64 data files, encompassing
separate sets from all three systems for each lower
extremity during the FIFA11+ "One Leg Squat"
exercise. A total of 2,048 data files were collected and
consolidated into a single Database.txt file for
correlation analysis. Quantitative analysis was
conducted using Microsoft Excel v.16.77.1 and
"jamovi" v.2.3.28.0, an open-source graphical
interface for R programming. Descriptive statistics
such as mean and standard deviation were employed
to characterize participant data and results.
Spearman's correlation analysis, a non-parametric
method, was applied to explore relationships between
biomechanical variables derived from the three
systems. Statistical significance was considered at p
< .05.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Participant Description
Thirty-two participants, comprising 16 women and 16
men, who were athletes and youth league football
players, took part in this correlational investigation.
Participants meeting specific inclusion and exclusion
criteria were selected for the study (see Table 1).
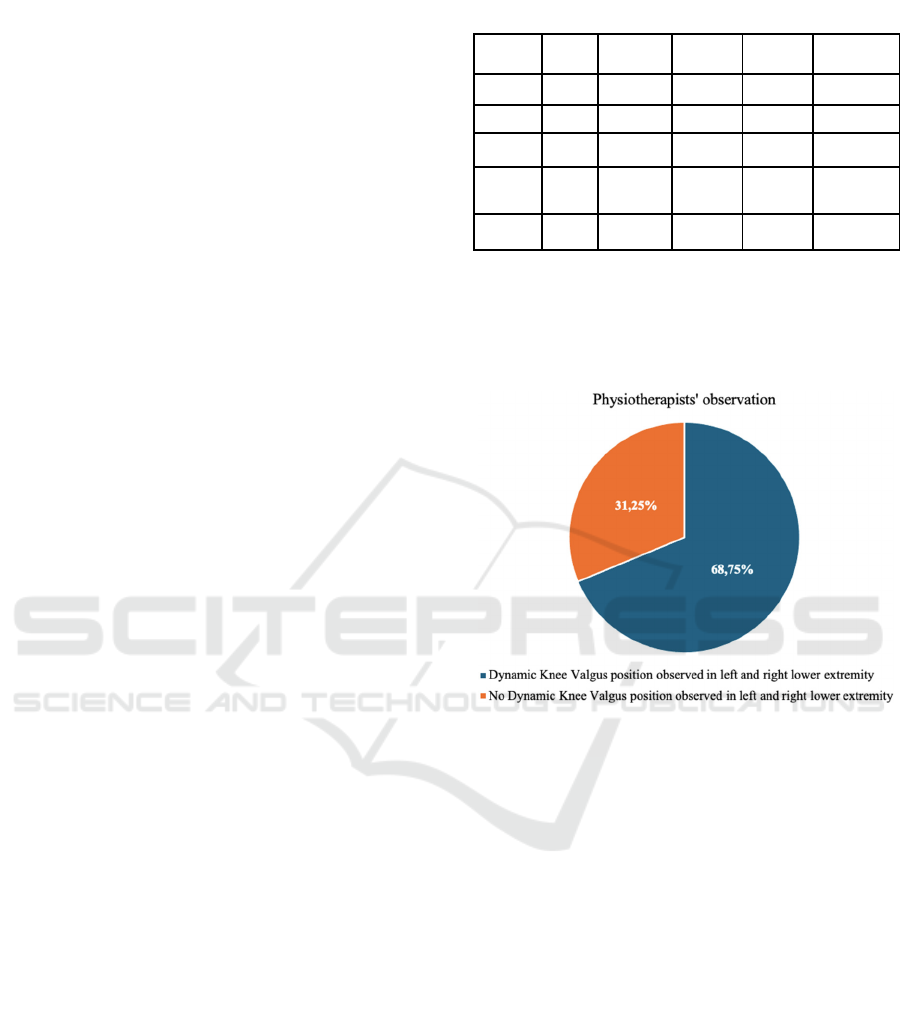
3.2 Prevalence of Dynamic Knee
Valgus in “One Leg Squat”
From the analysis of all the observed videos, in which
participants each performed the exercise "One Leg
Squat" 10 times for 2 repetitions with each leg, all
experts noted that a dynamic knee valgus position
characterized by adduction and internal rotation of the
Table 1: Characteristics of the study participants.
Mean Median Standard
deviation
(SD)
Minimum Maximum
BMI
20.8 20.8 2.065
17.3
27.2
Age
(years)
14.6 15.0 0.495 14 15
Weight
(kg)
59.8
58.0
6.413
50.0
78.6
Height
(cm)
169.4
169.0
4.662
159
181
EU size
40.6 40.0 1.961 37.0 44.0
thigh, knee abduction, lower leg external rotation,
ankle eversion, and excessive foot pronation was
observed in 68.75% of cases. In 31.25% of cases, a
dynamic knee valgus position was not observed (see
Figure 4).
Figure 4: Physiotherapists' assessment of the watched
videos for the left and right lower extremity.
3.3 Correlation Analysis of Lower
Limb Biomechanics
The study analysed various correlations involving the
right and left lower limbs, with significant findings
indicated by correlation coefficients (r) and
corresponding p-values. Correlations were
categorized as weak (r ≤ 0.2), moderate (0.2 < r ≤ 0.5),
or strong (0.5 < r ≤ 1) (refer to Appendix (Table 2 and
Table 3).
3.3.1 Left Lower Extremity
Strong Positive Correlation
A statistically significant strong positive correlation
was found between the changes in the centre of
pressure of the plantar surface of the foot COP2x,
which represents the position of the centre of pressure
in the medial part of the plantar surface of the foot,
Biomechanics of the Lower Extremity in Youth Football League: FIFA 11+ One Leg Squat Analysis
135
and the electrical activity of the musculus gluteus
medius (r=0.543; p < .001).
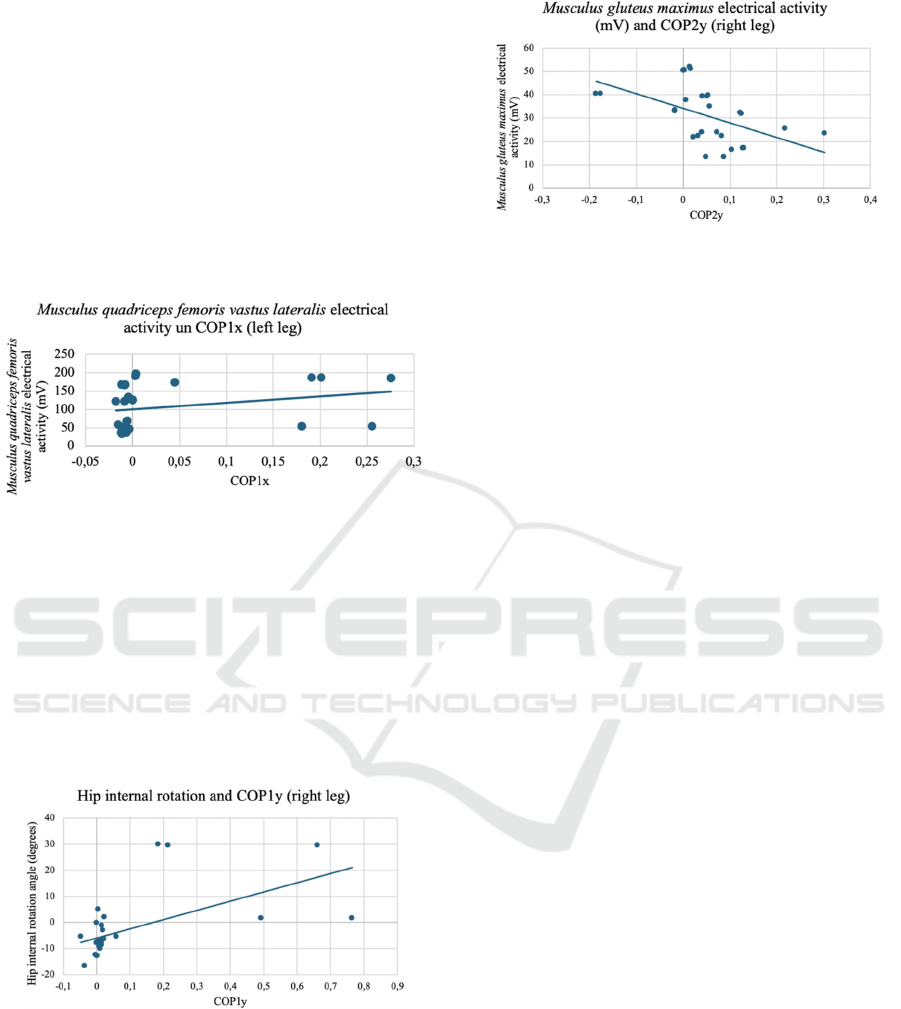
Moderate Positive Correlation
A statistically significant moderate positive
correlation was found between hip adduction and hip
joint internal rotation (r=0.408; p < .001); between
changes in the centre of pressure of the plantar surface
of the foot COP1x, which represents the position of
the centre of pressure in the medial part of the plantar
surface of the foot, and the electrical activity of the
musculus quadriceps femoris vastus lateralis
(r=0.401; p < .001) (see Figure 5).
Figure 5: Moderate positive correlation between COP1x
and the electrical activity of the musculus quadriceps
femoris vastus lateralis (left leg).
3.3.2 Right Lower Extremity
Strong Positive Correlation
A strong positive correlation was found between hip
internal rotation and hip adduction (r=0.591; p <
.001); between internal rotation of the hip joint and
changes in the centre of pressure of the plantar surface
of the foot, COP1y (r=0.599; p < .001) (see Figure 6).
Figure 6: Strong positive correlation between internal
rotation of the hip joint and COP1y (right leg).
Strong Negative Correlation
A strong negative correlation was found between
changes in the centre of pressure of the plantar surface
of the foot COP2y, and the electrical activity of the
musculus gluteus maximus (r=-0.603; p < .001) (see
Figure 7).
Figure 7: Strong negative correlation between COP2y and
the electrical activity of the musculus gluteus maximus
(right leg).
3.4 Discussion
The study's results demonstrate that the COPx, COPy,
and COPw parameters derived from the DAid®
during "One Leg Squat" exercise are reliable
indicators of the changes in the centre of pressure of
the plantar surface of the foot. Additionally, joint
angles measured by the NOTCH® and muscle
activity recorded by the PLUX® serve as reliable
indicators of lower limb performance during the task.
These findings underscore the potential of using one
smart sensor systems to provide an individualised
approach during functional tasks.
The statistically significant strong correlations
between hip joint adduction, hip joint internal rotation
angles, gluteus muscular activation, and COPx, COPy,
and COPw values highlight the interconnectedness of
lower limb dynamics measured by sensor systems. The
consistency of these findings with those of Kim et al.
(2021), which demonstrated a relationship between
increased dynamic valgus position of the knee joint and
increased foot pronation, hip joint adduction, and
internal rotation, further validates the use of these
parameters in assessing lower limb performance. The
use of advanced measurement techniques such as two-
dimensional video analysis in previous studies
complements our use of smart sensor systems, offering
robust evidence for these biomechanical relationships.
However, the practical application of multiple
smart sensor systems in real-time biofeedback
monitoring presents challenges. The setup of these
systems is often time-consuming and restricts the
freedom of movement necessary for executing
activities (Masalskyi et al., 2024). To address these
limitations, the development of smart clothing with
integrated motion-monitoring functionality combined
with mixed reality (MR) approaches offers a promising
solution. By using MR head-mounted displays
(HMDs), athletes can receive visual and auditory
icSPORTS 2024 - 12th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
136

feedback in real-time, enhancing the utility of
biofeedback during training sessions.
Moreover, the integration of smart sensor system
information into Virtual Reality (VR) environments
can create immersive and interactive 3D simulations.
These VR systems can simulate real-world scenarios,
providing athletes with biofeedback in a controlled
environment conducive to movement and skill
development (Hamad et al., 2022). By offering a
dynamic and engaging training platform, VR systems
can potentially revolutionise how athletes train and
develop their skills.
Despite these promising findings, this study has
several limitations. First, the sample size was
relatively small, which may affect the generalizability
of the results.
Additionally, the study was conducted in a
controlled environment, which may not fully replicate
the complexities and variabilities of real-world
athletic settings. Future research should aim to
address these limitations by including larger, more
diverse populations and by conducting studies in
more varied and realistic environments. Investigating
the long-term effects of using MR and VR systems
for biofeedback on athletic performance and injury
prevention would also be beneficial.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Study findings support using the DAid® smart sock
system as the sole biofeedback system for evaluating
lower limb motion during functional tasks and
highlight the potential of wireless sensors in
monitoring the biomechanical changes of the lower
extremity movements for Football Youth League
players.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is funded by the Latvian Council of
Science, project Smart textile solutions as biofeedback
method for injury prevention for Latvian football youth
league players, project No. lzp-2023/1-0027.
REFERENCES
Ahn I, Gwak G, Hwang U, Yoo H, Kwon O. (2024).
Comparison of Foot Pressure Distribution During
Single-leg Squat in Individuals with and Without
Pronated Foot. Physical Therapy Korea;31:40-47.
https://doi.org/10.12674/ptk.2024.31.1.40
Bawa, A., Banitsas, K., & Abbod, M. (2021). A Review on
the Use of Microsoft Kinect for Gait Abnormality and
Postural Disorder Assessment. Journal of healthcare
engineering, 2021, 4360122. https://doi.org/10.1155/
2021/4360122
Bizzini, M., & Dvorak, J. (2015). FIFA 11+: an effective
programme to prevent football injuries in various player
groups worldwide-a narrative review. British journal of
sports medicine, 49(9), 577–579. https://doi.org/10.
1136/bjsports-2015-094765
Brindle, R. A., Bleakley, C. M., Taylor, J. B., Queen, R. M.,
& Ford, K. R. (2022). Validity of estimating center of
pressure during walking and running with plantar load
from a three-sensor wireless insole. Wearable
technologies, 3, e8. https://doi.org/10.1017/wtc.2022.5
Chen, B., Liu, P., Xiao, F., Liu, Z., & Wang, Y. (2021).
Review of the Upright Balance Assessment Based on
the Force Plate. International journal of environmental
research and public health, 18(5), 2696.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052696
Claiborne, T.L.; Armstrong, C.W.; Gandhi, V.; Pincivero,
D.M. (2006). Relationship between Hip and Knee
Strength and Knee Valgus during a Single Leg Squat. J.
Appl. Biomech, 22, 41–50
Di Paolo, S., Nijmeijer, E. M., Bragonzoni, L., Gokeler, A.,
& Benjaminse, A. (2023). Definition of High-Risk
Motion Patterns for Female ACL Injury Based on
Football-Specific Field Data: A Wearable Sensors Plus
Data Mining Approach. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland),
23(4), 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042176
Halaki, M., & Gi, K. (2012). Normalization of EMG
Signals: To Normalize or Not to Normalize and What
to Normalize to? InTech. doi: 10.5772/49957
Hamad, A., & Jia, B. (2022). How Virtual Reality
Technology Has Changed Our Lives: An Overview of
the Current and Potential Applications and Limitations.
International journal of environmental research and
public health, 19(18), 11278. https://doi.org/10.
3390/ijerph191811278
Hermens, H. J., Freriks, B., Disselhorst-Klug, C., & Rau,
G. (2000). Development of recommendations for
SEMG sensors and sensor placement
procedures. Journal of electromyography and
kinesiology: official journal of the International Society
of Electrophysiological Kinesiology, 10(5), 361–374.
https://doi.org/10.1016/s1050-6411(00)00027-4
Hribernik, Matevž, Anton Umek, Sašo Tomažič, and Anton
Kos. (2022). "Review of Real-Time Biomechanical
Feedback Systems in Sport and Rehabilitation" Sensors
22, no. 8: 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22083006
Januskevica, A., Semjonova, G., Oks, A., Katashev, A., &
Eizentals, P. (2020). Evaluation of the Foot Performance
in "Single Leg Squat" Test of Female Athletes using
Smart Socks. In icSPORTS (pp. 161-168).
Jones, S., Almousa, S., Gibb, A., Allamby, N., Mullen, R.,
Andersen, T. E., & Williams, M. (2019). Injury
incidence, prevalence and severity in high-level male
Biomechanics of the Lower Extremity in Youth Football League: FIFA 11+ One Leg Squat Analysis
137
youth football: a systematic review. Sports medicine,
49(12), 1879-1899.
Khan, D., Al Mudawi, N., Abdelhaq, M., Alazeb, A.,
Alotaibi, S. S., Algarni, A., & Jalal, A. (2024). A
Wearable Inertial Sensor Approach for Locomotion and
Localization Recognition on Physical Activity. Sensors
(Basel, Switzerland), 24(3), 735. https://doi.org/10.
3390/s24030735
Khandakar, A., Mahmud, S., Chowdhury, M. E. H., Reaz, M.
B. I., Kiranyaz, S., Mahbub, Z. B., Ali, S. H. M., Bakar,
A. A. A., Ayari, M. A., Alhatou, M., Abdul-Moniem, M.,
& Faisal, M. A. A. (2022). Design and Implementation
of a Smart Insole System to Measure Plantar Pressure and
Temperature. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 22(19),
7599. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197599
Kim, H. S., Yoo, H. I., Hwang, U. J., & Kwon, O. Y. (2021).
Comparison of dynamic knee valgus during single-leg
step down between people with and without pronated
foot using two-dimensional video analysis. Physical
Therapy Korea, 28(4), 266-272.
Longo, U. G., De Salvatore, S., Carnevale, A., Tecce, S. M.,
Bandini, B., Lalli, A., Schena, E., & Denaro, V. (2022).
Optical Motion Capture Systems for 3D Kinematic
Analysis in Patients with Shoulder Disorders.
International journal of environmental research and
public health, 19(19), 12033. https://doi.org/10.3390/
ijerph191912033
Masalskyi, Viktor, Dominykas Čičiurėnas, Andrius
Dzedzickis, Urtė Prentice, Gediminas Braziulis, and
Vytautas Bučinskas. (2024). "Synchronization of
Separate Sensors’ Data Transferred through a Local
Wi-Fi Network: A Use Case of Human-Gait
Monitoring" Future Internet 16, no. 2: 36.
https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16020036
Neamatallah, Z.; Herrington, L.; Jones, R. (2020). An
investigation into the role of gluteal muscle strength
and EMG activity in controlling HIP and knee motion
during landing tasks. Phys. Ther. Sport, 43
Oks, A., Katashev, A., Eizentals, P., Rozenstoka, S., & Suna,
D. (2020). Smart socks: New effective method of gait
monitoring for systems with limited number of plantar
sensors. Health and Technology, 10(4), 853-860.
Sadigursky, D., Braid, J. A., De Lira, D. N. L., Machado,
B. A. B., Carneiro, R. J. F., & Colavolpe, P. O. (2017).
The FIFA 11+ injury prevention program for soccer
players: a systematic review. BMC sports science,
medicine and rehabilitation, 9(1), 1-8.
Semjonova, G., Davidovica, A., Kozlovskis, N., Okss, A.,
& Katashevs, A. (2022). Smart Textile Sock System for
Athletes’ Self-Correction during Functional Tasks:
Formative Usability Evaluation. Sensors, 22(13), 4779.
Suo, X., Tang, W., & Li, Z. (2024). Motion Capture
Technology in Sports Scenarios: A Survey. Sensors
(Basel, Switzerland), 24(9), 2947. https://doi.org/10.
3390/s24092947
Tanaka, A., Visi, F., Di Donato, B., Klang, M., &
Zbyszyński, M. (2024). An End-to-End Musical
Instrument System That Translates Electromyogram
Biosignals to Synthesized Sound. Computer Music
Journal, 1-40.
Ziagkas, E., Loukovitis, A., Zekakos, D. X., Chau, T. D.,
Petrelis, A., & Grouios, G. (2021). A Novel Tool for
Gait Analysis: Validation Study of the Smart Insole
PODOSmart
®
. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 21(17),
5972. https://doi.org/10.3390/s211759.
APPENDIX
Table 2: Correlation of left lower extremity.
Correlation
type
1
st
Parameter 2
nd
Parameter Coefficient Significancy
(p)
Strong positive COP1x COP2x r= 0,506
p
< .001
COP2x Musculus gluteus medius electrical activity r= 0,543 p < .001
COP1w COP2w r= 0,836 p < .001
Moderate
positive
Hip joint flexion Musculus biceps femoris electrical activity r=0,408 p < .001
Hip joint adduction Hip joint internal rotation r=0,408 p < .001
M
usculus
g
luteus maximus electrical activity
M
usculus gluteus medius electrical activity r= 0,462
p
< .001
COP2x Musculus gluteus maximus electrical
activity
r= 0,418 p < .001
Knee joint flexion Musculus quadriceps femoris vastus
lateralis electrical activity
r= 0,469 p < .001
COP1x COP1y r= 0,479
p
< .001
COP1x Musculus quadriceps femoris vastus
lateralis electrical activity
r= 0,401 p < .001
COP1y COP2y r= 0,456
p
< .001
Strong negative COP1w Musculus gluteus maximus electrical
activity
r= -0,517 p < .001
icSPORTS 2024 - 12th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
138
Table 2: Correlation of left lower extremity. (cont.)
Moderate
negative
Knee joint flexion Hip joint flexion r= -0,45 p < .001
Musculus quadriceps femoris vastus lateralis
electrical activity
Hip joint flexion r= -0,469 p < .001
COP2w Musculus gluteus maximus electrical
activity
r= -0,42 p < .001
Musculus quadriceps femoris vastus lateralis
electrical activity
Musculus biceps femoris electrical activity r= -0,427 p < .001
Table 3: Correlation of right lower extremity.
Correlation
type
1
st
Parameter 2
nd
Parameter
Coefficient Significancy
(p)
Strong
positive
Hip joint flexion Musculus biceps femoris electrical activity r= 0,585 p < .001
Hip joint adduction Hip joint internal rotation r= 0,591 p < .001
Hip joint adduction COP1y r= 0,836 p < .001
Hip joint internal rotation COP1y r= 0,599
p
< .001
Knee joint flexion Musculus quadriceps femoris vastus
lateralis electrical activity
r= 0,654 p < .001
COP1w COP2w r= 0,783
p
< .001
Strong
negative
Knee joint flexion Hip joint flexion r= -0,639
p
< .001
Musculus quadriceps femoris vastus lateralis
electrical activity
Hip joint flexion r= -0,599 p < .001
COP2w Hip joint adduction r= -0,588
p
< .001
Hip joint internal rotation COP1w r= -0,662
p
< .001
COP1w
M
usculus gluteus maximus electrical activity r= -0,658
p
< .001
COP2y
M
usculus gluteus maximus electrical activity r= -0,603
p
< .001
COP2w
M
usculus gluteus maximus electrical activity r= -0,637
p
< .001
Biomechanics of the Lower Extremity in Youth Football League: FIFA 11+ One Leg Squat Analysis
139
