
Prediction Web Application Based on a Machine Learning Model to
Reduce Robberies and Thefts Rate in Los Olivos,
San Martín De Porres and Comas
Mederos Sanchez, Luis Estefano
a
, Zelada Padilla, Carlos Antonio
b
and Pedro S. Castañeda
c
Faculty of Information Systems Engineering, Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas, Surco, Lima, Peru
Keywords: Machine Learning, Robbery, Thefts, Python, Random Forest Regressor, Web Application,
IBM Watson Learning Machine.
Abstract: Robberies and thefts in the districts of Los Olivos, San Martin de Porres and Comas in Lima, Peru are a
constant problem. The scarce police presence on the streets makes these areas ripe for crime. This project
proposes analyze crime rates across the public authorities to take measures that might reduce the crime rate
with the development of a Machine Learning model, through the use of Random Forest (RF) and a dataset
with information from districts in similar situations to those raised in the project. The proposed solution
includes a web application interface for data input and analysis, that will be used by municipal entities and
everyone. Performance metrics such as Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE)
were included, with results showing MAEs of 29.194, 45.219, and 75.572 and RMSEs of 39.651, 58.199, and
93.110 from other districts with the same condition. The study concludes with a refinement of machine
learning methodologies for crime prediction and emphasizes the potential for citizen engagement in crime
prevention.
1 INTRODUCTION
The issue of citizen insecurity is not only evident in
Lima's districts but also constitutes a nationwide
phenomenon of concern. As per an analysis
conducted in 2023 by the National Institute of
Statistics and Informatics (INEI), during the period
from November 2021 to April 2022, 21.1% of the
urban population in Lima aged 15 and older fell
victim to some form of criminal activity. This statistic
experienced a surge to 25% within the November
2023 timeframe.
Hence, it is of paramount importance to devise
strategic solutions that can assist Peru in reducing this
crime rate. It must be emphasized that attempting to
encompass all of Lima and every existing criminal
offense is not a viable option, as in terms of Machine
Learning, the indiscriminate use of extensive data in
an initial version can compromise the model's
accuracy. Therefore, the primary focus of this
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-5039-194X
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-5065-1411
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1865-1293
solution will be on specific districts and types of
crimes.
In this context, the districts under consideration
are Los Olivos, San Martin de Porres (SMP), and
Comas. Furthermore, the targeted crimes will be
robberies and thefts. The rationale behind selecting
these focal points is their high crime rates, making
them known as crime hotspots. For instance, a 2022
ranking by the Legal Defense Institute (IDL)
identified Los Olivos, SMP, and Comas as the
districts with the highest volumes of robberies and
thefts, with estimated figures of 2232 and 2381; 1153
and 1192; 1650 and 2450, respectively.
Therefore, the objective of this project is to
provide citizens, governmental entities, and law
enforcement agencies with the opportunity to gain
greater insight into future crime rates in these
districts. This initiative enables entities to conduct
analyses and assessments, leading to more accurate
decision-making regarding crime, the reduction of
Sanchez, M., Estefano, L., Padilla, Z., Antonio, C. and Castañeda, P. S.
Prediction Web Application Based on a Machine Learning Model to Reduce Robberies and Thefts Rate in Los Olivos, San Martín De Porres and Comas.
DOI: 10.5220/0012906800003825
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2024), pages 191-198
ISBN: 978-989-758-718-4; ISSN: 2184-3252
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
191

criminality, and the enhancement of public security
systems to uphold the well-being of the populace.
The system operates through a web application
where entities can input crime data. This information
flows into a database connected to a machine learning
model utilizing algorithms such as RF, producing
actionable insights. The following proposal is a
solution that, utilizing machine learning models,
enables predictions about the impact or priority of
crimes based on historical data. The subsequent
sections of this document are as follows: Section 2
conducts a comprehensive literature review of
various crime management solutions. In Section 3, a
meticulous depiction of the proposal is furnished,
accentuating the architecture, the proposed model and
the interface web solution. Section 4 elucidates the
findings, while Section 5 presents the conclusions and
future work.
2 BACKGROUND & RELATED
WORK
In 2020, a study explored the determinants of
organized crime by foreign terrorist criminals using
Machine Learning (ML) tools. They measured
environmental and organizational characteristics
within known terrorist organizations and applied
inductive research designs to examine criminal
behavior patterns, RF classification algorithms were
employed to predict when a terrorist organization
would engage in future criminal activities. Results
showed organizational factors outweighed
environmental factors in the classifier specifications,
suggesting organizational variables are crucial in
explaining the connection between terrorism and
organized crime (Semmelbeck and Besaw, 2020).
This study provided insights into the importance of
organizational variables and the efficacy of RF in
analyzing data patterns.
In a different context, another study aimed to
construct a predictive model to analyze crime data in
South Africa from 2005 to 2016. The goal was to
detect hidden patterns and generate reports for
implementing crime prevention measures within the
country. The research used linear regression
methodology to investigate crime trends, aiding
authorities. They utilized Python (PY) libraries for
data visualization to showcase correlations between
crimes in provinces over the established years. The
data parameters included registered crimes,
population density of each province, and the number
of police stations. The study found that the linear
regression model predicted crime rates in South
Africa with an accuracy of 84.7% indicating a strong
relationship between crime occurrence, population,
and province density (Obagbuwa and Abidoye,
2021).
Salcedo-González et al. (2023) focuses on
developing predictive geovisualization tools aimed at
controlling and preventing criminal activities, using
information provided by the National Police of
Colombia (PONAL). The study includes real-time
events for constant evaluation and training and the
used variables from the dataset: "timestamp,"
"latitude," "longitude," and "case code". Finally, the
results of the model with a better performance were
the 1D Convolutional Neural Network, with an
RMSE value of 0.285, indicating it is closer to zero.
Another study focused on developing a machine
learning algorithm to analyze criminals' anti-
investigation behavior, aiming to understand its
relationship with increasing crime rates. The Support
Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm was employed as
an effective classifier, utilizing decision boundaries to
separate data into two categories, with the goal of
identifying intelligent patterns allowing criminals to
commit crimes undetected through subsequent
investigations. Results concluded that, compared to
various algorithms, the RF algorithm achieved the
highest prediction accuracy, reaching 98.05% with 12
included features and 4770 support vectors (Zhang
and Lei, 2022). The experimental part highlights the
significant influence of criminals evading traditional
investigations on society. This approach would
confirm that the results truly impact problem
resolution.
In 2023, a study aimed to determine the most
effective machine learning models for predicting
criminal recidivism among convicted offenders in
Ukraine. Using artificial intelligence algorithms and
blockchain tools, the research analyzed a database
containing records of over 13,000 Ukrainian offenders
to identify factors influencing repeated offenses.
Various machine learning models such as DT, RF, and
SVM were employed to determine the most accurate
model. The study revealed that Gradient Boosted
Trees, RF, and DT techniques achieved prediction
accuracy levels of 98.3%. Furthermore, factors
contributing to criminal recidivism were identified,
including a 67% likelihood of reoffending among
convicts receiving lenient sentences, as well as
significant impacts of educational attainment,
particularly among first or second-time offenders.
Lastly, the number of suspended or actual convictions
played a role in the recidivism trend for third-time
offenders (Kovalchuk et al., 2023).
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
192

In the same way in 2023, a project for crime
prediction like homicides conducted in Bogota,
Colombia used data provided by the national police of
Colombia, covering the period from 2012 to 2017. In
the results, after training and testing the model, suggest
that the RF algorithm outperforms the other proposed
techniques, which are SVM, NBC, and KNN, proving
to be the most effective (Rodrigues et al., 2023).
Moreover, a study in Saudi Arabia aimed to
identify the most suitable ML algorithms for
predicting criminal activity in different regions.
Through various ML techniques, the Naive-Bayes
Classifier (NBC) was found to be the most accurate,
achieving a higher performance than other classifiers
in both Mixed Data Analysis (FAMD) and Principal
Component Analysis (PCA) methods, with an
accuracy of 97.53% and 97.10%, respectively
(Albahli et al., 2020). However, incorporating
different types of crimes in the model might have
impacted the results.
Additionally, a scientific article addressed the
prediction of potential targets for suicide attacks in
Pakistan using machine learning algorithms. By
analyzing terrorism data from the South Asia
Terrorism Portal (SATP), the study achieved notable
accuracy rates with algorithms such as Naive Bayes
(NB) and Sequential Minimal Optimization (SMO),
reaching precision rates of 72.17% and 71.30%,
respectively. These classifiers facilitated the
identification of specific individuals prone to
committing terrorist acts, including variables such as
location, day, month, province and city (Mahmood
and Ghani, 2021). This research shows a significant
advancement in using machine learning to predict
profiles of individuals engaging in terrorist activities.
In Roses et al. (2021), spatial crime simulation
techniques were developed to understand crime
mechanisms using machine learning on robbery data
from New York City between June 2014 and June
2015. Four simulation scenarios were created to
evaluate the model's performance. The first scenario
used the decision tree algorithm, with metrics like
RMSE and Predictive Accuracy Index (PAI). The
results indicate a PAI of 3% and an RMSE of 0.040.
Furthermore, research was conducted to produce
a prediction and forecasting model for crimes in
Chicago and Los Angeles using ML and Deep
Learning (DL) techniques. Eight different algorithms
were tested, including Support vector machine
(SVM), RF, DT, XGBoost, Multilayer Perceptron
(MLP), and logistic regression. The analysis yielded
two categories of results: accuracy percentages for
Chicago and Los Angeles data. XGBoost and logistic
regression algorithms achieved the highest accuracy
percentages for Chicago data, with 94% and 90%
accuracy, respectively. For Los Angeles data, the k-
nearest neighbors (KNN) algorithm demonstrated the
best performance, achieving an 89% accuracy, while
XGBoost reached an 88% accuracy (Safat et al.,
2021). It's important to note that predictions with
higher accuracy were obtained for crime data
collected in Chicago.
A study conducted an analysis to design an ML
model for predicting crimes in Porto, Portugal, by
combining data mining, geospatial technology, and
ML to identify high-risk areas and make accurate
predictions. Comparing various ML algorithms with
crime data from 2016 to 2018, the RF algorithm
yielded the best results, with a 99% True Positive
Rate (TPR) in testing and an 83% accuracy (Saraiva
et al., 2022). This research underscores the
importance of using logistic regression and RF in
similar projects due to their successful outcomes with
recent crime data.
In Baek et al (2021), an intelligent security system
is proposed to predict various types of crimes based on
a ML model, utilizing crime report summaries for
prediction. They primarily employ Deep Neural
Network (DNN) and Convolutional Neural Network
(CNN) architectures. Data is gathered from The Korea
Information System of Criminal Justice (KICS). The
DNN and CNN models are trained with a split of 60%
training (3000 crime cases), 20% validation (1000
crime cases), and 20% testing (1000 crime cases).
Metrics such as Accuracy, Precision, Recall, and F1-
Score are used to assess model accuracy. The CNN
model achieves the best results, with 91%, 92%, 82%,
and 84% in the mentioned metrics, respectively. The
authors' proposal represents a significant project in the
targeted area of study, as a real-time prediction model
will greatly assist law enforcement entities in decision-
making, whether it involves increasing police presence
in certain areas or taking specific actions in particular
cases.
In another research analysis, the city of Boston
has witnessed a significant shift in crime rates to the
extent that conducting a comprehensive and
analytical data analysis for better investigation
becomes challenging. The study aims to employ a
supervised learning approach by adding DT and RF
algorithms, along with Principal Component Analysis
(PCA), to the already mentioned algorithms. For the
study's development, they utilized records from the
Boston Police Department (BPD). The results
indicated that RF PCA achieved an accuracy of 60%
and an F1-score of 56%, followed by decision tree
PCA with an accuracy of 56% and an F1-score of
50% (Sharma et al., 2021). From the study, it can be
Prediction Web Application Based on a Machine Learning Model to Reduce Robberies and Thefts Rate in Los Olivos, San Martín De Porres
and Comas
193

highlighted that the precision levels are not high,
which is attributed to the poor distribution of crime
data, with few attributes contributing to better
prediction correlation.
Finally, in a study conducted in 2021, the focus
was on addressing the problem of crime using ML
models like RF algorithm to long-term forecast the
number of thefts in micro-locations in Dallas, Texas.
Additionally, performance was compared with other
techniques such as Risk Terrain Modeling (RTM) and
Kernel Density Estimation (KDE). The dataset used
was from the Dallas Open Data portal, where training
spanned from June 2014 to May 2016, with testing
from June 2016 to May 2018. The results showed that
RF outperformed the other techniques, with a PAI
value of 330.05, the highest (Wheeler and Steenbeek,
2021).
In summary, the literature reveals notable
advancements in using ML techniques to predict
various aspects of criminal behavior. However, there
are also differences and limitations within the studies.
Common findings include the effectiveness of ML
algorithms like RF and Support Vector Machine
(SVM) in crime prediction tasks across diverse
contexts. For instance, RF was found to be highly
accurate in predicting terrorist activities and criminal
recidivism, while SVM showed promise in
identifying patterns of anti-investigation behavior
among offenders. On the other hand, while some
focus on specific crime types or geographical regions,
others explore broader trends in criminal activity.
These differences underscore the multifaceted nature
of crime prediction and the need for tailored
methodologies to address specific challenges.
3 SYSTEM DESIGN
3.1 Architecture
The logical architecture of this project is structured to
accommodate different types of users, each with
specific roles and capabilities within the web
application. The system is initiated by either a user or
an administrator who accesses the application
through a web browser. Depending on their role, they
are presented with distinct interfaces and options.
Additionally, there is a guest user with limited
functionality, primarily granted access to some of the
options available to a regular user, such as obtaining
a prediction.
Both the administrator and the user have the ability
to request predictions. When a user submits a
prediction request, the web application communicates
with the model via Flask, filtering the uploaded
information to generate a prediction using the Random
Forest (RF) algorithm. During this process, the model
consults the database stored in MongoDB, where it
validates key variables such as date, type of robbery,
motorcycle use, amount, and weapon use, ensuring that
the data aligns with the necessary criteria for accurate
prediction. The administrator, beyond requesting
predictions, has the capability to upload new data,
which is crucial for enhancing the model's precision
over time. The administrator is also responsible for
overseeing the registration of users within the
application, ensuring effective management and
control.
Furthermore, the user can register a crime and
access valuable information on how to avoid
becoming a victim of theft or robbery. The detailed
functionalities and interactions of these components
are illustrated in the Figure 1.
3.2 Model
The model is based on RF algorithm, developed with
Python in Google Colab Platform. To train the model,
the dataset had to go through a data quality and
cleaning process. This phase involves checking
duplicate data, delete null data, and filter the data to
have just the information that the model requires.
Initially, the dataset counted with 169,000 registers,
after the data and quality and cleaning process the
dataset counts with 100,000 registers.
During the training phase, an additional column
was added to the dataset, the “Pandemic” field. This
variable is important for the training process because,
before the COVID-19 pandemic situation, the crime
rate was high. However, after the pandemic began,
the crime rate decreased a lot, because most people
were at home.
This variable helped the model to identify the
pandemic situation and give a better prediction. The
information used for the training phase was thefts and
robberies registered from 2016 to 2018, and the
information used to validate the prediction is from
July 2021 to December 2022.
Finally, three more columns were considered: the
first was "previous month", the second "two months
ago", and the last "three months ago". The reason for
this is that being a regression column of the total
number of crimes recorded, including those recorded
consecutively over the past three months.
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
194
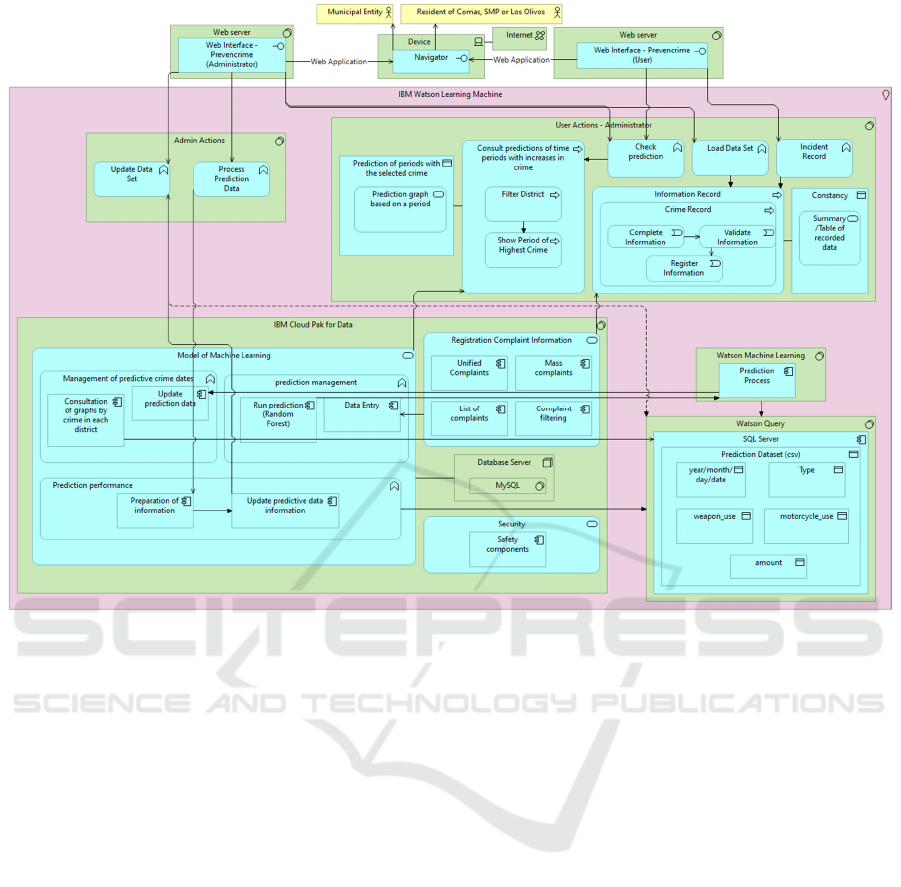
Figure 1: Logical Architecture of the Web Application.
3.3 Interface
The web application is specifically designed for
police or government entities, using technologies
such as ReactJS, HTML5 and CSS to provide an
intuitive and responsive interface. This platform
allows for the input and reception of data, which are
stored in a database and analyzed using the IBM
Watson machine learning model implemented in
Python. The analysis results are presented
quantitatively and graphically, facilitating their
understanding and use for informed decision-making.
Additionally, the interface allows for constant
adjustments and feedback, optimizing the accuracy of
the results. The user accesses into user interface (UI)
to appreciate all the functionalities offered by the web
frontend, while the web server backend handles client
requests and communicates with the Machine
Learning API. This API provides the interface to
interact with the Machine Learning model, including
the trained models, data processing, and the services
it offers. Additionally, security is a fundamental
feature in preventing potential threats to data loss.
Therefore, a security and authentication layer has
been implemented to protect the Machine Learning
model and input data, ensuring the integrity and
confidentiality of the information
Finally, it is important to highlight that the web
application offers different functionalities based on the
user type. The main features available for each group
of users within the interface are presented below:
Municipal Entity:
• Update Dataset: Allows for the uploading and
updating of relevant datasets for analysis.
• Generate Reports: Facilitates the creation of
detailed reports based on the collected data.
• Verify Users: Enables the management and
verification of registered users.
Residents of Comas, SMP or Los Olivos:
• User Registration: Simplifies the registration
process for new users.
• Crime Registration: Registration of crimes by
registered users.
• View Charts: Provides access to interactive
charts for a better understanding of relevant
information.
Prediction Web Application Based on a Machine Learning Model to Reduce Robberies and Thefts Rate in Los Olivos, San Martín De Porres
and Comas
195
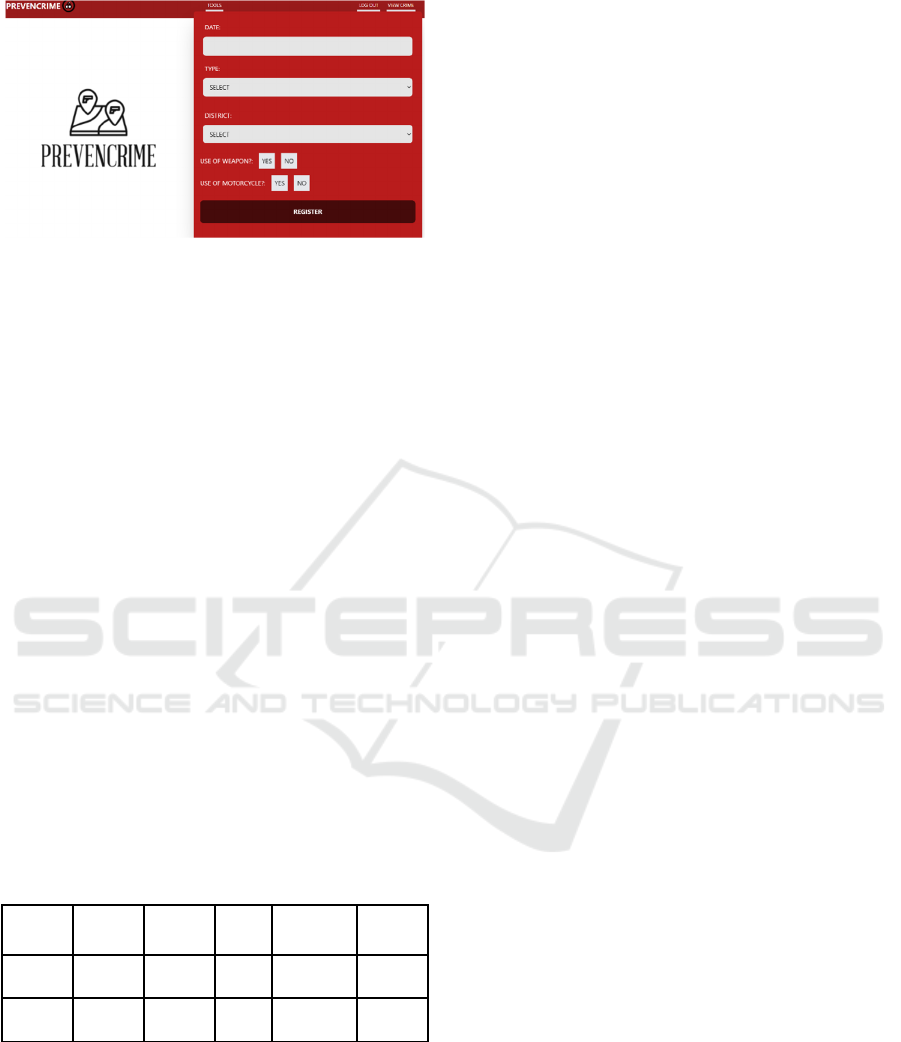
Figure 2: Crime Reporting Interface.
In figure 2, this section of the web application
represents the interface for registering crimes by users
or municipal entities. They can record information
about the complaint such as the date, type of crime,
frequency of occurrence of this crime, district it
belongs to, and lastly, characteristics such as whether
a weapon was used or if a motorcycle was involved,
this information will be utilized in the future to assess
the model's performance and support the authorities
by contributing to the collection of this information.
3.4 Dataset
A specific dataset has been selected for the proposed
solution and the development of the ML model. This
dataset focuses on the districts in Argentina and is
sourced from the Buenos Aires (BA) Data platform,
which aggregates over 300 datasets from 13
government areas (Ministerio de Seguridad de la
Nación, 2023). The change of information is based on
the dataset's robust and comprehensive structure,
evident in the columns, compared to what was found
in research platforms related to Lima Metropolitana.
The following table presents the dataset design:
Table 1: Dataset from BA data.
Date
Type Weapon Motor
cycle
District
Pandem
ic
10/14/
2016
Robbery NO NO Balvanera NO
05/23/
2022
Theft NO NO Villa
Lu
g
ano
YES
This dataset has many key columns with vital
information. It first contains a column of ‘Date’
which is a time series data of each event, this column
provides the analysis with temporal context to
identify patterns and trends in relation to the nature of
crimes.
The ‘Type’ column shows the nature of the event
including for example robbery and theft, providing
context for the type of criminal activity. The
‘Weapon’ column specifies whether a weapon was
involved in the crime, indicated as "YES" or "NO",
same case with the column ‘Motorcycle’. The column
of ‘District’ identifies the exact place where the event
took place, allowing the analysis of crime
distribution.
Finally, the column ‘Pandemic’ is an indication of
the crime occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic
or did not, considering the date between January 2020
and the end of 2022.
3.5 Indicators
The performance evaluation of the solution requires a
deep understanding of several key indicators. These
indicators provide a comprehensive view of the
system’s success and effectiveness in crime
prevention.
The MAE is a metric used to measure the
difference between two values and it indicates how
different the predicted value is from the actual or
observed value. For example, if we have actual
numbers like 3, 2.5 and the following predictions are
3.1, 2.5 so this indicates that the MAE value of 0.249
is the magnitude of errors in the observations, which
is satisfactory because the error is closer to zero
(Landa, 2021).
Finally, to understand the metric RMSE. First the
MSE was defined, which measures the average
squared error of the predictions, because calculates
the squared difference between the predictions and
the target. A higher MSE value indicates a worse
model and it is always non-negative. RMSE is the
square root of MSE, this square root adjustment
ensures that the error scale matches the scale of the
target values (Big Data, 2018).
4 RESULTS & DISCUSSION
Finally, in the results phase, the model demonstrated
robust performance across the tests in the districts in
Buenos Aires with the same crime situation as
districts in Lima, Peru, so the results obtained can be
implemented in the data structure in Lima to be able
to generate predictions in the future with the objective
of being a support to combat crime. The principal
metrics used to evaluate the model's accuracy were
RMSE and MAE. The model showed the following
results: in Villa Lugano, the MAE was 29.194 and the
RMSE was 39.651; in Recoleta, the MAE was 45.219
and the RMSE was 58.199; and in Balvanera, the
MAE was 75.572 and the RMSE was 93.110.
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
196

Figure 3: Bar chart comparing actual data and model predicted data in the Villa Lugano neighbourhood from 2021 to 2022.
In Villa Lugano, the lower MAE and RMSE
indicate that the model's predictions were very close
to the actual data, reflecting high accuracy. Recoleta,
while showing slightly higher error metrics, still
demonstrated reasonable predictive performance. In
Balvanera, the model's higher MAE and RMSE
suggest more significant deviations from the actual
values, indicating limitations, particularly when
confronted with extensive datasets with a higher
incidence of reported events.
During the prediction process, the model
consulted the MongoDB database to validate key
variables such as date, type of robbery, motorcycle
use, amount, and weapon use. This step ensured that
the data used for predictions was accurate and aligned
with the criteria necessary for reliable results.
However, despite these validations, the larger and
more complex datasets, particularly in areas like
Balvanera, presented challenges that resulted in
higher error margins compared to other districts.
As depicted in Figure 3, the model demonstrates
strong performance, particularly in Villa Lugano.
Instances of accurate forecasting include August
2021, where both real data and predictions align at
5.67%, December 2021 with a minimal deviation of
5.72% versus 5.75%, July 2022 showing a close
match at 5.55% and 5.61%, and finally, August 2022
displaying 5.65% against 5.61%. Additionally, it has
been found that the data in the columns, as well as the
context of the pandemic, have significantly affected
the performance of this type of this type of model.
Figure 4 shows that excluding factors like
consecutive months and the pandemic scenario, and
only considering the month and year, significantly
worsened the model's performance, with an RMSE of
39.46 and a MAE of 33.43, often deviating from real
data. The validation against MongoDB emphasized
the importance of including comprehensive data, such
as date, robbery type, motorcycle use, amount, and
weapon use, to improve prediction accuracy.
In summary, the metrics RMSE and MAE were
primary in this accuracy assessment, emphasizing the
necessity of discovering and incorporating more
detailed data to enhance predictive accuracy.
Figure 4: Line Chart from Villa Lugano (2021-2022).
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
According to this study, the ML model demonstrates a
strong ability to generate precise predictions, closely
aligning actual and predicted criminal rates, especially
when considering the pandemic's mitigating impact on
crime. This means that using the model with real-time
data will yield accurate results, effectively helping the
project achieve its main objective. Unlike previous
Prediction Web Application Based on a Machine Learning Model to Reduce Robberies and Thefts Rate in Los Olivos, San Martín De Porres
and Comas
197

related works, this project offers significant added
value through the integration of a web application and
continuous data updates, ensuring that predictions are
based on the most current information available. The
project addresses the pressing issue of rising crime in
specific districts and crime types, providing valuable
insights for decision-making to enhance public security
systems and reduce criminality. It also promotes
citizen engagement through the web application and
user interfaces.
This research enhances crime prediction by
developing an RF-based model that considers key
factors affecting accuracy. To further improve results,
the study suggests integrating advanced technology
and refining strategies to meet stakeholder needs.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are grateful to the Dirección de
Investigación de la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias
Aplicadas (UPC) for the support provided for this
research work through the incentive.
REFERENCES
Albahli, S., Alsaqabi, A., Aldhubayi, F., Rauf, H. T., Arif,
M. and Mohammed, M. A. (2020). Predicting the type
of crime: Intelligence gathering and crime analysis.
Computers, Materials & Continua 2021, 66(3), 2317-
2341. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2021.014113
Baek, M. S., Park, W., Park, J., Jang, K. H., and Lee, Y. T.
(2021). Smart Policing Technique with Crime Type and
Risk Score Prediction Based on Machine Learning for
Early Awareness of Risk Situation. IEEE Access,
9(2021), 131906-131915. https://doi.org/10.1109/
ACCESS.2021.3112682
Big Data. (2018). Aprendizaje Automático ML: Métricas de
Regresión. https://sitiobigdata.com/2018/08/27/machi
ne-learning-metricas-regresion-mse/
INEI. (2023). Estadísticas de Seguridad Ciudadana.
https://m.inei.gob.pe/media/MenuRecursivo/boletines/
estadisticas-de-seguridad-ciudadana-noviembre-2022-
abril-2023.pdf
Kovalchuk, O., Karpinski, M., Banakh, S., Kasianchuk, M.,
Shevchuk, R., and Zagorodna, N. (2023). Prediction
Machine Learning Models on Propensity Convicts to
Criminal Recidivism. Information (Switzerland),
(2023), 14(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/info14030161
Landa, N, (2021). Métricas en Regresión. Medium.
Mahmood, N and Ghani, M. (2021). Prediction of Extremist
Behaviour and Suicide Bombing from Terrorism
Contents Using Supervised Learning. Computers,
Materials and Continua (2022), 70(3), 4411-4428.
https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2022.013956
Ministerio de Seguridad de la Nación. (2023). SNIC -
Provincial. Estadísticas criminales en la República
Argentina por provincias. https://datos.gob.ar/dataset/
seguridad-snic---provincial-estadisticas-criminales-
republica-argentina-por-provincias
Obagbuwa, I., and Abidoye, A. (2021). South Africa Crime
Visualization, Trends Analysis, and Prediction Using
Machine Learning Linear Regression Technique.
Applied Computational Intelligence and Soft Computing,
(2021). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5537902
Rodrigues, A., González, J. A., and Mateu, J. (2023). A
conditional machine learning classification approach
for spatio-temporal risk assessment of crime data.
Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk
Assessment, (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-
023-02420-5
Roses, R., Kadar, C., and Malleson, N. (2021). A data-
driven agent-based simulation to predict crime patterns
in an urban environment. Computers, Environment and
Urban Systems, 89(2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.
compenvurbsys.2021.101660
Salcedo-Gonzalez, M., Suarez-Paez, J., Esteve, M., and
Palau, C. (2023). Spatiotemporal Predictive Geo-
Visualization of Criminal Activity for Application to
Real-Time Systems for Crime Deterrence, Prevention
and Control. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-
Information, (2023), 12(7). https://www.mdpi.com/
2220-9964/12/7/291
Safat, W., Asghar, S., and Gillani, S. A. (2021). Empirical
Analysis for Crime Prediction and Forecasting Using
Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques.
IEEE Access, 9(2021), 70080-70094. https://doi.
org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3078117
Saraiva, M., Matijošaitienė, I., Mishra, S., and Amante, A.
(2022). Crime Prediction and Monitoring in Porto,
Portugal, Using Machine Learning, Spatial and Text
Analytics. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-
Information, (2022), 11(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/
ijgi11070400
Semmelbeck, J. and Besaw, C. (2020). Exploring the
Determinants of Crime-Terror Cooperation using
Machine Learning. Journal of Quantitative Criminology,
(2020), 36(3), 527-558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10940-
019-09421-0
Sharma, H., Choudhury, T., and Kandwal, A. (2021).
Machine learning based analytical approach for
geographical analysis and prediction of Boston City
crime using geospatial dataset. GeoJournal, (2021).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-021-10485-4
Wheeler, A., and Steenbeek, W. (2021). Mapping the Risk
Terrain for Crime Using Machine Learning. Journal of
Quantitative Criminology, (2021), 37(2), 445 - 480.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10940-020-09457-7
Zhang, J and Lei, Y. (2022). Trend and Identification
Analysis of Anti-investigation Behavior in Crime by
Machine Learning Fusion Algorithm. Wireless
Communications and Mobile Computing, (2022).
https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1761154
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
198
