
Separating the Yes- from the No-Instances in the Number Partitioning
Problem
Ruben Horn
1 a
, Reitze Jansen
4 b
, Okke van Eck
4 c
and Daan van den Berg
2,3 d
1
Helmut-Schmidt-University, Hamburg, Germany
2
Department of Computer Science, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands
3
Department of Computer Science, VU Amsterdam, The Netherlands
4
Independent Researcher
Keywords:
Number Partitioning Problem, NP-hard, Branch-and-Bound Algorithm, Greedy Algorithms.
Abstract:
The (two-way) number partitioning problem (NPP) is a well known NP-complete decision problem in which a
set of (positive) integers must be split in such a way that the sum of both resulting subsets is equal. However, its
optimization problem variant is even harder, since the verification of partitions is only possible in polynomial
time for instances which have a perfect partition. We investigate the distribution of instances that have and
that do not have a perfect partition, and find that they are not randomly distributed in the instance space. Thus,
the hardness of any given instance might be predictable to some extent. We demonstrate that it is possible
to separate these two instance types visually using a linear time embedding into R
2
for instances of the same
template. Furthermore, we compare three greedy heuristic algorithms (greedy captains, greedy coach, and
greedy tyrant) and their difference to the solution from an exact branch-and-bound (BB) algorithm.
1 INTRODUCTION
The (two-way) number partitioning problem (NPP),
also known as “the easiest hard problem” (Brian
Hayes, 2002; Schreiber et al., 2018; Stephan Mertens,
2003), is the well-known NP-complete (Karp, 1972)
problem of partitioning a set of positive integers such
that both resulting subsets sum up to the same value.
This problem is a special case of the subset sum prob-
lem (SSP) where the aim is finding A ⊆ S such that
∑
A = t. For the NPP, t =
⌈
1
/2
∑
S
⌉
, meaning the set
must be split in two equally valued subsets. Com-
ing up with such a partition is hard, but verification
can be done in polynomial time for the decision vari-
ant of this problem. For many instances, however, no
perfect partition exists and yet, the optimization vari-
ant of the NPP might be relevant. For example, even
when it is impossible to split a group of football play-
ers into perfectly equal teams, the match should be
as fair as possible (cf. Brian Hayes, 2002). For the
decision variant, instances of the NPP which have a
perfect partition are referred to as yes-instances and
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6643-5582
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-0029-2882
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3600-5183
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5060-3342
those that do not as no-instances. For yes-instances,
the NP-hard optimization variant of the NPP is easy
in many cases, but for no-instances it is almost al-
ways hard, requiring many steps for an exact algo-
rithm. It is trivial to verify if a partition is perfect,
but not whether an imperfect one is optimal. An opti-
mization algorithm may terminate early upon finding
any single one of potentially many perfect partitions,
but only for yes-instances. Thus, separating yes- from
no-instances presents an interesting problem with po-
tential implications for the hardness classification of
the NPP.
It is known that the ratio between the number of
informational bits that represent the integers and their
value influence the hardness of an instance (Brian
Hayes, 2002; Richard Korf, 1998; Stephan Mertens,
2003). Recently, the influence of the distribution
of informational bits on the hardness of an instance
has been shown (Van den Berg and Adriaans, 2021;
Sazhinov et al., 2023). Obviously, a distribution
where one integer is larger than the sum of all oth-
ers yields a trivial no-instance. Larger instances with
integers in the same range are more likely to have
many perfect partitions, because the number of parti-
tions grows faster than the number of possible subset
sums (Richard Korf, 1998). For practical applications
such as scheduling (Seenu S. Reddi, 2008) or in the
Horn, R., Jansen, R., van Eck, O. and van den Berg, D.
Separating the Yes- from the No-Instances in the Number Partitioning Problem.
DOI: 10.5220/0012907000003837
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2024), pages 181-188
ISBN: 978-989-758-721-4; ISSN: 2184-3236
Copyright © 2024 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
181
container-trucking industry (Coslovich et al., 2006),
the use of heuristic algorithms for the optimization
variant of the NPP may arguably be admissible in or-
der to obtain a partition that is good enough in reason-
able time. Therefore, the optimization variant of the
NPP and specifically its hardness warrants investiga-
tion.
Section 2 tackles our question about the separabil-
ity of yes- and no-instances. In Section 2.1, we first
explain our method of generating suitable datasets for
our experiments. We describe both an exact algorithm
and an easy heuristic approach to the NPP: greedy al-
gorithms. Then, in Section 2.2, we present the re-
sults of our algorithm comparison and investigation
whether the instance type (yes- or no-instance) can
be predictable using the previously generated dataset.
Based on these results, in Section 3, we propose and
demonstrate a visualization approach to gain insight
into this property in Section 3.1 and Section 3.2 re-
spectively. Finally, we end with a discussion of our
findings and conclusion in Section 4.
The dataset and all source code is provided in an
online repository (Horn et al., 2024a).
The problem instances for the NPP were gener-
ated, solved and analyzed using Python 3, NumPy
(Harris et al., 2020), Pandas (The Pandas devel-
opment team, 2020) and swifter (Jason Carpenter,
2023), which is based on Dask (Matthew Rocklin,
2015), for parallel execution. For the visualization
of our results, we used Matplotlib (John D. Hunter,
2007) and seaborn (Michael L. Waskom, 2021). All
experiments were executed on the cluster HSUper us-
ing a single compute node running Linux 4.18 with
two CPUs for a total of 72 physical cores at 2.4 GHz
and with 256 GB of DDR4 memory. Generating and
analyzing the dataset took roughly 1.5 hours on this
system.
2 PREDICTABILITY OF THE NPP
Our conjecture is that, for the NPP, yes- and no-
instances are often very similar. If this is true, then
it may be impossible to efficiently distinguish them
without solving the instance. If, however, it is false,
then it might be worth it to assess the hardness of yes-
and no-instances separately.
2.1 Methods
2.1.1 Generating the Dataset
To investigate this conjecture, we randomly generate
a dataset expected to contain as many yes-instances
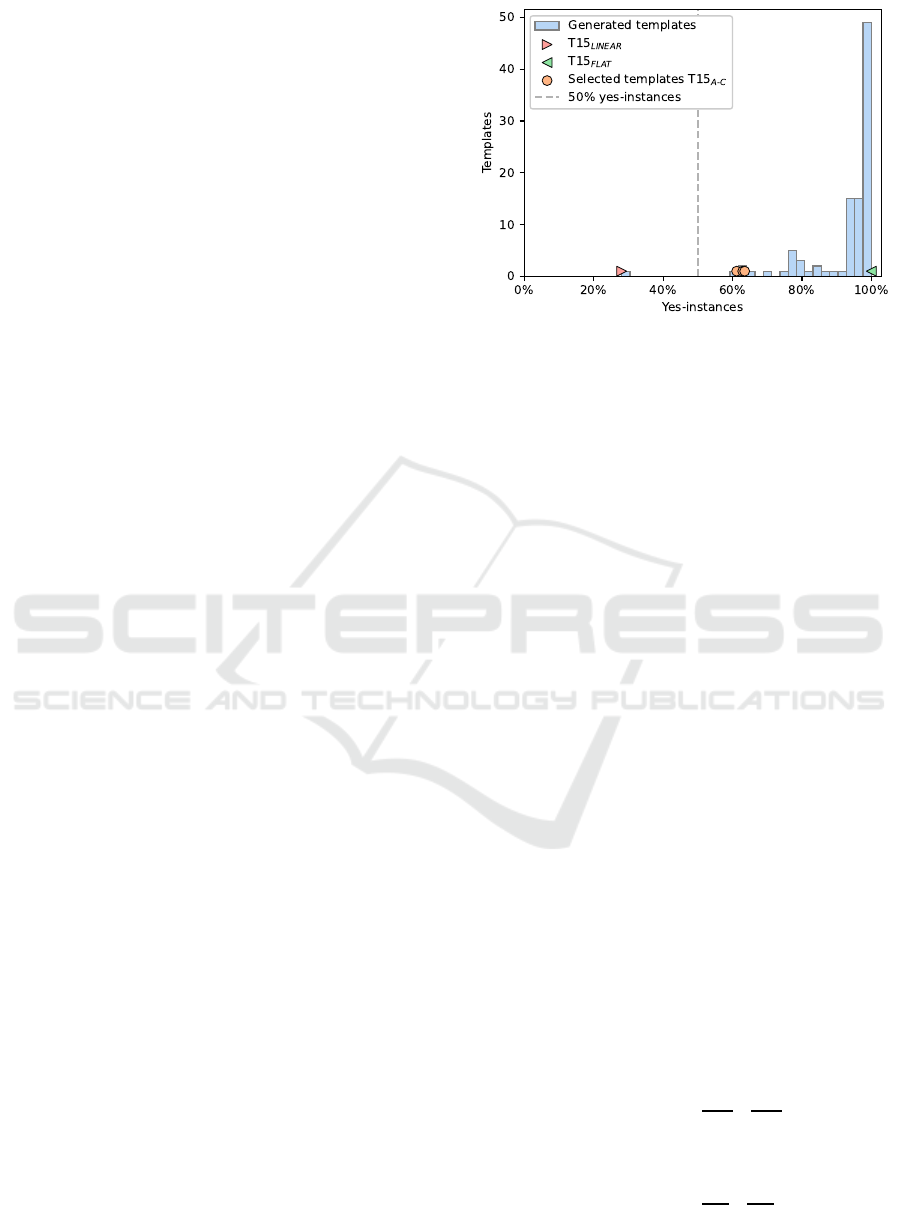
Figure 1: Histogram over the fraction of yes-instances for
100 templates generated, which have an informational bit
distribution slope between 0 and 1. Most templates produce
almost exclusively yes-instances. This can be partially at-
tributed to the small ratio of informational bits per integer
m to the number of integers n of
m
/n =
8
/15 ≈ 0.53.
as no-instances. To this end, we use the template
approach by Van den Berg and Adriaans (2021) to
generate similar instances of n = 15 integers with the
same distribution of informational bits for the same
template. A template consists of a list of numbers
which indicate the exact number of bits required to
represent the individual integers in a corresponding
instance, and therefore the range of possible integer
values from which to sample. For example, a value
of 3b in a template indicates that the corresponding
integer in an instance generated from it may have any
value between 4 = (100)
b
and 7 = (111)
b
. Thus, from
the template (3b,3b,4b,9b) for example, we might
generate the instance {4,7,8,405} or {5,6,13, 270}.
All generated templates and instances are sorted lists,
which is a prerequisite for the methods described in
this paper.
Since we suspect a correlation between the hard-
ness of instances and their instance type (yes- or
no-instance), we consider all so-called non-eccentric
templates between the linearly increasing template
T15
LINEAR
with a slope of 1 and flat template T15
FLAT
with a slope of 0, which generate both instance types
(Van den Berg and Adriaans, 2021; Sazhinov et al.,
2023) and can all be represented by the binary string
corresponding to their derivative:
T15
LINEAR
′
= (1,1,1,..,1)
| {z }
14 local slopes
...
T15
FLAT
′
= (0,0,0..,0)
| {z }
14 local slopes
Conversely, by integrating all possible bit strings with
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
182

a length of n − 1 = 14, one obtains all non-eccentric
templates with n integers and
∑
n
i=1
i = mn bits:
T15
LINEAR
= (1b,2b,3b,..,15b)
| {z }
120 bits over 15 integers
...
T15
FLAT
= (8b,8b,8b,..,8b)
| {z }
15×8=120 bits
We take 100 templates in regular intervals over all
enumerated template derivatives and compute the yes-
instance ratio by solving 1000 instances generated
from each selected template with an exact branch-
and-bound (BB) algorithm (Van den Berg and Adri-
aans, 2021). The distribution of yes-instances of the
templates is visualized in Figure 1. Since the ratio
m
/n of informational bits per integer m to the number
of integers n is small, most templates generate almost
exclusively yes-instances (cf. Brian Hayes, 2002).
We select three out of the 100 templates where the
probability of yes- and no-instances is between 35%
and 65% (Figure 1) and generate a dataset of 10,000
instances for each. From every problem instance, a
d1-mutant is created by flipping a single random bit
that is not the most significant bit (MSB) of an in-
teger, such that the distribution of informational bits
remains the same as in the original instance. This is
done by
1. selecting a random integer index i,
2. determining its number of bits m
i
,
3. selecting a random bit index i
b
< m
i
and
4. flipping bit i
b
of integer i.
If the distribution of yes- and no-instances is not
predictable (they could be thought of as being well-
mixed), then the instance type of the mutant instances
should not depend on the instance type of the origi-
nal instance and have a roughly equal probability of
being either a yes- or no-instance in both cases.
The bit distribution of the selected template T15
A
is given in Equation (1) and although 61.16% of
instances generated from this template were yes-
instances, it is as close as possible to an even split
between yes- and no-instances in our dataset. To im-
prove the soundness of our experiment, we also select
two other templates T15
B
in Equation (2) and T15
C
in
Equation (3) with 62.92% and 63.48 % yes-instances
respectively.
T15
A
= (3b,4b,5b,6b,6b, 7b,8b, 8b,9b,9b, (1)
9b,10b, 11b,12b,13b)
T15
B
= (4b,5b,6b,6b,6b, 6b,7b, 7b,8b,9b, (2)
10b,10b, 11b,12b,13b)
T15
C
= (4b,5b,5b,6b,6b, 6b,7b, 8b,8b,9b, (3)
10b,10b, 11b,12b,13b)
2.1.2 Hypothesis Formulation
Since yes- and no-instances are not very balanced in
any of the generated templates (Figure 1), we apply
a margin of ±15% in our experiments, so any ratio
of yes- and no-instances between 35/65 and 65/35 is
considered to have about the same of either. Thus,
our pessimistic assumption for the null hypothesis is
that yes- and no-instances must be not separable if
instances have only a 35% chance of changing their
instance type under mutation of a single bit.
2.1.3 Algorithms
Heuristic algorithms for NP-complete problems may,
in practice, be a preferable alternative to exact ones.
Sazhinov et al. (2023) investigated the performance
of three heuristic algorithms for the NPP by comput-
ing their heuristic deficiency, defined by Equation (4).
This metric determines the performance of a heuristic
algorithm H in relation to and exact method gener-
ating the optimal partition, such as the BB algorithm
described in Algorithm 1. Here A
H
and A
BB
are sub-
sets corresponding to the final partitions p
H
and p
BB
that are returned by the respective algorithms for an
instance S of the NPP.
Algorithm 1: Recursive pseudocode adaptation for
the NPP of the exact BB algorithm for the SSP by
Van den Berg and Adriaans (2021).
Data: Descending integer list S, index i ≤ |S|,
partition masks p, p
best
(initially
⃗
0)
Result: Optimal partition for S
if p better than p
best
then
p
best
:= p;
if p
best
imperfect and
∑
S
p
< ⌈
1
/2
∑
S⌉ then
recurse with i := i + 1 and p
i
:= 1;
if p
best
imperfect and
∑
S
p
< ⌈
1
/2
∑
S⌉ then
recurse with i := i + 1 and p
i
:= 0;
We perform this analysis across all generated in-
stances and, in addition to this metric for the quality
of the partition given by a heuristic algorithm, also in-
vestigate the similarity to the optimal partition, com-
puted from the Hamming distance between the binary
strings describing the corresponding partitions.
deficiency
H
(S,A
H
) =
∑
S −
∑
A
BB
∑
S −
∑
A
H
(4)
We choose the greedy algorithm due to its simplic-
ity and intuitiveness, and also because of its relatively
Separating the Yes- from the No-Instances in the Number Partitioning Problem
183
good performance (Sazhinov et al., 2023). However,
one can come up with different variants of a greedy
algorithm for the NPP which may, borrowing the ex-
ample by Brian Hayes (2002), represent different ap-
proaches to partitioning a group of children into two
football teams. This is reflected in the names that we
gave to the different variants:
1. The greedy captains algorithm, described ini-
tially by Brian Hayes (2002) (and probably most
widely used among children), in which the titular
captains take turns selecting the largest remaining
integer, always produces the same binary partition
p
greedy captains
= (1,0,1,0,1, ...).
2. The variation actually used by Brian Hayes (2002)
and Sazhinov et al. (2023) may be called the
greedy coach algorithm, since the largest integer
is assigned to the subsets with the smaller sum re-
gardless of turn.
3. Finally, the greedy tyrant algorithm is just the
greedy algorithm for the SSP with t =
⌈
1
/2
∑
S
⌉
and thereby for the NPP. The next largest integer
is assigned to the subset as long as the current sub-
set sum is smaller than t.
2.2 Results
2.2.1 Performance of Greedy Algorithms
Table 1 shows that this last variant, the greedy tyrant
algorithm, performs best over all instances from all
templates generated in Section 2.1.1 when compared
to the optimal partition, because it has the lowest
mean heuristic deficiency and its partition is struc-
turally closest to that of the exact algorithm having the
lowest Hamming distance. However, the large stan-
dard deviation of the difference in Table 1 shows that
the partition by even the greedy tyrant variant may be
completely different from that by the exact algorithm.
This indicates that applying a linear time greedy al-
gorithm may not be a useful preprocessing step for an
exact algorithm.
2.2.2 Instance Type Under Mutation
Contrary to the assumption of our null hypothesis in
Section 2.1.2, and as shown in Table 2, the over-
whelming majority of neighboring instances have the
same instance type after mutation instead of having
a roughly equal probability of being a yes- or no-
instance.
1
Since every problem instance has 120 −
15 = 105 bits that can potentially be flipped and thus
1
We omit reporting the results of the statistical test here
due to the unambiguity of these results.
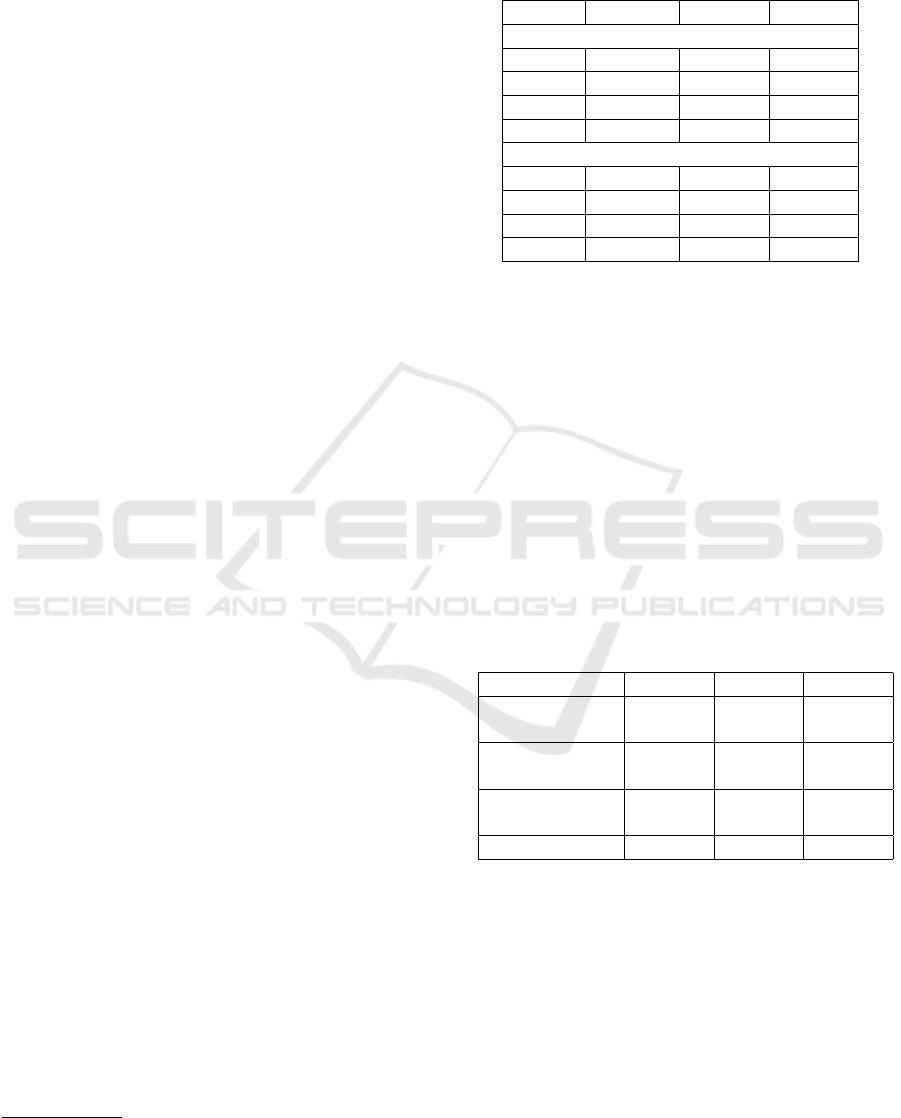
Table 1: The tyrant variant of the greedy algorithm on av-
erage performs best in terms of similarity of the integer as-
signments to the subsets compared to the BB approach and
heuristic deficiency.
Variant Captains Coach Tyrant
Hamming distance between p
H
and p
BB
µ 5.99023 5.57089 4.02619
σ 1.09324 1.66666 2.24574
min 1 0 0
max 7 7 7
Heuristic Deficiency
µ 1.23877 1.00390 1.00373
σ 0.14108 0.00649 0.00719
min 1.01593 1.0 1.0
max 1.93036 1.07699 1.18914
a corresponding number of possible d1-mutants, one
can use the obtained probabilities to estimate the aver-
age number of neighboring instances with a different
instance type. Given that the flip bit index was sam-
pled with uniform distribution, the almost symmetry
between instance changing from yes- to no-instance
under mutation and vice versa confirms the clustering
of instance types, considering that they were initially
somewhat unbalanced. Since the original instances
are slightly more likely to be yes-instances than no-
instances, the number of instances changing from no-
to yes-instances under mutation is just slightly higher
than the other way around.
Table 2: Analysis of the instance type of the originally gen-
erated instances and the corresponding instances derived us-
ing mutation over 10,000 pairs of instances per template.
Template T15
A
T15
B
T15
C
Initially
yes-instance
60.46 % 63.01 % 64.15 %
Yes-instance to
no-instance
6.64 % 6.38 % 6.81 %
No-instance to
yes-instace
7.43 % 7.47 % 7.95 %
Unchanged 85.93 % 86.15 % 85.24 %
3 VISUAL SEPARATION BY
INSTANCE TYPE
The results in Section 2.2.2 suggests that it might af-
ter all be possible to (somewhat) separate yes- and
no-instances, and we therefore investigate the prob-
ability of each variable bit of an instance to change
the instance type. A rudimentary visualization of the
influence of the bits on the instance type is given in
the bar plots in Figure 2 using the same dataset as be-
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
184
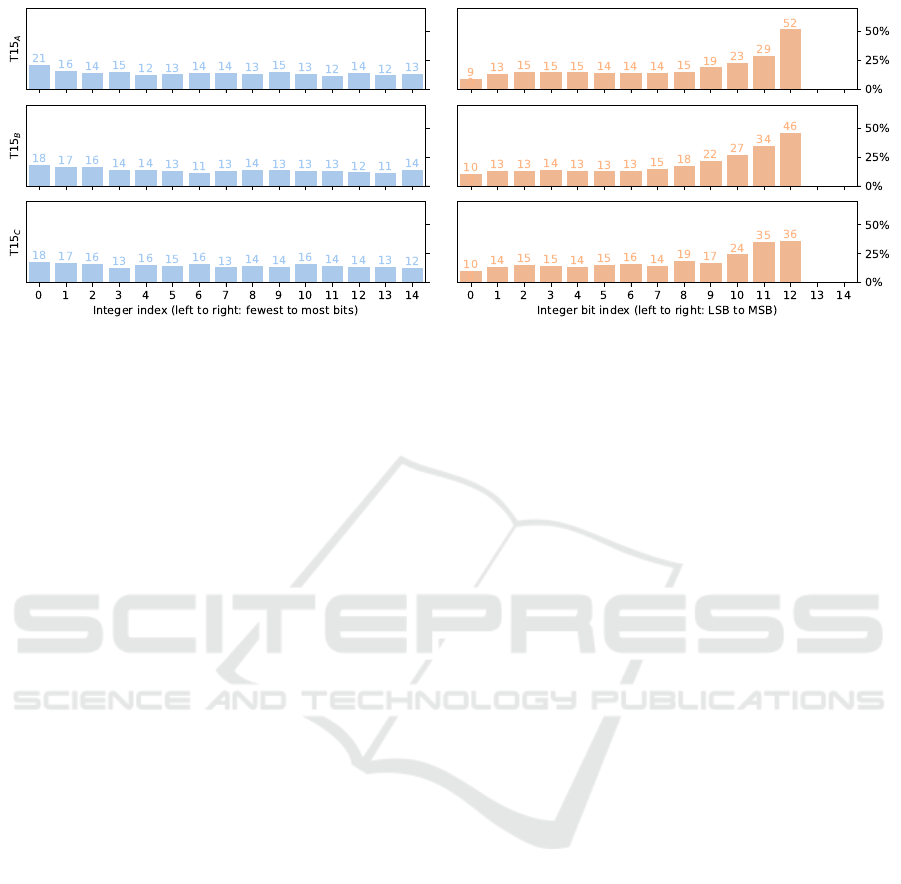
Figure 2: Probability of a one bit mutation to affect the instance type for all integer indices (left) and integer bit indices (right)
across the selected templates T15
A
, T15
B
, and T15
C
.
fore. The probability of a single bit mutation affect-
ing the instance type appears to be roughly the same
across all integers indices. Only for T15
A
does the in-
teger with the fewest bits have a considerably larger
influence, with 7.23 %pt. more compared to the av-
erage bit. On the level of integer bits, however, it ap-
pears that the influence of the mutation on the instance
type increases significantly with the bit index towards
the end. The bit just below the MSB of the integer
with the most bits thus appears to have the highest im-
pact on the instance type of between 36 % and 52 %,
depending on the template. Likewise, the least sig-
nificant bit (LSB) of any integer would be expected
to generally have a low effect on the instance type
because instances with an odd sum over all integers
are considered optimally partitioned with a difference
of 1 between both summed subsets (Schreiber et al.,
2018). However, it might also turn a yes-instance with
an odd sum into a no instance with a difference of 2
between the subset sums, therefore this bit can some-
times still influence the instance type.
Since the distribution of these bits over the inte-
gers (the template) is not captured by this represen-
tation, it is only valid for instances of the same tem-
plate. Therefore, our proposed method for embedding
instances into R
2
in such a way as to separate yes-
and no-instances, which we describe in the following
section, must be applied to instances of the same tem-
plate.
3.1 Proposed Embedding
There seems to be at least some hierarchical struc-
ture to the influence of the bit on the instance type of
the corresponding instance. We do not see the same
clear hirarchy for the integers, but also order them
from most to fewest bits to group integers with more
significant bits. Using this, it may be possible to vi-
sually separate yes- and no-instances to some extent.
Inspired by the quad tree data structure (Finkel and
Bentley, 1974), we apply binary space partitioning
going from MSB to LSB to embed all generated in-
stances belonging to the same template into R
2
. The
MSBs of all integers are skipped because they are not
variable. At every index the initial unit square is split
further, alternating between vertical and horizontal,
where the upper or right half is selected if the bit is
1 and the lower or left if it is 0. This yields a unique
point in linear time for the corresponding instance.
Note again that the distribution of the bits over the
integers is not captured by this embedding, so all em-
bedded instances must belong to the same template.
f
⃗
b,c
= 0.5 +
dim
⃗
b÷2
∑
i=0
2
−i
⃗
b
2i+c
− 0.5
x(S) = f
⃗
S
b
,0
y(S) = f
⃗
S
b
,1
(5)
Equation (5) describes the formula for the polyno-
mial for both Cartesian coordinates in the range of
[0;1] where
⃗
S
b
is the binary representation of the in-
stance S without MSBs from the integer with the
most bits to that with the fewest and from MSB
to LSB for each integer. For example, given S =
{4,6, 7} = {(100)
2
,(110)
2
,(111)
2
}, we obtain the
following representation:
⃗
S
b
= ( 11
|{z}
7
10
|{z}
6
00
|{z}
4
)
which is embedded at (0.8125,0.5625). Unlike
other dimensionality reduction approaches like t-SNE
(van der Maaten and Hinton, 2008), our approach is
Separating the Yes- from the No-Instances in the Number Partitioning Problem
185
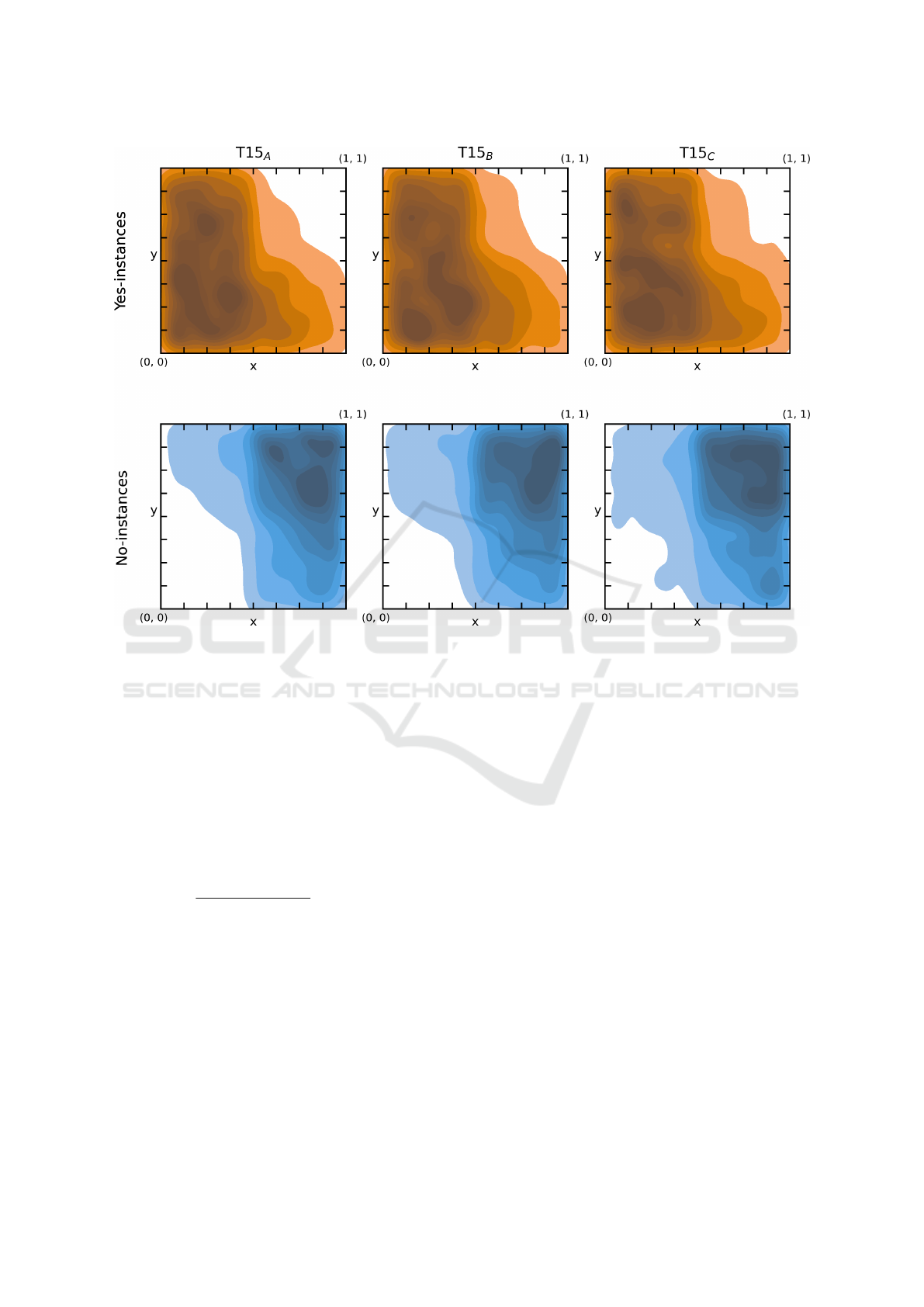
Figure 3: Density plot of the embeddings using Equation (5) of yes-instances (first row) and no-instances (second row)
generated from the templates T15
A-C
(columns). The distribution of yes- and no-instances seems to vary along somewhat of
a semi-diagonal for the R
2
-embedding.
linear, interpretable and a complete representation of
the underlying instance.
One may suspect a correlation between the in-
stance type and its hardness, the number of recursions
required to solve it. In order to see, whether this ex-
tends to the optimality of the optimal (imperfect) par-
tition, we additionally compute the relative discrep-
ancy given in Equation (6), which indicates the devi-
ation of the optimal from the perfect partition in per-
cent.
|⌈
1
/2
∑
S
⌉
−
∑
A
BB
|
⌈
1
/2
∑
S
⌉
× 100% (6)
3.2 Visualization of the Dataset
The density plot in Figure 3 of the previously
generated instances for T15
A-C
yields an imperfect
yet strong visual separation between yes- and no-
instances. Even though Figure 2 shows no apparent
influence of the integer index on the instance type, us-
ing the average bit values (R) over all integers as co-
efficients for f only yields a less clean separation of
yes- and no-instances. The hierarchical influence of
the integer bits means that the pattern emerging from
the embedding mostly persists even when only taking
a subset of less significant bits into account, discard-
ing up to two bits per integer. Thus, it appears that
instances are more likely to be a yes-instance if the
integers are similar to 2
i
and more likely to be a no-
instance if they are similar to 2
i
− 1.
Figure 4 shows the corresponding relative dis-
crepancy given by Equation (6) of the embedded in-
stances. Interestingly, the pattern is quite similar to
that of the distribution of instance types. Thus, it
seems that in regions where the probability of in-
stances being a yes-instance is lower, the optimality of
the optimal partition is probably also lower. The two
properties of the templates therefore appear somewhat
correlated in Figure 3 and 4.
4 DISCUSSION & CONCLUSION
Richard Korf (1998) and Brian Hayes (2002) showed
that the hardness of the NPP depends on the magni-
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
186
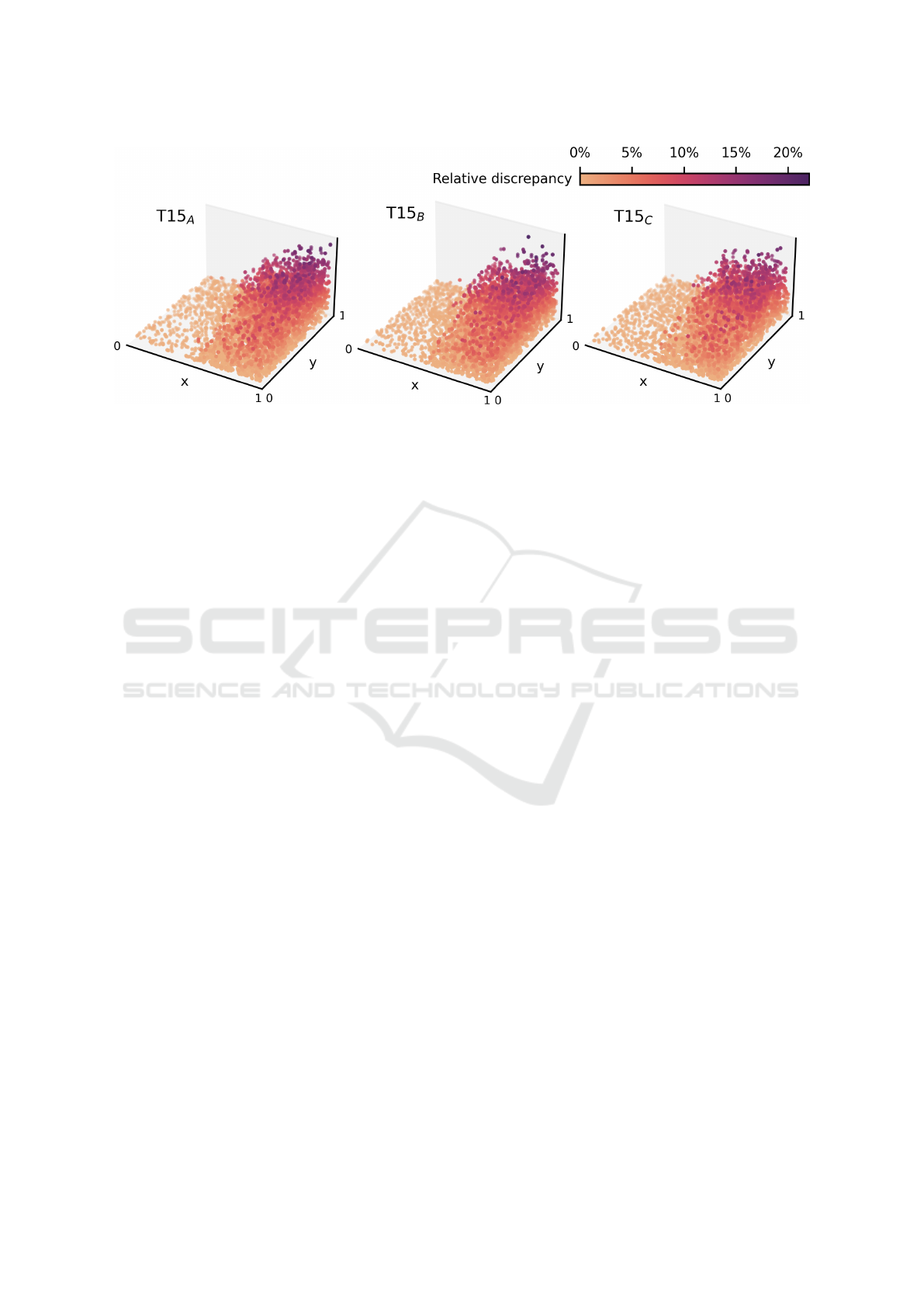
Figure 4: The relative discrepancy from Equation (6) of the optimal (imperfect) partitions for the corresponding instances
embedded into R
2
seems to also increase with the probability of being a no-instance from Figure 3.
tude of integers in the instances, as expressed by the
number of (informational) bits that represent them.
Van den Berg and Adriaans (2021) and Sazhinov et al.
(2023) recently extended this to also include the dis-
tribution of these bits over the instance for a fixed
number of bits and investigated the performance of
heuristic algorithms. We build on the work by Sazhi-
nov et al. (2023) and find that among three versions
of the greedy algorithm, the tyrant version, which is
equivalent to a backtracking free variant of the BB
algorithm by Van den Berg and Adriaans (2021), per-
forms best, but still deviates significantly from the op-
timal partition.
Regarding the hardness of the NPP, in this pa-
per we have looked at a different side of the same
coin: verification of the solution. We have investi-
gated the predictability of the instance type for three
selected templates. It is not the case that similar in-
stances are independent with respect to their instance
type, meaning that any yes-instance is more likely to
be surrounded by yes-instances in its 1-bit neighbor-
hood and a no-instance more likely to be surrounded
by no-instances.
Based on this insight, we propose a method which
provides a noticeable visual separation between yes-
and no-instances along the values of bits in order of
significance by embedding them into R
2
. However,
while the preliminary results presented in this study
suggest that the diagonal position of an instance in
R
2
may be an indicator for its probability of being
a yes-instance, the instance type density maps vary
between templates. This can even be seen between the
three templates with similar yes-instance probabilities
in Figure 3. In cases where the template produces
mostly either yes- or no-instances (e.g. T15
FLAT
or
T15
LINEAR
), such a separation is not possible.
Yes-instances are easy to verify, no-instances not.
One might argue that yes-instances, especially those
with many perfect partitions, are easier to solve as
well, since the algorithm can likely terminate after
fewer recursions upon finding any single one of them.
It thus seems that, to fully predict the hardness (ex-
pected number of recursions) of any given instance,
one must consider all three of the following features:
1. the amount of information it contains via the num-
ber of bits, 2. their distribution, and 3. the embedding
into R
2
as proposed in Section 3.1. Using these three
features, it may be possible to predict the hardness
of any given instance by creating a statistical model
to predict the number of recursions required to solve
it. Something similar has recently been done for in-
stances of the NPP with uniform bit distribution by
modeling the number of perfect partitions that exist
(Horn et al., 2024b). Perhaps it is time to revisit other
NP-complete problems and investigate them along the
dimension of yes-instance probability, since at least
for the asymmetric traveling salesperson problem its
hardness is known to be affected by the other two fea-
tures (Zhang and Korf, 1996) and also for the Hamil-
tonian cycle problem no-instances are harder than
yes-instances (Sleegers and Van den Berg, 2020).
As already mentioned by Van den Berg and Adri-
aans (2021), there appear to exist non-eccentric tem-
plates (having a binary derivative) which contain both
the easiest and hardest instances, probably both yes-
and no-instances respectively. This is similar to the
Hamiltonian cycle problem (Sleegers et al., 2022;
Sleegers and Van den Berg, 2022). One might as-
sume that easy and hard instances correspond to yes-
and no-instances, but it is not yet clear to us, whether
yes-instances are never harder than no-instances. Like
Sleegers and Van den Berg (2020, 2022) we might in-
Separating the Yes- from the No-Instances in the Number Partitioning Problem
187

vestigate this by evolving ever harder (yes-)instances
of the NPP using evolutionary algorithms (EAs). The
success of an EA approach to finding such instances,
however, hinges on the fabric of the search space. If
the relative discrepancy of the no-instances in Fig-
ure 4 is also an indicator for the hardness function
of the yes-instances, the latter might have a very high
frequency randomness and thus be particularly chal-
lenging for an EA.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Computational resources (HPC-cluster HSUper) have
been provided by the project hpc.bw. hpc.bw is
funded by dtec.bw – Digitalization and Technology
Research Center of the Bundeswehr. dtec.bw is
funded by the European Union – NextGenerationEU.
REFERENCES
Brian Hayes (2002). Computing Science: The Easiest Hard
Problem. American Scientist, 90(2):113–117.
Coslovich, L., Pesenti, R., and Ukovich, W. (2006). Large-
scale set partitioning problems: Some real-world in-
stances hide a beneficial structure. Ukio Technologinis
ir Ekonominis Vystymas, 12(1):18–22.
van den Berg, D. and Adriaans, P. (2021). Subset Sum
and the Distribution of Information. In Proceedings
of the 13th International Joint Conference on Compu-
tational Intelligence, pages 134–140.
Finkel, R. and Bentley, J. (1974). Quad trees: A data struc-
ture for retrieval on composite keys. Acta Inf., 4:1–9.
Harris, C. R., Millman, K. J., van der Walt, S. J., Gommers,
R., Virtanen, P., Cournapeau, D., Wieser, E., Taylor,
J., Berg, S., Smith, N. J., Kern, R., Picus, M., Hoyer,
S., van Kerkwijk, M. H., Brett, M., Haldane, A., del
R
´
ıo, J. F., Wiebe, M., Peterson, P., G
´
erard-Marchant,
P., Sheppard, K., Reddy, T., Weckesser, W., Abbasi,
H., Gohlke, C., and Oliphant, T. E. (2020). Array pro-
gramming with NumPy. Nature, 585(7825):357–362.
Horn, R., Jansen, R., van Eck, O., and van den Berg, D.
(2024a). Separating the Yes- from the No-Instances in
the Number Partitioning Problem. https://anonymous.
4open.science/r/NPP-24/. (Replication package).
Horn, R., Thomson, S. L., van den Berg, D., and Adriaans,
P. (2024b). The easiest hard problem: Now even eas-
ier. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary
Computation Conference Companion, GECCO ’24
Companion, page 97–98, New York, NY, USA. As-
sociation for Computing Machinery.
Jason Carpenter (2023). swifter. https://github.com/
jmcarpenter2/swifter/tree/1.4.0.
John D. Hunter (2007). Matplotlib: A 2d graphics environ-
ment. Computing in Science & Engineering, 9(3):90–
95.
Karp, R. M. (1972). Reducibility among Combinatorial
Problems, pages 85–103. Springer US, Boston, MA.
Matthew Rocklin (2015). Dask: Parallel computation with
blocked algorithms and task scheduling. In Huff,
K. and Bergstra, J., editors, Proceedings of the 14th
Python in Science Conference, pages 130–136.
Michael L. Waskom (2021). seaborn: statistical data visual-
ization. Journal of Open Source Software, 6(60):3021.
Richard Korf (1998). A complete anytime algorithm
for number partitioning. Artificial Intelligence,
106(2):181–203.
Sazhinov, N., Horn, R., Adriaans, P., and van den Berg,
D. (2023). The partition problem, and how the dis-
tribution of input bits affects the solving process. In
Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on
Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications.
Schreiber, E. L., Korf, R. E., and Moffitt, M. D. (2018). Op-
timal Multi-Way Number Partitioning. J. ACM, 65(4).
Seenu S. Reddi (2008). Graham’s schedules and the number
partition problem.
Sleegers, J., Thomson, S., and van Den Berg, D. (2022).
Universally hard hamiltonian cycle problem instances.
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Confer-
ence on Computational Intelligence. SCITEPRESS -
Science and Technology Publications.
Sleegers, J. and Van den Berg, D. (2020). Looking for the
hardest hamiltonian cycle problem instances. In Pro-
ceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference
on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2020) - ECTA,
pages 40–48. INSTICC, SciTePress.
Sleegers, J. and Van den Berg, D. (2022). The hardest
hamiltonian cycle problem instances: The plateau of
yes and the cliff of no. SN Comput. Sci., 3(5).
Stephan Mertens (2003). The easiest hard problem: Num-
ber partitioning.
The Pandas development team (2020). pandas-dev/pandas:
Pandas.
van der Maaten, L. and Hinton, G. (2008). Visualizing data
using t-SNE. Journal of Machine Learning Research,
9:2579–2605.
Zhang, W. and Korf, R. E. (1996). A study of complex-
ity transitions on the asymmetric traveling salesman
problem. Artificial Intelligence, 81(1):223–239. Fron-
tiers in Problem Solving: Phase Transitions and Com-
plexity.
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
188
