
Sustainability Meets Efficiency: Unveiling the Dual Impact on Supply
Chain Performance in the Retail Sector. A Case Study of JB Hi-Fi
Mu Li
Melbourne Business School, University of Melbourne, 200 Leicester St, Carlton, VIC 3053, Australia
Keywords: Corporate Sustainability, Supply Chain Management, Strategic Management, JB Hifi.
Abstract: In recent years, the interplay between environmental sustainability and commercial expansion has emerged
as a critical area of study. This investigation focuses on JB Hi-Fi, a key player in the Australian retail market,
to dissect how sustainable practices influence fundamental supply chain performance indicators, including
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), inventory turnover, and the operating cycle. By leveraging advanced Lasso
regression techniques to navigate the limitations of sparse data, this analysis uncovers nuanced effects: while
employee engagement significantly elevates supply chain efficiency, initiatives aimed at environmental
conservation, such as the recycling of soft plastics, introduce cost-related and operational complexities. This
study not only deepens the current discourse on balancing sustainability with supply chain optimization but
also offers unique perspectives for retailers striving to merge long-term environmental goals with business
efficiency. Furthermore, it lays a robust foundation for future research to further explore the dynamic
interconnections between sustainability measures and supply chain metrics, advocating for the integration of
broader datasets and a more diverse array of sustainability indicators to enrich the comprehension of these
critical relationships.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the contemporary business environment,
established firms have increasingly integrated
sustainability concepts into their supply chain
management strategies, driven by a dual imperative:
to mitigate risks and to forge a strategic pathway
towards long-term value creation. An illustrative
investigation by Ruiz-Real et al. delineates the
widespread adoption of sustainable supply chain
management (SSCM) policies across a diverse array
of over 30 nations and regions, encompassing a wide
spectrum of criteria such as supply chain ratings,
operating cycles, and environmental ratings, among
others (Ruiz-Real et al., 2018). Similarly, the scrutiny
of Walmart's sustainability report by Jones and
Comfort reveals a significant milestone wherein up to
20 essential goods were procured in compliance with
distinct sustainability standards, with the retail
behemoth achieving an 80% sustainability
compliance rate across its supply chain by 2018
(Jones & Comfort, 2020). This empirical evidence
underscores the profound influence of sustainability
on retail supply chain dynamics, precipitating a
recalibration of company strategies to accommodate
this new paradigm.
Moreover, the comparative analysis of CSR
reports from publicly traded retailers conducted by
Chkanikova and Mont, which focuses on strategic
adjustments in supply chain management, supplier
selection, and inventory lifecycle to enhance the PMI
index(Chkanikova & Mont, 2012), complements
Longo's examination of strategic modifications
within the environmental domain of retailers' supply
chains(Longo, 2012). These analyses collectively
highlight efforts to optimize logistics to curtail carbon
emissions, attain sustainability goals, and reduce
transportation costs by 15%. Despite these significant
insights, a lacuna persists in the literature, with these
studies failing to establish a direct correlation
between supply chain metrics and sustainability
goals, delineate specific sustainability goals
impacting different supply chain facets, or engage in
direct quantitative analysis of these dynamics.
Therefore, this article explores the relationship
between supply chain metrics and sustainability
goals, focusing on quantifying sustainability's impact
on supply networks. It is divided into methodology,
results, and discussion sections. The methodology
72
Li, M.
Sustainability Meets Efficiency: Unveiling the Dual Impact on Supply Chain Performance in the Retail Sector. A Case Study of JB Hi-Fi.
DOI: 10.5220/0012909000004508
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2024), pages 72-79
ISBN: 978-989-758-713-9
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

outlines selecting key performance indicators (KPIs)
for both supply chain and sustainability, data
gathering, and regression analysis to examine metric
relationships. Results detail this analysis, using
visuals for clarity. The discussion offers solutions and
insights for incorporating sustainability into supply
chains, aiming to aid retail managers in making
strategic decisions aligned with sustainability. This
analysis seeks to fill literature gaps, providing a
framework to understand sustainability's role in
enhancing supply chain resilience and sustainability.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Supply Chain Management,
Sustainability and Retail Business
Cycles Research
Berning and Venter provide additional insights into
retail supply chain management in the review
literature (Berning & Venter, 2015). They describe it
as a continuous process that influences the
sustainability expectations of suppliers. The authors
conducted semi-structured interviews with a major
retailer in South Africa to gather information on
suppliers' sustainability. An in-depth interview with a
major retailer in South Africa uncovered the
suppliers' eagerness to enhance their supply chain
hierarchy, emphasizing the significance of
sustainability. In their comprehensive study of the
retail market in China, Han and Guo found that
sustainable supply chain management necessitates a
holistic approach to achieve the integration of
economic, social, and environmental advantages
(Han & Guo, 2014). By examining the current state
of the retail industry and discussing sustainable
supply chain management, the researchers concluded
that companies must consider the entire supply chain
to attain long-term economic benefits and gain a
competitive edge. Sustained economic benefits and
advantages in competition over a lengthy period. The
literature emphasizes the significance of enhancing
collaboration to achieve supply chain sustainability,
underscores the crucial role of individuals and
communities in supply chain management, and offers
valuable recommendations for the report to choose
suitable sustainability indicators. Furthermore,
Negrutiu et al. employ a white paper from Roland
Berger, a well-known management consulting firm,
to offer an external viewpoint on the connection
between suppliers, logistics, and transportation
providers (Negrutiu et al., 2020). This perspective
highlights the trend towards reduced consumption
and increased efficiency in logistics and
transportation. It demonstrates the significant
enthusiasm of organizations and transporters to
minimize logistics and transportation expenses and
align them with sustainability objectives.
In the research-based literature, Rao et al.
conducted a mathematical modeling study on green e-
commerce. By establishing the relationship between
perceived ease of use (PEOU) and green consumption
(GC), the regression results in a correlation
coefficient of 0.12 and a strong correlation between
them, confirming the importance of a green supply
chain for the development of the retail industry (Rao
et al., 2021), while the study by Chauhan et al. also
utilizes data modeling. It measures the impact of
sustainable supply chain changes on a company's
product sales by dividing them into single and dual-
channel sales. In this study, the total cost of dual-
channel retailing was reduced by about 14.0625%,
product quality was improved by 80%, and consumer
satisfaction was improved (Chauhan et al., 2023). It
confirms the importance of optimizing the
operational cycle. In addition, de Vass et al.
emphasized the importance of IoT for sustainable
supply chain management at the big data level. They
conducted a large number of questionnaires
collection and collation in the data collection section
and analyzed the employee engagement by VIF as
3.3, i.e., it confirms the importance of the employees
for the supply chain management, which further helps
the report for the confirmation of the sustainable
variables (Vass et al., 2020).
2.2 Enterprise Sustainable Strategy
Adjustment
Ekinci et al. suggest that the study used a mixed
decision-making approach to assess the resilience and
overall score of the retail sector (Ekinci et al., 2024).
It enables resilience to be adjusted to the supply
chain's condition in different environments to meet
managerial needs. Vadakkepatt et al., on the other
hand, are keen on the dynamic assessment of social
dimensions involving the entire business process,
from raw material sourcing to product disposal, reuse,
or recycling, as well as the safety and well-being of
the employees to reflect the need for sustainable
development of the company.
(Vadakkepatt et al.,
2020) Besides, Carter and Rogers see SCM as a
holistic process that requires the development of
standards-compliant sustainable optimization for
each level of the supply chain.
(Carter & Rogers,
2008)
Sustainability Meets Efficiency: Unveiling the Dual Impact on Supply Chain Performance in the Retail Sector. A Case Study of JB Hi-Fi
73

In summary, the report gives a clear idea about
supply chain management and the choice of
sustainable variables by referring to different kinds of
literature. Based on a full understanding of supply
chain sustainability, the design of data modeling in
the literature is referenced for the construction of the
methodology. At the same time, the strategic
alignment of the firms covered in the literature will
provide more insights for the discussion part of the
report.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 The Introduction of JB HiFi
This paper investigates the correlation between
supply chain metrics and sustainability in retail,
focusing on JB Hi-Fi, an Australian consumer
electronics retailer. JB Hi-Fi emphasizes effective
inventory management and strategic partnerships to
streamline goods movement from production to
consumer. Its supply chain strategy incorporates
technological advancements to improve partner
coordination and adaptability. Key to its operations is
a commitment to sustainability, targeting packaging
waste reduction and logistic optimization to lower
carbon emissions. The company's 2023 Sustainability
Report highlights its digital transformation goals,
exploring blockchain for transparency and AI
analytics for demand forecasting, to enhance supply
chain efficiency and sustainability.
3.2 Data Selection and Source
In selecting the data, the report fully integrates the
important components of supply chain management
and corporate sustainability mentioned in the
previous literature. It incorporates the JB HiFi 2020-
2023 Sustainability Report. It aims to continuously
narrow down the number of variables selected, reduce
the data sample's instability and ensure the data's
accuracy.
3.2.1 Quantitative Data on Supply Chain
Management
This report will explore three of the supply chain's
most highly visible and relevant data to a company's
bottom line as the dependent variables to be analyzed.
First, supply chain cost signifies the value invested in
the supply chain, influencing how much value a
company expects to place on building a sustainable
supply chain. The variable chosen for the report is the
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), which includes the
direct costs of making a product, such as raw
materials, direct labor, and other direct costs of the
production process. It visualizes the initial cost at the
top of the supply chain and is easily obtained from
annual reports. Second, inventory turnover is the
variable of choice in defense of supply chain
efficiency. It reflects how often a company sells and
replaces inventory over a given period. It can be used
to assess a company's ability to manage its inventory
efficiently, and a high inventory turnover ratio may
indicate that a company can manage its inventory
efficiently and quickly convert it into sales. It is also
one of the key indicators that reflect supply chain
management. In addition to the above two metrics,
the operating cycle is also one of the chosen metrics,
which signifies the average number of days the
complete supply chain is in operation and the number
of days within which the company can make dynamic
adjustments to its supply chain. These three variables
interpret the study of supply chain management from
a three-dimensional perspective and are considered
Supply Chain Performance Indicators for data
modeling.
3.2.2 Quantitative Data on Supply Chain
Sustainability
This study will gather three quantitative metrics about
the JB HiFi Sustainability study's "most aligned with
the sustainability." The Sustainability Report includes
the number of individuals chosen by JB HiFi in
partnership with TGG who have an employee
engagement rating of over 70% and have been in the
job market for at least 5 years in the "People" section.
These diligent employees are involved in several
aspects of the supply chain, such as transportation,
loading, translating, inventory counting, and order
administration. Their inclusion is vital to the
company's sustainability and was selected as a
quantitative sustainability metric. Furthermore,
regarding the "Community" aspect discussed in the
Sustainability Report, it has selected the aggregate
sum of funds that JB HiFi AU contributes to the
community annually. This financial contribution is
deemed a "sustainable investment" by the company
and is utilized to enhance and streamline various
operations throughout the supply chain. Operations.
The Sustainability Report states that significant
financial backing for carbon optimization, employee
welfare, and community delivery services makes it a
key quantitative measure of sustainability.
Additionally, the Sustainability Report places
significant importance on the "Environment." JB
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
74

HiFi, the top electronics retailer in Australia,
produces a significant quantity of soft plastic garbage
annually. To assess the company's overall
environmental impact, recycling this waste was
selected as the third sustainability indicator.
In summary, the report selects COGS, Inventory
Turnover, and Operating Cycle as the dependent
factors, while "People," "Community," and
"Environment" are picked as the independent
variables. The objective is to optimize the alignment
between the company's supply chain management
and sustainability requirements and ensure that the
final model is standardized and precise.
3.3 Establishment of Data Model and
Selection of Regression Tools
3.3.1 Establishment of Data Model
As this report focuses on exploring the quantitative
relationship between supply chain management and
sustainability indicators, the report mainly used to
conduct multiple linear regressions. The benefit of
multiple linear regressions is that they are able to be
illustrated by multiple models of the same level, for
COGS, inventory turnover, and whether or not the
operating cycle is affected by the sustainability
variables can be presented specifically and illustrated
by regression tests. At the same time, this also greatly
preserves the direct influence between the dependent
and independent variables, reducing omitted
variables and measurement error.
Supply Chain Performance Indicator
= 𝛽0+𝛽1×People
+ 𝛽2
× Community + 𝛽3
×Environmen
t
+ 𝜀
(1)
In the model developed, 𝛽0 is the intercept term,
𝛽1, 𝛽2, 𝛽3 correspond to employee engagement,
community donations, and soft plastic recycling
respectively, and 𝜀 is the error term. This is the initial
mathematical regression model that have constructed
and will be brought in for regression analysis after
proper instrument selection.
3.3.2 Lasso Regressions
This study on JB Hi-Fi's sustainability efforts faced
challenges due to a small dataset with only four data
points. To overcome the limitations of Ordinary Least
Squares (OLS) regression, which is prone to
overfitting with such datasets, it employed Lasso
regression. Lasso, or the Least Absolute Shrinkage
and Selection Operator, incorporates a regularization
parameter to mitigate overfitting and selectively
identify the most significant predictors by penalizing
the absolute size of the regression coefficients. This
approach is effective in datasets with predictors
nearly equal to the number of observations, as it
simplifies the model, enhances prediction accuracy,
and improves interpretability.
By applying Lasso regression, it focused on
identifying the critical factors influencing JB Hi-Fi's
sustainability key performance indicators (KPIs),
including Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), Inventory
Turnover, and Operating Cycle. Despite Lasso
regression introducing some bias, it compensates by
lowering variance and improving the model's
predictive reliability, which is crucial for drawing
dependable conclusions from limited data. This
methodology allowed us to derive more accurate
insights into how JB Hi-Fi's sustainability initiatives
impact its operational metrics, providing valuable
guidance for strategic decision-making. The
effectiveness of Lasso regression in this context
underscores its utility in extracting meaningful
insights from constrained datasets.
3.3.3 Python Analysis Tool
Python serves as the primary tool for analyzing JB Hi-
Fi's sustainability data due to its powerful ecosystem
and ease of use. Its libraries, including pandas,
NumPy, and sci-kit-learn, facilitate complex data
analyses like Lasso regression, streamlining data
handling, and statistical modeling. Python's
supportive community fosters innovation, making it
ideal for sustainability studies. Moreover, its
scalability and automation enhance the accuracy and
applicability of analytical insights, supporting JB Hi-
Fi's data-driven decision-making.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Data Summary
The report imports the organized and summarized
data into Python and describes the data to get the
organized summary tables. The table presents the
three variables involved in supply chain management.
The mean value of COGS is AUD 3936.75 million,
and the data ranges from AUD 3797.4 to AUD 4076.7
million. Inventory turnover has a mean value of 7.41
times, a minimum value of 6.84 times, and a
maximum value of 8.27 times. The mean value of the
Sustainability Meets Efficiency: Unveiling the Dual Impact on Supply Chain Performance in the Retail Sector. A Case Study of JB Hi-Fi
75
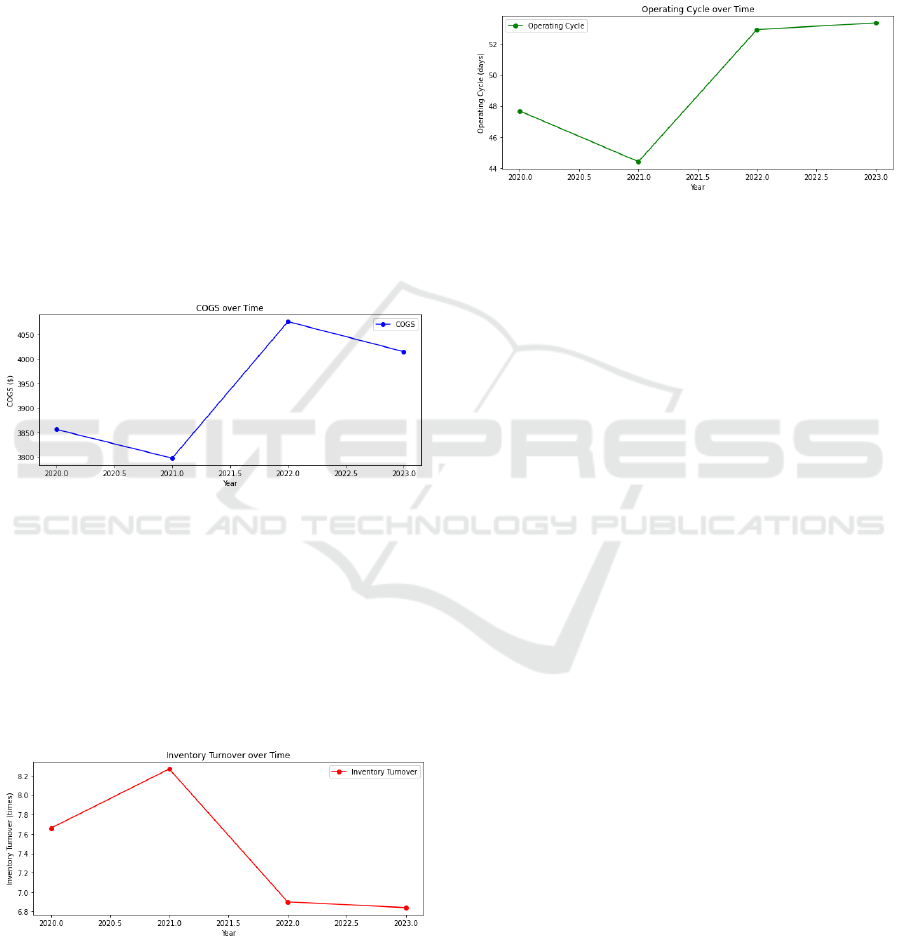
operating cycle is 49.59 days, ranging from 44.41
days to 53.35 days. In addition, regarding
sustainability quantification, the mean value of the
number of loyal employees is 1034 (rounded) with a
standard deviation of 155. with a minimum value of
904 and a maximum value of 1233. at the same time,
the mean value of the community investment is about
AUD 316 million, with a range of data from about
296 million to about 332 million. As for recycled soft
plastics, the mean value is 57,166kg, and the data
ranges from 49,580kg to 65,934kg. It shows that JB
HiFi has good supply chain management, and all the
supply chain and sustainability metrics are in the
middle of the road.
4.2 Time Series Plots of SCM Variables
After completing the overview of the report's data, the
report produces time-series images of the temporal
changes in the three variables of the SCM.
Figure 1: COGs time series plot.
Figure 1 shows the cost of goods sold (COGS)
from 2020 to 2023. COGS increases significantly
from 2020 to 2021, thanks to the spike in online sales
volume brought about by Covid-19, then rises sharply
in 2022 before flattening slightly in 2023. The general
trend shows an overall increase in the cost of goods
sold during this period. However, the overall situation
is under SCM control.
Figure 2: Inventory turnover time series plot.
As shown in Figure 2, inventory turnover
measures how often inventory is sold and replaced
over time. From 2020 to 2021, the inventory turnover
ratio increased, indicating that inventory is being
turned over at a faster rate. However, from 2021 to
2022, a spike in online purchases led to a sharp drop
in inventory, and JB HiFi stocks up on merchandise
in large quantities. By 2023, inventory turns will
remain low, which could indicate excess inventory or
slowing sales.
Figure 3: Operating cycle time series plot.
Figure 3 displays the duration, in days, that a
company requires to convert its purchases into cash
inflows from sales. The data suggests a rising trend
from 2020 to 2023. It indicates that the duration for
the company to sell its product and get payments is
growing, which may indicate possible inefficiencies
in the sales and collections procedures.
4.3 The Lasso Regressions
Since the report only uses data within the period of
the sustainability report (i.e., only four years of data),
the amount of data is too small for stable OLS
regression and is prone to multicollinearity. Lasso
regression allows for a more refined analysis without
adding more variables, reducing the model's
instability. It will complete the regularization analysis
by adding penalty terms. In the model, it starts with
data clarity and use the python runtime environment
to create the relevant 𝛼 variables suitable for lasso
regression.
The report got the best 𝛼-variable of 39.4421 for
COGs, 0.1485 for Inventory turnover, and 0.9545 for
the operating cycle through the data. After that, it
needs to perform Lasso regression for each of the
three variables according to the mathematical model
that have established to get three different sets of data:
Firstly, for COGs. With the optimal 𝛼 variable,
the intercept term is 3936.3499 million AUD.
However, the people and community part of it is
almost all zero, i.e., the effect of these two sustainable
quantitative variables on COGs is insignificant.
Meanwhile, the environment component is shown as
58.5465, which means that when the plastic collection
is increased, the supply chain cost also increases.
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
76

There is a conflict between the company's efforts to
reduce supply chain costs and maintain sustainability
and the measures to protect the environment, which
have increased supply chain costs.
Secondly, the intercept term for the inventory
turnover ratio is 7.4175, which means that the
community does not affect the inventory turnover
ratio. Among the other two sustainability variables,
the growth of people increases the inventory turnover
rate, which shows the positive effect of having
enough dedicated employees on the sustainability of
supply management. On the contrary, the
environment decreases the inventory turnover, i.e., -
0.3322, which indicates a negative correlation
between the two. The initiative to recycle soft plastics
has caused inventory turnover to become more
difficult.
Finally, in the direction of the operating cycle, the
intercept term is 49.5899 (approximately equal to 50
days). In this case, the Community still does not play
any role, and the People component is negative with
an impact value of -0.4608, which again implies that
a sufficient number of dedicated employees can help
reduce the operating cycle, thus facilitating the SCM
to change strategy. On the other hand, the
environment had a positive impact with a value of
2.2503, which means that the increased task of
collecting soft plastics made the reform of the supply
chain, which was already poorly turned around,
difficult.
To summarize, after identifying the optimal 𝛼
variable through Lasso analysis, it can get the
following conclusions: the People variable has a good
impact on all SCM variables (except COGs), the
Community has no impact, and the environment (the
initiative to recycle soft plastics) may have increased
the burden on SCM. Specific reasons for this, as well
as measures for improvement, will be explored
below.
4.4 Bootstrap Stability Analysis and
Risk Management
To assess the risk associated with the three
sustainability variables (people, community, and
environment), the report performs a risk analysis by
looking at the variability of the predictions made by
the model. A bootstrap approach was used to generate
predictive distributions for each variable, and metrics
such as variance or confidence intervals were then
looked at for those predictions. It will provide an
estimate of risk based on the variability of the model's
predictions. A high standard deviation of the
bootstrap predictions indicates a high risk or
uncertainty in the model predictions.
By comparing the mean and standard deviation of
the predictions, this model remains essentially stable
after doing the Lasso regression. Taking COGs as an
example, the predicted mean of COGs is 3893.0600,
which is the same as the predicted means of the other
sustainability variables (3902.1845, 3968.0725, and
4005.6815), which means that the model tends to
fundamentally remain linear into the future (i.e.,
future studies can utilize linear regression as well).
Similarly, in the standard deviation, the variance of
COGs is 57.6611, which is the same as the standard
deviation of the other sustainable variables, again
indicating the stability of the model. After utilizing
Bootstrap for prediction, the stability of the model
was ensured, avoiding widespread measurement error
and multicollinearity.
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Result Analysis and Reason
Explanation
By combining the regression results, the modeling
study shows a significant association between JB Hi-
Fi's sustainability indicators and supply chain
management indicators. In particular, employee
engagement (the "People" variable) positively affects
the supply chain management variables (except the
cost of goods), indicating that active employee
participation is essential for improving supply chain
efficiency and reducing operational cycle time.
Employees with good engagement can speed up the
supply chain process to a certain extent, improve
supply chain management efficiency, and avoid delay
problems. Meanwhile, the Community component
does not significantly impair, confirming that
community investment does not create any enablers
or impediments to the supply chain. However,
environmental protection measures (especially the
soft plastic recycling program) seem to hurt supply
chain costs and inventory turnover, suggesting that
promoting sustainable practices may have a negative
impact on supply chain efficiency and cost-
effectiveness.
There are multiple reasons for this phenomenon.
First, environmental protection measures usually
require initial capital investment and operating costs,
which may temporarily increase the overall cost of
the supply chain; as mentioned by Morcillo-Bellido
and Duran-Heras in their study, environmental
protection is a "difficult and complex" process
Sustainability Meets Efficiency: Unveiling the Dual Impact on Supply Chain Performance in the Retail Sector. A Case Study of JB Hi-Fi
77

(Morcillo-Bellido & Duran-Heras, 2020). It is a
"difficult and complex" process that requires
significant upfront investment. It shows that too much
investment in the supply chain can lead to rigidity in
supply chain management. Secondly, implementing
new sustainable practices may take time to adjust and
optimize, which may initially hinder the fluidity and
efficiency of the supply chain. Finally, the positive
impact of employee engagement emphasizes the
importance of human resources in supply chain
management, and a report by Gencer suggests that
supply chain performance can be effectively
enhanced by increasing employee responsibility and
engagement. It also coincides with the findings of the
report (Gencer, 2017).
5.2 Suggestions on Future
Sustainability of Supply Chain
In response to this analysis, the report provides some
recommendations for the future sustainability of JB
HiFi's supply chain. Firstly, it is essential to continue
to enhance employee training. In particular, enhance
employee training in sustainable supply chain
management, such as low-carbon transportation,
smart warehousing, and AI supply order review. It
will increase employee engagement and efficiency
while accomplishing the company's sustainability
goals. Secondly, it is important to make the right
sustainable investments for community investment.
JB HiFi mentioned refining the sustainable
investment program in its 2023 sustainability report.
Therefore, the company can invest in more
sustainable projects to meet the development needs in
the future, such as packaging recycling, delivery
protection for senior citizens, and pickup accessibility
service stations., which will contribute to supply
chain efficiency to a certain extent. Finally, in terms
of the environment, it is important to balance
environmental protection with cost-effectiveness.
Companies should look for ways to reduce the cost of
environmental measures, such as investing in more
efficient recycling technologies or exploring the
possibility of partnering with other businesses to
share resources. It can avoid negative impacts on the
cost and flexibility of the supply chain itself.
5.3 Study Design Limitations and
Model Defects
Although this study provides valuable insights into JB
Hi-Fi, there are still some issues with model design
and reporting. First, reporting is limited by the
amount of data. As the report only uses sustainability
indicators from the time period of the JB Hi-Fi
Sustainability Report's release, which is only four
years, the dataset used is relatively small. This may
limit the ability to generalize the model and the
robustness of the conclusions. Second, for the
selection of variables, the report selected only three
representative quantitative sustainability variables,
but there may be other important factors that were not
taken into account. The omitted variables may also
have implications for certain aspects of supply chain
management. Finally, for model construction,
although Lasso regression was used to minimize the
risk of overfitting, the small sample data may still
lead to an overly complex model, affecting its
predictive ability. Moreover, the Lasso model cannot
completely solve the problem of model instability,
and the discussion of supply chain management and
sustainability should be more in-depth and use a more
stable and logical research-oriented model.
6 CONCLUSION
This research delves into the complex interplay
between sustainability initiatives and their impact on
supply chain metrics within JB Hi-Fi, a leading
Australian retail company. It critically examines the
sustainability practices in supply chain management,
uncovering both benefits and challenges. The study
finds that employee engagement is key to enhancing
supply chain performance, highlighting the critical
role of human elements in achieving sustainability.
Conversely, environmental strategies, particularly
soft plastic recycling efforts, present a dilemma by
increasing operational costs and potentially slowing
inventory turnover. This dichotomy underscores the
intricate challenges retailers face in aligning
sustainability goals with operational efficiency. The
study calls for a nuanced approach to sustainable
supply chain management and advocates for more
comprehensive sustainability metrics and extended
research to understand the long-term effects. It
emphasizes the strategic importance of integrating
sustainability into supply chain management beyond
compliance, essential for maintaining
competitiveness in the retail industry. This
investigation opens new avenues for academic and
practical advancements in the nexus of sustainability
and supply chain management, offering significant
implications for both scholars and practitioners.
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
78

REFERENCES
Berning, A., & Venter, C, 2015. Sustainable Supply Chain
Engagement in a Retail. Environment. Sustainability,
7(5), 6246–6263.
Carter, C.R., & Rogers, D. S, 2008. Aspects of sustainable
supply chain management(SSCM): conceptual
framework and empirical example. Supply Chain
Management: An International Journal, 13(5), 362-
371.
Chauhan, R., Majumder, A., & Kumar, V, 2023. The impact
of adopting customization policy and sustainability for
improving consumer service in a dual-channel retailing.
Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 75(12),
103504.
Chkanikova, O., & Mont, O. ,2012. Corporate Supply
Chain Responsibility: Drivers and Barriers for
Sustainable Food Retailing. Corporate Social
Responsibility and Environmental Management, 22(2),
65–82.
Ekinci, E., Sezer, M. D., Mangla, S. K., & Kazancoglu, Y.
2024. Building sustainable resilient supply chain in
retail sector under disruption. Journal of Cleaner
Production, 434(5), 139980.
Gencer, Y. G., 2017. Supply Chain Management in
Retailing Business, IGI Global.
Han, J., & Guo, Y., 2014. Sustainable Supply Chain
Management in Retail Industry. Proceedings of the
2014 International Conference on Information,
Business and Education Technology, 3(2).
Jones, P., & Comfort, D., 2020. Sustainability in Retail
Supply Chains. International Journal of Sales, Retailing
and Marketing, 9(2), 51–60.
Longo, F., 2012. Sustainable supply chain design: an
application example in local business retail. Simulation,
88(12), 1484–1498.
Morcillo-Bellido, J., & Duran-Heras, A., 2020.
Sustainability Governance Mechanisms in Supply
Chains. An Application in the Retail Sector.
Sustainability, 12(17), 6911.
Negrutiu, C., Vasiliu, C., & Enache, C., 2020. Sustainable
Entrepreneurship in the Transport and Retail Supply
Chain Sector. Journal of Risk and Financial
Management, 13(11), 267.
Rao, P., Balasubramanian, S., Vihari, N., Jabeen, S.,
Shukla, V., & Chanchaichujit, J., 2021. The e-
commerce supply chain and environmental
sustainability: An empirical investigation on the online
retail sector. Cogent Business & Management, 8(1).
Ruiz-Real, J., Uribe-Toril, J., Gázquez-Abad, J., & de Pablo
Valenciano, J., 2018. Sustainability and Retail:
Analysis of Global Research. Sustainability, 11(1), 14.
Vadakkepatt, G. G., Winterich, K. P., Mittal, V., Zinn, W.,
Beitelspacher, L., Aloysius, J., Ginger, J., & Reilman,
J., 2020. Sustainable Retailing. Journal of Retailing,
97(1).
Vass, T., Shee, H., & Miah, S. J., 2020. Iot in supply chain
management: a narrative on retail sector sustainability.
International Journal of Logistics Research and
Applications, 24(6), 1–20.
Sustainability Meets Efficiency: Unveiling the Dual Impact on Supply Chain Performance in the Retail Sector. A Case Study of JB Hi-Fi
79
