
Value Co-Creation in the Era of Social Networking: Exploring the
Social Commerce Value Creation Model Based on Xiaohongshu
Limu Liu
a
The University of Sydney, Business School, Australia
Keywords: Social Commerce, Value Creation, User Engagement, Community Building, Xiaohongshu.
Abstract: This study delves into the mechanisms and operational models of value creation in social commerce,
particularly highlighting its rapid development in the context of Web 2.0 and the COVID-19 pandemic, as
well as how social commerce distinguishes itself from traditional e-commerce with its S2B2C business model.
By adopting Xiaohongshu as a case study, this paper analyzes the key elements for successfully implementing
social commerce strategies, including user engagement, content sharing, community building, and their
promotion of commercial value and social impact. The research finds that through enhancing social
interaction and user-generated content, social commerce platforms can not only improve consumers' shopping
experiences and brand loyalty but also foster co-creation of value, thereby generating greater value for both
businesses and consumers. This paper contributes to the field of social commerce by proposing a theoretical
model for social commerce value creation, clarifying the relationship between user needs, platform strategy,
and business models. For businesses and platforms aiming for success in social commerce, this research
emphasizes the importance of promoting user participation, building a sense of community, and innovating
platform technology and algorithms. Moreover, the study extends the relevant policy implications based on
existing research.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, influenced by the Covid-19 pandemic
and the development of Web 2.0 (Ukpadi &
Karjaluoto, 2017), the social commerce industry has
experienced an explosive growth. According to
Becdach et al., (2022), the size of the social commerce
market in the United States is expected to reach $79.6
billion by 2025. As shown in Figure 1, the social
commerce market has rapidly developed in recent
years (Becdach et al., 2022). Furthermore, the study
indicates that people have a strong preference for
purchasing goods in large quantities through
applications and websites (Napawut et al., 2022).
Social commerce differs from the traditional B2C
(Business to Customer) business model adopted by e-
commerce enterprises, following instead an S2B2C
(Supplier to Business to Customer) business model.
This means that goods are transferred from suppliers
to community leaders through social commerce
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-9836-7846
platforms, and ultimately to consumers (Busalim &
Hussin, 2016; Lin et al., 2017).
Figure 1: US retail social-commerce sales, $billions.
Although the potential for growth in social commerce
is significant, research on its value creation
mechanisms and operational models remains
relatively limited. This paper aims to explore the
mechanisms of value creation in social commerce and
Liu, L.
Value Co-Creation in the Era of Social Networking: Exploring the Social Commerce Value Creation Model Based on Xiaohongshu.
DOI: 10.5220/0012909200004508
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2024), pages 85-94
ISBN: 978-989-758-713-9
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
85

its operational models, with a special focus on
strategies for co-creating value through social
platforms, enhancing consumer participation, and
increasing commercial value. Considering the
limitations of existing research, this paper adopts a
case study approach, using Xiaohongshu as an
example, to analyze its social commerce model and
success factors, thereby constructing a theoretical
model of value creation in social commerce. This
paper not only reveals how to create commercial and
social value through user engagement, content
sharing, and community building but also provides
theoretical support and practical guidance for
businesses implementing social commerce strategies.
Through an in-depth analysis of the Xiaohongshu
case, this paper aims to provide a more
comprehensive understanding of the value creation
process in the field of social commerce, bringing
implications and insights to the industry.
This study's structure is outlined as follows:
initially, it presents the research context and rationale,
succeeded by an exploration of pertinent literature to
elucidate the notion of social commerce and its value
generation mechanisms. Subsequently, employing a
case study on Xiaohongshu, the investigation delves
into its approach to social commerce and strategies for
generating value. Following the case study findings, a
theoretical framework for value creation within social
commerce is developed. The study concludes with
suggestions for the social commerce sector.
2 THEORETICAL
BACKGROUND
2.1 Social Commerce
Social commerce, as described by Busalim & Hussin
(2016), predominantly involves the use of online
commerce mechanisms that integrate social media
and Web 2.0 technologies. It is understood as the
integration of social media conventions with Web 2.0
technologies, facilitating platforms that enable users
to interact and disseminate business-relevant
information. The construct of social commerce
emerges from the confluence of three key elements:
Web 2.0 technologies, social media platforms, and
traditional e-commerce practices (Busalim & Hussin,
2016).
Moreover, the concept of social commerce
extends to employing social networks or media to
enhance user engagement in various online
commercial activities like marketing, information
exchange, and purchasing (Zhao et al., 2023). This
definition reflects the dynamic nature of social
commerce, incorporating newer forms of interactivity
such as live broadcasts and community-based
commerce. Distinct from conventional e-commerce,
social commerce prioritizes social interactions within
online communities, leveraging electronic word of
mouth (e-WOM) and user-generated content to foster
a social shopping environment.
Furthermore, social commerce businesses
cultivate trust and community feeling via social
networks, providing tailored shopping journeys and
adding value through superior customer service and
engagement. Social media plays a crucial role in
enabling users to exchange experiences and
knowledge about products, significantly impacting
their online buying behaviors and overall shopping
experiences. Social commerce's distinctive features
offer companies the chance to enhance customer
relationships, yielding economic advantages like
heightened sales and effective marketing strategies.
By engaging in information-sharing activities, social
commerce participants provide social support
throughout the online purchasing process,
contributing to brand loyalty and the development of
active online communities (Lin et al., 2017).
2.2 Value Creation in Social Commerce
Per Teece (2010), the generation of value is seen as
the process through which companies produce value
for their stakeholders through the provision of
products and services that satisfy these stakeholders'
needs. Additionally, as previously discussed, social
media facilitates the sharing of shopping experiences
and product insights, impacting the purchase
decisions and experiences of other users.
Consequently, in the realm of social commerce,
stakeholders encompass not just the social commerce
platforms but also the users themselves. This study
brings into focus the notion of value co-creation,
defined as the collaborative effort between consumers
and providers in the creative process of designing and
developing new products or services (Yu et al., 2020).
This approach highlights the transition from the
conventional product-centric logic to a service-
dominant logic that is centered around the customer,
where customers evolve from being merely recipients
to becoming active participants in creation.
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
86

Particularly in social commerce, the concept of
value co-creation is further amplified within social
media contexts, such as social networking sites,
online brand communities, and discussion forums,
which provide fertile ground for co-creation activities
or a co-creation ecosystem. For instance, Schau et al.
(2009) discovered that effective brand communities
enhance brand value over time through a mutual value
creation process with consumers. As mediums of
interactive communication, social commerce
platforms not only offer businesses abundant
opportunities for engagement and interaction but also
draw a wide audience and sustain a richness of
information, thereby facilitating numerous
collaborative possibilities.
Hence, the realization of value co-creation in
social commerce is contingent upon user engagement,
trust, and dedication. Social commerce platforms act
as digital spaces where users can exchange
experiences and information, engage socially, and
utilize collaborative features that support group
interaction, collaboration, and the achievement of
collective goals through the platform. This illustrates
that social commerce platforms serve not only as
facilitators of value co-creation but also as catalysts
in the value co-creation process.
3 VALUE CREATION ANALYSIS:
TAKING XIAOHONGSHU AS
AN EXAMPLE
Given the above analysis and research on value
creation and co-creation in Social Commerce, the
following section will further analyze the
mechanisms of value creation in social commerce
through a case study of Xiaohongshu.
3.1 Company Background
Xiaohongshu is a social media and e-commerce
platform that offers users a space to share and
discover products, lifestyles, and various experiences.
Users can share their shopping experiences and
product reviews through social interactions such as
posting, commenting, and liking, and they can also
purchase products directly on the platform. As of July
2019, Xiaohongshu's user base exceeded 300 million
(Xiaohongshu, 2024), and as of September 2023,
Xiaohongshu's monthly active users reached
approximately 199 million (Thomala, 2023), making
it China's largest social commerce platform.
As a social media and sharing platform,
Xiaohongshu allows users to post information and
choose the sections where their posts will be
published. Users can share articles about their travels,
shopping experiences, lifestyles, and even complaints
or mood essays (Eastward Media, 2023).
Xiaohongshu provides a platform for all participants,
including businesses, suppliers, and customers, to
freely share any information.
This approach not only increases product visibility
but also establishes a community-based trust system
where genuine experiences and feedback influence
purchasing decisions. These strategies allow suppliers
to conduct precise market segmentation and
personalized marketing, significantly contributing to
a detailed understanding of consumer behavior
(Zhong & Liang, 2024).
Moreover, Xiaohongshu's social commerce
model, by establishing a content and community-
driven platform, deepens the interactive relationship
between brands, suppliers, and consumers. It serves
not just as a place for information sharing but also as
a bridge for interaction between Key Opinion Leaders
(KOLs) and consumers, directly influencing
consumers' purchasing decisions through the sharing
and feedback within the community. Content creators
on Xiaohongshu, by posting genuine experiences
related to product use, provide references for other
users, thereby fostering a trust-based purchasing
environment (Zhong & Liang, 2024). Additionally,
the data analysis tools on the Xiaohongshu platform
offer businesses the possibility of targeted marketing
(Zhao & Zhou, 2023), enabling them to tailor
marketing strategies based on consumer behavior and
preferences, further driving product innovation and
market expansion.
3.2 Analysis of Customer Engagement
on Xiaohongshu
In the studies by Wang et al. (2022) and Zhong &
Liang (2024), an in-depth exploration was conducted
on the impact of user-generated content on
Xiaohongshu and its influence on the decision-
making process in a social commerce environment.
These studies reveal that users on Xiaohongshu are
both consumers and content creators who not only
engage in content creation and sharing but also
participate with suppliers in the design and
development of new product activities. Consumer
Value Co-Creation in the Era of Social Networking: Exploring the Social Commerce Value Creation Model Based on Xiaohongshu
87
behavior is significantly influenced by other users'
comments and shared content, especially for those
lacking knowledge in specific areas, relying more on
information within the community. The studies
emphasize that content and language of posts have a
deeper impact on consumer behavior than images,
with active users and frequent content creators having
the most significant influence on consumer
preferences. Further, Zhong & Liang (2024) focused
on how community leaders and the platform itself
play a key role in shaping consumer behavior and
preferences through active content creation and
frequent interactions with suppliers and consumers.
These studies collectively showcase the crucial role
of user-generated content in shaping consumer
decision-making processes, highlight the importance
of interactive modes in a social commerce
environment, and how these interactions enhance
connections between consumers and content creators,
promoting the co-creation process of new product
activities.
Moreover, in the study by Wu (2023), the
uniqueness of Xiaohongshu as a social commerce
platform was explored, especially its significant
differences from other social commerce platforms.
The research points out that user engagement on
Xiaohongshu goes far beyond simple sharing and
communication; users actively participate in value co-
creation activities based on group relationships. This
indicates that ordinary consumers, influenced by the
community, are likely to become content producers,
actively sharing their insights and experiences. This
transformation blurs the traditional roles of
community owners in social commerce, suggesting
that every user has the potential to become a
community leader, thus participating in the co-
creation process. This finding reshapes our
understanding of community dynamics and user
engagement models in social commerce, emphasizing
that on platforms like Xiaohongshu, value co-creation
is not the exclusive domain of a few content creators
or community leaders but a process in which all users
participate and shape together.
Furthermore, the platform actively interacts with
community leaders, sellers, and consumers to ensure
the quality and authenticity of the content posted, and
at the same time motivates users to produce high-
quality content (Jin & Yu, 2021). Therefore, for social
commerce, the platform's role is not limited to
regulation but also involves ensuring the quality and
authenticity of the content published by users
(suppliers, businesses, customers).
Platform management also affects consumer
behavior. The study by Lin and Shen (2023) utilized
the SOR model to deepen the research on the
purchasing intentions of consumers in social
commerce, where user trust needs to be obtained
through platform supervision, and platform
management's reinforcement of content management
measures can positively increase users' purchasing
intentions.
In summary, Xiaohongshu differs from other
social commerce platforms in that the platform
transitions from generating demand within general
communities, choosing merchants on the community
platform, or randomly selecting merchants for
purchases, to creating value through targeted
marketing and fixed traffic flow. This means
transitioning from user A or a community leader
posting content, directing traffic to user B or other
merchants in the value co-creation process.
Accordingly, Xiaohongshu's social commerce
operation model can be summarized as shown in
Figure 2.
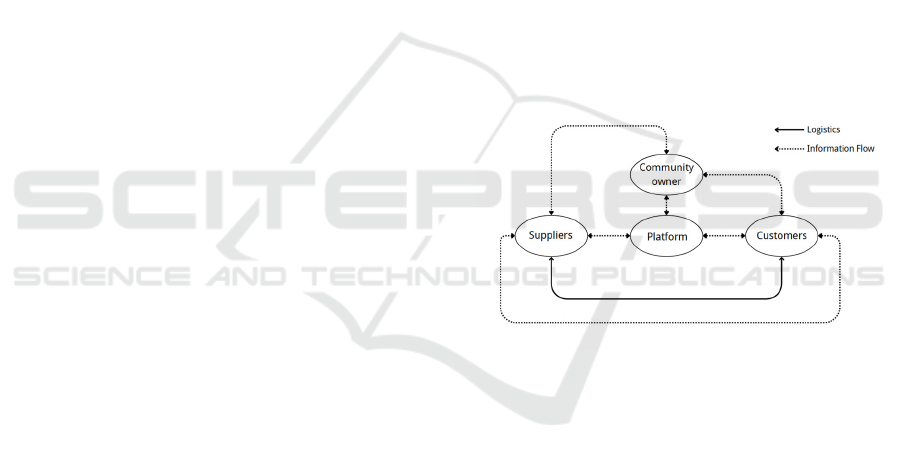
Figure 2: Xiaohongshu social commerce operation model
In summary, this model explains Xiaohongshu's
Social Commerce Operation Model, where dashed
lines represent the flow of information, indicating the
sharing of information among platforms, suppliers,
and community owners within the social commerce
operation mode of Xiaohongshu. Each participant
involved in this business model influences each other
and collaborates in the conception of products'
operational activities, as well as in their design and
development. Suppliers, the actual producers of the
products, can deliver goods directly to consumers and
engage with them in customer service or after-sales
work. This also reduces the supply chain and complex
distribution processes, improving the operational
efficiency of producers and reducing profit loss
during the product delivery process.
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
88
3.3 How Xiaohongshu Constructs a
Value Co-Creation Circle in Social
Commerce
Next, as shown in Figure 3, the value co-creation
circle formed by the social commerce business model
on Xiaohongshu.
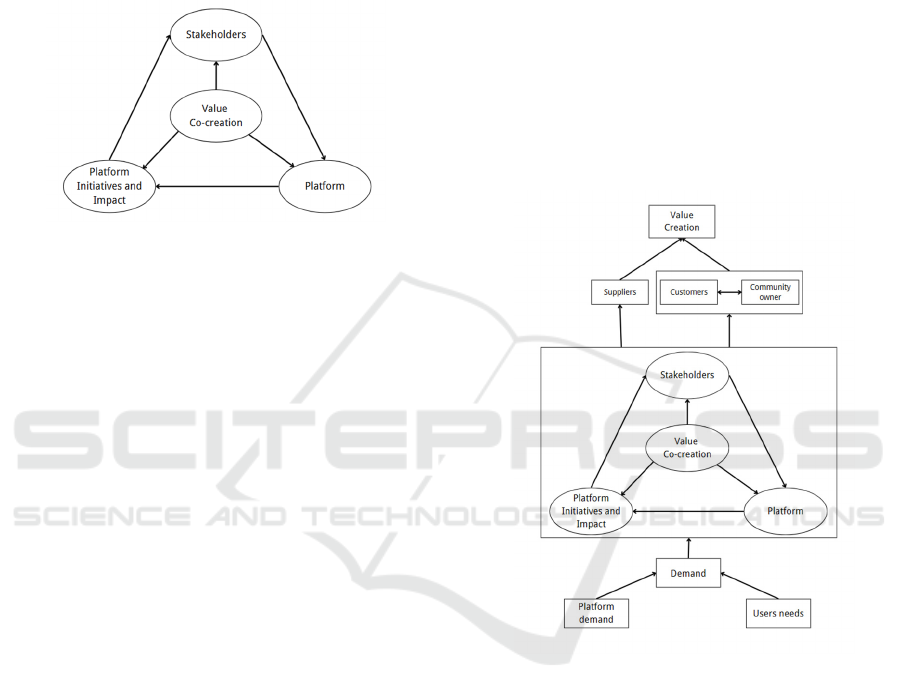
Figure 3: Xiaohongshu social commerce value co-creation
circle.
In this model, the platform refers to the social
commerce platform, which is Xiaohongshu. It
provides the digital infrastructure for business,
content sharing, and community building. Then,
Platform Initiatives and Impact represent the
technology and marketing methods of the platform,
including technology and algorithms. This includes
incentivizing users to post high-quality content and
making recommendations based on data, which also
enhances the consumer's purchasing experience
(Zhao & Zhou, 2023). The stakeholders are
participants in the platform, such as suppliers,
customers, or community owners. As previously
mentioned, the platform's profit-driven algorithm
recommendations stimulate users, turning more of
them into content creators. The high-quality content
produced by these creators attracts more consumers to
make purchases, boosting sales and cultivating a
vibrant content ecosystem for the platform.
The core of this value creation circle is co-creation
of value, where all parties contribute to and derive
value from interactions and exchanges within the
ecosystem. According to Wu (2023), for consumers
among the stakeholders, their experience with the
platform is enhanced due to personalized content and
a sense of community. For businesses, this leads to
increased brand awareness, consumer insights, and
higher sales conversion rates. Content creators gain
more opportunities for monetizing their traffic and
audience growth due to the platform's promotions.
Finally, the platform itself benefits as the quality of
content created by content creators gradually
improves, and user engagement increases with the
quality of the community (Wu, 2023); ultimately
translating into profits for the platform.
3.4 Xiaohongshu Social Commerce
Value Co-Creation Conclusion
Model
Based on the analysis above, the Social Commerce
value co-creation model shown in Figure 4 can be
derived, which explains how Social Commerce
generates value. In the following analysis, this
model's value creation mechanisms will be detailed,
using Xiaohongshu as a template.
Figure 4: Social Commerce Value Co-Creation Model
Based on Xiaohongshu.
3.4.1 Users Demand Analysis
In this model, demand is divided into user and
platform needs, where the popularity of social media
allows users to showcase their desire for self-
expression on a broader stage, and online
communities provide participants with a platform for
expression (Liao et al., 2023). Forums that allow free
expression of opinions promote users' desire to
express, thus motivating consumers and suppliers to
co-create value for the community.
In the field of e-commerce, research by Amin et
al. (2016) delved into the needs of participants,
finding that both merchants and consumers focus their
Value Co-Creation in the Era of Social Networking: Exploring the Social Commerce Value Creation Model Based on Xiaohongshu
89

core needs on improving shopping efficiency.
Specifically, consumers seek a convenient and
efficient shopping experience, requiring ample
product information to make informed purchasing
choices. This reflects a high demand for information
accessibility and simplification of the shopping
process. On the other hand, merchants aim to connect
with consumers more effectively by integrating the
internet, smart technologies, data analysis, and social
media tools, aiming to enhance marketing efficiency
and customer satisfaction. This indicates that both
suppliers and demand sides view improving shopping
efficiency as a core need in the e-commerce
environment. Therefore, participants in e-commerce
need to focus on optimizing the shopping process and
information delivery mechanisms to meet the market
and individuals' dual pursuit of efficiency and
convenience.
Wu (2023) identified that people naturally
gravitate towards forming or joining groups driven by
their social instincts. The collective experiences,
stories, and feelings serve as the cohesive bond that
envelops individuals, creating a communal
"atmosphere" akin to a surrounding nebula, in which
individuals find themselves deeply embedded. This
effect is particularly evident among fans of various
sports teams who come together. In the sphere of
Social Commerce, this implies that individuals
sharing similar purchasing goals are drawn together
by the allure of group exploration, making such
collective dynamics a cornerstone for building
communities within social commerce. This insight
sheds light on a novel way to comprehend how
communities within social commerce take shape,
emphasizing the critical importance of common
experiences, emotions, and needs in fostering the
formation of these communities.
3.4.2 Platform Demand Analysis
The investigation by Tajvidi et al., (2020) delved into
the notion, drivers, and processes behind brand co-
creation, along with the role of social commerce
technologies and the social attributes in mediating the
interaction between consumers and brands. This
research highlighted the profound effects of
information dissemination, social support, and the
quality of relationships on the co-creation of brands,
offering a model for fostering content-rich
communities and enhancing user retention. Moreover,
the study brought to light the critical role of
safeguarding privacy to preserve a robust social
commerce ecosystem.
In the context of social commerce platforms,
Tajvidi et al., (2020) underscored that elements like
social interactivity, social support, and the caliber of
relationships encourage consumers to jointly create
brand value, markedly influencing their buying
behaviors. These factors collectively contribute to
boosting user retention by facilitating increased user
engagement and satisfaction, ultimately improving
the profitability of the platform.
Specifically for Xiaohongshu, the platform
encourages user-generated content (UGC), with over
70% of posts created by users, fostering active
participation and content diversity. The platform
focuses on sharing authentic experiences, and this
marketing strategy based on real user word-of-mouth
constitutes the cornerstone of Xiaohongshu's
community marketing success. Through high-quality
community operations and product experience
sharing, Xiaohongshu continually enhances content
quality and trust in the platform (Chernavina, 2022).
Thus, building a high-quality content community and
enhancing user stickiness are key to Xiaohongshu's
success, with the platform continually innovating and
developing in this direction.
Additionally, research by Zhao et al. (2023)
discussed the key features of social commerce, such
as platform compatibility, relative advantage, and
user trust, and their importance in increasing user
purchasing behavior. By improving the operational
efficiency of the platform, these features' performance
can be enhanced, thereby increasing user satisfaction
and purchasing intentions. Moreover, social influence
mechanisms, like subjective norms and critical mass,
can also be strengthened by enhancing platform
efficiency, further promoting user purchasing
behavior.
In conclusion, as a social commerce platform,
how to stimulate consumers' desire to purchase is key
to maintaining the platform's survival and
development. By building high-quality content
communities and increasing user stickiness, as well as
improving the platform's operational efficiency,
consumer purchasing intentions can be effectively
enhanced, thereby bringing more profits to the
platform. Xiaohongshu has achieved user growth and
brought significant economic benefits to the platform
through strategies such as algorithm adjustment and
encouraging high-quality content creation (Thomala,
2023).
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
90

3.4.3 Social Commerce Value Creation
Analysis
Research by Wu, (2023) deeply analyzed that in the
era of "She Economy," with the improvement of
women's education level and the enhancement of
independence consciousness, female consumers have
become the core driving force of the consumer
market. In this era, women's consumption concepts
show more open and diversified characteristics,
especially on the Xiaohongshu platform, where
female users tend to share and purchase content
related to maternity and baby care, beauty and
skincare, clothing, etc. This not only reflects their
emphasis on self-expression but also their desire for a
high-quality life. Xiaohongshu effectively meets the
self-expression needs of female user groups through
its social and e-commerce functions, while also
providing a platform for the economic independence
and social status enhancement of women, reflecting
the growing influence of women in social and
economic fields.
Moreover, the primary age distribution of users on
the Xiaohongshu platform is between 20 and 40 years
old, whose shopping decisions are largely driven by
collective emotions and are based on trust in other
users in the community (Wu, 2023). This
consumption model effectively improves shopping
efficiency, transitioning from traditional comparative
shopping to a trust-based decision process, not only
enhancing the user shopping experience but also
promoting profit growth for businesses. For
merchants, the increase in the number of communities
and the improvement in community content quality
have enhanced consumers' trust in enterprises,
encouraged more users to participate in purchasing,
reduced dependence on traditional customer service,
improved business operation efficiency, and reduced
costs, demonstrating the significant potential of the
social commerce model in promoting economic
efficiency and social development.
Within Social Commerce, the decision to engage
with social commerce platforms is significantly
influenced by both technological aspects (such as the
tools and features of social media) and social elements
(including perceived value, pleasure, social impact,
and interaction) (Zhao et al., 2023). Therefore,
platforms continuously innovate to improve user
retention rates. As mentioned earlier, Xiaohongshu
enhances user experience by actively interacting with
platform users, merchants, etc., and ensuring the
production of high-quality content, and it also utilizes
new technologies and algorithms to ensure accurate
content delivery (Zhao & Zhou, 2023). These
measures have led to a series of explorations and
innovations in the Social Commerce field, driven by
profits to innovate and explore new business models.
In the context of Social Commerce, platforms like
Xiaohongshu demonstrate how the digital market
transcends mere economic transactions to create
vibrant community environments (Wu, 2023). By
integrating user-generated content (e.g., "unboxing"
videos), these platforms engage users in a cycle of
interaction and consumption that is deeply rooted in
shared emotions and community bonds. This process
not only enhances consumer experience by providing
a sense of belonging and identity but also increases
commercial value by intertwining commerce with
social participation and community building (Wu,
2023). Moreover, this interaction fosters a sense of
belonging and identity among users (primarily the
younger generation), who actively participate in
content creation and consumption. Through these
activities, the platform not only facilitates economic
transactions but also strengthens social bonds and
community cohesion, showcasing the ability of Social
Commerce to combine business objectives with social
significance, thereby making a positive contribution
to social welfare.
In the realm of Social Commerce, consumer status
is elevated through an ecosystem that integrates user-
generated content, fostering an interactive platform
where consumers transcend traditional roles to
become co-creators of value. This paradigm shift
underscores a more inclusive economic model,
valorizing consumer insights and contributions.
Hence, Social Commerce significantly democratizes
value creation, transforming consumers from passive
recipients to active participants in brand development
and innovation, thus enhancing their societal and
economic status (Wu, 2023; Liao et al., 2023) [16,20].
Social Commerce facilitates the fulfillment of
self-presentation needs by providing individuals with
a platform for online expression and identity
construction. Through participation in interaction and
content creation, users can align their digital personas
with their actual self-images. This not only enriches
their shopping experience by making it more
personalized but also enables them to actively
participate in shaping brand stories, thereby
strengthening their identity through recognition and
sharing of products on social networks (Wang et al.,
2024).
Value Co-Creation in the Era of Social Networking: Exploring the Social Commerce Value Creation Model Based on Xiaohongshu
91

Furthermore, the promotion of self-presentation
satisfaction becomes a key factor, allowing users to
carefully craft and share content that aligns with their
identity. This process not only allows for deep self-
expression but also cultivates richer interactions with
brands and their communities. Users actively
participate in value co-creation with brands by
contributing, sharing experiences, and feedback. This
dynamic significantly enhances user engagement,
loyalty, and the overall effectiveness of social
commerce strategies, emphasizing the key role of
self-presentation in the digital commerce
environment (Liao et al., 2023).
3.5 Summary: Innovations and
Achievements of Xiaohongshu in
Social Commerce
This case study delves into how Xiaohongshu
constructs a value co-creation ecosystem within the
social commerce domain, unveiling the following
discoveries and research outcomes:
(1) The Central Role of User-Generated Content
(UGC): Xiaohongshu has successfully built an active
community anchored on user-generated content,
which not only promotes widespread user
participation but also enhances the diversity and
quality of content. Users engage in content creation
and participate in the design and improvement of
products through interaction, significantly
influencing consumer decision-making.
(2) The Drive of Platform Strategy for Value Co-
Creation: Xiaohongshu encourages the production of
high-quality content through algorithm optimization
and incentive mechanisms, increasing user stickiness
and enhancing the platform's operational efficiency.
The platform's technological innovation and
marketing strategies enhance the consumer
purchasing experience, stimulating users' passion for
creation with precise content recommendations and
rewards for high-quality content.
(3) The Construction of Xiaohongshu's Value Co-
Creation Circle Model: Xiaohongshu's social
commerce model integrates advanced digital
infrastructure and algorithm optimization to promote
the generation of high-quality user-generated content
(UGC), and inspires users to transition from passive
receivers to content creators. The platform brings
together diverse participants such as suppliers,
consumers, and community managers, forming a
mutually beneficial content ecosystem. In this
framework, consumers enjoy personalized content
and a strengthened community experience, businesses
achieve brand promotion and sales growth, and
content creators gain more monetization
opportunities. Ultimately, this model not only
improves the platform's content quality and user
engagement but also significantly enhances its
commercial value and profitability, offering a
successful model for the social commerce field.
(4) This research thoroughly investigates the
processes of value co-creation within social
commerce by examining the case of Xiaohongshu,
leading to the development of a theoretical framework
that clarifies how user demands, platform policies,
and mechanisms for creating value interact. Crucially,
the insights and foundational elements of this model
extend beyond just Xiaohongshu, offering valuable
lessons for various social commerce platforms. The
generalization of this theoretical framework
emphasizes how the proliferation of social media has
ignited users' desires for self-expression, while online
communities offer platforms for participation,
encouraging both users and suppliers to co-create
value for the community. Moreover, an innovative
aspect of this theoretical framework is its proposal of
an integrated perspective, considering the crucial
roles of technological and social factors in user
engagement on social commerce platforms, as well as
highlighting the role of female consumers as the
driving force in the market under the "She Economy"
backdrop. The theoretical contribution of this
research lies not only in deepening and expanding
existing theories of social commerce but also in
providing a comprehensive framework for analyzing
and understanding the value co-creation process on
different social commerce platforms in future
research and practice. By emphasizing the broad
applicability and innovation of the theory, this study
offers new perspectives for academic research and
practical application in the field of social commerce.
4 LIMITATIONS AND OUTLOOK
This paper mainly focuses on the domestic market in
China, overlooking the dynamics and impact of
Xiaohongshu and similar platforms in the
international context. This limits the understanding of
global social commerce trends and the possibility of
extrapolating findings to other regions. Additionally,
the case study method specifically targets
Xiaohongshu, which operates mainly in China. This
narrow focus may not capture the full spectrum of
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
92

social commerce practices or the diverse business
models adopted by platforms in different countries.
As a result, the findings may not be fully applicable
or reflective of the global social commerce landscape.
Moreover, the study faces significant challenges in
obtaining precise revenue data related to social
commerce activities on Xiaohongshu. The platform's
revenue streams, especially those arising from the
complex web of user interactions, content creation,
and sales transactions, are intricate and not easily
quantifiable. The lack of such data hampers the ability
to fully assess the economic impact of social
commerce on the platform's overall performance.
Furthermore, given the multitude of merchants on the
platform, conducting a comprehensive study covering
all merchants operating on Xiaohongshu is
impractical. This limitation means the analysis might
not fully represent the diverse strategies, challenges,
and successes experienced by different merchants
within the platform ecosystem.
Considering these constraints, it's important to
approach the results of this study cautiously. Future
investigations could mitigate these constraints by
including data from international markets, broadening
the case study to cover a larger selection of platforms,
gathering more in-depth financial data, and
performing a thorough analysis of the diverse
merchants present on Xiaohongshu.
5 CONCLUSION
This paper systematically explores the theoretical
background of Social Commerce, the process of value
creation, and a specific analysis of Xiaohongshu as a
case study. The article first defines the concept of
social commerce, highlighting the integration of three
core elements: Web 2.0 technologies, social media,
and e-commerce, providing users with an interactive
online shopping environment characterized by user-
generated content. By delving into the role of value
creation in social commerce, this paper reveals the
importance of co-creation of value, i.e., how
businesses, consumers, and other stakeholders
collaboratively work through social media platforms
to jointly participate in the innovation process of
products and services. The case analysis of
Xiaohongshu further demonstrates the practical
application of this theory, especially how value co-
creation is achieved through establishing trust and a
sense of community, providing personalized
shopping experiences, and enhancing customer
service and interaction. Additionally, through specific
analyses of customer engagement and platform
strategies, this paper discusses how Xiaohongshu
successfully built a social commerce ecosystem that
fosters business innovation, improves efficiency,
enhances consumer status, and meets the needs for
self-expression.
Drawing from these findings, companies and
platforms aiming for success in social commerce
should prioritize enhancing user involvement,
fostering community bonds, and advancing
technological and algorithmic innovations. To begin
with, platforms and businesses ought to boost brand
trust and loyalty among users by better managing
community interactions and promoting the creation of
user-generated content (UGC), thereby streamlining
the value co-creation process. Moreover, there should
be a focus on improving data analysis capabilities and
tailoring recommendation algorithms to improve both
the shopping experience for users and the accuracy of
market targeting and marketing tactics for vendors.
Additionally, given the scope limitations of this study,
future investigations should include a wider variety of
social commerce platforms and explore international
markets for deeper insights. Lastly, to remain
competitive and achieve long-term growth,
businesses and platforms must stay attuned to the
evolving needs of social commerce users,
continuously refining their business approaches and
technological solutions.
REFERENCES
Ukpadi, D. C., & Karjaluoto, H. (2017). Consumers’
acceptance of information and communications
technology in tourism: A review. Telematics and
Informatics, 34(5), 618-644.
Becdach, C., Brodherson, M., Gersovitz, A., Glaser, D.,
Kubetz, Z., Magni, M., & Nakajima, J. (2022, October
19). Social commerce: The future of how consumers
interact with brands. McKinsey & Company.
Napawut, W., Siripipatthanakul, S., Phayaphrom, B.,
Siripipattanakul, S., & Limna, P. (2022). The Mediating
Effect of E-WOM on the Relationship Between Digital
Marketing Activities and Intention to Buy Via Shopee.
International Journal of Behavioral Analytics, 2(2), 1-13.
Busalim, A. H., & Hussin, A. R. C. (2016). Understanding
social commerce: A systematic literature review and
directions for further research. International Journal of
Information Management, 36(6), 1075-1088.
Lin, X., Li, Y., & Wang, X. (2017). Social commerce
research: Definition, research themes and the trends.
Value Co-Creation in the Era of Social Networking: Exploring the Social Commerce Value Creation Model Based on Xiaohongshu
93

International Journal of Information Management,
37(3), 190-201.
Teece, D. J. (2010). Business Models, Business Strategy
and Innovation. Long Range Planning, 43(2/3), 172-
194.
Yu, C., Tsai, C., Wang, Y., Lai K., & Tajvidi, M. (2020).
Towards building a value co-creation circle in social
commerce. Computers in Human Behavior, 108, Article
105476.
Schau, H. J., Muñiz, Jr. A. M., & Arnould, E. J. (2009).
How Brand Community Practices Create Value. Journal
of Marketing, 73(5), 30-51.
Xiaohongshu. (2024). About us.
Thomala, L. L. (2023). Monthly active users of
Xiaohongshu app in China 2020-2023.
Eastward Media. (2023, February 28). 2023 Xiaohongshu
Annual Lifestyle Trends | Embracing Real Life.
Zhong, H. Y., & Liang, J. (2024). Analysis of Social E-
commerce Platform Marketing Strategies from the
Perspective of Private Domain Traffic: The Case of
Xiaohongshu Platform. Communication and Copyright,1
Zhao, S. D., & Zhou, Y. (2023). Imaginary Mediators: A
Study on College Students' Attitudes Towards
Xiaohongshu's Personalized Recommendation
Algorithm. China Media Technology, 11.
Wang, Z., Huang, W., & Liu-Lastres, B. (2022). Impact of
user-generated travel posts on travel decisions: A
comparative study on Weibo and Xiaohongshu. Annals
of Tourism Research Empirical Insights, 3(2), Article
100064.
Wu, X. L. (2023). Behind 'Unboxing': Youth Interaction
and Consumption on Social Commerce Platforms —
The Case of Xiaohongshu. Contemporary Youth
Studies, 5.
Jin, Y., & Yu, H. (2021). Content governance mechanism
of social e-commerce platform from the perspective of
information ecology: A case study of Xiaohongshu. In
2021 2nd International Conference on E-Commerce and
Internet Technology (ECIT).
Lin, B., & Shen, B. (2023). Study of Consumers’ Purchase
Intentions on Community E-commerce Platform with
the SOR Model: A Case Study of China’s
“Xiaohongshu” App. Behavioral Science, 13(2), 1-17.
Liao, J., Pang, J., & Dong, X. (2023). More gain, more
give? The impact of brand community value on users’
value co-creation. Journal of Retailing and Consumer
Services, 74, Article 103389.
Amin, S., Kansana, K., & Majid, J. (2016). A Review
Paper on E-Commerce. In TIMS 2016-International
Conference.
Tajvidi, M., Richard, M., Wang, Y., & Hajli, N. (2020).
Brand co-creation through social commerce
information sharing: The role of social media. Journal
of Business Research, 121, 476-486.
Chernavina, K. (2022, June 29). 2022 Xiaohongshu user
trends and statistics. Hi-Com.
Zhao, L., Xu, Y., & Xu, X. (2023). The effects of trust and
platform innovation characteristics on consumer
behaviors in social commerce: A social influence
perspective. Electronic Commerce Research and
Applications, 60, Article 101284.
Wu, W. X. (2023). Research on Female Consumer Behavior
in Social Commerce Platforms: A Case Study of
Xiaohongshu. Western Broadcasting and Television,
44(24).
Wang, K., Chih, W., Honora, A., & Wu, Y. (2024).
Investigating antecedents of brand value co-creation
behaviors in social media based brand communities.
Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 64,
Article 101359.
Zhao, W., Hu, F., Wang, J., Shu, T., & Xu, Y. (2023). A
systematic literature review on social commerce:
Assessing the past and guiding the future. Electronic
Commerce Research and Applications, 57, Article
101219.
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
94
