
Flow Is Best, Fast and Scalable: The Incremental Parametric Cut for
Maximum Density and Other Ratio Subgraph Problems
Dorit S. Hochbaum
a
Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research, University of California, Berkeley, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Densest Subgraph, Graph Structures, Monotone Integer Programming, Breakpoints Algorithm, Conductance.
Abstract:
The maximum density subgraph, or densest subgraph, problem has numerous applications in analyzing graph
and community structures in social networks, DNA networks and financial networks. The densest subgraph
problem has been the subject of study since the early 80s and polynomial time flow-based algorithms are
known, yet research in the last couple of decades has been focused on developing heuristic methods for solv-
ing the problem claiming that flow computations are computationally prohibitive. We introduce here a new
polynomial time algorithm, the incremental parametric cut algorithm (IPC) that solves the maximum density
subgraph problem and many other max or min ratio problems in the complexity of a single minimum-cut.
A characterization of all these efficiently solvable ratio problems is given here as problems with monotone
integer programming formulations. IPC is much more efficient than the parametric cut algorithm since instead
of generating all breakpoints it explores only a tiny fraction of those breakpoints. Compared to the heuristic
methods, IPC not only guarantees optimality, but also runs orders of magnitude faster than the heuristic meth-
ods, as shown in an accompanying experimental study.
1 INTRODUCTION
We introduce here a new efficient algorithm for the
maximum density (MD), or densest, subgraph prob-
lem and many other ratio problems. The maximum
density subgraph problem is to identify a subset of
nodes in the graph that maximizes the density, de-
fined as the ratio of the weights of the edges with
both endpoints in the subset, divided by the sum of
weights of the nodes in the subgraph. The densest
subgraph has played a central role in analyzing net-
work structures since the 1970’s. The more recent ap-
plications of the problem are in the context of very
large scale networks, such as identifying emerging
cyber-communities (Kumar et al., 1999), DNA mo-
tif finding (Fratkin et al., 2006), and real-time story
identification (Angel et al., 2014).
The maximum density problem was studied since
the late 70’s. (Picard and Queyranne, 1982) are likely
the first to study the problem and recognize its link
to the max-flow min-cut problem. Their method was
based on a general “linearization” approach that ap-
plies for any ratio optimization problem, reducing it
to the λ-question, defined next, which they proposed
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2498-0512
to solve with a min-cut procedure on a related graph.
A general ratio problem max
x∈F
f (x)
g(x)
can be re-
duced to a sequence of calls to an oracle that provides
a yes/no answer to the λ-question:
Is there a feasible solution x ∈ F such that
f (x)
g(x)
> λ?
Or equivalently “Is there a feasible solution x ∈ F
such that f (x) − λg(x) > 0?”
To answer this λ-question it is sufficient to solve:
(λ-problem) max
x∈F
f (x) − λg(x).
If the maximum value is greater than 0 then there
is a feasible solution of ratio value strictly greater than
λ. Otherwise the answer is no. Specifically, if the
maximum value is strictly less than 0, then there is no
feasible solution of ratio value great or equal to λ. If
the answer is 0 then the respective optimal solution
for the λ-question has a ratio value of λ which is the
maximum ratio.
Therefore, any ratio problem that has the corre-
sponding λ-problem polynomial time solvable, and
the log of the number of possible values of the ratio
bounded by a polynomial quantity, is solvable in poly-
nomial time by applying binary search on the value of
the parameter λ.
(Picard and Queyranne, 1982) showed that the λ-
Hochbaum, D.
Flow Is Best, Fast and Scalable: The Incremental Parametric Cut for Maximum Density and Other Ratio Subgraph Problems.
DOI: 10.5220/0012917300003838
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2024) - Volume 1: KDIR, pages 275-282
ISBN: 978-989-758-716-0; ISSN: 2184-3228
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
275

problem for MD can be solved as a min-cut (mini-
mum s,t-cut) on a related graph, the construction of
which appeared ad-hoc. Their method was essentially
a predecessor of our IPC algorithm, showing that the
λ-problem for MD would be solved up to n times,
where n is the number of nodes in the graph. Here we
show a systematic method that maps any optimization
(and ratio) problem that is a monotone integer pro-
gram to an associated graph and therefore all these
problems are solvable in polynomial time, which as
proved here, is the complexity of one min-cut proce-
dure.
For the maximum density problem, a follow up
paper by (Goldberg, 1984) improved on the algorithm
of Picard and Queyranne, by using binary search on
the λ-problem making multiple call to a min-cut pro-
cedure, up to log n times for the edge-unweighted
node-unweighted problem. A major breakthrough,
the parametric flow procedure, was introduced in
(Gallo et al., 1989), identifying the solutions for all
values of the parameter λ that correspond to all possi-
ble solutions to the λ-problem, and in the complex-
ity of a single min-cut procedure. This parametric
procedure used the push-relabel algorithm of (Gold-
berg and Tarjan, 1988). Later (Hochbaum, 1998;
Hochbaum, 2008) showed a parametric cut proce-
dure using HPF (Hochbaum PseudoFlow) also with
the complexity of a single min-cut. We will refer to
this parametric procedure also as fully parametric, to
differentiate it from “simple” parametric, reviewed in
Section 2.2.
Despite its theoretical efficiency, the parametric
flow procedure has never been used to solve the
densest subgraph problem, to the best of our knowl-
edge. One contributing factor for the lack of use
is that there is no implementation available for the
parametric push-relabel version proposed by (Gallo
et al., 1989). (However, for HPF there is a para-
metric flow/cut implementation publicly available,
(Hochbaum, 2020a).) Instead, flow algorithms have
been employed using multiple calls to min-cut in a bi-
nary search process, resulting in high running times.
This perceived inefficiency gave rise to current state-
of-the-art algorithms for the maximum density prob-
lem that are based on greedy heuristics that do not
guarantee optimality, (Charikar, 2000), (Boob et al.,
2020), (Harb et al., 2022). A recent justification
for not using the polynomial time flow algorithms is
that “flow computations are expensive” (Boob et al.,
2020).
Our main contribution here is a new polynomial
time algorithm, the incremental parametric cut (IPC)
algorithm, that solves optimally and efficiently the
densest subgraph problem and many other minimum
or maximum ratio problems. We also provide an easy
characterization of the ratio problems that are solv-
able with this procedure, as those that can be for-
mulated as monotone integer programming problems.
For those problems we describe the respective s,t-
graph construction that follows from the formulation.
In a separate experimental study (Hochbaum
et al., 2024) we show that the number of breakpoints
IPC generates is in the range of 2 − 13 even for
datasets on millions of nodes and hundreds of mil-
lion edges, which is typically less than 1% of the total
number of breakpoints. This results in very fast run-
ning times that are orders of magnitude faster than
those of the parametric flow procedure and recent
state-of-the-art heuristics that do not produce optimal
solutions.
To summarize, the main contributions here are:
1. The incremental parametric cut algorithm IPC that
solves “monotone” ratio optimization problems in the
complexity of a single min-cut.
2. A new, previously unknown, formulation of dens-
est subgraph problem and its generalizations, that
uses half of the number of arcs as compared to the
known formulation.
3. An easy characterization of all ratio problems that
are solved by IPC. Examples are given in Table 1.
1.1 Ratio Problems Solved with IPC
Notation. We consider the graph representation of the
problems, firstly for undirected graphs corresponding
to symmetric problems. Let G = (V,E) denote an
undirected graph with n denoting the number of nodes
in V, and m denoting the number of edges in E. Every
edge [i, j] ∈ E has an associated weight w
i j
≥ 0. Let
the weighted degree of node i ∈ V be d
i
=
∑
[i, j]∈E
w
i j
.
For B
1
,B
2
⊆ V , let C(B
1
,B
2
) =
∑
[i, j]∈E,
i∈B
1
, j∈B
2
w
i j
be the
sum of weights of the edges between nodes in the
set B
1
and those in set B
2
. Let q
i
denote a nonneg-
ative cost value associated with each node, and u
i
, or
u
′
i
denote two types of values associated with each
node, which could be positive or negative. Let the
degree volume of a set of nodes S be d(S) =
∑
i∈S
d
i
,
q(S) =
∑
i∈S
q
i
and U(S) =
∑
i∈S
u
i
.
Some ratio problems are defined on directed
graphs, G = (V,A), where each arc (i, j) ∈ A has an
associated weight w
i j
≥ 0. The weighted outdegree
of a node i is d
+
i
=
∑
j|(i, j)∈A
w
i j
, and the outdegree
volume of a set of nodes S is d
+
(S) =
∑
i∈S
d
+
i
.
A sample list of some of the ratio problems solved
here is given in Table 1. The Max density problem
is defined with weighted edges but unit weight on the
nodes. This name refers more often to the special case
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
276

of the unweighted problem where both edges weights
are 1 and node weights are 1.
Many ratio problems appear in contexts where the
size of optimal set is bounded. For example, the ex-
pansion ratio of a graph problem is min
|S|≤
n
2
C(S,S)
|S|
.
This added size restriction turns the problem NP-hard.
The Cheeger constant problem is typically presented
as min
S⊂V
C(S,S)
min{d(S),d(
¯
S)
, which is equivalent to the
size restricted ratio problem min
d(S)≤
1
2
d(V)
C(S,S)
d(S)
. The
conductance problem is min
π(S)≤
1
2
π(V )
C(S,S)
π(S)
where π
i
is interpreted as the stationary probability of node i.
We add here the ∗ to the name of the problem to in-
dicate that there is no size restriction, and then the
problem is polynomial time solvable. For the min-
imization problems, the entire set of nodes V is of-
ten the optimal solution of value 0. To avoid that
trivial solution, the problem is typically solved on a
subgraph of nodes V
1
. For example Metis (Karypis
and Kumar, 1998) has been used to identify a sub-
graph which is likely to contain the optimal solution
for these problems and then the minimization is sub-
ject to
/
0 ⊂ S ⊆ V
1
.
Table 1: A list of some of the ratio problems solved with
the incremental parametric cut. *No size restriction.
Problem name Objective
Max density max
S⊆V
C(S,S)
|S|
Weighted max density max
S⊆V
C(S,S)
q(S)
Ratio quadratic Knapsack max
S⊆V
C(S,S)+U(S)
q(S)
HNC max
/
0⊂S⊂V
C(S,S)
C(S,S)
HNC-equivalent max
/
0⊂S⊂V
d(S)
C(S,S)
Max HNC-extension max
/
0⊂S⊂V
U(S)
C(S,S)+U
′
(S)
Expansion ratio* min
/
0⊂S⊂V
C(S,S)
|S|
Cheeger*/HNC min
/
0⊂S⊂V
C(S,S)
d(S)
Conductance* min
/
0⊂S⊂V
C(S,S)
q(S)
The problem HNC (Hochbaum Normalize Cut),
also named NC’ or SNC, was presented in (Sharon
et al., 2006) as an NP-hard problem identical to
the Normalized Cut (Shi and Malik, 2000), but
shown polynomial time solvable in (Hochbaum,
2010). The same mistake was repeated in (Fortunato,
2010), who stated that Cheeger*/HNC, equation (22),
min
/
0⊂S⊂V
C(S,S)
d(S)
, is the normalized cut problem and
NP-hard.
2 THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
2.1 Characterization of Polynomial
Time Solvability: Monotone Ratio
Problems
If the linearized problem can be formulated as mono-
tone integer programming, IPM
1
, then it is solvable
with a min-cut procedure on an associated s,t graph,
where the graph construction is uniquely mapped
from the formulation, (Hochbaum, 2002).
IPM problems are classified as monotone IP2 and
monotone IP3 where IP3 generalizes IP2. An inte-
ger program is a monotone IP2 if each constraint con-
tains at most two of the variables that appear with
opposite sign coefficients. An integer program is a
monotone IP3 if each constraint contains at most two
of the variables that appear with opposite sign coef-
ficients and a third variable that appears in that con-
straint only. (There is an additional requirement that
the “third variables” must have nonnegative coeffi-
cients in a minimization objective function, and non-
positive coefficients in a maximization objective func-
tion.) It is thus easy to recognize whether a formula-
tion is monotone.
The formulation of monotone integer program for
a set of n x-variables and a set of constraints involving
a collection of pairs of variables A and a respective set
of z-variables is,
(IPM) max
n
∑
i=1
w
i
x
i
−
∑
(i, j)∈A
e
i j
z
i j
s.t. a
i j
x
i
− b
i j
x
j
≤ c
i j
+ z
i j
∀ (i, j) ∈ A
ℓ
i
≤ x
i
≤ u
i
, integer ∀ i ∈ V
z
i j
≥ 0, integer ∀ (i, j) ∈ A.
Here there is a restriction that the coefficients of
e
i j
in the objective function are nonnegative for max-
imization and non-positive for minimization.
Any IPM problem is equivalent to the following
binary s-excess problem which is formulated on the
variables x
i
= 1 iff node i is in the optimal set S:
(s-excess) max
∑
j∈V
w
i
x
i
−
∑
(i, j)∈A
u
i j
z
i j
subject to x
i
− x
j
≤ z
i j
for (i, j) ∈ A
x
j
binary j = 1, . ..,n
z
i j
binary (i, j) ∈ A.
The respective graph G
st
is constructed as follows,
(Hochbaum, 2002): We add nodes s and t to the graph
G, with an arc from s to every positive weight node i,
1
We use the acronym IPM rather than MIP so as not to
confuse it with Mixed Integer Programming
Flow Is Best, Fast and Scalable: The Incremental Parametric Cut for Maximum Density and Other Ratio Subgraph Problems
277

of capacity u
si
= w
i
, and an arc from every negative
weight node j to t of capacity u
jt
= −w
j
. Let this
added set of arcs, adjacent to s and t (source node and
sink node respectively) be denoted by A
st
. The arcs
of A each carry the capacity u
i j
which is infinite if
the constraint has only two variables. The graph G
st
is then (V ∪ {s,t},A ∪ A
st
). The proof of the follow-
ing lemma is given in (Hochbaum, 2002) and omitted
here.
Lemma 1. S
∗
is a set of maximum s-excess capacity
in the original graph G if and only if S
∗
is the source
set of a minimum s,t-cut in the associated graph G
st
.
We say that a ratio problem is a monotone inte-
ger program (IPM), if the corresponding λ-problem
is IPM. For the λ-problem, the corresponding flow
graph G
λ
has arc capacities that are functions of the
parameter λ. An s,t-graph is said to be a parametric
flow graph if it has source-adjacent capacities that are
monotone non-increasing with the parameter λ and
the sink-adjacent capacities that are monotone non-
decreasing with λ (or vice versa). For a λ-problem
represented as a parametric flow graph, G
λ
, the para-
metric cut procedure solves the λ-problem, for all val-
ues of the parameter. This is the case for all the prob-
lems listed in Table 1 and many more.
2.2 Parametric Cut, Nestedness and the
“Continue” Property
Let the minimum cut for graph G
λ
be (S
λ
,
¯
S
λ
) with
S
λ
the “source set” of the minimum cut and
¯
S
λ
the
“sink set”. A property of the parametric flow graph
is that as the values of λ are increasing, the source
sets of the minimum cuts can only decrease, each a
subset of the previous. Formally, for a monotone in-
creasing sequence of p λ values, λ
1
< λ
2
< . . . <
λ
p
, the corresponding optimal solutions, the source
sets of the minimum cuts in the graph G
λ
, satisfy
S
λ
1
⊇ S
λ
2
⊇ ... ⊇ S
λ
p
, and the respective sink sets
satisfy
/
0 =
¯
S
λ
0
⊆
¯
S
λ
1
⊆ .. . ⊆
¯
S
λ
p
. This property
is called nestedness and is proved as a corollary of
the parametric flow algorithms of (Gallo et al., 1989;
Hochbaum, 1998; Hochbaum, 2008). As the value
of the parameter λ increases, the respective cut so-
lutions change when the sink set strictly increases.
The values of the parameter where the change occurs
are called breakpoints. Because of the nestedness the
solution set changes by adding at least one node to
the sink set, and therefore there are at most n break-
points. For ℓ breakpoints, λ
′
1
< λ
′
2
< ... < λ
′
ℓ
, the
respective sink sets are strict subsets of each other:
¯
S
λ
′
1
⊂
¯
S
λ
′
1
⊂ . . . ⊂
¯
S
λ
′
ℓ
.
There are two variants of the parametric cut pro-
cedure. The fully parametric variant generates all the
breakpoints (see (Hochbaum, 2020a)). The simple
parametric variant takes as input a sequence of val-
ues of λ, or a sequence of source adjacent capacities
and sink adjacent capacities that are monotone non-
increasing on one side, and monotone non-decreasing
on the other, (Hochbaum, 2020b), and outputs the
minimum cut solution for each of them. A property
required of a min-cut max-flow algorithm in order for
either the fully or simple parametric cut to work in the
complexity of a single min-cut procedure, T (n, m), is
the continue property: Once an optimal solution has
been found for one setting of the capacities, it is used
as the initial solution for the new problem with up-
dated, monotone, capacities. This is done while main-
taining the labels and the invariant structure of the al-
gorithm, which for HPF is called normalized tree. To-
date, only push-relabel and HPF are max-flow min-
cut algorithms that have the continue property. For
HPF the routine HPF-para-continue(λ,S) is the part
that takes a solution, which is the subset S in the re-
lated graph, and updated capacities corresponding to
λ to find the optimal solution for the updated problem
which is a subset of S.
The continue operation for HPF using monotonic-
ity is referred to as HPF-para-continue and takes as
input the solution source set for the value of λ pre-
viously used, that is guaranteed to contain the opti-
mal ratio solution (because of nestedness, and the new
value λ).
2.3 The Concave Envelope of the
Breakpoints
For a general maximum ratio problem max
x∈F
f (x)
g(x)
,
we consider the graph that maps any value of g(x) =
B, so-called “budget”, to the maximum value of
f (x
B
) = argmax
x∈F
f (x)|g(x) ≤ B, referred to as the
“benefit”. Finding those maximum benefits is in gen-
eral NP-hard.
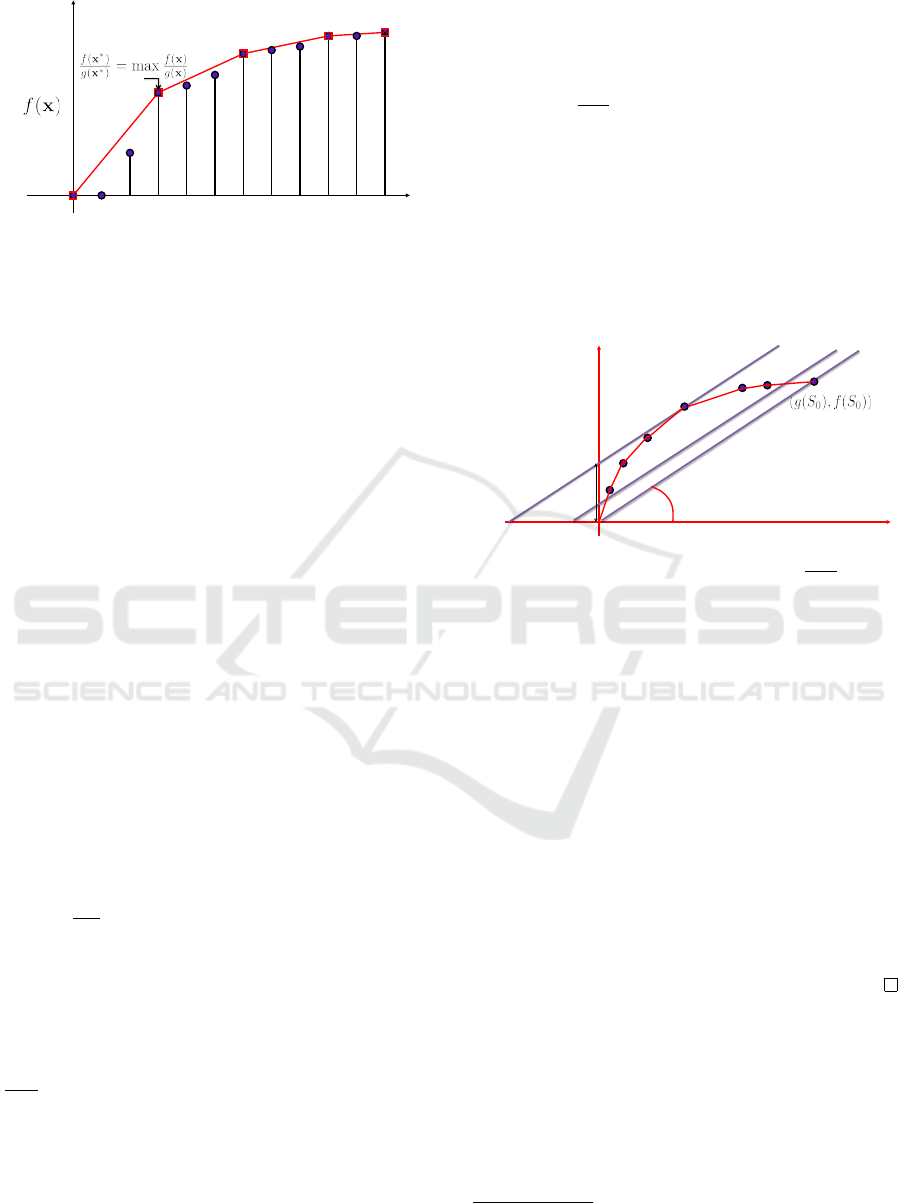
Consider the lower envelope of all the lines that
have the entire collection of optimal solutions below
them. This envelope, shown in red line segments in
Figure 1, is concave piecewise linear and the points
at which the line segment changes, are called break-
points (marked by boxes in Figure 1).
The ratio value corresponding to each optimal
point is the slope of the line connecting it to the ori-
gin. Hence the first, leftmost, breakpoint is also the
optimal solution to the maximum ratio problem.
The properties of the concave envelope were stud-
ied, in the context of the dynamic evolution problem,
in (Hochbaum, 2009). These properties include:
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
278
Benefit
Budget
B
Figure 1: The concave envelope, the breakpoints and the
ratio maximizing solution.
• The concave envelope and breakpoints are found
with fully parametric cut procedure, (Hochbaum,
2020a).
• The breakpoints of the envelope correspond to the
breakpoints of the respective parametric cut solu-
tions, and the left derivative at the ith breakpoint
is equal to the ith parameter breakpoint value λ
′
i
.
• At the breakpoints of the envelope the solutions
are optimal.
• The first breakpoint – the smallest positive budget
breakpoint – corresponds to the solution which at-
tains the largest ratio of the benefit to the budget.
• The breakpoints correspond to solutions that are
nested and their number is at most n, the number
of variables, or nodes, in the respective graph.
For the respective minimization problems the en-
velope of the breakpoints is convex, and the first
breakpoint corresponds to the solution that attains the
smallest ratio of benefit to budget, see e.g. Figure 5.
2.4 Incremental Parametric Cut
Procedure
Consider the general ratio maximization problem
max
x∈F
f (x)
g(x)
where any feasible vector x
′
is associ-
ated with a subset of nodes in the associated graph,
S
′
= {i ∈ V |x
′
i
= 1}.
The procedure starts with a set of nodes S
0
that
is to contain the optimal ratio solution, which for the
maximum density problem can be the entire graph,
S
0
= V . The initial value of the parameter is λ
0
=
f (S
)
)
g(S
0
)
. Solving the λ
0
-problem either provides a so-
lution with strictly higher ratio value, that is also a
breakpoint solution, or else its value is 0 and there-
fore it is the maximum ratio solution. Because of
the nested property, each subsequent solution set is
strictly contained in the previous iteration’s solution
set. The value of the ratio is then updated and used
as λ in the next iteration. Let S
0
be an initial feasible
solution.
PROCEDURE INCREMENTAL PARAMETRIC
( f (), g(), S
0
⊆ F ,k=0).
Step 1: λ
k
=
f (S
k
)
g(S
k
)
.
Step 2: HPF-para-continue(λ
k
,S
k
) to solve
improve(λ
k
) = max
S⊆F ∩S
k
f (S) − λ
k
g(S).
Let S
k+1
= argmax
S⊆F ∩S
k
f (S) − λ
k
g(S).
Step 3: If {improve(λ
k
) > 0} let k := k + 1. Go to step 1,
else stop. Output S
∗
= S
k
.
We now prove the correctness of the procedure in
that it visits a sequence of budget-decreasing break-
points.
λ0
Δ
Budget
Benefit
λ0
Figure 2: Identifying a breakpoint with λ
0
=
f (S
0
)
g(S
0
)
subgra-
dient, skipping over several breakpoints.
Lemma 2. The optimal solution to max
x∈F
f (x) −
λ
0
g(x), x
1
, is either a breakpoint on the concave en-
velope at a budget < g(x
0
) and with strictly larger ra-
tio than that of x
0
, or x
1
= x
0
and it is the maximum
ratio solution.
Proof. Consider the line equation f (x) = λ
0
g(x) + ∆
where ∆ the intercept of the line, of slope λ
0
, on the
vertical axis, as in Figure 2. Maximizing ∆ is equiv-
alent to max
x∈F
f (x) − λ
0
g(x) = ∆
∗
. Therefore the
line f (x) = λ
0
g(x) + ∆
∗
lies above all feasible solu-
tions and is tangent to the concave envelope at break-
point x
1
, where x
1
= argmax
x∈F
f (x) − λ
0
g(x). x
1
is
a breakpoint with a left subgradient equal to λ
ℓ
and
right subgradient equal to λ
r
, such that λ
ℓ
≥ λ
0
≥
λ
r
.
The complexity of the incremental parametric cut
procedure is that of a single min-cut HPF procedure
on the graph, T (n, m). More precisely, the complexity
is T (n, m) + O(qn) where q is the number of break-
points visited.
2
As noted in the introduction, this
number is very small in practice.
2
(Hochbaum, 2023) mistakenly stated that such a pro-
cedure visits adjacent breakpoints.
Flow Is Best, Fast and Scalable: The Incremental Parametric Cut for Maximum Density and Other Ratio Subgraph Problems
279

3 THE METHOD FOR
WEIGHTED MAX DENSITY
Let the weighted maximum density problem, WMD,
be given on a graph G = (V,E) with positive edge
weights u
i j
and node weights q
i
, max
S⊆V
C(S,S)
q(S)
. The
standard integer programming formulation of the
problem has binary variables for each node i ∈ V :
x
i
= 1 if node i is selected in S and 0 otherwise, and
binary variables for each edge [i, j] ∈ E, y
i j
= 1 if both
i and j are in S, and 0 otherwise. With this notation
the formulation of WMD is,
(WMD) max
∑
[i, j]∈E
u
i j
y
i j
∑
j∈V
q
i
x
i
subject to x
i
≤ y
i j
for [i, j] ∈ E
x
j
≤ y
i j
for [i, j] ∈ E
x
j
binary j ∈ V
y
i j
binary [i, j] ∈ E
The graph corresponding to this IP2 formulation
has m + n nodes, one for each variable. We next
present a general procedure for generating an equiv-
alent compact (monotone) formulation for WMD and
other ratio problems. Let d
i
denote the weighted de-
gree of node i in G: d
i
=
∑
j|[i, j]∈E
u
i j
, and d(S) =
∑
i∈S
d
i
. It is easy to see that for any non-empty
subset of nodes S ⊂ V , we have the identity d(S) =
2C(S, S) + C(S,
¯
S). Therefore, C(S, S) =
1
2
(d(S) −
C(S,
¯
S)).
Hence, max
S⊆V
C(S,S)
q(S)
=
1
2
max
S⊆V
d(S)−C(S,
¯
S)
q(S)
which is formulated as monotone integer program
as well, with up to 3 variables per inequality using
the same x-variables as in WMD, and “cut” variables
z
i j
that are equal to 1 if i ∈ S and j ∈
¯
S and zero
otherwise:
(WMD-compact) max
∑
j∈V
d
i
x
i
−
∑
[i, j]∈E
u
i j
z
i j
∑
j∈V
2q
i
x
i
subject to x
i
− x
j
≤ z
i j
for [i, j] ∈ E
x
j
− x
i
≤ z
ji
for [i, j] ∈ E
x
j
binary j ∈ V
z
i j
,z
ji
binary [i, j] ∈ E.
The graph associated with the linearized problem,
λ-WMD-compact, has one node for each x
i
variable
and two arcs for each edge in E resulting in a compact
formulation on n + 2 nodes and 2m + 2n arcs.
Improved Formulation and Smaller Associated
Graph. For WMD as well as for any ratio prob-
lem that includes only C(S, S) along with linear terms,
there is an even more efficient formulation that in-
cludes only one z
i j
variable for every pair that has
positive utility, instead of two. This results in a graph
with n +2 nodes and m + 2n arcs which is about half
of the number of arcs as compared to the formulation
above.
The key is to observe that the problem can be rep-
resented on a directed graph G = (V,A) where for
each pair i and j with positive utility and i < j there
is one arc (i, j) ∈ A from i to j.
k
i
1
n
j
s
t
max{w
1
,0} max{−w
1
,0}
max{w
i
,0} max{−w
i
,0}
max{w
j
,0}
max{−w
j
,0}
u
1i
u
jn
u
i j
u
ik
max{w
k
,0}
max{−w
k
,0}
max{w
n
,0} max{−w
n
,0}
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
s
j
t
max{d
+
j
+ u
j j
− λq
j
,0} max{λq
j
− d
+
j
− u
j j
,0}
Figure 3: The flow graph G
λ
for λ-WMD-compact1.
Let d
+
i
be the weighted out-degree of node i in
G: d
+
i
=
∑
j|(i, j)∈A
u
i j
. Then, for any subset of nodes
S ⊂ V, d
+
(S) = C(S, S) +C(S,
¯
S). Therefore (WMD-
compact1) is an IPM formulation of WMD:
(WMD-compact1) max
∑
j∈V
d
+
i
x
i
−
∑
(i, j)∈A
u
i j
z
i j
∑
j∈V
q
i
x
i
subject to x
i
− x
j
≤ z
i j
for (i, j) ∈ A
x
j
binary ∀ j ∈ V
z
i j
binary ∀(i, j) ∈ A.
The objective function of the linearized ratio
problem for the λ-question of (WMD-compact1)
is, (λ-WMD) max
∑
j∈V
d
+
i
x
i
−
∑
(i, j)∈A
u
i j
z
i j
−
λ
∑
j∈V
q
i
x
i
. The associated graph for this λ-WMD
is given in Figure 3 which is obviously a parametric
flow graph.
We conclude with an example of finding the
densest subgraph with IPC, reported in (Hochbaum
et al., 2024), in the dataset COM-YOUTUBE with n =
1134890 m = 2987624 from (Leskovec and Krevl,
2014). The running time of IPC for this dataset is
1.892 sec. The concave envelope of the breakpoints
is shown in Figure 4.
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
280
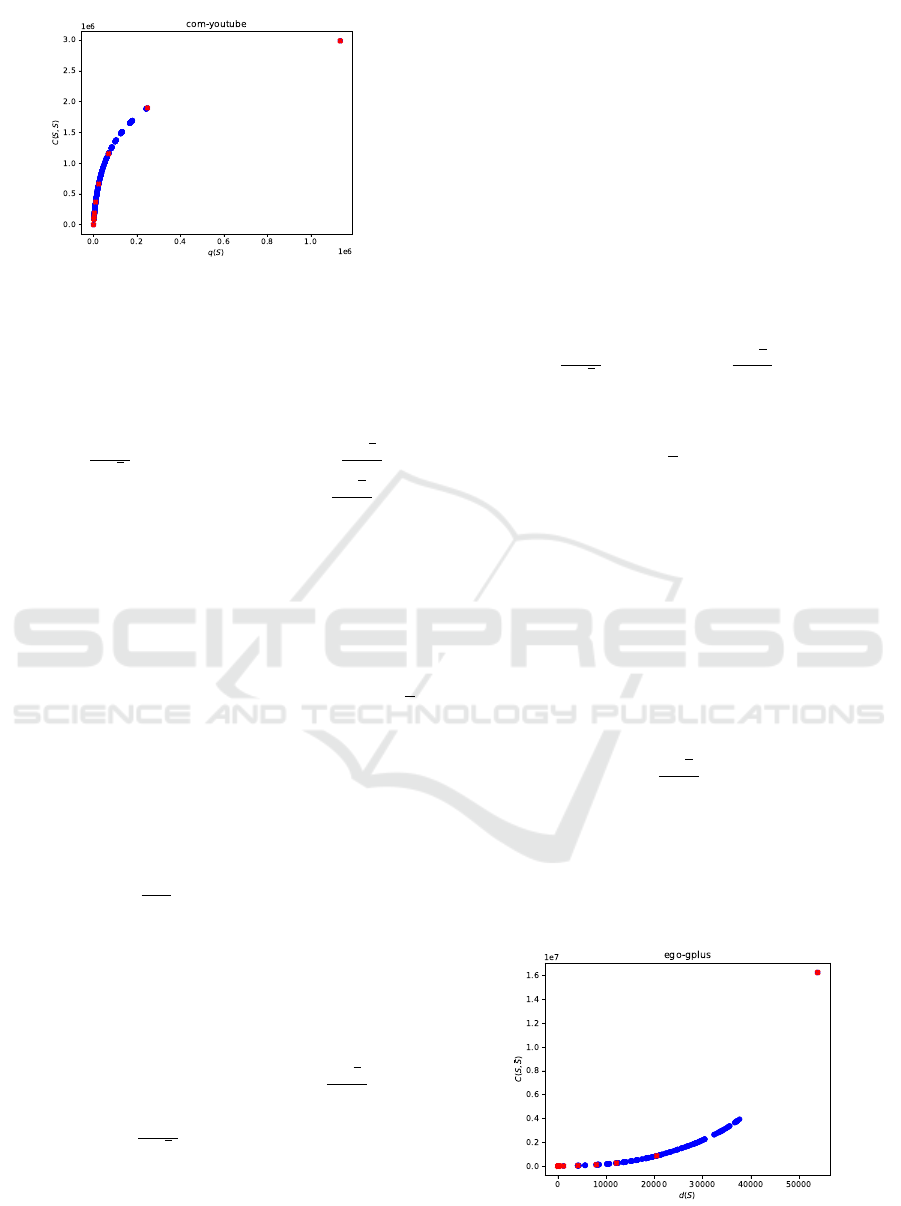
Figure 4: The concave envelope of all 1253 breakpoints, in
blue, versus 9 breakpoints explored by IPC, in red. (Cour-
tesy: A. Irribarra-Cort
´
es).
4 APPLICATIONS OF IPC
We consider here the three ratio problems: HNC
max
/
0⊂S⊂V
C(S,S)
C(S,S)
, Cheeger’s* min
/
0⊂S⊂V
C(S,S)
d(S)
and
conductance*/HNC-extension min
/
0⊂S⊂V
C(S,S)
q(S)
.
We first show, directly from the problem state-
ment, that HNC is an IPM ratio problem. Then pro-
vide a transformation showing that HNC is equivalent
to Cheeger*’s, and obviously conductance is a slight
generalization of both. We then give the formulation
for all three problems that leads to the parametric flow
graph that is solved with IPC.
We first comment on the use of the constraint
/
0 ⊂ S ⊂ V in ratio problems involving the cut C(S,S).
For such problems, unlike WMD, if unrestricted the
solution will be the entire graph with cut value 0. In
general that means that to solve such problems it is
necessary to use seeds which are subsets of nodes so
at least one belongs to the sink set and at least one
belongs to the source set. For these problems, when
they have size constraint, such as for Cheeger’s, of
the form d(S) ≤
d(V)
2
, the problems are NP-hard. To
address the issue of the seeds and to solve the size re-
stricted ratio problems heuristically one can choose to
first identify a subset of the graph where the optimal
subgraph may reside. This was done for example us-
ing the Metis graph partitioning heuristic of (Karypis
and Kumar, 1998) by (Lang and Rao, 2004). Once
the subgraph satisfying the size restriction is found,
say V
′
, the problem becomes min
/
0⊂S⊂V
′
C(S,S)
d(S)
.
Consider the integer programming formulation of
HNC max
/
0⊂S⊂V
C(S,S)
C(S,S)
with edge weights w
i j
and bi-
nary variables x
i
, y
i j
and z
i j
. Let x
i
= 1 if i ∈ S, y
i j
= 1
if both i and j in S and z
i j
= 1 if i ∈ S j ∈
¯
S. The fol-
lowing is the linearized formulation λ-HNC:
(λ-HNC) max
∑
[i, j]∈E
w
i j
y
i j
− λ
∑
j∈V
w
i j
z
i j
subject to x
i
≤ y
i j
for [i, j] ∈ E
x
j
≤ y
i j
for [i, j] ∈ E
x
i
− x
j
≤ z
i j
for [i, j] ∈ E
x
j
− x
i
≤ z
ji
for [i, j] ∈ E
x
j
binary j ∈ V
z
i j
,z
ji
,y
i j
binary [i, j] ∈ E
This monotone integer program maps into an as-
sociated graph on m + n + 2 nodes and 2m + 2n
arcs. A compact formulation of HNC, equivalent to
Cheeger’s*, is given in the next lemma (proof omitted
for lack of space):
Lemma 3. The following two problems are
equivalent and have the same optimal solutions:
max
/
0⊂S⊂V
C(S,S)
C(S,S)
, and min
/
0⊂S⊂V
C(S,S)
d(S)
.
Therefore solving HNC-extension, or conduc-
tance*, provides solutions to all three problems since
setting q
i
= d
i
is HNC or Cheeger’s* problem. The
problem min
/
0⊂S⊂V
C(S, S) − λq(S) is formulated as
follows.
(λ-HNC-extension)min
∑
[i, j]∈E
u
i j
z
i j
− λ
∑
j∈V
q
i
x
i
subject to x
i
− x
j
≤ z
i j
for [i, j] ∈ E
x
j
− x
i
≤ z
ji
for [i, j] ∈ E
x
j
binary j ∈ V
z
i j
,z
ji
binary [i, j] ∈ E.
The graph associated with this monotone integer
program has n + 2 nodes and 2m + 2n arcs which im-
proves on the number of nodes m + n + 2 in the λ-
HNC formulation.
To conclude we provide an example of solving
Cheeger’s* on a subgraph V
′
delivered by the Metis
procedure, min
/
0⊂S⊂V
′
C(S,S)
d(S)
applied to the dataset
EGO-GPLUS of size n = 107614 m = 12238285, from
(Leskovec and Krevl, 2014) (reported in (Hochbaum
et al., 2024)). The convex envelope shown in Fig-
ure 5 illustrates the difference between the set of all
breakpoints, generated with the fully parametric cut
procedure, versus the set of points explored by IPC.
Figure 5: The convex envelope of all 291 breakpoints, in
blue, versus 11 breakpoints explored by IPC, in red. (Cour-
tesy: A. Irribarra-Cort
´
es).
Flow Is Best, Fast and Scalable: The Incremental Parametric Cut for Maximum Density and Other Ratio Subgraph Problems
281

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported in part by the AI4OPT
institute NSF award 2112533.
REFERENCES
Angel, A., Koudas, N., Sarkas, N., Srivastava, D., Svend-
sen, M., and Tirthapura, S. (2014). Dense subgraph
maintenance under streaming edge weight updates for
real-time story identification. The VLDB journal,
23:175–199.
Boob, D., Gao, Y., Peng, R., Sawlani, S., Tsourakakis, C.,
Wang, D., and Wang, J. (2020). Flowless: Extract-
ing densest subgraphs without flow computations. In
Proceedings of The Web Conference 2020, pages 573–
583.
Charikar, M. (2000). Greedy approximation algorithms for
finding dense components in a graph. In International
workshop on approximation algorithms for combina-
torial optimization, pages 84–95. Springer.
Fortunato, S. (2010). Community detection in graphs.
Physics reports, 486(3-5):75–174.
Fratkin, E., Naughton, B. T., Brutlag, D. L., and Bat-
zoglou, S. (2006). Motifcut: regulatory motifs find-
ing with maximum density subgraphs. Bioinformat-
ics, 22(14):e150–e157.
Gallo, G., Grigoriadis, M. D., and Tarjan, R. E. (1989). A
fast parametric maximum flow algorithm and applica-
tions. SIAM Journal on Computing, 18(1):30–55.
Goldberg, A. V. (1984). Finding a maximum density sub-
graph. UC Berkeley manuscript.
Goldberg, A. V. and Tarjan, R. E. (1988). A new approach
to the maximum-flow problem. Journal of the ACM
(JACM), 35(4):921–940.
Harb, E., Quanrud, K., and Chekuri, C. (2022). Faster and
scalable algorithms for densest subgraph and decom-
position. Advances in Neural Information Processing
Systems, 35:26966–26979.
Hochbaum, D. S. (1998). The pseudoflow algorithm and
the pseudoflow-based simplex for the maximum flow
problem. In Integer Programming and Combinato-
rial Optimization: 6th International IPCO Confer-
ence Houston, Texas, June 22–24, 1998 Proceedings
6, pages 325–337. Springer.
Hochbaum, D. S. (2002). Solving integer programs
over monotone inequalities in three variables: A
framework for half integrality and good approxima-
tions. European Journal of Operational Research,
140(2):291–321.
Hochbaum, D. S. (2008). The pseudoflow algorithm: A new
algorithm for the maximum-flow problem. Operations
research, 56(4):992–1009.
Hochbaum, D. S. (2009). Dynamic evolution of economi-
cally preferred facilities. European Journal of Opera-
tional Research, 193(3):649–659.
Hochbaum, D. S. (2010). Polynomial time algorithms for
ratio regions and a variant of normalized cut. IEEE
transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelli-
gence, 32(5):889–898.
Hochbaum, D. S. (2020a). Hpf - hochbaum’s
pseudoflow. Accessed: May 28, 2022,
https://riot.ieor.berkeley.edu/Applications/full-
para-HPF/pseudoflow-parametric-cut.html.
Hochbaum, D. S. (2020b). Pseudoflow (simple) parametric
maximum flow solver version 1.0. Accessed: May 28,
2022, https://riot.ieor.berkeley.edu/Applications/
Pseudoflow/parametric.html.
Hochbaum, D. S. (2023). Unified new techniques for np-
hard budgeted problems with applications in team col-
laboration, pattern recognition, document summariza-
tion, community detection and imaging. Proceedings
of the 15th International Joint Conference on Knowl-
edge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowl-
edge Management, 1:365–372.
Hochbaum, D. S., Irribarra-Cort
´
es, A., and As
´
ın-Ach
´
a, R.
(2024). Fast and optimal incremental parametric pro-
cedure for the densest subgraph problem: An experi-
mental study. UC Berkeley manuscript.
Karypis, G. and Kumar, V. (1998). A fast and high qual-
ity multilevel scheme for partitioning irregular graphs.
SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 20(1):359–
392.
Kumar, R., Raghavan, P., Rajagopalan, S., and Tomkins,
A. (1999). Trawling the web for emerging cyber-
communities. Computer networks, 31(11-16):1481–
1493.
Lang, K. and Rao, S. (2004). A flow-based method for
improving the expansion or conductance of graph
cuts. In Integer Programming and Combinatorial
Optimization: 10th International IPCO Conference,
New York, NY, USA, June 7-11, 2004. Proceedings 10,
pages 325–337. Springer.
Leskovec, J. and Krevl, A. (2014). SNAP Datasets: Stan-
ford large network dataset collection. http://snap.
stanford.edu/data.
Picard, J.-C. and Queyranne, M. (1982). A network flow
solution to some nonlinear 0-1 programming prob-
lems, with applications to graph theory. Networks,
12(2):141–159.
Sharon, E., Galun, M., Sharon, D., Basri, R., and Brandt, A.
(2006). Hierarchy and adaptivity in segmenting visual
scenes. Nature, 442(7104):810–813.
Shi, J. and Malik, J. (2000). Normalized cuts and image
segmentation. IEEE Transactions on pattern analysis
and machine intelligence, 22(8):888–905.
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
282
