
The Impact of AI on Business Students’ Career Choices
Zihang Gong
a
Business Analytics, School of Business, Macau University of Science and Technology,
Macao Special Administrative Region, 999078, China
Keywords: AI, Business, Salary, Job, Educational Level.
Abstract: The growing popularity and evolving nature of artificial intelligence (AI) technology have significantly
influenced numerous industries and sectors in contemporary society. Concurrently, there has been a noticeable
shift towards AI-related majors in higher education. Given the diverse range of business disciplines, the
question of whether business students should acquire AI skills in their career choices merits thorough
examination. This study relies on salary report data compiled by Kaggle, encompassing 6,704 samples from
surveys, job boards, and other public sources. Utilizing regression analysis and data virtualization techniques,
the study objectively assesses the impact of AI technology on business operations and its subsequent effect
on compensation. The findings reveal that, aside from master's degree holders, there exists a notable
association between the salary of undergraduate and doctoral graduates and the extent of AI involvement in
their work. Furthermore, the study identifies a correlation between educational level and salary. Additionally,
across all business-related professions, personal work experience is found to have a greater influence on salary
than educational qualifications.
1 INTRODUCTION
The present situation of social employment is
experiencing a marked deterioration. The COVID-19
pandemic has exerted considerable influence on the
conduct of businesses, leading to a substantial decline
in recruitment demand. Additionally, numerous small
and micro-enterprises are confronted with a critical
survival challenge. As the primary providers of
employment opportunities for graduates, the
struggling state of small, medium, and micro-
enterprises has had a profound impact on the
employment landscape. The Employment Market
Sentiment Index (CIER Index) serves as a crucial
metric to gauge the state of the job market. According
to the "China Job Market Sentiment Report" issued
by Zhaopin Ltd, the increase in the number of job
applicants in the first quarter of 2022 surpassed the
growth in recruitment needs, resulting in a decline in
the CIER index. This indicates that the present
employment situation is not optimistic (Yan,2022).
Simultaneously, the widespread utilization of
digital technologies, including artificial intelligence,
big data, and cloud computing, has exerted a
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-6563-5800
significant influence on diverse industries (Chen,
2019). Taking accounting work as an illustrative
example, certain conventional roles such as
fundamental accounting and cashiers might undergo
gradual disappearance, whereas others will
adaptively evolve alongside alterations in market
demand. In order to acclimatize to the perpetual
advancement of enterprise technology and business
models, novel, comprehensive accounting positions
will arise as necessitated by the evolving era (Wu,
2023).
College graduates, being a crucial segment in the
job market, possess employment quality that is a
fundamental prerequisite for the superior
advancement of higher education. In the present
challenging employment landscape, the employment
difficulties faced by university students have become
increasingly apparent. Being a susceptible segment of
the workforce, their employment situation deserves
greater consideration. Statistics indicate that in 2019,
the number of individuals supported by various
education funding schemes throughout the country
reached 106 million, an increase of 8.05% year-on-
168
Gong, Z.
The Impact of AI on Business Students’ Career Choices.
DOI: 10.5220/0012917700004508
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2024), pages 168-174
ISBN: 978-989-758-713-9
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

year, with a total allocation of 212.6 billion yuan
(Chen, 2022).
A preliminary examination of employment
recommendations and adaptive strategies across
various business sectors has been undertaken.
Notably, sectors like finance and accounting have
garnered significant attention due to their extensive
workforce, long-standing history, and traditional
stronghold status within the business world.
Nevertheless, these industries also encounter
challenges such as limited salary growth, rigid job
responsibilities, and industry saturation. The evolving
economic landscape has given birth to novel
industries. Graduates born in the early 2000s have
demonstrated a keen interest in emerging professions,
attaching greater importance to salary scales and
industry outlooks. According to a survey conducted
by the United Questionnaire Network of the Social
Survey Center of China Youth Daily, over 90% of the
surveyed graduates born in the early 2000s expressed
an interest in pursuing new careers, with more than
30% expressing considerable enthusiasm.
Furthermore, their job search preferences have
become increasingly diverse (Yan, 2022).
As such, the research will zero in on the evolving
business landscapes and investigate their integration
with AI technology. Through comparing various
business roles, it strives to offer an accurate portrayal
of the diverse professional landscapes prevailing in
modern business schools, thus providing young
individuals with ample references for pursuing either
traditional or emerging career paths (Wei, 2023).
This article is grounded in Kaggle's salary report
data, alongside surveys, recruitment platforms, and
various public resources, to delve into the precise
influence of AI on salaries within the business sector.
With the ultimate goal of achieving optimal
remuneration under identical circumstances, this
research evaluates the necessity of AI proficiency
among business students based on the analytical
outcomes. Furthermore, the author considers multiple
variables, including work experience and educational
attainment, to offer tailored guidance for personal
development among diverse student groups. This
approach aims to equip them with the necessary skills
to thrive in the age of AI.
2 METHOD
The primary source of data employed in this article
originates from the Salary_Data dataset, which was
procured from the Kaggle website. This dataset
encompasses a diverse array of sources,
encompassing surveys, recruitment websites, and
other publicly accessible resources. A comprehensive
collection of 6704 data points was compiled. The
dataset encompasses six variables: age, gender,
experience, job, education, and salary (Alekseeva,
2021). While these variables are rich in content, age,
and gender are deemed irrelevant in this study due to
the authors' focus on the broader context of the
research. These two variables are particularly delicate
when addressing social audience groups and are often
influenced by geography or specific job restrictions
without further reference.
Using Excel-based skill data processing
techniques, including regression analysis and data
virtualization, the author meticulously sifted through
6704 data points (Seamans, 2018). Recognizing the
vast array of business-related professions, a focused
selection of six mid-level positions was made,
drawing from a comprehensive survey of business
school graduates: Data Analyst, Digital Marketing
Manager, Human Analyst, Marketing Manager,
Operations Manager, and Product Manager. Notably,
three of these roles - Data Analyst, Digital Marketing
Manager, and Marketing Analyst - exhibit a high
degree of integration with the AI industry, hence their
classification as highly relevant. On the other hand,
Operations Manager and Product Manager are
deemed moderately related, while Human Resource
Manager and Marketing Manager are considered less
so. Following this filtering process, 1333 data items
that met the established criteria remained.
Subsequently, two non-pertinent variables, Age and
Gender, were discarded. The refined dataset now
comprises three independent variables: Education
Level, Job Title, and Years of Experience, and the
dependent variable: is salary.
2.1 Data Processing
2.1.1 Group A: Relevance of Job Wages to
Jobs and AI
This study aims to investigate the influence of
varying positions on salary scales. To ensure the
precision of the findings, education level is
introduced as an additional crucial variable. The
educational level is categorized into three tiers:
Bachelor's, Master's, and PhD. The data for each of
these tiers is processed independently. To uphold the
study's rigor, a confidence interval of 95% has been
established.
In Table 1, solely undergraduate-level data is
presented. Within this table, data is further segmented
into high, medium, and low levels, and processed
The Impact of AI on Business Students’ Career Choices
169
accordingly. To facilitate statistical analysis, dummy
coding is employed, assigning numerical values of 1,
2, and 3 to high, medium, and low levels,
respectively. The data in Table 2 exclusively pertains
to the master's level, and the processing approach
mirrors that of Table 1. Similarly, the data in Table 3
solely concerns the doctoral level, adhering to the
same processing methodologies as the preceding
tables.
2.1.2 Group B: The Relationship Between
Education Level and Salary
Unlike the processing approach employed by Group
A, the author has categorized the data into three
distinct groups: High, Medium, and Low, based
solely on the Job Title. Each of these sheets has been
assigned a confidence interval of 95%. By adjusting
for job type, an independent and thorough analysis of
educational attainment can be conducted.
Table 4 presents a detailed breakdown of the
High-level data, encompassing the four distinct
education levels: High School, Bachelor, Master, and
PhD. To facilitate analysis, virtual data values have
been assigned to each level: 0, 1, 2, and 3,
respectively. Table 5 showcases Medium-level data,
which includes three education levels: Bachelor,
Master, and PhD. For these levels, the virtual data
assignments are 1, 2, and 3. Table 6 solely focuses on
PhD-level data, while still incorporating three
education levels: Bachelor, Master, and PhD.
Similarly, the virtual data assignments for these levels
are 1, 2, and 3.
2.1.3 Group C: Work Experience or
Education, Which One Has a Greater
Impact on Salary?
In addressing this problem, given the involvement of
multiple variables, the author deemed it necessary to
employ the virtual data processing method again,
building upon the foundation established by Group B.
Specifically, the objective is to determine the mean
value of "Years of Experience" across three distinct
data categories: High, Medium, and Low.
Subsequently, any data point with a mean value equal
to or less than the computed mean will be assigned a
value of 0, while those exceeding the mean will be
assigned a value of 1. Notably, Variable 1 signifies
education level, while Variable 2 represents work
experience.
To assess which factor exerts a more significant
influence on salary, a comparison of the P values
across various groups is essential. In ensuring the
reliability of the results, the authors have established
a confidence interval of 95%. Referring to the data
presented in Table 7, the average "Year of
Experience" for the High level is 4.75. Consequently,
any data point with a value less than or equal to 4.75
will be set to 0, while those exceeding 4.75 will be set
to 1. Similarly, Table 8 reveals an average "Year of
Experience" of 7.85 for the Medium level, resulting
in a similar binary classification. Finally, Table 9
indicates an average value of 9.55 for the Low level,
leading to the same binary assignment of data points.
2.2 Experimental Hypothesis
Group A: Education level directly correlates with the
job salary's relation to AI. As education rises, so does
its connection with AI-related salaries.
Group B: AI-reliant jobs show a positive correlation
between salary and varying education levels. Higher
education is linked to stronger salary correlations,
while lower education is linked to weaker ones.
Group C: When considering both education and work
experience's impact on salary, work experience has a
greater influence than education.
3 RESULT
3.1 Data Results
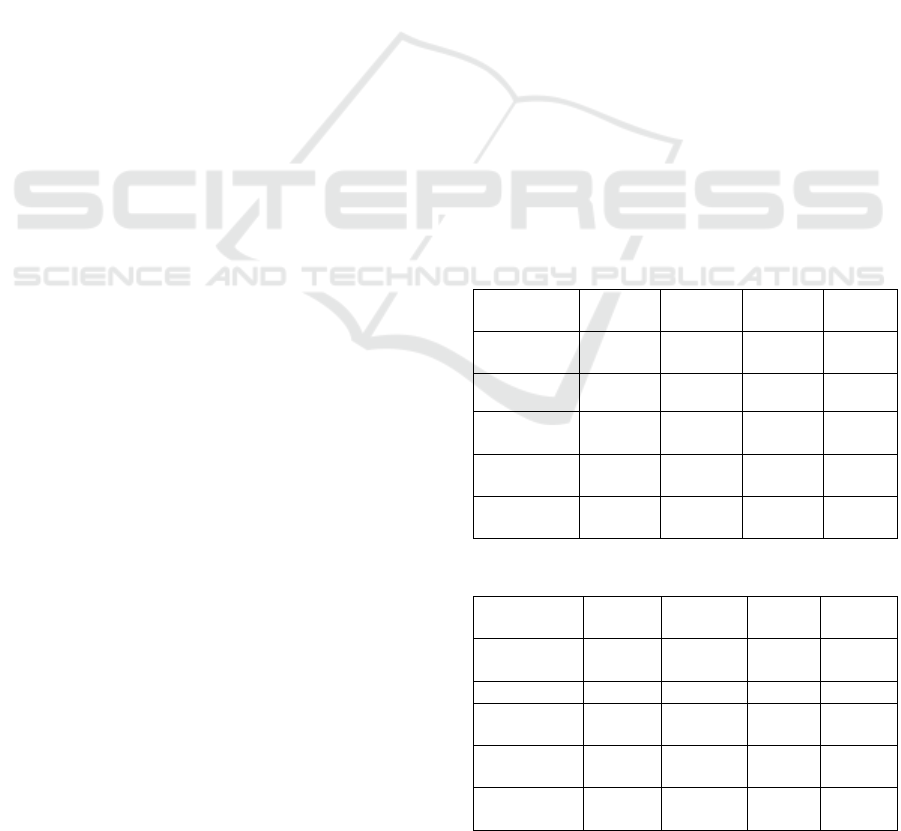
Table 1: Regression Statistics of Bachelor’s Level.
Regression
Statistics
Multiple R
0.108973
96
Observations 800
Coefficie
nts
Standard
Erro
r
t Stat P-value
Intercept
115541.7
866
3401.052
362
33.97236
335
3.5603E
-157
Panel Data
-6182.
235018
1996.306
423
-3.0968
36711
0.00202
442
Table 2: Regression Statistics of Master’s Level.
Regression
Statistics
Multiple R
0.070651
773
Observations 489
Coefficie
nts
Standard
Erro
r
t Stat P-value
Intercept
128990.2
249
5178.532
452
24.9086
447
6.37301
E-89
Panel Data
3353.428
839
2145.432
756
1.56305
474
0.118689
274
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
170
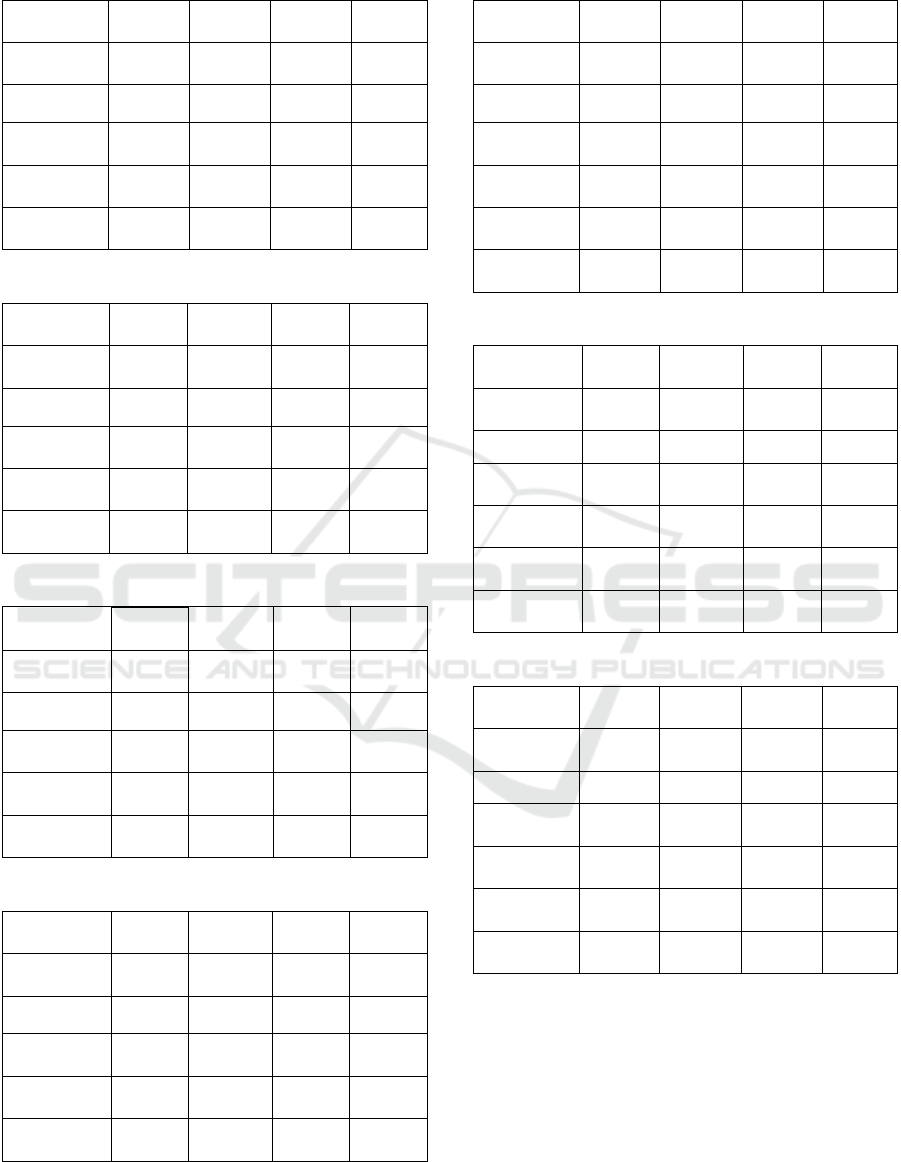
Table 3: Regression Statistics of PhD Level.
Regression
Statistics
Multiple R
0.461040
894
Observations 37
Coefficie
nts
Standard
Erro
r
t Stat P-value
Intercept
237887.3
239
48651.95
594
4.889573
695
2.23849
E-05
Panel Data
-52517.
60563
17086.00
54
-3.0737
20533
0.00408
0626
Table 4: Regression Statistics of High-level Data.
Regression
Statistics
Multiple R
0.04387
0473
Observations 547
Coefficie
nts
Standard
Erro
r
t Stat P-value
Intercept
102188.
6636
5037.271
112
20.2865
1254
1.386E-
68
Panel Data
4152.33
8037
4050.454
961
1.02515
3489
0.30574
5563
Table 5: Regression Statistics of Medium-level Data.
Regression
Statistics
Multiple R
0.60814
8459
Observations 427
Coefficie
nts
Standard
Erro
r
t Stat P-value
Intercept
52163.0
9322
5256.446
047
9.92364
2847
5.15933
E-21
Penal Data
56465.8
0508
3575.240
803
15.7935
6698
1.52897
E-44
Table 6: Regression Statistics of Low-level Data.
Regression
Statistics
Multiple R
0.14643
1147
Observations 359
Coefficie
nts
Standard
Erro
r
t Stat P-value
Intercept
98218.3
0422
6145.214
753
15.9828
9208
9.38245
E-44
Years of
Experience
8959.98
2982
3203.560
13
2.79688
3036
0.00543
9286
Table 7: Regression Statistics of High-level Data.
Regression
Statistics
Multiple R
0.681154
913
Observations 547
Coefficie
nts
Standard
Erro
r
t Stat P-value
Intercept
111081.0
93
3717.679
256
29.87914
916
8.1448E
-117
Va r i a ble 1
-22293.
70502
3212.293
588
-6.9401
20638
1.11855
E-11
Va r i a ble 2
59093.66
22
2728.927
027
21.65454
1
1.84851
E-75
Table 8: Regression Statistics of Medium-level Data.
Regression
Statistics
Multiple R
0.81616
2725
Observations 427
Coefficie
nts
Standard
Erro
r
t Stat P-value
Intercept
52658.6
6536
3830.749
238
13.7463
0969
8.0736E-
36
Va r i a ble 1
37604.9
1234
2781.003
443
13.5220
6608
6.83981
E-35
Va r i a ble 2
55037.6
5919
2837.410
618
19.3971
4289
1.85588
E-60
Table 9: Regression Statistics of Low-level Data.
Regression
Statistics
Multiple R
0.588060
39
observations 359
Coefficie
nts
Standard
Erro
r
t Stat P-value
Intercept
98428.26
418
5031.590
994
19.56205
588
2.19329
E-58
Va r i a ble 1
-486.17
68246
2717.654
546
-0.1788
95741
0.85812
1333
Va r i a ble 2
40726.11
713
3065.321
143
13.28608
496
5.41459
E-33
3.2 Experimental Results
The confidence intervals of the above charts are all
set to 95%. With the above data, you researchers can
find:
Group A: The results of Table 1 demonstrate
statistical significance, albeit with a weak correlation.
Conversely, the findings presented in Table 2 fail to
exhibit significance, and the correlation is weak.
The Impact of AI on Business Students’ Career Choices
171

Lastly, Table 3 shows both statistical significance and
a strong correlation.
After careful analysis, it is evident that the salary
of individuals holding a bachelor's degree
demonstrates a limited association with the AI sector.
In contrast, graduates with a master's degree exhibit
negligible correlation with the AI industry when it
comes to salary. However, a strong link is observed
between the salary of PhD graduates and the AI field.
Group B: The statistical significance of the data
presented in Table 4 is lacking, indicating a non-
significant correlation. Similarly, while the findings
in Table 5 and Table 6 demonstrate statistical
significance, they do not exhibit a strong correlation.
It is evident that in professions that are heavily
reliant on AI, the influence of educational attainment
on remuneration is relatively minor. Conversely, in
professions that have a moderate association with AI,
the link between salary and educational level is more
pronounced, typically manifesting as higher levels of
education leading to higher salaries. In professions
that have a tenuous connection to AI, a certain degree
of correlation exists between educational attainment
and salary, albeit not a strong one.
Group C: Tables 7, 8, and 9 indicate that Variable
2 is smaller across all job types. Specifically, for high-
level job types, work experience has a more
significant influence on salary compared to
educational experience. Similarly, for medium-level
job types, the impact of work experience on salary
surpasses the influence of educational experience.
Lastly, for low-level job types, work experience
remains the primary factor determining salary,
outweighing the influence of educational experience.
Judging from these three situations, no matter
what business-related occupation you are engaged in,
the impact of work experience on salary is generally
greater than the impact of educational experience on
salary.
After a thorough examination, the disparities
observed between Groups A and B can be attributed
primarily to the varying levels of professional
proficiency among their members. Research
conducted by Fang Ning and colleagues has revealed
that the marketplace holds a significant demand for
undergraduate students. Specifically, 66.39% of
employers express a preference for undergraduate
students over master's degree holders. Conversely,
only 13.68% of employers prefer master's degree
holders over undergraduate students. This
recruitment preference is primarily determined by the
extent to which an individual's skills align with the
requirements of the job, accounting for 60.05% of the
decision-making process (Fang, 2020).
It is noteworthy that employers highly regard the
diverse abilities of undergraduate and postgraduate
students, encompassing self-motivation, values, self-
confidence, oral communication skills, problem-
solving proficiency, and team collaboration abilities.
Notably, 55% of companies maintain that the work
competency of master's students in similar positions
does not significantly surpass that of undergraduates.
Consequently, the majority of employers do not
endorse the notion that only graduates with master's
degrees can secure superior employment
opportunities (Fang, 2020).
In terms of the specific perspectives held by
enterprises, it is noteworthy that 42.04% of
enterprises emphasize the importance of not solely
focusing on academic qualifications, but rather giving
greater consideration to personal abilities.
Furthermore, 4.8% of enterprises believe that
undergraduates possess considerable potential and
room for development once they have undergone
systematic training. Additionally, 43.38% of
enterprises maintain that, apart from certain
specialized technical positions, there is not a
significant difference in quality between master's
students and undergraduates. Notably, only 9.7% of
companies hold the view that academic qualifications
are of utmost importance (Fang, 2020).
From the perspective of talent demand within the
AI industry, employers place a greater emphasis on
candidates' personal abilities than on their academic
qualifications. When evaluating candidates' abilities,
employers prioritize professionalism, followed by
professional ability. Notably, demands for
professional ethics, self-motivation, initiative, and
collaboration skills are particularly acute. These
abilities are primarily shaped by an individual's
fundamental character traits, perseverance, and work
ethic, rather than being directly influenced by
academic qualifications. While master's degree
holders may possess superior professional abilities,
these skills are relatively less in demand among
employers.
From the employers' perspective on evaluation
criteria, undergraduate students exhibit a high level of
proficiency in work-related abilities. Notably, there is
no significant difference in performance between
undergraduate and master's degree students,
indicating that academic qualifications do not solely
determine an individual's practical capabilities.
Indeed, over half of employers maintain that the work
capabilities of undergraduate students are comparable
to those of master's degree holders.
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
172

3.3 Personal Development Suggestions
For novice students entering the realm of business,
selecting a major serves as a pivotal junction.
Whether they opt for business analysis, which holds
a strong nexus with AI technology, or major in
finance and human resources management, which
maintain a more tenuous tie with AI technology, it is
imperative for students to ascertain their career
aspirations and craft corresponding plans for
academic advancement and professional
development.
Firstly, those who opt for business analytics as
their field of study are often drawn to it due to its close
association with the prevalent AI technology. In this
domain, the significance of personal practical
proficiency is paramount (Liu, 2023). This
necessitates, alongside theoretical knowledge, the
mastery of practical analytical tools and techniques,
enabling students to leverage data in decision-making
and generate value for enterprises. This proficiency is
not solely contingent upon academic qualifications
but also hinges upon practical experience and skill
enhancement. The diverse resources and avenues
offered by the institution, including internships and
project-based practice, furnish students with an ideal
platform to hone these abilities. Consequently, for
students pursuing business analysis as their major, the
utilization of these resources and the accumulation of
practical work experience hold the utmost importance
in standing out during the job search process.
Certainly, this is not to suggest that the
significance of academic credentials be disregarded
by those pursuing a business analysis major. Indeed,
within the realm of business analysis, the possession
of an advanced degree frequently offers students a
wider array of development opportunities.
Nevertheless, alongside academic credentials, an
individual's practical abilities hold equal significance.
During the job search, companies tend to prioritize
the actual skills and potential of candidates,
surpassing mere academic qualifications. Therefore,
alongside the pursuit of academic credentials,
students majoring in business analysis must also
prioritize the enhancement of their own abilities.
On the contrary, students pursuing majors such as
finance or human resource management may not
possess the same level of specialization as those
majoring in business analysis. Nonetheless, this does
not negate the significance of academic qualifications
for these students (Liu, 2023). Quite the contrary,
enhancing their academic credentials often affords
them a competitive edge. This is attributed to the fact
that these majors demand a profound academic
foundation and knowledge reserve. For instance,
finance majors must master intricate financial
theories and analytical tools, whereas human resource
management majors must comprehend organizational
behavior, labor laws, and pertinent knowledge. By
persevering in their studies, these students can not
only acquire more structured academic training but
also elevate their professional qualities and
comprehensive abilities.
Furthermore, as technology continues to evolve,
AI technology is increasingly infiltrating sectors like
finance and human resources management.
Consequently, it's crucial for students pursuing these
majors to acquire a fundamental understanding and
proficiency in AI technology (Huang, 2023). While
they might not directly utilize AI technology in the
same manner as business analysis majors,
comprehending AI's applications, potential, and
integration with their respective fields will
undoubtedly afford them a competitive edge in their
future professional pursuits.
Therefore, for novice students venturing into the
realm of business, regardless of their chosen
discipline, it is imperative to clarify their career
aspirations and devise corresponding plans for
academic pursuits and professional development. In
sectors that prioritize artificial intelligence, personal,
hands-on capabilities hold the utmost significance;
whereas in domains like finance and human resources
management, the enhancement of academic
credentials and professional attributes is equally
crucial (Li, 2023). Furthermore, comprehending and
proficiency in AI technology stand as pivotal factors
for future career advancement. By leveraging the
resources and opportunities offered by the institution,
and consistently enhancing their practical skills and
professional attributes, students in the field of
business can secure a rewarding position upon
graduation and realize their career aspirations.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The research conducted by Group A has identified a
potential trend: there appears to be no substantial
direct link between the salary offered to master's
degree graduates and their employment in the AI
industry. This observation can potentially be
attributed to the diverse factors that influence salary
levels in the AI industry, encompassing work
The Impact of AI on Business Students’ Career Choices
173

experience, proficiency in skills, and the size of the
employing company, among others. Consequently,
when pursuing a career path, master's degree
graduates should not solely prioritize the higher
salaries offered in the AI industry, but rather, they
should holistically consider various pertinent factors.
The research undertaken by Group B has also
uncovered an intriguing trend: in professions that are
closely aligned with AI, disparities in educational
attainment do not significantly impact salary
outcomes. This could be due to the fact that in the
realm of AI, proficiency in skills and accumulated
experience are deemed more crucial than academic
qualifications. Regardless of one's educational level,
as long as one possesses the requisite skills and
experience, they are likely to be offered comparable
salary levels. This revelation holds significant
implications for both the education sector and
individuals seeking employment. The education
sector, particularly, ought to prioritize the cultivation
of practical abilities and skills, while job seekers need
to place a stronger emphasis on skill development and
the accumulation of practical experience.
The experimental findings of Group C align with
the widespread societal recognition that work
experience holds greater significance than
educational attainment. This finding echoes the
results obtained by Groups A and B, further
highlighting the importance of practical experience
and skills in career advancement.
This experiment relied primarily on limited real-
world data, which is accurate and representative but
may be incomplete. Extreme values or insufficient
data could influence the conclusion and deviate from
the actual situation. Extreme values may be caused by
errors or abnormal events, and if not handled properly,
they could significantly impact the conclusions. For
instance, limited data on doctoral job searches may
lead to overly optimistic conclusions. Ignoring other
factors, such as educational attainment, could also
lead to biased or one-sided conclusions. Despite these
limitations, careful design and in-depth analysis
allowed the experiment to draw valuable conclusions.
Future research will aim to improve methods and
techniques for more accurate conclusions.
REFERENCES
Chun, C., 2019. The promotion and impact of artificial
intelligence on the financial industry. Hebei Enterprise,
7, 60-61.
Chen, C., 2022. Research on the impact of financial aid on
the employment quality of college students with
difficulties—taking J University as an example.
Jiangxi: East China. Jiaotong University.
Hang, W., 2023. ChatGPT’s challenges and opportunities
for business. Foreign Economics and Management, 45,
9, 69-78.
Liudmila, A., et al. 2021. The demand for AI skills in the
labor market. Labour economics, 71.
Mian, Y., Fengcheng, L., Dong, Y., 2022. Problems and
countermeasures in the employment of college students.
Human Resources Development, 23, 61-63.
Maoyong, H., 2023. Asymmetric empowerment: the
iterative effect of artificial intelligence on employment
skills and educational intervention. Education and
Occupation, 1028, 4, 5-12.
Mingyu, L., 2023. Analysis and practical exploration of the
causes of college students’ employment difficulties
under the new situation. Economic Research Guide, 16,
135-137.
Ning, F, 2020. Comparative study on the employment
competitiveness of undergraduates and master's
students - based on the two dimensions of student
cognition and employer evaluation. Journal of Liaoning
Radio and Television University, 4, 87- 90.
Robert; S, 2018. AI, labor, productivity and the need for
firm-level data. National Bureau of Economic Research.
Wen, W., 2023. Duan Research on the training of
accounting talents in applied undergraduate colleges
under the background of artificial intelligence. Foreign
Economic and Trade, 5, 100-103.
Yongmou, L., 2023. The impact of "AI unemployment" on
contemporary youth and its response. Youth
Exploration, 1, 43-51.
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
174
